NT
-
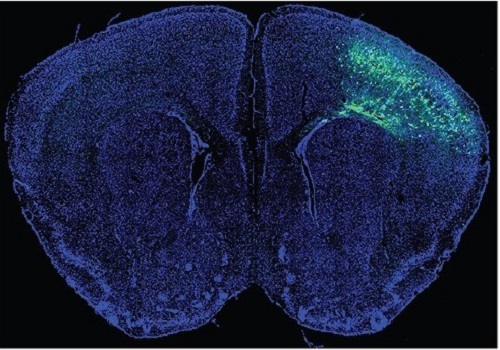 A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 12700
A Mechanism Underlying Most Common Cause of Epileptic Seizures Revealed
An interdisciplinary study shows that neurons carrying somatic mutations in MTOR can lead to focal epileptogenesis via non-cell-autonomous hyperexcitability of nearby nonmutated neurons
During fetal development, cells should migrate to the outer edge of the brain to form critical connections for information transfer and regulation in the body. When even a few cells fail to move to the correct location, the neurons become disorganized and this results in focal cortical dysplasia. This condition is the most common cause of seizures that cannot be controlled with medication in children and the second most common cause in adults.
Now, an interdisciplinary team studying neurogenetics, neural networks, and neurophysiology at KAIST has revealed how dysfunctions in even a small percentage of cells can cause disorder across the entire brain. They published their results on June 28 in Annals of Neurology.
The work builds on a previous finding, also by a KAIST scientists, who found that focal cortical dysplasia was caused by mutations in the cells involved in mTOR, a pathway that regulates signaling between neurons in the brain.
“Only 1 to 2% of neurons carrying mutations in the mTOR signaling pathway that regulates cell signaling in the brain have been found to include seizures in animal models of focal cortical dysplasia,” said Professor Jong-Woo Sohn from the Department of Biological Sciences. “The main challenge of this study was to explain how nearby non-mutated neurons are hyperexcitable.”
Initially, the researchers hypothesized that the mutated cells affected the number of excitatory and inhibitory synapses in all neurons, mutated or not. These neural gates can trigger or halt activity, respectively, in other neurons. Seizures are a result of extreme activity, called hyperexcitability. If the mutated cells upend the balance and result in more excitatory cells, the researchers thought, it made sense that the cells would be more susceptible to hyperexcitability and, as a result, seizures.
“Contrary to our expectations, the synaptic input balance was not changed in either the mutated or non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. “We turned our attention to a protein overproduced by mutated neurons.”
The protein is adenosine kinase, which lowers the concentration of adenosine. This naturally occurring compound is an anticonvulsant and works to relax vessels. In mice engineered to have focal cortical dysplasia, the researchers injected adenosine to replace the levels lowered by the protein. It worked and the neurons became less excitable.
“We demonstrated that augmentation of adenosine signaling could attenuate the excitability of non-mutated neurons,” said Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering.
The effect on the non-mutated neurons was the surprising part, according to Paik. “The seizure-triggering hyperexcitability originated not in the mutation-carrying neurons, but instead in the nearby non-mutated neurons,” he said.
The mutated neurons excreted more adenosine kinase, reducing the adenosine levels in the local environment of all the cells. With less adenosine, the non-mutated neurons became hyperexcitable, leading to seizures.
“While we need further investigate into the relationship between the concentration of adenosine and the increased excitation of nearby neurons, our results support the medical use of drugs to activate adenosine signaling as a possible treatment pathway for focal cortical dysplasia,” Professor Lee said.
The Suh Kyungbae Foundation, the Korea Health Technology Research and Development Project, the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the National Research Foundation in Korea funded this work.
-Publication:Koh, H.Y., Jang, J., Ju, S.H., Kim, R., Cho, G.-B., Kim, D.S., Sohn, J.-W., Paik, S.-B. and Lee, J.H. (2021), ‘Non–Cell Autonomous Epileptogenesis in Focal Cortical Dysplasia’ Annals of Neurology, 90: 285 299. (https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.26149)
-ProfileProfessor Jeong Ho Lee Translational Neurogenetics Labhttps://tnl.kaist.ac.kr/ Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering KAIST
Professor Se-Bum Paik Visual System and Neural Network Laboratory http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/ Department of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
Professor Jong-Woo Sohn Laboratory for Neurophysiology, https://sites.google.com/site/sohnlab2014/home Department of Biological SciencesKAIST
Dr. Hyun Yong Koh Translational Neurogenetics LabGraduate School of Medical Science and EngineeringKAIST
Dr. Jaeson Jang Ph.D.Visual System and Neural Network LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain Engineering KAIST
Sang Hyeon Ju M.D.Laboratory for NeurophysiologyDepartment of Biological SciencesKAIST
2021.08.26 View 12700 -
 KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 8600
KPC4IR Helping to Create Global Standards for Virtual Transactions
KPC4IR will join the task force for the Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards
The KAIST Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) will participate in a global initiative to create global standards for virtual asset transactions. As a member of the GI-TRUST (Global Implementation of Travel Rule Standards) task force, the KPC4IR will develop technical standards and relevant policies that support the global implementation of the travel rule for virtual assets in compliance with the recommendations of the Financial Action Task Force’s (FATF).
The FATF is an intergovernmental organization founded in 1989 by the G7 to develop policies to combat money laundering. In June 2019, the FATF extended its Recommendation 16, commonly known as the “travel rule,” to virtual asset services providers (VASPs), requiring both financial institutions and VASPs to aggregate information on the senders and recipients of wire transfers and exchange this information between parties to create a suitable audit trail.
According to the FATF’s recommendation and the G20’s support, jurisdictions, especially G20 member countries, have now applied the travel rule to their respective local laws. Korea also amended the Act on Reporting and Using Specified Financial Transaction Information in March 2020 to include virtual assets in their regulatory scope by March 2022.
The GI-TRUST task force will collaborate with global and local organizations developing travel rule technologies and offer a neutral assessment of proposed solutions. Their activities are aimed at standardizing related authentication protocols and security technologies that help VASPs comply with the travel rule.
The task force will also aid in the pilot testing of travel rule solutions for certain VASPs in Korea. Afterwards, the task force will report on the performance and reliability of the tested travel rule solutions for actual virtual asset transactions, in compliance with the FATF’s guidance.
Besides the KPC4IR, the GI-TRUST task force includes the Global Blockchain Business Council (GBBC), International Digital Asset Exchange Association (IDAXA), and Korea Blockchain Association (KBCA).
Director of the KPC4IR Professor So Young Kim will co-chair the task force. Professor Kim said their approach should be prudential in dealing with the regulations that rely on secure real-name data on top of the opposing governance style of pseudonymization, distribution, and recombination.
She explained, “KAIST has designed the co-evolution of technologies and institutions in conjunction with the global leaders’ groups such as the World Economic Forum and the EC Joint Research Center.”
She expects KAIST’s interdisciplinary, global cooperation to untie the entangled problem between regulations and technologies that obstruct future pathways.
2021.07.30 View 8600 -
 VP Sang Yup Lee Honored with the Pony Chung Innovation Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee became the recipient of the Innovation Award by the Pony Chung Foundation that was established to honor the late Se-yung Chung, the former chairman of Hyundai Development Company. He will receive 200 million KRW in prize money. Chairman Chung developed Korea’s first domestically manufactured automobile, ‘Pony,’ in the mid-1970s that became the cornerstone of Korea’s auto industry today.
Distinguished Professor Lee, from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, is a pioneering scholar in the field of systems metabolic engineering who developed various micro-organisms for producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds.
He recently was elected as a foreign member of the Royal Society in the UK and is the first Korean ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) in the US as well as one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) in the US.
2021.07.13 View 9814
VP Sang Yup Lee Honored with the Pony Chung Innovation Award
Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee became the recipient of the Innovation Award by the Pony Chung Foundation that was established to honor the late Se-yung Chung, the former chairman of Hyundai Development Company. He will receive 200 million KRW in prize money. Chairman Chung developed Korea’s first domestically manufactured automobile, ‘Pony,’ in the mid-1970s that became the cornerstone of Korea’s auto industry today.
Distinguished Professor Lee, from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, is a pioneering scholar in the field of systems metabolic engineering who developed various micro-organisms for producing a wide range of fuels, chemicals, materials, and natural compounds.
He recently was elected as a foreign member of the Royal Society in the UK and is the first Korean ever elected into the National Academy of Inventors (NAI) in the US as well as one of 13 scholars elected as an International Member of both the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) in the US.
2021.07.13 View 9814 -
 Professor Jung Receives the Hansong Science Award
Professor Yousung Jung of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has been selected as the recipient of the 5th Hansong Science Award in Chemistry. The award recognizes young and mid-career scholars who made outstanding achievement in physics, chemistry, and life sciences. Recipients receive 50 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Jung was recognized for finding a new way to predict synthesis potentials when designing data-based materials and molecules through AI-powered inverse technology. Conventionally, new material discovery mainly relied on a method where the new materials were proposed by an expert’s intuition or experimental trial, then synthesized to measure the properties of the material before it was used. However, this method took a lot of time, which resulted in an inefficient discovery process.
Professor Jung’s AI reverse design technology is reported to be more efficient for discovering new materials by finding crystal structures with desired properties using data and AI algorithms.
"AI reverse design technology can accelerate the development of new materials and new drugs," Professor Jung said. "It can be used as an algorithm for future autonomous laboratories implemented by robots, algorithms, and data without human intervention," he added.
2021.07.13 View 7044
Professor Jung Receives the Hansong Science Award
Professor Yousung Jung of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has been selected as the recipient of the 5th Hansong Science Award in Chemistry. The award recognizes young and mid-career scholars who made outstanding achievement in physics, chemistry, and life sciences. Recipients receive 50 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Jung was recognized for finding a new way to predict synthesis potentials when designing data-based materials and molecules through AI-powered inverse technology. Conventionally, new material discovery mainly relied on a method where the new materials were proposed by an expert’s intuition or experimental trial, then synthesized to measure the properties of the material before it was used. However, this method took a lot of time, which resulted in an inefficient discovery process.
Professor Jung’s AI reverse design technology is reported to be more efficient for discovering new materials by finding crystal structures with desired properties using data and AI algorithms.
"AI reverse design technology can accelerate the development of new materials and new drugs," Professor Jung said. "It can be used as an algorithm for future autonomous laboratories implemented by robots, algorithms, and data without human intervention," he added.
2021.07.13 View 7044 -
 Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 11296
Hydrogel-Based Flexible Brain-Machine Interface
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, but behaves ‘stealthily’ inside the brain when wet
Professor Seongjun Park’s research team and collaborators revealed a newly developed hydrogel-based flexible brain-machine interface. To study the structure of the brain or to identify and treat neurological diseases, it is crucial to develop an interface that can stimulate the brain and detect its signals in real time. However, existing neural interfaces are mechanically and chemically different from real brain tissue. This causes foreign body response and forms an insulating layer (glial scar) around the interface, which shortens its lifespan.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a ‘brain-mimicking interface’ by inserting a custom-made multifunctional fiber bundle into the hydrogel body. The device is composed not only of an optical fiber that controls specific nerve cells with light in order to perform optogenetic procedures, but it also has an electrode bundle to read brain signals and a microfluidic channel to deliver drugs to the brain.
The interface is easy to insert into the body when dry, as hydrogels become solid. But once in the body, the hydrogel will quickly absorb body fluids and resemble the properties of its surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing foreign body response.
The research team applied the device on animal models, and showed that it was possible to detect neural signals for up to six months, which is far beyond what had been previously recorded. It was also possible to conduct long-term optogenetic and behavioral experiments on freely moving mice with a significant reduction in foreign body responses such as glial and immunological activation compared to existing devices.
“This research is significant in that it was the first to utilize a hydrogel as part of a multifunctional neural interface probe, which increased its lifespan dramatically,” said Professor Park. “With our discovery, we look forward to advancements in research on neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s or Parkinson’s disease that require long-term observation.”
The research was published in Nature Communications on June 8, 2021. (Title: Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity) The study was conducted jointly with an MIT research team composed of Professor Polina Anikeeva, Professor Xuanhe Zhao, and Dr. Hyunwoo Yook.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) grant for emerging research, Korea Medical Device Development Fund, KK-JRC Smart Project, KAIST Global Initiative Program, and Post-AI Project.
-PublicationPark, S., Yuk, H., Zhao, R. et al. Adaptive and multifunctional hydrogel hybrid probes for long-term sensing and modulation of neural activity. Nat Commun 12, 3435 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-23802-9
-ProfileProfessor Seongjun ParkBio and Neural Interfaces LaboratoryDepartment of Bio and Brain EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.13 View 11296 -
 Professor Heung-Sun Sim the MSIT Scientist of July
Professor Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics was selected as the Scientist of July by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Professor Sim was recognized for his research of the Kondo effect, which opened a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. His research revealed that the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This phenomenon is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed. The research was reported in Nature in March 2020. With this award, Professor Sim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2021.07.12 View 7379
Professor Heung-Sun Sim the MSIT Scientist of July
Professor Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics was selected as the Scientist of July by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Professor Sim was recognized for his research of the Kondo effect, which opened a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. His research revealed that the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This phenomenon is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed. The research was reported in Nature in March 2020. With this award, Professor Sim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2021.07.12 View 7379 -
 Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 13381
Repurposed Drugs Present New Strategy for Treating COVID-19
Virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assays identifies best therapeutic medication candidates
A joint research group from KAIST and Institut Pasteur Korea has identified repurposed drugs for COVID-19 treatment through virtual screening and cell-based assays. The research team suggested the strategy for virtual screening with greatly reduced false positives by incorporating pre-docking filtering based on shape similarity and post-docking filtering based on interaction similarity. This strategy will help develop therapeutic medications for COVID-19 and other antiviral diseases more rapidly. This study was reported at the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS).
Researchers screened 6,218 drugs from a collection of FDA-approved drugs or those under clinical trial and identified 38 potential repurposed drugs for COVID-19 with this strategy. Among them, seven compounds inhibited SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero cells. Three of these drugs, emodin, omipalisib, and tipifarnib, showed anti-SARS-CoV-2 activity in human lung cells, Calu-3.
Drug repurposing is a practical strategy for developing antiviral drugs in a short period of time, especially during a global pandemic. In many instances, drug repurposing starts with the virtual screening of approved drugs. However, the actual hit rate of virtual screening is low and most of the predicted drug candidates are false positives.
The research group developed effective filtering algorithms before and after the docking simulations to improve the hit rates. In the pre-docking filtering process, compounds with similar shapes to the known active compounds for each target protein were selected and used for docking simulations. In the post-docking filtering process, the chemicals identified through their docking simulations were evaluated considering the docking energy and the similarity of the protein-ligand interactions with the known active compounds.
The experimental results showed that the virtual screening strategy reached a high hit rate of 18.4%, leading to the identification of seven potential drugs out of the 38 drugs initially selected.
“We plan to conduct further preclinical trials for optimizing drug concentrations as one of the three candidates didn’t resolve the toxicity issues in preclinical trials,” said Woo Dae Jang, one of the researchers from KAIST.
“The most important part of this research is that we developed a platform technology that can rapidly identify novel compounds for COVID-19 treatment. If we use this technology, we will be able to quickly respond to new infectious diseases as well as variants of the coronavirus,” said Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee.
This work was supported by the KAIST Mobile Clinic Module Project funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF). The National Culture Collection for Pathogens in Korea provided the SARS-CoV-2 (NCCP43326).
-PublicationWoo Dae Jang, Sangeun Jeon, Seungtaek Kim, and Sang Yup Lee. Drugs repurposed for COVID-19 by virtual screening of 6,218 drugs and cell-based assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (https://doi/org/10.1073/pnas.2024302118)
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup LeeMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.07.08 View 13381 -
 Quantum Laser Turns Energy Loss into Gain
A new laser that generates quantum particles can recycle lost energy for highly efficient, low threshold laser applications
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
The researchers found another unique and counter-intuitive feature of this design. Normally, energy is lost during laser operation. But in this system, as energy loss increased, the amount of energy needed to induce lasing decreased. Exploiting this phenomenon could lead to the development of high efficiency, low threshold lasers for future quantum optical devices.
“This system applies a concept of quantum physics known as parity-time reversal symmetry,” explains Professor Cho. “This is an important platform that allows energy loss to be used as gain. It can be used to reduce laser threshold energy for classical optical devices and sensors, as well as quantum devices and controlling the direction of light.”
The key is the design and materials. The hexagonal microcavity divides light particles into two different modes: one that passes through the upward-facing triangle of the hexagon and another that passes through its downward-facing triangle. Both modes of light particles have the same energy and path but don’t interact with each other.
However, the light particles do interact with other particles called excitons, provided by the hexagonal microcavity, which is made of semiconductors. This interaction leads to the generation of new quantum particles called polaritons that then interact with each other to generate the polariton laser. By controlling the degree of loss between the microcavity and the semiconductor substrate, an intriguing phenomenon arises, with the threshold energy becoming smaller as energy loss increases. This research was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and Korea’s National Research Foundation.
-PublicationSong,H.G, Choi, M, Woo, K.Y. Yong-Hoon Cho Room-temperature polaritonic non-Hermitian system with single microcavityNature Photonics (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00820-z)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.07 View 10018
Quantum Laser Turns Energy Loss into Gain
A new laser that generates quantum particles can recycle lost energy for highly efficient, low threshold laser applications
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
The researchers found another unique and counter-intuitive feature of this design. Normally, energy is lost during laser operation. But in this system, as energy loss increased, the amount of energy needed to induce lasing decreased. Exploiting this phenomenon could lead to the development of high efficiency, low threshold lasers for future quantum optical devices.
“This system applies a concept of quantum physics known as parity-time reversal symmetry,” explains Professor Cho. “This is an important platform that allows energy loss to be used as gain. It can be used to reduce laser threshold energy for classical optical devices and sensors, as well as quantum devices and controlling the direction of light.”
The key is the design and materials. The hexagonal microcavity divides light particles into two different modes: one that passes through the upward-facing triangle of the hexagon and another that passes through its downward-facing triangle. Both modes of light particles have the same energy and path but don’t interact with each other.
However, the light particles do interact with other particles called excitons, provided by the hexagonal microcavity, which is made of semiconductors. This interaction leads to the generation of new quantum particles called polaritons that then interact with each other to generate the polariton laser. By controlling the degree of loss between the microcavity and the semiconductor substrate, an intriguing phenomenon arises, with the threshold energy becoming smaller as energy loss increases. This research was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and Korea’s National Research Foundation.
-PublicationSong,H.G, Choi, M, Woo, K.Y. Yong-Hoon Cho Room-temperature polaritonic non-Hermitian system with single microcavityNature Photonics (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00820-z)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.07 View 10018 -
 Study of T Cells from COVID-19 Convalescents Guides Vaccine Strategies
Researchers confirm that most COVID-19 patients in their convalescent stage carry stem cell-like memory T cells for months
A KAIST immunology research team found that most convalescent patients of COVID-19 develop and maintain T cell memory for over 10 months regardless of the severity of their symptoms. In addition, memory T cells proliferate rapidly after encountering their cognate antigen and accomplish their multifunctional roles. This study provides new insights for effective vaccine strategies against COVID-19, considering the self-renewal capacity and multipotency of memory T cells.
COVID-19 is a disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. When patients recover from COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2-specific adaptive immune memory is developed. The adaptive immune system consists of two principal components: B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that eliminate infected cells. The current results suggest that the protective immune function of memory T cells will be implemented upon re-exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Recently, the role of memory T cells against SARS-CoV-2 has been gaining attention as neutralizing antibodies wane after recovery. Although memory T cells cannot prevent the infection itself, they play a central role in preventing the severe progression of COVID-19. However, the longevity and functional maintenance of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells remain unknown.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his collaborators investigated the characteristics and functions of stem cell-like memory T cells, which are expected to play a crucial role in long-term immunity. Researchers analyzed the generation of stem cell-like memory T cells and multi-cytokine producing polyfunctional memory T cells, using cutting-edge immunological techniques.
This research is significant in that revealing the long-term immunity of COVID-19 convalescent patients provides an indicator regarding the long-term persistence of T cell immunity, one of the main goals of future vaccine development, as well as evaluating the long-term efficacy of currently available COVID-19 vaccines.
The research team is presently conducting a follow-up study to identify the memory T cell formation and functional characteristics of those who received COVID-19 vaccines, and to understand the immunological effect of COVID-19 vaccines by comparing the characteristics of memory T cells from vaccinated individuals with those of COVID-19 convalescent patients.
PhD candidate Jae Hyung Jung and Dr. Min-Seok Rha, a clinical fellow at Yonsei Severance Hospital, who led the study together explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of COVID-19 immunity and establish an index for COVID-19 vaccine-induced memory T cells.”
“This study is the world’s longest longitudinal study on differentiation and functions of memory T cells among COVID-19 convalescent patients. The research on the temporal dynamics of immune responses has laid the groundwork for building a strategy for next-generation vaccine development,” Professor Shin added. This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on June 30.
-Publication:
Jung, J.H., Rha, MS., Sa, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell memory is sustained in COVID-19 convalescent patients for 10 months with successful development of stem cell-like memory T cells. Nat Communications 12, 4043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24377-1
-Profile:
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin
Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (http://liid.kaist.ac.kr/)
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.07.05 View 12691
Study of T Cells from COVID-19 Convalescents Guides Vaccine Strategies
Researchers confirm that most COVID-19 patients in their convalescent stage carry stem cell-like memory T cells for months
A KAIST immunology research team found that most convalescent patients of COVID-19 develop and maintain T cell memory for over 10 months regardless of the severity of their symptoms. In addition, memory T cells proliferate rapidly after encountering their cognate antigen and accomplish their multifunctional roles. This study provides new insights for effective vaccine strategies against COVID-19, considering the self-renewal capacity and multipotency of memory T cells.
COVID-19 is a disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. When patients recover from COVID-19, SARS-CoV-2-specific adaptive immune memory is developed. The adaptive immune system consists of two principal components: B cells that produce antibodies and T cells that eliminate infected cells. The current results suggest that the protective immune function of memory T cells will be implemented upon re-exposure to SARS-CoV-2.
Recently, the role of memory T cells against SARS-CoV-2 has been gaining attention as neutralizing antibodies wane after recovery. Although memory T cells cannot prevent the infection itself, they play a central role in preventing the severe progression of COVID-19. However, the longevity and functional maintenance of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T cells remain unknown.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and his collaborators investigated the characteristics and functions of stem cell-like memory T cells, which are expected to play a crucial role in long-term immunity. Researchers analyzed the generation of stem cell-like memory T cells and multi-cytokine producing polyfunctional memory T cells, using cutting-edge immunological techniques.
This research is significant in that revealing the long-term immunity of COVID-19 convalescent patients provides an indicator regarding the long-term persistence of T cell immunity, one of the main goals of future vaccine development, as well as evaluating the long-term efficacy of currently available COVID-19 vaccines.
The research team is presently conducting a follow-up study to identify the memory T cell formation and functional characteristics of those who received COVID-19 vaccines, and to understand the immunological effect of COVID-19 vaccines by comparing the characteristics of memory T cells from vaccinated individuals with those of COVID-19 convalescent patients.
PhD candidate Jae Hyung Jung and Dr. Min-Seok Rha, a clinical fellow at Yonsei Severance Hospital, who led the study together explained, “Our analysis will enhance the understanding of COVID-19 immunity and establish an index for COVID-19 vaccine-induced memory T cells.”
“This study is the world’s longest longitudinal study on differentiation and functions of memory T cells among COVID-19 convalescent patients. The research on the temporal dynamics of immune responses has laid the groundwork for building a strategy for next-generation vaccine development,” Professor Shin added. This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and KAIST, and was published in Nature Communications on June 30.
-Publication:
Jung, J.H., Rha, MS., Sa, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell memory is sustained in COVID-19 convalescent patients for 10 months with successful development of stem cell-like memory T cells. Nat Communications 12, 4043 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24377-1
-Profile:
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin
Laboratory of Immunology & Infectious Diseases (http://liid.kaist.ac.kr/)
Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
KAIST
2021.07.05 View 12691 -
 Alumni Professor Cho at NYU Endows Scholarship for Female Computer Scientists
Alumni Professor Kyunghyun Cho at New York University endowed the “Lim Mi-Sook Scholarship” at KAIST for female computer scientists in honor of his mother.
Professor Cho, a graduate of the School of Computing in 2011 completed his master’s and PhD at Alto University in Finland in 2014. He has been teaching at NYU since 2015 and received the Samsung Ho-Am Prize for Engineering this year in recognition of his outstanding researches in the fields of machine learning and AI.
“I hope this will encourage young female students to continue their studies in computer science and encourage others to join the discipline in the future, thereby contributing to building a more diverse community of computer scientists,” he said in his written message. His parents and President Kwang Hyung Lee attended the donation ceremony held at the Daejeon campus on June 24.
Professor Cho has developed neural network machine learning translation algorithm that is widely being used in translation engines. His contributions to AI-powered translations and innovation in the industry led him to win one of the most prestigious prizes in Korea.
He decided to donate his 300 million KRW prize money to fund two 100 million KRW scholarships named after each of his parents: the Lim Mi-Sook Scholarship is for female computer scientists and the Bae-Gyu Scholarly Award for Classics is in honor of his father, who is a Korean literature professor at Soongsil University in Korea. He will also fund a scholarship at Alto University.
“I recall there were less than five female students out of 70 students in my cohort during my undergraduate studies at KAIST even in later 2000s. Back then, it just felt natural that boys majored computer science and girls in biology.”
He said he wanted to acknowledge his mother, who had to give up her teaching career in the 1980s to take care of her children. “It made all of us think more about the burden of raising children that is placed often disproportionately on mothers and how it should be better distributed among parents, relatives, and society in order to ensure and maximize equity in education as well as career development and advances.”
He added, “As a small step to help build a more diverse environment, I have decided to donate to this fund to provide a small supplement to the small group of female students majoring in computer science.
2021.07.01 View 9078
Alumni Professor Cho at NYU Endows Scholarship for Female Computer Scientists
Alumni Professor Kyunghyun Cho at New York University endowed the “Lim Mi-Sook Scholarship” at KAIST for female computer scientists in honor of his mother.
Professor Cho, a graduate of the School of Computing in 2011 completed his master’s and PhD at Alto University in Finland in 2014. He has been teaching at NYU since 2015 and received the Samsung Ho-Am Prize for Engineering this year in recognition of his outstanding researches in the fields of machine learning and AI.
“I hope this will encourage young female students to continue their studies in computer science and encourage others to join the discipline in the future, thereby contributing to building a more diverse community of computer scientists,” he said in his written message. His parents and President Kwang Hyung Lee attended the donation ceremony held at the Daejeon campus on June 24.
Professor Cho has developed neural network machine learning translation algorithm that is widely being used in translation engines. His contributions to AI-powered translations and innovation in the industry led him to win one of the most prestigious prizes in Korea.
He decided to donate his 300 million KRW prize money to fund two 100 million KRW scholarships named after each of his parents: the Lim Mi-Sook Scholarship is for female computer scientists and the Bae-Gyu Scholarly Award for Classics is in honor of his father, who is a Korean literature professor at Soongsil University in Korea. He will also fund a scholarship at Alto University.
“I recall there were less than five female students out of 70 students in my cohort during my undergraduate studies at KAIST even in later 2000s. Back then, it just felt natural that boys majored computer science and girls in biology.”
He said he wanted to acknowledge his mother, who had to give up her teaching career in the 1980s to take care of her children. “It made all of us think more about the burden of raising children that is placed often disproportionately on mothers and how it should be better distributed among parents, relatives, and society in order to ensure and maximize equity in education as well as career development and advances.”
He added, “As a small step to help build a more diverse environment, I have decided to donate to this fund to provide a small supplement to the small group of female students majoring in computer science.
2021.07.01 View 9078 -
 Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 11682
Prof. Sang Wan Lee Selected for 2021 IBM Academic Award
Professor Sang Wan Lee from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2021 IBM Global University Program Academic Award. The award recognizes individual faculty members whose emerging science and technology contains significant interest for universities and IBM.
Professor Lee, whose research focuses on artificial intelligence and computational neuroscience, won the award for his research proposal titled A Neuroscience-Inspired Approach for Metacognitive Reinforcement Learning. IBM provides a gift of $40,000 to the recipient’s institution in recognition of the selection of the project but not as a contract for services.
Professor Lee’s project aims to exploit the unique characteristics of human reinforcement learning. Specifically, he plans to examines the hypothesis that metacognition, a human’s ability to estimate their uncertainty level, serves to guide sample-efficient and near-optimal exploration, making it possible to achieve an optimal balance between model-based and model-free reinforcement learning.
He was also selected as the winner of the Google Research Award in 2016 and has been working with DeepMind and University College London to conduct basic research on decision-making brain science to establish a theory on frontal lobe meta-enhance learning.
"We plan to conduct joint research for utilizing brain-based artificial intelligence technology and frontal lobe meta-enhanced learning technology modeling in collaboration with an international research team including IBM, DeepMind, MIT, and Oxford,” Professor Lee said.
2021.06.25 View 11682 -
 Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 10176
Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 10176