Scale+lab
-
 Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9752
Principle behind increasing the catalytic property of nanocatalysts proven
The technology that allows full control of the catalytic property of nanocatalysts using oxide formation on nanocatalysts has been developed by KAIST researchers. The breakthrough opens up the possibility of the development of a new kind of catalysts that maximizes catalytic property and minimizes waste.
*nanocatalyst is a material that catalyzes gas reactions on its surface. It is composed of a high surface area oxide scaffold with nano-sized metal particles dispersed.
The team was led by Professor Park Jeong Young of the KAIST EEWS Graduate School and consists of Kamran Qadir Ph.D. candidate (1st Author), Professor Joo Sang Hoon of UNIST, Professor Moon Bong Jin of Hanyang University, and Professor Gabor Somorajai of UC Berkeley. Support for the research was provided from Ministry of Education Science and Technology, National Research Foundation, and Ministry of Knowledge Economy. The results were published as the online edition of Nano Letters: “Intrinsic Relation between Catalytic Activity of CO Oxidation on Ru Nanoparticles and Ru Oxides Uncovered with Ambient Pressure XPS”.
Catalysts are included in above 80% of all the products used in everyday life and are therefore included in most aspects of our lives.
The focus on nanocatalysts is based on finding solutions to increasing the efficiency for application to energy production and for solving environmental issues.
Most nanocatalysts are composed of nanoparticles and oxides where the nanoparticles increase the surface area of the catalyst to increase its activity.
The efficiency of a nanocatalyst is affected by the surface oxide of the nanoparticles. However the proving of this assumption remained difficult to do as it required in-situ measurement of the oxide state of the nanoparticles in the specific environment. Thus far, the experiments were conducted in a vacuum and therefore did not reflect the actual behavior in real life. The recently developed X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy allows for measurement of the oxidization state at standard atmospheric pressure.
Professor Park’s research team successfully measured the oxidization state of the nanoparticle using the atmospheric pressure X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy in the specified environment.
They confirmed the effect the oxidization state on the catalytic effect of the nanoparticles and additionally found that a thin layer of oxide can increase the catalytic effect and the effectiveness of the nanoparticle can controlled by the oxidation state.
2012.11.29 View 9752 -
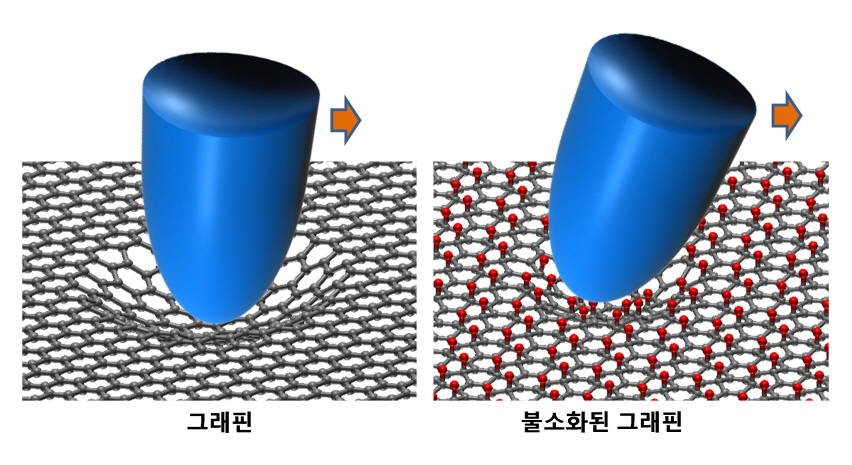 KAIST researchers verify and control the mechanical properties of graphene
KAIST researchers have successfully verified and controlled the mechanical properties of graphene, a next-generation material. Professor Park Jung Yong from the EEWS Graduate School and Professor Kim Yong Hyun from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology have succeeded in fluorinating a single atomic-layered graphene sample and controlling its frictional and adhesive properties. This is the first time the frictional properties of graphene have been examined at the atomic level, and the technology is expected to be applied to nano-sized robots and microscopic joints.
Graphene is often dubbed “the dream material” because of its ability to conduct high amounts of electricity even when bent, making it the next-generation substitute for silicon semiconductors, paving the way for flexible display and wearable computer technologies. Graphene also has high potential applications in mechanical engineering because of its great material strength, but its mechanical properties remained elusive until now.
Professor Park’s research team successfully produced individual graphene samples with fluorine-deficiency at the atomic level by placing the samples in Fluoro-xenon (XeF2) gas and applying heat. The surface of the graphene was scanned using a micro probe and a high vacuum atomic microscope to measure its dynamic properties.
The research team found that the fluorinated graphene sample had 6 times more friction and 0.7 times more adhesiveness than the original graphene. Electrical measurements confirmed the fluorination process, and the analysis of the findings helped setup the theory of frictional changes in graphene.
Professor Park stated that “graphene can be used for the lubrication of joints in nano-sized devices” and that this research has numerous applications such as the coating of graphene-based microdynamic devices.
This research was published in the online June edition of Nano Letters and was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Education and the National Research Foundation as part of the World Class University (WCU) program.
2012.07.24 View 18232
KAIST researchers verify and control the mechanical properties of graphene
KAIST researchers have successfully verified and controlled the mechanical properties of graphene, a next-generation material. Professor Park Jung Yong from the EEWS Graduate School and Professor Kim Yong Hyun from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology have succeeded in fluorinating a single atomic-layered graphene sample and controlling its frictional and adhesive properties. This is the first time the frictional properties of graphene have been examined at the atomic level, and the technology is expected to be applied to nano-sized robots and microscopic joints.
Graphene is often dubbed “the dream material” because of its ability to conduct high amounts of electricity even when bent, making it the next-generation substitute for silicon semiconductors, paving the way for flexible display and wearable computer technologies. Graphene also has high potential applications in mechanical engineering because of its great material strength, but its mechanical properties remained elusive until now.
Professor Park’s research team successfully produced individual graphene samples with fluorine-deficiency at the atomic level by placing the samples in Fluoro-xenon (XeF2) gas and applying heat. The surface of the graphene was scanned using a micro probe and a high vacuum atomic microscope to measure its dynamic properties.
The research team found that the fluorinated graphene sample had 6 times more friction and 0.7 times more adhesiveness than the original graphene. Electrical measurements confirmed the fluorination process, and the analysis of the findings helped setup the theory of frictional changes in graphene.
Professor Park stated that “graphene can be used for the lubrication of joints in nano-sized devices” and that this research has numerous applications such as the coating of graphene-based microdynamic devices.
This research was published in the online June edition of Nano Letters and was supported by the Ministry of Science, Technology, and Education and the National Research Foundation as part of the World Class University (WCU) program.
2012.07.24 View 18232