AR
-
 Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho publishes Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
KAIST Biological and Brain Engineering Department’s Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho edited the Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology with three scholars, all experts of Systems Biology in England, Germany and the United States. It is rare that a Korean scientist edits a world renowned academic science encyclopaedia.
The Encyclopaedia, published by the New York office of Springer Verlag, was a grand international project five years in the making by 28 editors and 391 scientists with expertise in Systems Biology from around the world. The Encyclopaedia compiles various research areas of Systems Biology, the new academic paradigm of the 21st century through the integration of IT and BT, comprehensively on 3,000 pages in 4 four volumes.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, who led this international project, majored in electrical engineering and pioneered the field of Systems Biology, the integrated study of biological sciences and engineering, as a new integrated field of IT since the 1990s. The professor has achieved various innovative research results since then. Recently he has investigated “kernel,” an evolutionary core structure in complex biological networks and developed a new cancer treatment through the state space analysis of the molecular network of cancer cells. His work was published in Science Signalling, a sister journal of Science, as a cover story several times, and contributed to foundational research as well as commercialisation of the integrated fields of IT and BT.
2013.08.27 View 9952
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho publishes Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho
KAIST Biological and Brain Engineering Department’s Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho edited the Encyclopaedia of Systems Biology with three scholars, all experts of Systems Biology in England, Germany and the United States. It is rare that a Korean scientist edits a world renowned academic science encyclopaedia.
The Encyclopaedia, published by the New York office of Springer Verlag, was a grand international project five years in the making by 28 editors and 391 scientists with expertise in Systems Biology from around the world. The Encyclopaedia compiles various research areas of Systems Biology, the new academic paradigm of the 21st century through the integration of IT and BT, comprehensively on 3,000 pages in 4 four volumes.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, who led this international project, majored in electrical engineering and pioneered the field of Systems Biology, the integrated study of biological sciences and engineering, as a new integrated field of IT since the 1990s. The professor has achieved various innovative research results since then. Recently he has investigated “kernel,” an evolutionary core structure in complex biological networks and developed a new cancer treatment through the state space analysis of the molecular network of cancer cells. His work was published in Science Signalling, a sister journal of Science, as a cover story several times, and contributed to foundational research as well as commercialisation of the integrated fields of IT and BT.
2013.08.27 View 9952 -
 Secondary, High Capacity Battery developed from Rice Husks
Rice husks, a waste product from rice polishing, has been successfully utilized as the silicon anode for use in high capacity lithium ion secondary batteries. The new silicon anode derived from rice husks exhibit superior output and lifespan.
Professor Choi Jang Wook (The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Park Seung Min (Department of Biochemistry) and their respective research teams separated naturally occurring, highly porous silica material within the rice husks and developed a 3-dimensional, highly porous silicon anode material.
The result of the research effort was published in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal, a world renowned journal in the field of natural sciences.
Silicon has attracted much attention as anode material for next generation lithium ion secondary batteries because it exhibits 3~5 times higher capacity than conventional graphene. The high capacity will pave the way to lithium secondary batteries with higher energy densities than conventional batteries. It is anticipated that the application of silicon batteries will yield electronic devices with a longer duration for use in addition to electronic vehicles boasting longer mileage.
The silicon anode is based on the 3-dimensional, highly porous structure of rice husks which remedies the problematic extreme volume expansion of conventional silicon anodes.
Utilization of inexpensive rice husks to create high value silicon anodes will cause a ripple effect on the industry and academia.
2013.08.23 View 10990
Secondary, High Capacity Battery developed from Rice Husks
Rice husks, a waste product from rice polishing, has been successfully utilized as the silicon anode for use in high capacity lithium ion secondary batteries. The new silicon anode derived from rice husks exhibit superior output and lifespan.
Professor Choi Jang Wook (The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Park Seung Min (Department of Biochemistry) and their respective research teams separated naturally occurring, highly porous silica material within the rice husks and developed a 3-dimensional, highly porous silicon anode material.
The result of the research effort was published in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal, a world renowned journal in the field of natural sciences.
Silicon has attracted much attention as anode material for next generation lithium ion secondary batteries because it exhibits 3~5 times higher capacity than conventional graphene. The high capacity will pave the way to lithium secondary batteries with higher energy densities than conventional batteries. It is anticipated that the application of silicon batteries will yield electronic devices with a longer duration for use in addition to electronic vehicles boasting longer mileage.
The silicon anode is based on the 3-dimensional, highly porous structure of rice husks which remedies the problematic extreme volume expansion of conventional silicon anodes.
Utilization of inexpensive rice husks to create high value silicon anodes will cause a ripple effect on the industry and academia.
2013.08.23 View 10990 -
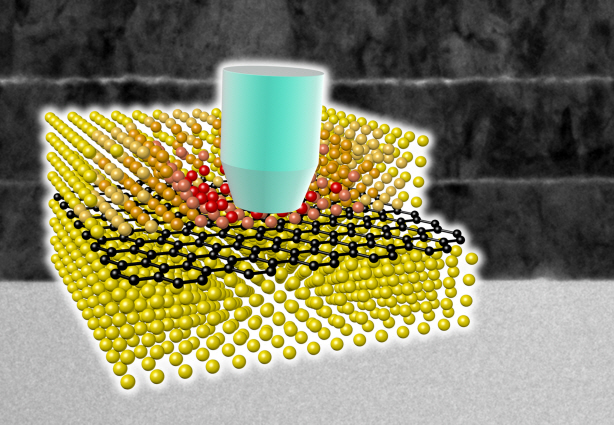 Ultra-High Strength Metamaterial Developed Using Graphene
New metamaterial has been developed, exhibiting hundreds of times greater strength than pure metals.
Professor Seung Min, Han and Yoo Sung, Jeong (Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Seok Woo, Jeon (Department of Material Science and Engineering) have developed a composite nanomaterial. The nanomaterial consists of graphene inserted in copper and nickel and exhibits strengths 500 times and 180 times, respectively, greater than that of pure metals. The result of the research was published on the July 2nd online edition in Nature Communications journal.
Graphene displays strengths 200 times greater than that of steel, is stretchable, and is flexible. The U.S. Army Armaments Research, Development and Engineering Center developed a graphene-metal nanomaterial but failed to drastically improve the strength of the material.
To maximize the strength increased by the addition of graphene, the KAIST research team created a layered structure of metal and graphene. Using CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), the team grew a single layer of graphene on a metal deposited substrate and then deposited another metal layer. They repeated this process to produce a metal-graphene multilayer composite material, utilizing a single layer of graphene. Micro-compression tests within Transmission Electronic Microscope and Molecular Dynamics simulations effectively showed the strength enhancing effect and the dislocation movement in grain boundaries of graphene on an atomic level.
The mechanical characteristics of the graphene layer within the metal-graphene composite material successfully blocked the dislocations and cracks from external damage from traveling inwards. Therefore the composite material displayed strength beyond conventional metal-metal multilayer materials. The copper-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 70nm exhibited 500 times greater (1.5GPa) strength than pure copper. Nickel-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 100nm showed 180 times greater (4.0GPa) strength than pure nickel.
It was found that there is a clear relationship between the interplanar distance and the strength of the multilayer material. A smaller interplanar distance made the dislocation movement more difficult and therefore increased the strength of the material. Professor Han, who led the research, commented, “the result is astounding as 0.00004% in weight of graphene increased the strength of the materials by hundreds of times” and “improvements based on this success, especially mass production with roll-to-roll process or metal sintering process in the production of ultra-high strength, lightweight parts for automobile and spacecraft, may become possible.” In addition, Professor Han mentioned that “the new material can be applied to coating materials for nuclear reactor construction or other structural materials requiring high reliability.”
The research project received support from National Research Foundation, Global Frontier Program, KAIST EEWS-KINC Program and KISTI Supercomputer and was a collaborative effort with KISTI (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information), KBSI (Korea Basic Science Institute), Stanford University, and Columbia University.
A schematic diagram shows the structure of metal-graphene multi-layers. The metal-graphene multi-layered composite materials, containing a single-layered graphene, block the dislocation movement of graphene layers, resulting in a greater strength in the materials.
2013.08.23 View 16420
Ultra-High Strength Metamaterial Developed Using Graphene
New metamaterial has been developed, exhibiting hundreds of times greater strength than pure metals.
Professor Seung Min, Han and Yoo Sung, Jeong (Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Seok Woo, Jeon (Department of Material Science and Engineering) have developed a composite nanomaterial. The nanomaterial consists of graphene inserted in copper and nickel and exhibits strengths 500 times and 180 times, respectively, greater than that of pure metals. The result of the research was published on the July 2nd online edition in Nature Communications journal.
Graphene displays strengths 200 times greater than that of steel, is stretchable, and is flexible. The U.S. Army Armaments Research, Development and Engineering Center developed a graphene-metal nanomaterial but failed to drastically improve the strength of the material.
To maximize the strength increased by the addition of graphene, the KAIST research team created a layered structure of metal and graphene. Using CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition), the team grew a single layer of graphene on a metal deposited substrate and then deposited another metal layer. They repeated this process to produce a metal-graphene multilayer composite material, utilizing a single layer of graphene. Micro-compression tests within Transmission Electronic Microscope and Molecular Dynamics simulations effectively showed the strength enhancing effect and the dislocation movement in grain boundaries of graphene on an atomic level.
The mechanical characteristics of the graphene layer within the metal-graphene composite material successfully blocked the dislocations and cracks from external damage from traveling inwards. Therefore the composite material displayed strength beyond conventional metal-metal multilayer materials. The copper-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 70nm exhibited 500 times greater (1.5GPa) strength than pure copper. Nickel-graphene multilayer material with an interplanar distance of 100nm showed 180 times greater (4.0GPa) strength than pure nickel.
It was found that there is a clear relationship between the interplanar distance and the strength of the multilayer material. A smaller interplanar distance made the dislocation movement more difficult and therefore increased the strength of the material. Professor Han, who led the research, commented, “the result is astounding as 0.00004% in weight of graphene increased the strength of the materials by hundreds of times” and “improvements based on this success, especially mass production with roll-to-roll process or metal sintering process in the production of ultra-high strength, lightweight parts for automobile and spacecraft, may become possible.” In addition, Professor Han mentioned that “the new material can be applied to coating materials for nuclear reactor construction or other structural materials requiring high reliability.”
The research project received support from National Research Foundation, Global Frontier Program, KAIST EEWS-KINC Program and KISTI Supercomputer and was a collaborative effort with KISTI (Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information), KBSI (Korea Basic Science Institute), Stanford University, and Columbia University.
A schematic diagram shows the structure of metal-graphene multi-layers. The metal-graphene multi-layered composite materials, containing a single-layered graphene, block the dislocation movement of graphene layers, resulting in a greater strength in the materials.
2013.08.23 View 16420 -
 Two Dimensions of Value: Dopamine Neurons Represent Reward but not Aversiveness
Professor Christopher D. Fiorillo of the Bio & Brain Engineering (http://ineuron.kaist.ac.kr/web/home.html) at KAIST published a research paper in the August 2 issue of Science. The title of the paper is “Two Dimensions of Value: Dopamine Neurons Represent Reward but not Aversiveness.” The following is an introduction of his research work:
To make decisions, we need to estimate the value of sensory stimuli and motor actions, their “goodness” and “badness.” We can imagine that good and bad are two ends of a single continuum, or dimension, of value. This would be analogous to the single dimension of light intensity, which ranges from dark on one end to bright light on the other, with many shades of gray in between. Past models of behavior and learning have been based on a single continuum of value, and it has been proposed that a particular group of neurons (brain cells) that use dopamine as a neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) represent the single dimension of value, signaling both good and bad.
The experiments reported here show that dopamine neurons are sensitive to the value of reward but not punishment (like the aversiveness of a bitter taste). This demonstrates that reward and aversiveness are represented as two discrete dimensions (or categories) in the brain. “Reward” refers to the category of good things (food, water, sex, money, etc.), and “punishment” to the category of bad things (stimuli associated with harm to the body and that cause pain or other unpleasant sensations or emotions).
Rather than having one neurotransmitter (dopamine) to represent a single dimension of value, the present results imply the existence of four neurotransmitters to represent two dimensions of value. Dopamine signals evidence for reward (“gains”) and some other neurotransmitter presumably signals evidence against reward (“losses”). Likewise, there should be a neurotransmitter for evidence of danger and another for evidence of safety. It is interesting that there are three other neurotransmitters that are analogous to dopamine in many respects (serotonin, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine), and it is possible that they could represent the other three value signals.
For the research article, please visit: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/341/6145/546.abstract
For the Science 2nd issue, please visit: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/current#ResearchArticles
Illustration of Value Dimension
2013.08.08 View 8415
Two Dimensions of Value: Dopamine Neurons Represent Reward but not Aversiveness
Professor Christopher D. Fiorillo of the Bio & Brain Engineering (http://ineuron.kaist.ac.kr/web/home.html) at KAIST published a research paper in the August 2 issue of Science. The title of the paper is “Two Dimensions of Value: Dopamine Neurons Represent Reward but not Aversiveness.” The following is an introduction of his research work:
To make decisions, we need to estimate the value of sensory stimuli and motor actions, their “goodness” and “badness.” We can imagine that good and bad are two ends of a single continuum, or dimension, of value. This would be analogous to the single dimension of light intensity, which ranges from dark on one end to bright light on the other, with many shades of gray in between. Past models of behavior and learning have been based on a single continuum of value, and it has been proposed that a particular group of neurons (brain cells) that use dopamine as a neurotransmitter (chemical messenger) represent the single dimension of value, signaling both good and bad.
The experiments reported here show that dopamine neurons are sensitive to the value of reward but not punishment (like the aversiveness of a bitter taste). This demonstrates that reward and aversiveness are represented as two discrete dimensions (or categories) in the brain. “Reward” refers to the category of good things (food, water, sex, money, etc.), and “punishment” to the category of bad things (stimuli associated with harm to the body and that cause pain or other unpleasant sensations or emotions).
Rather than having one neurotransmitter (dopamine) to represent a single dimension of value, the present results imply the existence of four neurotransmitters to represent two dimensions of value. Dopamine signals evidence for reward (“gains”) and some other neurotransmitter presumably signals evidence against reward (“losses”). Likewise, there should be a neurotransmitter for evidence of danger and another for evidence of safety. It is interesting that there are three other neurotransmitters that are analogous to dopamine in many respects (serotonin, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine), and it is possible that they could represent the other three value signals.
For the research article, please visit: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/341/6145/546.abstract
For the Science 2nd issue, please visit: http://www.sciencemag.org/content/current#ResearchArticles
Illustration of Value Dimension
2013.08.08 View 8415 -
 2013 International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST)
The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST) is a global forum organized by KAIST undergraduate students to promote the exchange of ideas and facilitate the discussion of issues that are important to science, technology, society, and higher education. The ICISTS-KAIST conference has been held annually every summer since 2005, inviting distinguished speakers and guests from all around the world to share their insights and expertise with students gathered from Korea and abroad. Last year alone, more than 300 students from 22 nations and 40 speakers participated in the event.
Originally, the ICISTS-KAIST was established by KAIST students who were inspired by the Harvard Project for Asian and International Relations (HPAIR), which is one of the Harvard’s largest annual student conferences in Asia.
This year, 335 students from 103 universities in 22 countries joined the conference that was held on August 5th-9th in Daejeon, making the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST the biggest science and engineering gathering hosted by university students in Asia. About 36% of the participants were international students.
The theme of the conference was “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society,” in which students and speakers addressed issues on how to harmonize the speed of scientific progress with the development of important values in society, as well as to explore solutions to overcome the chasm, if any, between the boundaries of science and society.
In his opening remarks, President Steve Kang said, “Creativity and innovation are born out of openness. Therefore, it is essential for young scientists and engineers to communicate with people from different cultural and political backgrounds. Through this kind of global interaction and exchange of ideas and views, students will have an opportunity to deepen their understanding of the world and to better examine the purpose of their intellectual exploration in science and technology.” At the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST, 25 distinguished speakers participated including Walter Bender, a former director of the Media Lab at MIT and David Christian, a professor of Macquarie University in Australia.
2013.08.08 View 11004
2013 International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST)
The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST) is a global forum organized by KAIST undergraduate students to promote the exchange of ideas and facilitate the discussion of issues that are important to science, technology, society, and higher education. The ICISTS-KAIST conference has been held annually every summer since 2005, inviting distinguished speakers and guests from all around the world to share their insights and expertise with students gathered from Korea and abroad. Last year alone, more than 300 students from 22 nations and 40 speakers participated in the event.
Originally, the ICISTS-KAIST was established by KAIST students who were inspired by the Harvard Project for Asian and International Relations (HPAIR), which is one of the Harvard’s largest annual student conferences in Asia.
This year, 335 students from 103 universities in 22 countries joined the conference that was held on August 5th-9th in Daejeon, making the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST the biggest science and engineering gathering hosted by university students in Asia. About 36% of the participants were international students.
The theme of the conference was “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society,” in which students and speakers addressed issues on how to harmonize the speed of scientific progress with the development of important values in society, as well as to explore solutions to overcome the chasm, if any, between the boundaries of science and society.
In his opening remarks, President Steve Kang said, “Creativity and innovation are born out of openness. Therefore, it is essential for young scientists and engineers to communicate with people from different cultural and political backgrounds. Through this kind of global interaction and exchange of ideas and views, students will have an opportunity to deepen their understanding of the world and to better examine the purpose of their intellectual exploration in science and technology.” At the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST, 25 distinguished speakers participated including Walter Bender, a former director of the Media Lab at MIT and David Christian, a professor of Macquarie University in Australia.
2013.08.08 View 11004 -
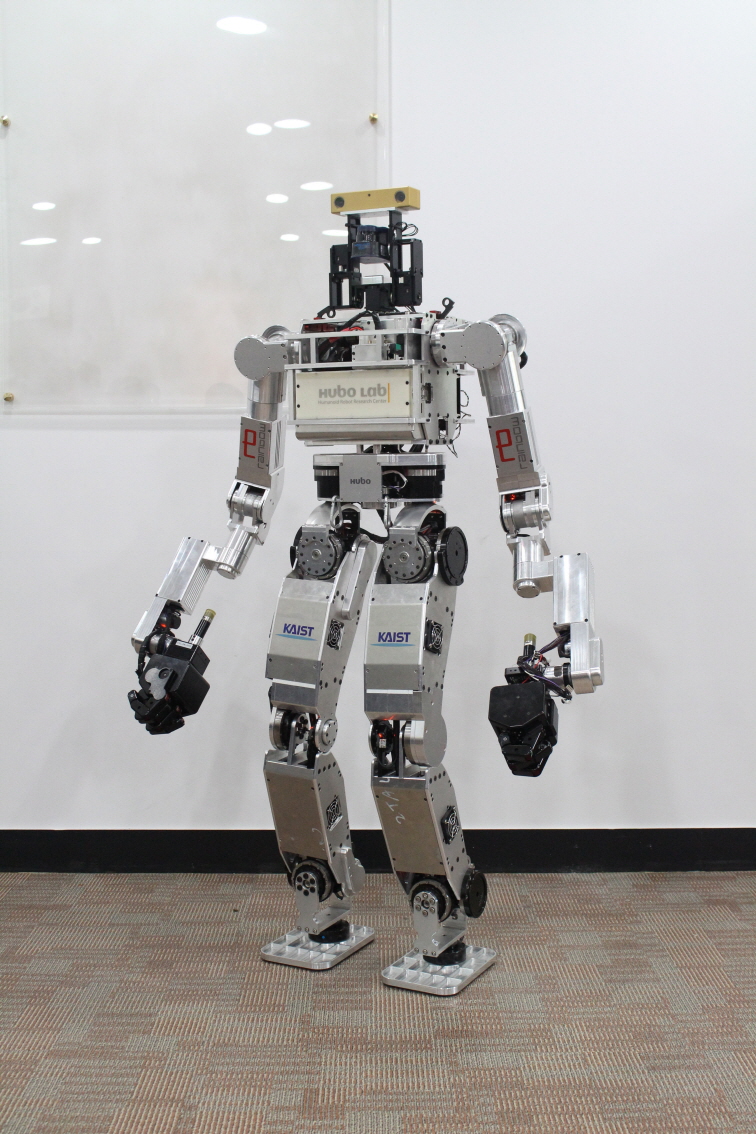 KAIST's HUBO Ready for DARPA's Robotics Challenge Trials
When walking on muddy or bumpy roads, the two arms of DRC-HUBO become extra legs, enabling stable and agile movements.
The Humanoid Robot Research Center (HUBO Lab, http://hubolab.kaist.ac.kr) at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Rainbow Co., a spin-off venture company of the university, unveiled a new model of HUBO that will be entered in an international robotics competition scheduled later this year.
The competition is hosted and sponsored by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which is called the DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC). Kicked off in October 2012, the DRC’s goal is to spur the development of advanced robots that can assist humans in mitigating and recovering from future natural and man-made disasters.
KAIST’s humanoid robot, HUBO, was originally created by Jun-Ho Oh, a distinguished professor of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in 2004. Since then, the robot has gone through technological advancements, with the latest version of HUBO II released in 2012. So far, 12 HUBOs have been exported for further studies in robotics to universities, research institutes, and private companies in the US, China, and Singapore.
In tandem with Rainbow Co. (www.rainbow-robot.com), Professor Oh and his research team recently developed DRC-HUBO, which will compete as Team DRC-HUBO led by Drexel University at the DRC trials to be held in December 2013. Team DRC-HUBO is consisted of KAIST and nine US institutions.
DRC-HUBO is designed to perform difficult but essential activities required when responding to disaster scenes. The robot will have to fulfill eight tasks assigned by the DRC at the upcoming event such as driving a utility vehicle, walking across rough terrain, climbing a ladder, and using hand tools.
Unlike the previous models of HUBO, DRC-HUBO boasts several distinctive, enhanced features. Chief among them is the way the robot interacts with the external environment. Without complex sensors installed throughout the body, DRC-HUBO can control each joint of the arms and legs in compliance with the dynamics dictated by the external environment.
For example, when DRC-HUBO is faced with a rock falling from above while climbing up a ladder, the robot’s arms and legs naturally give in to the force of external changes. Accordingly, as the robot dodges the rock, its body and joints smoothly sway to absorb shock so that the fingers can keep a tight grip on the ladder, and the feet are planted firmly on the rail of the ladder, not losing balance.
In addition, DRC-HUBO can switch from bipedal to quadrupedal walking and vice versa. This provides the robot with greater stability to walk on uneven terrain or to climb up a hill. The robot’s arms and legs are elongated to better meet the challenges demanded by the DRC competition. DRC-HUBO’s two arms swing back and forth to form legs when necessary, thereby walking freely backwards and forwards.
The robot has gotten stronger grip as well. The right hand has four fingers (with one triggering finger that operates independently from the other three fingers), and the left hand has three fingers. All three fingers on both hands are actuated synchronously for gripping. The fingers are sophisticated enough to steer the wheel of a vehicle or grab a ladder to climb up, and strong enough to hold 15 lbs in one hand.
“With a full 34 degrees of freedom (DOF), DRC-HUBO stands 4.7 ft tall and weighs 120 lbs. All in all, the robot has been improved and extensively refurbished from the past models of HUBOs to compete at the DRC Trials. It has better vision and coordination. The legs and arms have become stronger,” said Professor Oh.
“Although the robot is still a prototype, it has important capabilities that can be utilized in advancing humanoid robots in general. One example is the way its arms can be used as extra legs to support the robot’s body, offering more flexibility in providing aid to humans.”
2013.07.25 View 14697
KAIST's HUBO Ready for DARPA's Robotics Challenge Trials
When walking on muddy or bumpy roads, the two arms of DRC-HUBO become extra legs, enabling stable and agile movements.
The Humanoid Robot Research Center (HUBO Lab, http://hubolab.kaist.ac.kr) at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Rainbow Co., a spin-off venture company of the university, unveiled a new model of HUBO that will be entered in an international robotics competition scheduled later this year.
The competition is hosted and sponsored by the US Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), which is called the DARPA Robotics Challenge (DRC). Kicked off in October 2012, the DRC’s goal is to spur the development of advanced robots that can assist humans in mitigating and recovering from future natural and man-made disasters.
KAIST’s humanoid robot, HUBO, was originally created by Jun-Ho Oh, a distinguished professor of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in 2004. Since then, the robot has gone through technological advancements, with the latest version of HUBO II released in 2012. So far, 12 HUBOs have been exported for further studies in robotics to universities, research institutes, and private companies in the US, China, and Singapore.
In tandem with Rainbow Co. (www.rainbow-robot.com), Professor Oh and his research team recently developed DRC-HUBO, which will compete as Team DRC-HUBO led by Drexel University at the DRC trials to be held in December 2013. Team DRC-HUBO is consisted of KAIST and nine US institutions.
DRC-HUBO is designed to perform difficult but essential activities required when responding to disaster scenes. The robot will have to fulfill eight tasks assigned by the DRC at the upcoming event such as driving a utility vehicle, walking across rough terrain, climbing a ladder, and using hand tools.
Unlike the previous models of HUBO, DRC-HUBO boasts several distinctive, enhanced features. Chief among them is the way the robot interacts with the external environment. Without complex sensors installed throughout the body, DRC-HUBO can control each joint of the arms and legs in compliance with the dynamics dictated by the external environment.
For example, when DRC-HUBO is faced with a rock falling from above while climbing up a ladder, the robot’s arms and legs naturally give in to the force of external changes. Accordingly, as the robot dodges the rock, its body and joints smoothly sway to absorb shock so that the fingers can keep a tight grip on the ladder, and the feet are planted firmly on the rail of the ladder, not losing balance.
In addition, DRC-HUBO can switch from bipedal to quadrupedal walking and vice versa. This provides the robot with greater stability to walk on uneven terrain or to climb up a hill. The robot’s arms and legs are elongated to better meet the challenges demanded by the DRC competition. DRC-HUBO’s two arms swing back and forth to form legs when necessary, thereby walking freely backwards and forwards.
The robot has gotten stronger grip as well. The right hand has four fingers (with one triggering finger that operates independently from the other three fingers), and the left hand has three fingers. All three fingers on both hands are actuated synchronously for gripping. The fingers are sophisticated enough to steer the wheel of a vehicle or grab a ladder to climb up, and strong enough to hold 15 lbs in one hand.
“With a full 34 degrees of freedom (DOF), DRC-HUBO stands 4.7 ft tall and weighs 120 lbs. All in all, the robot has been improved and extensively refurbished from the past models of HUBOs to compete at the DRC Trials. It has better vision and coordination. The legs and arms have become stronger,” said Professor Oh.
“Although the robot is still a prototype, it has important capabilities that can be utilized in advancing humanoid robots in general. One example is the way its arms can be used as extra legs to support the robot’s body, offering more flexibility in providing aid to humans.”
2013.07.25 View 14697 -
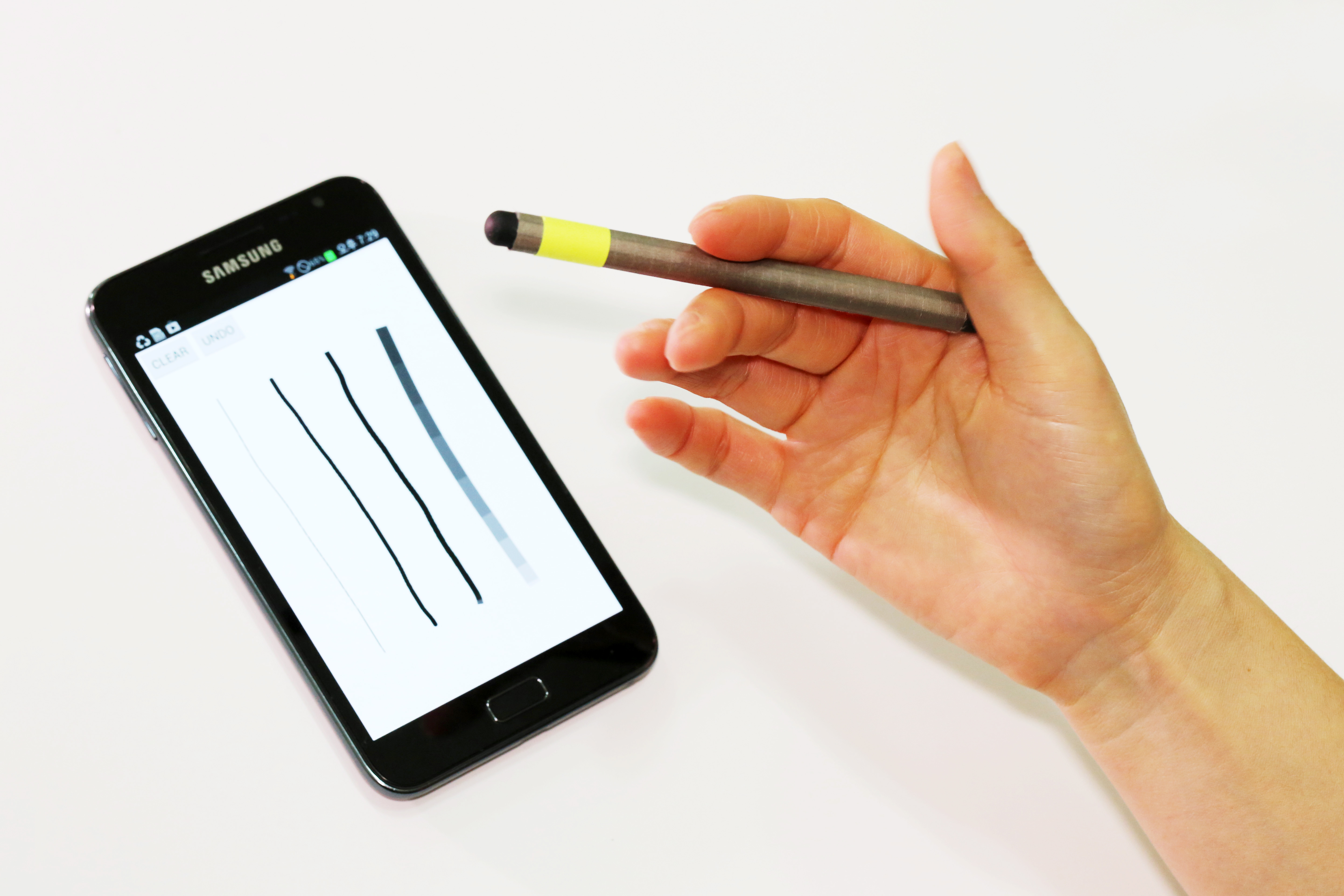 A magnetic pen for smartphones adds another level of conveniences
Utilizing existing features on smartphones, the MagPen provides users with a compatible and simple input tool regardless of the type of phones they are using.
A doctoral candidate at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a magnetically driven pen interface that works both on and around mobile devices. This interface, called the MagPen, can be used for any type of smartphones and tablet computers so long as they have magnetometers embedded in.
Advised by Professor Kwang-yun Wohn of the Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST, Sungjae Hwang, a Ph.D. student, created the MagPen in collaboration with Myung-Wook Ahn, a master"s student at the GSCT of KAIST, and Andrea Bianchi, a professor at Sungkyunkwan University.
Almost all mobile devices today provide location-based services, and magnetometers are incorporated in the integrated circuits of smartphones or tablet PCs, functioning as compasses. Taking advantage of built-in magnetometers, Hwang"s team came up with a technology that enabled an input tool for mobile devices such as a capacitive stylus pen to interact more sensitively and effectively with the devices" touch screen. Text and command entered by a stylus pen are expressed better on the screen of mobile devices than those done by human fingers.
The MagPen utilizes magnetometers equipped with smartphones, thus there is no need to build an additional sensing panel for a touchscreen as well as circuits, communication modules, or batteries for the pen. With an application installed on smartphones, it senses and analyzes the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet embedded in a standard capacitive stylus pen.
Sungjae Hwang said, "Our technology is eco-friendly and very affordable because we are able to improve the expressiveness of the stylus pen without requiring additional hardware beyond those already installed on the current mobile devices. The technology allows smartphone users to enjoy added convenience while no wastes generated."
The MagPen detects the direction at which a stylus pen is pointing; selects colors by dragging the pen across smartphone bezel; identifies pens with different magnetic properties; recognizes pen-spinning gestures; and estimates the finger pressure applied to the pen.
Notably, with its spinning motion, the MagPen expands the scope of input gestures recognized by a stylus pen beyond its existing vocabularies of gestures and techniques such as titling, hovering, and varying pressures. The tip of the pen switches from a pointer to an eraser and vice versa when spinning. Or, it can choose the thickness of the lines drawn on a screen by spinning.
"It"s quite remarkable to see that the MagPen can understand spinning motion. It"s like the pen changes its living environment from two dimensions to three dimensions. This is the most creative characteristic of our technology," added Sungjae Hwang.
Hwang"s initial research result was first presented at the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces organized by the Association for Computing Machinery and held on March 19-22 in Santa Monica, the US.
In the next month of August, the research team will present a paper on the MagPen technology, entitled "MagPen: Magnetically Driven Pen Interaction On and Around Conventional Smartphones" and receive an Honorable Mention Award at the 15th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services (MobileHCI 2013) to be held in Germany.
In addition to the MagPen, Hwang and his team are conducting other projects to develop different types of magnetic gadgets (collectively called "MagGetz") that include the Magnetic Marionette, a magnetic cover for a smartphone, which offers augmented interactions with the phone, as well as magnetic widgets such as buttons and toggle interface.
Hwang has filed ten patents for the MagGetz technology.
Youtube Links: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NkPo2las7wc, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J9GtgyzoZmM
2013.07.25 View 11430
A magnetic pen for smartphones adds another level of conveniences
Utilizing existing features on smartphones, the MagPen provides users with a compatible and simple input tool regardless of the type of phones they are using.
A doctoral candidate at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a magnetically driven pen interface that works both on and around mobile devices. This interface, called the MagPen, can be used for any type of smartphones and tablet computers so long as they have magnetometers embedded in.
Advised by Professor Kwang-yun Wohn of the Graduate School of Culture Technology (GSCT) at KAIST, Sungjae Hwang, a Ph.D. student, created the MagPen in collaboration with Myung-Wook Ahn, a master"s student at the GSCT of KAIST, and Andrea Bianchi, a professor at Sungkyunkwan University.
Almost all mobile devices today provide location-based services, and magnetometers are incorporated in the integrated circuits of smartphones or tablet PCs, functioning as compasses. Taking advantage of built-in magnetometers, Hwang"s team came up with a technology that enabled an input tool for mobile devices such as a capacitive stylus pen to interact more sensitively and effectively with the devices" touch screen. Text and command entered by a stylus pen are expressed better on the screen of mobile devices than those done by human fingers.
The MagPen utilizes magnetometers equipped with smartphones, thus there is no need to build an additional sensing panel for a touchscreen as well as circuits, communication modules, or batteries for the pen. With an application installed on smartphones, it senses and analyzes the magnetic field produced by a permanent magnet embedded in a standard capacitive stylus pen.
Sungjae Hwang said, "Our technology is eco-friendly and very affordable because we are able to improve the expressiveness of the stylus pen without requiring additional hardware beyond those already installed on the current mobile devices. The technology allows smartphone users to enjoy added convenience while no wastes generated."
The MagPen detects the direction at which a stylus pen is pointing; selects colors by dragging the pen across smartphone bezel; identifies pens with different magnetic properties; recognizes pen-spinning gestures; and estimates the finger pressure applied to the pen.
Notably, with its spinning motion, the MagPen expands the scope of input gestures recognized by a stylus pen beyond its existing vocabularies of gestures and techniques such as titling, hovering, and varying pressures. The tip of the pen switches from a pointer to an eraser and vice versa when spinning. Or, it can choose the thickness of the lines drawn on a screen by spinning.
"It"s quite remarkable to see that the MagPen can understand spinning motion. It"s like the pen changes its living environment from two dimensions to three dimensions. This is the most creative characteristic of our technology," added Sungjae Hwang.
Hwang"s initial research result was first presented at the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces organized by the Association for Computing Machinery and held on March 19-22 in Santa Monica, the US.
In the next month of August, the research team will present a paper on the MagPen technology, entitled "MagPen: Magnetically Driven Pen Interaction On and Around Conventional Smartphones" and receive an Honorable Mention Award at the 15th International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction with Mobile Devices and Services (MobileHCI 2013) to be held in Germany.
In addition to the MagPen, Hwang and his team are conducting other projects to develop different types of magnetic gadgets (collectively called "MagGetz") that include the Magnetic Marionette, a magnetic cover for a smartphone, which offers augmented interactions with the phone, as well as magnetic widgets such as buttons and toggle interface.
Hwang has filed ten patents for the MagGetz technology.
Youtube Links: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NkPo2las7wc, http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=J9GtgyzoZmM
2013.07.25 View 11430 -
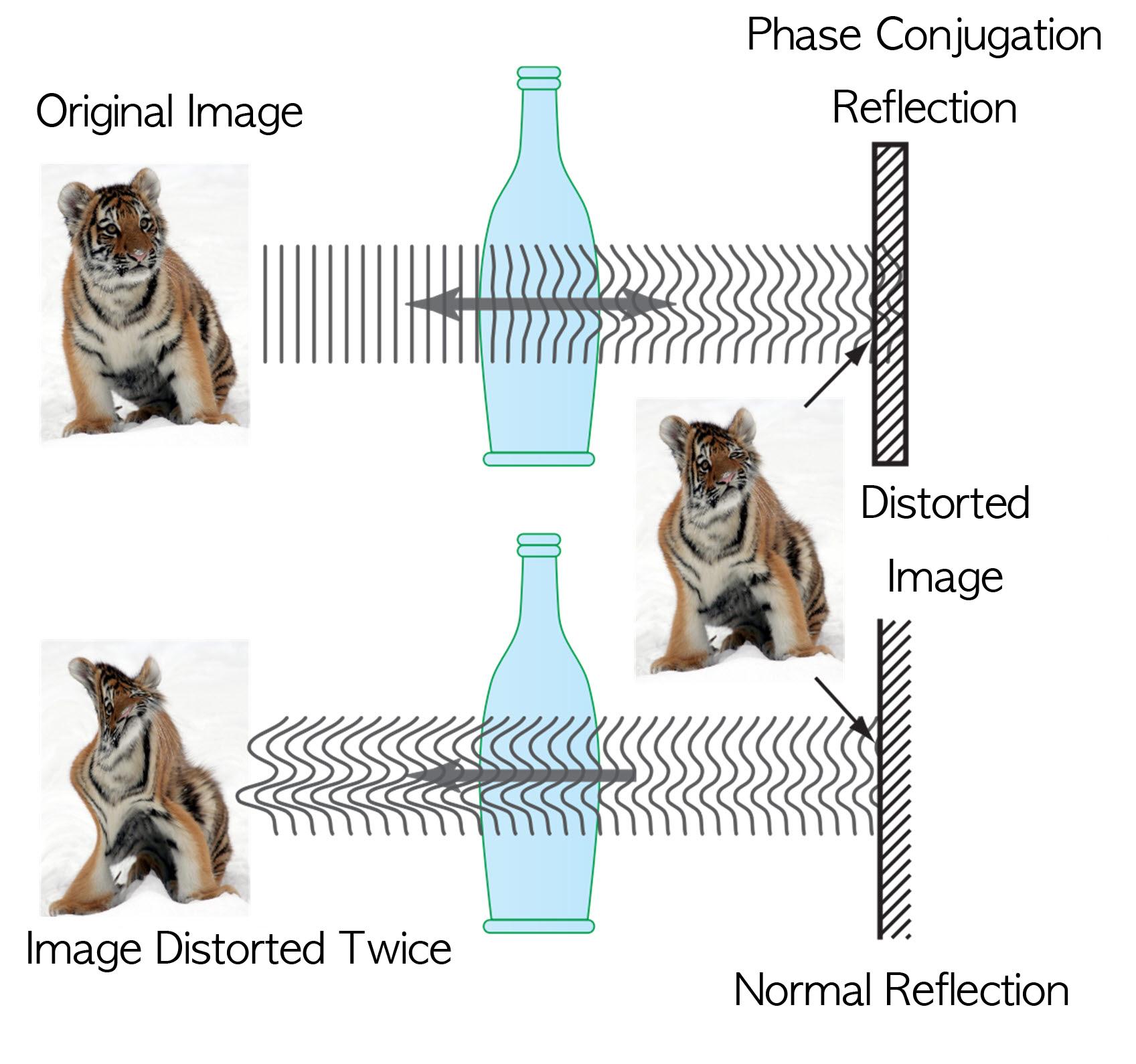 Technology Developed to Control Light Scattering Using Holography
Published on May 29th Nature Scientific Reports online
Recently, a popular article demonstrated that an opaque glass becomes transparent as transparent tape is applied to the glass. The scientific principle is that light is less scattered as the rough surface of the opaque glass is filled by transparent tape, thereby making things behind the opaque glass look clearer.
Professor Yong-Keun Park from KAIST’s Department of Physics, in a joint research with MIT Spectroscopy Lab, has developed a technology to easily control light scattering using holography. Their results are published on Nature’s Scientific Reports May 29th online edition.
This technology allows us to see things behind visual obstructions such as cloud and smoke, or even human skin that is highly scattering, optically thick materials. The research team applied the holography technology that records both the direction and intensity of light, and controlled light scattering of obstacles lied between an observer and a target image. The team was able to retrieve the original image by recording the information of scattered light and reflecting the light precisely to the other side.This phenomenon is known as “phase conjugation” in physics. Professor Park’s team applied phase conjugation and digital holography to observe two-dimensional image behind a highly scattering wall. “This technology will be utilized in many fields of physics, optics, nanotechnology, medical science, and even military science,” said Professor Park. “This is different from what is commonly known as penetrating camera or invisible clothes.” He nevertheless drew the line at over-interpreting the technology, “Currently, the significance is on the development of the technology itself that allows us to accurately control the scattering of light."
Figure I. Observed Images
Figure II. Light Scattering Control
2013.07.19 View 9017
Technology Developed to Control Light Scattering Using Holography
Published on May 29th Nature Scientific Reports online
Recently, a popular article demonstrated that an opaque glass becomes transparent as transparent tape is applied to the glass. The scientific principle is that light is less scattered as the rough surface of the opaque glass is filled by transparent tape, thereby making things behind the opaque glass look clearer.
Professor Yong-Keun Park from KAIST’s Department of Physics, in a joint research with MIT Spectroscopy Lab, has developed a technology to easily control light scattering using holography. Their results are published on Nature’s Scientific Reports May 29th online edition.
This technology allows us to see things behind visual obstructions such as cloud and smoke, or even human skin that is highly scattering, optically thick materials. The research team applied the holography technology that records both the direction and intensity of light, and controlled light scattering of obstacles lied between an observer and a target image. The team was able to retrieve the original image by recording the information of scattered light and reflecting the light precisely to the other side.This phenomenon is known as “phase conjugation” in physics. Professor Park’s team applied phase conjugation and digital holography to observe two-dimensional image behind a highly scattering wall. “This technology will be utilized in many fields of physics, optics, nanotechnology, medical science, and even military science,” said Professor Park. “This is different from what is commonly known as penetrating camera or invisible clothes.” He nevertheless drew the line at over-interpreting the technology, “Currently, the significance is on the development of the technology itself that allows us to accurately control the scattering of light."
Figure I. Observed Images
Figure II. Light Scattering Control
2013.07.19 View 9017 -
 Joint Research Center on EEWS with Hyundai Heavy Industries Plans to Open
The research center will conduct collaborative R&D projects on energy, environment, water, and sustainability for the next five years.Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), the world’s largest shipbuilding company, signed an MOU with KAIST for future business development and joint research collaboration.
KAIST and HHI signed an MOU as an agreement to establish the “HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center (HK Research Center) on June 21st.”
The major mission of the HK Research Center is to build a strong base for creating future businesses through developing fundamental, core technology in the field of EEWS and designing business models based on the new technology.
Toward this goal, HHI will sponsor the R&D budget and operation expenses of the research center for the next five years.
Prior to the signing of the MOU, a delegation from HHI, led by the Vice President, Mr. Si-Young Hwang, visited the Office of EEWS Initiative at KAIST and held a workshop. During the workshop, HHI and KAIST agreed to collaborate in fields such as LNG-propelled ships, solar power generation, energy storage, fuel cells, and CO2 capture.
KAIST has run a EEWS graduate program that receives government grants over the last five years, with a research emphasis on energy, environment, water, and sustainability, which are crucial issues to humankind in the 21st century. The EEWS program achieved 24 core technological developments and educates more than 200 masters- and PhD-degree students annually.
The EEWS program also emphasizes commercializing its research outcomes. Through the annual Business Planning Competition and Investment Drive, there have been eight new companies founded by alumni and professors over the last five years of the program. The HK Research Center will be an excellent foundation for future education and research in EEWS.
Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of the HK Research Center and the director of the EEWS Initiative, said, “This event is a benchmarking example of Industry-KAIST collaboration. We hope that the HK Research Center will be a place for disruptive innovations to translate into creative business opportunities.”
MOU signed for Hyundai Heavy Industries-KAIST EEWS Research Center
2013.07.15 View 9074
Joint Research Center on EEWS with Hyundai Heavy Industries Plans to Open
The research center will conduct collaborative R&D projects on energy, environment, water, and sustainability for the next five years.Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI), the world’s largest shipbuilding company, signed an MOU with KAIST for future business development and joint research collaboration.
KAIST and HHI signed an MOU as an agreement to establish the “HHI-KAIST EEWS Research Center (HK Research Center) on June 21st.”
The major mission of the HK Research Center is to build a strong base for creating future businesses through developing fundamental, core technology in the field of EEWS and designing business models based on the new technology.
Toward this goal, HHI will sponsor the R&D budget and operation expenses of the research center for the next five years.
Prior to the signing of the MOU, a delegation from HHI, led by the Vice President, Mr. Si-Young Hwang, visited the Office of EEWS Initiative at KAIST and held a workshop. During the workshop, HHI and KAIST agreed to collaborate in fields such as LNG-propelled ships, solar power generation, energy storage, fuel cells, and CO2 capture.
KAIST has run a EEWS graduate program that receives government grants over the last five years, with a research emphasis on energy, environment, water, and sustainability, which are crucial issues to humankind in the 21st century. The EEWS program achieved 24 core technological developments and educates more than 200 masters- and PhD-degree students annually.
The EEWS program also emphasizes commercializing its research outcomes. Through the annual Business Planning Competition and Investment Drive, there have been eight new companies founded by alumni and professors over the last five years of the program. The HK Research Center will be an excellent foundation for future education and research in EEWS.
Professor Jae-Kyu Lee, the head of the HK Research Center and the director of the EEWS Initiative, said, “This event is a benchmarking example of Industry-KAIST collaboration. We hope that the HK Research Center will be a place for disruptive innovations to translate into creative business opportunities.”
MOU signed for Hyundai Heavy Industries-KAIST EEWS Research Center
2013.07.15 View 9074 -
 Chin-Wan Chung, a professor of computer science, received the best paper award from ACM
The Korea Times reported on July 12, 2013 that Chin-Wan Chung, a professor of computer science at KAIST, won the best paper award by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). For the article, please click the link:
http://koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/people/2013/07/178_139132.html
2013.07.15 View 7463
Chin-Wan Chung, a professor of computer science, received the best paper award from ACM
The Korea Times reported on July 12, 2013 that Chin-Wan Chung, a professor of computer science at KAIST, won the best paper award by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM). For the article, please click the link:
http://koreatimes.co.kr/www/news/people/2013/07/178_139132.html
2013.07.15 View 7463 -
 Prof. Song Chong received the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize Paper Award
The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Communications Society (ComSoc), a renowned global network of professionals with a common interest in advancing communications technologies, has announced the winner of the 2013 William R. Bennett Prize in the field of communications networking. The prize was given to a Korean research team led by Song Chong, Professor of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and Injong Rhee, Professor of Computer Science at North Carolina State University. In addition, Dr. Minsu Shin, Dr. Seongik Hong, and Dr. Seong Joon Kim of Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. as well as Professor Kyunghan Lee from Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology were recognized for their contribution.
The William R. Bennett Prize for communications networking has been awarded each year since 1994 in recognition of the best paper published in any journal financially sponsored or co-sponsored by ComSoc in the previous three calendar years. Only one paper per year is selected based on its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews. Among the previous award winners are Robert Gallager of MIT, and Steven Low of the California Institute of Technology, and Kang G. Shin of the University of Michigan.
The Korean research team’s paper, On the Levy-Walk Nature of Human Mobility, was published in the June 2011 issue of IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, a bimonthly journal co-sponsored by the IEEE ComSoc, the IEEE Computer Society, and the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) with its Special Interest Group on Data Communications (SIGCOMM).
In the paper, the research team proposed a new statistical model to effectively analyze the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life. The team handed out GPS (global positioning system) devices to 100 participants residing in five different university campuses in Korea and the US and collected data on their movements for 226 days. The mobility pattern obtained from the experiment predicted accurately how the participants actually moved around during their routines. Since publication, the paper has been cited by other papers approximately 350 times.
The team’s research results will apply to many fields such as the prevention and control of epidemics, the design of efficient communications networks, and the development of urban and transportation system.
The research team received the award on June 10th at the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) held in Budapest, Hungary, from June 9-13, 2013.
Professor Song Chong
2013.07.06 View 14029
Prof. Song Chong received the IEEE William R. Bennett Prize Paper Award
The IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) Communications Society (ComSoc), a renowned global network of professionals with a common interest in advancing communications technologies, has announced the winner of the 2013 William R. Bennett Prize in the field of communications networking. The prize was given to a Korean research team led by Song Chong, Professor of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and Injong Rhee, Professor of Computer Science at North Carolina State University. In addition, Dr. Minsu Shin, Dr. Seongik Hong, and Dr. Seong Joon Kim of Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. as well as Professor Kyunghan Lee from Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology were recognized for their contribution.
The William R. Bennett Prize for communications networking has been awarded each year since 1994 in recognition of the best paper published in any journal financially sponsored or co-sponsored by ComSoc in the previous three calendar years. Only one paper per year is selected based on its quality, originality, scientific citation index, and peer reviews. Among the previous award winners are Robert Gallager of MIT, and Steven Low of the California Institute of Technology, and Kang G. Shin of the University of Michigan.
The Korean research team’s paper, On the Levy-Walk Nature of Human Mobility, was published in the June 2011 issue of IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, a bimonthly journal co-sponsored by the IEEE ComSoc, the IEEE Computer Society, and the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) with its Special Interest Group on Data Communications (SIGCOMM).
In the paper, the research team proposed a new statistical model to effectively analyze the pattern of individual human mobility in daily life. The team handed out GPS (global positioning system) devices to 100 participants residing in five different university campuses in Korea and the US and collected data on their movements for 226 days. The mobility pattern obtained from the experiment predicted accurately how the participants actually moved around during their routines. Since publication, the paper has been cited by other papers approximately 350 times.
The team’s research results will apply to many fields such as the prevention and control of epidemics, the design of efficient communications networks, and the development of urban and transportation system.
The research team received the award on June 10th at the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC) held in Budapest, Hungary, from June 9-13, 2013.
Professor Song Chong
2013.07.06 View 14029 -
 KAIST Placed 3rd in the World's Best 100 Emerging Universities
The Times Higher Education (THE) published its world university rankings on June 20, 2013. It is a list of the best 100 universities whose histories are 50 years old or younger. KAIST was ranked 3rd in the list, two places up from the 5th last year. Forbes and Reuters carried a story on the top ten emerging universities out of the listed 100 institutions, highlighting strong showings in the Asian region. For the articles, please see the attached file (Forbes) or click the link (Reuters) below:
http://www.reuters.com/article/2013/06/19/education-university-rankings-idUSL2N0EU1HZ20130619
2013.06.22 View 7833
KAIST Placed 3rd in the World's Best 100 Emerging Universities
The Times Higher Education (THE) published its world university rankings on June 20, 2013. It is a list of the best 100 universities whose histories are 50 years old or younger. KAIST was ranked 3rd in the list, two places up from the 5th last year. Forbes and Reuters carried a story on the top ten emerging universities out of the listed 100 institutions, highlighting strong showings in the Asian region. For the articles, please see the attached file (Forbes) or click the link (Reuters) below:
http://www.reuters.com/article/2013/06/19/education-university-rankings-idUSL2N0EU1HZ20130619
2013.06.22 View 7833