nanoparticle
-
 KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 9736
KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 9736 -
 New Chiral Nanostructures to Extend the Material Platform
Researchers observed a wide window of chiroptical activity from nanomaterials
A research team transferred chirality from the molecular scale to a microscale to extend material platforms and applications. The optical activity from this novel chiral material encompasses to short-wave infrared region.
This platform could serve as a powerful strategy for hierarchical chirality transfer through self-assembly, generating broad optical activity and providing immense applications including bio, telecommunication, and imaging technique. This is the first observation of such a wide window of chiroptical activity from nanomaterials.
“We synthesized chiral copper sulfides using cysteine, as the stabilizer, and transferring the chirality from molecular to the microscale through self-assembly,” explained Professor Jihyeon Yeom from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who led the research. The result was reported in ACS Nano on September 14.
Chiral nanomaterials provide a rich platform for versatile applications. Tuning the wavelength of polarization rotation maxima in the broad range is a promising candidate for infrared neural stimulation, imaging, and nanothermometry. However, the majority of previously developed chiral nanomaterials revealed the optical activity in a relatively shorter wavelength range, not in short-wave infrared.
To achieve chiroptical activity in the short-wave infrared region, materials should be in sub-micrometer dimensions, which are compatible with the wavelength of short-wave infrared region light for strong light-matter interaction. They also should have the optical property of short-wave infrared region absorption while forming a structure with chirality.
Professor Yeom’s team induced self-assembly of the chiral nanoparticles by controlling the attraction and repulsion forces between the building block nanoparticles. During this process, molecular chirality of cysteine was transferred to the nanoscale chirality of nanoparticles, and then transferred to the micrometer scale chirality of nanoflowers with 1.5-2 2 μm dimensions formed by the self-assembly.
“We will work to expand the wavelength range of chiroptical activity to the short-wave infrared region, thus reshaping our daily lives in the form of a bio-barcode that can store vast amount of information under the skin,” said Professor Yeom.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, the National Research Foundation of Korea,the KAIST URP Program, the KAIST Creative Challenging Research Program, Samsung and POSCO Science Fellowship.
-PublicationKi Hyun Park, Junyoung Kwon, Uichang Jeong, Ji-Young Kim, Nicholas A.Kotov, Jihyeon Yeom, “Broad Chrioptical Activity from Ultraviolet to Short-Wave Infrared by Chirality Transfer from Molecular to Micrometer Scale," September 14, 2021 ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c05888)
-ProfileProfessor Jihyeon YeomNovel Nanomaterials for New Platforms LaboratoryDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.10.22 View 10552
New Chiral Nanostructures to Extend the Material Platform
Researchers observed a wide window of chiroptical activity from nanomaterials
A research team transferred chirality from the molecular scale to a microscale to extend material platforms and applications. The optical activity from this novel chiral material encompasses to short-wave infrared region.
This platform could serve as a powerful strategy for hierarchical chirality transfer through self-assembly, generating broad optical activity and providing immense applications including bio, telecommunication, and imaging technique. This is the first observation of such a wide window of chiroptical activity from nanomaterials.
“We synthesized chiral copper sulfides using cysteine, as the stabilizer, and transferring the chirality from molecular to the microscale through self-assembly,” explained Professor Jihyeon Yeom from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, who led the research. The result was reported in ACS Nano on September 14.
Chiral nanomaterials provide a rich platform for versatile applications. Tuning the wavelength of polarization rotation maxima in the broad range is a promising candidate for infrared neural stimulation, imaging, and nanothermometry. However, the majority of previously developed chiral nanomaterials revealed the optical activity in a relatively shorter wavelength range, not in short-wave infrared.
To achieve chiroptical activity in the short-wave infrared region, materials should be in sub-micrometer dimensions, which are compatible with the wavelength of short-wave infrared region light for strong light-matter interaction. They also should have the optical property of short-wave infrared region absorption while forming a structure with chirality.
Professor Yeom’s team induced self-assembly of the chiral nanoparticles by controlling the attraction and repulsion forces between the building block nanoparticles. During this process, molecular chirality of cysteine was transferred to the nanoscale chirality of nanoparticles, and then transferred to the micrometer scale chirality of nanoflowers with 1.5-2 2 μm dimensions formed by the self-assembly.
“We will work to expand the wavelength range of chiroptical activity to the short-wave infrared region, thus reshaping our daily lives in the form of a bio-barcode that can store vast amount of information under the skin,” said Professor Yeom.
This study was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, the National Research Foundation of Korea,the KAIST URP Program, the KAIST Creative Challenging Research Program, Samsung and POSCO Science Fellowship.
-PublicationKi Hyun Park, Junyoung Kwon, Uichang Jeong, Ji-Young Kim, Nicholas A.Kotov, Jihyeon Yeom, “Broad Chrioptical Activity from Ultraviolet to Short-Wave Infrared by Chirality Transfer from Molecular to Micrometer Scale," September 14, 2021 ACS Nano (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c05888)
-ProfileProfessor Jihyeon YeomNovel Nanomaterials for New Platforms LaboratoryDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
2021.10.22 View 10552 -
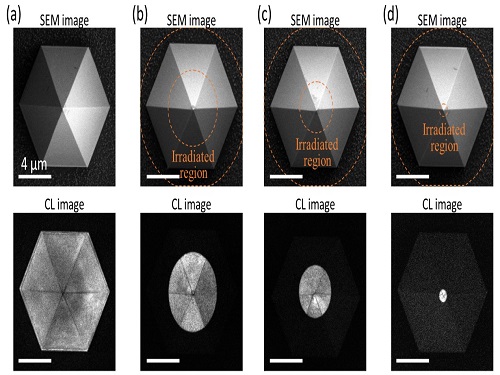 Quantum Emitters: Beyond Crystal Clear to Single-Photon Pure
‘Nanoscale Focus Pinspot’ can quench only the background noise without changing the optical properties of the quantum emitter and the built-in photonic structure
Photons, fundamental particles of light, are carrying these words to your eyes via the light from your computer screen or phone. Photons play a key role in the next-generation quantum information technology, such as quantum computing and communications. A quantum emitter, capable of producing a single, pure photon, is the crux of such technology but has many issues that have yet to be solved, according to KAIST researchers.
A research team under Professor Yong-Hoon Cho has developed a technique that can isolate the desired quality emitter by reducing the noise surrounding the target with what they have dubbed a ‘nanoscale focus pinspot.’ They published their results on June 24 in ACS Nano.
“The nanoscale focus pinspot is a structurally nondestructive technique under an extremely low dose ion beam and is generally applicable for various platforms to improve their single-photon purity while retaining the integrated photonic structures,” said lead author Yong-Hoon Cho from the Department of Physics at KAIST.
To produce single photons from solid state materials, the researchers used wide-bandgap semiconductor quantum dots — fabricated nanoparticles with specialized potential properties, such as the ability to directly inject current into a small chip and to operate at room temperature for practical applications. By making a quantum dot in a photonic structure that propagates light, and then irradiating it with helium ions, researchers theorized that they could develop a quantum emitter that could reduce the unwanted noisy background and produce a single, pure photon on demand.
Professor Cho explained, “Despite its high resolution and versatility, a focused ion beam typically suppresses the optical properties around the bombarded area due to the accelerated ion beam’s high momentum. We focused on the fact that, if the focused ion beam is well controlled, only the background noise can be selectively quenched with high spatial resolution without destroying the structure.”
In other words, the researchers focused the ion beam on a mere pin prick, effectively cutting off the interactions around the quantum dot and removing the physical properties that could negatively interact with and degrade the photon purity emitted from the quantum dot.
“It is the first developed technique that can quench the background noise without changing the optical properties of the quantum emitter and the built-in photonic structure,” Professor Cho asserted.
Professor Cho compared it to stimulated emission depletion microscopy, a technique used to decrease the light around the area of focus, but leaving the focal point illuminated. The result is increased resolution of the desired visual target.
“By adjusting the focused ion beam-irradiated region, we can select the target emitter with nanoscale resolution by quenching the surrounding emitter,” Professor Cho said. “This nanoscale selective-quenching technique can be applied to various material and structural platforms and further extended for applications such as optical memory and high-resolution micro displays.” Korea’s National Research Foundation and the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation supported this work.
-PublicationMinho Choi, Seongmoon Jun, and Yong-Hoon Cho et al. ACS Nano‘Nanoscale Focus Pinspot for High-Purity Quantum Emitters via Focused-Ion-Beam-Induced Luminescence Quenching,’(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.1c00587)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.09.02 View 11018
Quantum Emitters: Beyond Crystal Clear to Single-Photon Pure
‘Nanoscale Focus Pinspot’ can quench only the background noise without changing the optical properties of the quantum emitter and the built-in photonic structure
Photons, fundamental particles of light, are carrying these words to your eyes via the light from your computer screen or phone. Photons play a key role in the next-generation quantum information technology, such as quantum computing and communications. A quantum emitter, capable of producing a single, pure photon, is the crux of such technology but has many issues that have yet to be solved, according to KAIST researchers.
A research team under Professor Yong-Hoon Cho has developed a technique that can isolate the desired quality emitter by reducing the noise surrounding the target with what they have dubbed a ‘nanoscale focus pinspot.’ They published their results on June 24 in ACS Nano.
“The nanoscale focus pinspot is a structurally nondestructive technique under an extremely low dose ion beam and is generally applicable for various platforms to improve their single-photon purity while retaining the integrated photonic structures,” said lead author Yong-Hoon Cho from the Department of Physics at KAIST.
To produce single photons from solid state materials, the researchers used wide-bandgap semiconductor quantum dots — fabricated nanoparticles with specialized potential properties, such as the ability to directly inject current into a small chip and to operate at room temperature for practical applications. By making a quantum dot in a photonic structure that propagates light, and then irradiating it with helium ions, researchers theorized that they could develop a quantum emitter that could reduce the unwanted noisy background and produce a single, pure photon on demand.
Professor Cho explained, “Despite its high resolution and versatility, a focused ion beam typically suppresses the optical properties around the bombarded area due to the accelerated ion beam’s high momentum. We focused on the fact that, if the focused ion beam is well controlled, only the background noise can be selectively quenched with high spatial resolution without destroying the structure.”
In other words, the researchers focused the ion beam on a mere pin prick, effectively cutting off the interactions around the quantum dot and removing the physical properties that could negatively interact with and degrade the photon purity emitted from the quantum dot.
“It is the first developed technique that can quench the background noise without changing the optical properties of the quantum emitter and the built-in photonic structure,” Professor Cho asserted.
Professor Cho compared it to stimulated emission depletion microscopy, a technique used to decrease the light around the area of focus, but leaving the focal point illuminated. The result is increased resolution of the desired visual target.
“By adjusting the focused ion beam-irradiated region, we can select the target emitter with nanoscale resolution by quenching the surrounding emitter,” Professor Cho said. “This nanoscale selective-quenching technique can be applied to various material and structural platforms and further extended for applications such as optical memory and high-resolution micro displays.” Korea’s National Research Foundation and the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation supported this work.
-PublicationMinho Choi, Seongmoon Jun, and Yong-Hoon Cho et al. ACS Nano‘Nanoscale Focus Pinspot for High-Purity Quantum Emitters via Focused-Ion-Beam-Induced Luminescence Quenching,’(https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.1c00587)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.09.02 View 11018 -
 Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 14056
Extremely Stable Perovskite Nanoparticles Films for Next-Generation Displays
Researchers have reported an extremely stable cross-linked perovskite nanoparticle that maintains a high photoluminescence quantum yield (PLQY) for 1.5 years in air and harsh liquid environments. This stable material’s design strategies, which addressed one of the most critical problems limiting their practical application, provide a breakthrough for the commercialization of perovskite nanoparticles in next-generation displays and bio-related applications.
According to the research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, their development can survive in severe environments such as water, various polar solvents, and high temperature with high humidity without additional encapsulation. This development is expected to enable perovskite nanoparticles to be applied to high color purity display applications as a practical color converting material. This result was published as the inside front cover article in Advanced Materials.
Perovskites, which consist of organics, metals, and halogen elements, have emerged as key elements in various optoelectronic applications. The power conversion efficiency of photovoltaic cells based on perovskites light absorbers has been rapidly increased. Perovskites are also great promise as a light emitter in display applications because of their low material cost, facile wavelength tunability, high (PLQY), very narrow emission band width, and wider color gamut than inorganic semiconducting nanocrystals and organic emitters. Thanks to these advantages, perovskites have been identified as a key color-converting material for next-generation high color-purity displays. In particular, perovskites are the only luminescence material that meets Rec. 2020 which is a new color standard in display industry.
However, perovskites are very unstable against heat, moisture, and light, which makes them almost impossible to use in practical applications. To solve these problems, many researchers have attempted to physically prevent perovskites from coming into contact with water molecules by passivating the perovskite grain and nanoparticle surfaces with organic ligands or inorganic shell materials, or by fabricating perovskite-polymer nanocomposites. These methods require complex processes and have limited stability in ambient air and water. Furthermore, stable perovskite nanoparticles in the various chemical environments and high temperatures with high humidity have not been reported yet.
The research team in collaboration with Seoul National University develops siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films. Here, perovskite nanoparticles are chemically crosslinked with thermally stable siloxane molecules, thereby significantly improving the stability of the perovskite nanoparticles without the need for any additional protecting layer.
Siloxane-encapsulated perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited a high PLQY (> 70%) value, which can be maintained over 600 days in water, various chemicals (alcohol, strong acidic and basic solutions), and high temperatures with high humidity (85℃/85%). The research team investigated the mechanisms impacting the chemical crosslinking and water molecule-induced stabilization of perovskite nanoparticles through various photo-physical analysis and density-functional theory calculation.
The research team confirmed that displays based on their siloxane-perovskite nanoparticle composite films exhibited higher PLQY and a wider color gamut than those of Cd-based quantum dots and demonstrated perfect color converting properties on commercial mobile phone screens. Unlike what was commonly believed in the halide perovskite field, the composite films showed excellent bio-compatibility because the siloxane matrix prevents the toxicity of Pb in perovskite nanoparticle.
By using this technology, the instability of perovskite materials, which is the biggest challenge for practical applications, is greatly improved through simple encapsulation method.
“Perovskite nanoparticle is the only photoluminescent material that can meet the next generation display color standard. Nevertheless, there has been reluctant to commercialize it due to its moisture vulnerability. The newly developed siloxane encapsulation technology will trigger more research on perovskite nanoparticles as color conversion materials and will accelerate early commercialization,” Professor Bae said.
This work was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (WMC) of the Engineering Research Center (ERC) Project, and the Leadership Research Program funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Publication:
Junho Jang, Young-Hoon Kim, Sunjoon Park, Dongsuk Yoo, Hyunjin Cho, Jinhyeong Jang, Han Beom Jeong, Hyunhwan Lee, Jong Min Yuk, Chan Beum Park, Duk Young Jeon, Yong-Hyun Kim, Byeong-Soo Bae, and Tae-Woo Lee. “Extremely Stable Luminescent Crosslinked Perovskite Nanoparticles under Harsh Environments over 1.5 Years” Advanced Materials, 2020, 2005255. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202005255.
Link to download the full-text paper:
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.202005255
-Profile: Prof. Byeong-Soo Bae (Corresponding author)
bsbae@kaist.ac.kr
Lab. of Optical Materials & Coating
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
2020.12.29 View 14056 -
 New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 14380
New Nanoparticle Drug Combination For Atherosclerosis
Physicochemical cargo-switching nanoparticles (CSNP) designed by KAIST can help significantly reduce cholesterol and macrophage foam cells in arteries, which are the two main triggers for atherosclerotic plaque and inflammation.
The CSNP-based combination drug delivery therapy was proved to exert cholesterol-lowering, anti-inflammatory, and anti-proliferative functions of two common medications for treating and preventing atherosclerosis that are cyclodextrin and statin. Professor Ji-Ho Park and Dr. Heegon Kim from KAIST’s Department of Bio and Brain Engineering said their study has shown great potential for future applications with reduced side effects.
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory vascular disease that is characterized by the accumulation of cholesterol and cholesterol-loaded macrophage foam cells in the intima. When this atherosclerotic plaque clogs and narrows the artery walls, they restrict blood flow and cause various cardiovascular conditions such as heart attacks and strokes. Heart attacks and strokes are the world’s first and fifth causes of death respectively.
Oral statin administration has been used in clinics as a standard care for atherosclerosis, which is prescribed to lower blood cholesterol and inhibit its accumulation within the plaque. Although statins can effectively prevent the progression of plaque growth, they have only shown modest efficacy in eliminating the already-established plaque. Therefore, patients are required to take statin drugs for the rest of their lives and will always carry the risk of plaque ruptures that can trigger a blood clot.
To address these issues, Professor Park and Dr. Kim exploited another antiatherogenic agent called cyclodextrin. In their paper published in the Journal of Controlled Release on March 10, Professor Park and Dr. Kim reported that the polymeric formulation of cyclodextrin with a diameter of approximately 10 nanometers(nm) can accumulate within the atherosclerotic plaque 14 times more and effectively reduce the plaque even at lower doses, compared to cyclodextrin in a non-polymer structure.
Moreover, although cyclodextrin is known to have a cytotoxic effect on hair cells in the cochlea, which can lead to hearing loss, cyclodextrin polymers developed by Professor Park’s research group exhibited a varying biodistribution profile and did not have this side effect.
In the follow-up study reported in ACS Nano on April 28, the researchers exploited both cyclodextrin and statin and form the cyclodextrin-statin self-assembly drug complex, based on previous findings that each drug can exert local anti-atherosclerosis effect within the plaque. The complex formation processes were optimized to obtain homogeneous and stable nanoparticles with a diameter of about 100 nm for systematic injection.
The therapeutic synergy of cyclodextrin and statin could reportedly enhance plaque-targeted drug delivery and anti-inflammation. Cyclodextrin led to the regression of cholesterol in the established plaque, and the statins were shown to inhibit the proliferation of macrophage foam cells. The study suggested that combination therapy is required to resolve the complex inflammatory cholesterol-rich microenvironment within the plaque.
Professor Park said, “While nanomedicine has been mainly developed for the treatment of cancers, our studies show that nanomedicine can also play a significant role in treating and preventing atherosclerosis, which causes various cardiovascular diseases that are the leading causes of death worldwide.”
This work was supported by KAIST and the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publications:
1. Heegon Kim, Junhee Han, and Ji-Ho Park. (2020) ‘Cyclodextrin polymer improves atherosclerosis therapy and reduces ototoxicity’ Journal of Controlled Release. Volume 319. Page 77-86. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2019.12.021
2. Kim, H., et al. (2020) ‘Affinity-Driven Design of Cargo-Switching Nanoparticles to Leverage a Cholesterol-Rich Microenvironment for Atherosclerosis Therapy’ ACS Nano. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b08216
Profile: Ji-Ho Park, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jihopark@kaist.ac.kr
http://openwetware.org/wiki/Park_Lab
Biomaterials Engineering Laboratory (BEL)
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering (BIOENG)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Heegon Kim, Ph.D.
Postdoctoral Researcher
heegon@kaist.ac.kr
BEL, BIOENG, KAIST
(END)
2020.06.16 View 14380 -
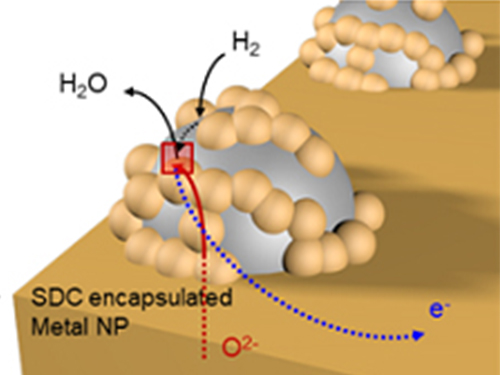 Unravelling Inherent Electrocatalysis to Improve the Performance of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
(Figure 1. Electrode structure for the precise evaluation of the metal nanoparticles’ electrochemical catalytic characteristics at a high temperature.)
A KAIST team presented an ideal electrode design to enhance the performance of high-temperature fuel cells. The new analytical platform with advanced nanoscale patterning method quantitatively revealed the electrochemical value of metal nanoparticles dispersed on the oxide electrode, thus leading to electrode design directions that can be used in a variety of eco-friendly energy technologies.
The team, working under Professor WooChul Jung and Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, described an accurate analysis of the reactivity of oxide electrodes boosted by metal nanoparticles, where all particles participate in the reaction. They identified how the metal catalysts activate hydrogen electro-oxidation on the ceria-based electrode surface and quantify how rapidly the reaction rate increases with the proper choice of metals.
Metal nanoparticles with diameters of 10 nanometers or less have become a key component in high-performance heterogeneous catalysts, primarily serving as a catalytic activator. Recent experimental and theoretical findings suggest that the optimization of the chemical nature at the metal and support interfaces is essential for performance improvement.
However, the high cost associated with cell fabrication and operation as well as poorer stability of metal nanoparticles at high temperatures have been a long-standing challenge. To solve this problem, the team utilized a globally recognized metal nano patterning technology that uses block copolymer self-assembled nano templates and succeeded in uniformly synthesizing metal particles 10 nanometers in size on the surface of oxide fuel cell electrodes. They also developed a technology to accurately analyze the catalyst characteristics of single particles at high temperatures and maximize the performance of a fuel cell with minimal catalyst use.
The research team confirmed that platinum, which is a commonly used metal catalyst, could boost fuel cell performance by as much as 21 times even at an amount of 300 nanograms, which only costs about 0.015 KRW.
The team quantitatively identified and compared the characteristics of widely used metal catalysts other than platinum, such as palladium, gold, and cobalt, and also elucidated the precise principle of catalyst performance through theoretical analysis.
(Figure 2. Comparison of the electrochemical catalytic characteristics for various 10nm metal nanoparticles (platinum, palladium, cobalt, gold) at a high temperature.)
Professor Jung said, "We have broken the conventional methods of increasing the amount of catalyst which have deemed inefficient and expensive. Our results suggest a clear idea for high performance fuel cells using very small amounts of nanoparticles. This technology can be applied to many different industrial fields, advancing the commercialization of eco-friendly energy technologies such as fuel cells that generate electricity and electrolytic cells that produce hydrogen from water.”
The research has been published as the cover article of Nature Nanotechnology in the March issue. This research was carried out with support from the Nano-Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2019.03.28 View 30719
Unravelling Inherent Electrocatalysis to Improve the Performance of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
(Figure 1. Electrode structure for the precise evaluation of the metal nanoparticles’ electrochemical catalytic characteristics at a high temperature.)
A KAIST team presented an ideal electrode design to enhance the performance of high-temperature fuel cells. The new analytical platform with advanced nanoscale patterning method quantitatively revealed the electrochemical value of metal nanoparticles dispersed on the oxide electrode, thus leading to electrode design directions that can be used in a variety of eco-friendly energy technologies.
The team, working under Professor WooChul Jung and Professor Sang Ouk Kim at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, described an accurate analysis of the reactivity of oxide electrodes boosted by metal nanoparticles, where all particles participate in the reaction. They identified how the metal catalysts activate hydrogen electro-oxidation on the ceria-based electrode surface and quantify how rapidly the reaction rate increases with the proper choice of metals.
Metal nanoparticles with diameters of 10 nanometers or less have become a key component in high-performance heterogeneous catalysts, primarily serving as a catalytic activator. Recent experimental and theoretical findings suggest that the optimization of the chemical nature at the metal and support interfaces is essential for performance improvement.
However, the high cost associated with cell fabrication and operation as well as poorer stability of metal nanoparticles at high temperatures have been a long-standing challenge. To solve this problem, the team utilized a globally recognized metal nano patterning technology that uses block copolymer self-assembled nano templates and succeeded in uniformly synthesizing metal particles 10 nanometers in size on the surface of oxide fuel cell electrodes. They also developed a technology to accurately analyze the catalyst characteristics of single particles at high temperatures and maximize the performance of a fuel cell with minimal catalyst use.
The research team confirmed that platinum, which is a commonly used metal catalyst, could boost fuel cell performance by as much as 21 times even at an amount of 300 nanograms, which only costs about 0.015 KRW.
The team quantitatively identified and compared the characteristics of widely used metal catalysts other than platinum, such as palladium, gold, and cobalt, and also elucidated the precise principle of catalyst performance through theoretical analysis.
(Figure 2. Comparison of the electrochemical catalytic characteristics for various 10nm metal nanoparticles (platinum, palladium, cobalt, gold) at a high temperature.)
Professor Jung said, "We have broken the conventional methods of increasing the amount of catalyst which have deemed inefficient and expensive. Our results suggest a clear idea for high performance fuel cells using very small amounts of nanoparticles. This technology can be applied to many different industrial fields, advancing the commercialization of eco-friendly energy technologies such as fuel cells that generate electricity and electrolytic cells that produce hydrogen from water.”
The research has been published as the cover article of Nature Nanotechnology in the March issue. This research was carried out with support from the Nano-Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2019.03.28 View 30719 -
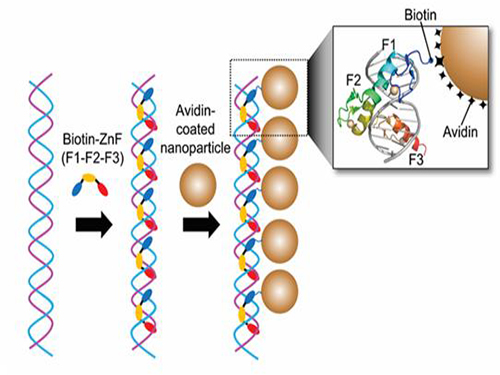 Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 13813
Nanoparticle Cluster Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Yiseul Ryu, a doctoral candidate, used the Zinc Finger protein that specifically binds to target DNA sequence to develop a new manufacturing technique for size-controllable magnetic Nanoparticle Clusters (NPCs). Their research results were published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition online on 25 November 2014.
NPCs are structures consisting of magnetic nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles, and quantum dots, each of which are smaller than 100 nm (10-9m). NPCs have a distinctive property of collectivity not seen in single nanoparticles.
Specifically NPCS differ in physical and optical properties such as Plasmon coupling absorbance, energy transfers between particles, electron transfers, and conductivity. Therefore, NPCs can be employed in biological and medical research as well as the development of nanoelectric and nanoplasmon devices.
To make use of these novel properties, the size and the composition of the cluster must be exquisitely controlled. However, previous techniques relied on chemical binding which required complex steps, making it difficult to control the size and composition of NPCs.
Professor Kim’s team used Zinc Finger, a DNA binding protein, to develop a NPCs manufacturing technique to create clusters of the desired size easily. The Zinc Finger protein contains a zinc ion and specifically recognizes DNA sequence upon binding, which allows the exquisite control of the size and the cluster composition. The technique is also bio-friendly.
Professor Kim’s team created linear structure of different sizes of NPCs using Zinc Finger proteins and three DNA sequences of different lengths. The NPCs they produced confirmed their ability to control the size and structure of the cluster by using different DNA lengths.
The NPCs showed tripled T2 relaxation rates compared to the existing MRI contrast media (Feridex) and effectively transported to targeted cells. The research findings show the potential use of NPCs in biological and medical fields such as MRI contrast media, fluorescence imaging, and drug transport.
The research used the specific binding property of protein and DNA to develop a new method to create an inorganic nanoparticle’s supramolecular assembly. The technique can be used and applied extensively in other nanoparticles for future research in diagnosis, imaging, and drug and gene delivery.
Figure 1. A Mimetic Diagram of NPCs Manufacturing Technique Using DNA Binding Protein Zinc Finger
Figure 2. Transmission Electron Microscopy Images showing different sizes of NPCs depending on the length of the DNA
2014.12.04 View 13813 -
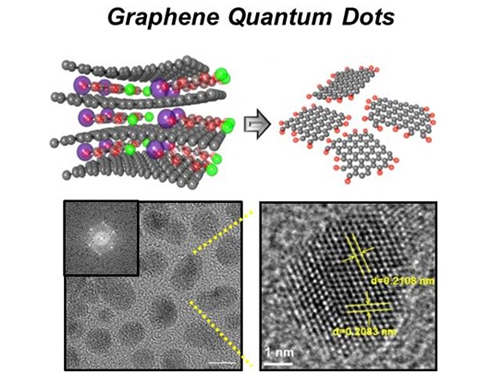 News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 14277
News Article on the Development of Synthesis Process for Graphene Quantum Dots
Before It's News, an international online news agency, highlighted the recent research conducted by KAIST professors (Seokwoo Jeon of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics, and Seunghyup Yoo of the Department of Electrical Engineering) on the development of synthesis process for graphene quantum dots, nanometer-sized round semiconductor nanoparticles that are very efficient at emitting photons. If commercialized, this synthetic technology will lead the way to the development of paper-thin displays in the future.
For the article, please go to the link below:
Before It’s News, September 3, 2014“Graphene quantum dots prove highly efficient in emitting light”
http://beforeitsnews.com/science-and-technology/2014/09/graphene-quantum-dots-prove-highly-efficient-in-emitting-light-2718190.html
2014.09.07 View 14277 -
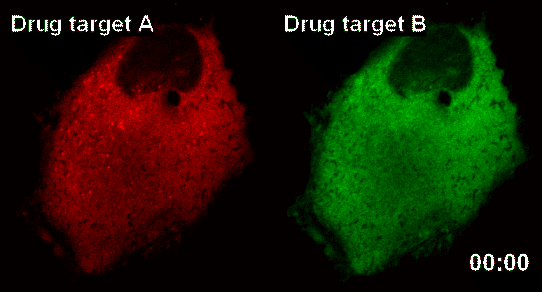 New Technology Developed for Analysis of New Drugs by Using Smart Nano-Sensors
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed the technology that allows biological nano particles to be implanted into human cells for monitoring the effect of new drugs in real time from within the cell. It is expected that this technology will boost the ability to weigh the effects and properties of a new drug more quickly and accurately.
Conventionally, the candidate drug was injected into the human body, and then its cells are extracted to analyze the effects of the drugs. The problem with this method was that the cells were analyzed at a ‘dead’ state which made it incredibly difficult to find candidate substances due to uncontrollable side effects. This made the development of new drugs very difficult despite the large costs and efforts invested into its development.
The research team latched onto the idea that nanoparticles can connect to form a large complex. The complex acts as a nanosensor which allows for real time observation of drug target and the drug itself binding.
The team named the nanosensor technology ‘InCell SMART-i’ and was named ‘Hot Paper’ of the September edition of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’ magazine, a world famous Chemistry Magazine.When a new drug injected into the human body, the drug and drug targets are gradually combined, and the smart nanosensor detects in real time the effect of the new drug as shown in the pictures above (shaded spot).
2011.09.19 View 10112
New Technology Developed for Analysis of New Drugs by Using Smart Nano-Sensors
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed the technology that allows biological nano particles to be implanted into human cells for monitoring the effect of new drugs in real time from within the cell. It is expected that this technology will boost the ability to weigh the effects and properties of a new drug more quickly and accurately.
Conventionally, the candidate drug was injected into the human body, and then its cells are extracted to analyze the effects of the drugs. The problem with this method was that the cells were analyzed at a ‘dead’ state which made it incredibly difficult to find candidate substances due to uncontrollable side effects. This made the development of new drugs very difficult despite the large costs and efforts invested into its development.
The research team latched onto the idea that nanoparticles can connect to form a large complex. The complex acts as a nanosensor which allows for real time observation of drug target and the drug itself binding.
The team named the nanosensor technology ‘InCell SMART-i’ and was named ‘Hot Paper’ of the September edition of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’ magazine, a world famous Chemistry Magazine.When a new drug injected into the human body, the drug and drug targets are gradually combined, and the smart nanosensor detects in real time the effect of the new drug as shown in the pictures above (shaded spot).
2011.09.19 View 10112 -
 Nanowerk Spotlight: Bacteria as environmentally friendly nanoparticle factories, Sep. 24, 2010
The Nanowerk.com is a leading portal site for nanotechnology and nanosciences, which runs a daily news section called “Spotlight.” On September 24, 2010, the Spotlight published an article on the latest developments of the research by a KAIST team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering Department. For the article, please click the link below:
Nanowerk Spotlight: Bacteria as environmentally friendly nanoparticle factories, Sep. 24, 2010
By Michael Berger.
http://www.nanowerk.com/spotlight/spotid=18188.php
2010.09.25 View 11756
Nanowerk Spotlight: Bacteria as environmentally friendly nanoparticle factories, Sep. 24, 2010
The Nanowerk.com is a leading portal site for nanotechnology and nanosciences, which runs a daily news section called “Spotlight.” On September 24, 2010, the Spotlight published an article on the latest developments of the research by a KAIST team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee of the Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering Department. For the article, please click the link below:
Nanowerk Spotlight: Bacteria as environmentally friendly nanoparticle factories, Sep. 24, 2010
By Michael Berger.
http://www.nanowerk.com/spotlight/spotid=18188.php
2010.09.25 View 11756