Daesoo+Kim
-
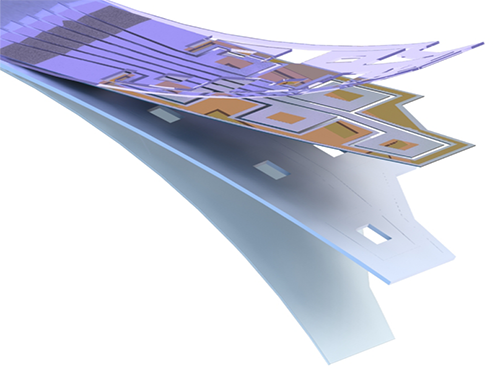 Flexible Drug Delivery Microdevice to Advance Precision Medicine
(Schematic view of flexible microdevice: The flexible drug delivery device for controlled release fabricated via inorganic laser lift off.)
A KAIST research team has developed a flexible drug delivery device with controlled release for personalized medicine, blazing the path toward theragnosis.
Theragnosis, an emerging medical technology, is gaining attention as key factor to advance precision medicine for its featuring simultaneous diagnosis and therapeutics. Theragnosis devices including smart contact lenses and microneedle patches integrate physiological data sensors and drug delivery devices. The controlled drug delivery boasts fewer side-effects, uniform therapeutic results, and minimal dosages compared to oral ingestion. Recently, some research groups conducted in-human applications of controlled-release bulky microchips for osteoporosis treatment. However they failed to demonstrate successful human-friendly flexible drug delivery systems for controlled release.
For this microdevice, the team under Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Science and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, fabricated a device on a rigid substrate and transferred a 50 µm-thick active drug delivery layer to the flexible substrate via inorganic laser lift off. The fabricated device shows mechanical flexibility while maintaining the capability of precise administration of exact dosages at desired times. The core technology is to produce a freestanding gold capping layer directly on top of the microreservoir with the drugs inside, which had been regarded as impossible in conventional microfabrication.
The developed flexible drug delivery system can be applied to smart contact lenses or the brain disease treatments by implanting them into cramped and corrugated organs. In addition, when powered wirelessly, it will represent a novel platform for personalized medicine. The team already proved through animal experimentation that treatment for brain epilepsy made progress by releasing anti-epileptic medication through the device.
Professor Lee believes the flexible microdevice will further expand the applications of smart contact lenses, therapeutic treatments for brain disease, and subcutaneous implantations for daily healthcare system. This study “Flexible Wireless Powered Drug Delivery System for Targeted Administration on Cerebral Cortex” was described in the June online issue of Nano Energy.
(Photo: The flexible drug delivery device for contolled relase attached on a glass rod.)
2018.08.13 View 9873
Flexible Drug Delivery Microdevice to Advance Precision Medicine
(Schematic view of flexible microdevice: The flexible drug delivery device for controlled release fabricated via inorganic laser lift off.)
A KAIST research team has developed a flexible drug delivery device with controlled release for personalized medicine, blazing the path toward theragnosis.
Theragnosis, an emerging medical technology, is gaining attention as key factor to advance precision medicine for its featuring simultaneous diagnosis and therapeutics. Theragnosis devices including smart contact lenses and microneedle patches integrate physiological data sensors and drug delivery devices. The controlled drug delivery boasts fewer side-effects, uniform therapeutic results, and minimal dosages compared to oral ingestion. Recently, some research groups conducted in-human applications of controlled-release bulky microchips for osteoporosis treatment. However they failed to demonstrate successful human-friendly flexible drug delivery systems for controlled release.
For this microdevice, the team under Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Science and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, fabricated a device on a rigid substrate and transferred a 50 µm-thick active drug delivery layer to the flexible substrate via inorganic laser lift off. The fabricated device shows mechanical flexibility while maintaining the capability of precise administration of exact dosages at desired times. The core technology is to produce a freestanding gold capping layer directly on top of the microreservoir with the drugs inside, which had been regarded as impossible in conventional microfabrication.
The developed flexible drug delivery system can be applied to smart contact lenses or the brain disease treatments by implanting them into cramped and corrugated organs. In addition, when powered wirelessly, it will represent a novel platform for personalized medicine. The team already proved through animal experimentation that treatment for brain epilepsy made progress by releasing anti-epileptic medication through the device.
Professor Lee believes the flexible microdevice will further expand the applications of smart contact lenses, therapeutic treatments for brain disease, and subcutaneous implantations for daily healthcare system. This study “Flexible Wireless Powered Drug Delivery System for Targeted Administration on Cerebral Cortex” was described in the June online issue of Nano Energy.
(Photo: The flexible drug delivery device for contolled relase attached on a glass rod.)
2018.08.13 View 9873 -
 Animal Cyborg: Behavioral Control by 'Toy' Craving Circuit
Children love to get toys from parents for their birthday present. This craving toward items also involves object hoarding disorders and shopping addiction. However, the biological meaning of why the brain pursues objects or items has remained unknown. Part of the answer may lie with a neural circuit in the hypothalamus associated with “object craving,” says neuroscientist Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
His research team found that some neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during playing with toys in mice. Thanks to optogenetics, they proved that these neurons in the hypothalamus actually governs obsessive behavior toward non-food objects in mice.
“When we stimulate a neuron in the hypothalamus of mice, they anxiously chased target objects. We found evidence that the neural circuits in the medial preoptic area (MPA) modulate “object craving,” the appetite for possessing objects” said Professor Kim.
Researchers also proved that the MPA circuit facilitate hunting behavior in response to crickets, a natural prey to mice, showing the role of this circuit for catching prey. Further, the MPA nerves send excitatory signals to the periaqueductal gray (PAG), located around the cerebral aqueduct, to create such behavior. The team named this circuit the ‘MPA-PAG’ circuit.
The team showed that they could control mammalian behavior for the first time with this scheme of MPA-Induced Drive Assisted Steering (MIDAS), in which a mouse chase the target objects in the front of head during stimulation of the MPA-PAG circuit. MIDAS allows mice to overcome obstacles to move in a desired path using optogenetics.
(Professor Daesoo Kim)
Professor Kim, who teamed up with Professor Phill Seung Lee in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, explained the significance of the research, “This study provides evidence to treat brain disorders such as compulsive hoarding and kleptomania. It also contributes to the development of technology to control the behavior of animals and humans using strong innate motivation, and thus could impact neuro-economics, defense, and disaster relief.”
He said the team would like to complete the neural circuit map governing behaviors of possession and hunting in the near future by exploring correlations with other neural behaviors controlling possessing and hunting activities.
This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and published in Nature Neuroscience in March 2018.
(Figure 1: Schematics showing possessive behavior induced by the MPA neural circuit)
(Figure 2: Schematics of the MIDAS system that controls mammals behavior using the desire to possess. A MIDAS mouse is following the bait object controlled wirelessly.)
2018.04.23 View 10541
Animal Cyborg: Behavioral Control by 'Toy' Craving Circuit
Children love to get toys from parents for their birthday present. This craving toward items also involves object hoarding disorders and shopping addiction. However, the biological meaning of why the brain pursues objects or items has remained unknown. Part of the answer may lie with a neural circuit in the hypothalamus associated with “object craving,” says neuroscientist Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST.
His research team found that some neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during playing with toys in mice. Thanks to optogenetics, they proved that these neurons in the hypothalamus actually governs obsessive behavior toward non-food objects in mice.
“When we stimulate a neuron in the hypothalamus of mice, they anxiously chased target objects. We found evidence that the neural circuits in the medial preoptic area (MPA) modulate “object craving,” the appetite for possessing objects” said Professor Kim.
Researchers also proved that the MPA circuit facilitate hunting behavior in response to crickets, a natural prey to mice, showing the role of this circuit for catching prey. Further, the MPA nerves send excitatory signals to the periaqueductal gray (PAG), located around the cerebral aqueduct, to create such behavior. The team named this circuit the ‘MPA-PAG’ circuit.
The team showed that they could control mammalian behavior for the first time with this scheme of MPA-Induced Drive Assisted Steering (MIDAS), in which a mouse chase the target objects in the front of head during stimulation of the MPA-PAG circuit. MIDAS allows mice to overcome obstacles to move in a desired path using optogenetics.
(Professor Daesoo Kim)
Professor Kim, who teamed up with Professor Phill Seung Lee in the Department of Mechanical Engineering, explained the significance of the research, “This study provides evidence to treat brain disorders such as compulsive hoarding and kleptomania. It also contributes to the development of technology to control the behavior of animals and humans using strong innate motivation, and thus could impact neuro-economics, defense, and disaster relief.”
He said the team would like to complete the neural circuit map governing behaviors of possession and hunting in the near future by exploring correlations with other neural behaviors controlling possessing and hunting activities.
This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and published in Nature Neuroscience in March 2018.
(Figure 1: Schematics showing possessive behavior induced by the MPA neural circuit)
(Figure 2: Schematics of the MIDAS system that controls mammals behavior using the desire to possess. A MIDAS mouse is following the bait object controlled wirelessly.)
2018.04.23 View 10541 -
 Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
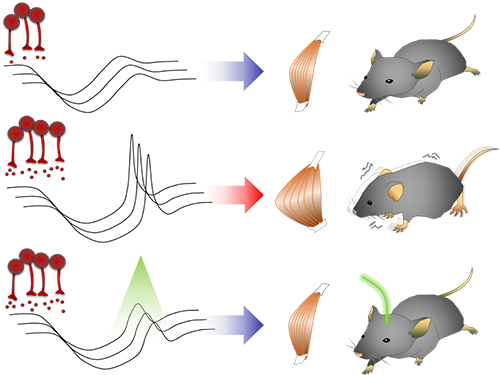
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11340
Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11340