MOU
-
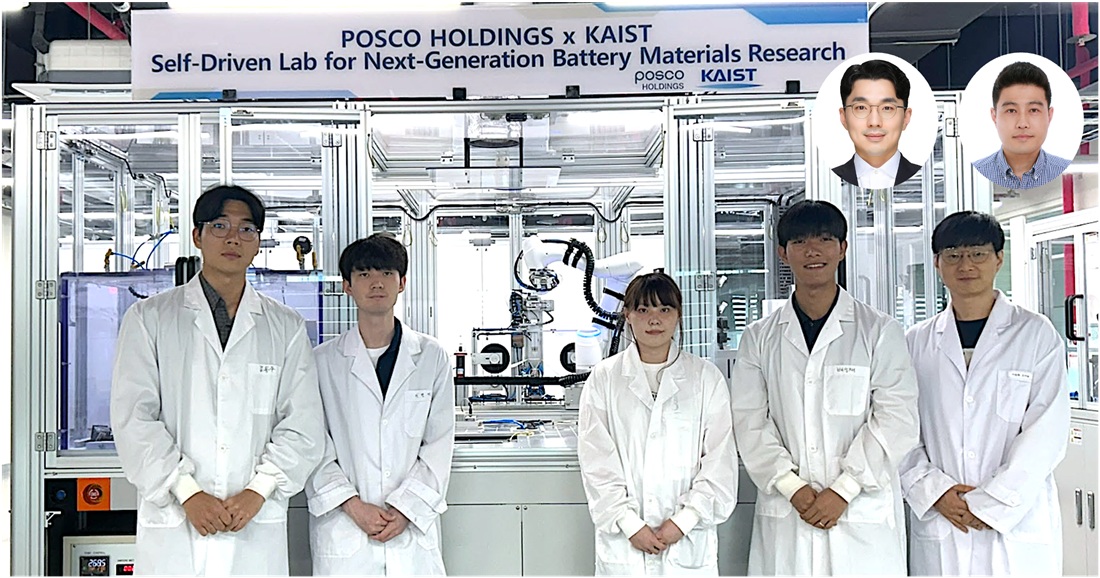 Material Innovation Realized with Robotic Arms and AI, Without Human Researchers
<(From Left) M.S candidate Dongwoo Kim from KAIST, Ph.D candidate Hyun-Gi Lee from KAIST, Intern Yeham Kang from KAIST, M.S candidate Seongjae Bae from KAIST, Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from KAIST, (From top right, from left) Senior Researcher Inchul Park from POSCO Holdings, Senior Researcher Jung Woo Park, senior researcher from POSCO Holdings>
A joint research team from industry and academia in Korea has successfully developed an autonomous lab that uses AI and automation to create new cathode materials for secondary batteries. This system operates without human intervention, drastically reducing researcher labor and cutting the material discovery period by 93%.
* Autonomous Lab: A platform that autonomously designs, conducts, and analyzes experiments to find the optimal material.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of August that the research team led by Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the team of LIB Materials Research Center in Energy Materials R&D Laboratories at POSCO Holdings' POSCO N.EX.T Hub (Director Ki Soo Kim), built the lab to explore cathode materials using AI and automation technology.
Developing secondary battery cathode materials is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process for skilled researchers. It involves extensive exploration of various compositions and experimental variables through weighing, transporting, mixing, sintering*, and analyzing samples.
* Sintering: A process in which powder particles are heated to form a single solid mass through thermal activation.
The research team's autonomous lab combines an automated system with an AI model. The system handles all experimental steps—weighing, mixing, pelletizing, sintering, and analysis—without human interference. The AI model then interprets the data, learns from it, and selects the best candidates for the next experiment.
<Figure 1. Outline of the Anode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
To increase efficiency, the team designed the automation system with separate modules for each process, which are managed by a central robotic arm. This modular approach reduces the system's reliance on the robotic arm.
The team also significantly improved the synthesis speed by using a new high-speed sintering method, which is 50 times faster than the conventional low-speed method. This allows the autonomous lab to acquire 12 times more material data compared to traditional, researcher-led experiments.
<Figure 2. Synthesis of Cathode Material Using a High-Speed Sintering Device>
The vast amount of data collected is automatically interpreted by the AI model to extract information such as synthesized phases and impurity ratios. This data is systematically stored to create a high-quality database, which then serves as training data for an optimization AI model. This creates a closed-loop experimental system that recommends the next cathode composition and synthesis conditions for the automated system.
* Closed-loop experimental system: A system that independently performs all experimental processes without researcher intervention.
Operating this intelligent automation system 24 hours a day can secure more than 12 times the experimental data and shorten material discovery time by 93%. For a project requiring 500 experiments, the system can complete the work in about 6 days, whereas a traditional researcher-led approach would take 84 days.
During development, POSCO Holdings team managed the overall project planning, reviewed the platform design, and co-developed the partial module design and AI-based experimental model. The KAIST team, led by Professor Dong-hwa Seo, was responsible for the actual system implementation and operation, including platform design, module fabrication, algorithm creation, and system verification and improvement.
Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of KAIST stated that this system is a solution to the decrease in research personnel due to the low birth rate in Korea. He expects it will enhance global competitiveness by accelerating secondary battery material development through the acquisition of high-quality data.
<Figure 3. Exterior View (Side) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
POSCO N.EX.T Hub plans to apply an upgraded version of this autonomous lab to its own research facilities after 2026 to dramatically speed up next-generation secondary battery material development. They are planning further developments to enhance the system's stability and scalability, and hope this industry-academia collaboration will serve as a model for using innovative technology in real-world R&D.
<Figure 4. Exterior View (Front) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
The research was spearheaded by Ph.D. student Hyun-Gi Lee, along with master's students Seongjae Bae and Dongwoo Kim from Professor Dong-Hwa Seo’s lab at KAIST. Senior researchers Jung Woo Park and Inchul Park from LIB Materials Research Center of POSCO N.EX.T Hub's Energy Materials R&D Laboratories (Director Jeongjin Hong) also participated.
2025.08.06 View 298
Material Innovation Realized with Robotic Arms and AI, Without Human Researchers
<(From Left) M.S candidate Dongwoo Kim from KAIST, Ph.D candidate Hyun-Gi Lee from KAIST, Intern Yeham Kang from KAIST, M.S candidate Seongjae Bae from KAIST, Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from KAIST, (From top right, from left) Senior Researcher Inchul Park from POSCO Holdings, Senior Researcher Jung Woo Park, senior researcher from POSCO Holdings>
A joint research team from industry and academia in Korea has successfully developed an autonomous lab that uses AI and automation to create new cathode materials for secondary batteries. This system operates without human intervention, drastically reducing researcher labor and cutting the material discovery period by 93%.
* Autonomous Lab: A platform that autonomously designs, conducts, and analyzes experiments to find the optimal material.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of August that the research team led by Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the team of LIB Materials Research Center in Energy Materials R&D Laboratories at POSCO Holdings' POSCO N.EX.T Hub (Director Ki Soo Kim), built the lab to explore cathode materials using AI and automation technology.
Developing secondary battery cathode materials is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process for skilled researchers. It involves extensive exploration of various compositions and experimental variables through weighing, transporting, mixing, sintering*, and analyzing samples.
* Sintering: A process in which powder particles are heated to form a single solid mass through thermal activation.
The research team's autonomous lab combines an automated system with an AI model. The system handles all experimental steps—weighing, mixing, pelletizing, sintering, and analysis—without human interference. The AI model then interprets the data, learns from it, and selects the best candidates for the next experiment.
<Figure 1. Outline of the Anode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
To increase efficiency, the team designed the automation system with separate modules for each process, which are managed by a central robotic arm. This modular approach reduces the system's reliance on the robotic arm.
The team also significantly improved the synthesis speed by using a new high-speed sintering method, which is 50 times faster than the conventional low-speed method. This allows the autonomous lab to acquire 12 times more material data compared to traditional, researcher-led experiments.
<Figure 2. Synthesis of Cathode Material Using a High-Speed Sintering Device>
The vast amount of data collected is automatically interpreted by the AI model to extract information such as synthesized phases and impurity ratios. This data is systematically stored to create a high-quality database, which then serves as training data for an optimization AI model. This creates a closed-loop experimental system that recommends the next cathode composition and synthesis conditions for the automated system.
* Closed-loop experimental system: A system that independently performs all experimental processes without researcher intervention.
Operating this intelligent automation system 24 hours a day can secure more than 12 times the experimental data and shorten material discovery time by 93%. For a project requiring 500 experiments, the system can complete the work in about 6 days, whereas a traditional researcher-led approach would take 84 days.
During development, POSCO Holdings team managed the overall project planning, reviewed the platform design, and co-developed the partial module design and AI-based experimental model. The KAIST team, led by Professor Dong-hwa Seo, was responsible for the actual system implementation and operation, including platform design, module fabrication, algorithm creation, and system verification and improvement.
Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of KAIST stated that this system is a solution to the decrease in research personnel due to the low birth rate in Korea. He expects it will enhance global competitiveness by accelerating secondary battery material development through the acquisition of high-quality data.
<Figure 3. Exterior View (Side) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
POSCO N.EX.T Hub plans to apply an upgraded version of this autonomous lab to its own research facilities after 2026 to dramatically speed up next-generation secondary battery material development. They are planning further developments to enhance the system's stability and scalability, and hope this industry-academia collaboration will serve as a model for using innovative technology in real-world R&D.
<Figure 4. Exterior View (Front) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
The research was spearheaded by Ph.D. student Hyun-Gi Lee, along with master's students Seongjae Bae and Dongwoo Kim from Professor Dong-Hwa Seo’s lab at KAIST. Senior researchers Jung Woo Park and Inchul Park from LIB Materials Research Center of POSCO N.EX.T Hub's Energy Materials R&D Laboratories (Director Jeongjin Hong) also participated.
2025.08.06 View 298 -
 RAIBO Runs over Walls with Feline Agility... Ready for Effortless Search over Mountaineous and Rough Terrains
< Photo 1. Research Team Photo (Professor Jemin Hwangbo, second from right in the front row) >
KAIST's quadrupedal robot, RAIBO, can now move at high speed across discontinuous and complex terrains such as stairs, gaps, walls, and debris. It has demonstrated its ability to run on vertical walls, leap over 1.3-meter-wide gaps, sprint at approximately 14.4 km/h over stepping stones, and move quickly and nimbly on terrain combining 30° slopes, stairs, and stepping stones. RAIBO is expected to be deployed soon for practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at our university announced on June 3rd that they have developed a quadrupedal robot navigation framework capable of high-speed locomotion at 14.4 km/h (4m/s) even on discontinuous and complex terrains such as walls, stairs, and stepping stones.
The research team developed a quadrupedal navigation system that enables the robot to reach its target destination quickly and safely in complex and discontinuous terrain.
To achieve this, they approached the problem by breaking it down into two stages: first, developing a planner for planning foothold positions, and second, developing a tracker to accurately follow the planned foothold positions.
First, the planner module quickly searches for physically feasible foothold positions using a sampling-based optimization method with neural network-based heuristics and verifies the optimal path through simulation rollouts.
While existing methods considered various factors such as contact timing and robot posture in addition to foothold positions, this research significantly reduced computational complexity by setting only foothold positions as the search space. Furthermore, inspired by the walking method of cats, the introduction of a structure where the hind feet step on the same spots as the front feet further significantly reduced computational complexity.
< Figure 1. High-speed navigation across various discontinuous terrains >
Second, the tracker module is trained to accurately step on planned positions, and tracking training is conducted through a generative model that competes in environments of appropriate difficulty.
The tracker is trained through reinforcement learning to accurately step on planned plots, and during this process, a generative model called the 'map generator' provides the target distribution.
This generative model is trained simultaneously and adversarially with the tracker to allow the tracker to progressively adapt to more challenging difficulties. Subsequently, a sampling-based planner was designed to generate feasible foothold plans that can reflect the characteristics and performance of the trained tracker.
This hierarchical structure showed superior performance in both planning speed and stability compared to existing techniques, and experiments proved its high-speed locomotion capabilities across various obstacles and discontinuous terrains, as well as its general applicability to unseen terrains.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo stated, "We approached the problem of high-speed navigation in discontinuous terrain, which previously required a significantly large amount of computation, from the simple perspective of how to select the footprint positions. Inspired by the placements of cat's paw, allowing the hind feet to step where the front feet stepped drastically reduced computation. We expect this to significantly expand the range of discontinuous terrain that walking robots can overcome and enable them to traverse it at high speeds, contributing to the robot's ability to perform practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches."
This research achievement was published in the May 2025 issue of the international journal Science Robotics.
Paper Title: High-speed control and navigation for quadrupedal robots on complex and discrete terrain, (https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.ads6192)YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/EZbM594T3c4?si=kfxLF2XnVUvYVIyk
2025.06.04 View 4843
RAIBO Runs over Walls with Feline Agility... Ready for Effortless Search over Mountaineous and Rough Terrains
< Photo 1. Research Team Photo (Professor Jemin Hwangbo, second from right in the front row) >
KAIST's quadrupedal robot, RAIBO, can now move at high speed across discontinuous and complex terrains such as stairs, gaps, walls, and debris. It has demonstrated its ability to run on vertical walls, leap over 1.3-meter-wide gaps, sprint at approximately 14.4 km/h over stepping stones, and move quickly and nimbly on terrain combining 30° slopes, stairs, and stepping stones. RAIBO is expected to be deployed soon for practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at our university announced on June 3rd that they have developed a quadrupedal robot navigation framework capable of high-speed locomotion at 14.4 km/h (4m/s) even on discontinuous and complex terrains such as walls, stairs, and stepping stones.
The research team developed a quadrupedal navigation system that enables the robot to reach its target destination quickly and safely in complex and discontinuous terrain.
To achieve this, they approached the problem by breaking it down into two stages: first, developing a planner for planning foothold positions, and second, developing a tracker to accurately follow the planned foothold positions.
First, the planner module quickly searches for physically feasible foothold positions using a sampling-based optimization method with neural network-based heuristics and verifies the optimal path through simulation rollouts.
While existing methods considered various factors such as contact timing and robot posture in addition to foothold positions, this research significantly reduced computational complexity by setting only foothold positions as the search space. Furthermore, inspired by the walking method of cats, the introduction of a structure where the hind feet step on the same spots as the front feet further significantly reduced computational complexity.
< Figure 1. High-speed navigation across various discontinuous terrains >
Second, the tracker module is trained to accurately step on planned positions, and tracking training is conducted through a generative model that competes in environments of appropriate difficulty.
The tracker is trained through reinforcement learning to accurately step on planned plots, and during this process, a generative model called the 'map generator' provides the target distribution.
This generative model is trained simultaneously and adversarially with the tracker to allow the tracker to progressively adapt to more challenging difficulties. Subsequently, a sampling-based planner was designed to generate feasible foothold plans that can reflect the characteristics and performance of the trained tracker.
This hierarchical structure showed superior performance in both planning speed and stability compared to existing techniques, and experiments proved its high-speed locomotion capabilities across various obstacles and discontinuous terrains, as well as its general applicability to unseen terrains.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo stated, "We approached the problem of high-speed navigation in discontinuous terrain, which previously required a significantly large amount of computation, from the simple perspective of how to select the footprint positions. Inspired by the placements of cat's paw, allowing the hind feet to step where the front feet stepped drastically reduced computation. We expect this to significantly expand the range of discontinuous terrain that walking robots can overcome and enable them to traverse it at high speeds, contributing to the robot's ability to perform practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches."
This research achievement was published in the May 2025 issue of the international journal Science Robotics.
Paper Title: High-speed control and navigation for quadrupedal robots on complex and discrete terrain, (https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.ads6192)YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/EZbM594T3c4?si=kfxLF2XnVUvYVIyk
2025.06.04 View 4843 -
 Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4847
Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4847 -
 Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 5316
Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 5316 -
 KAIST develops ‘Hoverbike’ to roam the future skies
< Photo 1. A group photo of the research team >
Hoverbike is a kind of next-generation mobility that can complement the existing transportation system and can be used as an air transportation means without traffic congestion through high-weight payloads and long-distance flights. It is expected that domestic researchers will contribute to the development of the domestic PAV* and UAM markets by developing a domestically developed manned/unmanned hybrid aircraft that escapes dependence on foreign technology through the development of a high-performance hoverbike.
*PAV: Personal Aerial Vehicle. It is a key element of future urban air mobility (UAM, Urban Air Mobility) and constitutes an important part of the next-generation transportation system.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of December that the research team of Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering successfully developed the core technology of a highly reliable multipurpose vertical takeoff and landing hoverbike that can be operated by both manned and unmanned vehicles.
This research was participated by the research teams of Professor Jae-Hung Han, Professor Ji-yun Lee, Professor Jae-myung Ahn, Professor Han-Lim Choi, and Professor Chang-Hun Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Professor Dongjin Lee of the Department of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles at Hanseo University, and Professor Jong-Oh Park of the Department of Electronics Engineering at Dong-A University.
The research team secured key technologies related to the optimal design of a multipurpose aircraft, hybrid propulsion system, highly reliable precision navigation and flight control system, autonomous flight, and fault detection for the development of a high-performance hoverbike.
< Figure 1. Key features of high-reliability multi-purpose hoverbike >
The hoverbike platform introduced a gasoline engine-based hybrid system to overcome the shortcomings of battery-based drones, achieving approximately 60% better performance and maximum payload weight compared to overseas technology levels. Through this, it is expected to be utilized in various fields such as emergency supply delivery, logistics, and rescue activities for civilian use, and military transport and mission support for military use.
The navigation system was applied by implementing multi-sensor fusion technology based on DGPS/INS* to enable stable flight even in environments without GPS or with weak signals using high-reliability precision navigation technology.
*DGPS/INS: Navigation solution combining high accuracy of Differential GPS (DGPS) and Inertial Navigation System (INS)
In addition, high-reliability flight control technology was developed to enable reliable maneuvering even under external factors such as payload and wind, and model uncertainty, and fault detection technology was also developed.
A guidance technique to automatically land on a helipad after selecting a safe automatic landing area by configuring a high-reliability autonomous flight system was implemented with high accuracy. Stable operation is possible even in complex environments through obstacle avoidance and automatic landing autonomous flight technology.
< Figure 2. Hoverbike prototype model >
Professor Hyochoong Bang, the research director, emphasized, “We have proven the high practicality of the hoverbike in various environments through high-reliability flight control and precision navigation technology.” He added, “The hoverbike is a promising research result that can not only provide a major path leading to PAVs and future aircraft, but also surpass existing drone technology by several levels. This achievement is even more meaningful because it is the result of five years of effort by eight joint research teams, including the project’s practitioners, PhD students Kwangwoo Jang and Hyungjoo Ahn.”
This study aims to secure core technologies for manned/unmanned multipurpose hoverbikes that can be utilized as new concept aircraft in the defense and civilian sectors. It started as the Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Defense Technology for Future Challenge Research and Development Project in 2019 and was completed in 2024 under the management of the Agency for Defense Development. It is scheduled to be exhibited for the first time at the 2025 Drone Show Korea (DSK2025), which will be held at BEXCO in Busan from February 26 to 28, 2025.
2024.12.27 View 6551
KAIST develops ‘Hoverbike’ to roam the future skies
< Photo 1. A group photo of the research team >
Hoverbike is a kind of next-generation mobility that can complement the existing transportation system and can be used as an air transportation means without traffic congestion through high-weight payloads and long-distance flights. It is expected that domestic researchers will contribute to the development of the domestic PAV* and UAM markets by developing a domestically developed manned/unmanned hybrid aircraft that escapes dependence on foreign technology through the development of a high-performance hoverbike.
*PAV: Personal Aerial Vehicle. It is a key element of future urban air mobility (UAM, Urban Air Mobility) and constitutes an important part of the next-generation transportation system.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of December that the research team of Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering successfully developed the core technology of a highly reliable multipurpose vertical takeoff and landing hoverbike that can be operated by both manned and unmanned vehicles.
This research was participated by the research teams of Professor Jae-Hung Han, Professor Ji-yun Lee, Professor Jae-myung Ahn, Professor Han-Lim Choi, and Professor Chang-Hun Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Professor Dongjin Lee of the Department of Unmanned Aerial Vehicles at Hanseo University, and Professor Jong-Oh Park of the Department of Electronics Engineering at Dong-A University.
The research team secured key technologies related to the optimal design of a multipurpose aircraft, hybrid propulsion system, highly reliable precision navigation and flight control system, autonomous flight, and fault detection for the development of a high-performance hoverbike.
< Figure 1. Key features of high-reliability multi-purpose hoverbike >
The hoverbike platform introduced a gasoline engine-based hybrid system to overcome the shortcomings of battery-based drones, achieving approximately 60% better performance and maximum payload weight compared to overseas technology levels. Through this, it is expected to be utilized in various fields such as emergency supply delivery, logistics, and rescue activities for civilian use, and military transport and mission support for military use.
The navigation system was applied by implementing multi-sensor fusion technology based on DGPS/INS* to enable stable flight even in environments without GPS or with weak signals using high-reliability precision navigation technology.
*DGPS/INS: Navigation solution combining high accuracy of Differential GPS (DGPS) and Inertial Navigation System (INS)
In addition, high-reliability flight control technology was developed to enable reliable maneuvering even under external factors such as payload and wind, and model uncertainty, and fault detection technology was also developed.
A guidance technique to automatically land on a helipad after selecting a safe automatic landing area by configuring a high-reliability autonomous flight system was implemented with high accuracy. Stable operation is possible even in complex environments through obstacle avoidance and automatic landing autonomous flight technology.
< Figure 2. Hoverbike prototype model >
Professor Hyochoong Bang, the research director, emphasized, “We have proven the high practicality of the hoverbike in various environments through high-reliability flight control and precision navigation technology.” He added, “The hoverbike is a promising research result that can not only provide a major path leading to PAVs and future aircraft, but also surpass existing drone technology by several levels. This achievement is even more meaningful because it is the result of five years of effort by eight joint research teams, including the project’s practitioners, PhD students Kwangwoo Jang and Hyungjoo Ahn.”
This study aims to secure core technologies for manned/unmanned multipurpose hoverbikes that can be utilized as new concept aircraft in the defense and civilian sectors. It started as the Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Defense Technology for Future Challenge Research and Development Project in 2019 and was completed in 2024 under the management of the Agency for Defense Development. It is scheduled to be exhibited for the first time at the 2025 Drone Show Korea (DSK2025), which will be held at BEXCO in Busan from February 26 to 28, 2025.
2024.12.27 View 6551 -
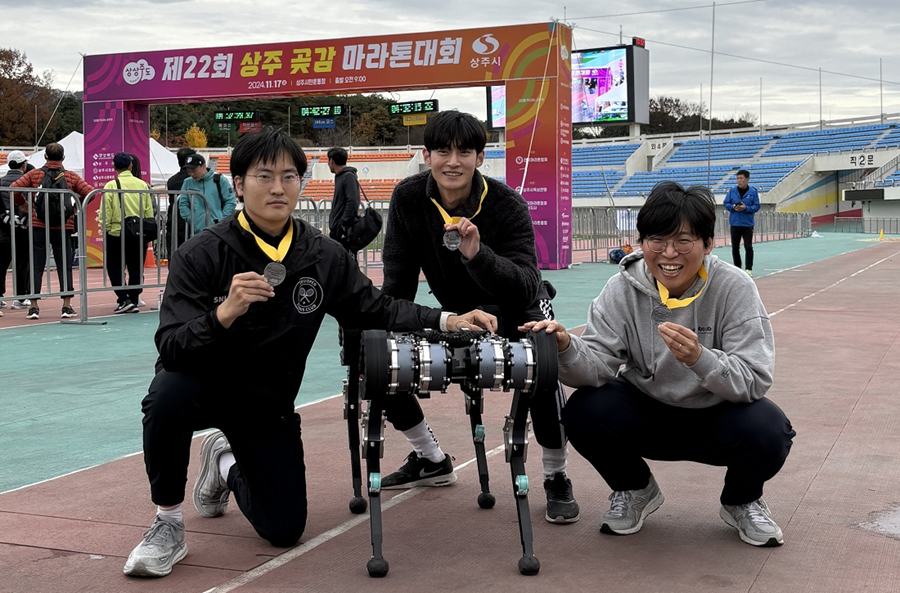 KAIST’s RAIBO2 becomes the World’s First Robo-dog to Successfully Complete a Full-course Marathon
KAIST's quadrupedal walking robot "RAIBO", which can run seamlessly on sandy beaches, has now evolved into "RAIBO2"and achieved the groundbreaking milestone by becomeing the world's first quadrupedal robot to successfully complete a full-course marathon in an official event.
< Photo 1. A group photo of RAIBO2 and the team after completing the full-course marathon >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of November that Professor Je Min Hwangbo's research team of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated in the 22nd Sangju Dried-Persimmon Marathon and completed the full-course race (42.195 km) with a time of 4 hours 19 minutes and 52 seconds.
< Photo 2. RAIBO2 after completing the full-course marathon with its official record presented on the photo wall >
The Sangju Dried Persimmon Marathon is known for its challenging course featuring two 50 m elevation climbs, each at the 14 km and 28 km marks, making it defficult for amateur runners. This made it an especially demanding challenge for the walking robot, as unexpected losses in efficiency could occur.
< Photo 3. RAIBO2 with the completion medal around its neck >
To prepare RAIBO2, Professor Hwangbo's team developed a walking controller using reinforcement learning algorithms within their proprietary simulation environment "RaiSim". This simulator allowed the team to simlate diverse terrains such as slopes, stairs, and icy roads to ensure stable walking performance.
In particular, RAIBO2's high torque transparency joint mechanism enable the robot to efficiently harvest energy on the downhill slopes to regain some of the energy used in climbing up steep hill.
In addition, the stability of the robot was greatly improved through the collaboration with RAION ROBOTICS Inc., a company founded by the researchers from Professor Hwangbo’s lab.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of power flow employed by the quadrupedal robot >
< Figure 2. The process of leg posture change of RAIBO2 walking at the most efficient walking speed of 3 m/s. By reducing the ground contact speed of the feet, the collision energy loss was reduced, and by minimizing the slipperiness of the foot upon contact, the body's kinetic energy was maintained towards the direction of the movement. >
Due to the nature of walking, pedal robots must employ highly complex systems that can withstand periodic vibrations from the frequent impacts that occur upon contact with the ground surface. Immediately after development, high efficiency was already recorded in short-distance experiments in the laboratory at the beginning of the year, but the manufacturing technology of RAION ROBOTICS significantly bolstered RAIBO's performance in running safely for a prolonged time of more than 4 hours among random pack of people in an actual marathon.
Compared to previous studies on improving walking efficiency, where external parts or software could not be changed and only limited improvements were made in some areas, Professor Hwangbo’s research team cited the fact that they were able to comprehensively solve problems by developing all steps and parts in-house, including mechanism design, electrical design, software, and artificial intelligence, as a key factor in improving efficiency.
Following the development of RAIBO1, the research team developed RAIBO2 and optimized all aspects of the robot. In particular, the team integrated the motor driver circuitry directly into the robot to minimize actuator losses and increase the control bandwidth, greatly improving walking efficiency and stability.
< Photo 4. RAIBO2 running the full-course marathon along human participants >
Choongin Lee, a Ph.D. Student that co-first author of the studies on RAIBO, said, “Through the marathon project, we demonstrated that RAIBO2 has the walking performance to stably execute services such as delivery and patrol in urban environments with many people and random objects,” and “In follow-up research, we will add autonomous navigation functions to RAIBO and strive to achieve the world’s best walking performance in mountainous and disaster environments.”
< Photo 5. RAIBO2 and co-first authors of the related research at the Ph.D. program of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST. (From left) Choongin Lee, Donghoon Youm, and Jeongsoo Park >
This research was conducted with the support of Samsung Electronics Future Technology Promotion Center and RAION ROBOTICS Inc.
2024.11.17 View 10283
KAIST’s RAIBO2 becomes the World’s First Robo-dog to Successfully Complete a Full-course Marathon
KAIST's quadrupedal walking robot "RAIBO", which can run seamlessly on sandy beaches, has now evolved into "RAIBO2"and achieved the groundbreaking milestone by becomeing the world's first quadrupedal robot to successfully complete a full-course marathon in an official event.
< Photo 1. A group photo of RAIBO2 and the team after completing the full-course marathon >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of November that Professor Je Min Hwangbo's research team of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated in the 22nd Sangju Dried-Persimmon Marathon and completed the full-course race (42.195 km) with a time of 4 hours 19 minutes and 52 seconds.
< Photo 2. RAIBO2 after completing the full-course marathon with its official record presented on the photo wall >
The Sangju Dried Persimmon Marathon is known for its challenging course featuring two 50 m elevation climbs, each at the 14 km and 28 km marks, making it defficult for amateur runners. This made it an especially demanding challenge for the walking robot, as unexpected losses in efficiency could occur.
< Photo 3. RAIBO2 with the completion medal around its neck >
To prepare RAIBO2, Professor Hwangbo's team developed a walking controller using reinforcement learning algorithms within their proprietary simulation environment "RaiSim". This simulator allowed the team to simlate diverse terrains such as slopes, stairs, and icy roads to ensure stable walking performance.
In particular, RAIBO2's high torque transparency joint mechanism enable the robot to efficiently harvest energy on the downhill slopes to regain some of the energy used in climbing up steep hill.
In addition, the stability of the robot was greatly improved through the collaboration with RAION ROBOTICS Inc., a company founded by the researchers from Professor Hwangbo’s lab.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of power flow employed by the quadrupedal robot >
< Figure 2. The process of leg posture change of RAIBO2 walking at the most efficient walking speed of 3 m/s. By reducing the ground contact speed of the feet, the collision energy loss was reduced, and by minimizing the slipperiness of the foot upon contact, the body's kinetic energy was maintained towards the direction of the movement. >
Due to the nature of walking, pedal robots must employ highly complex systems that can withstand periodic vibrations from the frequent impacts that occur upon contact with the ground surface. Immediately after development, high efficiency was already recorded in short-distance experiments in the laboratory at the beginning of the year, but the manufacturing technology of RAION ROBOTICS significantly bolstered RAIBO's performance in running safely for a prolonged time of more than 4 hours among random pack of people in an actual marathon.
Compared to previous studies on improving walking efficiency, where external parts or software could not be changed and only limited improvements were made in some areas, Professor Hwangbo’s research team cited the fact that they were able to comprehensively solve problems by developing all steps and parts in-house, including mechanism design, electrical design, software, and artificial intelligence, as a key factor in improving efficiency.
Following the development of RAIBO1, the research team developed RAIBO2 and optimized all aspects of the robot. In particular, the team integrated the motor driver circuitry directly into the robot to minimize actuator losses and increase the control bandwidth, greatly improving walking efficiency and stability.
< Photo 4. RAIBO2 running the full-course marathon along human participants >
Choongin Lee, a Ph.D. Student that co-first author of the studies on RAIBO, said, “Through the marathon project, we demonstrated that RAIBO2 has the walking performance to stably execute services such as delivery and patrol in urban environments with many people and random objects,” and “In follow-up research, we will add autonomous navigation functions to RAIBO and strive to achieve the world’s best walking performance in mountainous and disaster environments.”
< Photo 5. RAIBO2 and co-first authors of the related research at the Ph.D. program of the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST. (From left) Choongin Lee, Donghoon Youm, and Jeongsoo Park >
This research was conducted with the support of Samsung Electronics Future Technology Promotion Center and RAION ROBOTICS Inc.
2024.11.17 View 10283 -
 KAIST’s Beach-Roaming Quadrupedal Robot “RAIBO” to Run a Marathon!
“RAIBO”, KAIST’s four-legged robot featuring remarkable agility even on challenging terrains like sandy beaches, is now set to be the first in the world to complete a full marathon.
< Photo 1. A group photo of the research team of Professor Je Min Hwangbo (second from the right in the front row) of the Department of Mechanical Engineering who participated in the marathon event at 2024 Geumsan Insam Festival last September >
On the 17th of November, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Je Min Hwangbo’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed an upgraded version, “RAIBO2,” which will take on the full 42.195-kilometer course at the "Sangju Dried-Persimmon Marathon".
This is over double the previous maximum distance achieved by quadruped robots, which was limited to around 20 kilometers. The KAIST team has successfully developed a robot that can walk continuously for 43 kilometers on a single charge, completing the course in 4 hours and 40 minutes by following a GPS-guided path on the university’s main athletic field. Through this marathon, the team aims to demonstrate RAIBO2’s walking performance in an actual urban environment.
Previously, most measurements of walking robots’ travel distances were confined to controlled laboratory conditions or theoretical data. This marathon challenge is thus significant in that the robot will run alongside the general public in a real urban setting, marking the first attempt to validate the practical potential of four-legged robots in real environments.
Quadruped robots have shown advantages in challenging terrains, such as ice, sand, and mountainous areas, where they can walk stably. However, limited travel distance and running time have long been obstacles to wider applications.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of power flow employed by the quadruped robot >
Professor Hwangbo’s team designed every component of the robot, from its actuators to its mechanical structure, to overcome these limitations. Notably, they implemented an efficient walking control system based on reinforcement learning using their proprietary dynamic simulator “RaiSim”.
The team also collected and analyzed walking data from outdoor environments, creating a model to address walking losses. This model was then used to iteratively improve walking efficiency over one full year.
< Figure 2. The leg posture change process of RAIBO2 walking at the most efficient walking speed of 3 m/s. By reducing the ground contact speed of the feet, the collision energy loss was reduced, and by minimizing the slipperiness of the foot upon contact, the body's kinetic energy was maintained towards the direction of the movement. >
This is the team’s second attempt. Their first was during the marathon event at “Geumsan Insam Festival” in September when the robot’s battery ran out at the 37-kilometer mark, falling short of completion. The battery drained 10 kilometers earlier than expected due to frequent speed changes as the robot adjusted to the pacing of other runners on the course.
Following the initial attempt, the team focused on technical improvements for a successful finish. They enhanced control efficiency by implementing joint stiffness control directly onto the motor actuator and increased battery capacity by 33% by refining the internal structure. These improvements enabled the robot to cover a maximum distance of 67 kilometers on straight paths.
< Figure 3. Data from completing 43 km on a single charge at the main sports field on campus. Left) GPS data of the driving course used during autonomous running. Middle) Covered distance by the hour. Right) Energy consumption by module >
Choongin Lee, a Ph.D. student of RAI Lab who is one of the co-first author of this study, explained, “Our comprehensive analysis of walking losses in terms of mechanics, electrical systems, and walking methods was crucial to improving walking efficiency. This research marks an important milestone in extending the operating range of quadruped robots to urban environments.”
< Photo 2. A Photo from Practice Run>
This research was supported by the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center and RAION ROBOTICS Co., Ltd.
< Photo 3. A Photo from Practice Run >
2024.11.15 View 6975
KAIST’s Beach-Roaming Quadrupedal Robot “RAIBO” to Run a Marathon!
“RAIBO”, KAIST’s four-legged robot featuring remarkable agility even on challenging terrains like sandy beaches, is now set to be the first in the world to complete a full marathon.
< Photo 1. A group photo of the research team of Professor Je Min Hwangbo (second from the right in the front row) of the Department of Mechanical Engineering who participated in the marathon event at 2024 Geumsan Insam Festival last September >
On the 17th of November, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Je Min Hwangbo’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed an upgraded version, “RAIBO2,” which will take on the full 42.195-kilometer course at the "Sangju Dried-Persimmon Marathon".
This is over double the previous maximum distance achieved by quadruped robots, which was limited to around 20 kilometers. The KAIST team has successfully developed a robot that can walk continuously for 43 kilometers on a single charge, completing the course in 4 hours and 40 minutes by following a GPS-guided path on the university’s main athletic field. Through this marathon, the team aims to demonstrate RAIBO2’s walking performance in an actual urban environment.
Previously, most measurements of walking robots’ travel distances were confined to controlled laboratory conditions or theoretical data. This marathon challenge is thus significant in that the robot will run alongside the general public in a real urban setting, marking the first attempt to validate the practical potential of four-legged robots in real environments.
Quadruped robots have shown advantages in challenging terrains, such as ice, sand, and mountainous areas, where they can walk stably. However, limited travel distance and running time have long been obstacles to wider applications.
< Figure 1. Conceptual diagram of power flow employed by the quadruped robot >
Professor Hwangbo’s team designed every component of the robot, from its actuators to its mechanical structure, to overcome these limitations. Notably, they implemented an efficient walking control system based on reinforcement learning using their proprietary dynamic simulator “RaiSim”.
The team also collected and analyzed walking data from outdoor environments, creating a model to address walking losses. This model was then used to iteratively improve walking efficiency over one full year.
< Figure 2. The leg posture change process of RAIBO2 walking at the most efficient walking speed of 3 m/s. By reducing the ground contact speed of the feet, the collision energy loss was reduced, and by minimizing the slipperiness of the foot upon contact, the body's kinetic energy was maintained towards the direction of the movement. >
This is the team’s second attempt. Their first was during the marathon event at “Geumsan Insam Festival” in September when the robot’s battery ran out at the 37-kilometer mark, falling short of completion. The battery drained 10 kilometers earlier than expected due to frequent speed changes as the robot adjusted to the pacing of other runners on the course.
Following the initial attempt, the team focused on technical improvements for a successful finish. They enhanced control efficiency by implementing joint stiffness control directly onto the motor actuator and increased battery capacity by 33% by refining the internal structure. These improvements enabled the robot to cover a maximum distance of 67 kilometers on straight paths.
< Figure 3. Data from completing 43 km on a single charge at the main sports field on campus. Left) GPS data of the driving course used during autonomous running. Middle) Covered distance by the hour. Right) Energy consumption by module >
Choongin Lee, a Ph.D. student of RAI Lab who is one of the co-first author of this study, explained, “Our comprehensive analysis of walking losses in terms of mechanics, electrical systems, and walking methods was crucial to improving walking efficiency. This research marks an important milestone in extending the operating range of quadruped robots to urban environments.”
< Photo 2. A Photo from Practice Run>
This research was supported by the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center and RAION ROBOTICS Co., Ltd.
< Photo 3. A Photo from Practice Run >
2024.11.15 View 6975 -
 KAIST and Merck Sign MOU to Boost Biotech Innovation
< (From left) KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee and Merck CEO Matthias Heinzel >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Merck Life Science (CEO Matthias Heinzel) on May 29 to foster innovation and technology creation in advanced biotechnology.
Since May of last year, the two institutions have been discussing multidimensional innovation programs and will now focus on industry-academia cooperation to tackle bioindustry challenges with this MOU as a foundation.
KAIST will conduct joint research projects in various advanced biotechnology fields, such as synthetic biology, mRNA, cell line engineering, and organoids, using the chemical and biological portfolios provided by Merck.
Additionally, KAIST will establish an Experience Lab in collaboration with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. This lab will support the discovery and analysis of candidate substances in materials science and biology.
Programs to enhance researchers' capabilities will also be offered. Scholarships for graduate students and awards for professors will be implemented. Researchers will have opportunities to participate in global academic events and educational programs hosted by Merck, such as the Curious 2024 Future Insight Conference and the Innovation Cup.
M Ventures, a venture capital subsidiary of Merck Group, will collaborate with KAIST's startup institute to support technology commercialization and continue to develop their startup ecosystem.
The signing ceremony at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon was attended by the CEO of Merck Life Science and the President of KAIST along with representatives from both institutions.
Matthias Heinzel, a member of the Executive Board of Merck and CEO Life Science, said, “This agreement with KAIST is a significant step toward accelerating the development of the life science industry both in Korea and globally. Advancing life science research and fostering the next generation of scientists is essential for discovering new medicines to meet global health needs.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee responded, “We are pleased to share a vision for scientific advancement with Merck, a leading global technology company. We anticipate that this partnership will strengthen the connection between Merck’s life science business and the global scientific community.”
In March, Merck, a global science and technology company with over 350 years of history, announced a plan to invest 430 billion KRW (€300 million) to build a bioprocessing center in Daejeon, where KAIST is located. This is Merck's largest investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
2024.05.30 View 9593
KAIST and Merck Sign MOU to Boost Biotech Innovation
< (From left) KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee and Merck CEO Matthias Heinzel >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) with Merck Life Science (CEO Matthias Heinzel) on May 29 to foster innovation and technology creation in advanced biotechnology.
Since May of last year, the two institutions have been discussing multidimensional innovation programs and will now focus on industry-academia cooperation to tackle bioindustry challenges with this MOU as a foundation.
KAIST will conduct joint research projects in various advanced biotechnology fields, such as synthetic biology, mRNA, cell line engineering, and organoids, using the chemical and biological portfolios provided by Merck.
Additionally, KAIST will establish an Experience Lab in collaboration with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering. This lab will support the discovery and analysis of candidate substances in materials science and biology.
Programs to enhance researchers' capabilities will also be offered. Scholarships for graduate students and awards for professors will be implemented. Researchers will have opportunities to participate in global academic events and educational programs hosted by Merck, such as the Curious 2024 Future Insight Conference and the Innovation Cup.
M Ventures, a venture capital subsidiary of Merck Group, will collaborate with KAIST's startup institute to support technology commercialization and continue to develop their startup ecosystem.
The signing ceremony at KAIST's main campus in Daejeon was attended by the CEO of Merck Life Science and the President of KAIST along with representatives from both institutions.
Matthias Heinzel, a member of the Executive Board of Merck and CEO Life Science, said, “This agreement with KAIST is a significant step toward accelerating the development of the life science industry both in Korea and globally. Advancing life science research and fostering the next generation of scientists is essential for discovering new medicines to meet global health needs.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee responded, “We are pleased to share a vision for scientific advancement with Merck, a leading global technology company. We anticipate that this partnership will strengthen the connection between Merck’s life science business and the global scientific community.”
In March, Merck, a global science and technology company with over 350 years of history, announced a plan to invest 430 billion KRW (€300 million) to build a bioprocessing center in Daejeon, where KAIST is located. This is Merck's largest investment in the Asia-Pacific region.
2024.05.30 View 9593 -
 KAIST to begin Joint Research to Develop Next-Generation LiDAR System with Hyundai Motor Group
< (From left) Jong-Soo Lee, Executive Vice President at Hyundai Motor, Sang-Yup Lee, Senior Vice President for Research at KAIST >
The ‘Hyundai Motor Group-KAIST On-Chip LiDAR Joint Research Lab’ was opened at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon to develop LiDAR sensors for advanced autonomous vehicles.
The joint research lab aims to develop high-performance and compact on-chip sensors and new signal detection technology, which are essential in the increasingly competitive autonomous driving market. On-chip sensors, which utilize semiconductor manufacturing technology to add various functions, can reduce the size of LiDAR systems compared to conventional methods and secure price competitiveness through mass production using semiconductor fabrication processes.
The joint research lab will consist of about 30 researchers, including the Hyundai-Kia Institute of Advanced Technology Development research team and KAIST professors Sanghyeon Kim, Sangsik Kim, Wanyeong Jung, and Hamza Kurt from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, and will operate for four years until 2028.
KAIST will be leading the specialized work of each research team, such as for the development of silicon optoelectronic on-chip LiDAR components, the fabrication of high-speed, high-power integrated circuits to run the LiDAR systems, and the optimization and verification of LiDAR systems.
Hyundai Motor and Kia, together with Hyundai NGV, a specialized industry-academia cooperation institution, will oversee the operation of the joint research lab and provide support such as monitoring technological trends, suggesting research directions, deriving core ideas, and recommending technologies and experts to enhance research capabilities.
A Hyundai Motor Group official said, "We believe that this cooperation between Hyundai Motor Company and Kia, the leader in autonomous driving technology, and KAIST, the home of world-class technology, will hasten the achievement of fully autonomous driving." He added, "We will do our best to enable the lab to produce tangible results.”
Professor Sanghyeon Kim said, "The LiDAR sensor, which serves as the eyes of a car, is a core technology for future autonomous vehicle development that is essential for automobile companies to internalize."
2024.02.27 View 13244
KAIST to begin Joint Research to Develop Next-Generation LiDAR System with Hyundai Motor Group
< (From left) Jong-Soo Lee, Executive Vice President at Hyundai Motor, Sang-Yup Lee, Senior Vice President for Research at KAIST >
The ‘Hyundai Motor Group-KAIST On-Chip LiDAR Joint Research Lab’ was opened at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon to develop LiDAR sensors for advanced autonomous vehicles.
The joint research lab aims to develop high-performance and compact on-chip sensors and new signal detection technology, which are essential in the increasingly competitive autonomous driving market. On-chip sensors, which utilize semiconductor manufacturing technology to add various functions, can reduce the size of LiDAR systems compared to conventional methods and secure price competitiveness through mass production using semiconductor fabrication processes.
The joint research lab will consist of about 30 researchers, including the Hyundai-Kia Institute of Advanced Technology Development research team and KAIST professors Sanghyeon Kim, Sangsik Kim, Wanyeong Jung, and Hamza Kurt from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, and will operate for four years until 2028.
KAIST will be leading the specialized work of each research team, such as for the development of silicon optoelectronic on-chip LiDAR components, the fabrication of high-speed, high-power integrated circuits to run the LiDAR systems, and the optimization and verification of LiDAR systems.
Hyundai Motor and Kia, together with Hyundai NGV, a specialized industry-academia cooperation institution, will oversee the operation of the joint research lab and provide support such as monitoring technological trends, suggesting research directions, deriving core ideas, and recommending technologies and experts to enhance research capabilities.
A Hyundai Motor Group official said, "We believe that this cooperation between Hyundai Motor Company and Kia, the leader in autonomous driving technology, and KAIST, the home of world-class technology, will hasten the achievement of fully autonomous driving." He added, "We will do our best to enable the lab to produce tangible results.”
Professor Sanghyeon Kim said, "The LiDAR sensor, which serves as the eyes of a car, is a core technology for future autonomous vehicle development that is essential for automobile companies to internalize."
2024.02.27 View 13244 -
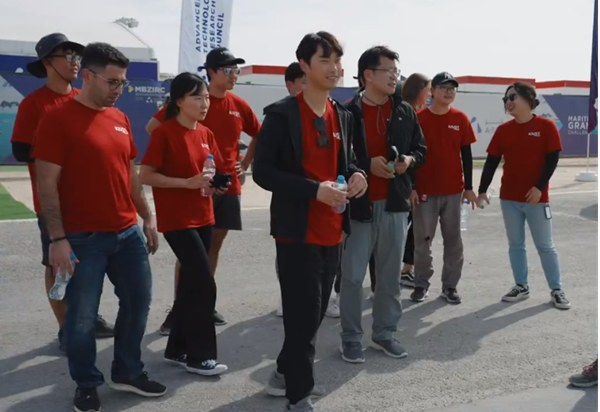 Team KAIST placed among top two at MBZIRC Maritime Grand Challenge
Representing Korean Robotics at Sea: KAIST’s 26-month strife rewarded
Team KAIST placed among top two at MBZIRC Maritime Grand Challenge
- Team KAIST, composed of students from the labs of Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical and Engineering, came through the challenge as the first runner-up winning the prize money totaling up to $650,000 (KRW 860 million).
- Successfully led the autonomous collaboration of unmanned aerial and maritime vehicles using cutting-edge robotics and AI technology through to the final round of the competition held in Abu Dhabi from January 10 to February 6, 2024.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee), reported on the 8th that Team KAIST, led by students from the labs of Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, with Pablo Aviation as a partner, won a total prize money of $650,000 (KRW 860 million) at the Maritime Grand Challenge by the Mohamed Bin Zayed International Robotics Challenge (MBZIRC), finishing first runner-up.
This competition, which is the largest ever robotics competition held over water, is sponsored by the government of the United Arab Emirates and organized by ASPIRE, an organization under the Abu Dhabi Ministry of Science, with a total prize money of $3 million.
In the competition, which started at the end of 2021, 52 teams from around the world participated and five teams were selected to go on to the finals in February 2023 after going through the first and second stages of screening. The final round was held from January 10 to February 6, 2024, using actual unmanned ships and drones in a secluded sea area of 10 km2 off the coast of Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates. A total of 18 KAIST students and Professor Jinwhan Kim and Professor Hyunchul Shim took part in this competition at the location at Abu Dhabi.
Team KAIST will receive $500,000 in prize money for taking second place in the final, and the team’s prize money totals up to $650,000 including $150,000 that was as special midterm award for finalists.
The final mission scenario is to find the target vessel on the run carrying illegal cargoes among many ships moving within the GPS-disabled marine surface, and inspect the deck for two different types of stolen cargo to recover them using the aerial vehicle to bring the small cargo and the robot manipulator topped on an unmanned ship to retrieve the larger one. The true aim of the mission is to complete it through autonomous collaboration of the unmanned ship and the aerial vehicle without human intervention throughout the entire mission process. In particular, since GPS cannot be used in this competition due to regulations, Professor Jinwhan Kim's research team developed autonomous operation techniques for unmanned ships, including searching and navigating methods using maritime radar, and Professor Hyunchul Shim's research team developed video-based navigation and a technology to combine a small autonomous robot with a drone.
The final mission is to retrieve cargo on board a ship fleeing at sea through autonomous collaboration between unmanned ships and unmanned aerial vehicles without human intervention. The overall mission consists the first stage of conducting the inspection to find the target ship among several ships moving at sea and the second stage of conducting the intervention mission to retrieve the cargoes on the deck of the ship. Each team was given a total of three opportunities, and the team that completed the highest-level mission in the shortest time during the three attempts received the highest score.
In the first attempt, KAIST was the only team to succeed in the first stage search mission, but the competition began in earnest as the Croatian team also completed the first stage mission in the second attempt. As the competition schedule was delayed due to strong winds and high waves that continued for several days, the organizers decided to hold the finals with the three teams, including the Team KAIST and the team from Croatia’s the University of Zagreb, which completed the first stage of the mission, and Team Fly-Eagle, a team of researcher from China and UAE that partially completed the first stage. The three teams were given the chance to proceed to the finals and try for the third attempt, and in the final competition, the Croatian team won, KAIST took the second place, and the combined team of UAE-China combined team took the third place. The final prize to be given for the winning team is set at $2 million with $500,000 for the runner-up team, and $250,000 for the third-place.
Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, who served as the advisor for Team KAIST, said, “I would like to express my gratitude and congratulations to the students who put in a huge academic and physical efforts in preparing for the competition over the past two years. I feel rewarded because, regardless of the results, every bit of efforts put into this up to this point will become the base of their confidence and a valuable asset in their growth into a great researcher.” Sol Han, a doctoral student in mechanical engineering who served as the team leader, said, “I am disappointed of how narrowly we missed out on winning at the end, but I am satisfied with the significance of the output we’ve got and I am grateful to the team members who worked hard together for that.”
HD Hyundai, Rainbow Robotics, Avikus, and FIMS also participated as sponsors for Team KAIST's campaign.
2024.02.09 View 15609
Team KAIST placed among top two at MBZIRC Maritime Grand Challenge
Representing Korean Robotics at Sea: KAIST’s 26-month strife rewarded
Team KAIST placed among top two at MBZIRC Maritime Grand Challenge
- Team KAIST, composed of students from the labs of Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical and Engineering, came through the challenge as the first runner-up winning the prize money totaling up to $650,000 (KRW 860 million).
- Successfully led the autonomous collaboration of unmanned aerial and maritime vehicles using cutting-edge robotics and AI technology through to the final round of the competition held in Abu Dhabi from January 10 to February 6, 2024.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee), reported on the 8th that Team KAIST, led by students from the labs of Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, with Pablo Aviation as a partner, won a total prize money of $650,000 (KRW 860 million) at the Maritime Grand Challenge by the Mohamed Bin Zayed International Robotics Challenge (MBZIRC), finishing first runner-up.
This competition, which is the largest ever robotics competition held over water, is sponsored by the government of the United Arab Emirates and organized by ASPIRE, an organization under the Abu Dhabi Ministry of Science, with a total prize money of $3 million.
In the competition, which started at the end of 2021, 52 teams from around the world participated and five teams were selected to go on to the finals in February 2023 after going through the first and second stages of screening. The final round was held from January 10 to February 6, 2024, using actual unmanned ships and drones in a secluded sea area of 10 km2 off the coast of Abu Dhabi, the capital of the United Arab Emirates. A total of 18 KAIST students and Professor Jinwhan Kim and Professor Hyunchul Shim took part in this competition at the location at Abu Dhabi.
Team KAIST will receive $500,000 in prize money for taking second place in the final, and the team’s prize money totals up to $650,000 including $150,000 that was as special midterm award for finalists.
The final mission scenario is to find the target vessel on the run carrying illegal cargoes among many ships moving within the GPS-disabled marine surface, and inspect the deck for two different types of stolen cargo to recover them using the aerial vehicle to bring the small cargo and the robot manipulator topped on an unmanned ship to retrieve the larger one. The true aim of the mission is to complete it through autonomous collaboration of the unmanned ship and the aerial vehicle without human intervention throughout the entire mission process. In particular, since GPS cannot be used in this competition due to regulations, Professor Jinwhan Kim's research team developed autonomous operation techniques for unmanned ships, including searching and navigating methods using maritime radar, and Professor Hyunchul Shim's research team developed video-based navigation and a technology to combine a small autonomous robot with a drone.
The final mission is to retrieve cargo on board a ship fleeing at sea through autonomous collaboration between unmanned ships and unmanned aerial vehicles without human intervention. The overall mission consists the first stage of conducting the inspection to find the target ship among several ships moving at sea and the second stage of conducting the intervention mission to retrieve the cargoes on the deck of the ship. Each team was given a total of three opportunities, and the team that completed the highest-level mission in the shortest time during the three attempts received the highest score.
In the first attempt, KAIST was the only team to succeed in the first stage search mission, but the competition began in earnest as the Croatian team also completed the first stage mission in the second attempt. As the competition schedule was delayed due to strong winds and high waves that continued for several days, the organizers decided to hold the finals with the three teams, including the Team KAIST and the team from Croatia’s the University of Zagreb, which completed the first stage of the mission, and Team Fly-Eagle, a team of researcher from China and UAE that partially completed the first stage. The three teams were given the chance to proceed to the finals and try for the third attempt, and in the final competition, the Croatian team won, KAIST took the second place, and the combined team of UAE-China combined team took the third place. The final prize to be given for the winning team is set at $2 million with $500,000 for the runner-up team, and $250,000 for the third-place.
Professor Jinwhan Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, who served as the advisor for Team KAIST, said, “I would like to express my gratitude and congratulations to the students who put in a huge academic and physical efforts in preparing for the competition over the past two years. I feel rewarded because, regardless of the results, every bit of efforts put into this up to this point will become the base of their confidence and a valuable asset in their growth into a great researcher.” Sol Han, a doctoral student in mechanical engineering who served as the team leader, said, “I am disappointed of how narrowly we missed out on winning at the end, but I am satisfied with the significance of the output we’ve got and I am grateful to the team members who worked hard together for that.”
HD Hyundai, Rainbow Robotics, Avikus, and FIMS also participated as sponsors for Team KAIST's campaign.
2024.02.09 View 15609 -
 KAIST gearing up to train physician-scientists and BT Professionals joining hands with Boston-based organizations
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 29th that it has signed MOUs with Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system and a world-class research-oriented hospital, and Moderna, a biotechnology company that developed a COVID-19 vaccine at the Langham Hotel in Boston, MA, USA on the morning of April 28th (local time). The signing ceremony was attended by officials from each institution joined by others headed by Minister LEE Young of the Korean Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS), and Commissioner LEE Insil of the Korean Intellectual Property Office.
< Photo 1. Photo from the Signing of MOU between KAIST-Harvard University Massachusetts General Hospital and KAIST-Moderna >
Mass General is the first and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School in Boston, USA, and it is one of the most innovative hospitals in the world being the alma mater of more than 13 Nobel Prize winners and the home of the Mass General Research Institute, the world’s largest hospital-based research program that utilizes an annual research budget of more than $1.3 billion.
KAIST signed a general agreement to explore research and academic exchange with Mass General in September of last year and this MOU is a part of its follow-ups.
Mass General works with Harvard and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), as well as local hospitals, to support students learn the theories of medicine and engineering, and gain rich clinical research experience.
Through this MOU, KAIST will explore cooperation with an innovative ecosystem created through the convergence of medicine and engineering. In particular, KAIST’s goal is to develop a Korean-style training program and implement a differentiated educational program when establishing the science and technology-oriented medical school in the future by further strengthening the science and engineering part of the training including a curriculum on artificial intelligence (AI) and the likes there of.
Also, in order to foster innovative physician-scientists, KAIST plans to pursue cooperation to develop programs for exchange of academic and human resources including programs for student and research exchanges and a program for students of the science and technology-oriented medical school at KAIST to have a chance to take part in practical training at Mass General.
David F.M. Brown, MD, Mass General President, said, “The collaboration with KAIST has a wide range of potentials, including advice on training of physician-scientists, academic and human resource exchanges, and vitalization of joint research by faculty from both institutions. Through this agreement, we will be able to actively contribute to global cooperation and achieve mutual goals.”
Meanwhile, an MOU between KAIST and Moderna was also held on the same day. Its main focus is to foster medical experts in cooperation with KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), and plans to cooperate in various ways in the future, including collaborating for development of vaccine and new drugs, virus research, joint mRNA research, and facilitation of technology commercialization.
In over 10 years since its inception, Moderna has transformed from a research-stage company advancing programs in the field of messenger RNA (mRNA) to an enterprise with a diverse clinical portfolio of vaccines and therapeutics across seven modalities. The Company has 48 programs in development across 45 development candidates, of which 38 are currently in active clinical trials.
“We are grateful to have laid a foundation for collaboration to foster industry experts with the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, a leader of science and technology innovation in Korea,” said Arpa Garay, Chief Commercial Officer, Moderna. “Based on our leadership and expertise in developing innovative mRNA vaccines and therapeutics, we hope to contribute to educating and collaborating with professionals in the bio-health field of Korea.“
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST, said, “We deem this occasion to be of grave significance to be able to work closely with Massachusetts General Hospital, one of the world's best research-oriented hospitals, and Moderna, one of the most influential biomedical companies.”
President Lee continued, "On the basis of the collaboration with the two institutions, we will be able to bring up qualified physician-scientists and global leaders of the biomedical business who will solve problems of human health and their progress will in turn, accelerate the national R&D efforts in general and diversify the industry."
2023.04.29 View 17440
KAIST gearing up to train physician-scientists and BT Professionals joining hands with Boston-based organizations
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 29th that it has signed MOUs with Massachusetts General Hospital, a founding member of the Mass General Brigham health care system and a world-class research-oriented hospital, and Moderna, a biotechnology company that developed a COVID-19 vaccine at the Langham Hotel in Boston, MA, USA on the morning of April 28th (local time). The signing ceremony was attended by officials from each institution joined by others headed by Minister LEE Young of the Korean Ministry of SMEs and Startups (MSS), and Commissioner LEE Insil of the Korean Intellectual Property Office.
< Photo 1. Photo from the Signing of MOU between KAIST-Harvard University Massachusetts General Hospital and KAIST-Moderna >
Mass General is the first and largest teaching hospital of Harvard Medical School in Boston, USA, and it is one of the most innovative hospitals in the world being the alma mater of more than 13 Nobel Prize winners and the home of the Mass General Research Institute, the world’s largest hospital-based research program that utilizes an annual research budget of more than $1.3 billion.
KAIST signed a general agreement to explore research and academic exchange with Mass General in September of last year and this MOU is a part of its follow-ups.
Mass General works with Harvard and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), as well as local hospitals, to support students learn the theories of medicine and engineering, and gain rich clinical research experience.
Through this MOU, KAIST will explore cooperation with an innovative ecosystem created through the convergence of medicine and engineering. In particular, KAIST’s goal is to develop a Korean-style training program and implement a differentiated educational program when establishing the science and technology-oriented medical school in the future by further strengthening the science and engineering part of the training including a curriculum on artificial intelligence (AI) and the likes there of.
Also, in order to foster innovative physician-scientists, KAIST plans to pursue cooperation to develop programs for exchange of academic and human resources including programs for student and research exchanges and a program for students of the science and technology-oriented medical school at KAIST to have a chance to take part in practical training at Mass General.
David F.M. Brown, MD, Mass General President, said, “The collaboration with KAIST has a wide range of potentials, including advice on training of physician-scientists, academic and human resource exchanges, and vitalization of joint research by faculty from both institutions. Through this agreement, we will be able to actively contribute to global cooperation and achieve mutual goals.”
Meanwhile, an MOU between KAIST and Moderna was also held on the same day. Its main focus is to foster medical experts in cooperation with KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE), and plans to cooperate in various ways in the future, including collaborating for development of vaccine and new drugs, virus research, joint mRNA research, and facilitation of technology commercialization.
In over 10 years since its inception, Moderna has transformed from a research-stage company advancing programs in the field of messenger RNA (mRNA) to an enterprise with a diverse clinical portfolio of vaccines and therapeutics across seven modalities. The Company has 48 programs in development across 45 development candidates, of which 38 are currently in active clinical trials.
“We are grateful to have laid a foundation for collaboration to foster industry experts with the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology, a leader of science and technology innovation in Korea,” said Arpa Garay, Chief Commercial Officer, Moderna. “Based on our leadership and expertise in developing innovative mRNA vaccines and therapeutics, we hope to contribute to educating and collaborating with professionals in the bio-health field of Korea.“
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST, said, “We deem this occasion to be of grave significance to be able to work closely with Massachusetts General Hospital, one of the world's best research-oriented hospitals, and Moderna, one of the most influential biomedical companies.”
President Lee continued, "On the basis of the collaboration with the two institutions, we will be able to bring up qualified physician-scientists and global leaders of the biomedical business who will solve problems of human health and their progress will in turn, accelerate the national R&D efforts in general and diversify the industry."
2023.04.29 View 17440 -
 KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 12713
KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 12713