Adhesion
-
 KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 5538
KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 5538 -
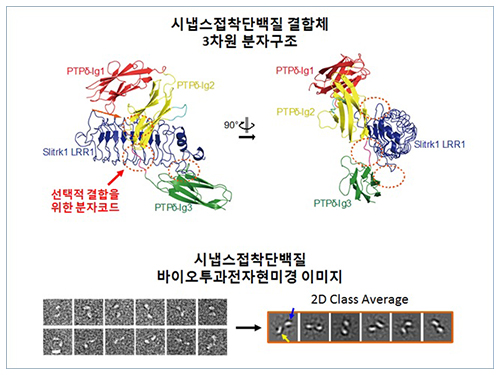 Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 13512
Structure of Neuron-Connecting Synaptic Adhesion Molecules Discovered
A research team has found the three-dimensional structure of synaptic adhesion molecules, which orchestrate synaptogenesis. The research findings also propose the mechanism of synapses in its initial formation. Some brain diseases such as obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) or bipolar disorders arise from a malfunction of synapses. The team expects the findings to be applied in investigating pathogenesis and developing medicines for such diseases.
The research was conducted by a Master’s candidate Kee Hun Kim, Professor Ji Won Um from Yonsei University, and Professor Beom Seok Park from Eulji University under the guidance of Professor Homin Kim from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, KAIST, and Professor Jaewon Ko from Yonsei University. Sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea, the research findings were published online in the November 14th issue of Nature Communications.
A protein that exists in the neuronal transmembrane, Slitrk, interacts with the presynaptic leukocyte common antigen-related receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (LAR-RPTPs) and forms a protein complex. It is involved in the development of synapses in the initial stage, and balances excitatory and inhibitory signals of neurons.
It is known that a disorder in those two proteins cause a malfunction of synapses, resulting in neuropsychosis such as autism, epilepsy, OCD, and bipolar disorders. However, because the structure as well as synaptogenic function of these proteins were not understood, the development of cures could not progress.
The research team discovered the three-dimensional structure of two synaptic adhesion molecules like Slitrk and LAR-RPTPs and identified the regions of interaction through protein crystallography and transmission electron microscopy (TEM). Furthermore, they found that the formation of the synapse is induced after the combination of two synaptic adhesion molecules develops a cluster.
Professor Kim said, “The research findings will serve as a basis of understanding the pathogenesis of brain diseases which arises from a malfunction of synaptic adhesion molecules. In particular, this is a good example in which collaboration between structural biology and neurobiology has led to a fruitful result.” Professor Ko commented that “this will give new directions to synaptic formation-related-researches by revealing the molecular mechanism of synaptic adhesion molecules.”
Figure 1: Overview of the PTPd Ig1–3/Slitrk1 LRR1 complex.
Figure 2: Representative negative-stained electron microscopy images of Slitrk1 Full ectodomain (yellow arrows indicate the horseshoe-shaped LRR domains). The typical horseshoe-shaped structures and the randomness of the relative positions of each LRR domain can be observed from the two-dimensional class averages displayed in the orange box.
Figure 3: Model of the two-step presynaptic differentiation process mediated by the biding of Slitrks to LAR-RPTPs and subsequent lateral assembly of trans-synaptic LAR-RPTPs/Slitrik complexes.
2014.11.28 View 13512