AR
-
 Solutal Marangoni Flows of Miscible Liquid Drive Transport without Surface Contamination
(Professor Hyoungsoo Kim, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST)
A research team led by Hyoungsoo Kim, a professor of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, succeeded in quantifying the phenomenon called, the Marangoni effect, which occurs at the interface between alcohol and water. It is expected that this finding will be a valuable resource used for effectively removing impurities from a surface fluid without any contamination, and developing materials that can replace surfactants.
This research, co-conducted with a research team led by Professor Howard A. Stone at Princeton University, was published online in Nature Physics on July 31.
The Marangoni effect, also known as tears of wine, is generated when two fluids having a different surface tension meet, causing finite mixing, spreading time and length scale. Typically, people believe that infinitely miscible liquids immediately mix together; however, it is not always true according to this paper.
The typical surface tension of alcohol is three times lower than that of water, and this different surface tension generates the Marangoni-driven convection flow at the interface of the two liquids. In addition, there is a certain amount of time required for them to mix.
This phenomenon has been discussed many times since it was discovered in early the 20th century, yet there was a limit to quantifying and explaining it.
Professor Kim, considering the mixing and spreading mechanism, used various flow visualization techniques and equipment for capturing high speed images in his experiment.
Through the flow visualization methods, the team succeeded in quantifying and explaining the complex, physicochemical phenomenon generated between water and alcohol. Moreover, they developed a theoretical model to predict the physicochemical hydrodynamic phenomena.
The theoretical model can predict the speed of Marangoni-driven convection flow, the area of a drop of alcohol and the time required to develop the flow field. Hence, this model can map out types of materials (e.g., alcohol) and the volume of a drop of liquid as applicable to target a specific situation.
Moreover, the research team believes that the interfacial flow enables the driving of bulk flows and that it can be a source of technology for effectively delivering drugs and removing impurities from a surface of substance without causing secondary contamination.
Above all, the results show a possibility for replacing surfactant with alcohol as a material used for delivering drugs. In the case of the drug delivery, some drugs are encapsulated with a surfactant in order to be effectively transported in vivo; however, the surfactant accumulates in the body, which can cause various side effects, such as heart disease. Therefore, using new materials like alcohol for drug delivery will contribute to preventing the side effects caused by the surfactant.
“The surfactant is used for delivering drugs, but it is difficult to be expelled from the body. This will cause various side effects, such as heart diseases in asthmatic patients,” said Professor Kim. “I hope that using new materials, like alcohol, will free people from these side effects.”
(Marangoni-driven convection flow generated at the interface between water and alcohol, and the flow visualization results)
- A drop of alcohol on a water surface
- Comparison of mixing structures on the surface
- Marangoni mixing flow under the free surface
2017.08.18 View 8414
Solutal Marangoni Flows of Miscible Liquid Drive Transport without Surface Contamination
(Professor Hyoungsoo Kim, Department of Mechanical Engineering, KAIST)
A research team led by Hyoungsoo Kim, a professor of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST, succeeded in quantifying the phenomenon called, the Marangoni effect, which occurs at the interface between alcohol and water. It is expected that this finding will be a valuable resource used for effectively removing impurities from a surface fluid without any contamination, and developing materials that can replace surfactants.
This research, co-conducted with a research team led by Professor Howard A. Stone at Princeton University, was published online in Nature Physics on July 31.
The Marangoni effect, also known as tears of wine, is generated when two fluids having a different surface tension meet, causing finite mixing, spreading time and length scale. Typically, people believe that infinitely miscible liquids immediately mix together; however, it is not always true according to this paper.
The typical surface tension of alcohol is three times lower than that of water, and this different surface tension generates the Marangoni-driven convection flow at the interface of the two liquids. In addition, there is a certain amount of time required for them to mix.
This phenomenon has been discussed many times since it was discovered in early the 20th century, yet there was a limit to quantifying and explaining it.
Professor Kim, considering the mixing and spreading mechanism, used various flow visualization techniques and equipment for capturing high speed images in his experiment.
Through the flow visualization methods, the team succeeded in quantifying and explaining the complex, physicochemical phenomenon generated between water and alcohol. Moreover, they developed a theoretical model to predict the physicochemical hydrodynamic phenomena.
The theoretical model can predict the speed of Marangoni-driven convection flow, the area of a drop of alcohol and the time required to develop the flow field. Hence, this model can map out types of materials (e.g., alcohol) and the volume of a drop of liquid as applicable to target a specific situation.
Moreover, the research team believes that the interfacial flow enables the driving of bulk flows and that it can be a source of technology for effectively delivering drugs and removing impurities from a surface of substance without causing secondary contamination.
Above all, the results show a possibility for replacing surfactant with alcohol as a material used for delivering drugs. In the case of the drug delivery, some drugs are encapsulated with a surfactant in order to be effectively transported in vivo; however, the surfactant accumulates in the body, which can cause various side effects, such as heart disease. Therefore, using new materials like alcohol for drug delivery will contribute to preventing the side effects caused by the surfactant.
“The surfactant is used for delivering drugs, but it is difficult to be expelled from the body. This will cause various side effects, such as heart diseases in asthmatic patients,” said Professor Kim. “I hope that using new materials, like alcohol, will free people from these side effects.”
(Marangoni-driven convection flow generated at the interface between water and alcohol, and the flow visualization results)
- A drop of alcohol on a water surface
- Comparison of mixing structures on the surface
- Marangoni mixing flow under the free surface
2017.08.18 View 8414 -
 Professor Dan Keun Sung Endows Scholarship in Honor of His Retirement
Professor Dan Keun Sung in the School of Electrical Engineering contributed a 100 million KRW scholarship fund this month to KAIST to mark his retirement after more than three decades of work.
“As my retirement date comes closer, I have been thinking about what I could do for the school. I wanted to leave something behind, even though it’s small, for my lifelong school and students. I am hoping that this scholarship fund will benefit the members of KAIST.”
This isn’t his first time making a donation to KAIST. In 2013, Professor Sung donated ten million KRW, which was his cash prize from the 9th Haedong Academic Award of The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS). At that time, Professor Sung had the chance to create a scholarship fund in his name; however, he wanted to highlight that the scholarship fund was for ‘someone,’ not created by ‘someone.’ In that sense, his scholarship fund was created with no name to benefit students in the School of Electrical Engineering. His colleagues and students supported his idea. Professor Seonghwan Cho, students, and alumni also participated in fund raising efforts, which reached 55 million KRW in total.
Professor Sung emphasized, “Donations should always be remembered, no matter how small they are.” He then explained his purpose for creating the scholarship fund by saying, “Fundraising can be truly meaningful to contributors, knowing that their money is going to supporting the school and students.”
Professor Sung, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Communication Society, started his post at KAIST in 1986. For the past 30 years, he has devoted himself to fostering young scholars and studying in the area of information and communication. He also participated in developing technologies for the resource management of various future cellular components, such as satellites, switchboards, and signaling networks.
2017.08.11 View 9300
Professor Dan Keun Sung Endows Scholarship in Honor of His Retirement
Professor Dan Keun Sung in the School of Electrical Engineering contributed a 100 million KRW scholarship fund this month to KAIST to mark his retirement after more than three decades of work.
“As my retirement date comes closer, I have been thinking about what I could do for the school. I wanted to leave something behind, even though it’s small, for my lifelong school and students. I am hoping that this scholarship fund will benefit the members of KAIST.”
This isn’t his first time making a donation to KAIST. In 2013, Professor Sung donated ten million KRW, which was his cash prize from the 9th Haedong Academic Award of The Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS). At that time, Professor Sung had the chance to create a scholarship fund in his name; however, he wanted to highlight that the scholarship fund was for ‘someone,’ not created by ‘someone.’ In that sense, his scholarship fund was created with no name to benefit students in the School of Electrical Engineering. His colleagues and students supported his idea. Professor Seonghwan Cho, students, and alumni also participated in fund raising efforts, which reached 55 million KRW in total.
Professor Sung emphasized, “Donations should always be remembered, no matter how small they are.” He then explained his purpose for creating the scholarship fund by saying, “Fundraising can be truly meaningful to contributors, knowing that their money is going to supporting the school and students.”
Professor Sung, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Communication Society, started his post at KAIST in 1986. For the past 30 years, he has devoted himself to fostering young scholars and studying in the area of information and communication. He also participated in developing technologies for the resource management of various future cellular components, such as satellites, switchboards, and signaling networks.
2017.08.11 View 9300 -
 Material-Independent Nanocoating Antimicrobial Spray Significantly Extends the Shelf Life of Produce
The edible coating on produce has drawn a great deal of attention in the food and agricultural industry. It could not only prolong postharvest shelf life of produce against external changes in the environment but also provide additional nutrients to be useful for human health. However, most versions of the coating have had intrinsic limitations in their practical application. First, highly specific interactions between coating materials and target surfaces are required for a stable and durable coating. Even further, the coating of bulk substrates, such as fruits, is time consuming or is not achievable in the conventional solution-based coating. In this respect, material-independent and rapid coating strategies are highly demanded.
The research team led by Professor Insung Choi of the Department of Chemistry developed a sprayable nanocoating technique using plant-derived polyphenol that can be applied to any surface. This new nanocoating process can be completed in seconds to form nanometer-thick films, allowing for the coating of commodity goods, such as shoe insoles and fruits, in a controlled fashion. For example, spray-coated mandarin oranges and strawberries show significantly-prolonged postharvest shelf life, suggesting the practical potential in edible coatings of perishable produce.
The technology has been patented and is currently being commercialized for widespread use as a means of preserving produce. The research results have recently been published in Scientific Reports on Aug 1.
Polyphenols, a metabolite of photosynthesis, possess several hydroxyl groups and are found in a large number of plants showing excellent antioxidant properties. They have been widely used as a nontoxic food additive and are known to exhibit antibacterial, as well as potential anti-carcinogenic capabilities. Polyphenols can also be used with iron ions, which are naturally found in the body, to form an adhesive complex, which has been used in leather tanning, ink, etc.
The research team combined these chemical properties of polyphenol-iron complexes with spray techniques to develop their nanocoating technology. Compared to conventional immersion coating methods, which dip substrates in specialized coating solutions, this spray technique can coat the select areas more quickly. The spray also prevents cross contamination, which is a big concern for immersion methods. The research team has showcased the spray’s ability to coat a variety of different materials, including metals, plastics, glass, as well as textile fabrics. The polyphenol complex has been used to form antifogging films on corrective lenses, as well as antifungal treatments for shoe soles, demonstrating the versatility of their technique.
Furthermore, the spray has been used to coat produce with a naturally antibacterial, edible film. The coatings significantly improved the shelf life of tangerines and strawberries, preserving freshness beyond 28 days and 58 hours, respectively. (Uncoated fruit decomposed and became moldy under the same conditions). See the image below.
a –I, II: Uncoated and coated tangerines incubated for 14 and 28 days in daily-life settings
b –I: Uncoated and coated strawberries incubated for 58 hours in daily-life settings
b –II: Statistical investigation of the resulting edibility.
Professor Choi said, “Nanocoating technologies are still in their infancy, but they have untapped potential for exciting applications. As we have shown, nanocoatings can be easily adapted for several different uses, and the creative combination of existing nanomaterials and coating methods can synergize to unlock this potential.”
2017.08.10 View 9390
Material-Independent Nanocoating Antimicrobial Spray Significantly Extends the Shelf Life of Produce
The edible coating on produce has drawn a great deal of attention in the food and agricultural industry. It could not only prolong postharvest shelf life of produce against external changes in the environment but also provide additional nutrients to be useful for human health. However, most versions of the coating have had intrinsic limitations in their practical application. First, highly specific interactions between coating materials and target surfaces are required for a stable and durable coating. Even further, the coating of bulk substrates, such as fruits, is time consuming or is not achievable in the conventional solution-based coating. In this respect, material-independent and rapid coating strategies are highly demanded.
The research team led by Professor Insung Choi of the Department of Chemistry developed a sprayable nanocoating technique using plant-derived polyphenol that can be applied to any surface. This new nanocoating process can be completed in seconds to form nanometer-thick films, allowing for the coating of commodity goods, such as shoe insoles and fruits, in a controlled fashion. For example, spray-coated mandarin oranges and strawberries show significantly-prolonged postharvest shelf life, suggesting the practical potential in edible coatings of perishable produce.
The technology has been patented and is currently being commercialized for widespread use as a means of preserving produce. The research results have recently been published in Scientific Reports on Aug 1.
Polyphenols, a metabolite of photosynthesis, possess several hydroxyl groups and are found in a large number of plants showing excellent antioxidant properties. They have been widely used as a nontoxic food additive and are known to exhibit antibacterial, as well as potential anti-carcinogenic capabilities. Polyphenols can also be used with iron ions, which are naturally found in the body, to form an adhesive complex, which has been used in leather tanning, ink, etc.
The research team combined these chemical properties of polyphenol-iron complexes with spray techniques to develop their nanocoating technology. Compared to conventional immersion coating methods, which dip substrates in specialized coating solutions, this spray technique can coat the select areas more quickly. The spray also prevents cross contamination, which is a big concern for immersion methods. The research team has showcased the spray’s ability to coat a variety of different materials, including metals, plastics, glass, as well as textile fabrics. The polyphenol complex has been used to form antifogging films on corrective lenses, as well as antifungal treatments for shoe soles, demonstrating the versatility of their technique.
Furthermore, the spray has been used to coat produce with a naturally antibacterial, edible film. The coatings significantly improved the shelf life of tangerines and strawberries, preserving freshness beyond 28 days and 58 hours, respectively. (Uncoated fruit decomposed and became moldy under the same conditions). See the image below.
a –I, II: Uncoated and coated tangerines incubated for 14 and 28 days in daily-life settings
b –I: Uncoated and coated strawberries incubated for 58 hours in daily-life settings
b –II: Statistical investigation of the resulting edibility.
Professor Choi said, “Nanocoating technologies are still in their infancy, but they have untapped potential for exciting applications. As we have shown, nanocoatings can be easily adapted for several different uses, and the creative combination of existing nanomaterials and coating methods can synergize to unlock this potential.”
2017.08.10 View 9390 -
 Students from Science Academies Shed a Light on KAIST
Recent KAIST statistics show that graduates from science academies distinguish themselves not only by their academic performance at KAIST but also in various professional careers after graduation.
Every year, approximately 20% of newly-enrolled students of KAIST are from science academies. In the case of the class of 2017, 170 students from science academies accounted for 22% of the newly-enrolled students. Moreover, they are forming a top-tier student group on campus. As shown in the table below, the ratio of students graduating early for either enrolling in graduate programs or landing a job indicates their excellent performance at KAIST.
There are eight science academies in Korea: Korea Science Academy of KAIST located in Busan, Seoul Science High School, Gyeonggi Science High School, Gwangju Science High School, Daejeon Science High School, Sejong Academy of Science and Arts, and Incheon Arts and Sciences Academy.
Recently, KAIST analyzed 532 university graduates from the class of 2012. It was found that 23 out of 63 graduates with the alma mater of science academies finished their degree early; as a result, the early graduation ratio of the class of 2012 stood at 36.5%. This percentage was significantly higher than that of students from other high schools.
Among the notable graduates, there was a student who made headlines with donation of 30 million KRW to KAIST. His donation was the largest donation from an enrolled student on record. His story goes back when Android smartphones were about to be distributed. Seung-Gyu Oh, then a student in the School of Electrical Engineering felt that existing subway apps were inconvenient, so he invented his own subway app that navigated the nearest subway lines in 2015. His app hit the market and ranked second in the subway app category. It had approximately five million users, which led to it generating advertising revenue. After the successful launch of the app, Oh accepted the takeover offered by Daum Kakao. He then donated 30 million KRW to his alma mater. “Since high school, I’ve always been thinking that I have received many benefits from my country and felt heavily responsible for it,” the alumnus of Korea Science of Academy and KAIST said. “I decided to make a donation to my alma mater, KAIST because I wanted to return what I had received from my country.” After graduation, Oh is now working for the web firm, Daum Kakao.
In May 24, 2017, the 41st International Collegiate Programming Contest, hosted by Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and sponsored by IBM, was held in Rapid City, South Dakota in the US. It is a prestigious contest that has been held annually since 1977. College students from around the world participate in this contest; and in 2017, a total of 50,000 students from 2,900 universities in 104 countries participated in regional competitions, and approximately 400 students made it to the final round, entering into a fierce competition. KAIST students also participated in this contest. The team was comprised of Ji-Hoon Ko, Jong-Won Lee, and Han-Pil Kang from the School of Computing. They are also alumni of Gyeonggi Science High School. They received the ‘First Problem Solver’ award and a bronze medal which came with a 3,000 USD cash prize.
Sung-Jin Oh, who also graduated from Korea Science Academy of KAIST, is a research professor at the Korea Institute of Advanced Study (KIAS). He is the youngest recipient of the ‘Young Scientist Award’, which he received by proving a hypothesis from Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity mathematically at the age of 27. After graduating from KAIST, Oh earned his master’s and doctorate degrees from Princeton University, completed his post-doctoral fellow at UC Berkeley, and is now immersing himself in research at KIAS.
Heui-Kwang Noh from the Department of Chemistry and Kang-Min Ahn from the School of Computing, who were selected to receive the presidential scholarship for science in 2014, both graduated from Gyeonggi Science High School. Noh was recognized for his outstanding academic capacity and was also chosen for the ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’ in 2015. The ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’, established in 1992 by the GE Foundation, aims at fostering talented students. This program is for post-secondary students who have both creativity and leadership. It selects five outstanding students and provides 3 million KRW per annum for a maximum of three years.
The grantees of this program have become influential people in various fields, including professors, executives, staff members of national/international firms, and researchers. And they are making a huge contribution to the development of engineering and science. Noh continues doing various activities, including the completion of his internship at ‘Harvard-MIT Biomedical Optics’ and the publication of a paper (3rd author) for the ACS Omega of American Chemical Society (ACS).
Ahn, a member of the Young Engineers Honor Society (YEHS) of the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, had an interest in startup businesses. In 2015, he founded DataStorm, a firm specializing in developing data solution, and merged with a cloud back-office, Jobis & Villains, in 2016. Ahn is continuing his business activities and this year he founded, and is successfully running, cocKorea.
“KAIST students whose alma mater are science academies form a top-tier group on campus and produce excellent performance,” said Associate Vice President for Admissions, Hayong Shin. “KAIST is making every effort to assist these students so that they can perform to the best of their ability.”
(Clockwise from top left: Seung-Gyu Oh, Sung-Jin Oh, Heui-Kwang Noh and Kang-Min Ahn)
2017.08.09 View 9234
Students from Science Academies Shed a Light on KAIST
Recent KAIST statistics show that graduates from science academies distinguish themselves not only by their academic performance at KAIST but also in various professional careers after graduation.
Every year, approximately 20% of newly-enrolled students of KAIST are from science academies. In the case of the class of 2017, 170 students from science academies accounted for 22% of the newly-enrolled students. Moreover, they are forming a top-tier student group on campus. As shown in the table below, the ratio of students graduating early for either enrolling in graduate programs or landing a job indicates their excellent performance at KAIST.
There are eight science academies in Korea: Korea Science Academy of KAIST located in Busan, Seoul Science High School, Gyeonggi Science High School, Gwangju Science High School, Daejeon Science High School, Sejong Academy of Science and Arts, and Incheon Arts and Sciences Academy.
Recently, KAIST analyzed 532 university graduates from the class of 2012. It was found that 23 out of 63 graduates with the alma mater of science academies finished their degree early; as a result, the early graduation ratio of the class of 2012 stood at 36.5%. This percentage was significantly higher than that of students from other high schools.
Among the notable graduates, there was a student who made headlines with donation of 30 million KRW to KAIST. His donation was the largest donation from an enrolled student on record. His story goes back when Android smartphones were about to be distributed. Seung-Gyu Oh, then a student in the School of Electrical Engineering felt that existing subway apps were inconvenient, so he invented his own subway app that navigated the nearest subway lines in 2015. His app hit the market and ranked second in the subway app category. It had approximately five million users, which led to it generating advertising revenue. After the successful launch of the app, Oh accepted the takeover offered by Daum Kakao. He then donated 30 million KRW to his alma mater. “Since high school, I’ve always been thinking that I have received many benefits from my country and felt heavily responsible for it,” the alumnus of Korea Science of Academy and KAIST said. “I decided to make a donation to my alma mater, KAIST because I wanted to return what I had received from my country.” After graduation, Oh is now working for the web firm, Daum Kakao.
In May 24, 2017, the 41st International Collegiate Programming Contest, hosted by Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and sponsored by IBM, was held in Rapid City, South Dakota in the US. It is a prestigious contest that has been held annually since 1977. College students from around the world participate in this contest; and in 2017, a total of 50,000 students from 2,900 universities in 104 countries participated in regional competitions, and approximately 400 students made it to the final round, entering into a fierce competition. KAIST students also participated in this contest. The team was comprised of Ji-Hoon Ko, Jong-Won Lee, and Han-Pil Kang from the School of Computing. They are also alumni of Gyeonggi Science High School. They received the ‘First Problem Solver’ award and a bronze medal which came with a 3,000 USD cash prize.
Sung-Jin Oh, who also graduated from Korea Science Academy of KAIST, is a research professor at the Korea Institute of Advanced Study (KIAS). He is the youngest recipient of the ‘Young Scientist Award’, which he received by proving a hypothesis from Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity mathematically at the age of 27. After graduating from KAIST, Oh earned his master’s and doctorate degrees from Princeton University, completed his post-doctoral fellow at UC Berkeley, and is now immersing himself in research at KIAS.
Heui-Kwang Noh from the Department of Chemistry and Kang-Min Ahn from the School of Computing, who were selected to receive the presidential scholarship for science in 2014, both graduated from Gyeonggi Science High School. Noh was recognized for his outstanding academic capacity and was also chosen for the ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’ in 2015. The ‘GE Foundation Scholar-Leaders Program’, established in 1992 by the GE Foundation, aims at fostering talented students. This program is for post-secondary students who have both creativity and leadership. It selects five outstanding students and provides 3 million KRW per annum for a maximum of three years.
The grantees of this program have become influential people in various fields, including professors, executives, staff members of national/international firms, and researchers. And they are making a huge contribution to the development of engineering and science. Noh continues doing various activities, including the completion of his internship at ‘Harvard-MIT Biomedical Optics’ and the publication of a paper (3rd author) for the ACS Omega of American Chemical Society (ACS).
Ahn, a member of the Young Engineers Honor Society (YEHS) of the National Academy of Engineering of Korea, had an interest in startup businesses. In 2015, he founded DataStorm, a firm specializing in developing data solution, and merged with a cloud back-office, Jobis & Villains, in 2016. Ahn is continuing his business activities and this year he founded, and is successfully running, cocKorea.
“KAIST students whose alma mater are science academies form a top-tier group on campus and produce excellent performance,” said Associate Vice President for Admissions, Hayong Shin. “KAIST is making every effort to assist these students so that they can perform to the best of their ability.”
(Clockwise from top left: Seung-Gyu Oh, Sung-Jin Oh, Heui-Kwang Noh and Kang-Min Ahn)
2017.08.09 View 9234 -
 KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 14649
KAIST Researchers Receive Awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology
(From left: Seon Young Park, Dr. So Young Choi, and Yoojin Choi)
Researchers in the laboratory of KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering swept awards at the 13th Asian Congress on Biotechnology held in Thailand last month. The conference awarded a total of eight prizes in the areas of best research and best poster presentation. This is an exceptional case in which members of one research team received almost half of the awards at an international conference.
Dr. So Young Choi received the Best Research Award, while Ph.D. candidates Yoojin Choi and Seon Young Park each received the Best Poster Presentation Award at the conference held in Khon Kaen, Thailand from July 23 to 27.
The Asian Congress on Biotechnology is an international conference in which scientists and industry experts in Asia and from around the world gather to present recent research findings in the field of biotechnology. At the conference, around 400 researchers in biotechnology from 25 countries, including Korea, gathered to present and discuss various research findings under the theme of “Bioinnovation and Bioeconomy.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee attended the conference to give the opening plenary lecture on the topic of ‘Systems Strategies in Biotechnology.’ Professor Lee announced, “I have attended international conferences with students for the last 20 years, but this is the first in which my team received three awards at an international conference that only honors a total of eight awards, three for Best Research and five for Best Presentation.”
Dr. Choi presented research results on poly (lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) synthesis through a biological method using micro-organisms and received the Best Research Award. PLGA is a random copolymer of DL-lactic and glycolic acids and is a biopolymer widely used for biomedical applications. PLGA is biodegradable, biocompatible, and nontoxic, and thus has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its use in implants, drug delivery, and sutures.
Dr. Choi’s research was deemed to be innovative for synthesizing PLGA from glucose and xylose in cells through metabolic engineering of E.Coli. Dr. Choi received her Ph.D. under the supervision of Distinguished Professor Lee this February and is currently conducting post-doc research.
Ph.D. candidate Choi presented her research on the use of recombinant E.Coli for the biological synthesis of various nanoparticles and received the Best Poster Presentation award. Choi used recombinant E.Coli-expressing proteins and peptides that adsorb to heavy metals to biologically synthesize diverse metal nanoparticles such as single-nanoparticle including gold and silver, quantum dots, and magnetic nanoparticles for the first time. The synthesized nanoparticles can be used in the fields of bio-imaging, diagnosis, environment, and energy.
Ph.D. candidate Park, who also received the Best Poster Presentation award, synthesized and increased production of astanxanthin, a strong antioxidant found in nature, in E.Coli using metabolic engineering. Astanxanthin is a carotenoid pigment found in salmon and shrimp that widely used in health products and cosmetics.
2017.08.01 View 14649 -
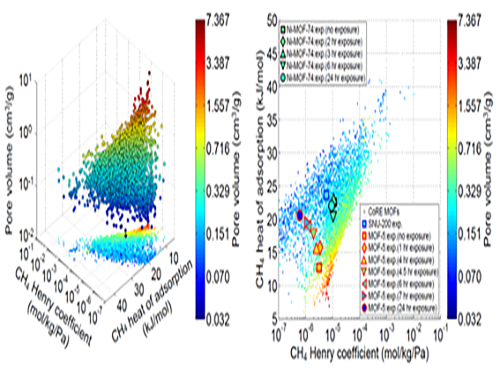 Analysis of Gas Adsorption Properties for Amorphous Porous Materials
Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a method to predict gas adsorption properties of amorphous porous materials.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have large surface area and high density of pores, making them appropriate for various energy and environmental-related applications. And although most MOFs are crystalline, these structures can deform during synthesis and/or industrial processes, leading to loss in long-range order. Unfortunately, without the structural information, existing computer simulation techniques cannot be used to model these materials.
In this research, Professor Kim’s research team demonstrated that one can replace the material properties of structurally deformed MOFs with those of crystalline MOFs to indirectly analyze/model the material properties of amorphous materials. First, the team conducted simulations on methane gas adsorption properties for over 12,000 crystalline MOFs to obtain a large training set data, and created a resulting structure-property map. Upon mapping the experimental data of amorphous MOFs onto the structure-property map, results showed that regardless of crystallinity, the gas adsorption properties of MOFs showed congruence and consistency amongst one another.
Based on these findings, selected crystalline MOFs with the most similar gas adsorption properties as the collapsed structure from the 12,000 candidates. Then, the team verified that the adsorption properties of these similar MOFs can be successfully transferred to the deformed MOFs across different temperatures and even to different gas molecules (e.g. hydrogen), demonstrating transferability of properties.
These findings allow material property prediction in porous materials such as MOFs without structural information, and the techniques here can be used to better predict and understand optimal materials for various applications including, carbon dioxide capture, gas storage and separations.
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Dae-Woon Lim at Kyoto University, Professor Myunghyun Paik at Seoul National University, Professor Minyoung Yoon at Gachon University, and Aadesh Harale at Saudi Arabian Oil Company. The research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online on 10 July and the co-first authors were Ph. D. candidate WooSeok Jeong and Professor Dae-Woon Lim.
This research was funded by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
(Figure 1. Trends in structure - material property map and in collapsed structures)
(Figure 2. Transferability between the experimental results of collapsed MOFs and the simulation results of crystalline MOFs)
2017.07.26 View 9695
Analysis of Gas Adsorption Properties for Amorphous Porous Materials
Professor Jihan Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a method to predict gas adsorption properties of amorphous porous materials.
Metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) have large surface area and high density of pores, making them appropriate for various energy and environmental-related applications. And although most MOFs are crystalline, these structures can deform during synthesis and/or industrial processes, leading to loss in long-range order. Unfortunately, without the structural information, existing computer simulation techniques cannot be used to model these materials.
In this research, Professor Kim’s research team demonstrated that one can replace the material properties of structurally deformed MOFs with those of crystalline MOFs to indirectly analyze/model the material properties of amorphous materials. First, the team conducted simulations on methane gas adsorption properties for over 12,000 crystalline MOFs to obtain a large training set data, and created a resulting structure-property map. Upon mapping the experimental data of amorphous MOFs onto the structure-property map, results showed that regardless of crystallinity, the gas adsorption properties of MOFs showed congruence and consistency amongst one another.
Based on these findings, selected crystalline MOFs with the most similar gas adsorption properties as the collapsed structure from the 12,000 candidates. Then, the team verified that the adsorption properties of these similar MOFs can be successfully transferred to the deformed MOFs across different temperatures and even to different gas molecules (e.g. hydrogen), demonstrating transferability of properties.
These findings allow material property prediction in porous materials such as MOFs without structural information, and the techniques here can be used to better predict and understand optimal materials for various applications including, carbon dioxide capture, gas storage and separations.
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Dae-Woon Lim at Kyoto University, Professor Myunghyun Paik at Seoul National University, Professor Minyoung Yoon at Gachon University, and Aadesh Harale at Saudi Arabian Oil Company. The research was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online on 10 July and the co-first authors were Ph. D. candidate WooSeok Jeong and Professor Dae-Woon Lim.
This research was funded by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
(Figure 1. Trends in structure - material property map and in collapsed structures)
(Figure 2. Transferability between the experimental results of collapsed MOFs and the simulation results of crystalline MOFs)
2017.07.26 View 9695 -
 KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 11539
KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 11539 -
 Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 7434
Professor Nam Jin Cho Selected as the Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Awardee
Professor Nam Jin Cho from the Department of Nuclear & Quantum Engineering was selected as the recipient of the 2017 ‘Eugene P. Wigner Reactor Physicist Award.’ The award, established in 1990 by the American Nuclear Society, honors individuals who have made outstanding contributions to the advancement of the field of reactor physics. The award is named after the late Eugene P. Wigner, a pioneer who helped nurture the nuclear age to technical maturity with his pioneering leadership in reactor design.
Professor Cho was recognized for his outstanding leadership and achievement in the field of nuclear physics, especially with his original research in analytic function expansion nodal methods, coarse-mesh angular dependent rebalance methods, and neutron transport calculations. A fellow of the ANS, Professor Cho is the first awardee from the Asian region.
Professor Cho gave all the credit to his colleagues and students at KAIST who have spared no effort while working together for three decades. “I am very grateful for the unique academic ambience which made this challenging work possible as well as the government’s continuing funding at the National Research Laboratory project.
2017.07.12 View 7434 -
 Cooperative Tumor Cell Membrane-Targeted Phototherapy
A KAIST research team led by Professor Ji-Ho Park in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST developed a technology for the effective treatment of cancer by delivering synthetic receptors throughout tumor tissue. The study, led by Ph.D. candidate Heegon Kim, was published online in Nature Communications on June 19.
Cancer targeted therapy generally refers to therapy targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and generation of cancer. The targeted delivery of therapeutics using targeting agents such as antibodies or nanomaterials has improved the precision and safety of cancer therapy.
However, the paucity and heterogeneity of identified molecular targets within tumors have resulted in poor and uneven distribution of targeted agents, thus compromising treatment outcomes.
To solve this problem, the team constructed a cooperative targeting system in which synthetic and biological nanocomponents participate together in the tumor cell membrane-selective localization of synthetic receptors to amplify the subsequent targeting of therapeutics. Here, synthetic and biological nanocomponents refer to liposomes and extracellular vesicles, respectively.
The synthetic receptors are first delivered selectively to tumor cell membranes in the perivascular region using liposomes. By hitchhiking with extracellular vesicles secreted by the cells, the synthetic receptors are transferred to neighboring cells and further spread throughout the tumor tissues where the molecular targets are limited.
Hitchhiking extracellular vesicles for delivery of synthetic receptors was possible since extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, mediate intercellular communications by transferring various biological components such as lipids, cytosolic proteins, and RNA through a membrane fusion process. They also play a supportive role in promoting tumor progression in that tumor-derived extracellular vesicles deliver oncogenic signals to normal host cells.
The team showed that this tumor cell membrane-targeted delivery of synthetic receptors led to a uniform distribution of synthetic receptors throughout a tumor and subsequently led to enhanced phototherapeutic efficacy of the targeted photosensitizer.
Professor Park said, “The cooperative tumor targeting system is expected to be applied in treating various diseases that are hard to target.”
The research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control funded by the Ministry for Health and Welfare.
(Ph.D. candidates Hee Gon Kim (left) and Chanhee Oh)
Figure 1. A schematic of a cooperative tumor targeting system via delivery of synthetic receptors.
Figure 2. A confocal microscopic image of a tumor section after cooperative targeting by synthetic receptor delivery. Green and magenta represent vessels and therapeutic agents inside a tumor respectively.
2017.07.07 View 10965
Cooperative Tumor Cell Membrane-Targeted Phototherapy
A KAIST research team led by Professor Ji-Ho Park in the Bio and Brain Engineering Department at KAIST developed a technology for the effective treatment of cancer by delivering synthetic receptors throughout tumor tissue. The study, led by Ph.D. candidate Heegon Kim, was published online in Nature Communications on June 19.
Cancer targeted therapy generally refers to therapy targeting specific molecules that are involved in the growth and generation of cancer. The targeted delivery of therapeutics using targeting agents such as antibodies or nanomaterials has improved the precision and safety of cancer therapy.
However, the paucity and heterogeneity of identified molecular targets within tumors have resulted in poor and uneven distribution of targeted agents, thus compromising treatment outcomes.
To solve this problem, the team constructed a cooperative targeting system in which synthetic and biological nanocomponents participate together in the tumor cell membrane-selective localization of synthetic receptors to amplify the subsequent targeting of therapeutics. Here, synthetic and biological nanocomponents refer to liposomes and extracellular vesicles, respectively.
The synthetic receptors are first delivered selectively to tumor cell membranes in the perivascular region using liposomes. By hitchhiking with extracellular vesicles secreted by the cells, the synthetic receptors are transferred to neighboring cells and further spread throughout the tumor tissues where the molecular targets are limited.
Hitchhiking extracellular vesicles for delivery of synthetic receptors was possible since extracellular vesicles, such as exosomes, mediate intercellular communications by transferring various biological components such as lipids, cytosolic proteins, and RNA through a membrane fusion process. They also play a supportive role in promoting tumor progression in that tumor-derived extracellular vesicles deliver oncogenic signals to normal host cells.
The team showed that this tumor cell membrane-targeted delivery of synthetic receptors led to a uniform distribution of synthetic receptors throughout a tumor and subsequently led to enhanced phototherapeutic efficacy of the targeted photosensitizer.
Professor Park said, “The cooperative tumor targeting system is expected to be applied in treating various diseases that are hard to target.”
The research was funded by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National R&D Program for Cancer Control funded by the Ministry for Health and Welfare.
(Ph.D. candidates Hee Gon Kim (left) and Chanhee Oh)
Figure 1. A schematic of a cooperative tumor targeting system via delivery of synthetic receptors.
Figure 2. A confocal microscopic image of a tumor section after cooperative targeting by synthetic receptor delivery. Green and magenta represent vessels and therapeutic agents inside a tumor respectively.
2017.07.07 View 10965 -
 Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 7520
Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 7520 -
 KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 11098
KAIST Professors Sweep the Best Science and Technology Award
(Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee (left) and Kyu-Young Whang)
Distinguished Professors Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Kyu-Young Whang of the College of Computing were selected as the winners of the "2017 Korea Best Science and Technology Award" by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) and the Korea Federation of Science and Technology Societies.
The award, which was established in 2003, is the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea annually. This is the first time that KAIST faculty members have swept the award since its founding.
Distinguished Professor Lee is renowned for his pioneering studies of system metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals by utilizing microorganisms. Professor Lee has developed a number of globally-recognized original technologies such as gasoline production using micro-organisms, a bio-butanol production process, microbes for producing nylon and plastic raw materials, and making native-like spider silk produced in metabolically engineering bacterium which is stronger than steel but finer than human hair.
System metabolism engineering was also selected as one of the top 10 promising technologies in the world in 2016 by the World Economic Forum. Selected as one of the world’s top 20 applied bioscientists in 2014 by Nature Biotechnology, he has many ‘first’ titles in his academic and research careers. He was the first Asian to win the James Bailey Award (2016) and Marvin Johnson Award (2012), the first Korean elected to both the US National Academy of Science (NAS) and the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) this year. He is the dean of KAIST institutes, a multi and interdisciplinary research institute at KAIST. He serves as co-chair of the Global Council on Biotechnology and as a member of the Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution at the World Economic Forum.
Distinguished Professor Whang, the first recipient in the field of computer science in this award, has been recognized for his lifetime achievement and contributions to the development of the software industry and the spreading of information culture. He has taken a pioneering role in presenting novel theories and innovative technologies in the field of database systems such as probabilistic aggregation, multidimensional indexing, query, and database and information retrieval. The Odysseus database management system Professor Hwang developed has been applied in many diverse fields of industry, while promoting the domestic software industry and its technical independence.
Professor Hwang is a fellow at the American Computer Society (ACM) and life fellow at IEEE. Professor Whang received the ACM SIGMOD Contributions Award in 2014 for his work promoting database research worldwide, the PAKDD Distinguished Contributions Award in 2014, and the DASFAA Outstanding Contributions Award in 2011 for his contributions to database and data mining research in the Asia-Pacific region. He is also the recipient of the prestigious Korea (presidential) Engineering Award in 2012.
2017.07.03 View 11098 -
 Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 7819
Professor Poong Hyun Seong Selected as Fellow of the ANS
Professor Poong Hyun Seong of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was selected as a fellow of the American Nuclear Society.
The selection was announced at their annual meeting held in San Francisco on June 12, in recognition of Professor Seong's contributions to the field of nuclear instrumentation, control andhuman factors engineering.
Founded in 1954, the American Nuclear Society selects scholars who have made outstanding achievements and contributions to the development of the nuclear engineering field each year.
Professor Seong's researches in the field of nuclear instrumentation, control and human factors engineering have contributed to the safe operation of nuclear power plants, to the development of systems to maintain nuclear power plants safely in the event of emergency and to the enhancement of effective response capabilities of nuclear power plant operators. His researches significantly contributed to the safety improvement of nuclear power plants and have been recognized worldwide.
Professor Seong said, "Korea has emerged as a nuclear powerhouse. I think not only my academic career but our national reputation in the field of nuclear research has been well recognized by our global peers.” Professor Seong has served as president of the Korean Nuclear Society, editor in chief of Nuclear Engineering and Technology, and as a commissioner of the Korean Nuclear Safety Commission. He is currently working as a commissioner of the Korean Atomic Energy Commission.
2017.06.29 View 7819