TR
-
 KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 4334
KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 4334 -
 KAIST Secures Core Technology for Ultra-High-Resolution Image Sensors
A joint research team from Korea and the United States has developed next-generation, high-resolution image sensor technology with higher power efficiency and a smaller size compared to existing sensors. Notably, they have secured foundational technology for ultra-high-resolution shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors, an area currently dominated by Sony, paving the way for future market entry.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of November that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Inha University and Yale University in the U.S., has developed an ultra-thin broadband photodiode (PD), marking a significant breakthrough in high-performance image sensor technology.
This research drastically improves the trade-off between the absorption layer thickness and quantum efficiency found in conventional photodiode technology. Specifically, it achieved high quantum efficiency of over 70% even in an absorption layer thinner than one micrometer (μm), reducing the thickness of the absorption layer by approximately 70% compared to existing technologies.
A thinner absorption layer simplifies pixel processing, allowing for higher resolution and smoother carrier diffusion, which is advantageous for light carrier acquisition while also reducing the cost. However, a fundamental issue with thinner absorption layers is the reduced absorption of long-wavelength light.
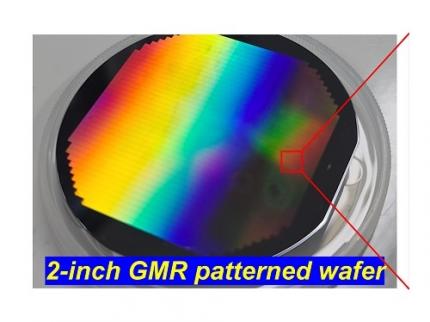
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor integrated on the Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) structure proposed in this study (left), a photograph of the fabricated wafer, and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the periodic patterns (right) >
The research team introduced a guided-mode resonance (GMR) structure* that enables high-efficiency light absorption across a wide spectral range from 400 nanometers (nm) to 1,700 nanometers (nm). This wavelength range includes not only visible light but also light the SWIR region, making it valuable for various industrial applications.
*Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) Structure: A concept used in electromagnetics, a phenomenon in which a specific (light) wave resonates (forming a strong electric/magnetic field) at a specific wavelength. Since energy is maximized under these conditions, it has been used to increase antenna or radar efficiency.
The improved performance in the SWIR region is expected to play a significant role in developing next-generation image sensors with increasingly high resolutions. The GMR structure, in particular, holds potential for further enhancing resolution and other performance metrics through hybrid integration and monolithic 3D integration with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-based readout integrated circuits (ROIC).
< Figure 2. Benchmark for state-of-the-art InGaAs-based SWIR pixels with simulated EQE lines as a function of TAL variation. Performance is maintained while reducing the absorption layer thickness from 2.1 micrometers or more to 1 micrometer or less while reducing it by 50% to 70% >
The research team has significantly enhanced international competitiveness in low-power devices and ultra-high-resolution imaging technology, opening up possibilities for applications in digital cameras, security systems, medical and industrial image sensors, as well as future ultra-high-resolution sensors for autonomous driving, aerospace, and satellite observation.
Professor Sang Hyun Kim, the lead researcher, commented, “This research demonstrates that significantly higher performance than existing technologies can be achieved even with ultra-thin absorption layers.”
< Figure 3. Top optical microscope image and cross-sectional scanning electron microscope image of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor fabricated on the GMR structure (left). Improved quantum efficiency performance of the ultra-thin image sensor (red) fabricated with the technology proposed in this study (right) >
The results of this research were published on 15th of November, in the prestigious international journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6), with Professor Dae-Myung Geum of Inha University (formerly a KAIST postdoctoral researcher) and Dr. Jinha Lim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Yale University) as co-first authors. (Paper title: “Highly-efficient (>70%) and Wide-spectral (400 nm -1700 nm) sub-micron-thick InGaAs photodiodes for future high-resolution image sensors”)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.11.22 View 4045
KAIST Secures Core Technology for Ultra-High-Resolution Image Sensors
A joint research team from Korea and the United States has developed next-generation, high-resolution image sensor technology with higher power efficiency and a smaller size compared to existing sensors. Notably, they have secured foundational technology for ultra-high-resolution shortwave infrared (SWIR) image sensors, an area currently dominated by Sony, paving the way for future market entry.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of November that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Inha University and Yale University in the U.S., has developed an ultra-thin broadband photodiode (PD), marking a significant breakthrough in high-performance image sensor technology.
This research drastically improves the trade-off between the absorption layer thickness and quantum efficiency found in conventional photodiode technology. Specifically, it achieved high quantum efficiency of over 70% even in an absorption layer thinner than one micrometer (μm), reducing the thickness of the absorption layer by approximately 70% compared to existing technologies.
A thinner absorption layer simplifies pixel processing, allowing for higher resolution and smoother carrier diffusion, which is advantageous for light carrier acquisition while also reducing the cost. However, a fundamental issue with thinner absorption layers is the reduced absorption of long-wavelength light.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor integrated on the Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) structure proposed in this study (left), a photograph of the fabricated wafer, and a scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of the periodic patterns (right) >
The research team introduced a guided-mode resonance (GMR) structure* that enables high-efficiency light absorption across a wide spectral range from 400 nanometers (nm) to 1,700 nanometers (nm). This wavelength range includes not only visible light but also light the SWIR region, making it valuable for various industrial applications.
*Guided-Mode Resonance (GMR) Structure: A concept used in electromagnetics, a phenomenon in which a specific (light) wave resonates (forming a strong electric/magnetic field) at a specific wavelength. Since energy is maximized under these conditions, it has been used to increase antenna or radar efficiency.
The improved performance in the SWIR region is expected to play a significant role in developing next-generation image sensors with increasingly high resolutions. The GMR structure, in particular, holds potential for further enhancing resolution and other performance metrics through hybrid integration and monolithic 3D integration with complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS)-based readout integrated circuits (ROIC).
< Figure 2. Benchmark for state-of-the-art InGaAs-based SWIR pixels with simulated EQE lines as a function of TAL variation. Performance is maintained while reducing the absorption layer thickness from 2.1 micrometers or more to 1 micrometer or less while reducing it by 50% to 70% >
The research team has significantly enhanced international competitiveness in low-power devices and ultra-high-resolution imaging technology, opening up possibilities for applications in digital cameras, security systems, medical and industrial image sensors, as well as future ultra-high-resolution sensors for autonomous driving, aerospace, and satellite observation.
Professor Sang Hyun Kim, the lead researcher, commented, “This research demonstrates that significantly higher performance than existing technologies can be achieved even with ultra-thin absorption layers.”
< Figure 3. Top optical microscope image and cross-sectional scanning electron microscope image of the InGaAs photodiode image sensor fabricated on the GMR structure (left). Improved quantum efficiency performance of the ultra-thin image sensor (red) fabricated with the technology proposed in this study (right) >
The results of this research were published on 15th of November, in the prestigious international journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6), with Professor Dae-Myung Geum of Inha University (formerly a KAIST postdoctoral researcher) and Dr. Jinha Lim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Yale University) as co-first authors. (Paper title: “Highly-efficient (>70%) and Wide-spectral (400 nm -1700 nm) sub-micron-thick InGaAs photodiodes for future high-resolution image sensors”)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.11.22 View 4045 -
 KAIST Researchers Introduce New and Improved, Next-Generation Perovskite Solar Cell
- KAIST-Yonsei university researchers developed innovative dipole technology to maximize near-infrared photon harvesting efficiency
- Overcoming the shortcoming of existing perovskite solar cells that cannot utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy
- Development of next-generation solar cell technology with high efficiency and high stability that can absorb near-infrared light beyond the existing visible light range with a perovskite-dipole-organic semiconductor hybrid structure
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jung-Yong Lee, Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee, and Master’s candidate Min Seok Kim of the School of Electrical Engineering >
Existing perovskite solar cells, which have the problem of not being able to utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy, have been developed by a Korean research team as an innovative technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture performance while greatly improving power conversion efficiency. This greatly increases the possibility of commercializing next-generation solar cells and is expected to contribute to important technological advancements in the global solar cell market.
The research team of Professor Jung-Yong Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) and Professor Woojae Kim of the Department of Chemistry at Yonsei University announced on October 31st that they have developed a high-efficiency and high-stability organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell production technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture beyond the existing visible light range.
The research team suggested and advanced a hybrid next-generation device structure with organic photo-semiconductors that complements perovskite materials limited to visible light absorption and expands the absorption range to near-infrared.
In addition, they revealed the electronic structure problem that mainly occurs in the structure and announced a high-performance solar cell device that dramatically solved this problem by introducing a dipole layer*.
*Dipole layer: A thin material layer that controls the energy level within the device to facilitate charge transport and forms an interface potential difference to improve device performance.
Existing lead-based perovskite solar cells have a problem in that their absorption spectrum is limited to the visible light region with a wavelength of 850 nanometers (nm) or less, which prevents them from utilizing approximately 52% of the total solar energy.
To solve this problem, the research team designed a hybrid device that combined an organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) with perovskite and implemented a solar cell that can absorb up to the near-infrared region.
In particular, by introducing a sub-nanometer dipole interface layer, they succeeded in alleviating the energy barrier between the perovskite and the organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), suppressing charge accumulation, maximizing the contribution to the near-infrared, and improving the current density (JSC) to 4.9 mA/cm².
The key achievement of this study is that the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the hybrid device has been significantly increased from 20.4% to 24.0%. In particular, this study achieved a high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) compared to previous studies, reaching 78% in the near-infrared region.
< Figure. The illustration of the mechanism of improving the electronic structure and charge transfer capability through Perovskite/organic hybrid device structure and dipole interfacial layers (DILs). The proposed dipole interfacial layer forms a strong interfacial dipole, effectively reducing the energy barrier between the perovskite and organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), and suppressing hole accumulation. This technology improves near-infrared photon harvesting and charge transfer, and as a result, the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell increases to 24.0%. In addition, it achieves excellent stability by maintaining performance for 1,200 hours even in an extremely humid environment. >
In addition, this device showed high stability, showing excellent results of maintaining more than 80% of the initial efficiency in the maximum output tracking for more than 800 hours even under extreme humidity conditions.
Professor Jung-Yong Lee said, “Through this study, we have effectively solved the charge accumulation and energy band mismatch problems faced by existing perovskite/organic hybrid solar cells, and we will be able to significantly improve the power conversion efficiency while maximizing the near-infrared light capture performance, which will be a new breakthrough that can solve the mechanical-chemical stability problems of existing perovskites and overcome the optical limitations.”
This study, in which KAIST School of Electrical Engineering Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee and Master's candidate Min Seok Kim participated as co-first authors, was published in the September 30th online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials. (Paper title: Suppressing Hole Accumulation Through Sub-Nanometer Dipole Interfaces in Hybrid Perovskite/Organic Solar Cells for Boosting Near-Infrared Photon Harvesting).
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.31 View 5513
KAIST Researchers Introduce New and Improved, Next-Generation Perovskite Solar Cell
- KAIST-Yonsei university researchers developed innovative dipole technology to maximize near-infrared photon harvesting efficiency
- Overcoming the shortcoming of existing perovskite solar cells that cannot utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy
- Development of next-generation solar cell technology with high efficiency and high stability that can absorb near-infrared light beyond the existing visible light range with a perovskite-dipole-organic semiconductor hybrid structure
< Photo. (From left) Professor Jung-Yong Lee, Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee, and Master’s candidate Min Seok Kim of the School of Electrical Engineering >
Existing perovskite solar cells, which have the problem of not being able to utilize approximately 52% of total solar energy, have been developed by a Korean research team as an innovative technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture performance while greatly improving power conversion efficiency. This greatly increases the possibility of commercializing next-generation solar cells and is expected to contribute to important technological advancements in the global solar cell market.
The research team of Professor Jung-Yong Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) and Professor Woojae Kim of the Department of Chemistry at Yonsei University announced on October 31st that they have developed a high-efficiency and high-stability organic-inorganic hybrid solar cell production technology that maximizes near-infrared light capture beyond the existing visible light range.
The research team suggested and advanced a hybrid next-generation device structure with organic photo-semiconductors that complements perovskite materials limited to visible light absorption and expands the absorption range to near-infrared.
In addition, they revealed the electronic structure problem that mainly occurs in the structure and announced a high-performance solar cell device that dramatically solved this problem by introducing a dipole layer*.
*Dipole layer: A thin material layer that controls the energy level within the device to facilitate charge transport and forms an interface potential difference to improve device performance.
Existing lead-based perovskite solar cells have a problem in that their absorption spectrum is limited to the visible light region with a wavelength of 850 nanometers (nm) or less, which prevents them from utilizing approximately 52% of the total solar energy.
To solve this problem, the research team designed a hybrid device that combined an organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ) with perovskite and implemented a solar cell that can absorb up to the near-infrared region.
In particular, by introducing a sub-nanometer dipole interface layer, they succeeded in alleviating the energy barrier between the perovskite and the organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), suppressing charge accumulation, maximizing the contribution to the near-infrared, and improving the current density (JSC) to 4.9 mA/cm².
The key achievement of this study is that the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the hybrid device has been significantly increased from 20.4% to 24.0%. In particular, this study achieved a high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) compared to previous studies, reaching 78% in the near-infrared region.
< Figure. The illustration of the mechanism of improving the electronic structure and charge transfer capability through Perovskite/organic hybrid device structure and dipole interfacial layers (DILs). The proposed dipole interfacial layer forms a strong interfacial dipole, effectively reducing the energy barrier between the perovskite and organic bulk heterojunction (BHJ), and suppressing hole accumulation. This technology improves near-infrared photon harvesting and charge transfer, and as a result, the power conversion efficiency of the solar cell increases to 24.0%. In addition, it achieves excellent stability by maintaining performance for 1,200 hours even in an extremely humid environment. >
In addition, this device showed high stability, showing excellent results of maintaining more than 80% of the initial efficiency in the maximum output tracking for more than 800 hours even under extreme humidity conditions.
Professor Jung-Yong Lee said, “Through this study, we have effectively solved the charge accumulation and energy band mismatch problems faced by existing perovskite/organic hybrid solar cells, and we will be able to significantly improve the power conversion efficiency while maximizing the near-infrared light capture performance, which will be a new breakthrough that can solve the mechanical-chemical stability problems of existing perovskites and overcome the optical limitations.”
This study, in which KAIST School of Electrical Engineering Ph.D. candidate Min-Ho Lee and Master's candidate Min Seok Kim participated as co-first authors, was published in the September 30th online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials. (Paper title: Suppressing Hole Accumulation Through Sub-Nanometer Dipole Interfaces in Hybrid Perovskite/Organic Solar Cells for Boosting Near-Infrared Photon Harvesting).
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.31 View 5513 -
 A KAIST Team Develops Face-Conforming LED Mask Showing 340% Improved Efficacy in Deep Skin Elasticity
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee has developed a deep skin-stimulating LED mask which has been verified in clinical trials to improve dermis elasticity by 340%.
< Figure 1. Overall concept of face-fit surface-lighting micro-LEDs (FSLED) mask. a. Optical image of the FSLED mask showing uniform surface-lighting. schematic illustration of the FSLED mask. The 2D to 3D transformation procedure b. Difference in cosmetic effect on deep skin elasticity, wrinkles, and sagging between FSLED mask and CLED mask. (improvement percentage in eight weeks) >
Conventional LED masks, with their rigid design, fail to conform closely to the skin's contours. This limitation causes substantial light reflection, with up to 90% reflected over a distance of 2 cm, reducing light penetration and limiting stimulation of the deep skin layers essential for effective skin rejuvenation.
To address these challenges, Professor Lee's team developed a face-conforming surface lighting micro-LED (FSLED) mask, which can provide uniform photostimulation to the dermis. The key technology lies in the mask's ability to deliver uniform light to deep skin tissues while maintaining a conformal skin attachment. This is achieved through a 3D origami structure, integrated with 3,770 micro-LEDs and flexible surface light-diffusion layer, minimizing the gaps between the light source and the skin.
In clinical trials involving 33 participants, the FSLED mask demonstrated a 340% improvement in deep skin elasticity compared to conventional LED masks, proving its efficacy in significantly reducing skin wrinkles, sagging and aging.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The FSLED mask provides cosmetic benefits to the entire facial dermis without the side effects of low-temperature burns, making home-care anti-aging treatment that enhances the quality of human life possible. The product is being manufactured by Fronics, KAIST startup company, and will be distributed globally through Amorepacific's network, with sales starting in November.”
This result titled “Clinical Validation of Face-fit Surface-lighting Micro Light-emitting Diode Mask for Skin Anti-aging Treatment”, in which Min Seo Kim, a student of the Master-Doctorate integrated program, and Jaehun An, a Ph.D. candidate, in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering of KAIST, took part as co-first authors, was published in Advanced Materials on October 22nd, 2024 (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202411651).
Introductory Video: Face-conforming surface LED mask for skin anti-aging ( https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kSccLwx8N_w )
2024.10.29 View 5778
A KAIST Team Develops Face-Conforming LED Mask Showing 340% Improved Efficacy in Deep Skin Elasticity
- A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee has developed a deep skin-stimulating LED mask which has been verified in clinical trials to improve dermis elasticity by 340%.
< Figure 1. Overall concept of face-fit surface-lighting micro-LEDs (FSLED) mask. a. Optical image of the FSLED mask showing uniform surface-lighting. schematic illustration of the FSLED mask. The 2D to 3D transformation procedure b. Difference in cosmetic effect on deep skin elasticity, wrinkles, and sagging between FSLED mask and CLED mask. (improvement percentage in eight weeks) >
Conventional LED masks, with their rigid design, fail to conform closely to the skin's contours. This limitation causes substantial light reflection, with up to 90% reflected over a distance of 2 cm, reducing light penetration and limiting stimulation of the deep skin layers essential for effective skin rejuvenation.
To address these challenges, Professor Lee's team developed a face-conforming surface lighting micro-LED (FSLED) mask, which can provide uniform photostimulation to the dermis. The key technology lies in the mask's ability to deliver uniform light to deep skin tissues while maintaining a conformal skin attachment. This is achieved through a 3D origami structure, integrated with 3,770 micro-LEDs and flexible surface light-diffusion layer, minimizing the gaps between the light source and the skin.
In clinical trials involving 33 participants, the FSLED mask demonstrated a 340% improvement in deep skin elasticity compared to conventional LED masks, proving its efficacy in significantly reducing skin wrinkles, sagging and aging.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said, “The FSLED mask provides cosmetic benefits to the entire facial dermis without the side effects of low-temperature burns, making home-care anti-aging treatment that enhances the quality of human life possible. The product is being manufactured by Fronics, KAIST startup company, and will be distributed globally through Amorepacific's network, with sales starting in November.”
This result titled “Clinical Validation of Face-fit Surface-lighting Micro Light-emitting Diode Mask for Skin Anti-aging Treatment”, in which Min Seo Kim, a student of the Master-Doctorate integrated program, and Jaehun An, a Ph.D. candidate, in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering of KAIST, took part as co-first authors, was published in Advanced Materials on October 22nd, 2024 (DOI: 10.1002/adma.202411651).
Introductory Video: Face-conforming surface LED mask for skin anti-aging ( https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kSccLwx8N_w )
2024.10.29 View 5778 -
 KAIST Introduces a Wearable Robot that Walks and Puts itself on to Disabled Persons
< Photo 1. WalkON Suit F1 - walking demonstration >
KAIST researchers have unveiled a new wearable robot developed for completely paralyzed persons that can walk to them so that the user can wear it right out of their wheelchairs without the help from others. Also, it was announced that Professor Kyoungchul Kong's team from KAIST will be participating in the wearable robot category of the 3rd Cybathlon, which is being held four years after the team’s gold medal win in 2020.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced this new version of the wearable robot for paraplegic people, WalkON Suit F1, by Professor Kyoungchul Kong (CEO and founder of Angel Robotics) of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering on the 24th of October.
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Kyoungchul Kong of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Researcher Seunghwan Kim (the competing athlete), and PhD candidate Jeongsu Park (the leader of Team KAIST) >
WalkON Suit is a wearable robot for people suffering with paraplegic disabilities that the research team has been continuously researching since 2015. This robot targets to assist persons with American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) Impairment Scale – A (complete paralysis) grade injury, the most severe level of paraplegia. Therefore, its development purpose is different from that of other rehabilitation therapy and muscle strength assisting robots currently being supplied nationally by Angel Robotics.
Professor Kong's research team first announced WalkON Suit 1 in 2016, and then introduced WalkON Suit 4 in 2020, increasing the walking speed to 3.2 km/h, achieving the normal walking speed of people with no disabilities. In addition, it demonstrated the ability to pass through obstacles such as narrow passages, doors, and stairs that can be encountered in daily life.
However, it had the same fundamental problem all wearable robots have, which is that they require the help of others to wear the robot. While you can walk without help from others once you are wearing the robot, you needed someone's help to put it on to begin with.
The newly released WalkON Suit F1 presented a technical solution to this fundamental problem. It applied a frontal-docking method instead of a rear-sitting method so that you can wear the robot right away without getting out of the wheelchair and into the robot, which would require help from others mid-transition.
< Photo 3. WalkON Suit F1 - suiting-up demonstration >
In addition, before wearing the robot, it can walk on its own like a humanoid robot and approaches the user. It is also implemented a function that actively controls the center of its weight against the pull of gravity so that it maintains balance without falling over even if the user pushes the robot otherwise. The outer design of the WalkON Suit F1, which crosses between a humanoid and a wearable robot, was done by Professor Hyunjoon Park of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST.
The original function of the wearable robot has also been greatly improved. The performance of the balance control was improved to allow the free use of both hands in upright state, as well as the freedom to take several steps without a cane.
Technological advancements at the components level are also noteworthy. Through close collaboration with Angel Robotics, all core components of the robot, such as the motor, reducer, motor driver, and main circuit, have been domestically produced. The output density of the motor and reducer modules has been improved by about two folds (based on power per weight) compared to the research team's existing technology, and the control performance of the motor driver has been improved by about three times (based on frequency response speed) compared to the best overseas technology.
In particular, the embedded software technology of the motor driver has been significantly improved so that advanced motion control algorithms can be stably implemented without using expensive higher-level controllers. In addition, visual recognition system for obstacle detection and an AI board for neural network application have been installed.
< Figure 1. WalkON Suit F1 shape and main specifications >
Professor Kong explained, “WalkON Suit is the culmination of wearable robot technology for the disabled,” and added, “The numerous components, control, and module technologies derived from WalkON Suit are setting the standard for the entire wearable robot industry.”
Professor Kong’s research team revealed WalkON Suit F1 and announced that they will be participating in the 3rd Cybathlon, which is being held after four years since the last event. In this competition, which will be held on October 27, Professor Kong’s lab, the Exo Lab will be participating with Jeongsu Park, a Ph.D. Student, as the leader and Seunghwan Kim, the lab’s staff researcher with complete paralysis, as the competing athlete.
The difficulty of the missions in this competition has been significantly increased compared to the previous competition, and the number of missions has increased from six to ten. Some missions have been criticized for being overly challenging, going beyond the level that can be encountered in everyday life.
< Photo 4. Cybathlon stadium (Angel Robotics Asia Hub) >
Regarding this, the team leader Jeongsu Park expressed his ambition, saying, “Since we already won first place in the previous competition, our goal in this competition is to show the technological gap rather than competing for rankings.”
The Cybathlon is a cyborg Olympics held every four years in Switzerland. This competition will be held in a hybrid format, with some participants taking part in Switzerland while others broadcasting live from stadiums in their own country on October 27. Professor Kong's research team will be participating via live broadcast from the competition facilities installed in Angel Robotics' Advanced Research Institute (Planet Daejeon).
< Photo 5. Photo of Team KAIST participating in Cybathlon 2024 >
The demonstration video of WalkON Suit F1 can be viewed through the link below.
Link: https://www.youtube.com/@KyoungchulKong_EXO-Lab
2024.10.24 View 10863
KAIST Introduces a Wearable Robot that Walks and Puts itself on to Disabled Persons
< Photo 1. WalkON Suit F1 - walking demonstration >
KAIST researchers have unveiled a new wearable robot developed for completely paralyzed persons that can walk to them so that the user can wear it right out of their wheelchairs without the help from others. Also, it was announced that Professor Kyoungchul Kong's team from KAIST will be participating in the wearable robot category of the 3rd Cybathlon, which is being held four years after the team’s gold medal win in 2020.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced this new version of the wearable robot for paraplegic people, WalkON Suit F1, by Professor Kyoungchul Kong (CEO and founder of Angel Robotics) of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering on the 24th of October.
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Kyoungchul Kong of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Researcher Seunghwan Kim (the competing athlete), and PhD candidate Jeongsu Park (the leader of Team KAIST) >
WalkON Suit is a wearable robot for people suffering with paraplegic disabilities that the research team has been continuously researching since 2015. This robot targets to assist persons with American Spinal Injury Association (ASIA) Impairment Scale – A (complete paralysis) grade injury, the most severe level of paraplegia. Therefore, its development purpose is different from that of other rehabilitation therapy and muscle strength assisting robots currently being supplied nationally by Angel Robotics.
Professor Kong's research team first announced WalkON Suit 1 in 2016, and then introduced WalkON Suit 4 in 2020, increasing the walking speed to 3.2 km/h, achieving the normal walking speed of people with no disabilities. In addition, it demonstrated the ability to pass through obstacles such as narrow passages, doors, and stairs that can be encountered in daily life.
However, it had the same fundamental problem all wearable robots have, which is that they require the help of others to wear the robot. While you can walk without help from others once you are wearing the robot, you needed someone's help to put it on to begin with.
The newly released WalkON Suit F1 presented a technical solution to this fundamental problem. It applied a frontal-docking method instead of a rear-sitting method so that you can wear the robot right away without getting out of the wheelchair and into the robot, which would require help from others mid-transition.
< Photo 3. WalkON Suit F1 - suiting-up demonstration >
In addition, before wearing the robot, it can walk on its own like a humanoid robot and approaches the user. It is also implemented a function that actively controls the center of its weight against the pull of gravity so that it maintains balance without falling over even if the user pushes the robot otherwise. The outer design of the WalkON Suit F1, which crosses between a humanoid and a wearable robot, was done by Professor Hyunjoon Park of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST.
The original function of the wearable robot has also been greatly improved. The performance of the balance control was improved to allow the free use of both hands in upright state, as well as the freedom to take several steps without a cane.
Technological advancements at the components level are also noteworthy. Through close collaboration with Angel Robotics, all core components of the robot, such as the motor, reducer, motor driver, and main circuit, have been domestically produced. The output density of the motor and reducer modules has been improved by about two folds (based on power per weight) compared to the research team's existing technology, and the control performance of the motor driver has been improved by about three times (based on frequency response speed) compared to the best overseas technology.
In particular, the embedded software technology of the motor driver has been significantly improved so that advanced motion control algorithms can be stably implemented without using expensive higher-level controllers. In addition, visual recognition system for obstacle detection and an AI board for neural network application have been installed.
< Figure 1. WalkON Suit F1 shape and main specifications >
Professor Kong explained, “WalkON Suit is the culmination of wearable robot technology for the disabled,” and added, “The numerous components, control, and module technologies derived from WalkON Suit are setting the standard for the entire wearable robot industry.”
Professor Kong’s research team revealed WalkON Suit F1 and announced that they will be participating in the 3rd Cybathlon, which is being held after four years since the last event. In this competition, which will be held on October 27, Professor Kong’s lab, the Exo Lab will be participating with Jeongsu Park, a Ph.D. Student, as the leader and Seunghwan Kim, the lab’s staff researcher with complete paralysis, as the competing athlete.
The difficulty of the missions in this competition has been significantly increased compared to the previous competition, and the number of missions has increased from six to ten. Some missions have been criticized for being overly challenging, going beyond the level that can be encountered in everyday life.
< Photo 4. Cybathlon stadium (Angel Robotics Asia Hub) >
Regarding this, the team leader Jeongsu Park expressed his ambition, saying, “Since we already won first place in the previous competition, our goal in this competition is to show the technological gap rather than competing for rankings.”
The Cybathlon is a cyborg Olympics held every four years in Switzerland. This competition will be held in a hybrid format, with some participants taking part in Switzerland while others broadcasting live from stadiums in their own country on October 27. Professor Kong's research team will be participating via live broadcast from the competition facilities installed in Angel Robotics' Advanced Research Institute (Planet Daejeon).
< Photo 5. Photo of Team KAIST participating in Cybathlon 2024 >
The demonstration video of WalkON Suit F1 can be viewed through the link below.
Link: https://www.youtube.com/@KyoungchulKong_EXO-Lab
2024.10.24 View 10863 -
 KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 4593
KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 4593 -
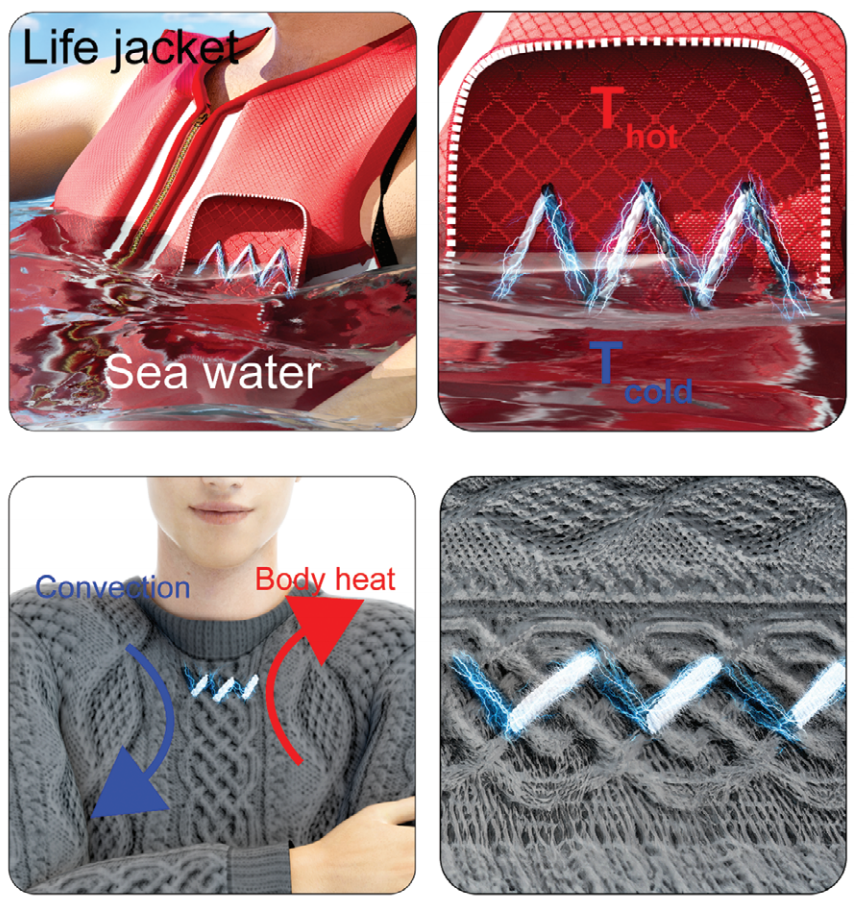 KAIST Develops Thread-like, Flexible Thermoelectric Materials Applicable in Extreme Environments
A team of Korean researchers developed a thermoelectric material that can be used in wearable devices, such as smart clothing, and while maintaining stable thermal energy performance even in extreme environments. It has dramatically resolved the dilemma of striking the balance between achieving good performance and the mechanical flexibility of thermoelectric materials, which has been a long-standing challenge in the field of thermoelectric materials, and has also proven the possibility of commercialization.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 21st that a joint research team of Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with the research teams of Professor Min-Wook Oh of Hanbat National University (President Yong Jun Oh) and Dr. Jun-Ho Jeong of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seoghyun Ryu), have successfully developed ‘bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) thermoelectric fibers,’ an innovative energy harvesting solution for next-generation flexible electronic devices.
Thermoelectric materials are materials that generate voltage when there is a temperature difference and convert thermal energy into electrical energy. Currently, about 70% of energy being lost as wasted heat, so due attention is being given to research on these as sustainable energy materials that can recover and harvesting energy from this waste heat.
Most of the heat sources around us are curved, such as the human body, vehicle exhaust pipes, and cooling fins. Inorganic thermoelectric materials based on ceramic materials boast high thermoelectric performance, but they are fragile and difficult to produce in curved shapes. On the other hand, flexible thermoelectric materials using existing polymer binders can be applied to surfaces of various shapes, but their performance was limited due to the low electrical conductivity and high thermal resistance of the polymer.
Existing flexible thermoelectric materials contain polymer additives, but the inorganic thermoelectric material developed by the research team is not flexible, so they overcame these limitations by twisting nano ribbons instead of additives to produce a thread-shaped thermoelectric material. Inspired by the flexibility of inorganic nano ribbons, the research team used a nanomold-based electron beam deposition technique to continuously deposit nano ribbons and then twisted them into a thread shape to create bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) inorganic thermoelectric fibers.
These inorganic thermoelectric fibers have higher bending strength than existing thermoelectric materials, and showed almost no change in electrical properties even after repeated bending and tensile tests of more than 1,000 times. The thermoelectric device created by the research team generates electricity using temperature differences, and if clothes are made with fiber-type thermoelectric devices, electricity can be generated from body temperature to operate other electronic devices.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram and actual image of the all-inorganic flexible thermoelectric yarn made without polymer additives >
In fact, the possibility of commercialization was proven through a demonstration of collecting energy by embedding thermoelectric fibers in life jackets or clothing. In addition, it opened up the possibility of building a high-efficiency energy harvesting system that recycles waste heat by utilizing the temperature difference between the hot fluid inside a pipe and the cold air outside in industrial settings.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung said, "The inorganic flexible thermoelectric material developed in this study can be used in wearable devices such as smart clothing, and it can maintain stable performance even in extreme environments, so it has a high possibility of being commercialized through additional research in the future." Professor Inkyu Park also emphasized, "This technology will become the core of next-generation energy harvesting technology, and it is expected to play an important role in various fields from waste heat utilization in industrial sites to personal wearable self-power generation devices."
This study, in which Hanhwi Jang, a Ph.D. student at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Junseong Ahn of Korea University, Sejong Campus, and Dr. Yongrok Jeong of Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute contributed equally as joint first authors, was published in the online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials on September 17, and was selected as the back-cover paper in recognition of its excellence. (Paper title: Flexible All-Inorganic Thermoelectric Yarns)
Meanwhile, this study was conducted through the Mid-career Researcher Support Program and the Future Materials Discovery Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the support from the Global Bio-Integrated Materials Center, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning (KEIT) upon the support by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.10.21 View 3652
KAIST Develops Thread-like, Flexible Thermoelectric Materials Applicable in Extreme Environments
A team of Korean researchers developed a thermoelectric material that can be used in wearable devices, such as smart clothing, and while maintaining stable thermal energy performance even in extreme environments. It has dramatically resolved the dilemma of striking the balance between achieving good performance and the mechanical flexibility of thermoelectric materials, which has been a long-standing challenge in the field of thermoelectric materials, and has also proven the possibility of commercialization.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 21st that a joint research team of Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with the research teams of Professor Min-Wook Oh of Hanbat National University (President Yong Jun Oh) and Dr. Jun-Ho Jeong of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seoghyun Ryu), have successfully developed ‘bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) thermoelectric fibers,’ an innovative energy harvesting solution for next-generation flexible electronic devices.
Thermoelectric materials are materials that generate voltage when there is a temperature difference and convert thermal energy into electrical energy. Currently, about 70% of energy being lost as wasted heat, so due attention is being given to research on these as sustainable energy materials that can recover and harvesting energy from this waste heat.
Most of the heat sources around us are curved, such as the human body, vehicle exhaust pipes, and cooling fins. Inorganic thermoelectric materials based on ceramic materials boast high thermoelectric performance, but they are fragile and difficult to produce in curved shapes. On the other hand, flexible thermoelectric materials using existing polymer binders can be applied to surfaces of various shapes, but their performance was limited due to the low electrical conductivity and high thermal resistance of the polymer.
Existing flexible thermoelectric materials contain polymer additives, but the inorganic thermoelectric material developed by the research team is not flexible, so they overcame these limitations by twisting nano ribbons instead of additives to produce a thread-shaped thermoelectric material. Inspired by the flexibility of inorganic nano ribbons, the research team used a nanomold-based electron beam deposition technique to continuously deposit nano ribbons and then twisted them into a thread shape to create bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) inorganic thermoelectric fibers.
These inorganic thermoelectric fibers have higher bending strength than existing thermoelectric materials, and showed almost no change in electrical properties even after repeated bending and tensile tests of more than 1,000 times. The thermoelectric device created by the research team generates electricity using temperature differences, and if clothes are made with fiber-type thermoelectric devices, electricity can be generated from body temperature to operate other electronic devices.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram and actual image of the all-inorganic flexible thermoelectric yarn made without polymer additives >
In fact, the possibility of commercialization was proven through a demonstration of collecting energy by embedding thermoelectric fibers in life jackets or clothing. In addition, it opened up the possibility of building a high-efficiency energy harvesting system that recycles waste heat by utilizing the temperature difference between the hot fluid inside a pipe and the cold air outside in industrial settings.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung said, "The inorganic flexible thermoelectric material developed in this study can be used in wearable devices such as smart clothing, and it can maintain stable performance even in extreme environments, so it has a high possibility of being commercialized through additional research in the future." Professor Inkyu Park also emphasized, "This technology will become the core of next-generation energy harvesting technology, and it is expected to play an important role in various fields from waste heat utilization in industrial sites to personal wearable self-power generation devices."
This study, in which Hanhwi Jang, a Ph.D. student at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Junseong Ahn of Korea University, Sejong Campus, and Dr. Yongrok Jeong of Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute contributed equally as joint first authors, was published in the online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials on September 17, and was selected as the back-cover paper in recognition of its excellence. (Paper title: Flexible All-Inorganic Thermoelectric Yarns)
Meanwhile, this study was conducted through the Mid-career Researcher Support Program and the Future Materials Discovery Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the support from the Global Bio-Integrated Materials Center, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning (KEIT) upon the support by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.10.21 View 3652 -
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 4942
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 4942 -
 KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 3223
KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 3223 -
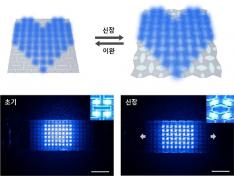 KAIST Develops Stretchable Displays Featuring 25% Expansion Without Image Distortion
Stretchable displays, praised for their spatial efficiency, design flexibility, and human-like flexibility, are seen as the next generation of display technology. A team of Korean researchers has developed a stretchable display that can expand by 25% while maintaining clear image quality without distortion. It can also stretch and contract up to 5,000 times at 15% expansion without any performance degradation, making it the first deformation-free stretchable display with a negative Poisson's ratio* developed in Korea.
*Poisson’s ratio of -1: A ratio where both width and length stretch equally, expressed as a negative value. A positive Poisson's ratio represents the ratio where horizontal stretching leads to vertical contraction, which is the case for most materials.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of August that a research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (Director of the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center) , in collaboration with the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials (President Seoghyeon Ryu), successfully developed a stretchable display substrate that suppresses image distortion through omnidirectional stretchability.
Currently, most stretchable displays are made with highly elastic elastomer* materials, but these materials possess a positive Poisson's ratio, causing unavoidable image distortion when the display is stretched.
*Elastomer: A polymer with elasticity similar to rubber.
To address this, the introduction of auxetic* meta-structures has been gaining attention. Unlike conventional materials, auxetic structures have a unique 'negative Poisson's ratio,' expanding in all directions when stretched in just one direction. However, traditional auxetic structures contain many empty spaces, limiting their stability and usability in display substrates.
*Auxetic structure: A special geometric structure that exhibits a negative Poisson's ratio.
To tackle the issue of image distortion, Professor Bae's research team developed a method to create a seamless surface for the auxetic meta-structure, achieving the ideal negative Poisson's ratio of -1 and overcoming the biggest challenge in auxetic meta-structures.
To overcome the second issue of elastic modulus*, the team inserted a textile made of glass fiber bundles with a diameter of just 25 micrometers (a quarter of the thickness of human hair) into the elastomer material. They then filled the empty spaces with the same elastomer, creating a flat and stable integrated film without gaps.
*Elastic Modulus: The ratio that indicates the extent of deformation when force is applied to a material. A higher elastic modulus means that the material is less likely to deform under force.
The research team theoretically identified that the difference in elasticity between the auxetic structure and the elastomer material directly influences the negative Poisson's ratio and successfully achieved an elasticity difference of over 230,000 times, producing a film with a Poisson's ratio of -1, the theoretical limit.
< Figure 2. Deformation of S-AUX film. a) Configurations and visualized principal strain distribution of the optimized S-AUX film at various strain rates. b) Biaxial stretching image. While pristine elastomer shrinks in the directions that were not stretched, S-AUX film developed in this study expands in all directions simultaneously while maintaining its original shape. >
Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, who led the study, explained, "Preventing image distortion using auxetic structures in stretchable displays is a core technology, but it has faced challenges due to the many empty spaces in the surface, making it difficult to use as a substrate. This research outcome is expected to significantly accelerate commercialization through high-resolution, distortion-free stretchable display applications that utilize the entire surface."
This study, co-authored by Dr. Yung Lee from KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Dr. Bongkyun Jang from the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, was published on August 20th in the international journal Nature Communications under the title "A seamless auxetic substrate with a negative Poisson's ratio of –1".
The research was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center at KAIST, the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, and LG Display.
< Figure 3. Structural configuration of the distortion-free display components on the S-AUX film and a contour image of a micro-LED chip transferred onto the S-AUX film. >
< Figure 4. Schematic illustrations and photographic images of the S-AUX film-based image: distortion-free display in its stretched state and released state. >
2024.09.20 View 4863
KAIST Develops Stretchable Displays Featuring 25% Expansion Without Image Distortion
Stretchable displays, praised for their spatial efficiency, design flexibility, and human-like flexibility, are seen as the next generation of display technology. A team of Korean researchers has developed a stretchable display that can expand by 25% while maintaining clear image quality without distortion. It can also stretch and contract up to 5,000 times at 15% expansion without any performance degradation, making it the first deformation-free stretchable display with a negative Poisson's ratio* developed in Korea.
*Poisson’s ratio of -1: A ratio where both width and length stretch equally, expressed as a negative value. A positive Poisson's ratio represents the ratio where horizontal stretching leads to vertical contraction, which is the case for most materials.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of August that a research team led by Professor Byeong-Soo Bae of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering (Director of the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center) , in collaboration with the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials (President Seoghyeon Ryu), successfully developed a stretchable display substrate that suppresses image distortion through omnidirectional stretchability.
Currently, most stretchable displays are made with highly elastic elastomer* materials, but these materials possess a positive Poisson's ratio, causing unavoidable image distortion when the display is stretched.
*Elastomer: A polymer with elasticity similar to rubber.
To address this, the introduction of auxetic* meta-structures has been gaining attention. Unlike conventional materials, auxetic structures have a unique 'negative Poisson's ratio,' expanding in all directions when stretched in just one direction. However, traditional auxetic structures contain many empty spaces, limiting their stability and usability in display substrates.
*Auxetic structure: A special geometric structure that exhibits a negative Poisson's ratio.
To tackle the issue of image distortion, Professor Bae's research team developed a method to create a seamless surface for the auxetic meta-structure, achieving the ideal negative Poisson's ratio of -1 and overcoming the biggest challenge in auxetic meta-structures.
To overcome the second issue of elastic modulus*, the team inserted a textile made of glass fiber bundles with a diameter of just 25 micrometers (a quarter of the thickness of human hair) into the elastomer material. They then filled the empty spaces with the same elastomer, creating a flat and stable integrated film without gaps.
*Elastic Modulus: The ratio that indicates the extent of deformation when force is applied to a material. A higher elastic modulus means that the material is less likely to deform under force.
The research team theoretically identified that the difference in elasticity between the auxetic structure and the elastomer material directly influences the negative Poisson's ratio and successfully achieved an elasticity difference of over 230,000 times, producing a film with a Poisson's ratio of -1, the theoretical limit.
< Figure 2. Deformation of S-AUX film. a) Configurations and visualized principal strain distribution of the optimized S-AUX film at various strain rates. b) Biaxial stretching image. While pristine elastomer shrinks in the directions that were not stretched, S-AUX film developed in this study expands in all directions simultaneously while maintaining its original shape. >
Professor Byeong-Soo Bae, who led the study, explained, "Preventing image distortion using auxetic structures in stretchable displays is a core technology, but it has faced challenges due to the many empty spaces in the surface, making it difficult to use as a substrate. This research outcome is expected to significantly accelerate commercialization through high-resolution, distortion-free stretchable display applications that utilize the entire surface."
This study, co-authored by Dr. Yung Lee from KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Dr. Bongkyun Jang from the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, was published on August 20th in the international journal Nature Communications under the title "A seamless auxetic substrate with a negative Poisson's ratio of –1".
The research was supported by the Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center at KAIST, the Korea Institute of Machinery & Materials, and LG Display.
< Figure 3. Structural configuration of the distortion-free display components on the S-AUX film and a contour image of a micro-LED chip transferred onto the S-AUX film. >
< Figure 4. Schematic illustrations and photographic images of the S-AUX film-based image: distortion-free display in its stretched state and released state. >
2024.09.20 View 4863 -
 KAIST finds ways for Bacteria to produce PET-like materials
Among various eco-friendly polymers, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) stand out for their excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility. They decompose naturally in soil and marine environments and are used in applications such as food packaging and medical products. However, natural PHA produced to date has faced challenges meeting various physical property requirements, such as durability and thermal stability, and has been limited in its commercial application due to low production concentrations. In light of this, KAIST researchers have recently developed a technology that could play a crucial role in solving the environmental pollution problem caused by plastics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on August 26th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, including Dr. Youngjoon Lee and master's student Minju Kang, has successfully developed a microbial strain that efficiently produces aromatic polyester* using systems metabolic engineering.
※ Aromatic polyester: A polymer containing aromatic compounds (specific carbon ring structures like benzene) and ester bonds.
In this study, the research team used metabolic engineering to enhance the metabolic flux of the biosynthetic pathway for the aromatic monomer phenyllactate (PhLA) in E. coli. They manipulated the metabolic pathway to increase the polymer fraction accumulated within the cells and employed computer simulations to predict the structure of PHA synthase and improve the enzyme based on the structure-function relationship.
Through subsequent fermentation optimization, the team achieved the world’s highest concentration (12.3±0.1 g/L) for the efficient production of poly (PhLA) and successfully produced polyester through a 30L scale fed-batch fermentation, demonstrating the possibility of industrial-level production. The produced aromatic polyesters showed enhanced thermal properties, improved mechanical properties, and potential for use as drug delivery carriers.
< Figure 1. Development schematics of aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research team also demonstrated that an exogenous phasin protein* plays a crucial role in increasing the intracellular polymer accumulation fraction, which is directly related to the economic feasibility and efficiency of non-natural PHA production. They improved PHA synthase using a rational enzyme design approach, predicting the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme through homology modeling (a method of predicting the three-dimensional structure of a new protein based on the structure of similar proteins) followed by molecular docking simulations (simulations that predict how well a monomer can bind to an enzyme) and molecular dynamics simulations (simulations that predict how molecules move and interact over time) to upgrade the enzyme into a mutant enzyme with enhanced monomer polymerization efficiency.
※ Exogenous phasin protein: Phasin is a protein related to PHA production, interacting with the cytoplasmic environment on the surface of granules of PHA, and playing a role in polymer accumulation and controlling the number and size of granules. In this study, genes encoding phasin proteins derived from various natural PHA-producing microorganisms were selected and introduced.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, co-first author of the paper, explained, "The significance of this study lies in the fact that we have achieved the world's highest concentration of microbial-based aromatic polyester production using eco-friendly materials and methods. This technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing the environmental pollution caused by plastics." Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee added, "This study, which presents various strategies for the high-efficiency production of useful polymers via systems metabolic engineering, is expected to make a significant contribution to solving climate change issues, particularly the recent plastic problem."
< Figure 2. Detailed development strategy for aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research findings were published on August 21st in Trends in Biotechnology, published by Cell, an international academic journal.
※ Paper Title: “Microbial production of an aromatic homopolyester”
※ Author Information: Youngjoon Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Minju Kang (KAIST, co-first author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, second author), So Young Choi (KAIST, third author), Jung Eun Yang (KAIST, fourth author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), totaling six authors.
This research was supported by the "Development of Next-Generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading the Bio-based Chemicals Industry" project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST, under the eco-friendly chemical technology development project aimed at substituting petroleum, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. It was also supported by the "Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic Using Microbial Cell Factories" project (Project Leader: Si Jae Park, Ewha Woman’s University).
2024.08.28 View 5479
KAIST finds ways for Bacteria to produce PET-like materials
Among various eco-friendly polymers, polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) stand out for their excellent biodegradability and biocompatibility. They decompose naturally in soil and marine environments and are used in applications such as food packaging and medical products. However, natural PHA produced to date has faced challenges meeting various physical property requirements, such as durability and thermal stability, and has been limited in its commercial application due to low production concentrations. In light of this, KAIST researchers have recently developed a technology that could play a crucial role in solving the environmental pollution problem caused by plastics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on August 26th that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, including Dr. Youngjoon Lee and master's student Minju Kang, has successfully developed a microbial strain that efficiently produces aromatic polyester* using systems metabolic engineering.
※ Aromatic polyester: A polymer containing aromatic compounds (specific carbon ring structures like benzene) and ester bonds.
In this study, the research team used metabolic engineering to enhance the metabolic flux of the biosynthetic pathway for the aromatic monomer phenyllactate (PhLA) in E. coli. They manipulated the metabolic pathway to increase the polymer fraction accumulated within the cells and employed computer simulations to predict the structure of PHA synthase and improve the enzyme based on the structure-function relationship.
Through subsequent fermentation optimization, the team achieved the world’s highest concentration (12.3±0.1 g/L) for the efficient production of poly (PhLA) and successfully produced polyester through a 30L scale fed-batch fermentation, demonstrating the possibility of industrial-level production. The produced aromatic polyesters showed enhanced thermal properties, improved mechanical properties, and potential for use as drug delivery carriers.
< Figure 1. Development schematics of aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research team also demonstrated that an exogenous phasin protein* plays a crucial role in increasing the intracellular polymer accumulation fraction, which is directly related to the economic feasibility and efficiency of non-natural PHA production. They improved PHA synthase using a rational enzyme design approach, predicting the three-dimensional structure of the enzyme through homology modeling (a method of predicting the three-dimensional structure of a new protein based on the structure of similar proteins) followed by molecular docking simulations (simulations that predict how well a monomer can bind to an enzyme) and molecular dynamics simulations (simulations that predict how molecules move and interact over time) to upgrade the enzyme into a mutant enzyme with enhanced monomer polymerization efficiency.
※ Exogenous phasin protein: Phasin is a protein related to PHA production, interacting with the cytoplasmic environment on the surface of granules of PHA, and playing a role in polymer accumulation and controlling the number and size of granules. In this study, genes encoding phasin proteins derived from various natural PHA-producing microorganisms were selected and introduced.
Dr. Youngjoon Lee, co-first author of the paper, explained, "The significance of this study lies in the fact that we have achieved the world's highest concentration of microbial-based aromatic polyester production using eco-friendly materials and methods. This technology is expected to play a crucial role in addressing the environmental pollution caused by plastics." Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee added, "This study, which presents various strategies for the high-efficiency production of useful polymers via systems metabolic engineering, is expected to make a significant contribution to solving climate change issues, particularly the recent plastic problem."
< Figure 2. Detailed development strategy for aromatic polyester producing microorganisms >
The research findings were published on August 21st in Trends in Biotechnology, published by Cell, an international academic journal.
※ Paper Title: “Microbial production of an aromatic homopolyester”
※ Author Information: Youngjoon Lee (KAIST, co-first author), Minju Kang (KAIST, co-first author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, second author), So Young Choi (KAIST, third author), Jung Eun Yang (KAIST, fourth author), Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author), totaling six authors.
This research was supported by the "Development of Next-Generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading the Bio-based Chemicals Industry" project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST, under the eco-friendly chemical technology development project aimed at substituting petroleum, funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT. It was also supported by the "Development of Platform Technology for the Production of Novel Aromatic Bioplastic Using Microbial Cell Factories" project (Project Leader: Si Jae Park, Ewha Woman’s University).
2024.08.28 View 5479 -
 The 3rd Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS 2024) Successfully Completed in Silicon Valley
The 2024 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2024 KAIST GESS), hosted by the Office of Global Initiatives under the KAIST International Office (Director Man-Sung Yim), was held for the third time. This program allows students to visit Silicon Valley, a global startup hub, to directly experience its famous startup ecosystem and develop their capabilities for global expansion. A total of 20 students were selected through applications, interviews, final presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations. Additionally, 17 students from the KAIST Impact MBA course at the KAIST Business School also participated.
Before starting the Silicon Valley program, participants received mentoring on business model development and pitching advice from a senior entrepreneur at KAIST for about two months, beginning last May. Afterward, they developed business items for each team at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon. For seven days, starting from June 23rd, workshops were held under the themes of global entrepreneurship, learning through failure, capital and network, and startup culture at KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center, JP Morgan, and Plug and Play Tech Center. This program's lecture series provided prospective entrepreneurs with the opportunity to systematically learn the mindset and gain the experience needed to start a global business.
The participants also visited local companies and gained experience in the field of global technology startups. Visits included Bear Robotics (CEO John Ha), Soundable Health (CEO Cathering Song), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Phantom AI (CEO Hyunggi Cho), B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), and Simple Steps (CEO Doyeon Kim). Lectures contained vivid experiences from Silicon Valley CEOs and company tours boosted the students' passion for entrepreneurship. In particular, Doyeon Kim, CEO of Simple Steps, which helps prevent career breaks for Korean female immigrants in Silicon Valley and allows talented female immigrants to demonstrate their abilities in society, said, “As a KAIST alumna entrepreneur, it was meaningful to share my experience with this generation of students who dream of starting a global business and creating social enterprises in the United States.”
This program also included a tour of Silicon Valley's big tech companies that have made a significant impact on the digital ecosystem through technological advancement and innovation. This included Broadcom, which maintains a strong global presence in the semiconductor and infrastructure software technology fields. At the invitation of Chairman Hock Tan, GESS participants had the opportunity to attend his lecture and ask questions. Chairman Tan, who received an honorary doctorate in engineering from KAIST last February, emphasized that experiencing failure and giving consistent effort over a long period of time are more important than anything else in order to grow as a global entrepreneur, and that technologies influencing the global market evolve over generations.
< Photo. Group photo of GESS 2024 participants at Broadcom with Chairman Hock Tan (center) ⓒBroadcom>
As part of this program, participants conducted a volunteer program called 'Let's play with AI+ Tech' with the Sunnyvale community in Silicon Valley and Foothill College to help grow together with the community. Through this program, GESS participants cultivated the virtues of a global leader. In this volunteer activity, low-income elementary school students and parents from the Sunnyvale community participated in chatbot training led by KAIST students, providing an opportunity to work with underprivileged groups in the local community.
In the final pitching event, the highlight of the program, local venture investors from Silicon Valley were invited as judges and evaluated the pitches for each team's business items. The participating students, who developed their own business models while receiving advice through face-to-face mentoring from a professional accelerator in Silicon Valley, showcased their creative and innovative ideas, presenting themselves as future global entrepreneurs. Merey Makhmutova (BS in Civil and Environmental Engineering) from the K-Bridge team, who won the final pitch, expressed her ambition: “Even before GESS pitch day, our team kept refining the pitch deck as we attended the lectures and benefitted from the mentoring. Our intense teamwork was a significant reason why we ultimately won first prize.” She added that K-Bridge aims to win an award at the upcoming UKC Pitching Competition and expressed her gratitude for being able to participate in this program. Arseniy Kan (BS in Electrical Engineering) from the KAIST Enablers team, who took second place, said, “The 2024 KAIST GESS Program became the most unforgettable and precious opportunity of my lifetime, and I dream of using this opportunity as a stepping stone to becoming a global entrepreneur.“ Additionally, Kangster (CEO Kang Kim), who won the Impact MBA final pitching session, had the opportunity to secure a meeting with a local investment company after their GESS final pitch.
The 2024 KAIST GESS was held in cooperation with the KAIST International Office, the KAIST College of Business, and Startup KAIST. Director Man-Sung Yim from the Office of Global Initiatives, who hosted the event, said, “KAIST students will grow into leaders with global influence and contribute to the international community by creating global value. At the same time, we hope to raise the international status of our university.” Professor Sangchan Park, who led the 17 Impact MBA students in this educational program, added, “Meeting with companies leading the global market and visiting Silicon Valley has been a valuable learning experience for students aiming to start a global startup.”
KAIST plans to continue promoting its global entrepreneurship education program by enriching its curriculum each year and helping students grow into entrepreneurs with the virtues of global leaders.
2024.07.03 View 7848
The 3rd Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS 2024) Successfully Completed in Silicon Valley
The 2024 Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (2024 KAIST GESS), hosted by the Office of Global Initiatives under the KAIST International Office (Director Man-Sung Yim), was held for the third time. This program allows students to visit Silicon Valley, a global startup hub, to directly experience its famous startup ecosystem and develop their capabilities for global expansion. A total of 20 students were selected through applications, interviews, final presentations, mentoring, and peer evaluations. Additionally, 17 students from the KAIST Impact MBA course at the KAIST Business School also participated.
Before starting the Silicon Valley program, participants received mentoring on business model development and pitching advice from a senior entrepreneur at KAIST for about two months, beginning last May. Afterward, they developed business items for each team at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon. For seven days, starting from June 23rd, workshops were held under the themes of global entrepreneurship, learning through failure, capital and network, and startup culture at KOTRA Silicon Valley Trade Center, JP Morgan, and Plug and Play Tech Center. This program's lecture series provided prospective entrepreneurs with the opportunity to systematically learn the mindset and gain the experience needed to start a global business.
The participants also visited local companies and gained experience in the field of global technology startups. Visits included Bear Robotics (CEO John Ha), Soundable Health (CEO Cathering Song), ImpriMed (CEO Sungwon Lim), Phantom AI (CEO Hyunggi Cho), B Garage (CEO Aiden Kim), and Simple Steps (CEO Doyeon Kim). Lectures contained vivid experiences from Silicon Valley CEOs and company tours boosted the students' passion for entrepreneurship. In particular, Doyeon Kim, CEO of Simple Steps, which helps prevent career breaks for Korean female immigrants in Silicon Valley and allows talented female immigrants to demonstrate their abilities in society, said, “As a KAIST alumna entrepreneur, it was meaningful to share my experience with this generation of students who dream of starting a global business and creating social enterprises in the United States.”
This program also included a tour of Silicon Valley's big tech companies that have made a significant impact on the digital ecosystem through technological advancement and innovation. This included Broadcom, which maintains a strong global presence in the semiconductor and infrastructure software technology fields. At the invitation of Chairman Hock Tan, GESS participants had the opportunity to attend his lecture and ask questions. Chairman Tan, who received an honorary doctorate in engineering from KAIST last February, emphasized that experiencing failure and giving consistent effort over a long period of time are more important than anything else in order to grow as a global entrepreneur, and that technologies influencing the global market evolve over generations.
< Photo. Group photo of GESS 2024 participants at Broadcom with Chairman Hock Tan (center) ⓒBroadcom>
As part of this program, participants conducted a volunteer program called 'Let's play with AI+ Tech' with the Sunnyvale community in Silicon Valley and Foothill College to help grow together with the community. Through this program, GESS participants cultivated the virtues of a global leader. In this volunteer activity, low-income elementary school students and parents from the Sunnyvale community participated in chatbot training led by KAIST students, providing an opportunity to work with underprivileged groups in the local community.
In the final pitching event, the highlight of the program, local venture investors from Silicon Valley were invited as judges and evaluated the pitches for each team's business items. The participating students, who developed their own business models while receiving advice through face-to-face mentoring from a professional accelerator in Silicon Valley, showcased their creative and innovative ideas, presenting themselves as future global entrepreneurs. Merey Makhmutova (BS in Civil and Environmental Engineering) from the K-Bridge team, who won the final pitch, expressed her ambition: “Even before GESS pitch day, our team kept refining the pitch deck as we attended the lectures and benefitted from the mentoring. Our intense teamwork was a significant reason why we ultimately won first prize.” She added that K-Bridge aims to win an award at the upcoming UKC Pitching Competition and expressed her gratitude for being able to participate in this program. Arseniy Kan (BS in Electrical Engineering) from the KAIST Enablers team, who took second place, said, “The 2024 KAIST GESS Program became the most unforgettable and precious opportunity of my lifetime, and I dream of using this opportunity as a stepping stone to becoming a global entrepreneur.“ Additionally, Kangster (CEO Kang Kim), who won the Impact MBA final pitching session, had the opportunity to secure a meeting with a local investment company after their GESS final pitch.
The 2024 KAIST GESS was held in cooperation with the KAIST International Office, the KAIST College of Business, and Startup KAIST. Director Man-Sung Yim from the Office of Global Initiatives, who hosted the event, said, “KAIST students will grow into leaders with global influence and contribute to the international community by creating global value. At the same time, we hope to raise the international status of our university.” Professor Sangchan Park, who led the 17 Impact MBA students in this educational program, added, “Meeting with companies leading the global market and visiting Silicon Valley has been a valuable learning experience for students aiming to start a global startup.”
KAIST plans to continue promoting its global entrepreneurship education program by enriching its curriculum each year and helping students grow into entrepreneurs with the virtues of global leaders.
2024.07.03 View 7848