chemistry
-
 KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3894
KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3894 -
 “Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs” for Semiconductor, Chemistry, and Computer Science Opened
< Photo of Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo (center) of the School of Electrical Engineering at the signboard unveiling ceremony >
KAIST held a ceremony to mark the opening of three additional ‘Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs’ on the morning of January 7th, 2025.
The “Next-Generation AI Semiconductor System Lab” by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, the “Molecular Spectroscopy and Chemical Dynamics Lab” by Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry, and the “Advanced Data Computing Lab” by Professor Sue Bok Moon of the School of Computer Science are the three new labs given the honored titled of the “Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab”.
The Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab is KAIST’s unique system that was set up to facilitate the collaboration between retiring professors and junior professors to continue the achievements and know-how the elders have accumulated over their academic career. Since its introduction in 2018, nine labs have been named to be the Cross-Generation Labs, and this year’s new addition brings the total up to twelve.
The ‘Next-Generation AI Semiconductor System Lab’ led by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo will be operated by Professor Joo-Young Kim of the same school.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo is a world-renowned scholar with outstanding research achievements in the field of on-device AI semiconductor design. Professor Joo-Young Kim is an up-and-coming researcher studying large language models and design of AI semiconductors for server computers, and is currently researching technologies to design PIM (Processing-in-Memory), a core technology in the field of AI semiconductors.
Their research goal is to systematically collaborate and transfer next-generation AI semiconductor design technology, including brain-mimicking AI algorithms such as deep neural networks and generative AI, to integrate core technologies, and to maximize the usability of R&D outputs, thereby further solidifying the position of Korean AI semiconductor companies in the global market.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo said, “I believe that, we will be able to present a development direction of for the next-generation AI semiconductors industries at home and abroad through collaborative research and play a key role in transferring and expanding global leadership.”
< Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry (middle), at the signboard unveiling ceremony for his laboratory >
The “Molecular Spectroscopy and Chemical Dynamics Laboratory”, where Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry is in charge, will be operated by Professor Tae Kyu Kim of the same department, and another professor in the field of spectroscopy and dynamics will join in the future.
Professor Sang Kyu Kim has secured technologies for developing unique experimental equipment based on ultrashort lasers and supersonic molecular beams, and is a world leader who has been creatively pioneering new fields of experimental physical chemistry.
The research goal is to describe chemical reactions and verify from a quantum mechanical perspective and introduce new theories and technologies to pursue a complete understanding of the principles of chemical reactions. In addition, the accompanying basic scientific knowledge will be applied to the design of new materials.
Professor Sang Kyu Kim said, “I am very happy to be able to pass on the research infrastructure to the next generation through this system, and I will continue to nurture it to grow into a world-class research lab through trans-generational collaborative research.”
< Photo of Professor Sue Bok Moon (center) at the signboard unveiling ceremony by the School of Computing >
Lastly, the “Advanced Data Computing Lab” led by Professor Sue Bok Moon is joined by Professor Mee Young Cha of the same school and Professor Wonjae Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology.
Professor Sue Bok Moon showed the infinite possibilities of large-scale data-based social network research through Cyworld, YouTube, and Twitter, and had a great influence on related fields beyond the field of computer science.
Professor Mee Young Cha is a data scientist who analyzes difficult social issues such as misinformation, poverty, and disaster detection using big data-based AI. She is the first Korean to be recognized for her achievements as the director of the Max Planck Institute in Germany, a world-class basic science research institute. Therefore, there is high expectation for synergy effects from overseas collaborative research and technology transfer and sharing among the participating professors of the collaborative research lab. Professor Wonjae Lee is researching dynamic interaction analysis between science and technology using structural topic models.
They plan to conduct research aimed at improving the analysis and understanding of negative influences occurring online, and in particular, developing a hateful precursor detection model using emotions and morality to preemptively block hateful expressions.
Professor Sue Bok Moon said, “Through this collaborative research lab, we will play a key role in conducting in-depth collaborative research on unexpected negative influences in the AI era so that we can have a high level of competitiveness worldwide.”
The ceremonies for the unveiling of the new Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab signboard were held in front of each lab from 10:00 AM on the 7th, in the attendance of President Kwang Hyung Lee, Senior Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, and other key officials of KAIST and the new staff members to join the laboratories.
2025.01.07 View 5022
“Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs” for Semiconductor, Chemistry, and Computer Science Opened
< Photo of Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo (center) of the School of Electrical Engineering at the signboard unveiling ceremony >
KAIST held a ceremony to mark the opening of three additional ‘Cross-Generation Collaborative Labs’ on the morning of January 7th, 2025.
The “Next-Generation AI Semiconductor System Lab” by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, the “Molecular Spectroscopy and Chemical Dynamics Lab” by Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry, and the “Advanced Data Computing Lab” by Professor Sue Bok Moon of the School of Computer Science are the three new labs given the honored titled of the “Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab”.
The Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab is KAIST’s unique system that was set up to facilitate the collaboration between retiring professors and junior professors to continue the achievements and know-how the elders have accumulated over their academic career. Since its introduction in 2018, nine labs have been named to be the Cross-Generation Labs, and this year’s new addition brings the total up to twelve.
The ‘Next-Generation AI Semiconductor System Lab’ led by Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo will be operated by Professor Joo-Young Kim of the same school.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo is a world-renowned scholar with outstanding research achievements in the field of on-device AI semiconductor design. Professor Joo-Young Kim is an up-and-coming researcher studying large language models and design of AI semiconductors for server computers, and is currently researching technologies to design PIM (Processing-in-Memory), a core technology in the field of AI semiconductors.
Their research goal is to systematically collaborate and transfer next-generation AI semiconductor design technology, including brain-mimicking AI algorithms such as deep neural networks and generative AI, to integrate core technologies, and to maximize the usability of R&D outputs, thereby further solidifying the position of Korean AI semiconductor companies in the global market.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo said, “I believe that, we will be able to present a development direction of for the next-generation AI semiconductors industries at home and abroad through collaborative research and play a key role in transferring and expanding global leadership.”
< Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry (middle), at the signboard unveiling ceremony for his laboratory >
The “Molecular Spectroscopy and Chemical Dynamics Laboratory”, where Professor Sang Kyu Kim of the Department of Chemistry is in charge, will be operated by Professor Tae Kyu Kim of the same department, and another professor in the field of spectroscopy and dynamics will join in the future.
Professor Sang Kyu Kim has secured technologies for developing unique experimental equipment based on ultrashort lasers and supersonic molecular beams, and is a world leader who has been creatively pioneering new fields of experimental physical chemistry.
The research goal is to describe chemical reactions and verify from a quantum mechanical perspective and introduce new theories and technologies to pursue a complete understanding of the principles of chemical reactions. In addition, the accompanying basic scientific knowledge will be applied to the design of new materials.
Professor Sang Kyu Kim said, “I am very happy to be able to pass on the research infrastructure to the next generation through this system, and I will continue to nurture it to grow into a world-class research lab through trans-generational collaborative research.”
< Photo of Professor Sue Bok Moon (center) at the signboard unveiling ceremony by the School of Computing >
Lastly, the “Advanced Data Computing Lab” led by Professor Sue Bok Moon is joined by Professor Mee Young Cha of the same school and Professor Wonjae Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology.
Professor Sue Bok Moon showed the infinite possibilities of large-scale data-based social network research through Cyworld, YouTube, and Twitter, and had a great influence on related fields beyond the field of computer science.
Professor Mee Young Cha is a data scientist who analyzes difficult social issues such as misinformation, poverty, and disaster detection using big data-based AI. She is the first Korean to be recognized for her achievements as the director of the Max Planck Institute in Germany, a world-class basic science research institute. Therefore, there is high expectation for synergy effects from overseas collaborative research and technology transfer and sharing among the participating professors of the collaborative research lab. Professor Wonjae Lee is researching dynamic interaction analysis between science and technology using structural topic models.
They plan to conduct research aimed at improving the analysis and understanding of negative influences occurring online, and in particular, developing a hateful precursor detection model using emotions and morality to preemptively block hateful expressions.
Professor Sue Bok Moon said, “Through this collaborative research lab, we will play a key role in conducting in-depth collaborative research on unexpected negative influences in the AI era so that we can have a high level of competitiveness worldwide.”
The ceremonies for the unveiling of the new Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab signboard were held in front of each lab from 10:00 AM on the 7th, in the attendance of President Kwang Hyung Lee, Senior Vice President for Research Sang Yup Lee, and other key officials of KAIST and the new staff members to join the laboratories.
2025.01.07 View 5022 -
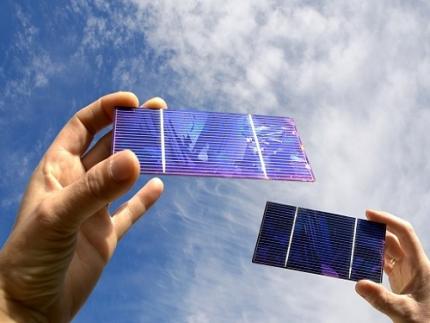 KAIST Researchers Introduce New and Improved, Next-Generation Perovskite Solar Cell
- KAIST-Yonsei university researchers developed innovative dipole technology to maximize near-infrared photon harvesting efficiency
- Overcoming the shortcoming of existing perovskite solar cells that cannot utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy
- Development of next-generation solar cell technology with high efficiency and high stability that can absorb near-infrared light beyond the existing visible light range with a perovskite-dipole-organic semiconductor hybrid structure
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jung-Yong Lee, Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee, and Master’s candidate Min Seok Kim of the School of Electrical Engineering >
Existing perovskite solar cells, which have the problem of not being able to utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy, have been developed by a Korean research team as an innovative technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture performance while greatly improving power conversion efficiency. This greatly increases the possibility of commercializing next-generation solar cells and is expected to contribute to important technological advancements in the global solar cell market.
The research team of Professor Jung-Yong Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) and Professor Woojae Kim of the Department of Chemistry at Yonsei University announced on October 31st that they have developed a high-efficiency and high-stability organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell production technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture beyond the existing visible light range.
The research team suggested and advanced a hybrid next-generation device structure with organic photo-semiconductors that complements perovskite materials limited to visible light absorption and expands the absorption range to near-infrared.
In addition, they revealed the electronic structure problem that mainly occurs in the structure and announced a high-performance solar cell device that dramatically solved this problem by introducing a dipole layer*.
*Dipole layer: A thin material layer that controls the energy level within the device to facilitate charge transport and forms an interface potential difference to improve device performance.
Existing lead-based perovskite solar cells have a problem in that their absorption spectrum is limited to the visible light region with a wavelength of 850 nanometers (nm) or less, which prevents them from utilizing approximately 52% of the total solar energy.
To solve this problem, the research team designed a hybrid device that combined an organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) with perovskite and implemented a solar cell that can absorb up to the near-infrared region.
In particular, by introducing a sub-nanometer dipole interface layer, they succeeded in alleviating the energy barrier between the perovskite and the organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), suppressing charge accumulation, maximizing the contribution to the near-infrared, and improving the current density (JSC) to 4.9 mA/cm².
The key achievement of this study is that the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the hybrid device has been significantly increased from 20.4% to 24.0%. In particular, this study achieved a high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) compared to previous studies, reaching 78% in the near-infrared region.
< Figure. The illustration of the mechanism of improving the electronic structure and charge transfer capability through Perovskite/organic hybrid device structure and dipole interfacial layers (DILs). The proposed dipole interfacial layer forms a strong interfacial dipole, effectively reducing the energy barrier between the perovskite and organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), and suppressing hole accumulation. This technology improves near-infrared photon harvesting and charge transfer, and as a result, the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell increases to 24.0%. In addition, it achieves excellent stability by maintaining performance for 1,200 hours even in an extremely humid environment. >
In addition, this device showed high stability, showing excellent results of maintaining more than 80% of the initial efficiency in the maximum output tracking for more than 800 hours even under extreme humidity conditions.
Professor Jung-Yong Lee said, “Through this study, we have effectively solved the charge accumulation and energy band mismatch problems faced by existing perovskite/organic hybrid solar cells, and we will be able to significantly improve the power conversion efficiency while maximizing the near-infrared light capture performance, which will be a new breakthrough that can solve the mechanical-chemical stability problems of existing perovskites and overcome the optical limitations.”
This study, in which KAIST School of Electrical Engineering Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee and Master's candidate Min Seok Kim participated as co-first authors, was published in the September 30th online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials. (Paper title: Suppressing Hole Accumulation Through Sub-Nanometer Dipole Interfaces in Hybrid Perovskite/Organic Solar Cells for Boosting Near-Infrared Photon Harvesting).
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.31 View 6956
KAIST Researchers Introduce New and Improved, Next-Generation Perovskite Solar Cell
- KAIST-Yonsei university researchers developed innovative dipole technology to maximize near-infrared photon harvesting efficiency
- Overcoming the shortcoming of existing perovskite solar cells that cannot utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy
- Development of next-generation solar cell technology with high efficiency and high stability that can absorb near-infrared light beyond the existing visible light range with a perovskite-dipole-organic semiconductor hybrid structure
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jung-Yong Lee, Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee, and Master’s candidate Min Seok Kim of the School of Electrical Engineering >
Existing perovskite solar cells, which have the problem of not being able to utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy, have been developed by a Korean research team as an innovative technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture performance while greatly improving power conversion efficiency. This greatly increases the possibility of commercializing next-generation solar cells and is expected to contribute to important technological advancements in the global solar cell market.
The research team of Professor Jung-Yong Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) and Professor Woojae Kim of the Department of Chemistry at Yonsei University announced on October 31st that they have developed a high-efficiency and high-stability organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell production technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture beyond the existing visible light range.
The research team suggested and advanced a hybrid next-generation device structure with organic photo-semiconductors that complements perovskite materials limited to visible light absorption and expands the absorption range to near-infrared.
In addition, they revealed the electronic structure problem that mainly occurs in the structure and announced a high-performance solar cell device that dramatically solved this problem by introducing a dipole layer*.
*Dipole layer: A thin material layer that controls the energy level within the device to facilitate charge transport and forms an interface potential difference to improve device performance.
Existing lead-based perovskite solar cells have a problem in that their absorption spectrum is limited to the visible light region with a wavelength of 850 nanometers (nm) or less, which prevents them from utilizing approximately 52% of the total solar energy.
To solve this problem, the research team designed a hybrid device that combined an organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) with perovskite and implemented a solar cell that can absorb up to the near-infrared region.
In particular, by introducing a sub-nanometer dipole interface layer, they succeeded in alleviating the energy barrier between the perovskite and the organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), suppressing charge accumulation, maximizing the contribution to the near-infrared, and improving the current density (JSC) to 4.9 mA/cm².
The key achievement of this study is that the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the hybrid device has been significantly increased from 20.4% to 24.0%. In particular, this study achieved a high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) compared to previous studies, reaching 78% in the near-infrared region.
< Figure. The illustration of the mechanism of improving the electronic structure and charge transfer capability through Perovskite/organic hybrid device structure and dipole interfacial layers (DILs). The proposed dipole interfacial layer forms a strong interfacial dipole, effectively reducing the energy barrier between the perovskite and organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), and suppressing hole accumulation. This technology improves near-infrared photon harvesting and charge transfer, and as a result, the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell increases to 24.0%. In addition, it achieves excellent stability by maintaining performance for 1,200 hours even in an extremely humid environment. >
In addition, this device showed high stability, showing excellent results of maintaining more than 80% of the initial efficiency in the maximum output tracking for more than 800 hours even under extreme humidity conditions.
Professor Jung-Yong Lee said, “Through this study, we have effectively solved the charge accumulation and energy band mismatch problems faced by existing perovskite/organic hybrid solar cells, and we will be able to significantly improve the power conversion efficiency while maximizing the near-infrared light capture performance, which will be a new breakthrough that can solve the mechanical-chemical stability problems of existing perovskites and overcome the optical limitations.”
This study, in which KAIST School of Electrical Engineering Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee and Master's candidate Min Seok Kim participated as co-first authors, was published in the September 30th online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials. (Paper title: Suppressing Hole Accumulation Through Sub-Nanometer Dipole Interfaces in Hybrid Perovskite/Organic Solar Cells for Boosting Near-Infrared Photon Harvesting).
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.31 View 6956 -
 Novel High-performance and Sustainable Paper Coating Material created by KAIST-Yonsei University Research Team to reduce microplastic pollution
What if there is a biodegradable packaging material with high performance without leaving microplastics?
Plastic pollution presents a global challenge that must be solved. In particular, packaging accounts for 30-50% of the total plastic consumption. While paper packaging is eco-friendly, it lacks crucial functionalities like moisture resistance and strength. Traditional coating materials exacerbate plastic pollution, prompting the need for sustainable alternatives.
Polyethylene (PE) and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) are typically used as coating materials to improve the low barrier properties of paper packaging, but these substances do not decompose and worsen microplastic pollution when disposed of in the natural environment. In response to this problem, packaging materials made from bio-based substances and biodegradable plastics have been developed, but in most cases, as the packaging performance improves, the biodegradability diminishes rapidly.
KAIST announced that a joint research team led by Professor Jaewook Myung of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Professor Hanseul Yang of the Department of Life Sciences, and Professor Jongcheol Seo of the Department of Packaging and Logistics <Figure 4. Back cover art of Green Chemistry journal of the latest volume, describing the boric acid cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper featuring marine biodegradability, biocompatibility, high barrier properties, and robustness developed through this study.>
at Yonsei University tackled the challenge of balancing packaging performance and sustainability. They successfully developed a sustainable, marine biodegradable, high-performance paper coating material.
* Biodegradable plastic: A plastic that can be decomposed by microorganisms in natural environments such as soil and ocean or artificial conditions such as industrial composting and anaerobic digestion by microorganisms.
*Microplastics: Tiny pieces of plastic less than 5 mm, produced during the decomposition of bulk plastic materials. Microplastics can persist in the sea for more than decades, causing severe marine pollution.
The team utilized boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), a biodegradable plastic, to coat the paper, thereby enhancing its biodegradability, barrier properties, and strength. The resulting coated paper exhibited superior performance compared to conventional plastics, with excellent barrier properties and physical strength, even in humid conditions.
<Figure 1. (a) Chemical structure of boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coating on paper, (b-c) Oxygen and water vapor barrier properties, (d-f) Tensile strength in dry and moist conditions. OTR: Oxygen transmission rate, WVTR: Water vapor transmission rate.>
The team also conducted an in-depth examination of biodegradation and biocompatibility to systematically evaluate the sustainability of the newly developed coated paper. Biodegradation was assessed by simulating the marine environment, known for its challenging biodegradability conditions. The team employed a respiratory system-based bioreactor to measure the degree of carbon mineralization into carbon dioxide. After 111 days of biodegradation, it was found that the coated papers achieved 59-82% biodegradation depending on the coating component. The phenomenon in which marine bacteria are decomposing the coating material was captured through a scanning electron microscope. In addition, in vitro biocompatibility was confirmed through human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, as well as high in-vivo biocompatibility of the coated paper was verified through mouse experiments.
Through this study, the joint research team proposed a coating strategy that can improve packaging performance while upholding sustainability to address the drawbacks of paper packaging. The boric acid-crosslinked PVA-coated paper eliminates the need for artificial composting conditions or sewage treatment facilities. Being biodegradable in natural environments and characterized by low toxicity, this newly coated paper does not exacerbate environmental pollution when accidentally discarded. Thus, it presents a sustainable substitute for plastic packaging materials.
<Figure 2. (a) Normal paper and boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper, (b) Biodegradation of the coated paper by marine bacteria, (c) Result of cytotoxicity test using human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. (d) Vital organs after one-month exposure of the coated papers to mice.>
Professor Jaewook Myung at KAIST, who led the sustainability study of coated paper, said, "The development of a marine biodegradable high-performance paper coating is the result of combining the innovative technologies of three leading research teams in each field." He said, “We will continue to develop sustainable materials with excellent performance.” Meanwhile, Professor Jongchul Seo of Yonsei University, who led the research on the development of high-performance paper coating, mentioned, “Through this research, we have developed a sustainable paper packaging technology that can replace non-degradable plastic packaging, and we expect the research outcome will be applied in industry,”.
<Figure 3. End-of-life scenario of papers coated by BA-crosslinked PVA in the marine environment. The coated papers potentially be disintegrated by marine microorganisms and ocean waves and tides. The depolymerization of PVA coating and paper is then mediated by extracellular depolymerases such as oxidases and cellulases, after which the small subunits (oligomers and monomers) are assimilated by microbial cells. The carbon components in the coated papers are ultimately mineralized into CO2, posing no harm in the ocean.>
The work was published in Green Chemistry and Food Chemistry journals. This study was conducted with the support of the Korea Research Foundation and the Korea Institute for Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Technology Planning and Evaluation, etc.
*Title of paper published in Green Chemistry: Boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol): biodegradable, biocompatible, robust, and high-barrier paper coating
※ Selected as the article for the back cover of the journal .
- Authors: Shinhyeong Choe, Seulki You, Kitae Park, Youngju Kim, Jehee Park, Yongjun Cho, Jongchul Seo, Hanseul Yang, and Jaewook Myung)
- Date: April 17, 2024
- DOI: 10.1039/D4GC00618F
*Title of paper published in Food Chemistry: Effect of epichlorohydrin treatment on the coating process and performance of high-barrier paper packaging
- Authors: Kitae Park, Shinhyeong Choe, Kambiz Sadeghi, Pradeep Kumar Panda, Jaewook Myung, Dowan Kim, and Jongchul Seo
- Date: February 19, 2024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138772
<Figure 4. Back cover art of Green Chemistry journal of the latest volume, describing the boric acid cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper featuring marine biodegradability, biocompatibility, high barrier properties, and robustness developed through this study.>
2024.05.22 View 8329
Novel High-performance and Sustainable Paper Coating Material created by KAIST-Yonsei University Research Team to reduce microplastic pollution
What if there is a biodegradable packaging material with high performance without leaving microplastics?
Plastic pollution presents a global challenge that must be solved. In particular, packaging accounts for 30-50% of the total plastic consumption. While paper packaging is eco-friendly, it lacks crucial functionalities like moisture resistance and strength. Traditional coating materials exacerbate plastic pollution, prompting the need for sustainable alternatives.
Polyethylene (PE) and ethylene vinyl alcohol (EVOH) are typically used as coating materials to improve the low barrier properties of paper packaging, but these substances do not decompose and worsen microplastic pollution when disposed of in the natural environment. In response to this problem, packaging materials made from bio-based substances and biodegradable plastics have been developed, but in most cases, as the packaging performance improves, the biodegradability diminishes rapidly.
KAIST announced that a joint research team led by Professor Jaewook Myung of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Professor Hanseul Yang of the Department of Life Sciences, and Professor Jongcheol Seo of the Department of Packaging and Logistics <Figure 4. Back cover art of Green Chemistry journal of the latest volume, describing the boric acid cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper featuring marine biodegradability, biocompatibility, high barrier properties, and robustness developed through this study.>
at Yonsei University tackled the challenge of balancing packaging performance and sustainability. They successfully developed a sustainable, marine biodegradable, high-performance paper coating material.
* Biodegradable plastic: A plastic that can be decomposed by microorganisms in natural environments such as soil and ocean or artificial conditions such as industrial composting and anaerobic digestion by microorganisms.
*Microplastics: Tiny pieces of plastic less than 5 mm, produced during the decomposition of bulk plastic materials. Microplastics can persist in the sea for more than decades, causing severe marine pollution.
The team utilized boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), a biodegradable plastic, to coat the paper, thereby enhancing its biodegradability, barrier properties, and strength. The resulting coated paper exhibited superior performance compared to conventional plastics, with excellent barrier properties and physical strength, even in humid conditions.
<Figure 1. (a) Chemical structure of boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coating on paper, (b-c) Oxygen and water vapor barrier properties, (d-f) Tensile strength in dry and moist conditions. OTR: Oxygen transmission rate, WVTR: Water vapor transmission rate.>
The team also conducted an in-depth examination of biodegradation and biocompatibility to systematically evaluate the sustainability of the newly developed coated paper. Biodegradation was assessed by simulating the marine environment, known for its challenging biodegradability conditions. The team employed a respiratory system-based bioreactor to measure the degree of carbon mineralization into carbon dioxide. After 111 days of biodegradation, it was found that the coated papers achieved 59-82% biodegradation depending on the coating component. The phenomenon in which marine bacteria are decomposing the coating material was captured through a scanning electron microscope. In addition, in vitro biocompatibility was confirmed through human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells, as well as high in-vivo biocompatibility of the coated paper was verified through mouse experiments.
Through this study, the joint research team proposed a coating strategy that can improve packaging performance while upholding sustainability to address the drawbacks of paper packaging. The boric acid-crosslinked PVA-coated paper eliminates the need for artificial composting conditions or sewage treatment facilities. Being biodegradable in natural environments and characterized by low toxicity, this newly coated paper does not exacerbate environmental pollution when accidentally discarded. Thus, it presents a sustainable substitute for plastic packaging materials.
<Figure 2. (a) Normal paper and boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper, (b) Biodegradation of the coated paper by marine bacteria, (c) Result of cytotoxicity test using human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. (d) Vital organs after one-month exposure of the coated papers to mice.>
Professor Jaewook Myung at KAIST, who led the sustainability study of coated paper, said, "The development of a marine biodegradable high-performance paper coating is the result of combining the innovative technologies of three leading research teams in each field." He said, “We will continue to develop sustainable materials with excellent performance.” Meanwhile, Professor Jongchul Seo of Yonsei University, who led the research on the development of high-performance paper coating, mentioned, “Through this research, we have developed a sustainable paper packaging technology that can replace non-degradable plastic packaging, and we expect the research outcome will be applied in industry,”.
<Figure 3. End-of-life scenario of papers coated by BA-crosslinked PVA in the marine environment. The coated papers potentially be disintegrated by marine microorganisms and ocean waves and tides. The depolymerization of PVA coating and paper is then mediated by extracellular depolymerases such as oxidases and cellulases, after which the small subunits (oligomers and monomers) are assimilated by microbial cells. The carbon components in the coated papers are ultimately mineralized into CO2, posing no harm in the ocean.>
The work was published in Green Chemistry and Food Chemistry journals. This study was conducted with the support of the Korea Research Foundation and the Korea Institute for Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Technology Planning and Evaluation, etc.
*Title of paper published in Green Chemistry: Boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol): biodegradable, biocompatible, robust, and high-barrier paper coating
※ Selected as the article for the back cover of the journal .
- Authors: Shinhyeong Choe, Seulki You, Kitae Park, Youngju Kim, Jehee Park, Yongjun Cho, Jongchul Seo, Hanseul Yang, and Jaewook Myung)
- Date: April 17, 2024
- DOI: 10.1039/D4GC00618F
*Title of paper published in Food Chemistry: Effect of epichlorohydrin treatment on the coating process and performance of high-barrier paper packaging
- Authors: Kitae Park, Shinhyeong Choe, Kambiz Sadeghi, Pradeep Kumar Panda, Jaewook Myung, Dowan Kim, and Jongchul Seo
- Date: February 19, 2024
- DOI: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2024.138772
<Figure 4. Back cover art of Green Chemistry journal of the latest volume, describing the boric acid cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper featuring marine biodegradability, biocompatibility, high barrier properties, and robustness developed through this study.>
2024.05.22 View 8329 -
 KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 11212
KAIST Research team develops anti-icing film that only requires sunlight
A KAIST research team has developed an anti-icing and de-icing film coating technology that can apply the photothermal effect of gold nanoparticles to industrial sites without the need for heating wires, periodic spray or oil coating of anti-freeze substances, and substrate design alterations.
The group led by Professor Hyoungsoo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering (Fluid & Interface Laboratory) and Professor Dong Ki Yoon from the Department of Chemistry (Soft Material Assembly Group) revealed on January 3 to have together developed an original technique that can uniformly pattern gold nanorod (GNR) particles in quadrants through simple evaporation, and have used this to develop an anti-icing and de-icing surface.
Many scientists in recent years have tried to control substrate surfaces through various coating techniques, and those involving the patterning of functional nanomaterials have gained special attention. In particular, GNR is considered a promising candidate nanomaterial for its biocompatibility, chemical stability, relatively simple synthesis, and its stable and unique property of surface plasmon resonance. To maximize the performance of GNR, it is important to achieve a high uniformity during film deposition, and a high level of rod alignment. However, achieving both criteria has thus far been a difficult challenge.
< Figure 1. Conceptual image to display Hydrodynamic mechanisms for the formation of a homogeneous quadrant cellulose nanocrystal(CNC) matrix. >
To solve this, the joint research team utilized cellulose nanocrystal (CNC), a next-generation functional nanomaterial that can easily be extracted from nature. By co-assembling GNR on CNC quadrant templates, the team could uniformly dry the film and successfully obtain a GNR film with a uniform alignment in a ring-shape. Compared to existing coffee-ring films, the highly uniform and aligned GNR film developed through this research showed enhanced plasmonic photothermal properties, and the team showed that it could carry out anti-icing and de-icing functions by simply irradiating light in the visible wavelength range.
< Figure 2. Optical and thermal performance evaluation results of gold nanorod film and demonstration of plasmonic heater for anti-icing and de-icing. >
Professor Hyoungsoo Kim said, “This technique can be applied to plastic, as well as flexible surfaces. By using it on exterior materials and films, it can generate its own heat energy, which would greatly save energy through voluntary thermal energy harvesting across various applications including cars, aircrafts, and windows in residential or commercial spaces, where frosting becomes a serious issue in the winter.” Professor Dong Ki Yoon added, “This research is significant in that we can now freely pattern the CNC-GNR composite, which was previously difficult to create into films, over a large area. We can utilize this as an anti-icing material, and if we were to take advantage of the plasmonic properties of gold, we can also use it like stained-glass to decorate glass surfaces.”
This research was conducted by Ph.D. candidate Jeongsu Pyeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and his co-first author Dr. Soon Mo Park (a KAIST graduate, currently a post-doctoral associate at Cornell University), and was pushed in the online volume of Nature Communication on December 8, 2023 under the title “Plasmonic Metasurfaces of Cellulose Nanocrystal Matrices with Quadrants of Aligned Gold Nanorods for Photothermal Anti-Icing." Recognized for its achievement, the research was also selected as an editor’s highlight for the journals Materials Science and Chemistry, and Inorganic and Physical Chemistry.
This research was supported by the Individual Basic Mid-Sized Research Fund from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Center for Multiscale Chiral Architectures.
2024.01.16 View 11212 -
 KAIST presents strategies for environmentally friendly and sustainable polyamides production
- Provides current research trends in bio-based polyamide production
- Research on bio-based polyamides production gains importance for achieving a carbon-neutral society
Global industries focused on carbon neutrality, under the slogan "Net-Zero," are gaining increasing attention. In particular, research on microbial production of polymers, replacing traditional chemical methods with biological approaches, is actively progressing.
Polyamides, represented by nylon, are linear polymers widely used in various industries such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and medical fields. They possess beneficial properties such as high tensile strength, electrical insulation, heat resistance, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Since the commercialization of nylon in 1938, approximately 7 million tons of polyamides are produced worldwide annually. Considering their broad applications and significance, producing polyamides through bio-based methods holds considerable environmental and industrial importance.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, including Dr. Jong An Lee and doctoral candidate Ji Yeon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled "Current Advancements in Bio-Based Production of Polyamides”. The paper was featured on the cover of the monthly issue of "Trends in Chemistry” by Cell Press.
As part of climate change response technologies, bio-refineries involve using biotechnological and chemical methods to produce industrially important chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass without relying on fossil resources. Notably, systems metabolic engineering, pioneered by KAIST's Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, is a research field that effectively manipulates microbial metabolic pathways to produce valuable chemicals, forming the core technology for bio-refineries. The research team has successfully developed high-performance strains producing a variety of compounds, including succinic acid, biodegradable plastics, biofuels, and natural products, using systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies.
The research team predicted that if bio-based polyamide production technology, which is widely used in the production of clothing and textiles, becomes widespread, it will attract attention as a future technology that can respond to the climate crisis due to its environment-friendly production technology. In this study, the research team comprehensively reviewed the bio-based polyamide production strategies. They provided insights into the advancements in polyamide monomer production using metabolically engineered microorganisms and highlighted the recent trends in bio-based polyamide advancements utilizing these monomers. Additionally, they reviewed the strategies for synthesizing bio-based polyamides through chemical conversion of natural oils and discussed the biodegradability and recycling of the polyamides. Furthermore, the paper presented the future direction in which metabolic engineering can be applied for the bio-based polyamide production, contributing to environmentally friendly and sustainable society.
Ji Yeon Kim, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, stated "The importance of utilizing systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies for bio-based polyamides production is becoming increasingly prominent in achieving carbon neutrality."
Professor Sang Yup Lee emphasized, "Amid growing concerns about climate change, the significance of environmentally friendly and sustainable industrial development is greater than ever. Systems metabolic engineering is expected to have a significant impact not only on the chemical industry but also in various fields."
< [Figure 1] A schematic overview of the overall process for polyamides production >
This paper by Dr. Jong An Lee, PhD student Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jung Ho Ahn, and Master Yeah-Ji Ahn from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was published in the December issue of 'Trends in Chemistry', an authoritative review journal in the field of chemistry published by Cell. It was published on December 7 as the cover paper and featured review.
※ Paper title: Current advancements in the bio-based production of polyamides
※ Author information: Jong An Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Jung Ho Ahn, Yeah-Ji Ahn, and Sang Yup Lee
This research was conducted with the support from the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and C1 gas refinery program by Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
< [Figure 2] Cover paper of the December issue of Trends in Chemistry >
2023.12.21 View 7508
KAIST presents strategies for environmentally friendly and sustainable polyamides production
- Provides current research trends in bio-based polyamide production
- Research on bio-based polyamides production gains importance for achieving a carbon-neutral society
Global industries focused on carbon neutrality, under the slogan "Net-Zero," are gaining increasing attention. In particular, research on microbial production of polymers, replacing traditional chemical methods with biological approaches, is actively progressing.
Polyamides, represented by nylon, are linear polymers widely used in various industries such as automotive, electronics, textiles, and medical fields. They possess beneficial properties such as high tensile strength, electrical insulation, heat resistance, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Since the commercialization of nylon in 1938, approximately 7 million tons of polyamides are produced worldwide annually. Considering their broad applications and significance, producing polyamides through bio-based methods holds considerable environmental and industrial importance.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, including Dr. Jong An Lee and doctoral candidate Ji Yeon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, published a paper titled "Current Advancements in Bio-Based Production of Polyamides”. The paper was featured on the cover of the monthly issue of "Trends in Chemistry” by Cell Press.
As part of climate change response technologies, bio-refineries involve using biotechnological and chemical methods to produce industrially important chemicals and biofuels from renewable biomass without relying on fossil resources. Notably, systems metabolic engineering, pioneered by KAIST's Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, is a research field that effectively manipulates microbial metabolic pathways to produce valuable chemicals, forming the core technology for bio-refineries. The research team has successfully developed high-performance strains producing a variety of compounds, including succinic acid, biodegradable plastics, biofuels, and natural products, using systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies.
The research team predicted that if bio-based polyamide production technology, which is widely used in the production of clothing and textiles, becomes widespread, it will attract attention as a future technology that can respond to the climate crisis due to its environment-friendly production technology. In this study, the research team comprehensively reviewed the bio-based polyamide production strategies. They provided insights into the advancements in polyamide monomer production using metabolically engineered microorganisms and highlighted the recent trends in bio-based polyamide advancements utilizing these monomers. Additionally, they reviewed the strategies for synthesizing bio-based polyamides through chemical conversion of natural oils and discussed the biodegradability and recycling of the polyamides. Furthermore, the paper presented the future direction in which metabolic engineering can be applied for the bio-based polyamide production, contributing to environmentally friendly and sustainable society.
Ji Yeon Kim, the co-first author of this paper from KAIST, stated "The importance of utilizing systems metabolic engineering tools and strategies for bio-based polyamides production is becoming increasingly prominent in achieving carbon neutrality."
Professor Sang Yup Lee emphasized, "Amid growing concerns about climate change, the significance of environmentally friendly and sustainable industrial development is greater than ever. Systems metabolic engineering is expected to have a significant impact not only on the chemical industry but also in various fields."
< [Figure 1] A schematic overview of the overall process for polyamides production >
This paper by Dr. Jong An Lee, PhD student Ji Yeon Kim, Dr. Jung Ho Ahn, and Master Yeah-Ji Ahn from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was published in the December issue of 'Trends in Chemistry', an authoritative review journal in the field of chemistry published by Cell. It was published on December 7 as the cover paper and featured review.
※ Paper title: Current advancements in the bio-based production of polyamides
※ Author information: Jong An Lee, Ji Yeon Kim, Jung Ho Ahn, Yeah-Ji Ahn, and Sang Yup Lee
This research was conducted with the support from the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and C1 gas refinery program by Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
< [Figure 2] Cover paper of the December issue of Trends in Chemistry >
2023.12.21 View 7508 -
 A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 12390
A Comprehensive Review of Biosynthesis of Inorganic Nanomaterials Using Microorganisms and Bacteriophages
There are diverse methods for producing numerous inorganic nanomaterials involving many experimental variables. Among the numerous possible matches, finding the best pair for synthesizing in an environmentally friendly way has been a longstanding challenge for researchers and industries.
A KAIST bioprocess engineering research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee conducted a summary of 146 biosynthesized single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials covering 55 elements in the periodic table synthesized using wild-type and genetically engineered microorganisms. Their research highlights the diverse applications of biogenic nanomaterials and gives strategies for improving the biosynthesis of nanomaterials in terms of their producibility, crystallinity, size, and shape.
The research team described a 10-step flow chart for developing the biosynthesis of inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages. The research was published at Nature Review Chemistry as a cover and hero paper on December 3.
“We suggest general strategies for microbial nanomaterial biosynthesis via a step-by-step flow chart and give our perspectives on the future of nanomaterial biosynthesis and applications. This flow chart will serve as a general guide for those wishing to prepare biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials using microbial cells,” explained Dr.Yoojin Choi, a co-author of this research.
Most inorganic nanomaterials are produced using physical and chemical methods and biological synthesis has been gaining more and more attention. However, conventional synthesis processes have drawbacks in terms of high energy consumption and non-environmentally friendly processes. Meanwhile, microorganisms such as microalgae, yeasts, fungi, bacteria, and even viruses can be utilized as biofactories to produce single and multi-element inorganic nanomaterials under mild conditions.
After conducting a massive survey, the research team summed up that the development of genetically engineered microorganisms with increased inorganic-ion-binding affinity, inorganic-ion-reduction ability, and nanomaterial biosynthetic efficiency has enabled the synthesis of many inorganic nanomaterials.
Among the strategies, the team introduced their analysis of a Pourbaix diagram for controlling the size and morphology of a product. The research team said this Pourbaix diagram analysis can be widely employed for biosynthesizing new nanomaterials with industrial applications.Professor Sang Yup Lee added, “This research provides extensive information and perspectives on the biosynthesis of diverse inorganic nanomaterials using microorganisms and bacteriophages and their applications. We expect that biosynthetic inorganic nanomaterials will find more diverse and innovative applications across diverse fields of science and technology.”
Dr. Choi started this research in 2018 and her interview about completing this extensive research was featured in an article at Nature Career article on December 4.
-ProfileDistinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee leesy@kaist.ac.krMetabolic &Biomolecular Engineering National Research Laboratoryhttp://mbel.kaist.ac.krDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.07 View 12390 -
 Three Professors Named to Highly Cited Researchers 2020 List
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry, Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor Jiyong Eom from the College of Business were named to Clarivate’s Highly Cited Researchers 2020 list.
Clarivate announced the researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. A total of 6,167 researchers from more than 60 countries were listed this year and 37 Korean scholars made the list.
The methodology that determines the “Who’s Who” of influential researchers draws on data and analyses performed by bibliometric experts and data scientists at the Institute for Scientific Information at Clarivate. It also uses the tallies to identify the countries and research institutions where these scientific elite are based. More than 6,000 researchers from 21 fields in the sciences, social sciences, and cross field categories were selected based on the number of highly cited papers they produced over an 11-year period from January 2009 to December 2019.
Professor Chang made the list six years in a row, while Professor Lee made it for four consecutive years, and Professor Eom for the last two years. Professor Chang’s group (http://sbchang.kaist.ac.kr) investigates catalytic hydrocarbon functionalization. Professor Lee (http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr) is a pioneering scholar in the field of metabolic engineering, systems, and synthetic biology. Professor Eom’s (https://kaistceps.quv.kr) research extends to energy and environmental economics and management, energy big data, and green information systems.
2020.11.30 View 10886
Three Professors Named to Highly Cited Researchers 2020 List
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry, Distinguished Professor Sang-Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor Jiyong Eom from the College of Business were named to Clarivate’s Highly Cited Researchers 2020 list.
Clarivate announced the researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. A total of 6,167 researchers from more than 60 countries were listed this year and 37 Korean scholars made the list.
The methodology that determines the “Who’s Who” of influential researchers draws on data and analyses performed by bibliometric experts and data scientists at the Institute for Scientific Information at Clarivate. It also uses the tallies to identify the countries and research institutions where these scientific elite are based. More than 6,000 researchers from 21 fields in the sciences, social sciences, and cross field categories were selected based on the number of highly cited papers they produced over an 11-year period from January 2009 to December 2019.
Professor Chang made the list six years in a row, while Professor Lee made it for four consecutive years, and Professor Eom for the last two years. Professor Chang’s group (http://sbchang.kaist.ac.kr) investigates catalytic hydrocarbon functionalization. Professor Lee (http://mbel.kaist.ac.kr) is a pioneering scholar in the field of metabolic engineering, systems, and synthetic biology. Professor Eom’s (https://kaistceps.quv.kr) research extends to energy and environmental economics and management, energy big data, and green information systems.
2020.11.30 View 10886 -
 Researchers Control Multiple Wavelengths of Light from a Single Source
KAIST researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit. The discovery will allow researchers to understand how to control these carbon dots and create new, environmentally responsible displays, lighting, and sensing technology.
Research into nanoparticles capable of emitting light, such as quantum dots, has been an active area of interest for the last decade and a half. These particles, or phosphors, are nanoparticles made out of various materials that are capable of emitting light at specific wavelengths by leveraging quantum mechanical properties of the materials. This provides new ways to develop lighting and display solutions as well as more precise detection and sensing in instruments.
As technology becomes smaller and more sophisticated, the usage of fluorescent nanoparticles has seen a dramatic increase in many applications due to the purity of the colors emitting from the dots as well as their tunability to meet desired optical properties.
Carbon dots, a type of fluorescent nanoparticles, have seen an increase in interest from researchers as a candidate to replace non-carbon dots, the construction of which requires heavy metals that are toxic to the environment. Since they are made up of mostly carbon, the low toxicity is an extremely attractive quality when coupled with the tunability of their inherent optical properties.
Another striking feature of carbon dots is their capability to emit multiple wavelengths of light from a single nanoparticle. This multi-wavelength emission can be stimulated under a single excitation source, enabling the simple and robust generation of white light from a single particle by emitting multiple wavelengths simultaneously.
Carbon dots also exhibit a concentration-dependent photoluminescence. In other words, the distance between individual carbon dots affects the light that the carbon dots subsequently emit under an excitation source. These combined properties make carbon dots a unique source that will result in extremely accurate detection and sensing.
This concentration-dependency, however, had not been fully understood. In order to fully utilize the capabilities of carbon dots, the mechanisms that govern the seemingly variable optical properties must first be uncovered. It was previously theorized that the concentration-dependency of carbon dots was due to a hydrogen bonding effect.
Now, a KAIST research team, led by Professor Do Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has posited and demonstrated that the dual-color-emissiveness is instead due to the interparticle distances between each carbon dot. This study was made available online in June 2020 ahead of final publication in the 36th Issue of Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics on September 28, 2020.
First author of the paper, PhD candidate Hyo Jeong Yoo, along with Professor Kim and researcher Byeong Eun Kwak, examined how the relative light intensity of the red and blue colors changed when varying the interparticle distances, or concentration, of the carbon dots. They found that as the concentration was adjusted, the light emitted from the carbon dots would transform. By varying the concentration, the team was able to control the relative intensity of the colors, as well as emit them simultaneously to generate a white light from a single source (See Figure).
“The concentration-dependence of the photoluminescence of carbon dots on the change of the emissive origins for different interparticle distances has been overlooked in previous research. With the analysis of the dual-color-emission phenomenon of carbon dots, we believe that this result may provide a new perspective to investigate their photoluminescence mechanism,” Yoo explained.
The newly analyzed ability to control the photoluminescence of carbon dots will likely be heavily utilized in the continued development of solid-state lighting applications and sensing.
Publication:
Yoo, H. J., Kwak, B. E., and Kim. D. H. (2020) Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Issue 36, Pages 20227-20237. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02120b
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dokim@kaist.ac.kr
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.23 View 11940
Researchers Control Multiple Wavelengths of Light from a Single Source
KAIST researchers have synthesized a collection of nanoparticles, known as carbon dots, capable of emitting multiple wavelengths of light from a single particle. Additionally, the team discovered that the dispersion of the carbon dots, or the interparticle distance between each dot, influences the properties of the light the carbon dots emit. The discovery will allow researchers to understand how to control these carbon dots and create new, environmentally responsible displays, lighting, and sensing technology.
Research into nanoparticles capable of emitting light, such as quantum dots, has been an active area of interest for the last decade and a half. These particles, or phosphors, are nanoparticles made out of various materials that are capable of emitting light at specific wavelengths by leveraging quantum mechanical properties of the materials. This provides new ways to develop lighting and display solutions as well as more precise detection and sensing in instruments.
As technology becomes smaller and more sophisticated, the usage of fluorescent nanoparticles has seen a dramatic increase in many applications due to the purity of the colors emitting from the dots as well as their tunability to meet desired optical properties.
Carbon dots, a type of fluorescent nanoparticles, have seen an increase in interest from researchers as a candidate to replace non-carbon dots, the construction of which requires heavy metals that are toxic to the environment. Since they are made up of mostly carbon, the low toxicity is an extremely attractive quality when coupled with the tunability of their inherent optical properties.
Another striking feature of carbon dots is their capability to emit multiple wavelengths of light from a single nanoparticle. This multi-wavelength emission can be stimulated under a single excitation source, enabling the simple and robust generation of white light from a single particle by emitting multiple wavelengths simultaneously.
Carbon dots also exhibit a concentration-dependent photoluminescence. In other words, the distance between individual carbon dots affects the light that the carbon dots subsequently emit under an excitation source. These combined properties make carbon dots a unique source that will result in extremely accurate detection and sensing.
This concentration-dependency, however, had not been fully understood. In order to fully utilize the capabilities of carbon dots, the mechanisms that govern the seemingly variable optical properties must first be uncovered. It was previously theorized that the concentration-dependency of carbon dots was due to a hydrogen bonding effect.
Now, a KAIST research team, led by Professor Do Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has posited and demonstrated that the dual-color-emissiveness is instead due to the interparticle distances between each carbon dot. This study was made available online in June 2020 ahead of final publication in the 36th Issue of Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics on September 28, 2020.
First author of the paper, PhD candidate Hyo Jeong Yoo, along with Professor Kim and researcher Byeong Eun Kwak, examined how the relative light intensity of the red and blue colors changed when varying the interparticle distances, or concentration, of the carbon dots. They found that as the concentration was adjusted, the light emitted from the carbon dots would transform. By varying the concentration, the team was able to control the relative intensity of the colors, as well as emit them simultaneously to generate a white light from a single source (See Figure).
“The concentration-dependence of the photoluminescence of carbon dots on the change of the emissive origins for different interparticle distances has been overlooked in previous research. With the analysis of the dual-color-emission phenomenon of carbon dots, we believe that this result may provide a new perspective to investigate their photoluminescence mechanism,” Yoo explained.
The newly analyzed ability to control the photoluminescence of carbon dots will likely be heavily utilized in the continued development of solid-state lighting applications and sensing.
Publication:
Yoo, H. J., Kwak, B. E., and Kim. D. H. (2020) Interparticle distance as a key factor for controlling the dual-emission properties of carbon dots. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, Issue 36, Pages 20227-20237. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/d0cp02120b
Profile:
Do Hyun Kim, Sc.D.
Professor
dokim@kaist.ac.kr
http://procal.kaist.ac.kr/
Process Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.23 View 11940 -
 A New Strategy for Early Evaluations of CO2 Utilization Technologies
- A three-step evaluation procedure based on technology readiness levels helps find the most efficient technology before allocating R&D manpower and investments in CO2 utilization technologies. -
Researchers presented a unified framework for early-stage evaluations of a variety of emerging CO2 utilization (CU) technologies. The three-step procedure allows a large number of potential CU technologies to be screened in order to identify the most promising ones, including those at low level of technical maturity, before allocating R&D manpower and investments.
When evaluating new technology, various aspects of the new technology should be considered. Its feasibility, efficiency, economic competitiveness, and environmental friendliness are crucial, and its level of technical maturity is also an important component for further consideration. However, most technology evaluation procedures are data-driven, and the amount of reliable data in the early stages of technology development has been often limited.
A research team led by Professor Jay Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST proposed a new procedure for evaluating the early development stages of emerging CU technologies which are applicable at various technology readiness levels (TRLs).
The procedure obtains performance indicators via primary data preparation, secondary data calculation, and performance indicator calculation, and the lead author of the study Dr. Kosan Roh and his colleagues presented a number of databases, methods, and computer-aided tools that can effectively facilitate the procedure.
The research team demonstrated the procedure through four case studies involving novel CU technologies of different types and at various TRLs. They confirmed the electrochemical CO2 reduction for the production of ten chemicals, the co-electrolysis of CO2 and water for ethylene production, the direct oxidation of CO2 -based methanol for oxymethylene dimethyl production, and the microalgal biomass co-firing for power generation.
The expected range of the performance indicators for low TRL technologies is broader than that for high TRL technologies, however, it is not the case for high TRL technologies as they are already at an optimized state. The research team believes that low TRL technologies will be significantly improved through future R&D until they are commercialized. “We plan to develop a systematic approach for such a comparison to help avoid misguided decision-making,” Professor Lee explained.
Professor Lee added, “This procedure allows us to conduct a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of new technology. On top of that, it helps make efficient and reliable assessment possible.”
The research team collaborated with Professor Alexander Mitsos, Professor André Bardow, and Professor Matthias Wessling at RWTH Aachen University in Germany. Their findings were reported in Green Chemistry on May 21. This work was supported by the Korea Carbon Capture and Sequestration R&D Center (KCRC).
Publications:
Roh, K., et al. (2020) ‘Early-stage evaluation of emerging CO2 utilization technologies at low technology readiness levels’ Green Chemistry. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc04440j
Profile: Jay Hyung Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
jayhlee@kaist.ac.kr
http://lense.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy System Engineering (LENSE)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.22 View 11680
A New Strategy for Early Evaluations of CO2 Utilization Technologies
- A three-step evaluation procedure based on technology readiness levels helps find the most efficient technology before allocating R&D manpower and investments in CO2 utilization technologies. -
Researchers presented a unified framework for early-stage evaluations of a variety of emerging CO2 utilization (CU) technologies. The three-step procedure allows a large number of potential CU technologies to be screened in order to identify the most promising ones, including those at low level of technical maturity, before allocating R&D manpower and investments.
When evaluating new technology, various aspects of the new technology should be considered. Its feasibility, efficiency, economic competitiveness, and environmental friendliness are crucial, and its level of technical maturity is also an important component for further consideration. However, most technology evaluation procedures are data-driven, and the amount of reliable data in the early stages of technology development has been often limited.
A research team led by Professor Jay Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST proposed a new procedure for evaluating the early development stages of emerging CU technologies which are applicable at various technology readiness levels (TRLs).
The procedure obtains performance indicators via primary data preparation, secondary data calculation, and performance indicator calculation, and the lead author of the study Dr. Kosan Roh and his colleagues presented a number of databases, methods, and computer-aided tools that can effectively facilitate the procedure.
The research team demonstrated the procedure through four case studies involving novel CU technologies of different types and at various TRLs. They confirmed the electrochemical CO2 reduction for the production of ten chemicals, the co-electrolysis of CO2 and water for ethylene production, the direct oxidation of CO2 -based methanol for oxymethylene dimethyl production, and the microalgal biomass co-firing for power generation.
The expected range of the performance indicators for low TRL technologies is broader than that for high TRL technologies, however, it is not the case for high TRL technologies as they are already at an optimized state. The research team believes that low TRL technologies will be significantly improved through future R&D until they are commercialized. “We plan to develop a systematic approach for such a comparison to help avoid misguided decision-making,” Professor Lee explained.
Professor Lee added, “This procedure allows us to conduct a comprehensive and systematic evaluation of new technology. On top of that, it helps make efficient and reliable assessment possible.”
The research team collaborated with Professor Alexander Mitsos, Professor André Bardow, and Professor Matthias Wessling at RWTH Aachen University in Germany. Their findings were reported in Green Chemistry on May 21. This work was supported by the Korea Carbon Capture and Sequestration R&D Center (KCRC).
Publications:
Roh, K., et al. (2020) ‘Early-stage evaluation of emerging CO2 utilization technologies at low technology readiness levels’ Green Chemistry. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1039/c9gc04440j
Profile: Jay Hyung Lee, Ph.D.
Professor
jayhlee@kaist.ac.kr
http://lense.kaist.ac.kr/
Laboratory for Energy System Engineering (LENSE)
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.22 View 11680 -
 Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8513
Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 8513 -
 Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 8792
Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 8792