Engineering
-
 A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
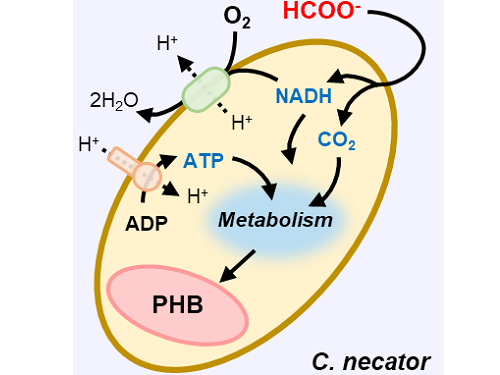
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 9565
A biohybrid system to extract 20 times more bioplastic from CO2 developed by KAIST researchers
As the issues surrounding global climate change intensify, more attention and determined efforts are required to re-grasp the issue as a state of “crisis” and respond to it properly. Among the various methods of recycling CO2, the electrochemical CO2 conversion technology is a technology that can convert CO2 into useful chemical substances using electrical energy. Since it is easy to operate facilities and can use the electricity from renewable sources like the solar cells or the wind power, it has received a lot of attention as an eco-friendly technology can contribute to reducing greenhouse gases and achieve carbon neutrality.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that the joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering succeeded in developing a technology that produces bioplastics from CO2 with high efficiency by developing a hybrid system that interlinked the electrochemical CO2 conversion and microbial bio conversion methods together. The results of the research, which showed the world's highest productivity by more than 20 times compared to similar systems, were published online on March 27th in the "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS)".
※ Paper title: Biohybrid CO2 electrolysis for the direct synthesis of polyesters from CO2
※ Author information: Jinkyu Lim (currently at Stanford Linear Accelerator Center, co-first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Won Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Hyunjoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author)
For the efficient conversion of CO2, high-efficiency electrode catalysts and systems are actively being developed. As conversion products, only compounds containing one or up to three carbon atoms are produced on a limited basis. Compounds of one carbon, such as CO, formic acid, and ethylene, are produced with relatively high efficiency. Liquid compounds of several carbons, such as ethanol, acetic acid, and propanol, can also be produced by these systems, but due to the nature of the chemical reaction that requires more electrons, there are limitations involving the conversion efficiency and the product selection.
Accordingly, a joint research team led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST developed a technology to produce bioplastics from CO2 by linking electrochemical conversion technology with bioconversion method that uses microorganisms.
This electrochemical-bio hybrid system is in the form of having an electrolyzer, in which electrochemical conversion reactions occur, connected to a fermenter, in which microorganisms are cultured. When CO2 is converted to formic acid in the electrolyzer, and it is fed into the fermenter in which the microbes like the Cupriavidus necator, in this case, consumes the carbon source to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), a microbial-derived bioplastic.
According to the research results of the existing hybrid concepts, there was a disadvantage of having low productivity or stopping at a non-continuous process due to problems of low efficiency of the electrolysis and irregular results arising from the culturing conditions of the microbes.
In order to overcome these problems, the joint research team made formic acid with a gas diffusion electrode using gaseous CO2. In addition, the team developed a 'physiologically compatible catholyte' that can be used as a culture medium for microorganisms as well as an electrolyte that allows the electrolysis to occur sufficiently without inhibiting the growth of microorganisms, without having to have a additional separation and purification process, which allowed the acide to be supplied directly to microorganisms.
Through this, the electrolyte solution containing formic acid made from CO2 enters the fermentation tank, is used for microbial culture, and enters the electrolyzer to be circulated, maximizing the utilization of the electrolyte solution and remaining formic acid. In addition, a filter was installed to ensure that only the electrolyte solution with any and all microorganisms that can affect the electrosis filtered out is supplied back to the electrolyzer, and that the microorganisms exist only in the fermenter, designing the two system to work well together with utmost efficiency.
Through the developed hybrid system, the produced bioplastic, poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB), of up to 83% of the cell dry weight was produced from CO2, which produced 1.38g of PHB from a 4 cm2 electrode, which is the world's first gram(g) level production and is more than 20 times more productive than previous research. In addition, the hybrid system is expected to be applied to various industrial processes in the future as it shows promises of the continuous culture system.
The corresponding authors, Professor Hyunjoo Lee and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted that “The results of this research are technologies that can be applied to the production of various chemical substances as well as bioplastics, and are expected to be used as key parts needed in achieving carbon neutrality in the future.”
This research was received and performed with the supports from the CO2 Reduction Catalyst and Energy Device Technology Development Project, the Heterogeneous Atomic Catalyst Control Project, and the Next-generation Biorefinery Source Technology Development Project to lead the Biochemical Industry of the Oil-replacement Eco-friendly Chemical Technology Development Program by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram and photo of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system.
(A) A conceptual scheme and (B) a photograph of the biohybrid CO2 electrolysis system. (C) A detailed scheme of reaction inside the system. Gaseous CO2 was converted to formate in the electrolyzer, and the formate was converted to PHB by the cells in the fermenter. The catholyte was developed so that it is compatible with both CO2 electrolysis and fermentation and was continuously circulated.
2023.03.30 View 9565 -
 KAIST researchers devises a technology to utilize ultrahigh-resolution micro-LED with 40% reduced self-generated heat
In the digitized modern life, various forms of future displays, such as wearable and rollable displays are required. More and more people are wanting to connect to the virtual world whenever and wherever with the use of their smartglasses or smartwatches. Even further, we’ve been hearing about medical diagnosis kit on a shirt and a theatre-hat. However, it is not quite here in our hands yet due to technical limitations of being unable to fit as many pixels as a limited surface area of a glasses while keeping the power consumption at the a level that a hand held battery can supply, all the while the resolution of 4K+ is needed in order to perfectly immerse the users into the augmented or virtual reality through a wireless smartglasses or whatever the device.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering re-examined the phenomenon of efficiency degradation of micro-LEDs with pixels in a size of micrometers (μm, one millionth of a meter) and found that it was possible to fundamentally resolve the problem by the use of epitaxial structure engineering.
Epitaxy refers to the process of stacking gallium nitride crystals that are used as a light emitting body on top of an ultrapure silicon or sapphire substrate used for μLEDs as a medium.
μLED is being actively studied because it has the advantages of superior brightness, contrast ratio, and lifespan compared to OLED. In 2018, Samsung Electronics commercialized a product equipped with μLED called 'The Wall'. And there is a prospect that Apple may be launching a μLED-mounted product in 2025.
In order to manufacture μLEDs, pixels are formed by cutting the epitaxial structure grown on a wafer into a cylinder or cuboid shape through an etching process, and this etching process is accompanied by a plasma-based process. However, these plasmas generate defects on the side of the pixel during the pixel formation process.
Therefore, as the pixel size becomes smaller and the resolution increases, the ratio of the surface area to the volume of the pixel increases, and defects on the side of the device that occur during processing further reduce the device efficiency of the μLED. Accordingly, a considerable amount of research has been conducted on mitigating or removing sidewall defects, but this method has a limit to the degree of improvement as it must be done at the post-processing stage after the grown of the epitaxial structure is finished.
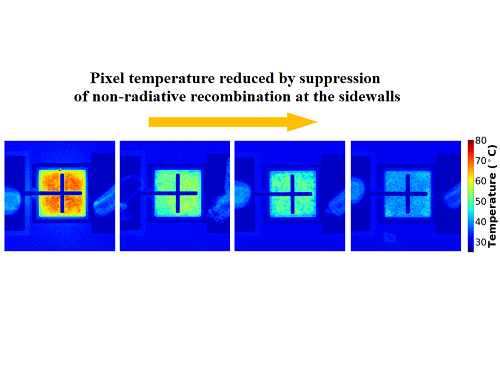
The research team identified that there is a difference in the current moving to the sidewall of the μLED depending on the epitaxial structure during μLED device operation, and based on the findings, the team built a structure that is not sensitive to sidewall defects to solve the problem of reduced efficiency due to miniaturization of μLED devices. In addition, the proposed structure reduced the self-generated heat while the device was running by about 40% compared to the existing structure, which is also of great significance in commercialization of ultrahigh-resolution μLED displays.
This study, which was led by Woo Jin Baek of Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team at the KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering as the first author with guidance by Professor Sang Hyeon Kim and Professor Dae-Myeong Geum of the Chungbuk National University (who was with the team as a postdoctoral researcher at the time) as corresponding authors, was published in the international journal, 'Nature Communications' on March 17th. (Title of the paper: Ultra-low-current driven InGaN blue micro light-emitting diodes for electrically efficient and self-heating relaxed microdisplay).
Professor Sang Hyeon Kim said, "This technological development has great meaning in identifying the cause of the drop in efficiency, which was an obstacle to miniaturization of μLED, and solving it with the design of the epitaxial structure.“ He added, ”We are looking forward to it being used in manufacturing of ultrahigh-resolution displays in the future."
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Future Technology Incubation Center.
Figure 1. Image of electroluminescence distribution of μLEDs fabricated from epitaxial structures with quantum barriers of different thicknesses while the current is running
Figure 2. Thermal distribution images of devices fabricated with different epitaxial structures under the same amount of light.
Figure 3. Normalized external quantum efficiency of the device fabricated with the optimized epitaxial structure by sizes.
2023.03.23 View 6498
KAIST researchers devises a technology to utilize ultrahigh-resolution micro-LED with 40% reduced self-generated heat
In the digitized modern life, various forms of future displays, such as wearable and rollable displays are required. More and more people are wanting to connect to the virtual world whenever and wherever with the use of their smartglasses or smartwatches. Even further, we’ve been hearing about medical diagnosis kit on a shirt and a theatre-hat. However, it is not quite here in our hands yet due to technical limitations of being unable to fit as many pixels as a limited surface area of a glasses while keeping the power consumption at the a level that a hand held battery can supply, all the while the resolution of 4K+ is needed in order to perfectly immerse the users into the augmented or virtual reality through a wireless smartglasses or whatever the device.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering re-examined the phenomenon of efficiency degradation of micro-LEDs with pixels in a size of micrometers (μm, one millionth of a meter) and found that it was possible to fundamentally resolve the problem by the use of epitaxial structure engineering.
Epitaxy refers to the process of stacking gallium nitride crystals that are used as a light emitting body on top of an ultrapure silicon or sapphire substrate used for μLEDs as a medium.
μLED is being actively studied because it has the advantages of superior brightness, contrast ratio, and lifespan compared to OLED. In 2018, Samsung Electronics commercialized a product equipped with μLED called 'The Wall'. And there is a prospect that Apple may be launching a μLED-mounted product in 2025.
In order to manufacture μLEDs, pixels are formed by cutting the epitaxial structure grown on a wafer into a cylinder or cuboid shape through an etching process, and this etching process is accompanied by a plasma-based process. However, these plasmas generate defects on the side of the pixel during the pixel formation process.
Therefore, as the pixel size becomes smaller and the resolution increases, the ratio of the surface area to the volume of the pixel increases, and defects on the side of the device that occur during processing further reduce the device efficiency of the μLED. Accordingly, a considerable amount of research has been conducted on mitigating or removing sidewall defects, but this method has a limit to the degree of improvement as it must be done at the post-processing stage after the grown of the epitaxial structure is finished.
The research team identified that there is a difference in the current moving to the sidewall of the μLED depending on the epitaxial structure during μLED device operation, and based on the findings, the team built a structure that is not sensitive to sidewall defects to solve the problem of reduced efficiency due to miniaturization of μLED devices. In addition, the proposed structure reduced the self-generated heat while the device was running by about 40% compared to the existing structure, which is also of great significance in commercialization of ultrahigh-resolution μLED displays.
This study, which was led by Woo Jin Baek of Professor Sang Hyeon Kim's research team at the KAIST School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering as the first author with guidance by Professor Sang Hyeon Kim and Professor Dae-Myeong Geum of the Chungbuk National University (who was with the team as a postdoctoral researcher at the time) as corresponding authors, was published in the international journal, 'Nature Communications' on March 17th. (Title of the paper: Ultra-low-current driven InGaN blue micro light-emitting diodes for electrically efficient and self-heating relaxed microdisplay).
Professor Sang Hyeon Kim said, "This technological development has great meaning in identifying the cause of the drop in efficiency, which was an obstacle to miniaturization of μLED, and solving it with the design of the epitaxial structure.“ He added, ”We are looking forward to it being used in manufacturing of ultrahigh-resolution displays in the future."
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Future Technology Incubation Center.
Figure 1. Image of electroluminescence distribution of μLEDs fabricated from epitaxial structures with quantum barriers of different thicknesses while the current is running
Figure 2. Thermal distribution images of devices fabricated with different epitaxial structures under the same amount of light.
Figure 3. Normalized external quantum efficiency of the device fabricated with the optimized epitaxial structure by sizes.
2023.03.23 View 6498 -
 KAIST leads AI-based analysis on drug-drug interactions involving Paxlovid
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th that an advanced AI-based drug interaction prediction technology developed by the Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team in the Department of Biochemical Engineering that analyzed the interaction between the PaxlovidTM ingredients that are used as COVID-19 treatment and other prescription drugs was published as a thesis. This paper was published in the online edition of 「Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of America」 (PNAS), an internationally renowned academic journal, on the 13th of March.
* Thesis Title: Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs (Authored by Yeji Kim (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Yong Ryu (Duksung Women's University, co-first author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, co-first author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author))
In this study, the research team developed DeepDDI2, an advanced version of DeepDDI, an AI-based drug interaction prediction model they developed in 2018. DeepDDI2 is able to compute for and process a total of 113 drug-drug interaction (DDI) types, more than the 86 DDI types covered by the existing DeepDDI.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict possible interactions between the ingredients (ritonavir, nirmatrelvir) of Paxlovid*, a COVID-19 treatment, and other prescription drugs. The research team said that while among COVID-19 patients, high-risk patients with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes are likely to be taking other drugs, drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions for Paxlovid have not been sufficiently analyzed, yet. This study was pursued in light of seeing how continued usage of the drug may lead to serious and unwanted complications.
* Paxlovid: Paxlovid is a COVID-19 treatment developed by Pfizer, an American pharmaceutical company, and received emergency use approval (EUA) from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2021.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict how Paxrovid's components, ritonavir and nirmatrelvir, would interact with 2,248 prescription drugs. As a result of the prediction, ritonavir was predicted to interact with 1,403 prescription drugs and nirmatrelvir with 673 drugs.
Using the prediction results, the research team proposed alternative drugs with the same mechanism but low drug interaction potential for prescription drugs with high adverse drug events (ADEs). Accordingly, 124 alternative drugs that could reduce the possible adverse DDI with ritonavir and 239 alternative drugs for nirmatrelvir were identified.
Through this research achievement, it became possible to use an deep learning technology to accurately predict drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and this is expected to play an important role in the digital healthcare, precision medicine and pharmaceutical industries by providing useful information in the process of developing new drugs and making prescriptions.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "The results of this study are meaningful at times like when we would have to resort to using drugs that are developed in a hurry in the face of an urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, that it is now possible to identify and take necessary actions against adverse drug reactions caused by drug-drug interactions very quickly.”
This research was carried out with the support of the KAIST New-Deal Project for COVID-19 Science and Technology and the Bio·Medical Technology Development Project supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Results of drug interaction prediction between Paxlovid ingredients and representative approved drugs using DeepDDI2
2023.03.16 View 7661
KAIST leads AI-based analysis on drug-drug interactions involving Paxlovid
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th that an advanced AI-based drug interaction prediction technology developed by the Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team in the Department of Biochemical Engineering that analyzed the interaction between the PaxlovidTM ingredients that are used as COVID-19 treatment and other prescription drugs was published as a thesis. This paper was published in the online edition of 「Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of America」 (PNAS), an internationally renowned academic journal, on the 13th of March.
* Thesis Title: Computational prediction of interactions between Paxlovid and prescription drugs (Authored by Yeji Kim (KAIST, co-first author), Jae Yong Ryu (Duksung Women's University, co-first author), Hyun Uk Kim (KAIST, co-first author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author))
In this study, the research team developed DeepDDI2, an advanced version of DeepDDI, an AI-based drug interaction prediction model they developed in 2018. DeepDDI2 is able to compute for and process a total of 113 drug-drug interaction (DDI) types, more than the 86 DDI types covered by the existing DeepDDI.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict possible interactions between the ingredients (ritonavir, nirmatrelvir) of Paxlovid*, a COVID-19 treatment, and other prescription drugs. The research team said that while among COVID-19 patients, high-risk patients with chronic diseases such as high blood pressure and diabetes are likely to be taking other drugs, drug-drug interactions and adverse drug reactions for Paxlovid have not been sufficiently analyzed, yet. This study was pursued in light of seeing how continued usage of the drug may lead to serious and unwanted complications.
* Paxlovid: Paxlovid is a COVID-19 treatment developed by Pfizer, an American pharmaceutical company, and received emergency use approval (EUA) from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in December 2021.
The research team used DeepDDI2 to predict how Paxrovid's components, ritonavir and nirmatrelvir, would interact with 2,248 prescription drugs. As a result of the prediction, ritonavir was predicted to interact with 1,403 prescription drugs and nirmatrelvir with 673 drugs.
Using the prediction results, the research team proposed alternative drugs with the same mechanism but low drug interaction potential for prescription drugs with high adverse drug events (ADEs). Accordingly, 124 alternative drugs that could reduce the possible adverse DDI with ritonavir and 239 alternative drugs for nirmatrelvir were identified.
Through this research achievement, it became possible to use an deep learning technology to accurately predict drug-drug interactions (DDIs), and this is expected to play an important role in the digital healthcare, precision medicine and pharmaceutical industries by providing useful information in the process of developing new drugs and making prescriptions.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "The results of this study are meaningful at times like when we would have to resort to using drugs that are developed in a hurry in the face of an urgent situations like the COVID-19 pandemic, that it is now possible to identify and take necessary actions against adverse drug reactions caused by drug-drug interactions very quickly.”
This research was carried out with the support of the KAIST New-Deal Project for COVID-19 Science and Technology and the Bio·Medical Technology Development Project supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure 1. Results of drug interaction prediction between Paxlovid ingredients and representative approved drugs using DeepDDI2
2023.03.16 View 7661 -
 The cause of disability in aged brain meningeal membranes identified
Due to the increase in average age, studies on changes in the brain following general aging process without serious brain diseases have also become an issue that requires in-depth studies. Regarding aging research, as aging progresses, ‘sugar’ accumulates in the body, and the accumulated sugar becomes a causative agent for various diseases such as aging-related inflammation and vascular disease. In the end, “surplus” sugar molecules attach to various proteins in the body and interfere with their functions.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee), a joint research team of Professor Pilnam Kim and Professor Yong Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, revealed on the 15th that it was confirmed that the function of being the “front line of defense” for the cerebrocortex of the brain meninges, the layers of membranes that surrounds the brain, is hindered when 'sugar' begins to build up on them as aging progresses.
Professor Kim's research team confirmed excessive accumulation of sugar molecules in the meninges of the elderly and also confirmed that sugar accumulation occurs mouse models in accordance with certain age levels. The meninges are thin membranes that surround the brain and exist at the boundary between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cortex and play an important role in protecting the brain. In this study, it was revealed that the dysfunction of these brain membranes caused by aging is induced by 'excess' sugar in the brain. In particular, as the meningeal membrane becomes thinner and stickier due to aging, a new paradigm has been provided for the discovery of the principle of the decrease in material exchange between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cerebral cortex.
This research was conducted by the Ph.D. candidate Hyo Min Kim and Dr. Shinheun Kim as the co-first authors to be published online on February 28th in the international journal, Aging Cell. (Paper Title: Glycation-mediated tissue-level remodeling of brain meningeal membrane by aging)
The meninges, which are in direct contact with the cerebrospinal fluid, are mainly composed of collagen, an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, and are composed of fibroblasts, which are cells that produce this protein. The cells that come in contact with collagen proteins that are attached with sugar have a low collagen production function, while the meningeal membrane continuously thins and collapses as the expression of collagen degrading enzymes increases.
Studies on the relationship between excess sugar molecules accumulation in the brain due to continued sugar intake and the degeneration of neurons and brain diseases have been continuously conducted. However, this study was the first to identify meningeal degeneration and dysfunction caused by glucose accumulation with the focus on the meninges itself, and the results are expected to present new ideas for research into approach towards discoveries of new treatments for brain disease.
Researcher Hyomin Kim, the first author, introduced the research results as “an interesting study that identified changes in the barriers of the brain due to aging through a convergent approach, starting from the human brain and utilizing an animal model with a biomimetic meningeal model”.
Professor Pilnam Kim's research team is conducting research and development to remove sugar that accumulated throughout the human body, including the meninges. Advanced glycation end products, which are waste products formed when proteins and sugars meet in the human body, are partially removed by macrophages. However, glycated products bound to extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen are difficult to remove naturally. Through the KAIST-Ceragem Research Center, this research team is developing a healthcare medical device to remove 'sugar residue' in the body.
This study was carried out with the National Research Foundation of Korea's collective research support.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of proposed mechanism showing aging‐related ECM remodeling through meningeal fibroblasts on the brain leptomeninges. Meningeal fibroblasts in the young brain showed dynamic COL1A1 synthetic and COL1‐interactive function on the collagen membrane. They showed ITGB1‐mediated adhesion on the COL1‐composed leptomeningeal membrane and induction of COL1A1 synthesis for maintaining the collagen membrane. With aging, meningeal fibroblasts showed depletion of COL1A1 synthetic function and altered cell–matrix interaction.
Figure 2. Representative rat meningeal images observed in the study. Compared to young rats, it was confirmed that type 1 collagen (COL1) decreased along with the accumulation of glycated end products (AGE) in the brain membrane of aged rats, and the activity of integrin beta 1 (ITGB1), a representative receptor corresponding to cell-collagen interaction. Instead, it was observed that the activity of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2), one of the tyrosine kinases, increased.
Figure 3. Substance flux through the brain membrane decreases with aging. It was confirmed that the degree of adsorption of fluorescent substances contained in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the brain membrane increased and the degree of entry into the periphery of the cerebral blood vessels decreased in the aged rats. In this study, only the influx into the brain was confirmed during the entry and exit of substances, but the degree of outflow will also be confirmed through future studies.
2023.03.15 View 7489
The cause of disability in aged brain meningeal membranes identified
Due to the increase in average age, studies on changes in the brain following general aging process without serious brain diseases have also become an issue that requires in-depth studies. Regarding aging research, as aging progresses, ‘sugar’ accumulates in the body, and the accumulated sugar becomes a causative agent for various diseases such as aging-related inflammation and vascular disease. In the end, “surplus” sugar molecules attach to various proteins in the body and interfere with their functions.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee), a joint research team of Professor Pilnam Kim and Professor Yong Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, revealed on the 15th that it was confirmed that the function of being the “front line of defense” for the cerebrocortex of the brain meninges, the layers of membranes that surrounds the brain, is hindered when 'sugar' begins to build up on them as aging progresses.
Professor Kim's research team confirmed excessive accumulation of sugar molecules in the meninges of the elderly and also confirmed that sugar accumulation occurs mouse models in accordance with certain age levels. The meninges are thin membranes that surround the brain and exist at the boundary between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cortex and play an important role in protecting the brain. In this study, it was revealed that the dysfunction of these brain membranes caused by aging is induced by 'excess' sugar in the brain. In particular, as the meningeal membrane becomes thinner and stickier due to aging, a new paradigm has been provided for the discovery of the principle of the decrease in material exchange between the cerebrospinal fluid and the cerebral cortex.
This research was conducted by the Ph.D. candidate Hyo Min Kim and Dr. Shinheun Kim as the co-first authors to be published online on February 28th in the international journal, Aging Cell. (Paper Title: Glycation-mediated tissue-level remodeling of brain meningeal membrane by aging)
The meninges, which are in direct contact with the cerebrospinal fluid, are mainly composed of collagen, an extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, and are composed of fibroblasts, which are cells that produce this protein. The cells that come in contact with collagen proteins that are attached with sugar have a low collagen production function, while the meningeal membrane continuously thins and collapses as the expression of collagen degrading enzymes increases.
Studies on the relationship between excess sugar molecules accumulation in the brain due to continued sugar intake and the degeneration of neurons and brain diseases have been continuously conducted. However, this study was the first to identify meningeal degeneration and dysfunction caused by glucose accumulation with the focus on the meninges itself, and the results are expected to present new ideas for research into approach towards discoveries of new treatments for brain disease.
Researcher Hyomin Kim, the first author, introduced the research results as “an interesting study that identified changes in the barriers of the brain due to aging through a convergent approach, starting from the human brain and utilizing an animal model with a biomimetic meningeal model”.
Professor Pilnam Kim's research team is conducting research and development to remove sugar that accumulated throughout the human body, including the meninges. Advanced glycation end products, which are waste products formed when proteins and sugars meet in the human body, are partially removed by macrophages. However, glycated products bound to extracellular matrix proteins such as collagen are difficult to remove naturally. Through the KAIST-Ceragem Research Center, this research team is developing a healthcare medical device to remove 'sugar residue' in the body.
This study was carried out with the National Research Foundation of Korea's collective research support.
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of proposed mechanism showing aging‐related ECM remodeling through meningeal fibroblasts on the brain leptomeninges. Meningeal fibroblasts in the young brain showed dynamic COL1A1 synthetic and COL1‐interactive function on the collagen membrane. They showed ITGB1‐mediated adhesion on the COL1‐composed leptomeningeal membrane and induction of COL1A1 synthesis for maintaining the collagen membrane. With aging, meningeal fibroblasts showed depletion of COL1A1 synthetic function and altered cell–matrix interaction.
Figure 2. Representative rat meningeal images observed in the study. Compared to young rats, it was confirmed that type 1 collagen (COL1) decreased along with the accumulation of glycated end products (AGE) in the brain membrane of aged rats, and the activity of integrin beta 1 (ITGB1), a representative receptor corresponding to cell-collagen interaction. Instead, it was observed that the activity of discoidin domain receptor 2 (DDR2), one of the tyrosine kinases, increased.
Figure 3. Substance flux through the brain membrane decreases with aging. It was confirmed that the degree of adsorption of fluorescent substances contained in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to the brain membrane increased and the degree of entry into the periphery of the cerebral blood vessels decreased in the aged rats. In this study, only the influx into the brain was confirmed during the entry and exit of substances, but the degree of outflow will also be confirmed through future studies.
2023.03.15 View 7489 -
 KAIST develops 'MetaVRain' that realizes vivid 3D real-life images
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) is a high-speed, low-power artificial intelligence (AI: Artificial Intelligent) semiconductor* MetaVRain, which implements artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering that can render images close to real life on mobile devices.
* AI semiconductor: Semiconductor equipped with artificial intelligence processing functions such as recognition, reasoning, learning, and judgment, and implemented with optimized technology based on super intelligence, ultra-low power, and ultra-reliability
The artificial intelligence semiconductor developed by the research team makes the existing ray-tracing*-based 3D rendering driven by GPU into artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering on a newly manufactured AI semiconductor, making it a 3D video capture studio that requires enormous costs. is not needed, so the cost of 3D model production can be greatly reduced and the memory used can be reduced by more than 180 times. In particular, the existing 3D graphic editing and design, which used complex software such as Blender, is replaced with simple artificial intelligence learning, so the general public can easily apply and edit the desired style.
* Ray-tracing: Technology that obtains images close to real life by tracing the trajectory of all light rays that change according to the light source, shape and texture of the object
This research, in which doctoral student Donghyun Han participated as the first author, was presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Design Conference (ISSCC) held in San Francisco, USA from February 18th to 22nd by semiconductor researchers from all over the world.
(Paper Number 2.7, Paper Title: MetaVRain: A 133mW Real-time Hyper-realistic 3D NeRF Processor with 1D-2D Hybrid Neural Engines for Metaverse on Mobile Devices (Authors: Donghyeon Han, Junha Ryu, Sangyeob Kim, Sangjin Kim, and Hoi-Jun Yoo))
Professor Yoo's team discovered inefficient operations that occur when implementing 3D rendering through artificial intelligence, and developed a new concept semiconductor that combines human visual recognition methods to reduce them. When a person remembers an object, he has the cognitive ability to immediately guess what the current object looks like based on the process of starting with a rough outline and gradually specifying its shape, and if it is an object he saw right before. In imitation of such a human cognitive process, the newly developed semiconductor adopts an operation method that grasps the rough shape of an object in advance through low-resolution voxels and minimizes the amount of computation required for current rendering based on the result of rendering in the past.
MetaVRain, developed by Professor Yu's team, achieved the world's best performance by developing a state-of-the-art CMOS chip as well as a hardware architecture that mimics the human visual recognition process. MetaVRain is optimized for artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering technology and achieves a rendering speed of up to 100 FPS or more, which is 911 times faster than conventional GPUs. In addition, as a result of the study, the energy efficiency, which represents the energy consumed per video screen processing, is 26,400 times higher than that of GPU, opening the possibility of artificial intelligence-based real-time rendering in VR/AR headsets and mobile devices.
To show an example of using MetaVRain, the research team developed a smart 3D rendering application system together, and showed an example of changing the style of a 3D model according to the user's preferred style. Since you only need to give artificial intelligence an image of the desired style and perform re-learning, you can easily change the style of the 3D model without the help of complicated software. In addition to the example of the application system implemented by Professor Yu's team, it is expected that various application examples will be possible, such as creating a realistic 3D avatar modeled after a user's face, creating 3D models of various structures, and changing the weather according to the film production environment. do.
Starting with MetaVRain, the research team expects that the field of 3D graphics will also begin to be replaced by artificial intelligence, and revealed that the combination of artificial intelligence and 3D graphics is a great technological innovation for the realization of the metaverse.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at KAIST, who led the research, said, “Currently, 3D graphics are focused on depicting what an object looks like, not how people see it.” The significance of this study was revealed as a study that enabled efficient 3D graphics by borrowing the way people recognize and express objects by imitating them.” He also foresaw the future, saying, “The realization of the metaverse will be achieved through innovation in artificial intelligence technology and innovation in artificial intelligence semiconductors, as shown in this study.”
Figure 1. Description of the MetaVRain demo screen
Photo of Presentation at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC)
2023.03.13 View 6670
KAIST develops 'MetaVRain' that realizes vivid 3D real-life images
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) is a high-speed, low-power artificial intelligence (AI: Artificial Intelligent) semiconductor* MetaVRain, which implements artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering that can render images close to real life on mobile devices.
* AI semiconductor: Semiconductor equipped with artificial intelligence processing functions such as recognition, reasoning, learning, and judgment, and implemented with optimized technology based on super intelligence, ultra-low power, and ultra-reliability
The artificial intelligence semiconductor developed by the research team makes the existing ray-tracing*-based 3D rendering driven by GPU into artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering on a newly manufactured AI semiconductor, making it a 3D video capture studio that requires enormous costs. is not needed, so the cost of 3D model production can be greatly reduced and the memory used can be reduced by more than 180 times. In particular, the existing 3D graphic editing and design, which used complex software such as Blender, is replaced with simple artificial intelligence learning, so the general public can easily apply and edit the desired style.
* Ray-tracing: Technology that obtains images close to real life by tracing the trajectory of all light rays that change according to the light source, shape and texture of the object
This research, in which doctoral student Donghyun Han participated as the first author, was presented at the International Solid-State Circuit Design Conference (ISSCC) held in San Francisco, USA from February 18th to 22nd by semiconductor researchers from all over the world.
(Paper Number 2.7, Paper Title: MetaVRain: A 133mW Real-time Hyper-realistic 3D NeRF Processor with 1D-2D Hybrid Neural Engines for Metaverse on Mobile Devices (Authors: Donghyeon Han, Junha Ryu, Sangyeob Kim, Sangjin Kim, and Hoi-Jun Yoo))
Professor Yoo's team discovered inefficient operations that occur when implementing 3D rendering through artificial intelligence, and developed a new concept semiconductor that combines human visual recognition methods to reduce them. When a person remembers an object, he has the cognitive ability to immediately guess what the current object looks like based on the process of starting with a rough outline and gradually specifying its shape, and if it is an object he saw right before. In imitation of such a human cognitive process, the newly developed semiconductor adopts an operation method that grasps the rough shape of an object in advance through low-resolution voxels and minimizes the amount of computation required for current rendering based on the result of rendering in the past.
MetaVRain, developed by Professor Yu's team, achieved the world's best performance by developing a state-of-the-art CMOS chip as well as a hardware architecture that mimics the human visual recognition process. MetaVRain is optimized for artificial intelligence-based 3D rendering technology and achieves a rendering speed of up to 100 FPS or more, which is 911 times faster than conventional GPUs. In addition, as a result of the study, the energy efficiency, which represents the energy consumed per video screen processing, is 26,400 times higher than that of GPU, opening the possibility of artificial intelligence-based real-time rendering in VR/AR headsets and mobile devices.
To show an example of using MetaVRain, the research team developed a smart 3D rendering application system together, and showed an example of changing the style of a 3D model according to the user's preferred style. Since you only need to give artificial intelligence an image of the desired style and perform re-learning, you can easily change the style of the 3D model without the help of complicated software. In addition to the example of the application system implemented by Professor Yu's team, it is expected that various application examples will be possible, such as creating a realistic 3D avatar modeled after a user's face, creating 3D models of various structures, and changing the weather according to the film production environment. do.
Starting with MetaVRain, the research team expects that the field of 3D graphics will also begin to be replaced by artificial intelligence, and revealed that the combination of artificial intelligence and 3D graphics is a great technological innovation for the realization of the metaverse.
Professor Hoi-Jun Yoo of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at KAIST, who led the research, said, “Currently, 3D graphics are focused on depicting what an object looks like, not how people see it.” The significance of this study was revealed as a study that enabled efficient 3D graphics by borrowing the way people recognize and express objects by imitating them.” He also foresaw the future, saying, “The realization of the metaverse will be achieved through innovation in artificial intelligence technology and innovation in artificial intelligence semiconductors, as shown in this study.”
Figure 1. Description of the MetaVRain demo screen
Photo of Presentation at the International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC)
2023.03.13 View 6670 -
 KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 8999
KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 8999 -
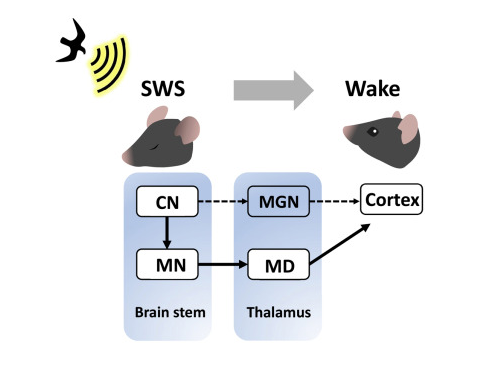 KAIST researchers discovers the neural circuit that reacts to alarm clock
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th that a research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Dr. Jeongjin Kim 's team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have identified the principle of awakening animals by responding to sounds even while sleeping.
Sleep is a very important physiological process that organizes brain activity and maintains health. During sleep, the function of sensory nerves is blocked, so the ability to detect danger in the proximity is reduced. However, many animals detect approaching predators and respond even while sleeping. Scientists thought that animals ready for danger by alternating between deep sleep and light sleep.
A research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim at KAIST discovered that animals have neural circuits that respond to sounds even during deep sleep. While awake, the medial geniculate thalamus responds to sounds, but during deep sleep, or Non-REM sleep, the Mediodorsal thalamus responds to sounds to wake up the brain.
As a result of the study, when the rats fell into deep sleep, the nerves of the medial geniculate thalamus were also sleeping, but the nerves of mediodorsal thalamus were awake and responded immediately to sounds. In addition, it was observed that when mediodorsal thalamus was inhibited, the rats could not wake up even when a sound was heard, and when the mediodorsal thalamus was stimulated, the rats woke up within a few seconds without sound.
This is the first study to show that sleep and wakefulness can transmit auditory signals through different neural circuits, and was reported in the international journal, Current Biology on February 7, and was highlighted by Nature. (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00354-0)
Professor Daesoo Kim explained, “The findings of this study can used in developing digital healthcare technologies to be used to improve understanding of disorders of senses and wakefulness seen in various brain diseases and to control the senses in the future.”
This research was carried out with the support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Research Foundation Program.
Figure 1. Traditionally, sound signals were thought to be propagated from the auditory nerve to the auditory thalamus. However, while in slow-wave sleep, the auditory nerve sends sound signals to the mediodorsal thalamic neurons via the brainstem nerve to induce arousal in the brain.
Figure 2. GRIK4 dorsomedial nerve in response to sound stimulation. The awakening effect is induced as the activity of the GRIK4 dorsal medial nerve increases based on the time when sound stimulation is given.
2023.03.03 View 5378
KAIST researchers discovers the neural circuit that reacts to alarm clock
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th that a research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences and Dr. Jeongjin Kim 's team from the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have identified the principle of awakening animals by responding to sounds even while sleeping.
Sleep is a very important physiological process that organizes brain activity and maintains health. During sleep, the function of sensory nerves is blocked, so the ability to detect danger in the proximity is reduced. However, many animals detect approaching predators and respond even while sleeping. Scientists thought that animals ready for danger by alternating between deep sleep and light sleep.
A research team led by Professor Daesoo Kim at KAIST discovered that animals have neural circuits that respond to sounds even during deep sleep. While awake, the medial geniculate thalamus responds to sounds, but during deep sleep, or Non-REM sleep, the Mediodorsal thalamus responds to sounds to wake up the brain.
As a result of the study, when the rats fell into deep sleep, the nerves of the medial geniculate thalamus were also sleeping, but the nerves of mediodorsal thalamus were awake and responded immediately to sounds. In addition, it was observed that when mediodorsal thalamus was inhibited, the rats could not wake up even when a sound was heard, and when the mediodorsal thalamus was stimulated, the rats woke up within a few seconds without sound.
This is the first study to show that sleep and wakefulness can transmit auditory signals through different neural circuits, and was reported in the international journal, Current Biology on February 7, and was highlighted by Nature. (https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-023-00354-0)
Professor Daesoo Kim explained, “The findings of this study can used in developing digital healthcare technologies to be used to improve understanding of disorders of senses and wakefulness seen in various brain diseases and to control the senses in the future.”
This research was carried out with the support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Research Foundation Program.
Figure 1. Traditionally, sound signals were thought to be propagated from the auditory nerve to the auditory thalamus. However, while in slow-wave sleep, the auditory nerve sends sound signals to the mediodorsal thalamic neurons via the brainstem nerve to induce arousal in the brain.
Figure 2. GRIK4 dorsomedial nerve in response to sound stimulation. The awakening effect is induced as the activity of the GRIK4 dorsal medial nerve increases based on the time when sound stimulation is given.
2023.03.03 View 5378 -
 KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 16446
KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 16446 -
 KAIST’s Robo-Dog “RaiBo” runs through the sandy beach
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th that a research team led by Professor Jemin Hwangbo of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot control technology that can walk robustly with agility even in deformable terrain such as sandy beach.
< Photo. RAI Lab Team with Professor Hwangbo in the middle of the back row. >
Professor Hwangbo's research team developed a technology to model the force received by a walking robot on the ground made of granular materials such as sand and simulate it via a quadrupedal robot. Also, the team worked on an artificial neural network structure which is suitable in making real-time decisions needed in adapting to various types of ground without prior information while walking at the same time and applied it on to reinforcement learning. The trained neural network controller is expected to expand the scope of application of quadrupedal walking robots by proving its robustness in changing terrain, such as the ability to move in high-speed even on a sandy beach and walk and turn on soft grounds like an air mattress without losing balance.
This research, with Ph.D. Student Soo-Young Choi of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author, was published in January in the “Science Robotics”. (Paper title: Learning quadrupedal locomotion on deformable terrain).
Reinforcement learning is an AI learning method used to create a machine that collects data on the results of various actions in an arbitrary situation and utilizes that set of data to perform a task. Because the amount of data required for reinforcement learning is so vast, a method of collecting data through simulations that approximates physical phenomena in the real environment is widely used.
In particular, learning-based controllers in the field of walking robots have been applied to real environments after learning through data collected in simulations to successfully perform walking controls in various terrains.
However, since the performance of the learning-based controller rapidly decreases when the actual environment has any discrepancy from the learned simulation environment, it is important to implement an environment similar to the real one in the data collection stage. Therefore, in order to create a learning-based controller that can maintain balance in a deforming terrain, the simulator must provide a similar contact experience.
The research team defined a contact model that predicted the force generated upon contact from the motion dynamics of a walking body based on a ground reaction force model that considered the additional mass effect of granular media defined in previous studies.
Furthermore, by calculating the force generated from one or several contacts at each time step, the deforming terrain was efficiently simulated.
The research team also introduced an artificial neural network structure that implicitly predicts ground characteristics by using a recurrent neural network that analyzes time-series data from the robot's sensors.
The learned controller was mounted on the robot 'RaiBo', which was built hands-on by the research team to show high-speed walking of up to 3.03 m/s on a sandy beach where the robot's feet were completely submerged in the sand. Even when applied to harder grounds, such as grassy fields, and a running track, it was able to run stably by adapting to the characteristics of the ground without any additional programming or revision to the controlling algorithm.
In addition, it rotated with stability at 1.54 rad/s (approximately 90° per second) on an air mattress and demonstrated its quick adaptability even in the situation in which the terrain suddenly turned soft.
The research team demonstrated the importance of providing a suitable contact experience during the learning process by comparison with a controller that assumed the ground to be rigid, and proved that the proposed recurrent neural network modifies the controller's walking method according to the ground properties.
The simulation and learning methodology developed by the research team is expected to contribute to robots performing practical tasks as it expands the range of terrains that various walking robots can operate on.
The first author, Suyoung Choi, said, “It has been shown that providing a learning-based controller with a close contact experience with real deforming ground is essential for application to deforming terrain.” He went on to add that “The proposed controller can be used without prior information on the terrain, so it can be applied to various robot walking studies.”
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
< Figure 1. Adaptability of the proposed controller to various ground environments. The controller learned from a wide range of randomized granular media simulations showed adaptability to various natural and artificial terrains, and demonstrated high-speed walking ability and energy efficiency. >
< Figure 2. Contact model definition for simulation of granular substrates. The research team used a model that considered the additional mass effect for the vertical force and a Coulomb friction model for the horizontal direction while approximating the contact with the granular medium as occurring at a point. Furthermore, a model that simulates the ground resistance that can occur on the side of the foot was introduced and used for simulation. >
2023.01.26 View 14577
KAIST’s Robo-Dog “RaiBo” runs through the sandy beach
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th that a research team led by Professor Jemin Hwangbo of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot control technology that can walk robustly with agility even in deformable terrain such as sandy beach.
< Photo. RAI Lab Team with Professor Hwangbo in the middle of the back row. >
Professor Hwangbo's research team developed a technology to model the force received by a walking robot on the ground made of granular materials such as sand and simulate it via a quadrupedal robot. Also, the team worked on an artificial neural network structure which is suitable in making real-time decisions needed in adapting to various types of ground without prior information while walking at the same time and applied it on to reinforcement learning. The trained neural network controller is expected to expand the scope of application of quadrupedal walking robots by proving its robustness in changing terrain, such as the ability to move in high-speed even on a sandy beach and walk and turn on soft grounds like an air mattress without losing balance.
This research, with Ph.D. Student Soo-Young Choi of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering as the first author, was published in January in the “Science Robotics”. (Paper title: Learning quadrupedal locomotion on deformable terrain).
Reinforcement learning is an AI learning method used to create a machine that collects data on the results of various actions in an arbitrary situation and utilizes that set of data to perform a task. Because the amount of data required for reinforcement learning is so vast, a method of collecting data through simulations that approximates physical phenomena in the real environment is widely used.
In particular, learning-based controllers in the field of walking robots have been applied to real environments after learning through data collected in simulations to successfully perform walking controls in various terrains.
However, since the performance of the learning-based controller rapidly decreases when the actual environment has any discrepancy from the learned simulation environment, it is important to implement an environment similar to the real one in the data collection stage. Therefore, in order to create a learning-based controller that can maintain balance in a deforming terrain, the simulator must provide a similar contact experience.
The research team defined a contact model that predicted the force generated upon contact from the motion dynamics of a walking body based on a ground reaction force model that considered the additional mass effect of granular media defined in previous studies.
Furthermore, by calculating the force generated from one or several contacts at each time step, the deforming terrain was efficiently simulated.
The research team also introduced an artificial neural network structure that implicitly predicts ground characteristics by using a recurrent neural network that analyzes time-series data from the robot's sensors.
The learned controller was mounted on the robot 'RaiBo', which was built hands-on by the research team to show high-speed walking of up to 3.03 m/s on a sandy beach where the robot's feet were completely submerged in the sand. Even when applied to harder grounds, such as grassy fields, and a running track, it was able to run stably by adapting to the characteristics of the ground without any additional programming or revision to the controlling algorithm.
In addition, it rotated with stability at 1.54 rad/s (approximately 90° per second) on an air mattress and demonstrated its quick adaptability even in the situation in which the terrain suddenly turned soft.
The research team demonstrated the importance of providing a suitable contact experience during the learning process by comparison with a controller that assumed the ground to be rigid, and proved that the proposed recurrent neural network modifies the controller's walking method according to the ground properties.
The simulation and learning methodology developed by the research team is expected to contribute to robots performing practical tasks as it expands the range of terrains that various walking robots can operate on.
The first author, Suyoung Choi, said, “It has been shown that providing a learning-based controller with a close contact experience with real deforming ground is essential for application to deforming terrain.” He went on to add that “The proposed controller can be used without prior information on the terrain, so it can be applied to various robot walking studies.”
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
< Figure 1. Adaptability of the proposed controller to various ground environments. The controller learned from a wide range of randomized granular media simulations showed adaptability to various natural and artificial terrains, and demonstrated high-speed walking ability and energy efficiency. >
< Figure 2. Contact model definition for simulation of granular substrates. The research team used a model that considered the additional mass effect for the vertical force and a Coulomb friction model for the horizontal direction while approximating the contact with the granular medium as occurring at a point. Furthermore, a model that simulates the ground resistance that can occur on the side of the foot was introduced and used for simulation. >
2023.01.26 View 14577 -
 Overview of the 30-year history of metabolic engineering
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST >
A research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Dr. So Young Choi, Dr. In Jin Cho, Da-Hee Ahn, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported the 30-year history of metabolic engineering, highlighting examples of recent progress in the field and contributions to sustainability and health. Their paper “Metabolic engineering for sustainability and health” was published online in the 40th anniversary special issue of Trends in Biotechnology on January 10, 2023.
Metabolic engineering, a discipline of engineering that modifies cell phenotypes through molecular and genetic-level manipulations to improve cellular activities, has been studied since the early 1990s, and has progressed significantly over the past 30 years. In particular, metabolic engineering has enabled the engineering of microorganisms for the development of microbial cell factories capable of efficiently producing chemicals and materials as well as degrading recalcitrant contaminants.
This review article revisited how metabolic engineering has advanced over the past 30 years, from the advent of genetic engineering techniques such as recombinant DNA technologies to recent breakthroughs in systems metabolic engineering and data science aided by artificial intelligence. The research team highlighted momentous events and achievements in metabolic engineering, providing both trends and future directions in the field. Metabolic engineering’s contributions to bio-based sustainable chemicals and clean energy, health, and bioremediation were also reviewed. Finally, the research team shared their perspectives on the future challenges impacting metabolic engineering than must be overcome in order to achieve advancements in sustainability and health.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Replacing fossil resource-based chemical processes with bio-based sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels, and materials using metabolic engineering has become our essential task for the future. By looking back on the 30+ years of metabolic engineering, we aimed to highlight the contributions of metabolic engineering to achieve sustainability and good health.” He added, “Metabolic engineering will play an increasingly important role as a key solution to the climate crisis, environmental pollution, food and energy shortages, and health problems in aging societies.”
< Figure: Metabolic Engineering Timeline >
2023.01.25 View 9799
Overview of the 30-year history of metabolic engineering
< Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST >
A research team comprised of Gi Bae Kim, Dr. So Young Choi, Dr. In Jin Cho, Da-Hee Ahn, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported the 30-year history of metabolic engineering, highlighting examples of recent progress in the field and contributions to sustainability and health. Their paper “Metabolic engineering for sustainability and health” was published online in the 40th anniversary special issue of Trends in Biotechnology on January 10, 2023.
Metabolic engineering, a discipline of engineering that modifies cell phenotypes through molecular and genetic-level manipulations to improve cellular activities, has been studied since the early 1990s, and has progressed significantly over the past 30 years. In particular, metabolic engineering has enabled the engineering of microorganisms for the development of microbial cell factories capable of efficiently producing chemicals and materials as well as degrading recalcitrant contaminants.
This review article revisited how metabolic engineering has advanced over the past 30 years, from the advent of genetic engineering techniques such as recombinant DNA technologies to recent breakthroughs in systems metabolic engineering and data science aided by artificial intelligence. The research team highlighted momentous events and achievements in metabolic engineering, providing both trends and future directions in the field. Metabolic engineering’s contributions to bio-based sustainable chemicals and clean energy, health, and bioremediation were also reviewed. Finally, the research team shared their perspectives on the future challenges impacting metabolic engineering than must be overcome in order to achieve advancements in sustainability and health.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “Replacing fossil resource-based chemical processes with bio-based sustainable processes for the production of chemicals, fuels, and materials using metabolic engineering has become our essential task for the future. By looking back on the 30+ years of metabolic engineering, we aimed to highlight the contributions of metabolic engineering to achieve sustainability and good health.” He added, “Metabolic engineering will play an increasingly important role as a key solution to the climate crisis, environmental pollution, food and energy shortages, and health problems in aging societies.”
< Figure: Metabolic Engineering Timeline >
2023.01.25 View 9799 -
 KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 9420
KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 9420 -
 A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 15839
A Quick but Clingy Creepy-Crawler that will MARVEL You
Engineered by KAIST Mechanics, a quadrupedal robot climbs steel walls and crawls across metal ceilings at the fastest speed that the world has ever seen.
< Photo 1. (From left) KAIST ME Prof. Hae-Won Park, Ph.D. Student Yong Um, Ph.D. Student Seungwoo Hong >
- Professor Hae-Won Park's team at the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal robot that can move at a high speed on ferrous walls and ceilings.
- It is expected to make a wide variety of contributions as it is to be used to conduct inspections and repairs of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, and transmission towers, offering an alternative to dangerous or risky activities required in hazardous environments while maintaining productivity and efficiency through automation and unmanning of such operations.
- The study was published as the cover paper of the December issue of Science Robotics.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor Hae-Won Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a quadrupedal walking robot that can move at high speed on steel walls and ceilings named M.A.R.V.E.L. - rightly so as it is a Magnetically Adhesive Robot for Versatile and Expeditious Locomotion as described in their paper, “Agile and Versatile Climbing on Ferromagnetic Surfaces with a Quadrupedal Robot.” (DOI: 10.1126/scirobotics.add1017)
To make this happen, Professor Park's research team developed a foot pad that can quickly turn the magnetic adhesive force on and off while retaining high adhesive force even on an uneven surface through the use of the Electro-Permanent Magnet (EPM), a device that can magnetize and demagnetize an electromagnet with little power, and the Magneto-Rheological Elastomer (MRE), an elastic material made by mixing a magnetic response factor, such as iron powder, with an elastic material, such as rubber, which they mounted on a small quadrupedal robot they made in-house, at their own laboratory. These walking robots are expected to be put into a wide variety of usage, including being programmed to perform inspections, repairs, and maintenance tasks on large structures made of steel, such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, large storage areas, and construction sites.
This study, in which Seungwoo Hong and Yong Um of the Department of Mechanical Engineering participated as co-first authors, was published as the cover paper in the December issue of Science Robotics.
< Image on the Cover of 2022 December issue of Science Robotics >
Existing wall-climbing robots use wheels or endless tracks, so their mobility is limited on surfaces with steps or irregularities. On the other hand, walking robots for climbing can expect improved mobility in obstacle terrain, but have disadvantages in that they have significantly slower moving speeds or cannot perform various movements.
In order to enable fast movement of the walking robot, the sole of the foot must have strong adhesion force and be able to control the adhesion to quickly switch from sticking to the surface or to be off of it. In addition, it is necessary to maintain the adhesion force even on a rough or uneven surface.
To solve this problem, the research team used the EPM and MRE for the first time in designing the soles of walking robots. An EPM is a magnet that can turn on and off the electromagnetic force with a short current pulse. Unlike general electromagnets, it has the advantage that it does not require energy to maintain the magnetic force. The research team proposed a new EPM with a rectangular structure arrangement, enabling faster switching while significantly lowering the voltage required for switching compared to existing electromagnets.
In addition, the research team was able to increase the frictional force without significantly reducing the magnetic force of the sole by covering the sole with an MRE. The proposed sole weighs only 169 g, but provides a vertical gripping force of about *535 Newtons (N) and a frictional force of 445 N, which is sufficient gripping force for a quadrupedal robot weighing 8 kg.
* 535 N converted to kg is 54.5 kg, and 445 N is 45.4 kg. In other words, even if an external force of up to 54.5 kg in the vertical direction and up to 45.4 kg in the horizontal direction is applied (or even if a corresponding weight is hung), the sole of the foot does not come off the steel plate.
MARVEL climbed up a vertical wall at high speed at a speed of 70 cm per second, and was able to walk while hanging upside down from the ceiling at a maximum speed of 50 cm per second. This is the world's fastest speed for a walking climbing robot. In addition, the research team demonstrated that the robot can climb at a speed of up to 35 cm even on a surface that is painted, dirty with dust and the rust-tainted surfaces of water tanks, proving the robot's performance in a real environment. It was experimentally demonstrated that the robot not only exhibited high speed, but also can switch from floor to wall and from wall to ceiling, and overcome 5-cm high obstacles protruding from walls without difficulty.
The new climbing quadrupedal robot is expected to be widely used for inspection, repair, and maintenance of large steel structures such as ships, bridges, transmission towers, oil pipelines, large storage areas, and construction sites. As the works required in these places involves risks such as falls, suffocation and other accidents that may result in serious injuries or casualties, the need for automation is of utmost urgency.
One of the first co-authors of the paper, a Ph.D. student, Yong Um of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, said, "By the use of the magnetic soles made up of the EPM and MRE and the non-linear model predictive controller suitable for climbing, the robot can speedily move through a variety of ferromagnetic surfaces including walls and ceilings, not just level grounds. We believe this would become a cornerstone that will expand the mobility and the places of pedal-mobile robots can venture into." He added, “These robots can be put into good use in executing dangerous and difficult tasks on steel structures in places like the shipbuilding yards.”
This research was carried out with support from the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers and Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering Co., Ltd..
< Figure 1. The quadrupedal robot (MARVEL) walking over various ferrous surfaces. (A) vertical wall (B) ceiling. (C) over obstacles on a vertical wall (D) making floor-to-wall and wall-to-ceiling transitions (E) moving over a storage tank (F) walking on a wall with a 2-kg weight and over a ceiling with a 3-kg load. >
< Figure 2. Description of the magnetic foot (A) Components of the magnet sole: ankle, Square Eletro-Permanent Magnet(S-EPM), MRE footpad. (B) Components of the S-EPM and MRE footpad. (C) Working principle of the S-EPM. When the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the left figure, magnetic flux comes out of the keeper and circulates through the steel plate, generating holding force (ON state). Conversely, if the magnetization direction is aligned as shown in the figure on the right, the magnetic flux circulates inside the S-EPM and the holding force disappears (OFF state). >
Video Introduction: Agile and versatile climbing on ferromagnetic surfaces with a quadrupedal robot - YouTube
2022.12.30 View 15839