ES
-
 Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 10450
Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 10450 -
 Seeking a New Economic and Industrial Paradigm
The School of Humanities & Social Science will offer the open lecture course titled ‘Seeking a New Economic and Industrial Paradigm’ from May11 to June 7. This is part of a quarterly lecture series run by the school and open to the public.
The open lecture is designed to provide opportunities for the public to identify future challenges and opportunities for Korea’s economy and industry. Experts in macroeconomics, finance, and global collaboration will provide glimpses of new directions for each sector as well as megatrends of emerging technologies on the heels of the 4th Industrial Revolution.
Jin Hyuk Yoo from the Bank of Korea will speak on the ‘Outlook and Challenges of the Korean Economy.’ He will identify the current economic situation and explain how to build on sustainable long-term economic growth in the opening course.
Won-Bin Lee of the Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade will present on the ‘New Industrial Policy in the Era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.’ His lecture will focus on fostering the local industry and creating its own ecosystem for furthering regional industries.
Dong-Hoon Lee of Donga ST will speak on the implications that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about in the medical industry. Won-Suk Choi of FnPricing will introduce the FN business model, presenting the risks and benefits of fintech in his lecture ‘Finance: Human and Technology.’
Jae-Hong Choi of the Institute of International Development Cooperation at Korea University will give a talk titled ‘Toward the World through Global Cooperation.’ He will present on the history of Korea’s global cooperation initiatives and the role of KOICA, introducing its emerging economic and industrial cooperation model.
Professor Jeounghoon Kim, who is responsible for the public lecture program, said, “Korea now faces very diverse social economic and industrial challenges and we seem to be lost while searching for a solution. The public will have an opportunity to understand the current economic situation and its industrial implications.”
For registration and more info, please visit http://hss.kaist.ac.kr.
2017.04.26 View 9235
Seeking a New Economic and Industrial Paradigm
The School of Humanities & Social Science will offer the open lecture course titled ‘Seeking a New Economic and Industrial Paradigm’ from May11 to June 7. This is part of a quarterly lecture series run by the school and open to the public.
The open lecture is designed to provide opportunities for the public to identify future challenges and opportunities for Korea’s economy and industry. Experts in macroeconomics, finance, and global collaboration will provide glimpses of new directions for each sector as well as megatrends of emerging technologies on the heels of the 4th Industrial Revolution.
Jin Hyuk Yoo from the Bank of Korea will speak on the ‘Outlook and Challenges of the Korean Economy.’ He will identify the current economic situation and explain how to build on sustainable long-term economic growth in the opening course.
Won-Bin Lee of the Korea Institute for Industrial Economics & Trade will present on the ‘New Industrial Policy in the Era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.’ His lecture will focus on fostering the local industry and creating its own ecosystem for furthering regional industries.
Dong-Hoon Lee of Donga ST will speak on the implications that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about in the medical industry. Won-Suk Choi of FnPricing will introduce the FN business model, presenting the risks and benefits of fintech in his lecture ‘Finance: Human and Technology.’
Jae-Hong Choi of the Institute of International Development Cooperation at Korea University will give a talk titled ‘Toward the World through Global Cooperation.’ He will present on the history of Korea’s global cooperation initiatives and the role of KOICA, introducing its emerging economic and industrial cooperation model.
Professor Jeounghoon Kim, who is responsible for the public lecture program, said, “Korea now faces very diverse social economic and industrial challenges and we seem to be lost while searching for a solution. The public will have an opportunity to understand the current economic situation and its industrial implications.”
For registration and more info, please visit http://hss.kaist.ac.kr.
2017.04.26 View 9235 -
 FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 10135
FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 10135 -
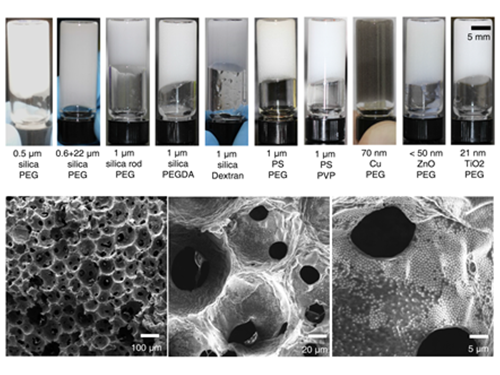 Processable High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Using Depletion Attraction
Professor Siyoung Choi’s research team from the KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering used physical force to successfully produce a stable emulsion.
Emulsions, commonly known as cosmetic products, refer to stably dispersed structures of oil droplets in water (or water droplets in oil). Pickering emulsions refer to emulsions stabilized using solid particles, instead of detergent. Traditionally, it is said that water and oil do not mix. Until recently, detergent was added to mix oil and water for dispersion. Emulsions have traditionally been produced using this technique and are currently used for products such as mayonnaise, sun block, and lotion.
On the other hand, Pickering emulsions have been used after stabilization of chemical treatments on solid particle surfaces to enhance adsorption power. However, there were limitations in its application, since the treatment process is complex and its applicable range remains limited. Instead of chemical treatment on Pickering emulsion surfaces, the research team mixed small macromolecules a few nanometer in size with larger solid particles (tens of nanometers to a few micrometers). This induced depletion force was used to successfully stabilize the emulsion.
Depletion force refers to the force a large number of small particles induces to aggregate the bigger particles, in order to secure free space for themselves. In short, the force induces an attraction between larger particles. Until now, depletion force could only be applied to solids and solid particles. However, the research team used macromolecules and large particles such as solid particles and oil droplets to show the applicability of depletion force between solids and liquids. By introducing macromolecules that act as smaller particles, hydrophilic solid particles enhanced the adsorption of solid particles to the oil droplet surface, while preventing dissociation from the particle surface, resulting in the maintenance of a stable state.
The research team confirmed the possibility of the simple production of various porous macromolecular materials using stable Pickering emulsions. Such porous macromolecules are expected to be applicable in separation film, systems engineering, drug delivery, and sensors, given their large surface area.
Professor KyuHan Kim, the first author said, “Until now, depletion force has only been used between solid colloid particles. This research has scientific significance since it is the first example of using depletion force between solid particles and liquid droplets.”
Professor Choi said, “Beyond its academic significance, this technology could contribute to industries and national competitiveness.” He continued, “Since this technology uses physical force, not chemical, to produce stable emulsion, it can be used regardless of the type of solid particle and macromolecule. Further, it could be used in customized porous material production for special purposes.”
The research was published in Nature Communications online on February 1. In particular, this research is significant since an undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, participated in the project as a second author through the KAIST Undergraduate Research Program (URP). This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Figure 1: Images of the inner structure of porous macromolecules produced using the new technology)
(Figure 2: Images showing the measurement of rheological properties of Pickering emulsions and system processability)
(Figure 3: Images showing a stable Pickering emulsion system)
2017.04.19 View 9610
Processable High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Using Depletion Attraction
Professor Siyoung Choi’s research team from the KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering used physical force to successfully produce a stable emulsion.
Emulsions, commonly known as cosmetic products, refer to stably dispersed structures of oil droplets in water (or water droplets in oil). Pickering emulsions refer to emulsions stabilized using solid particles, instead of detergent. Traditionally, it is said that water and oil do not mix. Until recently, detergent was added to mix oil and water for dispersion. Emulsions have traditionally been produced using this technique and are currently used for products such as mayonnaise, sun block, and lotion.
On the other hand, Pickering emulsions have been used after stabilization of chemical treatments on solid particle surfaces to enhance adsorption power. However, there were limitations in its application, since the treatment process is complex and its applicable range remains limited. Instead of chemical treatment on Pickering emulsion surfaces, the research team mixed small macromolecules a few nanometer in size with larger solid particles (tens of nanometers to a few micrometers). This induced depletion force was used to successfully stabilize the emulsion.
Depletion force refers to the force a large number of small particles induces to aggregate the bigger particles, in order to secure free space for themselves. In short, the force induces an attraction between larger particles. Until now, depletion force could only be applied to solids and solid particles. However, the research team used macromolecules and large particles such as solid particles and oil droplets to show the applicability of depletion force between solids and liquids. By introducing macromolecules that act as smaller particles, hydrophilic solid particles enhanced the adsorption of solid particles to the oil droplet surface, while preventing dissociation from the particle surface, resulting in the maintenance of a stable state.
The research team confirmed the possibility of the simple production of various porous macromolecular materials using stable Pickering emulsions. Such porous macromolecules are expected to be applicable in separation film, systems engineering, drug delivery, and sensors, given their large surface area.
Professor KyuHan Kim, the first author said, “Until now, depletion force has only been used between solid colloid particles. This research has scientific significance since it is the first example of using depletion force between solid particles and liquid droplets.”
Professor Choi said, “Beyond its academic significance, this technology could contribute to industries and national competitiveness.” He continued, “Since this technology uses physical force, not chemical, to produce stable emulsion, it can be used regardless of the type of solid particle and macromolecule. Further, it could be used in customized porous material production for special purposes.”
The research was published in Nature Communications online on February 1. In particular, this research is significant since an undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, participated in the project as a second author through the KAIST Undergraduate Research Program (URP). This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Figure 1: Images of the inner structure of porous macromolecules produced using the new technology)
(Figure 2: Images showing the measurement of rheological properties of Pickering emulsions and system processability)
(Figure 3: Images showing a stable Pickering emulsion system)
2017.04.19 View 9610 -
 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 9668
2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 9668 -
 Tactile Sensor for Robot Skin Advanced by KAIST Team
The joint research team of Professors Jung Kim and Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a tactile sensor that can act as skin for robots using silicon and carbon materials. This technology produced a sensor that can absorb shock and distinguish various forms of touch, and it is hoped to be used as robot skin in the future.
Skin serves an important role as the largest organ of the human body. As well as protecting major organs from external shock, skin also measures and distinguishes delicate tactile information and transfer it to the nervous system.
Current robotic sensory technology allows robots to have visual and auditory systems at nearly similar levels to human capacity, but there are limitations in tactile sensors that can detect changes in the environment throughout the body. To apply skin with similar functions as humans to robots, it is essential to develop skin sensor technology with high flexibility and high shock absorption. Another limitation for developing robot skin was connecting numerous sensors all over the body using electric wiring.
To overcome this problem, the research team combined silicon and carbon nanotubes (CNT) to produce a composite, which was then used in combination with a medical imaging technique called electrical impedance tomography (EIT). This led to technology that can distinguish various forms of force over a large area without electrical wiring.
The sensing material can distinguish the location and the size of various forms by touch, and thus can be applied to robot skin that can absorb shock as well as serves as a 3D computer interface and tactile sensor. It can withstand strong force such as a hammer strike, and can be re-used even after partial damage to the sensor by filling and hardening the damaged region with composite. Further, the sensor can be made by filling a 3D shape frame with silicon-nanotube composite. Using this technology, new forms of computer interaces can be developed with both curbed and flat surfaces.
This research was conducted through a collaboration between Professor Park, an expert in nanostructures and sensors, and Professor Kim, an expert in bio-robotics. Hence, the technology is likely to be applied in real products.
Professor Kim said, “Flexible tactile sensors can not only be directly adhered to the body, but they also provides information on modified states in multiple dimensions”. He continued, “This technology will contribute to the soft robot industry in the areas of robot skin and the field of wearable medical appliances.”
Professor Park said, “This technology implemented a next-generation user interface through the integration of functional nano-composite material and computer tomography.”
This research was published in Scientific Reports, a sister journal of Nature, online on January 25. This research was conducted as joint research by first author Hyo-Sang Lee, as well as Donguk Kwon and Ji-seung Cho, and was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
(Fiigrue 1: Robotic hand responding to resistance via a connection with the developed tactile sensor)
(Figure 2: Manufacturing process for pressure-resistant composite using silicon rubber and carbon nanotubes)
(Figure 3: Computer interface using pressure-resistant composite)
2017.04.17 View 13093
Tactile Sensor for Robot Skin Advanced by KAIST Team
The joint research team of Professors Jung Kim and Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a tactile sensor that can act as skin for robots using silicon and carbon materials. This technology produced a sensor that can absorb shock and distinguish various forms of touch, and it is hoped to be used as robot skin in the future.
Skin serves an important role as the largest organ of the human body. As well as protecting major organs from external shock, skin also measures and distinguishes delicate tactile information and transfer it to the nervous system.
Current robotic sensory technology allows robots to have visual and auditory systems at nearly similar levels to human capacity, but there are limitations in tactile sensors that can detect changes in the environment throughout the body. To apply skin with similar functions as humans to robots, it is essential to develop skin sensor technology with high flexibility and high shock absorption. Another limitation for developing robot skin was connecting numerous sensors all over the body using electric wiring.
To overcome this problem, the research team combined silicon and carbon nanotubes (CNT) to produce a composite, which was then used in combination with a medical imaging technique called electrical impedance tomography (EIT). This led to technology that can distinguish various forms of force over a large area without electrical wiring.
The sensing material can distinguish the location and the size of various forms by touch, and thus can be applied to robot skin that can absorb shock as well as serves as a 3D computer interface and tactile sensor. It can withstand strong force such as a hammer strike, and can be re-used even after partial damage to the sensor by filling and hardening the damaged region with composite. Further, the sensor can be made by filling a 3D shape frame with silicon-nanotube composite. Using this technology, new forms of computer interaces can be developed with both curbed and flat surfaces.
This research was conducted through a collaboration between Professor Park, an expert in nanostructures and sensors, and Professor Kim, an expert in bio-robotics. Hence, the technology is likely to be applied in real products.
Professor Kim said, “Flexible tactile sensors can not only be directly adhered to the body, but they also provides information on modified states in multiple dimensions”. He continued, “This technology will contribute to the soft robot industry in the areas of robot skin and the field of wearable medical appliances.”
Professor Park said, “This technology implemented a next-generation user interface through the integration of functional nano-composite material and computer tomography.”
This research was published in Scientific Reports, a sister journal of Nature, online on January 25. This research was conducted as joint research by first author Hyo-Sang Lee, as well as Donguk Kwon and Ji-seung Cho, and was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
(Fiigrue 1: Robotic hand responding to resistance via a connection with the developed tactile sensor)
(Figure 2: Manufacturing process for pressure-resistant composite using silicon rubber and carbon nanotubes)
(Figure 3: Computer interface using pressure-resistant composite)
2017.04.17 View 13093 -
 Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 9468
Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 9468 -
 A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 9982
A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 9982 -
 Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 11588
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 11588 -
 Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9370
Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9370 -
 Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 11264
Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 11264 -
 Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 12112
Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 12112