Ubiquitous+Mobile+Life+Systems+Lab
-
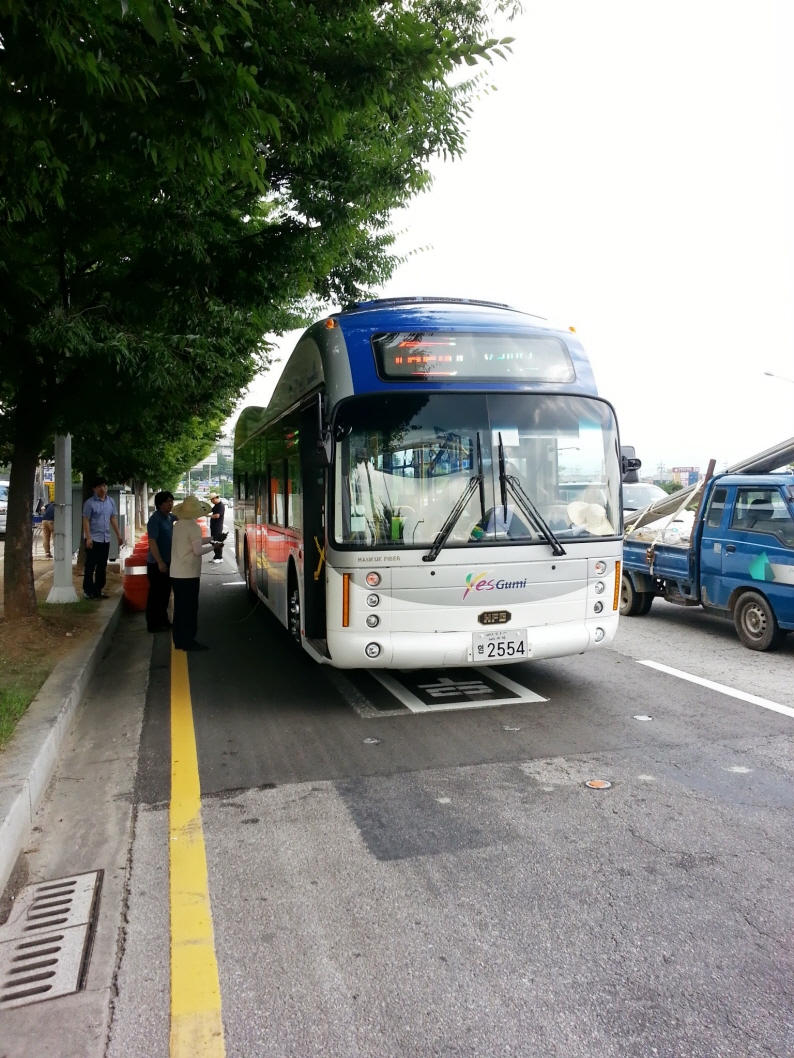 KAIST's wireless Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) runs inner city roads
For the first time anywhere, electric buses provide public transportation services and are recharged right from the road.
The Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV), developed by the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), is an electric vehicle that can be charged while stationary or driving, thus removing the need to stop at a charging station. Likewise, an OLEV tram does not require pantographs to feed power from electric wires strung above the tram route.
Following the development and operation of commercialized OLEV trams (at an amusement park in Seoul) and shuttle buses (at KAIST campus), respectively, the City of Gumi in South Korea, beginning on August 6th, is providing its citizens with OLEV public transportation services.
Two OLEV buses will run an inner city route between Gumi Train Station and In-dong district, for a total of 24 km roundtrip. The bus will receive 20 kHz and 100 kW (136 horsepower) electricity at an 85% maximum power transmission efficiency rate while maintaining a 17cm air gap between the underbody of the vehicle and the road surface.
OLEV is a groundbreaking technology that accelerates the development of purely electric vehicles as a viable option for future transportation systems, be they personal vehicles or public transit. This is accomplished by solving technological issues that limit the commercialization of electric vehicles such as price, weight, volume, driving distance, and lack of charging infrastructure.
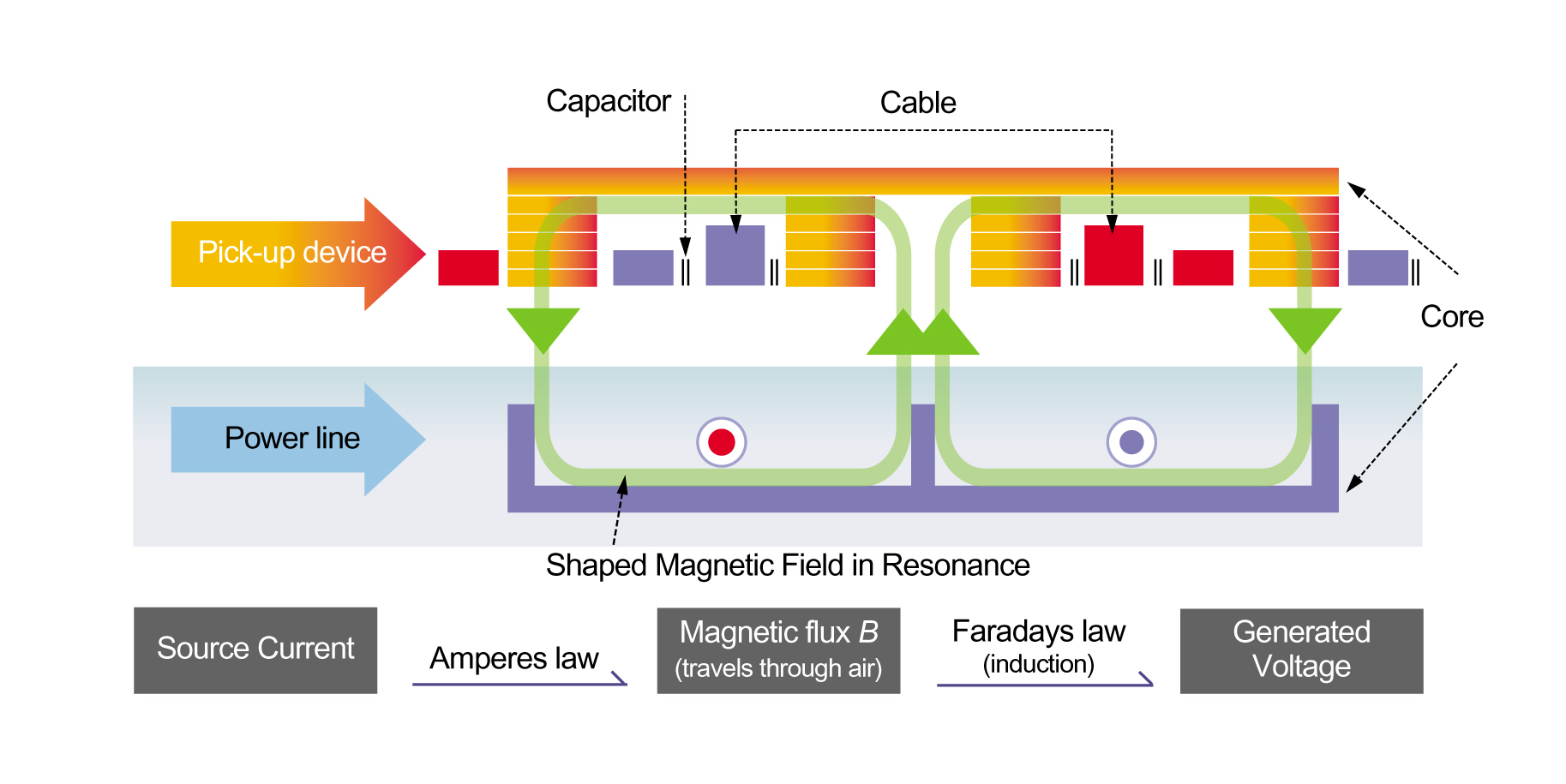
OLEV receives power wirelessly through the application of the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR)” technology. SMFIR is a new technology introduced by KAIST that enables electric vehicles to transfer electricity wirelessly from the road surface while moving. Power comes from the electrical cables buried under the surface of the road, creating magnetic fields. There is a receiving device installed on the underbody of the OLEV that converts these fields into electricity. The length of power strips installed under the road is generally 5%-15% of the entire road, requiring only a few sections of the road to be rebuilt with the embedded cables.
OLEV has a small battery (one-third of the size of the battery equipped with a regular electric car). The vehicle complies with the international electromagnetic fields (EMF) standards of 62.5 mG, within the margin of safety level necessary for human health. The road has a smart function as well, to distinguish OLEV buses from regular cars—the segment technology is employed to control the power supply by switching on the power strip when OLEV buses pass along, but switching it off for other vehicles, thereby preventing EMF exposure and standby power consumption. As of today, the SMFIR technology supplies 60 kHz and 180 kW of power remotely to transport vehicles at a stable, constant rate.
Dong-Ho Cho, a professor of the electrical engineering and the director of the Center for Wireless Power Transfer Technology Business Development at KAIST, said:
“It’s quite remarkable that we succeeded with the OLEV project so that buses are offering public transportation services to passengers. This is certainly a turning point for OLEV to become more commercialized and widely accepted for mass transportation in our daily living.”
After the successful operation of the two OLEV buses by the end of this year, Gumi City plans to provide ten more such buses by 2015.
2013.08.07 View 26869
KAIST's wireless Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) runs inner city roads
For the first time anywhere, electric buses provide public transportation services and are recharged right from the road.
The Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV), developed by the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), is an electric vehicle that can be charged while stationary or driving, thus removing the need to stop at a charging station. Likewise, an OLEV tram does not require pantographs to feed power from electric wires strung above the tram route.
Following the development and operation of commercialized OLEV trams (at an amusement park in Seoul) and shuttle buses (at KAIST campus), respectively, the City of Gumi in South Korea, beginning on August 6th, is providing its citizens with OLEV public transportation services.
Two OLEV buses will run an inner city route between Gumi Train Station and In-dong district, for a total of 24 km roundtrip. The bus will receive 20 kHz and 100 kW (136 horsepower) electricity at an 85% maximum power transmission efficiency rate while maintaining a 17cm air gap between the underbody of the vehicle and the road surface.
OLEV is a groundbreaking technology that accelerates the development of purely electric vehicles as a viable option for future transportation systems, be they personal vehicles or public transit. This is accomplished by solving technological issues that limit the commercialization of electric vehicles such as price, weight, volume, driving distance, and lack of charging infrastructure.
OLEV receives power wirelessly through the application of the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR)” technology. SMFIR is a new technology introduced by KAIST that enables electric vehicles to transfer electricity wirelessly from the road surface while moving. Power comes from the electrical cables buried under the surface of the road, creating magnetic fields. There is a receiving device installed on the underbody of the OLEV that converts these fields into electricity. The length of power strips installed under the road is generally 5%-15% of the entire road, requiring only a few sections of the road to be rebuilt with the embedded cables.
OLEV has a small battery (one-third of the size of the battery equipped with a regular electric car). The vehicle complies with the international electromagnetic fields (EMF) standards of 62.5 mG, within the margin of safety level necessary for human health. The road has a smart function as well, to distinguish OLEV buses from regular cars—the segment technology is employed to control the power supply by switching on the power strip when OLEV buses pass along, but switching it off for other vehicles, thereby preventing EMF exposure and standby power consumption. As of today, the SMFIR technology supplies 60 kHz and 180 kW of power remotely to transport vehicles at a stable, constant rate.
Dong-Ho Cho, a professor of the electrical engineering and the director of the Center for Wireless Power Transfer Technology Business Development at KAIST, said:
“It’s quite remarkable that we succeeded with the OLEV project so that buses are offering public transportation services to passengers. This is certainly a turning point for OLEV to become more commercialized and widely accepted for mass transportation in our daily living.”
After the successful operation of the two OLEV buses by the end of this year, Gumi City plans to provide ten more such buses by 2015.
2013.08.07 View 26869 -
 KAIST Develops Wireless Power Transfer Technology for High Capacity Transit
KAIST and the Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI) have developed a wireless power transfer technology that can be applied to high capacity transportation systems such as railways, harbor freight, and airport transportation and logistics. The technology supplies 60 kHz and 180 kW of power remotely to transport vehicles at a stable, constant rate.
KAIST and KRRI successfully showcased the wireless power transfer technology to the public on February 13, 2013 by testing it on the railroad tracks at Osong Station in Korea. Originally, this technology was developed as part of an electric vehicle system introduced by KAIST in 2011 known as the On-line Electric Vehicle (OLEV).
OLEV does not need to be parked at a charging station to have a fully powered battery. It gets charged while running, idling, and parking, enabling a reduction in size of the reserve battery down to one-fifth of the battery on board a regular electric car. The initial models of OLEV, a bus and a tram, receive 20 kHz and 100 kW power at an 85% transmission efficiency rate while maintaining a 20cm air gap between the underbody of vehicle and the road surface. OLEV complies with the national and international standards of 62.5 mG, a safety net for electromagnetic fields. In July 2013, for the first time since its development, OLEV will run on a regular road, an inner city route in the city of Gumi, requiring 40 minutes of driving each way.
Today’s technology demonstration offers further support that OLEV can be utilized for large-scale systems. Professor Dong-Ho Cho, Director of Center for Wireless Power Transfer Technology Business Development at KAIST, explained the recent improvements to OLEV:
“We have greatly improved the OLEV technology from the early development stage by increasing its power transmission density by more than three times. The size and weight of the power pickup modules have been reduced as well. We were able to cut down the production costs for major OLEV components, the power supply, and the pickup system, and in turn, OLEV is one step closer to being commercialized.”
If trains receive power wirelessly, the costs of railway wear and tear will be dramatically reduced. There will be no power rails, including electrical poles, required for the establishment of a railway system, and accordingly, lesser space will be needed. Tunnels will be built on a smaller scale, lowering construction costs. In addition, it will be helpful to overcome major obstacles that discourage the construction of high speed railway systems such as noise levels and problems in connecting pantograph and power rails.
KAIST and KRRI plan to apply the wireless power transfer technology to trams in May and high speed trains in September.
2013.03.19 View 13840
KAIST Develops Wireless Power Transfer Technology for High Capacity Transit
KAIST and the Korea Railroad Research Institute (KRRI) have developed a wireless power transfer technology that can be applied to high capacity transportation systems such as railways, harbor freight, and airport transportation and logistics. The technology supplies 60 kHz and 180 kW of power remotely to transport vehicles at a stable, constant rate.
KAIST and KRRI successfully showcased the wireless power transfer technology to the public on February 13, 2013 by testing it on the railroad tracks at Osong Station in Korea. Originally, this technology was developed as part of an electric vehicle system introduced by KAIST in 2011 known as the On-line Electric Vehicle (OLEV).
OLEV does not need to be parked at a charging station to have a fully powered battery. It gets charged while running, idling, and parking, enabling a reduction in size of the reserve battery down to one-fifth of the battery on board a regular electric car. The initial models of OLEV, a bus and a tram, receive 20 kHz and 100 kW power at an 85% transmission efficiency rate while maintaining a 20cm air gap between the underbody of vehicle and the road surface. OLEV complies with the national and international standards of 62.5 mG, a safety net for electromagnetic fields. In July 2013, for the first time since its development, OLEV will run on a regular road, an inner city route in the city of Gumi, requiring 40 minutes of driving each way.
Today’s technology demonstration offers further support that OLEV can be utilized for large-scale systems. Professor Dong-Ho Cho, Director of Center for Wireless Power Transfer Technology Business Development at KAIST, explained the recent improvements to OLEV:
“We have greatly improved the OLEV technology from the early development stage by increasing its power transmission density by more than three times. The size and weight of the power pickup modules have been reduced as well. We were able to cut down the production costs for major OLEV components, the power supply, and the pickup system, and in turn, OLEV is one step closer to being commercialized.”
If trains receive power wirelessly, the costs of railway wear and tear will be dramatically reduced. There will be no power rails, including electrical poles, required for the establishment of a railway system, and accordingly, lesser space will be needed. Tunnels will be built on a smaller scale, lowering construction costs. In addition, it will be helpful to overcome major obstacles that discourage the construction of high speed railway systems such as noise levels and problems in connecting pantograph and power rails.
KAIST and KRRI plan to apply the wireless power transfer technology to trams in May and high speed trains in September.
2013.03.19 View 13840 -
 Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16846
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16846