synapse
-
 A KAIST Research Team Observes the Processes of Memory and Cognition in Real Time
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons and 600 trillion synapses that exchange signals between the neurons to help us control the various functions of the brain including cognition, emotion, and memory. Interestingly, the number of synapses decrease with age or as a result of diseases like Alzheimer’s, and research on synapses thus attracts a lot of attention. However, limitations have existed in observing the dynamics of synapse structures in real time.
On January 9, a joint research team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Hyung-Bae Kwon from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and Professor Sangkyu Lee from the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) revealed that they have developed the world’s first technique to allow a real-time observation of synapse formation, extinction, and alterations.
Professor Heo’s team conjugated dimerization-dependent fluorescent proteins (ddFP) to synapses in order to observe the process in which synapses create connections between neurons in real time. The team named this technique SynapShot, by combining the words ‘synapse’ and snapshot’, and successfully tracked and observed the live formation and extinction processes of synapses as well as their dynamic changes.
< Figure 1. To observe dynamically changing synapses, dimerization-dependent fluorescent protein (ddFP) was expressed to observe flourescent signals upon synapse formation as ddFP enables fluorescence detection through reversible binding to pre- and postsynaptic terminals. >
Through a joint research project, the teams led by Professor Heo and Professor Sangkyu Lee at IBS together designed a SynapShot with green and red fluorescence, and were able to easily distinguish the synapse connecting two different neurons. Additionally, by combining an optogenetic technique that can control the function of a molecule using light, the team was able to observe the changes in the synapses while simultaneously inducing certain functions of the neurons using light.
Through more joint research with the team led by Professor Hyung-Bae Kwon at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Professor Heo’s team induced several situations on live mice, including visual discrimination training, exercise, and anaesthesia, and used SynapShot to observe the changes in the synapses during each situation in real time. The observations revealed that each synapse could change fairly quickly and dynamically. This was the first-ever case in which the changes in synapses were observed in a live mammal.
< Figure 2. Microscopic photos observed through changes of the flourescence of the synapse sensor (SynapShot) by cultivating the neurons of an experimental rat and expressing the SynapShot. The changes in the synapse that is created when the pre- and post-synaptic terminals come into contact and the synapse that disappears after a certain period of time are measured by the fluorescence of the SynapShot. >
Professor Heo said, “Our group developed SynapShot through a collaboration with domestic and international research teams, and have opened up the possibility for first-hand live observations of the quick and dynamic changes of synapses, which was previously difficult to do. We expect this technique to revolutionize research methodology in the neurological field, and play an important role in brightening the future of brain science.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Seungkyu Son (Ph.D. candidate), Jinsu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Dr. Kanghoon Jung from Johns Hopkins, was published in the online edition of Nature Methods on January 8 under the title “Real-time visualization of structural dynamics of synapses in live cells in vivo”, and will be printed in the February volume.
< Figure 3. Simultaneous use of green-SynapShot and red-SynapShot to distinguish and observe synapses with one post-terminal and different pre-terminals. >
< Figure 4. Dimer-dependent fluorescent protein (ddFP) exists as a green fluorescent protein as well as a red fluorescent protein, and can be applied together with blue light-activated optogenetic technology. After activating Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) by blue light using optogenetic technology, the strengthening of synaptic connections through signals of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is observed using red-SynapShot. >
< Figure 5. Micrographs showing real-time changing synapses in the visual cortex of mice trained through visual training using in vivo imaging techniques such as two-photon microscopy as well as at the cellular level. >
This research was supported by Mid-Sized Research Funds and the Singularity Project from KAIST, and by IBS.
2024.01.18 View 6308
A KAIST Research Team Observes the Processes of Memory and Cognition in Real Time
The human brain contains approximately 86 billion neurons and 600 trillion synapses that exchange signals between the neurons to help us control the various functions of the brain including cognition, emotion, and memory. Interestingly, the number of synapses decrease with age or as a result of diseases like Alzheimer’s, and research on synapses thus attracts a lot of attention. However, limitations have existed in observing the dynamics of synapse structures in real time.
On January 9, a joint research team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Hyung-Bae Kwon from Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and Professor Sangkyu Lee from the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) revealed that they have developed the world’s first technique to allow a real-time observation of synapse formation, extinction, and alterations.
Professor Heo’s team conjugated dimerization-dependent fluorescent proteins (ddFP) to synapses in order to observe the process in which synapses create connections between neurons in real time. The team named this technique SynapShot, by combining the words ‘synapse’ and snapshot’, and successfully tracked and observed the live formation and extinction processes of synapses as well as their dynamic changes.
< Figure 1. To observe dynamically changing synapses, dimerization-dependent fluorescent protein (ddFP) was expressed to observe flourescent signals upon synapse formation as ddFP enables fluorescence detection through reversible binding to pre- and postsynaptic terminals. >
Through a joint research project, the teams led by Professor Heo and Professor Sangkyu Lee at IBS together designed a SynapShot with green and red fluorescence, and were able to easily distinguish the synapse connecting two different neurons. Additionally, by combining an optogenetic technique that can control the function of a molecule using light, the team was able to observe the changes in the synapses while simultaneously inducing certain functions of the neurons using light.
Through more joint research with the team led by Professor Hyung-Bae Kwon at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Professor Heo’s team induced several situations on live mice, including visual discrimination training, exercise, and anaesthesia, and used SynapShot to observe the changes in the synapses during each situation in real time. The observations revealed that each synapse could change fairly quickly and dynamically. This was the first-ever case in which the changes in synapses were observed in a live mammal.
< Figure 2. Microscopic photos observed through changes of the flourescence of the synapse sensor (SynapShot) by cultivating the neurons of an experimental rat and expressing the SynapShot. The changes in the synapse that is created when the pre- and post-synaptic terminals come into contact and the synapse that disappears after a certain period of time are measured by the fluorescence of the SynapShot. >
Professor Heo said, “Our group developed SynapShot through a collaboration with domestic and international research teams, and have opened up the possibility for first-hand live observations of the quick and dynamic changes of synapses, which was previously difficult to do. We expect this technique to revolutionize research methodology in the neurological field, and play an important role in brightening the future of brain science.”
This research, conducted by co-first authors Seungkyu Son (Ph.D. candidate), Jinsu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Dr. Kanghoon Jung from Johns Hopkins, was published in the online edition of Nature Methods on January 8 under the title “Real-time visualization of structural dynamics of synapses in live cells in vivo”, and will be printed in the February volume.
< Figure 3. Simultaneous use of green-SynapShot and red-SynapShot to distinguish and observe synapses with one post-terminal and different pre-terminals. >
< Figure 4. Dimer-dependent fluorescent protein (ddFP) exists as a green fluorescent protein as well as a red fluorescent protein, and can be applied together with blue light-activated optogenetic technology. After activating Tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB) by blue light using optogenetic technology, the strengthening of synaptic connections through signals of brain-derived neurotrophic factor is observed using red-SynapShot. >
< Figure 5. Micrographs showing real-time changing synapses in the visual cortex of mice trained through visual training using in vivo imaging techniques such as two-photon microscopy as well as at the cellular level. >
This research was supported by Mid-Sized Research Funds and the Singularity Project from KAIST, and by IBS.
2024.01.18 View 6308 -
 A KAIST research team identifies a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse
Childhood neglect and/or abuse can induce extreme stress that significantly changes neural networks and functions during growth. This can lead to mental illnesses, including depression and schizophrenia, but the exact mechanism and means to control it were yet to be discovered.
On August 1, a KAIST research team led by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences announced the identification of excessive synapse removal mediated by astrocytes as the cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse trauma. Their research was published in Immunity, a top international journal in the field of immunology.
The research team discovered that the excessive astrocyte-mediated removal of excitatory synapses in the brain in response to stress hormones is a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood neglect and abuse. Clinical data have previously shown that high levels of stress can lead to various mental diseases, but the exact mechanism has been unknown. The results of this research therefore are expected to be widely applied to the prevention and treatment of such diseases.
The research team clinically screened an FDA-approved drug to uncover the mechanism that regulates the phagocytotic role of astrocytes, in which they capture external substances and eliminate them. As a result, the team found that synthetic glucocorticoids, namely stress hormones, enhanced astrocyte-mediated phagocytosis to an abnormal level. Glucocorticoids play essential roles in processes that maintain life, such as carbohydrate metabolism and anti-inflammation, but are also secreted in response to external stimuli such as stress, allowing the body to respond appropriately. However, excessive and long-term exposure to glucocorticoids caused by chronic stress can lead to various mental diseases including depression, cognitive disorders, and anxiety.
< Figure 1. Results of screening for compounds that increase astrocyte phagocytosis
(A) Discovered that synthetic glucocorticoid (stress hormone) increases the phagocytosis of astrocytes through screening of FDA-approved clinical compounds. (B-C) When treated with stress hormones, the phagocytosis of astrocytes is greatly increased, but this phenomenon is strongly suppressed by the GR antagonist (Mifepristone). CORT: corticosterone (stress hormone), Eplerenone: mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist, Mifepristone: glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonist >
To understand the changes in astrocyte functions caused by childhood stress, the research team used mice models with early social deprivation, and discovered that stress hormones bind to the glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) of astrocytes. This significantly increased the expression of Mer tyrosine kinase (MERK), which plays an essential role in astrocyte phagocytosis. Surprisingly, out of the various neurons in the cerebral cortex, astrocytes would eliminate only the excitatory synapses of specific neurons. The team found that this builds abnormal neural networks, which can lead to complex behavioral abnormalities such as social deficiencies and depression in adulthood.
The team also observed that microglia, which also play an important role in cerebral immunity, did not contribute to synapse removal in the mice models with early social deprivation. This confirms that the response to stress hormones during childhood is specifically astrocyte-mediated.
To find out whether these results are also applicable in humans, the research team used a brain organoid grown from human-induced pluripotent stem cells to observe human responses to stress hormones. The team observed that the stress hormones induced astrocyte GRs and phagocyte activation in the human brain organoid as well, and confirmed that the astrocytes subsequently eliminated excessive amounts of excitatory synapses. By showing that mice and humans both showed the same synapse control mechanism in response to stress, the team suggested that this discovery is applicable to mental disorders in humans.
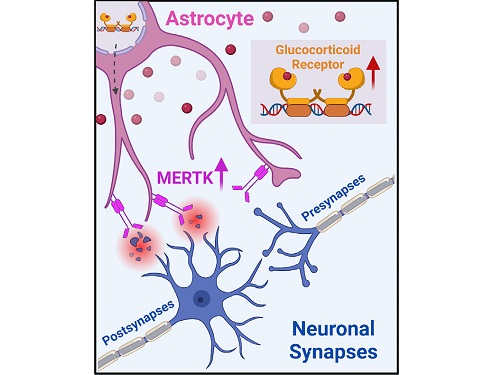
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the study published in Immunity. Excessive stress hormone secretion in childhood increases the expression of the MERTK phagocytic receptor through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) of astrocytes, resulting in excessive elimination of excitatory synapses. Excessive synaptic elimination by astrocytes during brain development causes permanent damage to brain circuits, resulting in abnormal neural activity in the adult brain and psychiatric behaviors such as depression and anti-social tendencies. >
Prof. Won-Suk Chung said, “Until now, we did not know the exact mechanism for how childhood stress caused brain diseases. This research was the first to show that the excessive phagocytosis of astrocytes could be an important cause of such diseases.” He added, “In the future, controlling the immune response of astrocytes will be used as a fundamental target for understanding and treating brain diseases.”
This research, written by co-first authors Youkyeong Byun (Ph.D. candidate) and Nam-Shik Kim (post-doctoral associate) from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, was published in the internationally renowned journal Immunity, a sister magazine of Cell and one of the best journal in the field of immunology, on July 31 under the title "Stress induces behavioral abnormalities by increasing expression of phagocytic receptor MERTK in astrocytes to promote synapse phagocytosis."
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC).
2023.08.04 View 7207
A KAIST research team identifies a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse
Childhood neglect and/or abuse can induce extreme stress that significantly changes neural networks and functions during growth. This can lead to mental illnesses, including depression and schizophrenia, but the exact mechanism and means to control it were yet to be discovered.
On August 1, a KAIST research team led by Professor Won-Suk Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences announced the identification of excessive synapse removal mediated by astrocytes as the cause of mental diseases induced by childhood abuse trauma. Their research was published in Immunity, a top international journal in the field of immunology.
The research team discovered that the excessive astrocyte-mediated removal of excitatory synapses in the brain in response to stress hormones is a cause of mental diseases induced by childhood neglect and abuse. Clinical data have previously shown that high levels of stress can lead to various mental diseases, but the exact mechanism has been unknown. The results of this research therefore are expected to be widely applied to the prevention and treatment of such diseases.
The research team clinically screened an FDA-approved drug to uncover the mechanism that regulates the phagocytotic role of astrocytes, in which they capture external substances and eliminate them. As a result, the team found that synthetic glucocorticoids, namely stress hormones, enhanced astrocyte-mediated phagocytosis to an abnormal level. Glucocorticoids play essential roles in processes that maintain life, such as carbohydrate metabolism and anti-inflammation, but are also secreted in response to external stimuli such as stress, allowing the body to respond appropriately. However, excessive and long-term exposure to glucocorticoids caused by chronic stress can lead to various mental diseases including depression, cognitive disorders, and anxiety.
< Figure 1. Results of screening for compounds that increase astrocyte phagocytosis
(A) Discovered that synthetic glucocorticoid (stress hormone) increases the phagocytosis of astrocytes through screening of FDA-approved clinical compounds. (B-C) When treated with stress hormones, the phagocytosis of astrocytes is greatly increased, but this phenomenon is strongly suppressed by the GR antagonist (Mifepristone). CORT: corticosterone (stress hormone), Eplerenone: mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) antagonist, Mifepristone: glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonist >
To understand the changes in astrocyte functions caused by childhood stress, the research team used mice models with early social deprivation, and discovered that stress hormones bind to the glucocorticoid receptors (GRs) of astrocytes. This significantly increased the expression of Mer tyrosine kinase (MERK), which plays an essential role in astrocyte phagocytosis. Surprisingly, out of the various neurons in the cerebral cortex, astrocytes would eliminate only the excitatory synapses of specific neurons. The team found that this builds abnormal neural networks, which can lead to complex behavioral abnormalities such as social deficiencies and depression in adulthood.
The team also observed that microglia, which also play an important role in cerebral immunity, did not contribute to synapse removal in the mice models with early social deprivation. This confirms that the response to stress hormones during childhood is specifically astrocyte-mediated.
To find out whether these results are also applicable in humans, the research team used a brain organoid grown from human-induced pluripotent stem cells to observe human responses to stress hormones. The team observed that the stress hormones induced astrocyte GRs and phagocyte activation in the human brain organoid as well, and confirmed that the astrocytes subsequently eliminated excessive amounts of excitatory synapses. By showing that mice and humans both showed the same synapse control mechanism in response to stress, the team suggested that this discovery is applicable to mental disorders in humans.
< Figure 2. A schematic diagram of the study published in Immunity. Excessive stress hormone secretion in childhood increases the expression of the MERTK phagocytic receptor through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) of astrocytes, resulting in excessive elimination of excitatory synapses. Excessive synaptic elimination by astrocytes during brain development causes permanent damage to brain circuits, resulting in abnormal neural activity in the adult brain and psychiatric behaviors such as depression and anti-social tendencies. >
Prof. Won-Suk Chung said, “Until now, we did not know the exact mechanism for how childhood stress caused brain diseases. This research was the first to show that the excessive phagocytosis of astrocytes could be an important cause of such diseases.” He added, “In the future, controlling the immune response of astrocytes will be used as a fundamental target for understanding and treating brain diseases.”
This research, written by co-first authors Youkyeong Byun (Ph.D. candidate) and Nam-Shik Kim (post-doctoral associate) from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, was published in the internationally renowned journal Immunity, a sister magazine of Cell and one of the best journal in the field of immunology, on July 31 under the title "Stress induces behavioral abnormalities by increasing expression of phagocytic receptor MERTK in astrocytes to promote synapse phagocytosis."
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea grant, the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), and the Korea Dementia Research Center (KDRC).
2023.08.04 View 7207 -
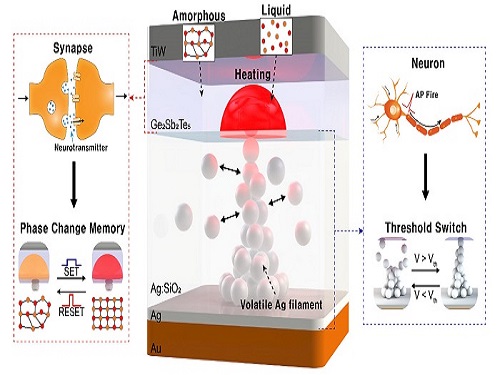 Neuromorphic Memory Device Simulates Neurons and Synapses
Simultaneous emulation of neuronal and synaptic properties promotes the development of brain-like artificial intelligence
Researchers have reported a nano-sized neuromorphic memory device that emulates neurons and synapses simultaneously in a unit cell, another step toward completing the goal of neuromorphic computing designed to rigorously mimic the human brain with semiconductor devices.
Neuromorphic computing aims to realize artificial intelligence (AI) by mimicking the mechanisms of neurons and synapses that make up the human brain. Inspired by the cognitive functions of the human brain that current computers cannot provide, neuromorphic devices have been widely investigated. However, current Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)-based neuromorphic circuits simply connect artificial neurons and synapses without synergistic interactions, and the concomitant implementation of neurons and synapses still remains a challenge. To address these issues, a research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering implemented the biological working mechanisms of humans by introducing the neuron-synapse interactions in a single memory cell, rather than the conventional approach of electrically connecting artificial neuronal and synaptic devices.
Similar to commercial graphics cards, the artificial synaptic devices previously studied often used to accelerate parallel computations, which shows clear differences from the operational mechanisms of the human brain. The research team implemented the synergistic interactions between neurons and synapses in the neuromorphic memory device, emulating the mechanisms of the biological neural network. In addition, the developed neuromorphic device can replace complex CMOS neuron circuits with a single device, providing high scalability and cost efficiency.
The human brain consists of a complex network of 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. The functions and structures of neurons and synapses can flexibly change according to the external stimuli, adapting to the surrounding environment. The research team developed a neuromorphic device in which short-term and long-term memories coexist using volatile and non-volatile memory devices that mimic the characteristics of neurons and synapses, respectively. A threshold switch device is used as volatile memory and phase-change memory is used as a non-volatile device. Two thin-film devices are integrated without intermediate electrodes, implementing the functional adaptability of neurons and synapses in the neuromorphic memory.
Professor Keon Jae Lee explained, "Neurons and synapses interact with each other to establish cognitive functions such as memory and learning, so simulating both is an essential element for brain-inspired artificial intelligence. The developed neuromorphic memory device also mimics the retraining effect that allows quick learning of the forgotten information by implementing a positive feedback effect between neurons and synapses.”
This result entitled “Simultaneous emulation of synaptic and intrinsic plasticity using a memristive synapse” was published in the May 19, 2022 issue of Nature Communications.
-Publication:Sang Hyun Sung, Tae Jin Kim, Hyera Shin, Tae Hong Im, and Keon Jae Lee (2022) “Simultaneous emulation of synaptic and intrinsic plasticity using a memristive synapse,” Nature Communications May 19, 2022 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30432-2)
-Profile:Professor Keon Jae Leehttp://fand.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.20 View 13974
Neuromorphic Memory Device Simulates Neurons and Synapses
Simultaneous emulation of neuronal and synaptic properties promotes the development of brain-like artificial intelligence
Researchers have reported a nano-sized neuromorphic memory device that emulates neurons and synapses simultaneously in a unit cell, another step toward completing the goal of neuromorphic computing designed to rigorously mimic the human brain with semiconductor devices.
Neuromorphic computing aims to realize artificial intelligence (AI) by mimicking the mechanisms of neurons and synapses that make up the human brain. Inspired by the cognitive functions of the human brain that current computers cannot provide, neuromorphic devices have been widely investigated. However, current Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)-based neuromorphic circuits simply connect artificial neurons and synapses without synergistic interactions, and the concomitant implementation of neurons and synapses still remains a challenge. To address these issues, a research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering implemented the biological working mechanisms of humans by introducing the neuron-synapse interactions in a single memory cell, rather than the conventional approach of electrically connecting artificial neuronal and synaptic devices.
Similar to commercial graphics cards, the artificial synaptic devices previously studied often used to accelerate parallel computations, which shows clear differences from the operational mechanisms of the human brain. The research team implemented the synergistic interactions between neurons and synapses in the neuromorphic memory device, emulating the mechanisms of the biological neural network. In addition, the developed neuromorphic device can replace complex CMOS neuron circuits with a single device, providing high scalability and cost efficiency.
The human brain consists of a complex network of 100 billion neurons and 100 trillion synapses. The functions and structures of neurons and synapses can flexibly change according to the external stimuli, adapting to the surrounding environment. The research team developed a neuromorphic device in which short-term and long-term memories coexist using volatile and non-volatile memory devices that mimic the characteristics of neurons and synapses, respectively. A threshold switch device is used as volatile memory and phase-change memory is used as a non-volatile device. Two thin-film devices are integrated without intermediate electrodes, implementing the functional adaptability of neurons and synapses in the neuromorphic memory.
Professor Keon Jae Lee explained, "Neurons and synapses interact with each other to establish cognitive functions such as memory and learning, so simulating both is an essential element for brain-inspired artificial intelligence. The developed neuromorphic memory device also mimics the retraining effect that allows quick learning of the forgotten information by implementing a positive feedback effect between neurons and synapses.”
This result entitled “Simultaneous emulation of synaptic and intrinsic plasticity using a memristive synapse” was published in the May 19, 2022 issue of Nature Communications.
-Publication:Sang Hyun Sung, Tae Jin Kim, Hyera Shin, Tae Hong Im, and Keon Jae Lee (2022) “Simultaneous emulation of synaptic and intrinsic plasticity using a memristive synapse,” Nature Communications May 19, 2022 (DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-30432-2)
-Profile:Professor Keon Jae Leehttp://fand.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2022.05.20 View 13974 -
 Astrocytes Eat Connections to Maintain Plasticity in Adult Brains
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections — the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger — are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
“Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases,” said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures.”
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
“Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity,” Professor Chung said. “Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain.”
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
“Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity,” Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group’s preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
“Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders,” Professor Chung said. “It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute basic research program.
Other contributors include Joon-Hyuk Lee and Se Young Lee, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); Ji-young Kim, Hyoeun Lee and Hyungju Park; Research Group for Neurovascular Unit, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI); Seulgi Noh, and Ji Young Mun, Research Group for Neural Circuit, KBRI. Kim, Noh and Park are also affiliated with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
-Profile
Professor Won-Suk Chung
Department of Biological Sciences
Gliabiology Lab (https://www.kaistglia.org/)
KAIST
-Publication
"Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis"
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03060-3
2020.12.24 View 12247
Astrocytes Eat Connections to Maintain Plasticity in Adult Brains
Developing brains constantly sprout new neuronal connections called synapses as they learn and remember. Important connections — the ones that are repeatedly introduced, such as how to avoid danger — are nurtured and reinforced, while connections deemed unnecessary are pruned away. Adult brains undergo similar pruning, but it was unclear how or why synapses in the adult brain get eliminated.
Now, a team of KAIST researchers has found the mechanism underlying plasticity and, potentially, neurological disorders in adult brains. They published their findings on December 23 in Nature.
“Our findings have profound implications for our understanding of how neural circuits change during learning and memory, as well as in diseases,” said paper author Won-Suk Chung, an assistant professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “Changes in synapse number have strong association with the prevalence of various neurological disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, frontotemporal dementia, and several forms of seizures.”
Gray matter in the brain contains microglia and astrocytes, two complementary cells that, among other things, support neurons and synapses. Microglial are a frontline immunity defense, responsible for eating pathogens and dead cells, and astrocytes are star-shaped cells that help structure the brain and maintain homeostasis by helping to control signaling between neurons. According to Professor Chung, it is generally thought that microglial eat synapses as part of its clean-up effort in a process known as phagocytosis.
“Using novel tools, we show that, for the first time, it is astrocytes and not microglia that constantly eliminate excessive and unnecessary adult excitatory synaptic connections in response to neuronal activity,” Professor Chung said. “Our paper challenges the general consensus in this field that microglia are the primary synapse phagocytes that control synapse numbers in the brain.”
Professor Chung and his team developed a molecular sensor to detect synapse elimination by glial cells and quantified how often and by which type of cell synapses were eliminated. They also deployed it in a mouse model without MEGF10, the gene that allows astrocytes to eliminate synapses. Adult animals with this defective astrocytic phagocytosis had unusually increased excitatory synapse numbers in the hippocampus. Through a collaboration with Dr. Hyungju Park at KBRI, they showed that these increased excitatory synapses are functionally impaired, which cause defective learning and memory formation in MEGF10 deleted animals.
“Through this process, we show that, at least in the adult hippocampal CA1 region, astrocytes are the major player in eliminating synapses, and this astrocytic function is essential for controlling synapse number and plasticity,” Chung said.
Professor Chung noted that researchers are only beginning to understand how synapse elimination affects maturation and homeostasis in the brain. In his group’s preliminary data in other brain regions, it appears that each region has different rates of synaptic elimination by astrocytes. They suspect a variety of internal and external factors are influencing how astrocytes modulate each regional circuit, and plan to elucidate these variables.
“Our long-term goal is understanding how astrocyte-mediated synapse turnover affects the initiation and progression of various neurological disorders,” Professor Chung said. “It is intriguing to postulate that modulating astrocytic phagocytosis to restore synaptic connectivity may be a novel strategy in treating various brain disorders.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Brain Research Institute basic research program.
Other contributors include Joon-Hyuk Lee and Se Young Lee, Department of Biological Sciences, Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST); Ji-young Kim, Hyoeun Lee and Hyungju Park; Research Group for Neurovascular Unit, Korea Brain Research Institute (KBRI); Seulgi Noh, and Ji Young Mun, Research Group for Neural Circuit, KBRI. Kim, Noh and Park are also affiliated with the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST).
-Profile
Professor Won-Suk Chung
Department of Biological Sciences
Gliabiology Lab (https://www.kaistglia.org/)
KAIST
-Publication
"Astrocytes phagocytose adult hippocampal synapses for circuit homeostasis"
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-03060-3
2020.12.24 View 12247 -
 Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
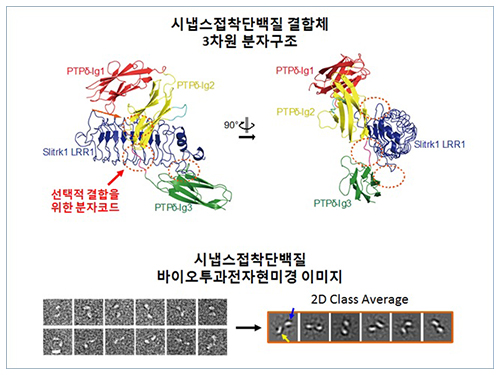
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 12629
Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 12629 -
 Professor Eunjoon Kim's team finds synapse-forming protein
Professor Eunjoon Kim’s team finds synapse-forming protein
- discover a new protein ‘NGL’ that promotes the formation of neuronal synapses
- can presume the cause of various brain disorders including schizophrenia
- will be published at Nature Neuroscience Vol. 9 in September
A new protein that promotes the formation of synapses in human brains was discovered by a Korean research team.
The team led by Eunjoon Kim, Professor of Department of Biological Sciences and Head of Creative Research Group of Synapse Formation), announced that it had discovered a new fact that NGL protein promotes the formation of neuronal synapses and this fact would be published in Nature Neuroscience Vol. 9 on September 18.
Professor Kim’s team discovered that a membrane protein named ‘NGL’ located at post synapse links with other membrane protein named netrin-G in pre synapse, acting as crosslink, and promotes the formation of a new synapse.
‘NGL’ is the second protein found to crosslink synapse, following neuoroligin. With the discovery of this new protein, the principle of synapse formation and the causes of various brain disorders can be presumed.
In the human brain, about more than 100 billion neuron cells and about 10,000 synapses compose neural circuit. A synapse is the place where innervation occurs between neuron cells. The formation of synapse induces the formation of neural circuit, and neural circuit is deeply related with various brain disorders as well as normal development of brains or brain functions.
“As netrin-G linked with NGL is related with schizonphrenia and neuoroligin and synapse crosslinking protein having a similar function with NGL is deeply related with mental retardation and autism, I think NGL is related with various brain disorders including schizophrenia.”
<Explanation of attached photos>
■ Photo1: Experiment for confirming NGL’s ability to form synapse No. 1
Mix ordinary cell (green) revealing NGL at its surface and neuron cell. Axon grows toward NGL (ordinary cell) located in the middle of ten o’clock direction and meets NGL, where NGL induces the formation of pre synapse (red) in the contacting axon.
Whether pre synapse has been formed can be told by the fluorescent dying (red) of pre synapse protein named Synapsin.
- Figure a-b: formation of synapse by NGL
- Figure c-d: transformed NGL losing synapse forming ability cannot form synapse
■ Photo 2: Experiment for confirming NGL’s ability to form synapse No. 2
When beads coated with NGL are scattered on neuron cell, the beads contact with the axon of the neuron cell (the beads are clearly visible at the phase differentiation image in the middle panel). At this time, NGL induces the formation of pre synapse (red) in the axon. Whether pre synapse has been formed can be told by the fluorescent dying (red) of pre synapse protein named SynPhy (panel a) or VGlut1 (panel b).
2006.09.21 View 16943
Professor Eunjoon Kim's team finds synapse-forming protein
Professor Eunjoon Kim’s team finds synapse-forming protein
- discover a new protein ‘NGL’ that promotes the formation of neuronal synapses
- can presume the cause of various brain disorders including schizophrenia
- will be published at Nature Neuroscience Vol. 9 in September
A new protein that promotes the formation of synapses in human brains was discovered by a Korean research team.
The team led by Eunjoon Kim, Professor of Department of Biological Sciences and Head of Creative Research Group of Synapse Formation), announced that it had discovered a new fact that NGL protein promotes the formation of neuronal synapses and this fact would be published in Nature Neuroscience Vol. 9 on September 18.
Professor Kim’s team discovered that a membrane protein named ‘NGL’ located at post synapse links with other membrane protein named netrin-G in pre synapse, acting as crosslink, and promotes the formation of a new synapse.
‘NGL’ is the second protein found to crosslink synapse, following neuoroligin. With the discovery of this new protein, the principle of synapse formation and the causes of various brain disorders can be presumed.
In the human brain, about more than 100 billion neuron cells and about 10,000 synapses compose neural circuit. A synapse is the place where innervation occurs between neuron cells. The formation of synapse induces the formation of neural circuit, and neural circuit is deeply related with various brain disorders as well as normal development of brains or brain functions.
“As netrin-G linked with NGL is related with schizonphrenia and neuoroligin and synapse crosslinking protein having a similar function with NGL is deeply related with mental retardation and autism, I think NGL is related with various brain disorders including schizophrenia.”
<Explanation of attached photos>
■ Photo1: Experiment for confirming NGL’s ability to form synapse No. 1
Mix ordinary cell (green) revealing NGL at its surface and neuron cell. Axon grows toward NGL (ordinary cell) located in the middle of ten o’clock direction and meets NGL, where NGL induces the formation of pre synapse (red) in the contacting axon.
Whether pre synapse has been formed can be told by the fluorescent dying (red) of pre synapse protein named Synapsin.
- Figure a-b: formation of synapse by NGL
- Figure c-d: transformed NGL losing synapse forming ability cannot form synapse
■ Photo 2: Experiment for confirming NGL’s ability to form synapse No. 2
When beads coated with NGL are scattered on neuron cell, the beads contact with the axon of the neuron cell (the beads are clearly visible at the phase differentiation image in the middle panel). At this time, NGL induces the formation of pre synapse (red) in the axon. Whether pre synapse has been formed can be told by the fluorescent dying (red) of pre synapse protein named SynPhy (panel a) or VGlut1 (panel b).
2006.09.21 View 16943