development
-
 Partnership Agreement between KAIST and SK Telecom for Cyber Security
KAIST
and SK Telecom, one of the largest wireless telecommunications operators in
Korea, signed a memorandum of understanding on the industry and university cooperation
to establish a research center for cyber security on March 18, 2014.
The
center will conduct research projects to improve privacy protection, develop core
technologies needed for cyber security, train engineers and researchers, and
host seminars and conferences.
The
two organizations will implement the first joint research project on the
development of software-defined network-based solutions and universal subscriber
identity module-based personal identification solutions.
2014.03.26 View 8493
Partnership Agreement between KAIST and SK Telecom for Cyber Security
KAIST
and SK Telecom, one of the largest wireless telecommunications operators in
Korea, signed a memorandum of understanding on the industry and university cooperation
to establish a research center for cyber security on March 18, 2014.
The
center will conduct research projects to improve privacy protection, develop core
technologies needed for cyber security, train engineers and researchers, and
host seminars and conferences.
The
two organizations will implement the first joint research project on the
development of software-defined network-based solutions and universal subscriber
identity module-based personal identification solutions.
2014.03.26 View 8493 -
 KAIST student wins Aerospace Student Papers Grand Prize
Dong-Il Yoo, a doctoral candidate under Professor Hyun-Chul Shim, at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, has been awarded the Second Prize Award at the 11th Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) Paper Contest. The award ceremony was held on October 30th at the media conference room at the KINTEX ADEX 2013 Exhibition in Seoul.
Yoo"s paper, titled "A Study on Virtual Pursuit Point-based Autonomous Air Combat Guidance Law for UCAV," is highly regarded for originality and creativity. The Field Robotics Center at the KAIST Institute, where Yoo conducted his research, also received the first prize at the 7th KAI Paper Contest.
The KAI Paper Contest was first organized in 2003 to promote academic interest and advance research and development in aerospace engineering among university students.
The KAI Paper Contest is one of the most prestigious contests in Korea. It is sponsored by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, the Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association.
Dong-Il Yoo (left) and Professor Hyun-Chul Shim (right)
2013.11.11 View 15419
KAIST student wins Aerospace Student Papers Grand Prize
Dong-Il Yoo, a doctoral candidate under Professor Hyun-Chul Shim, at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, has been awarded the Second Prize Award at the 11th Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) Paper Contest. The award ceremony was held on October 30th at the media conference room at the KINTEX ADEX 2013 Exhibition in Seoul.
Yoo"s paper, titled "A Study on Virtual Pursuit Point-based Autonomous Air Combat Guidance Law for UCAV," is highly regarded for originality and creativity. The Field Robotics Center at the KAIST Institute, where Yoo conducted his research, also received the first prize at the 7th KAI Paper Contest.
The KAI Paper Contest was first organized in 2003 to promote academic interest and advance research and development in aerospace engineering among university students.
The KAI Paper Contest is one of the most prestigious contests in Korea. It is sponsored by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, the Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association.
Dong-Il Yoo (left) and Professor Hyun-Chul Shim (right)
2013.11.11 View 15419 -
 KAIST announced a novel technology to produce gasoline by a metabolically engineered microorganism
A major scientific breakthrough in the development of renewable energy sources and other important chemicals; The research team succeeded in producing 580 mg of gasoline per liter of cultured broth by converting in vivo generated fatty acids
For many decades, we have been relying on fossil resources to produce liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and many industrial and consumer chemicals for daily use. However, increasing strains on natural resources as well as environmental issues including global warming have triggered a strong interest in developing sustainable ways to obtain fuels and chemicals.
Gasoline, the petroleum-derived product that is most widely used as a fuel for transportation, is a mixture of hydrocarbons, additives, and blending agents. The hydrocarbons, called alkanes, consist only of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Gasoline has a combination of straight-chain and branched-chain alkanes (hydrocarbons) consisted of 4-12 carbon atoms linked by direct carbon-carbon bonds.
Previously, through metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli (E. coli), there have been a few research results on the production of long-chain alkanes, which consist of 13-17 carbon atoms, suitable for replacing diesel. However, there has been no report on the microbial production of short-chain alkanes, a possible substitute for gasoline.
In the paper (entitled "Microbial Production of Short-chain Alkanes") published online in Nature on September 29, a Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) reported, for the first time, the development of a novel strategy for microbial gasoline production through metabolic engineering of E. coli.
The research team engineered the fatty acid metabolism to provide the fatty acid derivatives that are shorter than normal intracellular fatty acid metabolites, and introduced a novel synthetic pathway for the biosynthesis of short-chain alkanes. This allowed the development of platform E. coli strain capable of producing gasoline for the first time. Furthermore, this platform strain, if desired, can be modified to produce other products such as short-chain fatty esters and short-chain fatty alcohols.
In this paper, the Korean researchers described detailed strategies for 1) screening of enzymes associated with the production of fatty acids, 2) engineering of enzymes and fatty acid biosynthetic pathways to concentrate carbon flux towards the short-chain fatty acid production, and 3) converting short-chain fatty acids to their corresponding alkanes (gasoline) by introducing a novel synthetic pathway and optimization of culture conditions. Furthermore, the research team showed the possibility of producing fatty esters and alcohols by introducing responsible enzymes into the same platform strain.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "It is only the beginning of the work towards sustainable production of gasoline. The titer is rather low due to the low metabolic flux towards the formation of short-chain fatty acids and their derivatives. We are currently working on increasing the titer, yield and productivity of bio-gasoline. Nonetheless, we are pleased to report, for the first time, the production of gasoline through the metabolic engineering of E. coli, which we hope will serve as a basis for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce fuels and chemicals from renewable resources."
This research was supported by the Advanced Biomass Research and Development Center of Korea (ABC-2010-0029799) through the Global Frontier Research Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF), Republic of Korea. Systems metabolic engineering work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-2012M1A2A2026556) by MSIP through NRF.
Short-Chain Alkanes Generated from Renewable Biomass
This diagram shows the metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of short-chain alkanes (gasoline) from renewable biomass.
Nature Cover Page (September 29th, 2013)
2013.11.04 View 14250
KAIST announced a novel technology to produce gasoline by a metabolically engineered microorganism
A major scientific breakthrough in the development of renewable energy sources and other important chemicals; The research team succeeded in producing 580 mg of gasoline per liter of cultured broth by converting in vivo generated fatty acids
For many decades, we have been relying on fossil resources to produce liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and many industrial and consumer chemicals for daily use. However, increasing strains on natural resources as well as environmental issues including global warming have triggered a strong interest in developing sustainable ways to obtain fuels and chemicals.
Gasoline, the petroleum-derived product that is most widely used as a fuel for transportation, is a mixture of hydrocarbons, additives, and blending agents. The hydrocarbons, called alkanes, consist only of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Gasoline has a combination of straight-chain and branched-chain alkanes (hydrocarbons) consisted of 4-12 carbon atoms linked by direct carbon-carbon bonds.
Previously, through metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli (E. coli), there have been a few research results on the production of long-chain alkanes, which consist of 13-17 carbon atoms, suitable for replacing diesel. However, there has been no report on the microbial production of short-chain alkanes, a possible substitute for gasoline.
In the paper (entitled "Microbial Production of Short-chain Alkanes") published online in Nature on September 29, a Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) reported, for the first time, the development of a novel strategy for microbial gasoline production through metabolic engineering of E. coli.
The research team engineered the fatty acid metabolism to provide the fatty acid derivatives that are shorter than normal intracellular fatty acid metabolites, and introduced a novel synthetic pathway for the biosynthesis of short-chain alkanes. This allowed the development of platform E. coli strain capable of producing gasoline for the first time. Furthermore, this platform strain, if desired, can be modified to produce other products such as short-chain fatty esters and short-chain fatty alcohols.
In this paper, the Korean researchers described detailed strategies for 1) screening of enzymes associated with the production of fatty acids, 2) engineering of enzymes and fatty acid biosynthetic pathways to concentrate carbon flux towards the short-chain fatty acid production, and 3) converting short-chain fatty acids to their corresponding alkanes (gasoline) by introducing a novel synthetic pathway and optimization of culture conditions. Furthermore, the research team showed the possibility of producing fatty esters and alcohols by introducing responsible enzymes into the same platform strain.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "It is only the beginning of the work towards sustainable production of gasoline. The titer is rather low due to the low metabolic flux towards the formation of short-chain fatty acids and their derivatives. We are currently working on increasing the titer, yield and productivity of bio-gasoline. Nonetheless, we are pleased to report, for the first time, the production of gasoline through the metabolic engineering of E. coli, which we hope will serve as a basis for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce fuels and chemicals from renewable resources."
This research was supported by the Advanced Biomass Research and Development Center of Korea (ABC-2010-0029799) through the Global Frontier Research Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF), Republic of Korea. Systems metabolic engineering work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-2012M1A2A2026556) by MSIP through NRF.
Short-Chain Alkanes Generated from Renewable Biomass
This diagram shows the metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of short-chain alkanes (gasoline) from renewable biomass.
Nature Cover Page (September 29th, 2013)
2013.11.04 View 14250 -
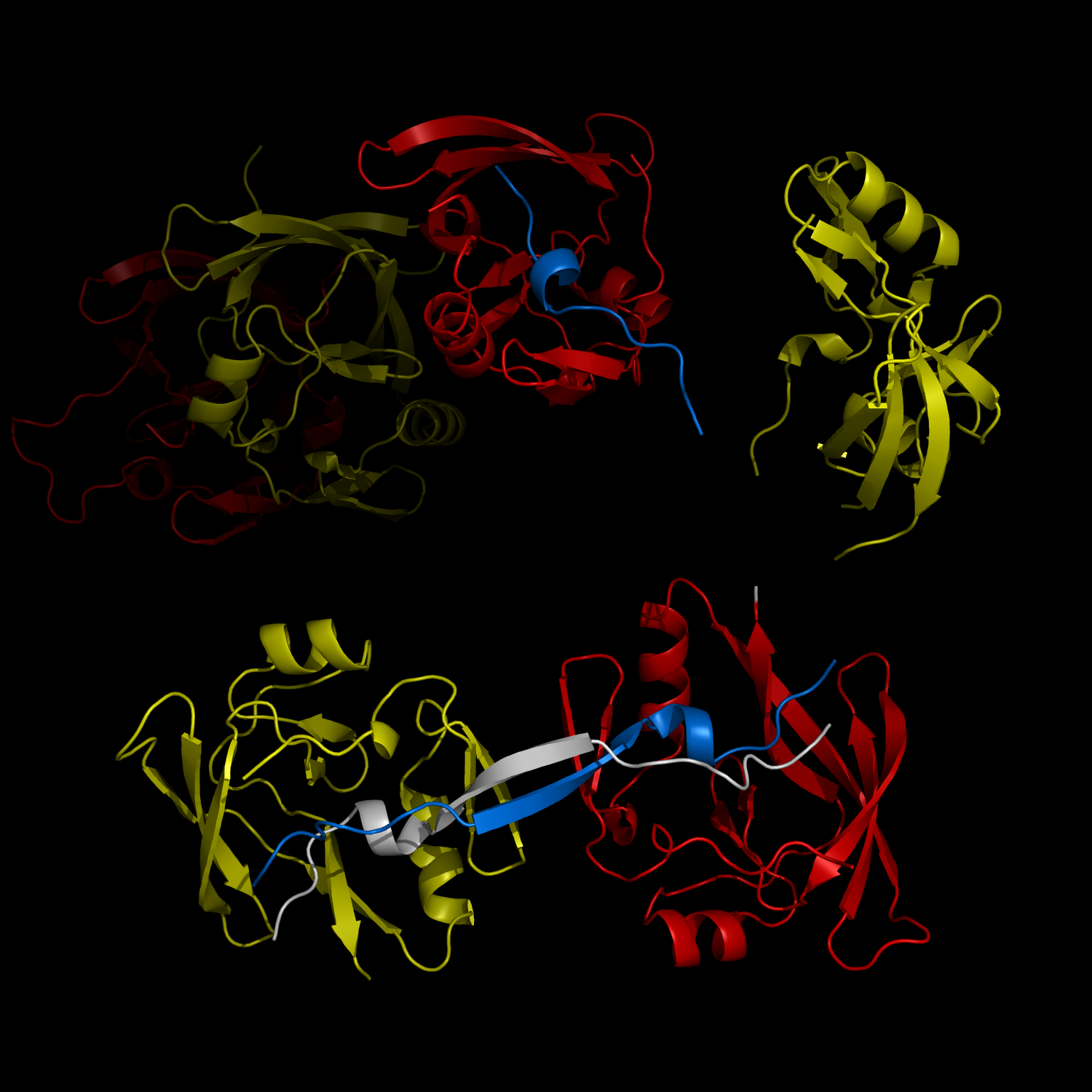 New Structural Insight into Neurodegenerative Disease
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) released their results on the structure and molecular details of the neurodegenerative disease-associated protein Ataxin-1. Mutations in Ataxin-1 cause the neurological disease, Spinocerebella Ataxia Type 1 (SCA1), which is characterized by a loss of muscular coordination and balance (ataxia), as is seen in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases.
SCA1-causing mutations in the ATAXIN1 gene alter the length of a glutamine stretch in the Ataxin-1 protein. The research team provides the first structural insight into the complex formation of ATAXIN-1 with its binding partner, Capicua (CIC). The team, led by Professor Ji-Joon Song from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, solved the structure of Ataxin-1 and CIC complex in atomic level revealing molecular details of the interaction between Ataxin-1 and CIC.
Professor Song explained his recent research work,
“We are able to see the intricate process of complex formation and reconfiguration of the two proteins when they interact with each other. Our work, we expect, will provide a new therapeutic target to modulate SCA1 neurodegenerative disease.”
Understanding structural and molecular details of proteins at the atomic level will help researchers to track the molecular pathogenesis of the disease and, ultimately, design targeted therapies or treatments for patients, rather than just relieving the symptoms of diseases.
Professor Song’s research paper, entitled “Structural Basis of Protein Complex Formation and Reconfiguration by Polyglutamine Disease Protein ATAXIN-1 and Capicua,” will be published in the March 15th issue of Genes & Development (www.genesdev.org).
Complex Formation and Reconfiguration of ATAXIN-1 and Capicua
The complex formation between a polyglutamine disease protein, ATXIN-1 and the transcriptional repressor Capicua (CIC) plays a critical role in SCA 1 pathogenesis. The image shows that the homodimerization of ATXIN-1 (yellow and red) is disrupted upon binding of CIC (blue). Furthermore, the binding of CIC to the ATXIN-1 induces a new form of ATXIN-1 dimerization mediated by CICs (ATXIN-1 AXH domains are shown in yellow and red, and CIC peptides shown in blue and white).
2013.04.02 View 10894
New Structural Insight into Neurodegenerative Disease
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) released their results on the structure and molecular details of the neurodegenerative disease-associated protein Ataxin-1. Mutations in Ataxin-1 cause the neurological disease, Spinocerebella Ataxia Type 1 (SCA1), which is characterized by a loss of muscular coordination and balance (ataxia), as is seen in Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s diseases.
SCA1-causing mutations in the ATAXIN1 gene alter the length of a glutamine stretch in the Ataxin-1 protein. The research team provides the first structural insight into the complex formation of ATAXIN-1 with its binding partner, Capicua (CIC). The team, led by Professor Ji-Joon Song from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, solved the structure of Ataxin-1 and CIC complex in atomic level revealing molecular details of the interaction between Ataxin-1 and CIC.
Professor Song explained his recent research work,
“We are able to see the intricate process of complex formation and reconfiguration of the two proteins when they interact with each other. Our work, we expect, will provide a new therapeutic target to modulate SCA1 neurodegenerative disease.”
Understanding structural and molecular details of proteins at the atomic level will help researchers to track the molecular pathogenesis of the disease and, ultimately, design targeted therapies or treatments for patients, rather than just relieving the symptoms of diseases.
Professor Song’s research paper, entitled “Structural Basis of Protein Complex Formation and Reconfiguration by Polyglutamine Disease Protein ATAXIN-1 and Capicua,” will be published in the March 15th issue of Genes & Development (www.genesdev.org).
Complex Formation and Reconfiguration of ATAXIN-1 and Capicua
The complex formation between a polyglutamine disease protein, ATXIN-1 and the transcriptional repressor Capicua (CIC) plays a critical role in SCA 1 pathogenesis. The image shows that the homodimerization of ATXIN-1 (yellow and red) is disrupted upon binding of CIC (blue). Furthermore, the binding of CIC to the ATXIN-1 induces a new form of ATXIN-1 dimerization mediated by CICs (ATXIN-1 AXH domains are shown in yellow and red, and CIC peptides shown in blue and white).
2013.04.02 View 10894 -
 Anonymous philanthropist donates 5.5 billion won to KAIST
An unnamed philanthropist donated a large sum of money to KAIST to be used as funds for the school"s development.
On September 6th, the donor met with President Suh to donate a sum of 5.5 billion won to the school for the development of science and technology.
A KAIST representative announced that the donor did not want to be named and that he was greatly impressed by President Suh"s and KAIST"s efforts towards reformation. The philanthropist wanted the donation to be used for research funds and financial aid.
President Suh said that "KAIST was deeply thankful and that it would work harder to show fulfill the donor"s wishes" and that the money would indeed be used for research and the students.
This was the 6th largest donation since the start of President Suh"s post in July 2006. Since 2006, the accumulated KAIST development fund has increased 30 times, from 5.9 billion won at the end of 2006 to 180 billion won in September 2012.
2012.09.24 View 7898
Anonymous philanthropist donates 5.5 billion won to KAIST
An unnamed philanthropist donated a large sum of money to KAIST to be used as funds for the school"s development.
On September 6th, the donor met with President Suh to donate a sum of 5.5 billion won to the school for the development of science and technology.
A KAIST representative announced that the donor did not want to be named and that he was greatly impressed by President Suh"s and KAIST"s efforts towards reformation. The philanthropist wanted the donation to be used for research funds and financial aid.
President Suh said that "KAIST was deeply thankful and that it would work harder to show fulfill the donor"s wishes" and that the money would indeed be used for research and the students.
This was the 6th largest donation since the start of President Suh"s post in July 2006. Since 2006, the accumulated KAIST development fund has increased 30 times, from 5.9 billion won at the end of 2006 to 180 billion won in September 2012.
2012.09.24 View 7898 -
 MOU: KAIST-Korea Internet & Security Agency
KAIST signed a MOU with the Korea Internet & Security Agency for the development of IT and International Security.
As a result of the MOU interaction in ▲Exchange of personnel and materials for cooperative research for information protection ▲Information protection policy and technology ▲Education and training for developing information protection personnel, will be increased.
Director of Cyber Security Research Center Joo Dae Joon commented, “Cyber-attack on national infrastructure like DDOS attacks can threaten the nation’s system” and that “the two institutes will establish a response system against cyber-attacks and train experts in information protection”.
2012.01.31 View 8927
MOU: KAIST-Korea Internet & Security Agency
KAIST signed a MOU with the Korea Internet & Security Agency for the development of IT and International Security.
As a result of the MOU interaction in ▲Exchange of personnel and materials for cooperative research for information protection ▲Information protection policy and technology ▲Education and training for developing information protection personnel, will be increased.
Director of Cyber Security Research Center Joo Dae Joon commented, “Cyber-attack on national infrastructure like DDOS attacks can threaten the nation’s system” and that “the two institutes will establish a response system against cyber-attacks and train experts in information protection”.
2012.01.31 View 8927 -
 Kazakhstan to develop E-Government, Green Economy innovative programs
Source: Trend, Feb. 25, 2011
The Kazakh Economic University (KazEU) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have signed a memo on joint work in the field of development of "E-Government" and "Green Economy" innovative programs. For more news, please go to the link, http://en.trend.az/capital/business/1836138.html.
2011.03.01 View 9883
Kazakhstan to develop E-Government, Green Economy innovative programs
Source: Trend, Feb. 25, 2011
The Kazakh Economic University (KazEU) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have signed a memo on joint work in the field of development of "E-Government" and "Green Economy" innovative programs. For more news, please go to the link, http://en.trend.az/capital/business/1836138.html.
2011.03.01 View 9883 -
 Cho Cheon Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation Initiated
KAIST established the Graduate School of Green Transportation in efforts to participate actively in the green transportation market and train experts in the field.
The opening ceremony was conducted in the KI building with President of KAIST Seo Nam Pyo and other dignitaries from Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Korea Rail Network Authority, Korea Airports Corporation, Korea Railroad Research Institute, Land, Transport and Maritime Experts Training Institute, Seoul Development Institute, LG Innotech, Hyundai Rotem, and other major companies in the field of transportation attending.
The graduate school was founded with funding from donation made by Chairman Cho Cheon Shik. Developer of OLEV Professor Cho Dong Ho is the dean of the school and 16 other professors are a part of the school.
Courses offered include ‘Transportation Technology’ and ‘Transportation management’ and will focus mostly on allowing students to be a part of the graduate school with flexibility.
In terms of research there is the OLEV and mobile harbor and research will be done on electric and electronics, mechanics, materials, aeronautics, maritime, construction, environment, and etc. and will be an interdisciplinary research.
A memorandum of understanding was signed by the companies mentioned above which has now paved the way for experts to be trained and thus upgrade the level of technology in the field of green transportation.
Professor Seo of KAIST commented, ‘Korea is ranked top 10 in the world for greenhouse gas emissions and it has become hard to avoid global pressure. The results of researched performed at KAIST will allow Korea to form a green, sustainable society leading in the field of green transportation and dominate the market.
2011.02.23 View 20778
Cho Cheon Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation Initiated
KAIST established the Graduate School of Green Transportation in efforts to participate actively in the green transportation market and train experts in the field.
The opening ceremony was conducted in the KI building with President of KAIST Seo Nam Pyo and other dignitaries from Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs, Korea Rail Network Authority, Korea Airports Corporation, Korea Railroad Research Institute, Land, Transport and Maritime Experts Training Institute, Seoul Development Institute, LG Innotech, Hyundai Rotem, and other major companies in the field of transportation attending.
The graduate school was founded with funding from donation made by Chairman Cho Cheon Shik. Developer of OLEV Professor Cho Dong Ho is the dean of the school and 16 other professors are a part of the school.
Courses offered include ‘Transportation Technology’ and ‘Transportation management’ and will focus mostly on allowing students to be a part of the graduate school with flexibility.
In terms of research there is the OLEV and mobile harbor and research will be done on electric and electronics, mechanics, materials, aeronautics, maritime, construction, environment, and etc. and will be an interdisciplinary research.
A memorandum of understanding was signed by the companies mentioned above which has now paved the way for experts to be trained and thus upgrade the level of technology in the field of green transportation.
Professor Seo of KAIST commented, ‘Korea is ranked top 10 in the world for greenhouse gas emissions and it has become hard to avoid global pressure. The results of researched performed at KAIST will allow Korea to form a green, sustainable society leading in the field of green transportation and dominate the market.
2011.02.23 View 20778 -
 KAIST Mobile Homepage Open
KAIST opened a mobile homepage (http://m.kaist.ac.kr) in order to provide an improved level of service to the public and KAIST family members.
The mobile homepage is made up of: notifications, KAIST news, cultural program guide, introduction of KAIST, campus map, undergraduate information, admission information, KAIST public relations pages.
Especially going into the KAIST public relations page and following ‘With-KAIST’ on twitter allows access to live feed of KAIST news and will be a good means of communications with the school and KAIST family members. This service was initiated on June of last year and has 559 followers.
The mobile homepage can be accessed on any smart phones like iPhone, Galaxy, etc.
Cho Joon Hyung IT Development Manger who was in charge of the development of the mobile homepage commented, “the mobile homepage was developed to meet the demand from smart phone users. Users will be able to access school related information heightening information accessibility”.
2011.02.21 View 9638
KAIST Mobile Homepage Open
KAIST opened a mobile homepage (http://m.kaist.ac.kr) in order to provide an improved level of service to the public and KAIST family members.
The mobile homepage is made up of: notifications, KAIST news, cultural program guide, introduction of KAIST, campus map, undergraduate information, admission information, KAIST public relations pages.
Especially going into the KAIST public relations page and following ‘With-KAIST’ on twitter allows access to live feed of KAIST news and will be a good means of communications with the school and KAIST family members. This service was initiated on June of last year and has 559 followers.
The mobile homepage can be accessed on any smart phones like iPhone, Galaxy, etc.
Cho Joon Hyung IT Development Manger who was in charge of the development of the mobile homepage commented, “the mobile homepage was developed to meet the demand from smart phone users. Users will be able to access school related information heightening information accessibility”.
2011.02.21 View 9638 -
 Success in differentiating Functional Vascular Progenitor Cells (VPC)
KAIST’s Professor Han Yong Man successfully differentiated vascular progenitor cells from human embryonic stem cells and reversed differentiated stem cells.
The research went beyond the current method of synthesis of embryonic body or mice cell ball culture and used the careful alteration of signal transmission system of the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate the formation of vascular progenitor cells.
The team controlled the MEK/ERK and BMP signal transmission system that serves an important role in the self replication of human embryonic stem cells and successfully differentiated 20% of the cells experimented on to vascular progenitor cells.
The vascular progenitor cells produced with such a method successfully differentiated into cells forming the endodermis of the blood vessel, vascular smooth muscle cells and hematopoietic cells in an environment outside of the human body and also successfully differentiated into blood vessels in nude mice.
In addition, the vascular progenitor cell derived from human embryonic cells successfully formed blood vessels or secreted vascular growth factors and increased the blood flow and the necrosis of blood vessels when injected into an animal with limb ischemic illness.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, 21st Century Frontier Research and Development Institution’s Cell Application Research Department and Professor Ko Kyu Young (KAIST), Professor Choi Chul Hee (KAIST), Professor Jeong Hyung Min (Cha Medical School) and Doctor Jo Lee Sook (Researcher in Korea Bio Engineering Institute) participated in it.
The results of the research was published as the cover paper of the September edition of “Blood (IF:10.55)”, the American Blood Journal and has been patented domestically and has finished registration of foreign PCT.
The results of the experiment opened the possibility of providing a patient specific cure using stem cells in the field of blood vessel illness.
2011.01.18 View 17928
Success in differentiating Functional Vascular Progenitor Cells (VPC)
KAIST’s Professor Han Yong Man successfully differentiated vascular progenitor cells from human embryonic stem cells and reversed differentiated stem cells.
The research went beyond the current method of synthesis of embryonic body or mice cell ball culture and used the careful alteration of signal transmission system of the human embryonic stem cells to differentiate the formation of vascular progenitor cells.
The team controlled the MEK/ERK and BMP signal transmission system that serves an important role in the self replication of human embryonic stem cells and successfully differentiated 20% of the cells experimented on to vascular progenitor cells.
The vascular progenitor cells produced with such a method successfully differentiated into cells forming the endodermis of the blood vessel, vascular smooth muscle cells and hematopoietic cells in an environment outside of the human body and also successfully differentiated into blood vessels in nude mice.
In addition, the vascular progenitor cell derived from human embryonic cells successfully formed blood vessels or secreted vascular growth factors and increased the blood flow and the necrosis of blood vessels when injected into an animal with limb ischemic illness.
The research was funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, 21st Century Frontier Research and Development Institution’s Cell Application Research Department and Professor Ko Kyu Young (KAIST), Professor Choi Chul Hee (KAIST), Professor Jeong Hyung Min (Cha Medical School) and Doctor Jo Lee Sook (Researcher in Korea Bio Engineering Institute) participated in it.
The results of the research was published as the cover paper of the September edition of “Blood (IF:10.55)”, the American Blood Journal and has been patented domestically and has finished registration of foreign PCT.
The results of the experiment opened the possibility of providing a patient specific cure using stem cells in the field of blood vessel illness.
2011.01.18 View 17928 -
 New Year's Message from President Nam-Pyo Suh
President Nam-Pyo Suh delivered a New Year’s message on January 3, 2011. While announcing plans to celebrate the 40th anniversary of KAIST throughout this year including a long-term development strategy for the university, Vision 2025, the president assessed the past accomplishments made in 2010 and laid out future prospects for 2011. The full text of his speech is attached below.
2011.01.05 View 11303
New Year's Message from President Nam-Pyo Suh
President Nam-Pyo Suh delivered a New Year’s message on January 3, 2011. While announcing plans to celebrate the 40th anniversary of KAIST throughout this year including a long-term development strategy for the university, Vision 2025, the president assessed the past accomplishments made in 2010 and laid out future prospects for 2011. The full text of his speech is attached below.
2011.01.05 View 11303 -
 KAIST sells eight HUBO 2 robots to US and Singapore.
HUBO, a humanoid robot developed by KAIST, has made its journey to the US and Singapore for the development of robotics engineering in those nations. Details on the movements of HOBO being exported aboard, please click the link of the news article:
http://www.slashgear.com/kaist-sells-eight-hubo-2-robots-to-us-and-singapore-14119320/
2010.12.20 View 13178
KAIST sells eight HUBO 2 robots to US and Singapore.
HUBO, a humanoid robot developed by KAIST, has made its journey to the US and Singapore for the development of robotics engineering in those nations. Details on the movements of HOBO being exported aboard, please click the link of the news article:
http://www.slashgear.com/kaist-sells-eight-hubo-2-robots-to-us-and-singapore-14119320/
2010.12.20 View 13178