Graduate+School+of+Culture+Technology
-
 Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center Opens
Distinguished visiting scholar soprano Sumi Jo gave a special lecture on May 13 at the KAIST auditorium. During the lecture, she talked about new technologies that will be introduced for future performing art stages while sharing some of the challenges she experienced before reaching to the stardom of the world stage. She also joined the KAIST student choral club ‘Chorus’ to perform the KAIST school song.
Professor Jo also opened the Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center on the same day along with President Kwang Hyung Lee and faculty members from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. The center will conduct AI and metaverse-based performing art technologies such as performer modeling via AI playing and motion creation, interactions between virtual and human players via sound analysis and motion recognition, as well as virtual stage and performing center modeling. The center will also carry out extensive stage production research applied to media convergence technologies.
Professor Juhan Nam, who heads the research center, said that the center is seeking collaborations with other universities such as Seoul National University and the Korea National University of Arts as well as top performing artists at home and abroad. He looks forward to the center growing into a collaborative center for future performing arts.
Professor Jo added that she will spare no effort to offer her experience and advice for the center’s future-forward performing arts research projects.
2022.05.16 View 8347
Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center Opens
Distinguished visiting scholar soprano Sumi Jo gave a special lecture on May 13 at the KAIST auditorium. During the lecture, she talked about new technologies that will be introduced for future performing art stages while sharing some of the challenges she experienced before reaching to the stardom of the world stage. She also joined the KAIST student choral club ‘Chorus’ to perform the KAIST school song.
Professor Jo also opened the Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center on the same day along with President Kwang Hyung Lee and faculty members from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. The center will conduct AI and metaverse-based performing art technologies such as performer modeling via AI playing and motion creation, interactions between virtual and human players via sound analysis and motion recognition, as well as virtual stage and performing center modeling. The center will also carry out extensive stage production research applied to media convergence technologies.
Professor Juhan Nam, who heads the research center, said that the center is seeking collaborations with other universities such as Seoul National University and the Korea National University of Arts as well as top performing artists at home and abroad. He looks forward to the center growing into a collaborative center for future performing arts.
Professor Jo added that she will spare no effort to offer her experience and advice for the center’s future-forward performing arts research projects.
2022.05.16 View 8347 -
 Study Finds Player-Character Relationships Affected Game Satisfaction in the Last of Us Part II
Research analyzed player experiences with a polarizing game and found differences in how the players related to their characters
The action adventure game ‘The Last of Us’ was a big hit worldwide in 2014. However, its sequel, the Last of Us Part II divided opinions in the game community when it was released in 2020.
A research team from the Games and Life Lab in the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST analyzed why the game players’ reviews were so polarized and found that player-character relationships influenced the game players’ satisfaction. This study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, will help developers of character-driven games foresee how different players will react to their games.
The team under Professor Young Yim Doh conducted in-depth interviews with 12 players from diverse nations, both those satisfied and dissatisfied with the game.
The team found that three elements affected the game players’ satisfaction. First, players’ satisfaction varied according to their tolerance of forced character switches. When a player is forced to switch their controlled figure in the game to another character that is introduced as the antagonist, most players initially had a negative reaction. The feeling of being forced to play in a way they didn’t want reduced their rights as a player. However, later on, some players viewed this character switch as an interesting transition and were more tolerant toward forced game play.
Second, the researchers found that the flexibility of character attachment is related to game satisfaction. Players who were unhappy about the game resisted building a relationship with the new antagonist character. Meanwhile, players who were happy about the game slowly formed an additional relationship with the new character. This led to the player feeling conflicting emotions, which satisfied players considered a meaningful experience of understanding a perspective of someone initially considered the enemy.
Lastly, the satisfaction of the play depended on how much the players could accept a changing character image in the game. Dissatisfied players found inconsistencies in the characters’ behavior and did not accept the new information about the characters. Meanwhile, satisfied players tried to understand and accept the new information and actions.
“Previous research on narrative games focused more on the game design than on the players’ experiences. To understand why reactions to the game were very different across players, we focused our research on differences in the players’ psychological experiences with the game.” said lead author and Master’s candidate Valérie Erb.
Co-author Dr. Seyeon Lee added, “This suggests that there is no one way to satisfy all players in a character-based narrative game. To satisfy a game’s players, it is important to understand the different players in the player base, target the right player group, and manage expectations accordingly.”
This research was supported by the Year 2020 Culture Technology R&D Program by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism and the Korea Creative Content Agency.
-PublicationErb V, Lee S, and Doh YY (2021) “Player-Character Relationship and Game Satisfaction in Narrative Game: Focus on Player Experience of Character Switch in The Last of Us Part II”
Frontiers in Psychology. 12:709926. (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.709926)
-ProfileProfessor Young Yim DohGames and Life LabGraduate School of Culture TechnologyKAIST
2021.11.15 View 7340
Study Finds Player-Character Relationships Affected Game Satisfaction in the Last of Us Part II
Research analyzed player experiences with a polarizing game and found differences in how the players related to their characters
The action adventure game ‘The Last of Us’ was a big hit worldwide in 2014. However, its sequel, the Last of Us Part II divided opinions in the game community when it was released in 2020.
A research team from the Games and Life Lab in the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST analyzed why the game players’ reviews were so polarized and found that player-character relationships influenced the game players’ satisfaction. This study, published in Frontiers in Psychology, will help developers of character-driven games foresee how different players will react to their games.
The team under Professor Young Yim Doh conducted in-depth interviews with 12 players from diverse nations, both those satisfied and dissatisfied with the game.
The team found that three elements affected the game players’ satisfaction. First, players’ satisfaction varied according to their tolerance of forced character switches. When a player is forced to switch their controlled figure in the game to another character that is introduced as the antagonist, most players initially had a negative reaction. The feeling of being forced to play in a way they didn’t want reduced their rights as a player. However, later on, some players viewed this character switch as an interesting transition and were more tolerant toward forced game play.
Second, the researchers found that the flexibility of character attachment is related to game satisfaction. Players who were unhappy about the game resisted building a relationship with the new antagonist character. Meanwhile, players who were happy about the game slowly formed an additional relationship with the new character. This led to the player feeling conflicting emotions, which satisfied players considered a meaningful experience of understanding a perspective of someone initially considered the enemy.
Lastly, the satisfaction of the play depended on how much the players could accept a changing character image in the game. Dissatisfied players found inconsistencies in the characters’ behavior and did not accept the new information about the characters. Meanwhile, satisfied players tried to understand and accept the new information and actions.
“Previous research on narrative games focused more on the game design than on the players’ experiences. To understand why reactions to the game were very different across players, we focused our research on differences in the players’ psychological experiences with the game.” said lead author and Master’s candidate Valérie Erb.
Co-author Dr. Seyeon Lee added, “This suggests that there is no one way to satisfy all players in a character-based narrative game. To satisfy a game’s players, it is important to understand the different players in the player base, target the right player group, and manage expectations accordingly.”
This research was supported by the Year 2020 Culture Technology R&D Program by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism and the Korea Creative Content Agency.
-PublicationErb V, Lee S, and Doh YY (2021) “Player-Character Relationship and Game Satisfaction in Narrative Game: Focus on Player Experience of Character Switch in The Last of Us Part II”
Frontiers in Psychology. 12:709926. (https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.709926)
-ProfileProfessor Young Yim DohGames and Life LabGraduate School of Culture TechnologyKAIST
2021.11.15 View 7340 -
 Diva Sumi Jo to Join the KAIST Faculty
Visiting Distinguished Professor Jo will enrich KAIST’s scholarship and inspire futuristic art and technology research
Soprano Sumi Jo will join the KAIST faculty from the spring 2022 semester. Named as a visiting distinguished professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology, she will give special leadership lectures. Her tenure will be through September 2024.
Jo joined the appointment ceremony held online at KAIST on October 14 from Portugal and expressed her high expectations for teaching KAIST students from next year. “I am very grateful for this opportunity to meet students at KAIST, the birthplace of advanced science and technology in Korea,” she said.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, who has stressed the importance of humanities and the arts in convergence studies of science and technology, lauded her joining the faculty as a big asset who will enrich KAIST’s scholarship. “Soprano Sumi Jo rose to stardom on the global music stage with her unrivaled talent and effort. I truly believe her experience and passion will inspire our students to expand their horizon of thought and knowledge,” said President Lee.
Distinguished Professor Jo will also participate in convergence research at the Graduate School of Culture Technology with KAIST professors and many other experts. The Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center at the Graduate School of Culture Technology will conduct research on the converging of imaging and audio processing technologies that will enhance virtual artists’ performances. Distinguished Professor Jo explained, “The world is changing so fast. I look forward to working on culture technology research at KAIST that will raise our life quality.”
Professor Juhan Nam from the Graduate School of Culture Technology said, “We look forward to working closely with her and her team to develop research themes that envision futuristic art combined with technology such as the metaverse and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Coloratura soprano Jo was born in Seoul and educated at Seoul National University and the Conservatorio Santa Cecilia in Italy. Among her teachers were Carolo Bergonzi and Giasnnelas Borelli. Following her graduation from the Conservatorio Santa Cecilia in 1985, she swept major international competitions in Seoul and Europe. In 1986, she was unanimously awarded the first prize in the Carlo Alberto Cappelli International Competition in Verona which is open only to the first-prize winners of major competitions.
Since her debut in the role of Gilda in Verdi’s Rigolleto in Italy in 1986, she has performed on the world's biggest stages along with noted maestros such as Herbert von Karajan, Georg Solti, Zubin Mehta, and James Levine. Distinguished Professor Jo, one of the most sought-after sopranos in the world, released more than 40 albums.
2021.10.15 View 6962
Diva Sumi Jo to Join the KAIST Faculty
Visiting Distinguished Professor Jo will enrich KAIST’s scholarship and inspire futuristic art and technology research
Soprano Sumi Jo will join the KAIST faculty from the spring 2022 semester. Named as a visiting distinguished professor in the Graduate School of Culture Technology, she will give special leadership lectures. Her tenure will be through September 2024.
Jo joined the appointment ceremony held online at KAIST on October 14 from Portugal and expressed her high expectations for teaching KAIST students from next year. “I am very grateful for this opportunity to meet students at KAIST, the birthplace of advanced science and technology in Korea,” she said.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee, who has stressed the importance of humanities and the arts in convergence studies of science and technology, lauded her joining the faculty as a big asset who will enrich KAIST’s scholarship. “Soprano Sumi Jo rose to stardom on the global music stage with her unrivaled talent and effort. I truly believe her experience and passion will inspire our students to expand their horizon of thought and knowledge,” said President Lee.
Distinguished Professor Jo will also participate in convergence research at the Graduate School of Culture Technology with KAIST professors and many other experts. The Sumi Jo Performing Arts Research Center at the Graduate School of Culture Technology will conduct research on the converging of imaging and audio processing technologies that will enhance virtual artists’ performances. Distinguished Professor Jo explained, “The world is changing so fast. I look forward to working on culture technology research at KAIST that will raise our life quality.”
Professor Juhan Nam from the Graduate School of Culture Technology said, “We look forward to working closely with her and her team to develop research themes that envision futuristic art combined with technology such as the metaverse and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Coloratura soprano Jo was born in Seoul and educated at Seoul National University and the Conservatorio Santa Cecilia in Italy. Among her teachers were Carolo Bergonzi and Giasnnelas Borelli. Following her graduation from the Conservatorio Santa Cecilia in 1985, she swept major international competitions in Seoul and Europe. In 1986, she was unanimously awarded the first prize in the Carlo Alberto Cappelli International Competition in Verona which is open only to the first-prize winners of major competitions.
Since her debut in the role of Gilda in Verdi’s Rigolleto in Italy in 1986, she has performed on the world's biggest stages along with noted maestros such as Herbert von Karajan, Georg Solti, Zubin Mehta, and James Levine. Distinguished Professor Jo, one of the most sought-after sopranos in the world, released more than 40 albums.
2021.10.15 View 6962 -
 KAIST-SM Entertainment Joint Research for Metaverse
“Culture scientist will play a role in the future of the entertainment industry”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee and SM Entertainment Founder and Chief Executive Producer Soo-Man Lee signed an MOU on joint research of the metaverse on June 23 at the Daejeon campus. SM Entertainment is the powerhouse of K-pop and Lee is a pioneering figure who helped Korean pop culture emerge into a global phenomenon.
The KAIST-SM metaverse partnership will bring out new culture technology that will lead the virtual entertainment industry by creating more dynamic and vivid digital technologies. KAIST will utilize its AI, robot, and network technologies, while SM will provide its content production expertise for this metaverse research.
President Lee said, “SM artists have mesmerized global audiences and opened new markets for K-Pop. Combining the creativity and cultural imagination of SM with technologies from KAIST, together we will make significant contributions to the advancement of virtual reality as well as the global entertainment industry.”
The Graduate School of Culture Technology has been engaging in a variety of creative projects incorporating science and technology for decades and will now actively participate in this metaverse project with SM.
CEP Lee explained, “The power of celebrities and avatars will rule the future entertainment industry. SM will make a leap forward to be a ‘first mover’ in the digital entertainment industry with this partnership with KAIST. This partnership will shape the new digital future of the entertainment industry boosted by cutting-edge technologies.”
CEP Lee also delivered a special lecture for the KAIST community via Zoom. Saying that producers in the future will be ‘culture scientists’, he stressed the importance of technology converging with culture.
“The key factor for K-pop’s success lies in the impressive technology of Korea. SM places a high priority on developing cultural technology and creating new artists and products combining this technology,” added Lee, citing the hologram contents of Beyond Live concerts and the new 4+4 girl group composed of four girls and four avatars called ‘Aespa.’
2021.06.25 View 9019
KAIST-SM Entertainment Joint Research for Metaverse
“Culture scientist will play a role in the future of the entertainment industry”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee and SM Entertainment Founder and Chief Executive Producer Soo-Man Lee signed an MOU on joint research of the metaverse on June 23 at the Daejeon campus. SM Entertainment is the powerhouse of K-pop and Lee is a pioneering figure who helped Korean pop culture emerge into a global phenomenon.
The KAIST-SM metaverse partnership will bring out new culture technology that will lead the virtual entertainment industry by creating more dynamic and vivid digital technologies. KAIST will utilize its AI, robot, and network technologies, while SM will provide its content production expertise for this metaverse research.
President Lee said, “SM artists have mesmerized global audiences and opened new markets for K-Pop. Combining the creativity and cultural imagination of SM with technologies from KAIST, together we will make significant contributions to the advancement of virtual reality as well as the global entertainment industry.”
The Graduate School of Culture Technology has been engaging in a variety of creative projects incorporating science and technology for decades and will now actively participate in this metaverse project with SM.
CEP Lee explained, “The power of celebrities and avatars will rule the future entertainment industry. SM will make a leap forward to be a ‘first mover’ in the digital entertainment industry with this partnership with KAIST. This partnership will shape the new digital future of the entertainment industry boosted by cutting-edge technologies.”
CEP Lee also delivered a special lecture for the KAIST community via Zoom. Saying that producers in the future will be ‘culture scientists’, he stressed the importance of technology converging with culture.
“The key factor for K-pop’s success lies in the impressive technology of Korea. SM places a high priority on developing cultural technology and creating new artists and products combining this technology,” added Lee, citing the hologram contents of Beyond Live concerts and the new 4+4 girl group composed of four girls and four avatars called ‘Aespa.’
2021.06.25 View 9019 -
 ‘Game&Art: Auguries of Fantasy’ Features Future of the Metaverse
‘Game & Art: Auguries of Fantasy,’ a special exhibition combining art and technology will feature the new future of metaverse fantasy. The show will be hosted at the Daejeon Creative Center at the Daejeon Museum of Art through September 5.
This show exhibits a combination of science and technology with culture and arts, and introduces young artists whose creativity will lead to new opportunities in games and art. The Graduate School of Culture Technology was designated as a leading culture content academy in 2020 by the Ministry of Culture, Sports & Tourism and the Korea Creative Content Agency for fostering the R&D workforce in creative culture technology.
NCsoft sponsored the show and also participated as an artist. It combined its game-composing elements and technologies with other genres, including data for game construction, scenarios for forming a worldview, and game art and sound. All of the contents can be experienced online in a virtual space as well as offline, and can be easily accessed through personal devices.
Characterized by the themes ‘timeless’ and ‘spaceless’ which connect the past, present, and future, and space created in the digital world. The exhibition gives audience members an opportunity to experience freedom beyond the constraints of time and space under the theme of a fantasy reality created by games and art.
"Computer games, which began in the 1980s, have become cultural content that spans generations, and games are now the fusion field for leading-edge technologies including computer graphics, sound, human-computer interactions, big data, and AI. They are also the best platform for artistic creativity by adding human imagination to technology," said Professor Joo-Han Nam from the Graduate School of Culture Technology, who led the project.
"Our artists wanted to convey various messages to our society through works that connect the past, present, and future through games."
Ju-young Oh's "Unexpected Scenery V2" and "Hope for Rats V2" display game-type media work that raises issues surrounding technology, such as the lack of understanding behind various scientific achievements, the history of accidental achievements, and the side effects of new conveniences.
Tae-Wan Kim, in his work themed ‘healing’ combined the real-time movement of particles which follows the movements of people recorded as digital data. Metadata is collected by sensors in the exhibition space, and floating particle forms are evolved into abstract graphic designs according to audio-visual responses.
Meanwhile, ‘SOS’ is a collaboration work from six KAIST researchers (In-Hwa Yeom, Seung-Eon Lee, Seong-Jin Jeon, Jin-Seok Hong, Hyung-Seok Yoon, and Sang-Min Lee). SOS is based on diverse perspectives embracing phenomena surrounding contemporary natural resources. Audience members follow a gamified path between the various media-elements composing the art’s environment. Through this process, the audience can experience various emotions such as curiosity, suspicion, and recovery.
‘Diversity’ by Sung-Hyun Kim uses devices that recognize the movements of hands and fingers to provide experiences exploring the latent space of game play images learned by deep neural networks. Image volumes generated by neural networks are visualized through physics-based, three-dimensional, volume-rendering algorithms, and a series of processes were implemented based on the self-written code.
2021.06.21 View 11778
‘Game&Art: Auguries of Fantasy’ Features Future of the Metaverse
‘Game & Art: Auguries of Fantasy,’ a special exhibition combining art and technology will feature the new future of metaverse fantasy. The show will be hosted at the Daejeon Creative Center at the Daejeon Museum of Art through September 5.
This show exhibits a combination of science and technology with culture and arts, and introduces young artists whose creativity will lead to new opportunities in games and art. The Graduate School of Culture Technology was designated as a leading culture content academy in 2020 by the Ministry of Culture, Sports & Tourism and the Korea Creative Content Agency for fostering the R&D workforce in creative culture technology.
NCsoft sponsored the show and also participated as an artist. It combined its game-composing elements and technologies with other genres, including data for game construction, scenarios for forming a worldview, and game art and sound. All of the contents can be experienced online in a virtual space as well as offline, and can be easily accessed through personal devices.
Characterized by the themes ‘timeless’ and ‘spaceless’ which connect the past, present, and future, and space created in the digital world. The exhibition gives audience members an opportunity to experience freedom beyond the constraints of time and space under the theme of a fantasy reality created by games and art.
"Computer games, which began in the 1980s, have become cultural content that spans generations, and games are now the fusion field for leading-edge technologies including computer graphics, sound, human-computer interactions, big data, and AI. They are also the best platform for artistic creativity by adding human imagination to technology," said Professor Joo-Han Nam from the Graduate School of Culture Technology, who led the project.
"Our artists wanted to convey various messages to our society through works that connect the past, present, and future through games."
Ju-young Oh's "Unexpected Scenery V2" and "Hope for Rats V2" display game-type media work that raises issues surrounding technology, such as the lack of understanding behind various scientific achievements, the history of accidental achievements, and the side effects of new conveniences.
Tae-Wan Kim, in his work themed ‘healing’ combined the real-time movement of particles which follows the movements of people recorded as digital data. Metadata is collected by sensors in the exhibition space, and floating particle forms are evolved into abstract graphic designs according to audio-visual responses.
Meanwhile, ‘SOS’ is a collaboration work from six KAIST researchers (In-Hwa Yeom, Seung-Eon Lee, Seong-Jin Jeon, Jin-Seok Hong, Hyung-Seok Yoon, and Sang-Min Lee). SOS is based on diverse perspectives embracing phenomena surrounding contemporary natural resources. Audience members follow a gamified path between the various media-elements composing the art’s environment. Through this process, the audience can experience various emotions such as curiosity, suspicion, and recovery.
‘Diversity’ by Sung-Hyun Kim uses devices that recognize the movements of hands and fingers to provide experiences exploring the latent space of game play images learned by deep neural networks. Image volumes generated by neural networks are visualized through physics-based, three-dimensional, volume-rendering algorithms, and a series of processes were implemented based on the self-written code.
2021.06.21 View 11778 -
 Play Games With No Latency
One of the most challenging issues for game players looks to be resolved soon with the introduction of a zero-latency gaming environment. A KAIST team developed a technology that helps game players maintain zero-latency performance. The new technology transforms the shapes of game design according to the amount of latency.
Latency in human-computer interactions is often caused by various factors related to the environment and performance of the devices, networks, and data processing. The term ‘lag’ is used to refer to any latency during gaming which impacts the user’s performance.
Professor Byungjoo Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology in collaboration with Aalto University in Finland presented a mathematical model for predicting players' behavior by understanding the effects of latency on players. This cognitive model is capable of predicting the success rate of a user when there is latency in a 'moving target selection' task which requires button input in a time constrained situation.
The model predicts the players’ task success rate when latency is added to the gaming environment. Using these predicted success rates, the design elements of the game are geometrically modified to help players maintain similar success rates as they would achieve in a zero-latency environment. In fact, this research succeeded in modifying the pillar heights of the Flappy Bird game, allowing the players to maintain their gaming performance regardless of the added latency.
Professor Lee said, "This technique is unique in the sense that it does not interfere with a player's gaming flow, unlike traditional methods which manipulate the game clock by the amount of latency. This study can be extended to various games such as reducing the size of obstacles in the latent computing environment.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University and led by PhD candidate Injung Lee, was presented during the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems last month in Glasgow in the UK.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2017R1C1B2002101, 2018R1A5A7025409), and the Aalto University Seed Funding Granted to the GamerLab respectively.
Figure 1. Overview of Geometric Compensation
Publication:
Injung Lee, Sunjun Kim, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Geometrically Compensating Effect of End-to-End Latency in Moving-Target Selection Games. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) . ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 560, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300790
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/TTi7dipAKJs
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Injung Lee, PhD Candidate
edndn@kaist.ac.kr
PhD Candidate
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Postdoc. Sunjun Kim, MD, PhD
kuaa.net@gmail.com
Postdoctoral Researcher
User Interfaces Group
Aalto University
https://www.aalto.fi Espoo 02150, Finland
(END)
2019.06.11 View 49134
Play Games With No Latency
One of the most challenging issues for game players looks to be resolved soon with the introduction of a zero-latency gaming environment. A KAIST team developed a technology that helps game players maintain zero-latency performance. The new technology transforms the shapes of game design according to the amount of latency.
Latency in human-computer interactions is often caused by various factors related to the environment and performance of the devices, networks, and data processing. The term ‘lag’ is used to refer to any latency during gaming which impacts the user’s performance.
Professor Byungjoo Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology in collaboration with Aalto University in Finland presented a mathematical model for predicting players' behavior by understanding the effects of latency on players. This cognitive model is capable of predicting the success rate of a user when there is latency in a 'moving target selection' task which requires button input in a time constrained situation.
The model predicts the players’ task success rate when latency is added to the gaming environment. Using these predicted success rates, the design elements of the game are geometrically modified to help players maintain similar success rates as they would achieve in a zero-latency environment. In fact, this research succeeded in modifying the pillar heights of the Flappy Bird game, allowing the players to maintain their gaming performance regardless of the added latency.
Professor Lee said, "This technique is unique in the sense that it does not interfere with a player's gaming flow, unlike traditional methods which manipulate the game clock by the amount of latency. This study can be extended to various games such as reducing the size of obstacles in the latent computing environment.”
This research, in collaboration with Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University and led by PhD candidate Injung Lee, was presented during the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems last month in Glasgow in the UK.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) (2017R1C1B2002101, 2018R1A5A7025409), and the Aalto University Seed Funding Granted to the GamerLab respectively.
Figure 1. Overview of Geometric Compensation
Publication:
Injung Lee, Sunjun Kim, and Byungjoo Lee. 2019. Geometrically Compensating Effect of End-to-End Latency in Moving-Target Selection Games. In Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI’19) . ACM, New York, NY, USA, Article 560, 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300790
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/TTi7dipAKJs
Profile: Prof. Byungjoo Lee, MD, PhD
byungjoo.lee@kaist.ac.kr
http://kiml.org/
Assistant Professor
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Injung Lee, PhD Candidate
edndn@kaist.ac.kr
PhD Candidate
Interactive Media Lab
Graduate School of Culture Technology (CT)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Postdoc. Sunjun Kim, MD, PhD
kuaa.net@gmail.com
Postdoctoral Researcher
User Interfaces Group
Aalto University
https://www.aalto.fi Espoo 02150, Finland
(END)
2019.06.11 View 49134 -
 Escalation of Competition Leads to Conflict in Competitive Networks of F1 Drivers
(Professor Wonjae Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology)
A new study has revealed that people with similar social status in similar age groups are more likely to clash with each other. This rivalry could likely lead to taking more risks in fair weather conditions.
Competition, while is often seen as beneficial, can escalate into destructive conflict. This occurs, for instance, when athletes sabotage each other or when rival executives get caught up in a career-derailing fight. These escalations, which lead to conflict, are especially likely among similar-status competitors, who are fraught with discordant understandings of who is superior to whom.
A research team of KAIST, the US Treasury, INSEAD, and the European School of Management and Technology (ESMT) examined the link between status similarity and conflict as well as the conditions under which this link holds by using panel data on Formula 1 races from 1970 through 2014. For the study, the research team analyzed a total of 506 collision cases by 355 F1 drivers over 45 years.
The team found that similar-status F1 drivers are more prone to collide, especially when they are age-similar, performing well, and feeling safe. When these boundary conditions are met, structural equivalence likely triggers antagonism among interactants.
This research deepens the understanding of when violent conflict emerges and when prevention efforts are called for. Professor Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST said, “People are not sure about their identity when facing competitors of a similar status. People tend to confirm their own stature by beating an opponent.”
The team investigated the factors that escalate competition into dangerous conflict. Recently, sociological theorizing claims that such escalations are particularly likely in pairs of structurally equivalent actors who have the same relations with the same third parties. Using the F1 data, the research team modeled the probability that two drivers would collide on a racetrack as a function of their structural equivalence in a dynamic network of competitive relationships.
Professor Lee added, “We fully understand that the drivers who ranked first and second are likely to have more conflict because they meet more frequently and know each other well. We also regulated all those conditions and confirmed that our hypothesis worked right throughout the data analysis.”
Professor Lee, who wrote his doctoral thesis on tennis tournaments for identifying the ideal organizational structure, said that sports tournaments would be best optimized for comprehending the nature of organizational structures. Tournaments, even those with rankings based on objective criteria, are in fact intensely social. However, most prior empirical work in this area has relied only on official information on competitors’ performance, thus failing to capture the important elements of past competitive encounters.
“It is not so easy to obtain data on rivalries and conflicts inside an organization. However, in sports, the performances of athletes are all recorded and the data can be utilized as a very objective methodology for understanding social relations and their structural affects.
Official positions in tournaments, although clearly informative, can also be reductionist –excluding the emotionally salient features of competitors’ histories and forcing competitors together on a scalar metric, even when the competitors themselves do not see each other as comparable.
The results from sample-split models are important for social networking research, which has paid scant attention to the contextual conditions in which structural equivalence is most consequential for social action – especially hostile social actions.
The study suggests that new work will benefit from examining how demographic overlap, network stability, and perceived costs of conflict “activate” a structurally equivalent relationship to the point that it is not only salient but also conducive to conflict.
Professor Lee said, “Sociology mainly investigates the positive results of social success and collaboration. This study shows that any violent activities, including homicide, also have something to do with organizational and social structural equivalence.”
This study was co-led by Professor Matthew Bothner from ESMT in Germany, Professor Henning Piezunk from INSEAD in France, and Dr. Richard Haynes from the US Treasury and was featured at the PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA) in March.
(Figure: Drivers' competitive network and collisions. Nodes are drivers. Nodes enricled in black are labeled by name. Edges denote joint competition in at least one race. Red edges connecting indicate that the two drivers collided at least once. Using Fruchtermna-Reingold, nodes are generally proximte to the extendt that their average structural equivalence (over all races, from 1970 to 2014) is high.)
2018.04.24 View 8129
Escalation of Competition Leads to Conflict in Competitive Networks of F1 Drivers
(Professor Wonjae Lee at the Graduate School of Culture Technology)
A new study has revealed that people with similar social status in similar age groups are more likely to clash with each other. This rivalry could likely lead to taking more risks in fair weather conditions.
Competition, while is often seen as beneficial, can escalate into destructive conflict. This occurs, for instance, when athletes sabotage each other or when rival executives get caught up in a career-derailing fight. These escalations, which lead to conflict, are especially likely among similar-status competitors, who are fraught with discordant understandings of who is superior to whom.
A research team of KAIST, the US Treasury, INSEAD, and the European School of Management and Technology (ESMT) examined the link between status similarity and conflict as well as the conditions under which this link holds by using panel data on Formula 1 races from 1970 through 2014. For the study, the research team analyzed a total of 506 collision cases by 355 F1 drivers over 45 years.
The team found that similar-status F1 drivers are more prone to collide, especially when they are age-similar, performing well, and feeling safe. When these boundary conditions are met, structural equivalence likely triggers antagonism among interactants.
This research deepens the understanding of when violent conflict emerges and when prevention efforts are called for. Professor Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST said, “People are not sure about their identity when facing competitors of a similar status. People tend to confirm their own stature by beating an opponent.”
The team investigated the factors that escalate competition into dangerous conflict. Recently, sociological theorizing claims that such escalations are particularly likely in pairs of structurally equivalent actors who have the same relations with the same third parties. Using the F1 data, the research team modeled the probability that two drivers would collide on a racetrack as a function of their structural equivalence in a dynamic network of competitive relationships.
Professor Lee added, “We fully understand that the drivers who ranked first and second are likely to have more conflict because they meet more frequently and know each other well. We also regulated all those conditions and confirmed that our hypothesis worked right throughout the data analysis.”
Professor Lee, who wrote his doctoral thesis on tennis tournaments for identifying the ideal organizational structure, said that sports tournaments would be best optimized for comprehending the nature of organizational structures. Tournaments, even those with rankings based on objective criteria, are in fact intensely social. However, most prior empirical work in this area has relied only on official information on competitors’ performance, thus failing to capture the important elements of past competitive encounters.
“It is not so easy to obtain data on rivalries and conflicts inside an organization. However, in sports, the performances of athletes are all recorded and the data can be utilized as a very objective methodology for understanding social relations and their structural affects.
Official positions in tournaments, although clearly informative, can also be reductionist –excluding the emotionally salient features of competitors’ histories and forcing competitors together on a scalar metric, even when the competitors themselves do not see each other as comparable.
The results from sample-split models are important for social networking research, which has paid scant attention to the contextual conditions in which structural equivalence is most consequential for social action – especially hostile social actions.
The study suggests that new work will benefit from examining how demographic overlap, network stability, and perceived costs of conflict “activate” a structurally equivalent relationship to the point that it is not only salient but also conducive to conflict.
Professor Lee said, “Sociology mainly investigates the positive results of social success and collaboration. This study shows that any violent activities, including homicide, also have something to do with organizational and social structural equivalence.”
This study was co-led by Professor Matthew Bothner from ESMT in Germany, Professor Henning Piezunk from INSEAD in France, and Dr. Richard Haynes from the US Treasury and was featured at the PNAS (Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA) in March.
(Figure: Drivers' competitive network and collisions. Nodes are drivers. Nodes enricled in black are labeled by name. Edges denote joint competition in at least one race. Red edges connecting indicate that the two drivers collided at least once. Using Fruchtermna-Reingold, nodes are generally proximte to the extendt that their average structural equivalence (over all races, from 1970 to 2014) is high.)
2018.04.24 View 8129 -
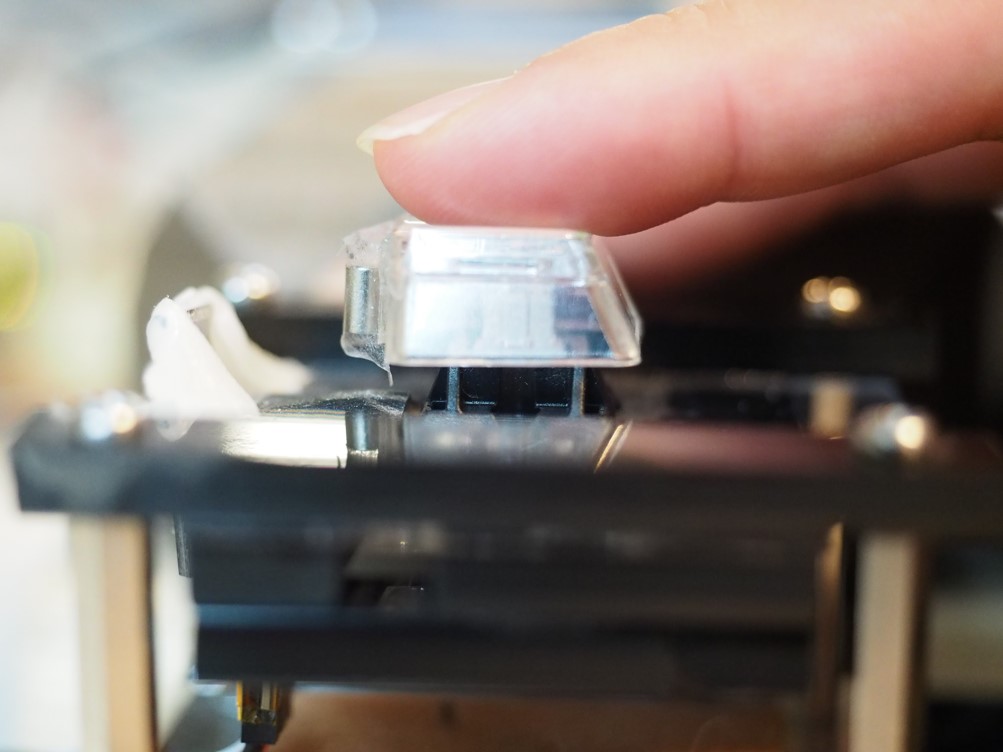 A New Theory Improves Button Designs
Pressing a button appears effortless. People easily dismisses how challenging it is. Researchers at KAIST and Aalto University in Finland, created detailed simulations of button-pressing with the goal of producing human-like presses.
The researchers argue that the key capability of the brain is a probabilistic model. The brain learns a model that allows it to predict a suitable motor command for a button. If a press fails, it can pick a very good alternative and try it out. "Without this ability, we would have to learn to use every button like it was new," tells Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST.
After successfully activating the button, the brain can tune the motor command to be more precise, use less energy and to avoid stress or pain. "These factors together, with practice, produce the fast, minimum-effort, elegant touch people are able to perform."
The brain uses probabilistic models also to extract information optimally from the sensations that arise when the finger moves and its tip touches the button. It "enriches" the ephemeral sensations optimally based on prior experience to estimate the time the button was impacted. For example, tactile sensation from the tip of the finger a better predictor for button activation than proprioception (angle position) and visual feedback.
Best performance is achieved when all sensations are considered together. To adapt, the brain must fuse their information using prior experiences. Professor Lee explains, "We believe that the brain picks up these skills over repeated button pressings that start already as a child. What appears easy for us now has been acquired over years."
The research was triggered by admiration of our remarkable capability to adapt button-pressing. Professor Antti Oulasvirta at Aalto University said, "We push a button on a remote controller differently than a piano key. The press of a skilled user is surprisingly elegant when looked at terms of timing, reliability, and energy use. We successfully press buttons without ever knowing the inner workings of a button. It is essentially a black box to our motor system. On the other hand, we also fail to activate buttons, and some buttons are known to be worse than others."
Previous research has shown that touch buttons are worse than push-buttons, but there has not been adequate theoretical explanation.
"In the past, there has been very little attention to buttons, although we use them all the time" says Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University. The new theory and simulations can be used to design better buttons.
"One exciting implication of the theory is that activating the button at the moment when the sensation is strongest will help users better rhythm their keypresses."
To test this hypothesis, the researchers created a new method for changing the way buttons are activated. The technique is called Impact Activation. Instead of activating the button at first contact, it activates it when the button cap or finger hits the floor with maximum impact.
The technique was 94% better in rapid tapping than the regular activation method for a push-button (Cherry MX switch) and 37% than a regular touchscreen button using a capacitive touch sensor. The technique can be easily deployed in touchscreens. However, regular physical keyboards do not offer the required sensing capability, although special products exist (e.g., the Wooting keyboard) on which it can be implemented.
The simulations shed new light on what happens during a button press. One problem the brain must overcome is that muscles do not activate as perfectly as we will, but every press is slightly different. Moreover, a button press is very fast, occurring within 100 milliseconds, and is too fast for correcting movement. The key to understanding button-pressing is therefore to understand how the brain adapts based on the limited sensations that are the residue of the brief press event.
The researchers also used the simulation to explain differences among physical and touchscreen-based button types. Both physical and touch buttons provide clear tactile signals from the impact of the tip with the button floor. However, with the physical button this signal is more pronounced and longer.
"Where the two button types also differ is the starting height of the finger, and this makes a difference," explains Professor Lee. "When we pull up the finger from the touchscreen, it will end up at different height every time. Its down-press cannot be as accurately controlled in time as with a push-button where the finger can rest on top of the key cap."
Three scientific articles, "Neuromechanics of a Button Press", "Impact activation improves rapid button pressing", and "Moving target selection: A cue integration model", will be presented at the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Montréal, Canada, in April 2018.
2018.03.22 View 8428
A New Theory Improves Button Designs
Pressing a button appears effortless. People easily dismisses how challenging it is. Researchers at KAIST and Aalto University in Finland, created detailed simulations of button-pressing with the goal of producing human-like presses.
The researchers argue that the key capability of the brain is a probabilistic model. The brain learns a model that allows it to predict a suitable motor command for a button. If a press fails, it can pick a very good alternative and try it out. "Without this ability, we would have to learn to use every button like it was new," tells Professor Byungjoo Lee from the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST.
After successfully activating the button, the brain can tune the motor command to be more precise, use less energy and to avoid stress or pain. "These factors together, with practice, produce the fast, minimum-effort, elegant touch people are able to perform."
The brain uses probabilistic models also to extract information optimally from the sensations that arise when the finger moves and its tip touches the button. It "enriches" the ephemeral sensations optimally based on prior experience to estimate the time the button was impacted. For example, tactile sensation from the tip of the finger a better predictor for button activation than proprioception (angle position) and visual feedback.
Best performance is achieved when all sensations are considered together. To adapt, the brain must fuse their information using prior experiences. Professor Lee explains, "We believe that the brain picks up these skills over repeated button pressings that start already as a child. What appears easy for us now has been acquired over years."
The research was triggered by admiration of our remarkable capability to adapt button-pressing. Professor Antti Oulasvirta at Aalto University said, "We push a button on a remote controller differently than a piano key. The press of a skilled user is surprisingly elegant when looked at terms of timing, reliability, and energy use. We successfully press buttons without ever knowing the inner workings of a button. It is essentially a black box to our motor system. On the other hand, we also fail to activate buttons, and some buttons are known to be worse than others."
Previous research has shown that touch buttons are worse than push-buttons, but there has not been adequate theoretical explanation.
"In the past, there has been very little attention to buttons, although we use them all the time" says Dr. Sunjun Kim from Aalto University. The new theory and simulations can be used to design better buttons.
"One exciting implication of the theory is that activating the button at the moment when the sensation is strongest will help users better rhythm their keypresses."
To test this hypothesis, the researchers created a new method for changing the way buttons are activated. The technique is called Impact Activation. Instead of activating the button at first contact, it activates it when the button cap or finger hits the floor with maximum impact.
The technique was 94% better in rapid tapping than the regular activation method for a push-button (Cherry MX switch) and 37% than a regular touchscreen button using a capacitive touch sensor. The technique can be easily deployed in touchscreens. However, regular physical keyboards do not offer the required sensing capability, although special products exist (e.g., the Wooting keyboard) on which it can be implemented.
The simulations shed new light on what happens during a button press. One problem the brain must overcome is that muscles do not activate as perfectly as we will, but every press is slightly different. Moreover, a button press is very fast, occurring within 100 milliseconds, and is too fast for correcting movement. The key to understanding button-pressing is therefore to understand how the brain adapts based on the limited sensations that are the residue of the brief press event.
The researchers also used the simulation to explain differences among physical and touchscreen-based button types. Both physical and touch buttons provide clear tactile signals from the impact of the tip with the button floor. However, with the physical button this signal is more pronounced and longer.
"Where the two button types also differ is the starting height of the finger, and this makes a difference," explains Professor Lee. "When we pull up the finger from the touchscreen, it will end up at different height every time. Its down-press cannot be as accurately controlled in time as with a push-button where the finger can rest on top of the key cap."
Three scientific articles, "Neuromechanics of a Button Press", "Impact activation improves rapid button pressing", and "Moving target selection: A cue integration model", will be presented at the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Montréal, Canada, in April 2018.
2018.03.22 View 8428 -
 Augmented Reality Application for Smart Tour
‘K-Culture Time Machine,’ an augmented and virtual reality application will create a new way to take a tour. Prof. Woon-taek Woo's research team of Graduate School of Culture Technology of KAIST developed AR/VR application for smart tourism.
The 'K-Culture Time Machine' application (iOS App Store app name: KCTM) was launched on iOS App Store in Korea on May 22 as a pilot service that is targetting the Changdeokgung Palace of Seoul.
The application provides remote experience over time and space for cultural heritage or relics thorough wearable 360-degree video. Users can remotely experience cultural heritage sites with 360-degree video provided by installing a smartphone in a smartphone HMD device, and can search information on historical figures, places, and events related to cultural heritage. Also, 3D reconstruction of lost cultural heritage can be experienced.
Without using wearable HMD devices, mobile-based cultural heritage guides can be provided based on the vision-based recognition on the cultural heritages. Through the embedded camera in smartphone, the application can identify the heritages and provide related information and contents of the hertages. For example, in Changdeokgung Palace, a user can move inside the Changdeokgung Palace from Donhwa-Gate (the main gate of the Changdeokgung Palace), Injeong-Jeon(main hall), Injeong-Moon (Main gate of Injeong-Jeon), and to Huijeongdang (rest place for the king). Through the 360 degree panoramic image or video, the user can experience the virtual scene of heritages.
The virtual 3D reconstruction of the seungjeongwon (Royal Secretariat) which does not exist at present can be shown of the east side of the Injeong-Jeon The functions can be experienced on a smartphone without a wearable device, and it would be a commercial application that can be utilized in the field once the augmented reality function which is under development is completed.
Professor Woo and his research team constructed and applied standardized metadata of cultural heritage database and AR/VR contents. Through this standardized metadata, unlike existing applications which are temporarily consumed after development, reusable and interoperable contents can be made.Professor Woo said, "By enhancing the interoperability and reusability of AR contents, we will be able to preoccupy new markets in the field of smart tourism."
The research was conducted through the joint work with Post Media (CEO Hong Seung-mo) in the CT R&D project of the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of Korea. The results of the research will be announced through the HCI International 2017 conference in Canada this July.
Figure 1. 360 degree panorama image / video function screen of 'K-Culture Time Machine'. Smartphone HMD allows users to freely experience various cultural sites remotely.
Figure 2. 'K-Culture Time Machine' mobile augmented reality function screen. By analyzing the location of the user and the screen viewed through the camera, information related to the cultural heritage are provided to enhance the user experience.
Figure 3. The concept of 360-degree panoramic video-based VR service of "K-Culture Time Machine", a wearable application supporting smart tour of the historical sites. Through the smartphone HMD, a user can remotely experience cultural heritage sites and 3D reconstruction of cultural heritage that does not currently exist.
2017.05.30 View 13074
Augmented Reality Application for Smart Tour
‘K-Culture Time Machine,’ an augmented and virtual reality application will create a new way to take a tour. Prof. Woon-taek Woo's research team of Graduate School of Culture Technology of KAIST developed AR/VR application for smart tourism.
The 'K-Culture Time Machine' application (iOS App Store app name: KCTM) was launched on iOS App Store in Korea on May 22 as a pilot service that is targetting the Changdeokgung Palace of Seoul.
The application provides remote experience over time and space for cultural heritage or relics thorough wearable 360-degree video. Users can remotely experience cultural heritage sites with 360-degree video provided by installing a smartphone in a smartphone HMD device, and can search information on historical figures, places, and events related to cultural heritage. Also, 3D reconstruction of lost cultural heritage can be experienced.
Without using wearable HMD devices, mobile-based cultural heritage guides can be provided based on the vision-based recognition on the cultural heritages. Through the embedded camera in smartphone, the application can identify the heritages and provide related information and contents of the hertages. For example, in Changdeokgung Palace, a user can move inside the Changdeokgung Palace from Donhwa-Gate (the main gate of the Changdeokgung Palace), Injeong-Jeon(main hall), Injeong-Moon (Main gate of Injeong-Jeon), and to Huijeongdang (rest place for the king). Through the 360 degree panoramic image or video, the user can experience the virtual scene of heritages.
The virtual 3D reconstruction of the seungjeongwon (Royal Secretariat) which does not exist at present can be shown of the east side of the Injeong-Jeon The functions can be experienced on a smartphone without a wearable device, and it would be a commercial application that can be utilized in the field once the augmented reality function which is under development is completed.
Professor Woo and his research team constructed and applied standardized metadata of cultural heritage database and AR/VR contents. Through this standardized metadata, unlike existing applications which are temporarily consumed after development, reusable and interoperable contents can be made.Professor Woo said, "By enhancing the interoperability and reusability of AR contents, we will be able to preoccupy new markets in the field of smart tourism."
The research was conducted through the joint work with Post Media (CEO Hong Seung-mo) in the CT R&D project of the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of Korea. The results of the research will be announced through the HCI International 2017 conference in Canada this July.
Figure 1. 360 degree panorama image / video function screen of 'K-Culture Time Machine'. Smartphone HMD allows users to freely experience various cultural sites remotely.
Figure 2. 'K-Culture Time Machine' mobile augmented reality function screen. By analyzing the location of the user and the screen viewed through the camera, information related to the cultural heritage are provided to enhance the user experience.
Figure 3. The concept of 360-degree panoramic video-based VR service of "K-Culture Time Machine", a wearable application supporting smart tour of the historical sites. Through the smartphone HMD, a user can remotely experience cultural heritage sites and 3D reconstruction of cultural heritage that does not currently exist.
2017.05.30 View 13074 -
 Open KAIST 2015
KAIST’s research environment and its most recent achievements were open to the public.
KAIST hosted “Open KAIST 2015” over two days from November 5-6, 2015 in which its 17 departments and three research centers were open to the public. The event is one of the largest events that KAIST holds, which permits such public viewings of its facilities. It is the eighth time it has taken place.
During this event, the departments and centers offered 64 programs including laboratory tours, research achievement exhibitions, department introductions, and special lectures.
The “Motion Capture System”of Professor Jun-Yong Noh’s lab (Graduate School of Culture Technology) drew particular attention.
The “Motion Capture System” expresses human and animal motion in three-dimensional (3D) space using infrared cameras and optic markers, which can then be applied to various industries such as movies, games, and animation. During the program, researchers themselves demonstrated the recording of the movement and its conversion into 3D characters.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho’s laboratory introduced the scientific mechanism behind the Light Emitting Diode (LED) as well as its manufacturing process under the topic:“A to Z of LED Production.” The reserachers explained that how green LED is much more efficient compared to previous light sources and presented applications that how it is widely used in everyday life in smart phones, electronic displays, and other mobile gadgets.
Professor Jun-tani of the Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering introduced “Humanoid Robot Nao’s Imitation of Human Motions.” Nao is an autonomous, programmable humanoid robot developed by a French robotics company based in Paris. Nao has an artificial neural circuit, which is the functional equivalent of a human brain, and can thus mimic the subject’s motions through learning.
In addition, Professor Hyo-Choong Bang (Department of Aerospace Engineering) in his lecture on “Unmanned Vehicle Research and Nano Satellites” and Professor Hyun Myung (Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering) on his lecture on “Future Civilization Robot System: the Jellyfish Elimination Robotic Swarm and the Wall-Climbing Drone” provided information on the progress of their respective research.
KAIST also displayed its most recent research achievements. A lecture on “Information Technology Convergence” offered a showroom for “Dr. M,” which is a mobile healthcare platform. Dr. M is a mobile healthcare system that collects and analyzes biosignals via a smart sensor attached to the human body that shows around 20 advanced technologies.
The Satellite Technology Research Center introduced the public to its “Get to Know Satellites” program on Korea’s first satellite “Our Star 1” in addition to showing the satellite assembly room and the satellite communication center.
Special lectures were also held for visitors. Professor Min-Hyuk Kim and Hye-Yeon Oh of the School of Computing talked about “Computer Graphics and Advanced Video Technology” and “Man and the Computer,” respectively, from the perspective of non-experts.
Another interesting feature was the “Wearable Computer Competition” in which college students held fashion shows with computers attached to their clothes.
Professor Jung Kwon Lee, the Dean of the College of Engineering, who led this event, said that “the Open KAIST, which is being held for the eighth time this year, is an excellent opportunity for the general public to experience KAIST’s research environment.” He hoped this could motivate young adults to widen their spectrum of scientific knowledge and raise affection for science.
2015.11.13 View 13493
Open KAIST 2015
KAIST’s research environment and its most recent achievements were open to the public.
KAIST hosted “Open KAIST 2015” over two days from November 5-6, 2015 in which its 17 departments and three research centers were open to the public. The event is one of the largest events that KAIST holds, which permits such public viewings of its facilities. It is the eighth time it has taken place.
During this event, the departments and centers offered 64 programs including laboratory tours, research achievement exhibitions, department introductions, and special lectures.
The “Motion Capture System”of Professor Jun-Yong Noh’s lab (Graduate School of Culture Technology) drew particular attention.
The “Motion Capture System” expresses human and animal motion in three-dimensional (3D) space using infrared cameras and optic markers, which can then be applied to various industries such as movies, games, and animation. During the program, researchers themselves demonstrated the recording of the movement and its conversion into 3D characters.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho’s laboratory introduced the scientific mechanism behind the Light Emitting Diode (LED) as well as its manufacturing process under the topic:“A to Z of LED Production.” The reserachers explained that how green LED is much more efficient compared to previous light sources and presented applications that how it is widely used in everyday life in smart phones, electronic displays, and other mobile gadgets.
Professor Jun-tani of the Department of Electronic and Electrical Engineering introduced “Humanoid Robot Nao’s Imitation of Human Motions.” Nao is an autonomous, programmable humanoid robot developed by a French robotics company based in Paris. Nao has an artificial neural circuit, which is the functional equivalent of a human brain, and can thus mimic the subject’s motions through learning.
In addition, Professor Hyo-Choong Bang (Department of Aerospace Engineering) in his lecture on “Unmanned Vehicle Research and Nano Satellites” and Professor Hyun Myung (Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering) on his lecture on “Future Civilization Robot System: the Jellyfish Elimination Robotic Swarm and the Wall-Climbing Drone” provided information on the progress of their respective research.
KAIST also displayed its most recent research achievements. A lecture on “Information Technology Convergence” offered a showroom for “Dr. M,” which is a mobile healthcare platform. Dr. M is a mobile healthcare system that collects and analyzes biosignals via a smart sensor attached to the human body that shows around 20 advanced technologies.
The Satellite Technology Research Center introduced the public to its “Get to Know Satellites” program on Korea’s first satellite “Our Star 1” in addition to showing the satellite assembly room and the satellite communication center.
Special lectures were also held for visitors. Professor Min-Hyuk Kim and Hye-Yeon Oh of the School of Computing talked about “Computer Graphics and Advanced Video Technology” and “Man and the Computer,” respectively, from the perspective of non-experts.
Another interesting feature was the “Wearable Computer Competition” in which college students held fashion shows with computers attached to their clothes.
Professor Jung Kwon Lee, the Dean of the College of Engineering, who led this event, said that “the Open KAIST, which is being held for the eighth time this year, is an excellent opportunity for the general public to experience KAIST’s research environment.” He hoped this could motivate young adults to widen their spectrum of scientific knowledge and raise affection for science.
2015.11.13 View 13493 -
 KAIST's Graduate School of Culture Technology Celebrates Its Tenth Anniversary
The Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST hosted a ceremony and a variety of events to celebrate its tenth anniversary on October 22, 2015, on campus.
Established in 2005 with the support of the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Korea, GSCT offers an intensive, in-depth education in culture technology, an interdisciplinary field first introduced in Korea by KAIST, which brings arts, humanities, science, and technology together in an academic and research arena.
Over the years, the graduate school has fostered top-notch researchers and professionals who have played a leading role in the development of a Korean culture contents industry that includes movies, broadcasting programs, music, games, and culture events.
After the anniversary ceremony, GSCT held a "Demo Day" to showcase its major research projects. A total of 41 projects were presented under the themes of “Art and Science,” “Human and Humane,” and “Virtual Reality vs Reality.”
In addition, there was a seminar held on GSTC’s ten-year accomplishment and future planning with the school’s Professors Sunghee Lee, Juyong Park, and Juhan Nam; a cultural event for the public called the “Talk Concert,” which included many professionals in culture industry and academia to share ideas and views; and the Homecoming Day for GSTC graduates. So far, the graduate school has produced 295 masters and 34 doctors. About 34% of its graduates are employed in the movie, game, and broadcasting sectors, 33% in the social networking service and Internet industry, and 33% in performing art and exhibition and event.
Dong-Man Lee, the Dean of KAIST's Graduate School of Culture Technology, said,
“We will continue to develop our school to lead the advancement of the Korean culture industry, contributing to the growth of Korean Wave, the popularity of Korean culture, in the global community.”
In the picture below, Dean Lee delivers a speech to celebrate the school’s tenth anniversary.
Soo-Man Lee, the founding chairman of S.M. Entertainment, speaks at the Talk Concert.
Scenes from the Demo Day
2015.10.26 View 9932
KAIST's Graduate School of Culture Technology Celebrates Its Tenth Anniversary
The Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST hosted a ceremony and a variety of events to celebrate its tenth anniversary on October 22, 2015, on campus.
Established in 2005 with the support of the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Korea, GSCT offers an intensive, in-depth education in culture technology, an interdisciplinary field first introduced in Korea by KAIST, which brings arts, humanities, science, and technology together in an academic and research arena.
Over the years, the graduate school has fostered top-notch researchers and professionals who have played a leading role in the development of a Korean culture contents industry that includes movies, broadcasting programs, music, games, and culture events.
After the anniversary ceremony, GSCT held a "Demo Day" to showcase its major research projects. A total of 41 projects were presented under the themes of “Art and Science,” “Human and Humane,” and “Virtual Reality vs Reality.”
In addition, there was a seminar held on GSTC’s ten-year accomplishment and future planning with the school’s Professors Sunghee Lee, Juyong Park, and Juhan Nam; a cultural event for the public called the “Talk Concert,” which included many professionals in culture industry and academia to share ideas and views; and the Homecoming Day for GSTC graduates. So far, the graduate school has produced 295 masters and 34 doctors. About 34% of its graduates are employed in the movie, game, and broadcasting sectors, 33% in the social networking service and Internet industry, and 33% in performing art and exhibition and event.
Dong-Man Lee, the Dean of KAIST's Graduate School of Culture Technology, said,
“We will continue to develop our school to lead the advancement of the Korean culture industry, contributing to the growth of Korean Wave, the popularity of Korean culture, in the global community.”
In the picture below, Dean Lee delivers a speech to celebrate the school’s tenth anniversary.
Soo-Man Lee, the founding chairman of S.M. Entertainment, speaks at the Talk Concert.
Scenes from the Demo Day
2015.10.26 View 9932 -
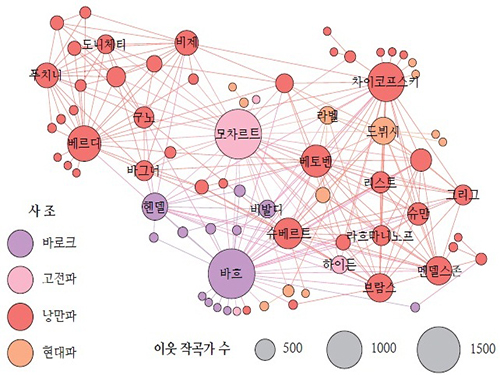 Big Data Reveals the Secret of Classical Music Creation
Professor Juyong Park of the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST and his research team have recently published the result of their study (“Topology and Evolution of the Network of Western Classical Music Composers”) on the dynamics of how classical music is created, stylized, and disseminated in EPJ Data Science online on April 22, 2015. For the press release issued by the journal, please go to the link below:
EPJ Data Science, May 6, 2015
“EPJ Data Science Highlight—Big Data Reveals Classical Music Creation Secrets”
http://www.epj.org/113-epj-ds/941-epjds-highlight-big-data-reveals-classical-music-creation-secrets
Researchers used big-data analysis and modelling technique to examine the complex, undercurrent network of classical music composers, which was constructed from the large volume of compact disc (CD) recordings data collected from an online retailer, ArkivMusic, and a music reference website, AllMusicGuide.
The study discovered that the basic characteristics of composers’ network are similar to many real-world networks, including the small-world property, the existence of a giant component, high clustering, and heavy-tailed degree distributions. The research team also found that composers collaborated and influenced each other and that composers’ networks grew over time.
The research showed that consumers of classical music CDs tend to listen together to the music of a certain group of different composers, offering a useful tool to understand how the music style and market develops. Based on this, the research team predicted the future of the classical music market would be centered on top composers, while maintaining diversity due to the growing number of new composers.
Professor Park said, “In recent years, technology greatly affects the way we consume culture and art. Accordingly, we see more and more artists and institutions try to incorporate technology into their creative process, and this will lead us to larger- and higher-quality data that can allow us to learn more about culture and art. The quantitative methodology we have demonstrated in our research will give us an opportunity to explore the nature of art and literature in novel ways.”
The European Physical Journal (EPJ) comprises a series of peer-reviewed journals, eleven in total, which cover physics and related subjects such as The Large Hadron Collider, condensed matter, particles, soft matter, and biological physics. The EPJ Data Science is the latest journal launched by EPJ.
Figure: Backbone of the Composer Network
The composer-composer network backbone, projected from the CD-composer network, reveals the major component of the network. The node sizes represent the composers’ degrees, and the colors represent their active periods.
2015.05.07 View 11698
Big Data Reveals the Secret of Classical Music Creation
Professor Juyong Park of the Graduate School of Culture Technology at KAIST and his research team have recently published the result of their study (“Topology and Evolution of the Network of Western Classical Music Composers”) on the dynamics of how classical music is created, stylized, and disseminated in EPJ Data Science online on April 22, 2015. For the press release issued by the journal, please go to the link below:
EPJ Data Science, May 6, 2015
“EPJ Data Science Highlight—Big Data Reveals Classical Music Creation Secrets”
http://www.epj.org/113-epj-ds/941-epjds-highlight-big-data-reveals-classical-music-creation-secrets
Researchers used big-data analysis and modelling technique to examine the complex, undercurrent network of classical music composers, which was constructed from the large volume of compact disc (CD) recordings data collected from an online retailer, ArkivMusic, and a music reference website, AllMusicGuide.
The study discovered that the basic characteristics of composers’ network are similar to many real-world networks, including the small-world property, the existence of a giant component, high clustering, and heavy-tailed degree distributions. The research team also found that composers collaborated and influenced each other and that composers’ networks grew over time.
The research showed that consumers of classical music CDs tend to listen together to the music of a certain group of different composers, offering a useful tool to understand how the music style and market develops. Based on this, the research team predicted the future of the classical music market would be centered on top composers, while maintaining diversity due to the growing number of new composers.
Professor Park said, “In recent years, technology greatly affects the way we consume culture and art. Accordingly, we see more and more artists and institutions try to incorporate technology into their creative process, and this will lead us to larger- and higher-quality data that can allow us to learn more about culture and art. The quantitative methodology we have demonstrated in our research will give us an opportunity to explore the nature of art and literature in novel ways.”
The European Physical Journal (EPJ) comprises a series of peer-reviewed journals, eleven in total, which cover physics and related subjects such as The Large Hadron Collider, condensed matter, particles, soft matter, and biological physics. The EPJ Data Science is the latest journal launched by EPJ.
Figure: Backbone of the Composer Network
The composer-composer network backbone, projected from the CD-composer network, reveals the major component of the network. The node sizes represent the composers’ degrees, and the colors represent their active periods.
2015.05.07 View 11698