materials
-
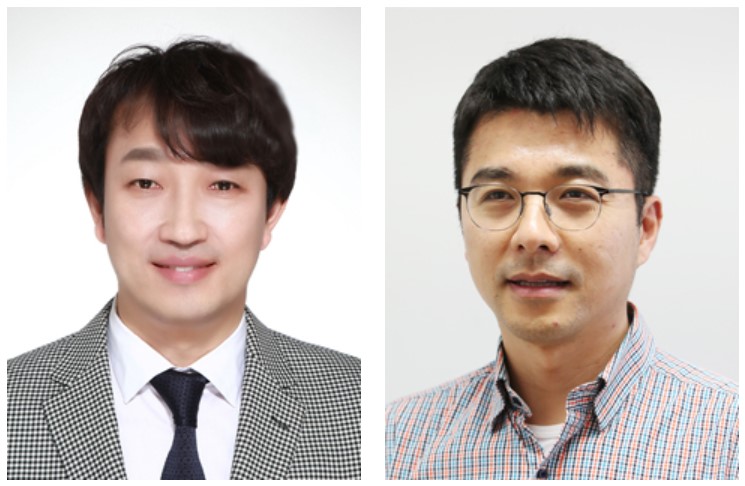 Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 12711
Two Professors Recognized for the National R&D Excellence 100
< Professor Haeng-Ki Lee (left) and Professor Jeong-Ho Lee (right) >
Two KAIST professors were listed among the 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 announced by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Korea Institute of S&T Evaluation and Planning.
Professor Haeng-Ki Lee from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering was recognized in the field of mechanics and materials for his research on developing new construction materials through the convergence of nano- and biotechnologies.
In the field of life and marine science, Professor Jeong-Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering was lauded for his research of diagnostic tools and therapies for glioblastoma and pediatric brain tumors.
A certificate from the Minister of Ministry of Science and ICT will be conferred to these two professors, and their names will be inscribed on a special 2019 National R&D Excellence 100 plaque to celebrate their achievements. The professors will also be given privileges during the process of new R&D project selection.
(END)
2019.10.15 View 12711 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 11118
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 11118 -
 Algorithm Identifies Optimal Pairs for Composing Metal-Organic Frameworks
The integration of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and other metal nanoparticles has increasingly led to the creation of new multifunctional materials. Many researchers have integrated MOFs with other classes of materials to produce new structures with synergetic properties.
Despite there being over 70,000 collections of synthesized MOFs that can be used as building blocks, the precise nature of the interaction and the bonding at the interface between the two materials still remains unknown. The question is how to sort out the right matching pairs out of 70,000 MOFs.
An algorithmic study published in Nature Communications by a KAIST research team presents a clue for finding the perfect pairs. The team, led by Professor Ji-Han Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a joint computational and experimental approach to rationally design MOF@MOFs, a composite of MOFs where an MOF is grown on a different MOF.
Professor Kim’s team, in collaboration with UNIST, noted that the metal node of one MOF can coordinately bond with the linker of a different MOF and the precisely matched interface configurations at atomic and molecular levels can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs.
They screened thousands of MOFs and identified optimal MOF pairs that can seamlessly connect to one another by taking advantage of the fact that the metal node of one MOF can form coordination bonds with the linkers of the second MOF. Six pairs predicted from the computational algorithm successfully grew into single crystals.
This computational workflow can readily extend into other classes of materials and can lead to the rapid exploration of the composite MOFs arena for accelerated materials development. Even more, the workflow can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs in the form of large single crystals, and thereby demonstrated the utility of rationally designing the MOF@MOFs.
This study is the first algorithm for predicting the synthesis of composite MOFs, to the best of their knowledge. Professor Kim said, “The number of predicted pairs can increase even more with the more general 2D lattice matching, and it is worth investigating in the future.”
This study was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
(Figure: An example of a rationally synthesized MOF@MOFs (cubic HKUST-1@MOF-5 ))
2019.08.30 View 17235
Algorithm Identifies Optimal Pairs for Composing Metal-Organic Frameworks
The integration of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) and other metal nanoparticles has increasingly led to the creation of new multifunctional materials. Many researchers have integrated MOFs with other classes of materials to produce new structures with synergetic properties.
Despite there being over 70,000 collections of synthesized MOFs that can be used as building blocks, the precise nature of the interaction and the bonding at the interface between the two materials still remains unknown. The question is how to sort out the right matching pairs out of 70,000 MOFs.
An algorithmic study published in Nature Communications by a KAIST research team presents a clue for finding the perfect pairs. The team, led by Professor Ji-Han Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, developed a joint computational and experimental approach to rationally design MOF@MOFs, a composite of MOFs where an MOF is grown on a different MOF.
Professor Kim’s team, in collaboration with UNIST, noted that the metal node of one MOF can coordinately bond with the linker of a different MOF and the precisely matched interface configurations at atomic and molecular levels can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs.
They screened thousands of MOFs and identified optimal MOF pairs that can seamlessly connect to one another by taking advantage of the fact that the metal node of one MOF can form coordination bonds with the linkers of the second MOF. Six pairs predicted from the computational algorithm successfully grew into single crystals.
This computational workflow can readily extend into other classes of materials and can lead to the rapid exploration of the composite MOFs arena for accelerated materials development. Even more, the workflow can enhance the likelihood of synthesizing MOF@MOFs in the form of large single crystals, and thereby demonstrated the utility of rationally designing the MOF@MOFs.
This study is the first algorithm for predicting the synthesis of composite MOFs, to the best of their knowledge. Professor Kim said, “The number of predicted pairs can increase even more with the more general 2D lattice matching, and it is worth investigating in the future.”
This study was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics.
(Figure: An example of a rationally synthesized MOF@MOFs (cubic HKUST-1@MOF-5 ))
2019.08.30 View 17235 -
 Artificial Muscles Bloom, Dance, and Wave
Wearing a flower brooch that blooms before your eyes sounds like magic. KAIST researchers have made it real with robotic muscles.
Researchers have developed an ultrathin, artificial muscle for soft robotics. The advancement, recently reported in the journal Science Robotics, was demonstrated with a robotic blooming flower brooch, dancing robotic butterflies and fluttering tree leaves on a kinetic art piece.
The robotic equivalent of a muscle that can move is called an actuator. The actuator expands, contracts or rotates like muscle fibers using a stimulus such as electricity. Engineers around the world are striving to develop more dynamic actuators that respond quickly, can bend without breaking, and are very durable. Soft, robotic muscles could have a wide variety of applications, from wearable electronics to advanced prosthetics.
The team from KAIST’s Creative Research Initiative Center for Functionally Antagonistic Nano-Engineering developed a very thin, responsive, flexible and durable artificial muscle. The actuator looks like a skinny strip of paper about an inch long. They used a particular type of material called MXene, which is class of compounds that have layers only a few atoms thick.
Their chosen MXene material (T3C2Tx) is made of thin layers of titanium and carbon compounds. It was not flexible by itself; sheets of material would flake off the actuator when bent in a loop. That changed when the MXene was “ionically cross-linked” — connected through an ionic bond — to a synthetic polymer. The combination of materials made the actuator flexible, while still maintaining strength and conductivity, which is critical for movements driven by electricity.
Their particular combination performed better than others reported. Their actuator responded very quickly to low voltage, and lasted for more than five hours moving continuously.
To prove the tiny robotic muscle works, the team incorporated the actuator into wearable art: an origami-inspired brooch mimics how a narcissus flower unfolds its petals when a small amount of electricity is applied. They also designed robotic butterflies that move their wings up and down, and made the leaves of a tree sculpture flutter.
“Wearable robotics and kinetic art demonstrate how robotic muscles can have fun and beautiful applications,” said Il-Kwon Oh, lead paper author and professor of mechanical engineering. “It also shows the enormous potential for small, artificial muscles for a variety of uses, such as haptic feedback systems and active biomedical devices.”
The team next plans to investigate more practical applications of MXene-based soft actuators and other engineering applications of MXene 2D nanomaterials.
2019.08.22 View 25583
Artificial Muscles Bloom, Dance, and Wave
Wearing a flower brooch that blooms before your eyes sounds like magic. KAIST researchers have made it real with robotic muscles.
Researchers have developed an ultrathin, artificial muscle for soft robotics. The advancement, recently reported in the journal Science Robotics, was demonstrated with a robotic blooming flower brooch, dancing robotic butterflies and fluttering tree leaves on a kinetic art piece.
The robotic equivalent of a muscle that can move is called an actuator. The actuator expands, contracts or rotates like muscle fibers using a stimulus such as electricity. Engineers around the world are striving to develop more dynamic actuators that respond quickly, can bend without breaking, and are very durable. Soft, robotic muscles could have a wide variety of applications, from wearable electronics to advanced prosthetics.
The team from KAIST’s Creative Research Initiative Center for Functionally Antagonistic Nano-Engineering developed a very thin, responsive, flexible and durable artificial muscle. The actuator looks like a skinny strip of paper about an inch long. They used a particular type of material called MXene, which is class of compounds that have layers only a few atoms thick.
Their chosen MXene material (T3C2Tx) is made of thin layers of titanium and carbon compounds. It was not flexible by itself; sheets of material would flake off the actuator when bent in a loop. That changed when the MXene was “ionically cross-linked” — connected through an ionic bond — to a synthetic polymer. The combination of materials made the actuator flexible, while still maintaining strength and conductivity, which is critical for movements driven by electricity.
Their particular combination performed better than others reported. Their actuator responded very quickly to low voltage, and lasted for more than five hours moving continuously.
To prove the tiny robotic muscle works, the team incorporated the actuator into wearable art: an origami-inspired brooch mimics how a narcissus flower unfolds its petals when a small amount of electricity is applied. They also designed robotic butterflies that move their wings up and down, and made the leaves of a tree sculpture flutter.
“Wearable robotics and kinetic art demonstrate how robotic muscles can have fun and beautiful applications,” said Il-Kwon Oh, lead paper author and professor of mechanical engineering. “It also shows the enormous potential for small, artificial muscles for a variety of uses, such as haptic feedback systems and active biomedical devices.”
The team next plans to investigate more practical applications of MXene-based soft actuators and other engineering applications of MXene 2D nanomaterials.
2019.08.22 View 25583 -
 Enhanced Natural Gas Storage to Help Reduce Global Warming
< Professor Atilhan (left) and Professor Yavuz (right) >
Researchers have designed plastic-based materials that can store natural gas more effectively. These new materials can not only make large-scale, cost-effective, and safe natural gas storage possible, but further hold a strong promise for combating global warming.
Natural gas (predominantly methane) is a clean energy alternative. It is stored by compression, liquefaction, or adsorption. Among these, adsorbed natural gas (ANG) storage is a more efficient, cheaper, and safer alternative to conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage approaches that have drawbacks such as low storage efficiency, high costs, and safety concerns. However, developing adsorptive materials that can more fully exploit the advantages of ANG storage has remained a challenging task.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Cafer T. Yavuz from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS), in collaboration with Professor Mert Atilhan’s group from Texas A&M University, synthesized 29 unique porous polymeric structures with inherent flexibility, and tested their methane gas uptake capacity at high pressures. These porous polymers had varying synthetic complexities, porosities, and morphologies, and the researchers subjected each porous polymer to pure methane gas under various conditions to study the ANG performances.
Of these 29 distinct chemical structures, COP-150 was particularly noteworthy as it achieved a high deliverable gravimetric methane working capacity when cycled between 5 and 100 bar at 273 K, which is 98% of the total uptake capacity. This result surpassed the target set by the United States Department of Energy (US DOE).
COP-150 is the first ever structure to fulfil both the gravimetric and volumetric requirements of the US DOE for successful vehicular use, and the total cost to produce the COP-150 adsorbent was only 1 USD per kilogram.
COP-150 can be produced using freely available and easily accessible plastic materials, and moreover, its synthesis takes place at room temperature, open to the air, and no previous purification of the chemicals is required. The pressure-triggered flexible structure of COP-150 is also advantageous in terms of the total working capacity of deliverable methane for real applications.
The research team believed that the increased pressure flexes the network structure of COP-150 showing “swelling” behavior, and suggested that the flexibility provides rapid desorption and thermal management, while the hydrophobicity and the nature of the covalently bonded framework allow these promising materials to tolerate harsh conditions.
This swelling mechanism of expansion-contraction solves two other major issues, the team noted. Firstly, when using adsorbents based on such a mechanism, unsafe pressure spikes that may occur due to temperature swings can be eliminated. In addition, contamination can also be minimized, since the adsorbent remains contracted when no gas is stored.
Professor Yavuz said, “We envision a whole host of new designs and mechanisms to be developed based on our concept. Since natural gas is a much cleaner fuel than coal and petroleum, new developments in this realm will help switching to the use of less polluting fuels.”
Professor Atilhan agreed the most important impact of their research is on the environment. “Using natural gas more than coal and petroleum will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We believe, one day, we might see vehicles equipped with our materials that are run by a cleaner natural gas fuel,” he added.
This study, reported in Nature Energy on July 8, was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants ( NRF-2016R1A2B4011027, NRF-2017M3A7B4042140, and NRF-2017M3A7B4042235).
< Suggested chemical structure of COP-150 >
< Initial ingredients (left) and final product (right) of COP-150 synthesis >
< Comparison of highest reported volumetric working capacities >
(END)
2019.08.09 View 27529
Enhanced Natural Gas Storage to Help Reduce Global Warming
< Professor Atilhan (left) and Professor Yavuz (right) >
Researchers have designed plastic-based materials that can store natural gas more effectively. These new materials can not only make large-scale, cost-effective, and safe natural gas storage possible, but further hold a strong promise for combating global warming.
Natural gas (predominantly methane) is a clean energy alternative. It is stored by compression, liquefaction, or adsorption. Among these, adsorbed natural gas (ANG) storage is a more efficient, cheaper, and safer alternative to conventional compressed natural gas (CNG) and liquefied natural gas (LNG) storage approaches that have drawbacks such as low storage efficiency, high costs, and safety concerns. However, developing adsorptive materials that can more fully exploit the advantages of ANG storage has remained a challenging task.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Cafer T. Yavuz from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS), in collaboration with Professor Mert Atilhan’s group from Texas A&M University, synthesized 29 unique porous polymeric structures with inherent flexibility, and tested their methane gas uptake capacity at high pressures. These porous polymers had varying synthetic complexities, porosities, and morphologies, and the researchers subjected each porous polymer to pure methane gas under various conditions to study the ANG performances.
Of these 29 distinct chemical structures, COP-150 was particularly noteworthy as it achieved a high deliverable gravimetric methane working capacity when cycled between 5 and 100 bar at 273 K, which is 98% of the total uptake capacity. This result surpassed the target set by the United States Department of Energy (US DOE).
COP-150 is the first ever structure to fulfil both the gravimetric and volumetric requirements of the US DOE for successful vehicular use, and the total cost to produce the COP-150 adsorbent was only 1 USD per kilogram.
COP-150 can be produced using freely available and easily accessible plastic materials, and moreover, its synthesis takes place at room temperature, open to the air, and no previous purification of the chemicals is required. The pressure-triggered flexible structure of COP-150 is also advantageous in terms of the total working capacity of deliverable methane for real applications.
The research team believed that the increased pressure flexes the network structure of COP-150 showing “swelling” behavior, and suggested that the flexibility provides rapid desorption and thermal management, while the hydrophobicity and the nature of the covalently bonded framework allow these promising materials to tolerate harsh conditions.
This swelling mechanism of expansion-contraction solves two other major issues, the team noted. Firstly, when using adsorbents based on such a mechanism, unsafe pressure spikes that may occur due to temperature swings can be eliminated. In addition, contamination can also be minimized, since the adsorbent remains contracted when no gas is stored.
Professor Yavuz said, “We envision a whole host of new designs and mechanisms to be developed based on our concept. Since natural gas is a much cleaner fuel than coal and petroleum, new developments in this realm will help switching to the use of less polluting fuels.”
Professor Atilhan agreed the most important impact of their research is on the environment. “Using natural gas more than coal and petroleum will significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We believe, one day, we might see vehicles equipped with our materials that are run by a cleaner natural gas fuel,” he added.
This study, reported in Nature Energy on July 8, was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grants ( NRF-2016R1A2B4011027, NRF-2017M3A7B4042140, and NRF-2017M3A7B4042235).
< Suggested chemical structure of COP-150 >
< Initial ingredients (left) and final product (right) of COP-150 synthesis >
< Comparison of highest reported volumetric working capacities >
(END)
2019.08.09 View 27529 -
 Micropatch Made of DNA
Researchers reported the fabrication of microstructure arrays of DNA materials using topographic control. This method provides a platform for forming multiscale hierarchical orientations of soft and biomaterials using a process of simple shearing and controlled evaporation on a patterned substrate. This approach enables the potential of patterning applications using DNA or other anisotropic biomaterials.
DNA is one of the most abundant biomaterials found in all living organisms in nature. It has unique characteristics of fine feature size and liquid crystalline phase, enabling to create various kinds of microstructure DNA arrays. Based on these characteristics, DNA has been used as a building block for “origami” and textile art at the nanometer scale.
A KAIST research team led by Professors Dong Ki Yoon and Hyungsoo Kim fabricated a DNA-based micropatch using the “coffee ring effect” and its multi-angle control technology, which was published online in Nature Communications on June 7.
The research team used cheap DNA material extracted from salmon to realize the micropatch structure with well-aligned knit or ice cream cone shapes. When the DNA material in an aqueous solution is rubbed between two solid substrates while water is evaporating, DNA chains are unidirectionally aligned to make a thin film such as in LCD display devices. The DNA chains can make more complex microstructures such as knit or a texture with ice cream cone shapes when the same procedure is carried out in topographical patterns like microposts (Figure 1). This can be applied to make metamaterials by mixing with functionalized gold nanorods to show plasmonic color.
Plasmon resonance is a phenomenon in which electrons vibrate uniformly on the surface of a substrate made of metal, reacting only to light that matches a specific energy to enhance the clarity and expression of colors. For this, the most important factor is the orientation in which the gold nanorods align. That is, when the rods are aligned side by side in one direction, the optical and electrical characteristics are maximized. The research team focused on this point and made the DNA micropatch as a frame to orient the gold nanorods in a unique shape and fabricated a plasmonic color film (Figure 2).
Professor Yoon said this study is meaningful in that it deals with the evaporation phenomenon, which has not been studied much in the field of polymers and biopolymers in terms of basic science. He explained, “This will also help maximize the efficiency of polymeric materials that can be orientated in coating, 2D, and 3D printing applications. Furthermore, DNA that exists infinitely in nature can be expected to have industrial application value as a new material since it can easily form complexes with other materials as described in this study.”
(Figure 1. The DNA micropatch using topographic control. (a) The experimental scheme.
(b) Enlarged image of (e). (c-e) Different micropatches made of DNA using different shearing directions.)
(Figure 2. The knit-like structures made of DNA-gold nanorod complex. (a,b) Optical
and polarized optical microscopy images. (c-f) Plasmonic colors reflected from aligned DNA-gold nanorod complex depending on the sample rotation.)
2019.07.01 View 34852
Micropatch Made of DNA
Researchers reported the fabrication of microstructure arrays of DNA materials using topographic control. This method provides a platform for forming multiscale hierarchical orientations of soft and biomaterials using a process of simple shearing and controlled evaporation on a patterned substrate. This approach enables the potential of patterning applications using DNA or other anisotropic biomaterials.
DNA is one of the most abundant biomaterials found in all living organisms in nature. It has unique characteristics of fine feature size and liquid crystalline phase, enabling to create various kinds of microstructure DNA arrays. Based on these characteristics, DNA has been used as a building block for “origami” and textile art at the nanometer scale.
A KAIST research team led by Professors Dong Ki Yoon and Hyungsoo Kim fabricated a DNA-based micropatch using the “coffee ring effect” and its multi-angle control technology, which was published online in Nature Communications on June 7.
The research team used cheap DNA material extracted from salmon to realize the micropatch structure with well-aligned knit or ice cream cone shapes. When the DNA material in an aqueous solution is rubbed between two solid substrates while water is evaporating, DNA chains are unidirectionally aligned to make a thin film such as in LCD display devices. The DNA chains can make more complex microstructures such as knit or a texture with ice cream cone shapes when the same procedure is carried out in topographical patterns like microposts (Figure 1). This can be applied to make metamaterials by mixing with functionalized gold nanorods to show plasmonic color.
Plasmon resonance is a phenomenon in which electrons vibrate uniformly on the surface of a substrate made of metal, reacting only to light that matches a specific energy to enhance the clarity and expression of colors. For this, the most important factor is the orientation in which the gold nanorods align. That is, when the rods are aligned side by side in one direction, the optical and electrical characteristics are maximized. The research team focused on this point and made the DNA micropatch as a frame to orient the gold nanorods in a unique shape and fabricated a plasmonic color film (Figure 2).
Professor Yoon said this study is meaningful in that it deals with the evaporation phenomenon, which has not been studied much in the field of polymers and biopolymers in terms of basic science. He explained, “This will also help maximize the efficiency of polymeric materials that can be orientated in coating, 2D, and 3D printing applications. Furthermore, DNA that exists infinitely in nature can be expected to have industrial application value as a new material since it can easily form complexes with other materials as described in this study.”
(Figure 1. The DNA micropatch using topographic control. (a) The experimental scheme.
(b) Enlarged image of (e). (c-e) Different micropatches made of DNA using different shearing directions.)
(Figure 2. The knit-like structures made of DNA-gold nanorod complex. (a,b) Optical
and polarized optical microscopy images. (c-f) Plasmonic colors reflected from aligned DNA-gold nanorod complex depending on the sample rotation.)
2019.07.01 View 34852 -
 Hydrogen-Natural Gas Hydrates Harvested by Natural Gas
A hydrogen-natural gas blend (HNGB) can be a game changer only if it can be stored safely and used as a sustainable clean energy resource. A recent study has suggested a new strategy for stably storing hydrogen, using natural gas as a stabilizer. The research proposed a practical gas phase modulator based synthesis of HNGB without generating chemical waste after dissociation for the immediate service.
The research team of Professor Jae Woo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in collaboration with the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) demonstrated that the natural gas modulator based synthesis leads to significantly reduced synthesis pressure simultaneously with the formation of hydrogen clusters in the confined nanoporous cages of clathrate hydrates. This approach minimizes the environmental impact and reduces operation costs since clathrate hydrates do not generate any chemical waste in both the synthesis and decomposition processes.
For the efficient storage and transportation of hydrogen, numerous materials have been investigated. Among others, clathrate hydrates offer distinct benefits. Clathrate hydrates are nanoporous inclusion compounds composed of a 3D network of polyhedral cages made of hydrogen-bonded ‘host’ water molecules and captured ‘guest’ gas or liquid molecules.
In this study, the research team used two gases, methane and ethane, which have lower equilibrium conditions compared to hydrogen as thermodynamic stabilizers. As a result, they succeeded in stably storing the hydrogen-natural gas compound in hydrates. According to the composition ratio of methane and ethane, structure I or II hydrates can be formed, both of which can stably store hydrogen-natural gas in low-pressure conditions.
The research team found that two hydrogen molecules are stored in small cages in tuned structure I hydrates, while up to three hydrogen molecules can be stored in both small and large cages in tuned structure II hydrates. Hydrates can store gas up to about 170-times its volume and the natural gas used as thermodynamic stabilizers in this study can also be used as an energy source.
The research team developed technology to produce hydrates from ice, produced hydrogen-natural gas hydrates by substitution, and successfully observed that the tuning phenomenon only occurs when hydrogen is involved in hydrate formation from the start for both structures of hydrates.
They expect that the findings can be applied to not only an energy-efficient gas storage material, but also a smart platform to utilize hydrogen natural gas blends, which can serve as a new alternative energy source with targeted hydrogen contents by designing synthetic pathways of mixed gas hydrates.
The research was published online in Energy Storage Materials on June 6, with the title ‘One-step formation of hydrogen clusters in clathrate hydrates stabilized via natural gas blending’.
Professor Lee said, “HNGB will utilize the existing natural gas infrastructure for transportation, so it is very likely that we can commercialize this hydrate system. We are investigating the kinetic performance through a follow-up strategy to increase the volume of gas storage.
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and BK21 plus program.
(Figure1. Schematics showing the storage method for hydrogen in a natural gas hydrate using a substitution method and storage method directly from ice to a hydrogen-natural gas hydrate.)
(Figure 2. Artificially synthesized and dissociated hydrogen-natural gas hydrates. The Raman spectra of tuned sI and sII hydrate showing the hydrogen clusters in each cage.)
2019.06.21 View 41949
Hydrogen-Natural Gas Hydrates Harvested by Natural Gas
A hydrogen-natural gas blend (HNGB) can be a game changer only if it can be stored safely and used as a sustainable clean energy resource. A recent study has suggested a new strategy for stably storing hydrogen, using natural gas as a stabilizer. The research proposed a practical gas phase modulator based synthesis of HNGB without generating chemical waste after dissociation for the immediate service.
The research team of Professor Jae Woo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in collaboration with the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) demonstrated that the natural gas modulator based synthesis leads to significantly reduced synthesis pressure simultaneously with the formation of hydrogen clusters in the confined nanoporous cages of clathrate hydrates. This approach minimizes the environmental impact and reduces operation costs since clathrate hydrates do not generate any chemical waste in both the synthesis and decomposition processes.
For the efficient storage and transportation of hydrogen, numerous materials have been investigated. Among others, clathrate hydrates offer distinct benefits. Clathrate hydrates are nanoporous inclusion compounds composed of a 3D network of polyhedral cages made of hydrogen-bonded ‘host’ water molecules and captured ‘guest’ gas or liquid molecules.
In this study, the research team used two gases, methane and ethane, which have lower equilibrium conditions compared to hydrogen as thermodynamic stabilizers. As a result, they succeeded in stably storing the hydrogen-natural gas compound in hydrates. According to the composition ratio of methane and ethane, structure I or II hydrates can be formed, both of which can stably store hydrogen-natural gas in low-pressure conditions.
The research team found that two hydrogen molecules are stored in small cages in tuned structure I hydrates, while up to three hydrogen molecules can be stored in both small and large cages in tuned structure II hydrates. Hydrates can store gas up to about 170-times its volume and the natural gas used as thermodynamic stabilizers in this study can also be used as an energy source.
The research team developed technology to produce hydrates from ice, produced hydrogen-natural gas hydrates by substitution, and successfully observed that the tuning phenomenon only occurs when hydrogen is involved in hydrate formation from the start for both structures of hydrates.
They expect that the findings can be applied to not only an energy-efficient gas storage material, but also a smart platform to utilize hydrogen natural gas blends, which can serve as a new alternative energy source with targeted hydrogen contents by designing synthetic pathways of mixed gas hydrates.
The research was published online in Energy Storage Materials on June 6, with the title ‘One-step formation of hydrogen clusters in clathrate hydrates stabilized via natural gas blending’.
Professor Lee said, “HNGB will utilize the existing natural gas infrastructure for transportation, so it is very likely that we can commercialize this hydrate system. We are investigating the kinetic performance through a follow-up strategy to increase the volume of gas storage.
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and BK21 plus program.
(Figure1. Schematics showing the storage method for hydrogen in a natural gas hydrate using a substitution method and storage method directly from ice to a hydrogen-natural gas hydrate.)
(Figure 2. Artificially synthesized and dissociated hydrogen-natural gas hydrates. The Raman spectra of tuned sI and sII hydrate showing the hydrogen clusters in each cage.)
2019.06.21 View 41949 -
 Professor Yim Decorated with the Chongjo Order of Merit
Professor Yong-Taek Yim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was awarded the highest order of merit, the “Chongjo Keunjong Medal,” bestowed to public officials by the government in celebration of Invention Day on May 27.
Professor Yim was recognized for his innovative achievements to increase royalty income by introducing an IP-based management system at the Korean Institute of Machinery & Materials. He served as the president of KIMM for three years from 2014.
His idea led to new approaches to help explore diverse revenue creating sources such as dividend earnings and share sales, apart from simply relying on technology transfer fees. His efforts to disseminate the in-house R&D results also led to the foundation of six tech-based startups and spinoffs, which generated 11.2 billion KRW in sales. He also helped set up three spinoffs abroad.
Professor Yim said, “I pushed employee invention as a new value creator at KIMM. I thank each and every researcher and staff member at KIMM who worked so hard to create such an innovative IP-based R&D environment.”
2019.05.28 View 7782
Professor Yim Decorated with the Chongjo Order of Merit
Professor Yong-Taek Yim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was awarded the highest order of merit, the “Chongjo Keunjong Medal,” bestowed to public officials by the government in celebration of Invention Day on May 27.
Professor Yim was recognized for his innovative achievements to increase royalty income by introducing an IP-based management system at the Korean Institute of Machinery & Materials. He served as the president of KIMM for three years from 2014.
His idea led to new approaches to help explore diverse revenue creating sources such as dividend earnings and share sales, apart from simply relying on technology transfer fees. His efforts to disseminate the in-house R&D results also led to the foundation of six tech-based startups and spinoffs, which generated 11.2 billion KRW in sales. He also helped set up three spinoffs abroad.
Professor Yim said, “I pushed employee invention as a new value creator at KIMM. I thank each and every researcher and staff member at KIMM who worked so hard to create such an innovative IP-based R&D environment.”
2019.05.28 View 7782 -
 The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 9272
The 1st Korea Toray Science and Technology Awardee, Prof. Sukbok Chang
(Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry)
The Korea Toray Science Foundation (KTSF) awarded the first Korea Toray Science Technology Award in basic science to Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry on September 19.
KTSF was established in January 2018, and its award goes to researchers who have significantly contributed to the development of chemistry and materials research with funds to support research projects.
Distinguished Professor Chang has devoted himself in organocatalysis research; in particular, his work on catalysts for effective lactam formation, which was an intricate problem, received great attention.
The award ceremony will take place in The Federation of Korean Industries Hall on October 31. KTFS board members, judges, and the CEO of Toray Industries Akihiro Nikkaku will attend the ceremony. Also, Dr. Ryoji Noyori, the Nobel Laureate in Chemistry, will give a talk on the role of chemistry and creative challenges as a researcher.
2018.10.04 View 9272 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 8267
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Announced as the Eni Award Recipient
(Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will be awarded the 2018 Eni Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize in recognition of his innovations in the fields of energy and environment. The award ceremony will take place at the Quirinal Palace, the official residence of Italian President Sergio Mattarella, who will also be attending on October 22.
Eni, an Italian multinational energy corporation established the Eni Award in 2008 to promote technological and research innovation of efficient and sustainable energy resources. The Advanced Environmental Solutions Prize is one of the three categories of the Eni Award. The other two categories are Energy Transition and Energy Frontiers. The Award for Advanced Environmental Solutions recognizes a researcher or group of scientists that has achieved internationally significant R&D results in the field of environmental protection and recovery. The Eni Award is referred to as the Nobel Award in the fields of energy and environment.
Professor Lee, a pioneering leader in systems metabolic engineering was honored with the award for his developing engineered bacteria to produce chemical products, fuels, and non-food biomass materials sustainably and with a low environmental impact. He has leveraged the technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environmentally friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass.
The award committee said that they considered the following elements in assessing Professor Lee’s achievement: the scientific relevance and the research innovation level; the impact on the energy system in terms of sustainability as well as fairer and broader access to energy; and the adequacy between technological and economic aspects.
Professor Lee, who already won two other distinguished prizes such as the George Washington Carver Award and the PV Danckwerts Memorial Lecture Award this year, said, “I am so glad that the international academic community as well as global industry leaders came to recognize our work that our students and research team has made for decades.”
Dr. Lee’s lab has been producing a lot of chemicals in environmentally friendly ways. Among them, many were biologically produced for the first time and some of these processes have been already commercialized. “We will continue to strive for research outcomes with two objectives: First, to develop bio-based processes suitable for sustainable chemical industry. The other is to contribute to the human healthcare system through development of platform technologies integrating medicine and nutrition,” he added.
2018.09.12 View 8267 -
 Lead-free, Efficient Perovskite for Photovoltaic Cells
(Clockwise from left: Post-doc Researcher Lamjed Debbichi, Master’s Candidate Songju Lee, Professor Min Seok Jang and Professor Hyungjun Kim)
A KAIST research team has proposed a perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6 that serves as a potential active material for highly efficient lead-free thin-film photovoltaic devices. This material is expected to lay the foundation to overcome previously known limitations of perovskite including its stability and toxicity issues.
As strong candidates for next-generation high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, perovskite photovoltaic cells have a maximum photoconversion efficiency of 22%, comparable to high-performance crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells. In addition, perovskite-based cells can be fabricated at low temperatures, thereby bringing about dramatic cost reductions.
However, it has been noted that conventional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials exhibit low stability, eventually degrading their performance and making them unfit for continued use. Moreover, their inclusion of lead has undermined their environmental friendliness.
In light of this, a joint team led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering has analyzed a previously discovered perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6, consisting of only inorganic substances and investigated its suitability for application in thin-film photovoltaic devices. Theoretical investigations suggests that this new perovskite material is not only as efficient but also more stable and environment friendly compared to the conventional perovskite materials. For this analysis, the team developed multiscale multiphysics simulation frameworks. Atomic-scale first-principle quantum calculations were carried out to study the optical properties of the proposed material, and device-scale electromagnetic simulations were conducted to suggest that the material could indeed serve as a promising photovoltaic substance at the device level.
From this point onward, the research team plans to extend the study in two directions: an empirical study to apply the perovskite material in real-world photovoltaic cells and a theoretical analysis to find the optimal and highly stable material for photovoltaic cells. The team said, “Perovskite materials are highly efficient, but in order to completely replace the conventional solar cells, their stability and toxicity issues must first be resolved.” They added that this research is expected to accelerate related studies in pursuit of high-efficiency, environment-friendly perovskite materials.
This research, led by post-doc researcher Lamjed Debbichi and master’s candidate Songju Lee, was selected as the front cover article of Advanced Materials on March 22.
Figure 1. Cover of Advanced Materials
Figure 2. Schematic of full solar cell device structure
2018.06.08 View 9628
Lead-free, Efficient Perovskite for Photovoltaic Cells
(Clockwise from left: Post-doc Researcher Lamjed Debbichi, Master’s Candidate Songju Lee, Professor Min Seok Jang and Professor Hyungjun Kim)
A KAIST research team has proposed a perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6 that serves as a potential active material for highly efficient lead-free thin-film photovoltaic devices. This material is expected to lay the foundation to overcome previously known limitations of perovskite including its stability and toxicity issues.
As strong candidates for next-generation high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, perovskite photovoltaic cells have a maximum photoconversion efficiency of 22%, comparable to high-performance crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells. In addition, perovskite-based cells can be fabricated at low temperatures, thereby bringing about dramatic cost reductions.
However, it has been noted that conventional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials exhibit low stability, eventually degrading their performance and making them unfit for continued use. Moreover, their inclusion of lead has undermined their environmental friendliness.
In light of this, a joint team led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering has analyzed a previously discovered perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6, consisting of only inorganic substances and investigated its suitability for application in thin-film photovoltaic devices. Theoretical investigations suggests that this new perovskite material is not only as efficient but also more stable and environment friendly compared to the conventional perovskite materials. For this analysis, the team developed multiscale multiphysics simulation frameworks. Atomic-scale first-principle quantum calculations were carried out to study the optical properties of the proposed material, and device-scale electromagnetic simulations were conducted to suggest that the material could indeed serve as a promising photovoltaic substance at the device level.
From this point onward, the research team plans to extend the study in two directions: an empirical study to apply the perovskite material in real-world photovoltaic cells and a theoretical analysis to find the optimal and highly stable material for photovoltaic cells. The team said, “Perovskite materials are highly efficient, but in order to completely replace the conventional solar cells, their stability and toxicity issues must first be resolved.” They added that this research is expected to accelerate related studies in pursuit of high-efficiency, environment-friendly perovskite materials.
This research, led by post-doc researcher Lamjed Debbichi and master’s candidate Songju Lee, was selected as the front cover article of Advanced Materials on March 22.
Figure 1. Cover of Advanced Materials
Figure 2. Schematic of full solar cell device structure
2018.06.08 View 9628 -
 New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 10660
New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 10660