Biophotonics+Laboratory
-
 Ultrathin Digital Camera Inspired by Xenos Peckii Eyes
(Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The visual system of Xenos peckii, an endoparasite of paper wasps, demonstrates distinct benefits for high sensitivity and high resolution, differing from the compound eyes of most insects. Taking their unique features, a KAIST team developed an ultrathin digital camera that emulates the unique eyes of Xenos peckii.
The ultrathin digital camera offers a wide field of view and high resolution in a slimmer body compared to existing imaging systems. It is expected to support various applications, such as monitoring equipment, medical imaging devices, and mobile imaging systems.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team are known for mimicking biological visual organs. The team’s past research includes an LED lens based on the abdominal segments of fireflies and biologically inspired anti-reflective structures.
Recently, the demand for ultrathin digital cameras has increased, due to the miniaturization of electronic and optical devices. However, most camera modules use multiple lenses along the optical axis to compensate for optical aberrations, resulting in a larger volume as well as a thicker total track length of digital cameras. Resolution and sensitivity would be compromised if these modules were to be simply reduced in size and thickness.
To address this issue, the team have developed micro-optical components, inspired from the visual system of Xenos peckii, and combined them with a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensor to achieve an ultrathin digital camera.
This new camera, measuring less than 2mm in thickness, emulates the eyes of Xenos peckii by using dozens of microprism arrays and microlens arrays. A microprism and microlens pair form a channel and the light-absorbing medium between the channels reduces optical crosstalk. Each channel captures the partial image at slightly different orientation, and the retrieved partial images are combined into a single image, thereby ensuring a wide field of view and high resolution.
Professor Jeong said, “We have proposed a novel method of fabricating an ultrathin camera. As the first insect-inspired, ultrathin camera that integrates a microcamera on a conventional CMOS image sensor array, our study will have a significant impact in optics and related fields.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Dongmin Keum and Kyung-Won Jang, was published in Light: Science & Applications on October 24, 2018.
Figure 1. Natural Xenos peckii eye and the biological inspiration for the ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
Figure 2. Optical images captured by the bioinspired ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
2018.12.31 View 9796
Ultrathin Digital Camera Inspired by Xenos Peckii Eyes
(Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
The visual system of Xenos peckii, an endoparasite of paper wasps, demonstrates distinct benefits for high sensitivity and high resolution, differing from the compound eyes of most insects. Taking their unique features, a KAIST team developed an ultrathin digital camera that emulates the unique eyes of Xenos peckii.
The ultrathin digital camera offers a wide field of view and high resolution in a slimmer body compared to existing imaging systems. It is expected to support various applications, such as monitoring equipment, medical imaging devices, and mobile imaging systems.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team are known for mimicking biological visual organs. The team’s past research includes an LED lens based on the abdominal segments of fireflies and biologically inspired anti-reflective structures.
Recently, the demand for ultrathin digital cameras has increased, due to the miniaturization of electronic and optical devices. However, most camera modules use multiple lenses along the optical axis to compensate for optical aberrations, resulting in a larger volume as well as a thicker total track length of digital cameras. Resolution and sensitivity would be compromised if these modules were to be simply reduced in size and thickness.
To address this issue, the team have developed micro-optical components, inspired from the visual system of Xenos peckii, and combined them with a CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) image sensor to achieve an ultrathin digital camera.
This new camera, measuring less than 2mm in thickness, emulates the eyes of Xenos peckii by using dozens of microprism arrays and microlens arrays. A microprism and microlens pair form a channel and the light-absorbing medium between the channels reduces optical crosstalk. Each channel captures the partial image at slightly different orientation, and the retrieved partial images are combined into a single image, thereby ensuring a wide field of view and high resolution.
Professor Jeong said, “We have proposed a novel method of fabricating an ultrathin camera. As the first insect-inspired, ultrathin camera that integrates a microcamera on a conventional CMOS image sensor array, our study will have a significant impact in optics and related fields.”
This research, led by PhD candidates Dongmin Keum and Kyung-Won Jang, was published in Light: Science & Applications on October 24, 2018.
Figure 1. Natural Xenos peckii eye and the biological inspiration for the ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
Figure 2. Optical images captured by the bioinspired ultrathin digital camera (Light: Science & Applications 2018)
2018.12.31 View 9796 -
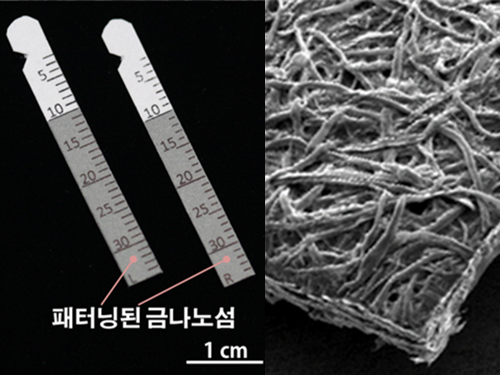 Gout Diagnostic Strip Using a Single Teardrop
A novel diagnostic strip for gout patients using a single teardrop has been announced by KAIST research team. This technology analyzes biological molecules in tears for a non-invasive diagnosis, significantly reducing the time and expense previously required for a diagnosis.
The research team under Professor Ki-Hun Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in developing an affordable and elaborate gout diagnostic strip by depositing metal nanoparticles on paper. This technology can not only be used in diagnostic medicine and drug testing, but also in various other areas such as field diagnoses that require prompt and accurate detection of a certain substance.
Gout induces pain in joints due to needle-shaped uric acid crystal build up. In general, therapeutic treatments exist to administer pain relief, stimulate uric acid discharge, and uric acid depressant. Such treatments work for temporary relief, but there have significant limitations. Thus, patients are required to regularly check uric acid concentrations, as well as control their diets. Therefore, simpler ways to measure uric acid would greatly benefit gout control and its prevention in a more affordable and convenient manner.
Existing gout diagnostic techniques include measuring uric acid concentrations from blood samples or observing uric acid crystals from joint synovial fluid under a microscope. These existing methods are invasive and time consuming. To overcome their limitations, the research team uniformly deposited gold nanoislands with nanoplasnomics properties on the surface of paper that can easily collect tears.
Nanoplasnomics techniques collect light on the surface of a metal nanostructure, and can be applied to disease and health diagnostic indicators as well as for genetic material detection. Further, metals such as gold absorb stronger light when it is irradiated, and thus can maximize light concentration on board surfaces while maintaining the properties of paper. The developed metal nanostructure production technology allows the flexible manufacturing of nanostructures on a large surface, which in turn allows flexible control of light concentrations.
The research team grafted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on paper diagnostic strips to allow uric acid concentration measurements in teardrops without additional indicators. The measured concentration in teardrops can be compared to blood uric acid concentrations for diagnosing gout.
Professor Jeong explained, “Based on these research results, our strip will make it possible to conduct low-cost, no indicator, supersensitive biological molecule analysis and fast field diagnosis using tears.” He continued, “Tears, as well as various other bodily fluids, can be used to contribute to disease diagnosis and physiological functional research.”
Ph.D. candidate Moonseong Park participated in the research as the first author of the paper that was published in the online edition of ACS Nano on December 14, 2016. Park said, “The strip will allow fast and simple field diagnosis, and can be produced on a large scale using the existing semiconductor process.”
(Figure 1. Optical image of paper gout diagnostic strip covered with gold)
(Figure 2. Scanning delectron microscopic image of paper gout diagnostic strip)
(Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope image of cellulos fiber coated with gold nanoislands)
(Figure 4. Gout diagnosis using tears)
2017.04.27 View 9916
Gout Diagnostic Strip Using a Single Teardrop
A novel diagnostic strip for gout patients using a single teardrop has been announced by KAIST research team. This technology analyzes biological molecules in tears for a non-invasive diagnosis, significantly reducing the time and expense previously required for a diagnosis.
The research team under Professor Ki-Hun Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in developing an affordable and elaborate gout diagnostic strip by depositing metal nanoparticles on paper. This technology can not only be used in diagnostic medicine and drug testing, but also in various other areas such as field diagnoses that require prompt and accurate detection of a certain substance.
Gout induces pain in joints due to needle-shaped uric acid crystal build up. In general, therapeutic treatments exist to administer pain relief, stimulate uric acid discharge, and uric acid depressant. Such treatments work for temporary relief, but there have significant limitations. Thus, patients are required to regularly check uric acid concentrations, as well as control their diets. Therefore, simpler ways to measure uric acid would greatly benefit gout control and its prevention in a more affordable and convenient manner.
Existing gout diagnostic techniques include measuring uric acid concentrations from blood samples or observing uric acid crystals from joint synovial fluid under a microscope. These existing methods are invasive and time consuming. To overcome their limitations, the research team uniformly deposited gold nanoislands with nanoplasnomics properties on the surface of paper that can easily collect tears.
Nanoplasnomics techniques collect light on the surface of a metal nanostructure, and can be applied to disease and health diagnostic indicators as well as for genetic material detection. Further, metals such as gold absorb stronger light when it is irradiated, and thus can maximize light concentration on board surfaces while maintaining the properties of paper. The developed metal nanostructure production technology allows the flexible manufacturing of nanostructures on a large surface, which in turn allows flexible control of light concentrations.
The research team grafted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on paper diagnostic strips to allow uric acid concentration measurements in teardrops without additional indicators. The measured concentration in teardrops can be compared to blood uric acid concentrations for diagnosing gout.
Professor Jeong explained, “Based on these research results, our strip will make it possible to conduct low-cost, no indicator, supersensitive biological molecule analysis and fast field diagnosis using tears.” He continued, “Tears, as well as various other bodily fluids, can be used to contribute to disease diagnosis and physiological functional research.”
Ph.D. candidate Moonseong Park participated in the research as the first author of the paper that was published in the online edition of ACS Nano on December 14, 2016. Park said, “The strip will allow fast and simple field diagnosis, and can be produced on a large scale using the existing semiconductor process.”
(Figure 1. Optical image of paper gout diagnostic strip covered with gold)
(Figure 2. Scanning delectron microscopic image of paper gout diagnostic strip)
(Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope image of cellulos fiber coated with gold nanoislands)
(Figure 4. Gout diagnosis using tears)
2017.04.27 View 9916 -
 Firefly inspired high efficiency LED technology developed
A firefly inspired, high efficiency self-illuminating LED has been developed.
Professor Jeong Gi Hoon (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) mimicked the nanostructure of the external layer of the illumination organ of a firefly and succeeded in fabricating high illumination efficiency LED lenses.
Conventional lenses required expensive anti-reflection coating. The developed lenses utilize the bio-inspired nanostructure on the surface of the lenses themselves to reduce the reflectivity of the lenses thereby decreasing production costs.
The developed antireflection nanostructure is expected to be applied to various digital devices and lighting fixtures.
Antireflective structures have been applied in various fields in order to enhance light efficiency However these structures have been limited to flat surfaces and therefore was difficult to implement to curved surfaces like LED lenses.
Professor Jeong’s team solved this problem by using three dimensional micro molding processes.
The team fabricated the nanostructure by forming a single nanoparticle layer on the silicon oxide and performing dry etching. On this nanostructure PDMS was poured and manipulated to fabricate a lens structure similar to that of a firefly.
The fabricated lens showed similar efficiency as conventional antireflection coating.
2012.11.29 View 9774
Firefly inspired high efficiency LED technology developed
A firefly inspired, high efficiency self-illuminating LED has been developed.
Professor Jeong Gi Hoon (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) mimicked the nanostructure of the external layer of the illumination organ of a firefly and succeeded in fabricating high illumination efficiency LED lenses.
Conventional lenses required expensive anti-reflection coating. The developed lenses utilize the bio-inspired nanostructure on the surface of the lenses themselves to reduce the reflectivity of the lenses thereby decreasing production costs.
The developed antireflection nanostructure is expected to be applied to various digital devices and lighting fixtures.
Antireflective structures have been applied in various fields in order to enhance light efficiency However these structures have been limited to flat surfaces and therefore was difficult to implement to curved surfaces like LED lenses.
Professor Jeong’s team solved this problem by using three dimensional micro molding processes.
The team fabricated the nanostructure by forming a single nanoparticle layer on the silicon oxide and performing dry etching. On this nanostructure PDMS was poured and manipulated to fabricate a lens structure similar to that of a firefly.
The fabricated lens showed similar efficiency as conventional antireflection coating.
2012.11.29 View 9774 -
 The output of terahertz waves enhanced by KAIST team
KAIST researchers have greatly improved the output of terahertz waves, the blue ocean of the optics world. This technology is expected to be applied to portable X-ray cameras, small bio-diagnostic systems, and in many other devices.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong"s research team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering used optical nano-antenna technology to increase the output of terahertz waves by three times.
Terahertz waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between 100GHz to 30THz. They are produced when a femtosecond (10^-15 s) pulse laser is shone on a semiconductor substrate with photoconduction antennas, causing a photocurrent pulse of one picosecond (10^-12 s). Their long wavelengths, in comparison to visible light and infrared rays, give terahertz waves a high penetration power with less energy than X-rays, making them less harmful to humans.
These qualities allow us to see through objects, just as X-rays do, but because terahertz waves absorb certain frequencies, we can detect hidden explosives or drugs, which was not possible with X-rays. We can even identify fake drugs. Furthermore, using the spectral information, we can analyze a material"s innate qualities without chemical processing, making it possible to identify skin diseases without harming the body. However, the output was not sufficient to be used in biosensors and other applications.
Prof. Jeong"s team added optical nano-antennas, made from gold nano-rods, in between the photoconduction antennas and optimized the structure. This resulted in nanoplasmonic resonance in the photoconduction substrate, increasing the degree of integration of the photocurrent pulse and resulting in a three times larger output.
Hence, it is not only possible to see through objects more clearly, but it is also possible to analyze components without a biopsy.
Professor Jeong explained, "This technology, coupled with the miniaturization of terahertz devices, can be applied to endoscopes to detect early epithelial cancer" and that he will focus on creating and commercializing these biosensor systems.
This research was published in the March issue of the international nanotechnology journal ACS Nano and was funded by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure: Mimetic diagram of a THz generator with nano-antennas
2012.04.29 View 14871
The output of terahertz waves enhanced by KAIST team
KAIST researchers have greatly improved the output of terahertz waves, the blue ocean of the optics world. This technology is expected to be applied to portable X-ray cameras, small bio-diagnostic systems, and in many other devices.
Professor Ki-Hun Jeong"s research team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering used optical nano-antenna technology to increase the output of terahertz waves by three times.
Terahertz waves are electromagnetic waves with frequencies between 100GHz to 30THz. They are produced when a femtosecond (10^-15 s) pulse laser is shone on a semiconductor substrate with photoconduction antennas, causing a photocurrent pulse of one picosecond (10^-12 s). Their long wavelengths, in comparison to visible light and infrared rays, give terahertz waves a high penetration power with less energy than X-rays, making them less harmful to humans.
These qualities allow us to see through objects, just as X-rays do, but because terahertz waves absorb certain frequencies, we can detect hidden explosives or drugs, which was not possible with X-rays. We can even identify fake drugs. Furthermore, using the spectral information, we can analyze a material"s innate qualities without chemical processing, making it possible to identify skin diseases without harming the body. However, the output was not sufficient to be used in biosensors and other applications.
Prof. Jeong"s team added optical nano-antennas, made from gold nano-rods, in between the photoconduction antennas and optimized the structure. This resulted in nanoplasmonic resonance in the photoconduction substrate, increasing the degree of integration of the photocurrent pulse and resulting in a three times larger output.
Hence, it is not only possible to see through objects more clearly, but it is also possible to analyze components without a biopsy.
Professor Jeong explained, "This technology, coupled with the miniaturization of terahertz devices, can be applied to endoscopes to detect early epithelial cancer" and that he will focus on creating and commercializing these biosensor systems.
This research was published in the March issue of the international nanotechnology journal ACS Nano and was funded by the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure: Mimetic diagram of a THz generator with nano-antennas
2012.04.29 View 14871