Advanced+Healthcare+Materials
-
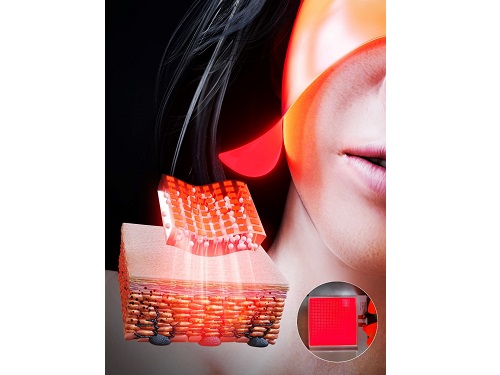 KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 11659
KAIST Team Develops Surface-Lighting MicroLED Patch with Significant Melanogenesis Inhibition Effect
A KAIST research team led by Ph.d candidate Jae Hee Lee and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering has developed a surface-lighting microLED patch for UV-induced melanogenesis inhibition.
Melanin is brown or dark pigments existing in the skin, which can be abnormally synthesized by external UV or stress. Since the excessive melanin leads to skin diseases such as spots and freckles, proper treatment is required to return normal skin condition.
Recently, LED-based photo-stimulators have been released for skin care, however, their therapeutic effect is still controversial. Since conventional LED stimulators cannot conformally attach to the human skin, distance-induced side effects are caused by light loss and high heat transfer. To achieve effective phototreatment, the LED stimulator needs to be irradiated in contact with the human skin surface, enabling proper and uniform light deliver to the dermis with minimal optical loss.
In this work, the research team fabricated skin-attachable surface-lighting microLED (SµLED, 4 × 4 cm2) patch by utilizing a thousand of microLED chips and silica-embedded light diffusion layer. 100 µm-sized LED chips are vertically-interconnected for high flexibility and low heat generation, allowing its long-term operation on the human skin.
< Image 1. The overall concept of SµLED patch. a) SµLED patch operated on the human skin. b) Schematic illustration of SµLED patch structure. c) 4 × 4 cm2-sized SµLED patch. d) Schematic illustration of the advantages of SµLED patch such as efficient light delivery, low heat generation, and surface-lighting irradiation. >
The research team confirmed melanogenesis inhibition by irradiating the SµLED patch and the conventional LED (CLED) on the artificial human skin and mice dorsal skin. The SµLED-treated groups of human cells and mouse tissues showed minimal epidermal photo-toxicity and consistently effective reduction in synthesized melanin, compared to CLED-treated groups. In addition, significant suppression of proteins/catalysts expression involved in melanin synthesis such as MITF (microphthalmia-associated transcription factor), Melan-A and tyrosinase was verified.
< Image 2. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on 3D human skin cells. a). Different irradiation conditions for a-MSH (major factor to stimulate melanin synthesis) treated cells. b) The ratio of pigmented area to total epidermis area. c) Relative variance of melanin level in 1 cm2-sized skin cells. A low variance means that melanin is evenly distributed, and a high variance means that the melanin is irregularly distributed. d) Optical images after in vitro experiments for 12 days. Scale bar, 1cm. e) Histological analysis of 3D skin, showing the greatest reduction in melanin after SµLED irradiation. Scale bar, 20 µm. >
< Image 3. The efficacy of melanogenesis inhibition on mouse dorsal skin. a) Optical images of mice dorsal skin after photo-treatment for 20 days. b) Histological analysis of mice dorsal skin. Less brown color means less expression of protein/catalysis involved in melanin synthesis. Scale bar, 50 µm. >
Prof. Keon Jae Lee said, “Our inorganic-based SµLED patch has outstanding characteristics in light efficiency, reliability, and durability. The SµLED patch is expected to give a great impact on the cosmetic field by reducing side effects and maximizing phototherapeutic effects.” The core technology of cosmetic SµLED has been transferred to Fronics co., Ltd, founded by Prof. Lee. Fronics is building foundry and equipment for mass production of SµLED masks for whole face cover and plans to release the products in March next year.
This paper entitled “Wearable Surface-Lighting Micro-Light-Emitting Diode Patch for Melanogenesis Inhibition” was published in the November 2022 issue of Advanced Healthcare Materials.
2022.11.22 View 11659 -
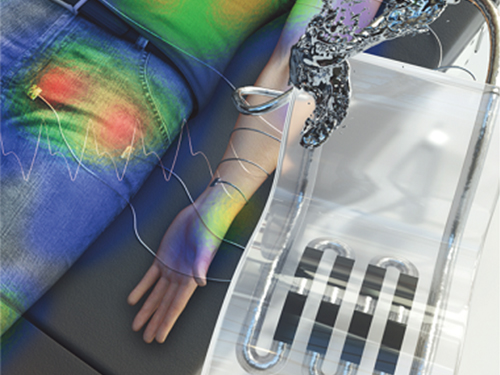 New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 15017
New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 15017