Cell+Press
-
 KAIST Unveils the Hidden Control Architecture of Brain Networks
(Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and his team)
A KAIST research team identified the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks. The control properties will contribute to providing a fundamental basis for the exogenous control of brain networks and, therefore, has broad implications in cognitive and clinical neuroscience.
Although efficiency and robustness are often regarded as having a trade-off relationship, the human brain usually exhibits both attributes when it performs complex cognitive functions. Such optimality must be rooted in a specific coordinated control of interconnected brain regions, but the understanding of the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks is lacking.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team investigated the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks. They employed an interdisciplinary approach that spans connectomics, neuroscience, control engineering, network science, and systems biology to examine the structural brain networks of various species and compared them with the control architecture of other biological networks, as well as man-made ones, such as social, infrastructural and technological networks.
In particular, the team reconstructed the structural brain networks of 100 healthy human adults by performing brain parcellation and tractography with structural and diffusion imaging data obtained from the Human Connectome Project database of the US National Institutes of Health.
The team developed a framework for analyzing the control architecture of brain networks based on the minimum dominating set (MDSet), which refers to a minimal subset of nodes (MD-nodes) that control the remaining nodes with a one-step direct interaction. MD-nodes play a crucial role in various complex networks including biomolecular networks, but they have not been investigated in brain networks.
By exploring and comparing the structural principles underlying the composition of MDSets of various complex networks, the team delineated their distinct control architectures. Interestingly, the team found that the proportion of MDSets in brain networks is remarkably small compared to those of other complex networks. This finding implies that brain networks may have been optimized for minimizing the cost required for controlling networks. Furthermore, the team found that the MDSets of brain networks are not solely determined by the degree of nodes, but rather strategically placed to form a particular control architecture.
Consequently, the team revealed the hidden control architecture of brain networks, namely, the distributed and overlapping control architecture that is distinct from other complex networks. The team found that such a particular control architecture brings about robustness against targeted attacks (i.e., preferential attacks on high-degree nodes) which might be a fundamental basis of robust brain functions against preferential damage of high-degree nodes (i.e., brain regions).
Moreover, the team found that the particular control architecture of brain networks also enables high efficiency in switching from one network state, defined by a set of node activities, to another – a capability that is crucial for traversing diverse cognitive states.
Professor Cho said, “This study is the first attempt to make a quantitative comparison between brain networks and other real-world complex networks. Understanding of intrinsic control architecture underlying brain networks may enable the development of optimal interventions for therapeutic purposes or cognitive enhancement.”
This research, led by Byeongwook Lee, Uiryong Kang and Hongjun Chang, was published in iScience (10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.017) on March 29, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic of identification of control architecture of brain networks.
Figure 2. Identified control architectures of brain networks and other real-world complex networks.
2019.04.23 View 39103
KAIST Unveils the Hidden Control Architecture of Brain Networks
(Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and his team)
A KAIST research team identified the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks. The control properties will contribute to providing a fundamental basis for the exogenous control of brain networks and, therefore, has broad implications in cognitive and clinical neuroscience.
Although efficiency and robustness are often regarded as having a trade-off relationship, the human brain usually exhibits both attributes when it performs complex cognitive functions. Such optimality must be rooted in a specific coordinated control of interconnected brain regions, but the understanding of the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks is lacking.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and his team investigated the intrinsic control architecture of brain networks. They employed an interdisciplinary approach that spans connectomics, neuroscience, control engineering, network science, and systems biology to examine the structural brain networks of various species and compared them with the control architecture of other biological networks, as well as man-made ones, such as social, infrastructural and technological networks.
In particular, the team reconstructed the structural brain networks of 100 healthy human adults by performing brain parcellation and tractography with structural and diffusion imaging data obtained from the Human Connectome Project database of the US National Institutes of Health.
The team developed a framework for analyzing the control architecture of brain networks based on the minimum dominating set (MDSet), which refers to a minimal subset of nodes (MD-nodes) that control the remaining nodes with a one-step direct interaction. MD-nodes play a crucial role in various complex networks including biomolecular networks, but they have not been investigated in brain networks.
By exploring and comparing the structural principles underlying the composition of MDSets of various complex networks, the team delineated their distinct control architectures. Interestingly, the team found that the proportion of MDSets in brain networks is remarkably small compared to those of other complex networks. This finding implies that brain networks may have been optimized for minimizing the cost required for controlling networks. Furthermore, the team found that the MDSets of brain networks are not solely determined by the degree of nodes, but rather strategically placed to form a particular control architecture.
Consequently, the team revealed the hidden control architecture of brain networks, namely, the distributed and overlapping control architecture that is distinct from other complex networks. The team found that such a particular control architecture brings about robustness against targeted attacks (i.e., preferential attacks on high-degree nodes) which might be a fundamental basis of robust brain functions against preferential damage of high-degree nodes (i.e., brain regions).
Moreover, the team found that the particular control architecture of brain networks also enables high efficiency in switching from one network state, defined by a set of node activities, to another – a capability that is crucial for traversing diverse cognitive states.
Professor Cho said, “This study is the first attempt to make a quantitative comparison between brain networks and other real-world complex networks. Understanding of intrinsic control architecture underlying brain networks may enable the development of optimal interventions for therapeutic purposes or cognitive enhancement.”
This research, led by Byeongwook Lee, Uiryong Kang and Hongjun Chang, was published in iScience (10.1016/j.isci.2019.02.017) on March 29, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic of identification of control architecture of brain networks.
Figure 2. Identified control architectures of brain networks and other real-world complex networks.
2019.04.23 View 39103 -
 Novel Strategies to Transform a Commercially Available Iboga Alkaloid to Post-Iboga Alkaloids
(PhD candidate HyeonggeunLim, Professor Sunkyu Han, PhD candidate Sikwang Seong)
KAIST chemists have synthesized seven different iboga and post-iboga natural products from commercially available catharanthine by mirroring nature’s biosynthetic post-modification of the iboga skeleton. They devised a novel strategy to biosynthesize the natural products via a series of selective and efficient oxidation and rearrangement reactions. This will serve as a stepping stone for developing therapeutic medications against cancer and narcotics addiction.
The research team, led by Professor Sunkyu Han, conceptualized and coined the term “Post-Iboga” alkaloids to describe the natural products that are biosynthetically derived from iboga-type alkaloids, which are composed of rearranged indole and/or isoquinuclidine backbones.
Iboga alkaloids have attracted significant attention from the scientific community due to their intriguing polycyclic structures and potential therapeutic uses against drug addictions. Nature has evolved to add architectural repertoires to this family of secondary metabolites by diversifying the iboga frameworks.
Notable examples are the FDA-approved anticancer drugs vinblastine and vincristine, both derived by the oxidative dimerization of catharanthine and vindoline subunits. Admittedly, synthetic foci toward the biosynthetic iboga-derivatives have historically been on these aforementioned dimeric natural products.
Recent natural product isolation studies on Tabernaemontana corymbosa and Ervatamia officinalis species have resulted in discoveries of various secondary metabolites that are biosynthetically derived from iboga alkaloids. These recent outbursts of iboga-derived natural product isolation reports have kindled interests toward these family of natural products.
The research team utilized (+)-catharanthine, the starting material for the industrial production of the anticancer drug Navelbine®. Well-orchestrated oxidations at the C19 position and the indole moiety of the catharanthine derivative, followed by differential rearrangements under acidic conditions, provided synthetic samples of voatinggine and tabertinggine respectively.
On the other hand, opportune oxidations at the C19 position and the alpha position of the tertiary amine moiety of the catharantine derivative, followed by a transhemiaminalization, produced the first synthetic sample of chippiine/dippinine-type natural product, dippinine B.
It is important to note that the chippiine and dippinine-type alkaloids have been targeted among synthetic chemists for over 30 years but had not succumbed to synthesis prior to this report.
Professor Han believes that their study will serve as a blueprint for further explorations of the synthesis, biosynthesis, and pharmacology of this emerging family of natural products. This study was published in Chem on November 15, 2018 (DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.10.009).
2018.11.16 View 6222
Novel Strategies to Transform a Commercially Available Iboga Alkaloid to Post-Iboga Alkaloids
(PhD candidate HyeonggeunLim, Professor Sunkyu Han, PhD candidate Sikwang Seong)
KAIST chemists have synthesized seven different iboga and post-iboga natural products from commercially available catharanthine by mirroring nature’s biosynthetic post-modification of the iboga skeleton. They devised a novel strategy to biosynthesize the natural products via a series of selective and efficient oxidation and rearrangement reactions. This will serve as a stepping stone for developing therapeutic medications against cancer and narcotics addiction.
The research team, led by Professor Sunkyu Han, conceptualized and coined the term “Post-Iboga” alkaloids to describe the natural products that are biosynthetically derived from iboga-type alkaloids, which are composed of rearranged indole and/or isoquinuclidine backbones.
Iboga alkaloids have attracted significant attention from the scientific community due to their intriguing polycyclic structures and potential therapeutic uses against drug addictions. Nature has evolved to add architectural repertoires to this family of secondary metabolites by diversifying the iboga frameworks.
Notable examples are the FDA-approved anticancer drugs vinblastine and vincristine, both derived by the oxidative dimerization of catharanthine and vindoline subunits. Admittedly, synthetic foci toward the biosynthetic iboga-derivatives have historically been on these aforementioned dimeric natural products.
Recent natural product isolation studies on Tabernaemontana corymbosa and Ervatamia officinalis species have resulted in discoveries of various secondary metabolites that are biosynthetically derived from iboga alkaloids. These recent outbursts of iboga-derived natural product isolation reports have kindled interests toward these family of natural products.
The research team utilized (+)-catharanthine, the starting material for the industrial production of the anticancer drug Navelbine®. Well-orchestrated oxidations at the C19 position and the indole moiety of the catharanthine derivative, followed by differential rearrangements under acidic conditions, provided synthetic samples of voatinggine and tabertinggine respectively.
On the other hand, opportune oxidations at the C19 position and the alpha position of the tertiary amine moiety of the catharantine derivative, followed by a transhemiaminalization, produced the first synthetic sample of chippiine/dippinine-type natural product, dippinine B.
It is important to note that the chippiine and dippinine-type alkaloids have been targeted among synthetic chemists for over 30 years but had not succumbed to synthesis prior to this report.
Professor Han believes that their study will serve as a blueprint for further explorations of the synthesis, biosynthesis, and pharmacology of this emerging family of natural products. This study was published in Chem on November 15, 2018 (DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2018.10.009).
2018.11.16 View 6222 -
 Mechanism Leading to Cortical Malformation from Brain-Only Mutations Identified
Focal malformations of cortical development (FMCDs) are a heterogeneous group of brain cortical abnormalities. These conditions are the most common causes of medically refractory epilepsy in children and are highly associated with intellectual disability, developmental delay, and autism-spectrum disorders. Despite a broad spectrum of cortical abnormalities in FMCDs, the defective migration of neuronal cells is considered a key pathological hallmark.
A research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee in the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST has recently investigated the molecular mechanism of defective neuronal migration in FMCDs. Their research results were published online in Neuron on June 21, 2018.
The research team previously demonstrated that brain-only mutations in the mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) gene causes focal cortical dysplasia, one major form of FMCDs leading to intractable epilepsy in children. However, the molecular mechanisms by which brain-only mutations in MTOR lead to cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration in FMCDs remain unclear.
To study the molecular mechanism of brain cortical dyslamination, the research team utilized patients’ brain tissues and modeled the MTOR mutation-carrying cell and animal models recapitulating the pathogenesis and symptoms of FMCD patients. By performing comprehensive molecular genetic experiments, they found that the formation of primary cilia, one of cellular organelles, was disrupted in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons and demonstrated that this ciliary disruption was a cause of cortical dyslamination in FMCDs.
MTOR mutations prevented degradation of the OFD1 protein, one of the negative regulators of ciliary formation. As a result, the OFD1 protein was abnormally accumulated in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons, causing focal cortical dyslamination. By suppressing the expression of the OFD1 protein, the research team was able to rescue the defective formation of primary cilia, leading to the restoration of cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration considerably.
Based on these results, the research team is carrying out further research to develop novel therapeutics for patients with FMCDs caused by brain-only mutations.
This work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation and Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy.
The research paper is titled “Brain Somatic Mutations in MTOR Disrupt Neuronal Ciliogenesis, Leading to Focal Cortical Dyslamination.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.039)
Picture 1: The disrupted formation of primary cilia in brain tissues of FMCD mouse models and patients with FMCDs caused by brain somatic mutations in MTOR.
Picture 2: The rescue of defective ciliary formation in FMCD mouse models leading to the restoration of cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration.
2018.07.02 View 8929
Mechanism Leading to Cortical Malformation from Brain-Only Mutations Identified
Focal malformations of cortical development (FMCDs) are a heterogeneous group of brain cortical abnormalities. These conditions are the most common causes of medically refractory epilepsy in children and are highly associated with intellectual disability, developmental delay, and autism-spectrum disorders. Despite a broad spectrum of cortical abnormalities in FMCDs, the defective migration of neuronal cells is considered a key pathological hallmark.
A research team led by Professor Jeong Ho Lee in the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering at KAIST has recently investigated the molecular mechanism of defective neuronal migration in FMCDs. Their research results were published online in Neuron on June 21, 2018.
The research team previously demonstrated that brain-only mutations in the mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) gene causes focal cortical dysplasia, one major form of FMCDs leading to intractable epilepsy in children. However, the molecular mechanisms by which brain-only mutations in MTOR lead to cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration in FMCDs remain unclear.
To study the molecular mechanism of brain cortical dyslamination, the research team utilized patients’ brain tissues and modeled the MTOR mutation-carrying cell and animal models recapitulating the pathogenesis and symptoms of FMCD patients. By performing comprehensive molecular genetic experiments, they found that the formation of primary cilia, one of cellular organelles, was disrupted in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons and demonstrated that this ciliary disruption was a cause of cortical dyslamination in FMCDs.
MTOR mutations prevented degradation of the OFD1 protein, one of the negative regulators of ciliary formation. As a result, the OFD1 protein was abnormally accumulated in MTOR mutation-carrying neurons, causing focal cortical dyslamination. By suppressing the expression of the OFD1 protein, the research team was able to rescue the defective formation of primary cilia, leading to the restoration of cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration considerably.
Based on these results, the research team is carrying out further research to develop novel therapeutics for patients with FMCDs caused by brain-only mutations.
This work was supported by grants from the Suh Kyungbae Foundation and Citizens United for Research in Epilepsy.
The research paper is titled “Brain Somatic Mutations in MTOR Disrupt Neuronal Ciliogenesis, Leading to Focal Cortical Dyslamination.” (Digital Object Identifier #: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.039)
Picture 1: The disrupted formation of primary cilia in brain tissues of FMCD mouse models and patients with FMCDs caused by brain somatic mutations in MTOR.
Picture 2: The rescue of defective ciliary formation in FMCD mouse models leading to the restoration of cortical dyslamination and defective neuronal migration.
2018.07.02 View 8929 -
 Activation of Bystander Immune Cells during Acute Hepatitis A.
A KAIST research team has identified a process of tissue damage caused by bystander immune cells in acute viral infections. This research will pave the way for research to understand the principles of tissue damage in viral infections and immune diseases, and can point toward a possible therapeutic target for the treatment.
Upon viral infection, viral replication itself destroys human cells, but in some cases, viral replication is not the direct cause of the tissue damage. In particular, the destruction of infected cells is the primary cause of tissue damage during non-cytopathic viral infections such as hepatitis A virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. However, the underlying pathological mechanisms involved in the tissue damage during viral infections have not been fully elucidated.
Specificity is one of the most important characteristics of the immune system. In general, infection from a certain virus specifically activates immune cells targeting the virus, while other immune cells specific to different viruses remain inactive.
An immune cell not specific to an infected virus is called a bystander immune cell. A phenomenon that activates irrelevant immune cells not originally targeting the infecting virus, called the activation of bystander immune cells, is already known to the world; however, its clinical significance has not been investigated thoroughly.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and Professor Su-Hyung Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed patients with acute hepatitis A, in collaboration with Chung-Ang University Hospital.
The team found not only immune cells specifically targeting the hepatitis A virus were activated, but also bystander immune cells were activated and involved in the damaging of liver tissues during acute hepatitis A.
According to the research, when a person is infected with hepatitis A virus, hepatitis A virus-infected cells produce IL-15, which induces the activation of bystander immune cells. Activated bystander immune cells exert innate-like cytotoxicity, triggered by activating receptors NKG2D and NKp30 and this can lead to liver injury.
Through describing the cause of excessive tissue damage during acute viral hepatitis, the research outcome is expected to provide critical contributions for the development of potential therapeutic intervention that can minimize tissue damage caused by viral hepatitis and immune disorders.
Professor Shin said, “This is a novel research case that discovered the clinical significance of bystander immune cell activation, which was previously unknown. We will continue to work on establishing treatments which could prevent tissue damage in viral and immune diseases in the future.”
This research was published in Immunity on January 2.
Figure 1. Graphical abstract
2018.03.06 View 7352
Activation of Bystander Immune Cells during Acute Hepatitis A.
A KAIST research team has identified a process of tissue damage caused by bystander immune cells in acute viral infections. This research will pave the way for research to understand the principles of tissue damage in viral infections and immune diseases, and can point toward a possible therapeutic target for the treatment.
Upon viral infection, viral replication itself destroys human cells, but in some cases, viral replication is not the direct cause of the tissue damage. In particular, the destruction of infected cells is the primary cause of tissue damage during non-cytopathic viral infections such as hepatitis A virus, hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus. However, the underlying pathological mechanisms involved in the tissue damage during viral infections have not been fully elucidated.
Specificity is one of the most important characteristics of the immune system. In general, infection from a certain virus specifically activates immune cells targeting the virus, while other immune cells specific to different viruses remain inactive.
An immune cell not specific to an infected virus is called a bystander immune cell. A phenomenon that activates irrelevant immune cells not originally targeting the infecting virus, called the activation of bystander immune cells, is already known to the world; however, its clinical significance has not been investigated thoroughly.
Professor Eui-Cheol Shin and Professor Su-Hyung Park from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering analyzed patients with acute hepatitis A, in collaboration with Chung-Ang University Hospital.
The team found not only immune cells specifically targeting the hepatitis A virus were activated, but also bystander immune cells were activated and involved in the damaging of liver tissues during acute hepatitis A.
According to the research, when a person is infected with hepatitis A virus, hepatitis A virus-infected cells produce IL-15, which induces the activation of bystander immune cells. Activated bystander immune cells exert innate-like cytotoxicity, triggered by activating receptors NKG2D and NKp30 and this can lead to liver injury.
Through describing the cause of excessive tissue damage during acute viral hepatitis, the research outcome is expected to provide critical contributions for the development of potential therapeutic intervention that can minimize tissue damage caused by viral hepatitis and immune disorders.
Professor Shin said, “This is a novel research case that discovered the clinical significance of bystander immune cell activation, which was previously unknown. We will continue to work on establishing treatments which could prevent tissue damage in viral and immune diseases in the future.”
This research was published in Immunity on January 2.
Figure 1. Graphical abstract
2018.03.06 View 7352 -
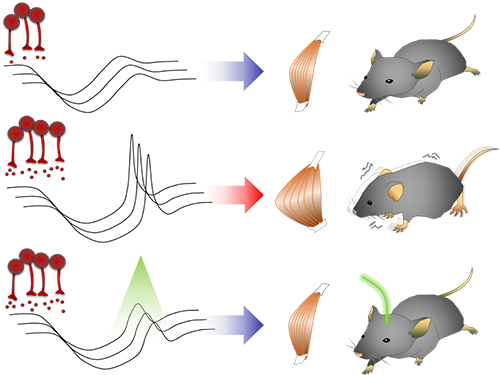 Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11333
Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11333 -
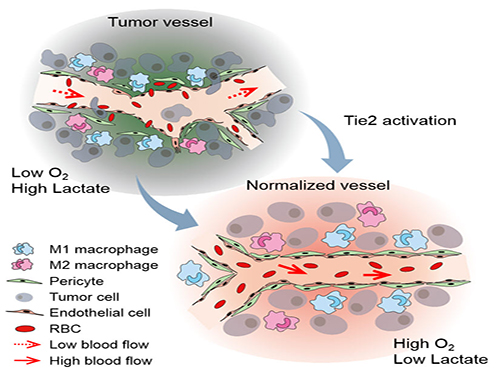 The Antibody That Normalizes Tumor Vessels
Researchers also discover that their antisepsis antibody reduces glioma, lung and breast cancer progression in mice.
A research team at the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) discovered that the antisepsis antibody ABTAA (Ang2-Binding and Tie2-Activating Antibody) reduces tumor volume and improves the delivery of anti-cancer drugs. Published in Cancer Cell, this study demonstrates that ABTAA restores the structural and functional integrity of tumor blood vessels in three different tumor models: breast, lungs, and brain.
Blood vessels inside and around an established tumor can be described as a chaotic and dysfunctional labyrinth. While the inner walls of healthy blood vessels are surrounded and supported by endothelial cells and other cells called pericytes, in the established tumor, the endothelial junctions are broken apart and pericytes are also detached. Blood flow into and from the tumor is severely retarded and tumor vessels lacking an intact vessel wall become leaky. This microenvironment causes limited drug delivery to the tumor and leads to inadequate oxygen supply (hypoxia) and even metastasis.
The research team led by Professor Gou-Young Koh at KAIST’s Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering found that the antibody ABTAA normalizes the tumor vessels and hence, change the whole tumor microenvironment. “We call it normalization of tumor vessels, because it resembles closely the wall architecture of healthy, normal vessels,” explains PARK Jin-Sung, first author of the study. And continues: “Tumor can adapt to hypoxia and get more aggressive, so we tried to prevent this transition by normalizing tumor vessels. ABTAA changes the whole tumor environment, oxygenation status and level of lactate, so that the immune cells and drugs can reach the core regions of the tumor more easily. In this way, we create a favorable ground for tumor treatment.”
In an attempt to generate antibodies targeting the protein Ang2, which is specifically expressed by endothelial cells in stressful conditions like in tumor, the team unexpectedly discovered that ABTAA has a peculiar way of working and a dual function. ABTAA indeed not only blocks Ang2, but also activates Tie2 at the same time. Tie2 is a receptor present on the cell membrane of endothelial cells. ABTAA causes Ang2 to cluster together and to strongly activate Tie2 receptors. “If we activate Tie2, we can efficiently normalize tumor vessels, enhance drug delivery and change the whole microenvironment,” explains KOH Gou Young, Director of the Center for Vascular Research.
Several pharmaceutical companies are developing Ang2-blocking antibodies to cure cancer. However, even if these antibodies significantly inhibit tumor progression, they do not stop tumor hypoxia. Moreover, most of the anti-cancer drugs target the tumor at its early stage, when tumors are still hard to diagnose. ABTAA, instead, works with tumors that are already rooted: “When the tumor is established, hypoxia is the main driver of tumor progression. So, if we eliminate hypoxia, we make the tumor milder, by reducing its progression and metastasis,” comments Koh.
Figure: Schematic drawing of a blood vessel around tumors before and after treatment with ABTAA. The picture above shows a typical tumor vasculature characterized by damaged walls, red blood cells leakage and detached pericytes. Activating Tie2 on endothelial cells with the antibody ABTAA restores the normal vessel architecture: endothelial and pericytes on the vessel walls are stabilized, the delivery of blood is improved, and the anticancer drugs are more likely to reach the tumor core.
The researchers tested ABTAA in mice with three different types of tumors that show high levels of Ang2: glioma (a type of a brain tumor), lung carcinoma, and breast cancer. They also compared the effect of ABTAA with ABA, another antibody that blocks Ang2 but misses the Tie2 activating properties. In all three cases, ABTAA was superior to ABA in inducing tumor vessel normalization, which led to a better delivery of the anti-cancer drugs into the tumor core region.
Glioma is one of the so-called intractable diseases, because of its poor prognosis and treatment. Professor Koh’s team found that the glioma volume was reduced 39% by ABTAA and 17% by ABA. ABTAA profoundly reduced vascular leakage and edema formation in glioma through promoting vascular tightening. Moreover, when ABTAA was administered together with the chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide (TMZ), the tumor volume reduces further (76% by ABTAA+TMZ, 51% by ABA+TMZ, and 36% by TMZ).
In the Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumor model, the team administered ABTAA together with a chemotherapeutic drug called cisplatin (Cpt) and observed a greater suppression of tumor growth (52%) compared with the controls and increased overall survival. Moreover, ABTAA+Cpt led to a marked increase in necrotic area within tumors.
Finally, in a spontaneous breast cancer model, ABTAA delayed tumor growth and enhanced the anti-tumor effect of Cpt.
Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS)
Figure: The antibody ABTAA alone and in combination with other anti-cancer drugs have a beneficial effect in reducing tumor volume. ABTAA was tested in mice with brain tumor (glioma), lung or breast cancer. The image shows the improvements: reduction in glioma tumor size, reduction in metastatic colonies in lung tumor and decrease in necrotic regions in breast tumor.
In the future, the team would like to further understand the underlying relationship between faulty blood vessels and diseases. “We would like to apply this antibody to an organ that is rich in blood vessels, that is the eye, and see if this antibody can be useful to treat eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy,” concludes Koh.
Professor Gou-Young Koh (left) and Jin-Sung Park (right)
2016.12.16 View 9517
The Antibody That Normalizes Tumor Vessels
Researchers also discover that their antisepsis antibody reduces glioma, lung and breast cancer progression in mice.
A research team at the Center for Vascular Research within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) discovered that the antisepsis antibody ABTAA (Ang2-Binding and Tie2-Activating Antibody) reduces tumor volume and improves the delivery of anti-cancer drugs. Published in Cancer Cell, this study demonstrates that ABTAA restores the structural and functional integrity of tumor blood vessels in three different tumor models: breast, lungs, and brain.
Blood vessels inside and around an established tumor can be described as a chaotic and dysfunctional labyrinth. While the inner walls of healthy blood vessels are surrounded and supported by endothelial cells and other cells called pericytes, in the established tumor, the endothelial junctions are broken apart and pericytes are also detached. Blood flow into and from the tumor is severely retarded and tumor vessels lacking an intact vessel wall become leaky. This microenvironment causes limited drug delivery to the tumor and leads to inadequate oxygen supply (hypoxia) and even metastasis.
The research team led by Professor Gou-Young Koh at KAIST’s Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering found that the antibody ABTAA normalizes the tumor vessels and hence, change the whole tumor microenvironment. “We call it normalization of tumor vessels, because it resembles closely the wall architecture of healthy, normal vessels,” explains PARK Jin-Sung, first author of the study. And continues: “Tumor can adapt to hypoxia and get more aggressive, so we tried to prevent this transition by normalizing tumor vessels. ABTAA changes the whole tumor environment, oxygenation status and level of lactate, so that the immune cells and drugs can reach the core regions of the tumor more easily. In this way, we create a favorable ground for tumor treatment.”
In an attempt to generate antibodies targeting the protein Ang2, which is specifically expressed by endothelial cells in stressful conditions like in tumor, the team unexpectedly discovered that ABTAA has a peculiar way of working and a dual function. ABTAA indeed not only blocks Ang2, but also activates Tie2 at the same time. Tie2 is a receptor present on the cell membrane of endothelial cells. ABTAA causes Ang2 to cluster together and to strongly activate Tie2 receptors. “If we activate Tie2, we can efficiently normalize tumor vessels, enhance drug delivery and change the whole microenvironment,” explains KOH Gou Young, Director of the Center for Vascular Research.
Several pharmaceutical companies are developing Ang2-blocking antibodies to cure cancer. However, even if these antibodies significantly inhibit tumor progression, they do not stop tumor hypoxia. Moreover, most of the anti-cancer drugs target the tumor at its early stage, when tumors are still hard to diagnose. ABTAA, instead, works with tumors that are already rooted: “When the tumor is established, hypoxia is the main driver of tumor progression. So, if we eliminate hypoxia, we make the tumor milder, by reducing its progression and metastasis,” comments Koh.
Figure: Schematic drawing of a blood vessel around tumors before and after treatment with ABTAA. The picture above shows a typical tumor vasculature characterized by damaged walls, red blood cells leakage and detached pericytes. Activating Tie2 on endothelial cells with the antibody ABTAA restores the normal vessel architecture: endothelial and pericytes on the vessel walls are stabilized, the delivery of blood is improved, and the anticancer drugs are more likely to reach the tumor core.
The researchers tested ABTAA in mice with three different types of tumors that show high levels of Ang2: glioma (a type of a brain tumor), lung carcinoma, and breast cancer. They also compared the effect of ABTAA with ABA, another antibody that blocks Ang2 but misses the Tie2 activating properties. In all three cases, ABTAA was superior to ABA in inducing tumor vessel normalization, which led to a better delivery of the anti-cancer drugs into the tumor core region.
Glioma is one of the so-called intractable diseases, because of its poor prognosis and treatment. Professor Koh’s team found that the glioma volume was reduced 39% by ABTAA and 17% by ABA. ABTAA profoundly reduced vascular leakage and edema formation in glioma through promoting vascular tightening. Moreover, when ABTAA was administered together with the chemotherapeutic drug temozolomide (TMZ), the tumor volume reduces further (76% by ABTAA+TMZ, 51% by ABA+TMZ, and 36% by TMZ).
In the Lewis Lung Carcinoma (LLC) tumor model, the team administered ABTAA together with a chemotherapeutic drug called cisplatin (Cpt) and observed a greater suppression of tumor growth (52%) compared with the controls and increased overall survival. Moreover, ABTAA+Cpt led to a marked increase in necrotic area within tumors.
Finally, in a spontaneous breast cancer model, ABTAA delayed tumor growth and enhanced the anti-tumor effect of Cpt.
Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Sciences (IBS)
Figure: The antibody ABTAA alone and in combination with other anti-cancer drugs have a beneficial effect in reducing tumor volume. ABTAA was tested in mice with brain tumor (glioma), lung or breast cancer. The image shows the improvements: reduction in glioma tumor size, reduction in metastatic colonies in lung tumor and decrease in necrotic regions in breast tumor.
In the future, the team would like to further understand the underlying relationship between faulty blood vessels and diseases. “We would like to apply this antibody to an organ that is rich in blood vessels, that is the eye, and see if this antibody can be useful to treat eye diseases such as age-related macular degeneration and diabetic retinopathy,” concludes Koh.
Professor Gou-Young Koh (left) and Jin-Sung Park (right)
2016.12.16 View 9517 -
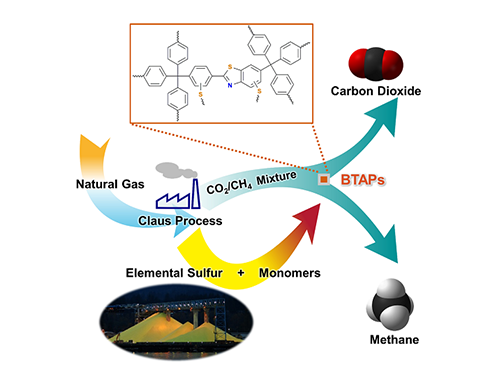 Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur for Microporous Polymer Synthesis
Using elemental sulfur as an alternative chemical feedstock, KAIST researchers have produced novel microporous polymers to sift CO2 from methane in natural-gas processing.
Methane, a primary component of natural gas, has emerged recently as an important energy source, largely owing to its abundance and relatively clean nature compared with other fossil fuels. In order to use natural gas as a fuel, however, it must undergo a procedure called “hydrodesulfurization” or “natural gas sweetening” to reduce sulfur-dioxide emissions from combustion of fossil fuels. This process leads to excessive and involuntary production of elemental sulfur. Although sulfur is one of the world’s most versatile and common elements, it has relatively few large-scale applications, mostly for gunpowder and sulfuric acid production.
Thus, the development of synthetic and processing methods to convert sulfur into useful chemicals remains a challenge. A research team led by Professor Ali Coskun from the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has recently introduced a new approach to resolving this problem by employing elemental sulfur directly in the synthesis of microporous polymers for the process of natural-gas sweetening.
Natural gas, containing varying amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), is generally treated with amine solutions, followed by the regeneration of these solutions at increased temperatures to release captured CO2 and H2S. A two-step separation is involved in removing these gases. The amine solutions first remove H2S, and then CO2 is separated from methane (CH4) with either amine solutions or porous sorbents such as microporous polymers.
Using elemental sulfur and organic linkers, the research team developed a solvent and catalyst-free strategy for the synthesis of ultramicroporous benzothiazole polymers (BTAPs) in quantitative yields. BTAPs were found to be highly porous and showed exceptional physiochemical stability. In-situ chemical impregnation of sulfur within the micropores increased CO2 affinity of the sorbent, while limiting diffusion of CH4. BTAPs, as low-cost, scalable solid-sorbents, showed outstanding CO2 separation ability for flue gas, as well as for natural and landfill gas conditions.
The team noted that: “Each year, millions of tons of elemental sulfur are generated as a by-product of petroleum refining and natural-gas processing, but industries and businesses lacked good ideas for using it. Our research provides a solution: the direct utilization of elemental sulfur into the synthesis of ultramicroporous polymers that can be recycled back into an efficient and sustainable process for CO2 separation. Our novel polymeric materials offer new possibilities for the application of a little-used natural resource, sulfur, to provide a sustainable solution to challenging environmental issues.”
This work was published online in Chem on September 8, 2016 and also highlighted in C&EN (Chemical & Engineering News) by the American Chemical Society (ACS) on September 19, 2016. The research paper was entitled “Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur in the Synthesis of Microporous Polymers for Natural Gas Sweetening.” (DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2016.08.003)
Figure 1. A Schematic Image of Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur
This image shows direct utilization of elemental sulfur in the synthesis of microporous polymers and its gas separation performance.
Figure 2. BTAP’s Breakthrough Experiment under Pre-mixed Gas Conditions
This data presents the breakthrough measurements for CO2-containing binary gas-mixture streams with different feed-gas compositions to investigate the CO2 capture capacity of ultramicroporous benzothiazole polymers (BTAPs) for large-scale applications under simulated conditions of natural and landfill gases.
2016.10.05 View 9675
Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur for Microporous Polymer Synthesis
Using elemental sulfur as an alternative chemical feedstock, KAIST researchers have produced novel microporous polymers to sift CO2 from methane in natural-gas processing.
Methane, a primary component of natural gas, has emerged recently as an important energy source, largely owing to its abundance and relatively clean nature compared with other fossil fuels. In order to use natural gas as a fuel, however, it must undergo a procedure called “hydrodesulfurization” or “natural gas sweetening” to reduce sulfur-dioxide emissions from combustion of fossil fuels. This process leads to excessive and involuntary production of elemental sulfur. Although sulfur is one of the world’s most versatile and common elements, it has relatively few large-scale applications, mostly for gunpowder and sulfuric acid production.
Thus, the development of synthetic and processing methods to convert sulfur into useful chemicals remains a challenge. A research team led by Professor Ali Coskun from the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) has recently introduced a new approach to resolving this problem by employing elemental sulfur directly in the synthesis of microporous polymers for the process of natural-gas sweetening.
Natural gas, containing varying amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and hydrogen sulfide (H2S), is generally treated with amine solutions, followed by the regeneration of these solutions at increased temperatures to release captured CO2 and H2S. A two-step separation is involved in removing these gases. The amine solutions first remove H2S, and then CO2 is separated from methane (CH4) with either amine solutions or porous sorbents such as microporous polymers.
Using elemental sulfur and organic linkers, the research team developed a solvent and catalyst-free strategy for the synthesis of ultramicroporous benzothiazole polymers (BTAPs) in quantitative yields. BTAPs were found to be highly porous and showed exceptional physiochemical stability. In-situ chemical impregnation of sulfur within the micropores increased CO2 affinity of the sorbent, while limiting diffusion of CH4. BTAPs, as low-cost, scalable solid-sorbents, showed outstanding CO2 separation ability for flue gas, as well as for natural and landfill gas conditions.
The team noted that: “Each year, millions of tons of elemental sulfur are generated as a by-product of petroleum refining and natural-gas processing, but industries and businesses lacked good ideas for using it. Our research provides a solution: the direct utilization of elemental sulfur into the synthesis of ultramicroporous polymers that can be recycled back into an efficient and sustainable process for CO2 separation. Our novel polymeric materials offer new possibilities for the application of a little-used natural resource, sulfur, to provide a sustainable solution to challenging environmental issues.”
This work was published online in Chem on September 8, 2016 and also highlighted in C&EN (Chemical & Engineering News) by the American Chemical Society (ACS) on September 19, 2016. The research paper was entitled “Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur in the Synthesis of Microporous Polymers for Natural Gas Sweetening.” (DOI: 10.1016/j.chempr.2016.08.003)
Figure 1. A Schematic Image of Direct Utilization of Elemental Sulfur
This image shows direct utilization of elemental sulfur in the synthesis of microporous polymers and its gas separation performance.
Figure 2. BTAP’s Breakthrough Experiment under Pre-mixed Gas Conditions
This data presents the breakthrough measurements for CO2-containing binary gas-mixture streams with different feed-gas compositions to investigate the CO2 capture capacity of ultramicroporous benzothiazole polymers (BTAPs) for large-scale applications under simulated conditions of natural and landfill gases.
2016.10.05 View 9675 -
 Professor Sang Yup Lee Appointed Founding Board Member of Cell Systems
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed a member of the founding editorial board of the newly established journal Cell Systems.
Cell Systems will be a sister journal of Cell, one of the three most prestigious scientific journals along with Nature and Science, that publishes a wide range of papers on biological engineering. The first issue of Cell Systems will be published this July.
Cell Systems plans to publish innovative discoveries, reviews of various research instruments, and research findings on integrated and quantified systems in the field of biology.
Professor Lee is a pioneer in metabolic engineering of microorganism with a focus on biopolymers and metabolites production. He is the editor-in-chief of Biotechnology Journal and serves on the editorial board of numerous international journals. He is also a member of the Global Agenda Council of the World Economic Forum and the Presidential Advisory Committee on Science and Technology in Korea.
Professor Lee said, “Cell Systems will present research findings that discuss whole biological systems methodically.” He continued, “I hope many research findings of Korean scholars will be published in Cell Systems, which will become a representative journal of systems biology and systems biological engineering.”
2015.02.13 View 10540
Professor Sang Yup Lee Appointed Founding Board Member of Cell Systems
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has been appointed a member of the founding editorial board of the newly established journal Cell Systems.
Cell Systems will be a sister journal of Cell, one of the three most prestigious scientific journals along with Nature and Science, that publishes a wide range of papers on biological engineering. The first issue of Cell Systems will be published this July.
Cell Systems plans to publish innovative discoveries, reviews of various research instruments, and research findings on integrated and quantified systems in the field of biology.
Professor Lee is a pioneer in metabolic engineering of microorganism with a focus on biopolymers and metabolites production. He is the editor-in-chief of Biotechnology Journal and serves on the editorial board of numerous international journals. He is also a member of the Global Agenda Council of the World Economic Forum and the Presidential Advisory Committee on Science and Technology in Korea.
Professor Lee said, “Cell Systems will present research findings that discuss whole biological systems methodically.” He continued, “I hope many research findings of Korean scholars will be published in Cell Systems, which will become a representative journal of systems biology and systems biological engineering.”
2015.02.13 View 10540