Biomedical+Mathematics+Group
-
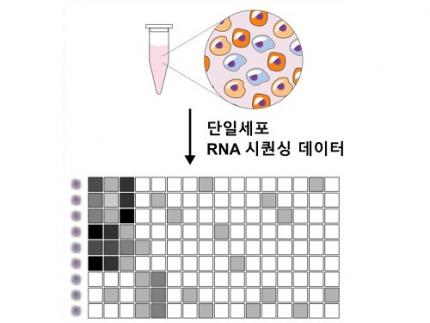 Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 5248
Revolutionary 'scLENS' Unveiled to Decode Complex Single-Cell Genomic Data
Unlocking biological information from complex single-cell genomic data has just become easier and more precise, thanks to the innovative 'scLENS' tool developed by the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the IBS Center for Mathematical and Computational Sciences led by Chief Investigator Jae Kyoung Kim, who is also a professor at KAIST. This new finding represents a significant leap forward in the field of single-cell transcriptomics.
Single-cell genomic analysis is an advanced technique that measures gene expression at the individual cell level, revealing cellular changes and interactions that are not observable with traditional genomic analysis methods. When applied to cancer tissues, this analysis can delineate the composition of diverse cell types within a tumor, providing insights into how cancer progresses and identifying key genes involved during each stage of progression.
Despite the immense potential of single-cell genomic analysis, handling the vast amount of data that it generates has always been challenging. The amount of data covers the expression of tens of thousands of genes across hundreds to thousands of individual cells. This not only results in large datasets but also introduces noise-related distortions, which arise in part due to current measurement limitations.
< Figure 1. Overview of scLENS (single-cell Low-dimensional embedding using the effective Noise Subtract) >
(Left) Current dimensionality reduction methods for scRNA-seq data involve conventional data preprocessing steps, such as log normalization, followed by manual selection of signals from the scaled data. However, this study reveals that the high levels of sparsity and variability in scRNA-seq data can lead to signal distortion during the data preprocessing, compromising the accuracy of downstream analyses.
(Right) To address this issue, the researchers integrated L2 normalization into the conventional preprocessing pipeline, effectively mitigating signal distortion. Moreover, they developed a novel signal detection algorithm that eliminates the need for user intervention by leveraging random matrix theory-based noise filtering and signal robustness testing. By incorporating these techniques, scLENS enables accurate and automated analysis of scRNA-seq data, overcoming the limitations of existing dimensionality reduction methods.
Corresponding author Jae Kyoung Kim highlighted, “There has been a remarkable advancement in experimental technologies for analyzing single-cell transcriptomes over the past decade. However, due to limitations in data analysis methods, there has been a struggle to fully utilize valuable data obtained through extensive cost and time."
Researchers have developed numerous analysis methods over the years to discern biological signals from this noise. However, the accuracy of these methods has been less than satisfactory. A critical issue is that determining signal and noise thresholds often depends on subjective decisions from the users.
The newly developed scLENS tool harnesses Random Matrix Theory and Signal robustness test to automatically differentiate signals from noise without relying on subjective user input.
First author Hyun Kim stated, "Previously, users had to arbitrarily decide the threshold for signal and noise, which compromised the reproducibility of analysis results and introduced subjectivity. scLENS eliminates this problem by automatically detecting signals using only the inherent structure of the data."
During the development of scLENS, researchers identified the fundamental reasons for inaccuracies in existing analysis methods. They found that commonly used data preprocessing methods distort both biological signals and noise. The new preprocessing approach that scLENS offers is free from such distortions.
By resolving issues related to noise threshold determined by subjective user choice and signal distortion in conventional data preprocessing, scLENS significantly outperforms existing methods in accuracy. Additionally, scLENS automates the laborious process of signal dimension selection, allowing researchers to extract biological signals conveniently and automatically.
CI Kim added, "scLENS solves major issues in single-cell transcriptome data analysis, substantially improving the accuracy and efficiency throughout the analysis process. This is a prime example of how fundamental mathematical theories can drive innovation in life sciences research, allowing researchers to more quickly and accurately answer biological questions and uncover secrets of life that were previously hidden."
This research was published in the international journal 'Nature Communications' on April 27.
Terminology
* Single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq): A technique used to measure gene expression levels in individual cells, providing insights into cell heterogeneity and rare cell types.
* Dimensionality reduction: A method to reduce the number of features or variables in a dataset while preserving the most important information, making data analysis more manageable and interpretable.
* Random matrix theory: A mathematical framework used to model and analyze the properties of large, random matrices, which can be applied to filter out noise in high-dimensional data.
* Signal robustness test: Among the signals, this test selects signals that are robust to the slight perturbation in data because real biological signals should be invariant for such slight modification in the data.
2024.05.09 View 5248 -
 Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
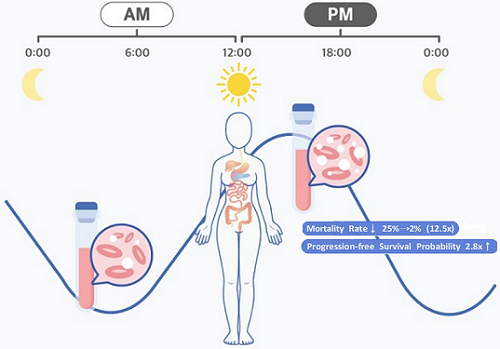
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 7157
Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 7157 -
 Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 13245
Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 13245