Science
-
 Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 27699
Image Analysis to Automatically Quantify Gender Bias in Movies
Many commercial films worldwide continue to express womanhood in a stereotypical manner, a recent study using image analysis showed. A KAIST research team developed a novel image analysis method for automatically quantifying the degree of gender bias in films.
The ‘Bechdel Test’ has been the most representative and general method of evaluating gender bias in films. This test indicates the degree of gender bias in a film by measuring how active the presence of women is in a film. A film passes the Bechdel Test if the film (1) has at least two female characters, (2) who talk to each other, and (3) their conversation is not related to the male characters.
However, the Bechdel Test has fundamental limitations regarding the accuracy and practicality of the evaluation. Firstly, the Bechdel Test requires considerable human resources, as it is performed subjectively by a person. More importantly, the Bechdel Test analyzes only a single aspect of the film, the dialogues between characters in the script, and provides only a dichotomous result of passing the test, neglecting the fact that a film is a visual art form reflecting multi-layered and complicated gender bias phenomena. It is also difficult to fully represent today’s various discourse on gender bias, which is much more diverse than in 1985 when the Bechdel Test was first presented.
Inspired by these limitations, a KAIST research team led by Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology proposed an advanced system that uses computer vision technology to automatically analyzes the visual information of each frame of the film. This allows the system to more accurately and practically evaluate the degree to which female and male characters are discriminatingly depicted in a film in quantitative terms, and further enables the revealing of gender bias that conventional analysis methods could not yet detect.
Professor Lee and his researchers Ji Yoon Jang and Sangyoon Lee analyzed 40 films from Hollywood and South Korea released between 2017 and 2018. They downsampled the films from 24 to 3 frames per second, and used Microsoft’s Face API facial recognition technology and object detection technology YOLO9000 to verify the details of the characters and their surrounding objects in the scenes.
Using the new system, the team computed eight quantitative indices that describe the representation of a particular gender in the films. They are: emotional diversity, spatial staticity, spatial occupancy, temporal occupancy, mean age, intellectual image, emphasis on appearance, and type and frequency of surrounding objects.
Figure 1. System Diagram
Figure 2. 40 Hollywood and Korean Films Analyzed in the Study
According to the emotional diversity index, the depicted women were found to be more prone to expressing passive emotions, such as sadness, fear, and surprise. In contrast, male characters in the same films were more likely to demonstrate active emotions, such as anger and hatred.
Figure 3. Difference in Emotional Diversity between Female and Male Characters
The type and frequency of surrounding objects index revealed that female characters and automobiles were tracked together only 55.7 % as much as that of male characters, while they were more likely to appear with furniture and in a household, with 123.9% probability.
In cases of temporal occupancy and mean age, female characters appeared less frequently in films than males at the rate of 56%, and were on average younger in 79.1% of the cases. These two indices were especially conspicuous in Korean films.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed that many commercial films depict women from a stereotypical perspective. I hope this result promotes public awareness of the importance of taking prudence when filmmakers create characters in films.”
This study was supported by KAIST College of Liberal Arts and Convergence Science as part of the Venture Research Program for Master’s and PhD Students, and will be presented at the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW) on November 11 to be held in Austin, Texas.
Publication:
Ji Yoon Jang, Sangyoon Lee, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Quantification of Gender Representation Bias in Commercial Films based on Image Analysis. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM Conference on Computer-Supported Cooperative Work and Social Computing (CSCW). ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 198, 29 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3359300
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://files.cargocollective.com/611692/cscw198-jangA--1-.pdf
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Ji Yoon Jang, M.S.
yoone3422@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangyoon Lee, M.S. Candidate
sl2820@kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2019.10.17 View 27699 -
 A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 29593
A Mathematical Model Reveals Long-Distance Cell Communication Mechanism
How can tens of thousands of people in a large football stadium all clap together with the same beat even though they can only hear the people near them clapping?
A combination of a partial differential equation and a synthetic circuit in microbes answers this question. An interdisciplinary collaborative team of Professor Jae Kyoung Kim at KAIST, Professor Krešimir Josić at the University of Houston, and Professor Matt Bennett at Rice University has identified how a large community can communicate with each other almost simultaneously even with very short distance signaling. The research was reported at Nature Chemical Biology.
Cells often communicate using signaling molecules, which can travel only a short distance. Nevertheless, the cells can also communicate over large distances to spur collective action. The team revealed a cell communication mechanism that quickly forms a network of local interactions to spur collective action, even in large communities.
The research team used an engineered transcriptional circuit of combined positive and negative feedback loops in E. coli, which can periodically release two types of signaling molecules: activator and repressor. As the signaling molecules travel over a short distance, cells can only talk to their nearest neighbors. However, cell communities synchronize oscillatory gene expression in spatially extended systems as long as the transcriptional circuit contains a positive feedback loop for the activator.
Professor Kim said that analyzing and understanding such high-dimensional dynamics was extremely difficult. He explained, “That’s why we used high-dimensional partial differential equation to describe the system based on the interactions among various types of molecules.” Surprisingly, the mathematical model accurately simulates the synthesis of the signaling molecules in the cell and their spatial diffusion throughout the chamber and their effect on neighboring cells.
The team simplified the high-dimensional system into a one-dimensional orbit, noting that the system repeats periodically. This allowed them to discover that cells can make one voice when they lowered their own voice and listened to the others. “It turns out the positive feedback loop reduces the distance between moving points and finally makes them move all together. That’s why you clap louder when you hear applause from nearby neighbors and everyone eventually claps together at almost the same time,” said Professor Kim.
Professor Kim added, “Math is a powerful as it simplifies complex thing so that we can find an essential underlying property. This finding would not have been possible without the simplification of complex systems using mathematics."
The National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Robert A. Welch Foundation, the Hamill Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the T.J. Park Science Fellowship of POSCO supported the research.
(Figure: Complex molecular interactions among microbial consortia is simplified as interactions among points on a limit cycle (right).)
2019.10.15 View 29593 -
 Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 10232
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon selected as the 2019 SUHF Young Investigator
< Professor Ki-Jun Yoon >
Professor Ki-Jun Yoon from the Department of Biological Sciences was named one of four recipients of the 2019 Suh Kyung-Bae Science Foundation (SUHF) Young Investigator Awards.
The SUHF is a non-profit organization established in 2016 and funded by a personal donation of 300 billion KRW in shares from Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh of the Amorepacific Group. The primary purpose of the foundation is to serve as a platform to nurture and provide comprehensive long-term support for creative and passionate young Korean scientists committed to pursuing research in the field of life sciences. The SUHF selects three to five scientists through an open recruiting process every year, and grants each scientist a maximum of 2.5 billion KRW over a period of up to five years.
Since January this year, the foundation received 83 research proposals from scientists across the nation, especially from those who had less than five years of experience as professors, and selected the four recipients, including Professor Yoon.
Professor Yoon was recognized for his contributions to the advancement of research on how post-transcriptional mechanisms may modulate stem cell properties. His research project involves deciphering the molecular mechanisms controlling RNA metabolism in neural stem cells during normal development, and how alterations in RNA regulatory programs lead to human brain disorders.
< (From left) Professor Joo-Hong Park, Professor Yuree Lee, Chairman and CEO Kyung-Bae Suh, Professor Eunjung Lee, Professor Ki-Jun Yoon, ⓒ Amorepacific Group >
The other awards were given to Professor Joo-Hong Park and Professor Yuree Lee of Seoul National University, and Professor Eunjung Lee of Boston Children's Hospital and Harvard Medical School.
The awards ceremony was held on September 18 at the Amorepacific Headquarters in Seoul.
With these four new awardees, a total of 14 scientists have been named as SUHF Young Investigators to date.
(END)
2019.09.23 View 10232 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 12000
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 12000 -
 Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 29456
Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Pressure Sensor to Increase Practical Applicability
< Professor Steve Park (left) and the First Author Mr. Jinwon Oh (right) >
Researchers have designed a flexible pressure sensor that is expected to have a much wider applicability. A KAIST research team fabricated a piezoresistive pressure sensor of high uniformity with low hysteresis by chemically grafting a conductive polymer onto a porous elastomer template.
The team discovered that the uniformity of pore size and shape is directly related to the uniformity of the sensor. The team noted that by increasing pore size and shape variability, the variability of the sensor characteristics also increases.
Researchers led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering confirmed that compared to other sensors composed of randomly sized and shaped pores, which had a coefficient of variation in relative resistance change of 69.65%, their newly developed sensor exhibited much higher uniformity with a coefficient of variation of 2.43%. This study was reported in Small as the cover article on August 16.
Flexible pressure sensors have been actively researched and widely applied in electronic equipment such as touch screens, robots, wearable healthcare devices, electronic skin, and human-machine interfaces. In particular, piezoresistive pressure sensors based on elastomer‐conductive material composites hold significant potential due to their many advantages including a simple and low-cost fabrication process.
Various research results have been reported for ways to improve the performance of piezoresistive pressure sensors, most of which have been focused on increasing the sensitivity. Despite its significance, maximizing the sensitivity of composite-based piezoresistive pressure sensors is not necessary for many applications. On the other hand, sensor-to-sensor uniformity and hysteresis are two properties that are of critical importance to realize any application.
The importance of sensor-to-sensor uniformity is obvious. If the sensors manufactured under the same conditions have different properties, measurement reliability is compromised, and therefore the sensor cannot be used in a practical setting.
In addition, low hysteresis is also essential for improved measurement reliability. Hysteresis is a phenomenon in which the electrical readings differ depending on how fast or slow the sensor is being pressed, whether pressure is being released or applied, and how long and to what degree the sensor has been pressed. When a sensor has high hysteresis, the electrical readings will differ even under the same pressure, making the measurements unreliable.
Researchers said they observed a negligible hysteresis degree which was only 2%. This was attributed to the strong chemical bonding between the conductive polymer and the elastomer template, which prevents their relative sliding and displacement, and the porosity of the elastomer that enhances elastic behavior.
“This technology brings forth insight into how to address the two critical issues in pressure sensors: uniformity and hysteresis. We expect our technology to play an important role in increasing practical applications and the commercialization of pressure sensors in the near future,” said Professor Park.
This work was conducted as part of the KAIST‐funded Global Singularity Research Program for 2019, and also supported by the KUSTAR‐KAIST Institute.
Figure 1. Image of a porous elastomer template with uniform pore size and shape (left), Graph showing high uniformity in the sensors’ performance (right).
Figure 2. Hysteresis loops of the sensor at different pressure levels (left), and after a different number of cycles (right).
Figure 3. The cover page of Small Journal, Volume 15, Issue 33.
Publication:
Jinwon Oh, Jin‐Oh Kim, Yunjoo Kim, Han Byul Choi, Jun Chang Yang, Serin Lee, Mikhail Pyatykh, Jung Kim, Joo Yong Sim, and Steve Park. 2019. Highly Uniform and Low Hysteresis Piezoresistive Pressure Sensors Based on Chemical Grafting of Polypyrrole on Elastomer Template with Uniform Pore Size. Small. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KgaA, Weinheim, Germany, Volume No. 15, Issue No. 33, Full Paper No. 201901744, 8 pages. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201901744
Profile: Prof. Steve Park, MS, PhD
stevepark@kaist.ac.kr
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Mr. Jinwon Oh, MS
jwoh1701@gmail.com
http://steveparklab.kaist.ac.kr/
Researcher
Organic and Nano Electronics Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Jung Kim, MS, PhD
jungkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://medev.kaist.ac.kr/
Professor
Biorobotics Laboratory
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Joo Yong Sim, PhD
jsim@etri.re.kr
Researcher
Bio-Medical IT Convergence Research Department
Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI)
https://www.etri.re.krDaejeon 34129, Korea
(END)
2019.08.19 View 29456 -
 Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 30257
Accurate Detection of Low-Level Somatic Mutation in Intractable Epilepsy
KAIST medical scientists have developed an advanced method for perfectly detecting low-level somatic mutation in patients with intractable epilepsy. Their study showed that deep sequencing replicates of major focal epilepsy genes accurately and efficiently identified low-level somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
According to the study, their diagnostic method could increase the accuracy up to 100%, unlike the conventional sequencing analysis, which stands at about 30% accuracy. This work was published in Acta Neuropathologica.
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder common in children. Approximately one third of child patients are diagnosed with intractable epilepsy despite adequate anti-epileptic medication treatment.
Somatic mutations in mTOR pathway genes, SLC35A2, and BRAF are the major genetic causes of intractable epilepsies. A clinical trial to target Focal Cortical Dysplasia type II (FCDII), the mTOR inhibitor is underway at Severance Hospital, their collaborator in Seoul, Korea. However, it is difficult to detect such somatic mutations causing intractable epilepsy because their mutational burden is less than 5%, which is similar to the level of sequencing artifacts. In the clinical field, this has remained a standing challenge for the genetic diagnosis of somatic mutations in intractable epilepsy.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee’s team at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed paired brain and peripheral tissues from 232 intractable epilepsy patients with various brain pathologies at Severance Hospital using deep sequencing and extracted the major focal epilepsy genes.
They narrowed down target genes to eight major focal epilepsy genes, eliminating almost all of the false positive calls using deep targeted sequencing. As a result, the advanced method robustly increased the accuracy and enabled them to detect low-level somatic mutations in unmatched Formalin Fixed Paraffin Embedded (FFPE) brain samples, the most clinically relevant samples.
Professor Lee conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Dong Suk Kim and Hoon-Chul Kang at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University. He said, “This advanced method of genetic analysis will improve overall patient care by providing more comprehensive genetic counseling and informing decisions on alternative treatments.”
Professor Lee has investigated low-level somatic mutations arising in the brain for a decade. He is developing innovative diagnostics and therapeutics for untreatable brain disorders including intractable epilepsy and glioblastoma at a tech-startup called SoVarGen. “All of the technologies we used during the research were transferred to the company. This research gave us very good momentum to reach the next phase of our startup,” he remarked.
The work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation, a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Korean Health Technology R&D Project from the Ministry of Health & Welfare, and the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development.
(Figure: Landscape of somatic and germline mutations identified in intractable epilepsy patients. a Signaling pathways for all of the mutated genes identified in this study. Bold: somatic mutation, Regular: germline mutation. b The distribution of variant allelic frequencies (VAFs) of identified somatic mutations. c The detecting rate and types of identified mutations according to histopathology. Yellow: somatic mutations, green: two-hit mutations, grey: germline mutations.)
2019.08.14 View 30257 -
 Professor Sang Gyu Kim Receives Yeochon Award for Ecology
Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the winner of the 12th Yeochon Award for Ecology presented by the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research.
The award was conferred on August 13 in Jeju at the annual conference co-hosted by the Ecological Society of Korea and the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research. Professor Kim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his achievements and contributions in studying herbivorous insects ‘rice weevils’ and their host plant ‘wild tobacco’, especially for having explored the known facts in traditional ecology at the molecular level. His findings are presented in his paper titled ‘Trichobaris weevils distinguish amongst toxic host plants by sensing volatiles that do not affect larval performance’ published in Molecular Ecology in July 2016.
Furthermore, Professor Kim’s research team is continuing their work to identify the ecological functions of plant metabolites as well as interactions between flowers and insect vectors at the molecular level. In doing so, the team edits genes in various plant species using the latest gene editing technology.
The Yeochon Award for Ecology was first established in 2005 with funds donated by a senior ecologist, the late Honorary Professor Joon-Ho Kim of Seoul National University. The award is named after the professor’s pen name “Yeochon” and is intended to encourage promising next-generation ecologists to produce outstanding research achievements in the field of basic ecology.
Professor Kim said, “I will take this award as encouragement to continue taking challenging risks to observe ecological phenomenon from a new perspective. I will continue my research with my students with joy and enthusiasm.”
2019.08.14 View 7763
Professor Sang Gyu Kim Receives Yeochon Award for Ecology
Professor Sang-Gyu Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the winner of the 12th Yeochon Award for Ecology presented by the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research.
The award was conferred on August 13 in Jeju at the annual conference co-hosted by the Ecological Society of Korea and the Yeochon Association for Ecological Research. Professor Kim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his achievements and contributions in studying herbivorous insects ‘rice weevils’ and their host plant ‘wild tobacco’, especially for having explored the known facts in traditional ecology at the molecular level. His findings are presented in his paper titled ‘Trichobaris weevils distinguish amongst toxic host plants by sensing volatiles that do not affect larval performance’ published in Molecular Ecology in July 2016.
Furthermore, Professor Kim’s research team is continuing their work to identify the ecological functions of plant metabolites as well as interactions between flowers and insect vectors at the molecular level. In doing so, the team edits genes in various plant species using the latest gene editing technology.
The Yeochon Award for Ecology was first established in 2005 with funds donated by a senior ecologist, the late Honorary Professor Joon-Ho Kim of Seoul National University. The award is named after the professor’s pen name “Yeochon” and is intended to encourage promising next-generation ecologists to produce outstanding research achievements in the field of basic ecology.
Professor Kim said, “I will take this award as encouragement to continue taking challenging risks to observe ecological phenomenon from a new perspective. I will continue my research with my students with joy and enthusiasm.”
2019.08.14 View 7763 -
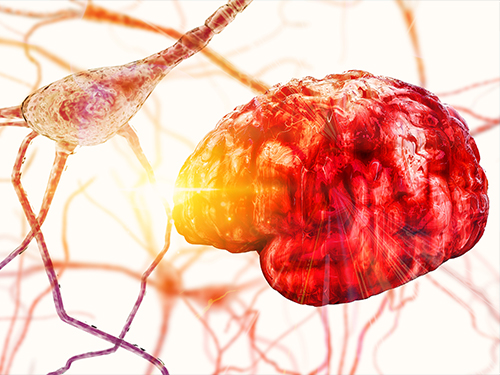 Newly Identified Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Answers the Key Questions on Brain Clearance
(Figure: Schematic images of location and features of meningeal lymphatic vessels and their changes associated with ageing.)
Just see what happens when your neighborhood’s waste disposal system is out of service. Not only do the piles of trash stink but they can indeed hinder the area’s normal functioning. That is also the case when the brain’s waste management is on the blink.
The buildup of toxic proteins in the brain causes a massive damage to the nerves, leading to cognitive dysfunction and increased probability of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Though the brain drains its waste via the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), little has been understood about an accurate route for the brain’s cleansing mechanism.
Medical scientists led by Professor Gou Young Koh at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering have reported the basal side of the skull as the major route, so called “hotspot” for CSF drainage.
They found that basal meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) function as the main plumbing pipes for CSF. They confirmed macromolecules in the CSF mainly runs through the basal mLVs. Notably, the team also revealed that the brain’s major drainage system, specifically basal mLVs are impaired with aging. Their findings have been reported in the journal Nature on July 24.
Throughout our body, excess fluids and waste products are removed from tissues via lymphatic vessels. It was only recently discovered that the brain also has a lymphatic drainage system. mLVs are supposed to carry waste from the brain tissue fluid and the CSF down the deep cervical lymph nodes for disposal. Still scientist are left with one perplexing question — where is the main exit for the CSF? Though mLVs in the upper part of the skull (dorsal meningeal lymphatic vessels) were reported as the brain’s clearance pathways in 2014, no substantial drainage mechanism was observed in that section.
“As a hidden exit for CSF, we looked into the mLVs trapped within complex structures at the base of the skull,” says Dr. Ji Hoon Ahn, the first author of this study. The researchers used several techniques to characterize the basal mLVs in detail. They used a genetically engineered lymphatic-reporter mouse model to visualize mLVs under a fluorescence microscope. By performing a careful examination of the mice skull, they found distinctive features of basal mLVs that make them suitable for CSF uptake and drainage. Just like typical functional lymphatic vessels, basal mLVs are found to have abundant lymphatic vessel branches with finger-like protrusions. Additionally, valves inside the basal mLVs allow the flow to go in one direction. In particular, they found that the basal mLVs are closely located to the CSF. Dr. Hyunsoo Cho, the first author of this study explains, “All up, it seemed a solid case that basal mLVs are the brain’s main clearance pathways.
The researchers verified such specialized morphologic characteristics of basal mLVs indeed facilitate the CSF uptake and drainage. Using CSF contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a rat model, they found that CSF is drained preferentially through the basal mLVs. They also utilized a lymphatic-reporter mouse model and discovered that fluorescence-tagged tracer injected into the brain itself or the CSF is cleared mainly through the basal mLVs. Jun-Hee Kim, the first author of this study notes, “We literally saw that the brain clearance mechanism utilizing basal outflow route to exit the skull.
It has long been suggested that CSF turnover and drainage declines with ageing. However, alteration of mLVs associated with ageing is poorly understood. In this study, the researchers observed changes of mLVs in young (3-month-old) and aged (24~27-months-old) mice. They found that the structure of the basal mLVs and their lymphatic valves in aged mice become severely flawed, thus hampering CSF clearance. The corresponding author of this study, Dr. Koh says, “By characterizing the precise route for fluids leaving the brain, this study improves our understanding on how waste is cleared from the brain. Our findings also provide further insights into the role of impaired CSF clearance in the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.”
Many current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease target abnormally accumulated proteins, such as beta-amyloid. By mapping out a precise route for the brain’s waste clearance system, this study may be able to help find ways to improve the brain’s cleansing function. Such breakthrough might become quite a sensational strategy for eliminating the buildup of aging-related toxic proteins. “It definitely warrants more extensive investigation of mLVs in patients with age-related neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical investigation,” adds Professor Koh.
2019.07.25 View 33650
Newly Identified Meningeal Lymphatic Vessels Answers the Key Questions on Brain Clearance
(Figure: Schematic images of location and features of meningeal lymphatic vessels and their changes associated with ageing.)
Just see what happens when your neighborhood’s waste disposal system is out of service. Not only do the piles of trash stink but they can indeed hinder the area’s normal functioning. That is also the case when the brain’s waste management is on the blink.
The buildup of toxic proteins in the brain causes a massive damage to the nerves, leading to cognitive dysfunction and increased probability of developing neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Though the brain drains its waste via the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), little has been understood about an accurate route for the brain’s cleansing mechanism.
Medical scientists led by Professor Gou Young Koh at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering have reported the basal side of the skull as the major route, so called “hotspot” for CSF drainage.
They found that basal meningeal lymphatic vessels (mLVs) function as the main plumbing pipes for CSF. They confirmed macromolecules in the CSF mainly runs through the basal mLVs. Notably, the team also revealed that the brain’s major drainage system, specifically basal mLVs are impaired with aging. Their findings have been reported in the journal Nature on July 24.
Throughout our body, excess fluids and waste products are removed from tissues via lymphatic vessels. It was only recently discovered that the brain also has a lymphatic drainage system. mLVs are supposed to carry waste from the brain tissue fluid and the CSF down the deep cervical lymph nodes for disposal. Still scientist are left with one perplexing question — where is the main exit for the CSF? Though mLVs in the upper part of the skull (dorsal meningeal lymphatic vessels) were reported as the brain’s clearance pathways in 2014, no substantial drainage mechanism was observed in that section.
“As a hidden exit for CSF, we looked into the mLVs trapped within complex structures at the base of the skull,” says Dr. Ji Hoon Ahn, the first author of this study. The researchers used several techniques to characterize the basal mLVs in detail. They used a genetically engineered lymphatic-reporter mouse model to visualize mLVs under a fluorescence microscope. By performing a careful examination of the mice skull, they found distinctive features of basal mLVs that make them suitable for CSF uptake and drainage. Just like typical functional lymphatic vessels, basal mLVs are found to have abundant lymphatic vessel branches with finger-like protrusions. Additionally, valves inside the basal mLVs allow the flow to go in one direction. In particular, they found that the basal mLVs are closely located to the CSF. Dr. Hyunsoo Cho, the first author of this study explains, “All up, it seemed a solid case that basal mLVs are the brain’s main clearance pathways.
The researchers verified such specialized morphologic characteristics of basal mLVs indeed facilitate the CSF uptake and drainage. Using CSF contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in a rat model, they found that CSF is drained preferentially through the basal mLVs. They also utilized a lymphatic-reporter mouse model and discovered that fluorescence-tagged tracer injected into the brain itself or the CSF is cleared mainly through the basal mLVs. Jun-Hee Kim, the first author of this study notes, “We literally saw that the brain clearance mechanism utilizing basal outflow route to exit the skull.
It has long been suggested that CSF turnover and drainage declines with ageing. However, alteration of mLVs associated with ageing is poorly understood. In this study, the researchers observed changes of mLVs in young (3-month-old) and aged (24~27-months-old) mice. They found that the structure of the basal mLVs and their lymphatic valves in aged mice become severely flawed, thus hampering CSF clearance. The corresponding author of this study, Dr. Koh says, “By characterizing the precise route for fluids leaving the brain, this study improves our understanding on how waste is cleared from the brain. Our findings also provide further insights into the role of impaired CSF clearance in the development of age-related neurodegenerative diseases.”
Many current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease target abnormally accumulated proteins, such as beta-amyloid. By mapping out a precise route for the brain’s waste clearance system, this study may be able to help find ways to improve the brain’s cleansing function. Such breakthrough might become quite a sensational strategy for eliminating the buildup of aging-related toxic proteins. “It definitely warrants more extensive investigation of mLVs in patients with age-related neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease prior to clinical investigation,” adds Professor Koh.
2019.07.25 View 33650 -
 Deciphering Brain Somatic Mutations Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
Researchers have found a potential link between non-inherited somatic mutations in the brain and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers have identified somatic mutations in the brain that could contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Their findings were published in the journal Nature Communications last week.
Decades worth of research has identified inherited mutations that lead to early-onset familial AD. Inherited mutations, however, are behind at most half the cases of late onset sporadic AD, in which there is no family history of the disease. But the genetic factors causing the other half of these sporadic cases have been unclear.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and colleagues analysed the DNA present in post-mortem hippocampal formations and in blood samples from people aged 70 to 96 with AD and age-matched controls. They specifically looked for non-inherited somatic mutations in their brains using high-depth whole exome sequencing.
The team developed a bioinformatics pipeline that enabled them to detect low-level brain somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs) – mutations that involve the substitution of a single nucleotide with another nucleotide. Brain somatic SNVs have been reported on and accumulate throughout our lives and can sometimes be associated with a range of neurological diseases.
The number of somatic SNVs did not differ between individuals with AD and non-demented controls. Interestingly, somatic SNVs in AD brains arise about 4.8 times more slowly than in blood. When the team performed gene-set enrichment tests, 26.9 percent of the AD brain samples had pathogenic brain somatic SNVs known to be linked to hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which is one of major hallmarks of AD.
Then, they pinpointed a pathogenic SNV in the PIN1 gene, a cis/trans isomerase that balances phosphorylation in tau proteins, found in one AD patient’s brain. They found the mutation was 4.9 time more abundant in AT8-positive – a marker for hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins– neurons in the entorhinal cortex than the bulk hippocampal tissue. Furthermore, in a series of functional assays, they observed the mutation causing a loss of function in PIN1 and such haploinsufficiency increased the phosphorylation and aggregation of tau proteins.
“Our study provides new insights into the molecular genetic factors behind Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases potentially linked to somatic mutations in the brain,” said Professor Lee.
The team is planning to expand their study to a larger cohort in order to establish stronger links between these brain somatic mutations and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
(Figure 1. Bioinformatic pipeline for detecting low-level brain somatic mutations in AD and non-AD.)
(Figure 2. Pathogenic brain somatic mutations associated with tau phosphorylation are significantly enriched in AD brains.)
(Figure 3. A pathogenic brain somatic mutation in PIN1 (c. 477 C>T) is a loss-of-function and related functional assays show its haploinsufficiency increases phosphorylation and aggregation of tau.)
2019.07.19 View 37299
Deciphering Brain Somatic Mutations Associated with Alzheimer's Disease
Researchers have found a potential link between non-inherited somatic mutations in the brain and the progression of Alzheimer’s disease
Researchers have identified somatic mutations in the brain that could contribute to the development of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Their findings were published in the journal Nature Communications last week.
Decades worth of research has identified inherited mutations that lead to early-onset familial AD. Inherited mutations, however, are behind at most half the cases of late onset sporadic AD, in which there is no family history of the disease. But the genetic factors causing the other half of these sporadic cases have been unclear.
Professor Jeong Ho Lee at the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering and colleagues analysed the DNA present in post-mortem hippocampal formations and in blood samples from people aged 70 to 96 with AD and age-matched controls. They specifically looked for non-inherited somatic mutations in their brains using high-depth whole exome sequencing.
The team developed a bioinformatics pipeline that enabled them to detect low-level brain somatic single nucleotide variations (SNVs) – mutations that involve the substitution of a single nucleotide with another nucleotide. Brain somatic SNVs have been reported on and accumulate throughout our lives and can sometimes be associated with a range of neurological diseases.
The number of somatic SNVs did not differ between individuals with AD and non-demented controls. Interestingly, somatic SNVs in AD brains arise about 4.8 times more slowly than in blood. When the team performed gene-set enrichment tests, 26.9 percent of the AD brain samples had pathogenic brain somatic SNVs known to be linked to hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins, which is one of major hallmarks of AD.
Then, they pinpointed a pathogenic SNV in the PIN1 gene, a cis/trans isomerase that balances phosphorylation in tau proteins, found in one AD patient’s brain. They found the mutation was 4.9 time more abundant in AT8-positive – a marker for hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins– neurons in the entorhinal cortex than the bulk hippocampal tissue. Furthermore, in a series of functional assays, they observed the mutation causing a loss of function in PIN1 and such haploinsufficiency increased the phosphorylation and aggregation of tau proteins.
“Our study provides new insights into the molecular genetic factors behind Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases potentially linked to somatic mutations in the brain,” said Professor Lee.
The team is planning to expand their study to a larger cohort in order to establish stronger links between these brain somatic mutations and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.
(Figure 1. Bioinformatic pipeline for detecting low-level brain somatic mutations in AD and non-AD.)
(Figure 2. Pathogenic brain somatic mutations associated with tau phosphorylation are significantly enriched in AD brains.)
(Figure 3. A pathogenic brain somatic mutation in PIN1 (c. 477 C>T) is a loss-of-function and related functional assays show its haploinsufficiency increases phosphorylation and aggregation of tau.)
2019.07.19 View 37299 -
 High-Performance Sodium Ion Batteries Using Copper Sulfide
(Prof.Yuk and his two PhD candidates Parks)
Researchers presented a new strategy for extending sodium ion batteries’ cyclability using copper sulfide as the electrode material. This strategy has led to high-performance conversion reactions and is expected to advance the commercialization of sodium ion batteries as they emerge as an alternative to lithium ion batteries.
Professor Jong Min Yuk’s team confirmed the stable sodium storage mechanism using copper sulfide, a superior electrode material that is pulverization-tolerant and induces capacity recovery. Their findings suggest that when employing copper sulfide, sodium ion batteries will have a lifetime of more than five years with one charge per a day. Even better, copper sulfide, composed of abundant natural materials such as copper and sulfur, has better cost competitiveness than lithium ion batteries, which use lithium and cobalt.
Intercalation-type materials such as graphite, which serve as commercialized anode materials in lithium ion batteries, have not been viable for high-capacity sodium storage due to their insufficient interlayer spacing. Thus, conversion and alloying reactions type materials have been explored to meet higher capacity in the anode part. However, those materials generally bring up large volume expansions and abrupt crystallographic changes, which lead to severe capacity degradation.
The team confirmed that semi-coherent phase interfaces and grain boundaries in conversion reactions played key roles in enabling pulverization-tolerant conversion reactions and capacity recovery, respectively.
Most of conversion and alloying reactions type battery materials usually experience severe capacity degradations due to having completely different crystal structures and large volume expansion before and after the reactions. However, copper sulfides underwent a gradual crystallographic change to make the semi-coherent interfaces, which eventually prevented the pulverization of particles. Based on this unique mechanism, the team confirmed that copper sulfide exhibits a high capacity and high cycling stability regardless of its size and morphology.
Professor Yuk said, “Sodium ion batteries employing copper sulfide can advance sodium ion batteries, which could contribute to the development of low-cost energy storage systems and address the micro-dust issue”
This study was posted in Advanced Science on April 26 online and selected as the inside back cover for June issue.
(Figure: Schematic model demonstrating grain boundaries and phase interfaces formations.)
2019.07.15 View 29136
High-Performance Sodium Ion Batteries Using Copper Sulfide
(Prof.Yuk and his two PhD candidates Parks)
Researchers presented a new strategy for extending sodium ion batteries’ cyclability using copper sulfide as the electrode material. This strategy has led to high-performance conversion reactions and is expected to advance the commercialization of sodium ion batteries as they emerge as an alternative to lithium ion batteries.
Professor Jong Min Yuk’s team confirmed the stable sodium storage mechanism using copper sulfide, a superior electrode material that is pulverization-tolerant and induces capacity recovery. Their findings suggest that when employing copper sulfide, sodium ion batteries will have a lifetime of more than five years with one charge per a day. Even better, copper sulfide, composed of abundant natural materials such as copper and sulfur, has better cost competitiveness than lithium ion batteries, which use lithium and cobalt.
Intercalation-type materials such as graphite, which serve as commercialized anode materials in lithium ion batteries, have not been viable for high-capacity sodium storage due to their insufficient interlayer spacing. Thus, conversion and alloying reactions type materials have been explored to meet higher capacity in the anode part. However, those materials generally bring up large volume expansions and abrupt crystallographic changes, which lead to severe capacity degradation.
The team confirmed that semi-coherent phase interfaces and grain boundaries in conversion reactions played key roles in enabling pulverization-tolerant conversion reactions and capacity recovery, respectively.
Most of conversion and alloying reactions type battery materials usually experience severe capacity degradations due to having completely different crystal structures and large volume expansion before and after the reactions. However, copper sulfides underwent a gradual crystallographic change to make the semi-coherent interfaces, which eventually prevented the pulverization of particles. Based on this unique mechanism, the team confirmed that copper sulfide exhibits a high capacity and high cycling stability regardless of its size and morphology.
Professor Yuk said, “Sodium ion batteries employing copper sulfide can advance sodium ion batteries, which could contribute to the development of low-cost energy storage systems and address the micro-dust issue”
This study was posted in Advanced Science on April 26 online and selected as the inside back cover for June issue.
(Figure: Schematic model demonstrating grain boundaries and phase interfaces formations.)
2019.07.15 View 29136 -
 Mathematical Modeling Makes a Breakthrough for a New CRSD Medication
PhD Candidate Dae Wook Kim (Left) and Professor Jae Kyoung Kim (Right)
- Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy -
Mathematicians’ new modeling has identified major sources of interspecies and inter-individual variations in the clinical efficacy of a clock-modulating drug: photosensitivity and PER2 level. This enabled precision medicine for circadian disruption.
A KAIST mathematics research team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim, in collaboration with Pfizer, applied a combination of mathematical modeling and simulation tools for circadian rhythms sleep disorders (CRSDs) to analyze the animal data generated by Pfizer. This study was reported in Molecular Systems Biology as the cover article on July 8.
Pharmaceutical companies have conducted extensive studies on animals to determine the candidacy of this new medication. However, the results of animal testing do not always translate to the same effects in human trials. Furthermore, even between humans, efficacy differs across individuals depending on an individual’s genetic and environmental factors, which require different treatment strategies.
To overcome these obstacles, KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators developed adaptive chronotherapeutics to identify precise dosing regimens that could restore normal circadian phase under different conditions.
A circadian rhythm is a 24-hour cycle in the physiological processes of living creatures, including humans. A biological clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus in the human brain sets the time for various human behaviors such as sleep.
A disruption of the endogenous timekeeping system caused by changes in one’s life pattern leads to advanced or delayed sleep-wake cycle phase and a desynchronization between sleep-wake rhythms, resulting in CRSDs. To restore the normal timing of sleep, timing of the circadian clock could be adjusted pharmacologically.
Pfizer identified PF-670462, which can adjust the timing of circadian clock by inhibiting the core clock kinase of the circadian clock (CK1d/e). However, the efficacy of PF-670462 significantly differs between nocturnal mice and diurnal monkeys, whose sleeping times are opposite.
The research team discovered the source of such interspecies variations in drug response by performing thousands of virtual experiments using a mathematical model, which describes biochemical interactions among clock molecules and PF-670462. The result suggests that the effect of PF-670462 is reduced by light exposure in diurnal primates more than in nocturnal mice. This indicates that the strong counteracting effect of light must be considered in order to effectively regulate the circadian clock of diurnal humans using PF-670462.
Furthermore, the team also found the source of inter-patients variations in drug efficacy using virtual patients whose circadian clocks were disrupted due to various mutations. The degree of perturbation in the endogenous level of the core clock molecule PER2 affects the efficacy.
This explains why the clinical outcomes of clock-modulating drugs are highly variable and certain subtypes are unresponsive to treatment. Furthermore, this points out the limitations of current treatment strategies tailored to only the patient’s sleep and wake time but not to the molecular cause of sleep disorders.
PhD candidate Dae Wook Kim, who is the first author, said that this motivates the team to develop an adaptive chronotherapy, which identifies a personalized optimal dosing time of day by tracking the sleep-wake up time of patients via a wearable device and allows for a precision medicine approach for CRSDs.
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim said, "As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of a new drug candidate, which can improve the lives of so many patients. I hope this result promotes more collaborations in this translational research.”
This research was supported by a Pfizer grant to KAIST (G01160179), the Human Frontiers Science Program Organization (RGY0063/2017), and a National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea Grant (NRF-2016 RICIB 3008468 and NRF-2017-Fostering Core Leaders of the Future Basic Science Program/ Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program).
Figure 1. Interspecies and Inter-patients Variations in PF-670462 Efficacy
Figure 2. Journal Cover Page
Publication:
Dae Wook Kim, Cheng Chang, Xian Chen, Angela C Doran, Francois Gaudreault, Travis Wager, George J DeMarco, and Jae Kyoung Kim. 2019. Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy. Molecular Systems Biology. EMBO Press, Heidelberg, Germany, Vol. 15, Issue No. 7, Article, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20198838
Profile: Prof. Jae Kyoung Kim, PhD
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
Associate Professor
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dae Wook Kim, PhD Candidate
0308kdo@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
PhD Candidate
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dr. Cheng Chang, PhD
cheng.chang@pfizer.com
Associate Director of Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical Pharmacology, Global Product Development
Pfizer
https://www.pfizer.com/ Groton 06340, USA
(END)
2019.07.09 View 37010
Mathematical Modeling Makes a Breakthrough for a New CRSD Medication
PhD Candidate Dae Wook Kim (Left) and Professor Jae Kyoung Kim (Right)
- Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy -
Mathematicians’ new modeling has identified major sources of interspecies and inter-individual variations in the clinical efficacy of a clock-modulating drug: photosensitivity and PER2 level. This enabled precision medicine for circadian disruption.
A KAIST mathematics research team led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim, in collaboration with Pfizer, applied a combination of mathematical modeling and simulation tools for circadian rhythms sleep disorders (CRSDs) to analyze the animal data generated by Pfizer. This study was reported in Molecular Systems Biology as the cover article on July 8.
Pharmaceutical companies have conducted extensive studies on animals to determine the candidacy of this new medication. However, the results of animal testing do not always translate to the same effects in human trials. Furthermore, even between humans, efficacy differs across individuals depending on an individual’s genetic and environmental factors, which require different treatment strategies.
To overcome these obstacles, KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators developed adaptive chronotherapeutics to identify precise dosing regimens that could restore normal circadian phase under different conditions.
A circadian rhythm is a 24-hour cycle in the physiological processes of living creatures, including humans. A biological clock in the hypothalamic suprachiasmatic nucleus in the human brain sets the time for various human behaviors such as sleep.
A disruption of the endogenous timekeeping system caused by changes in one’s life pattern leads to advanced or delayed sleep-wake cycle phase and a desynchronization between sleep-wake rhythms, resulting in CRSDs. To restore the normal timing of sleep, timing of the circadian clock could be adjusted pharmacologically.
Pfizer identified PF-670462, which can adjust the timing of circadian clock by inhibiting the core clock kinase of the circadian clock (CK1d/e). However, the efficacy of PF-670462 significantly differs between nocturnal mice and diurnal monkeys, whose sleeping times are opposite.
The research team discovered the source of such interspecies variations in drug response by performing thousands of virtual experiments using a mathematical model, which describes biochemical interactions among clock molecules and PF-670462. The result suggests that the effect of PF-670462 is reduced by light exposure in diurnal primates more than in nocturnal mice. This indicates that the strong counteracting effect of light must be considered in order to effectively regulate the circadian clock of diurnal humans using PF-670462.
Furthermore, the team also found the source of inter-patients variations in drug efficacy using virtual patients whose circadian clocks were disrupted due to various mutations. The degree of perturbation in the endogenous level of the core clock molecule PER2 affects the efficacy.
This explains why the clinical outcomes of clock-modulating drugs are highly variable and certain subtypes are unresponsive to treatment. Furthermore, this points out the limitations of current treatment strategies tailored to only the patient’s sleep and wake time but not to the molecular cause of sleep disorders.
PhD candidate Dae Wook Kim, who is the first author, said that this motivates the team to develop an adaptive chronotherapy, which identifies a personalized optimal dosing time of day by tracking the sleep-wake up time of patients via a wearable device and allows for a precision medicine approach for CRSDs.
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim said, "As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of a new drug candidate, which can improve the lives of so many patients. I hope this result promotes more collaborations in this translational research.”
This research was supported by a Pfizer grant to KAIST (G01160179), the Human Frontiers Science Program Organization (RGY0063/2017), and a National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea Grant (NRF-2016 RICIB 3008468 and NRF-2017-Fostering Core Leaders of the Future Basic Science Program/ Global Ph.D. Fellowship Program).
Figure 1. Interspecies and Inter-patients Variations in PF-670462 Efficacy
Figure 2. Journal Cover Page
Publication:
Dae Wook Kim, Cheng Chang, Xian Chen, Angela C Doran, Francois Gaudreault, Travis Wager, George J DeMarco, and Jae Kyoung Kim. 2019. Systems approach reveals photosensitivity and PER2 level as determinants of clock-modulator efficacy. Molecular Systems Biology. EMBO Press, Heidelberg, Germany, Vol. 15, Issue No. 7, Article, 16 pages. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.20198838
Profile: Prof. Jae Kyoung Kim, PhD
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
Associate Professor
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dae Wook Kim, PhD Candidate
0308kdo@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
PhD Candidate
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Dr. Cheng Chang, PhD
cheng.chang@pfizer.com
Associate Director of Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical Pharmacology, Global Product Development
Pfizer
https://www.pfizer.com/ Groton 06340, USA
(END)
2019.07.09 View 37010 -
 Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 13923
Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 13923