College+of+Natural+Science
-
 Professor Heung-Sun Sim the MSIT Scientist of July
Professor Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics was selected as the Scientist of July by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Professor Sim was recognized for his research of the Kondo effect, which opened a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. His research revealed that the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This phenomenon is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed. The research was reported in Nature in March 2020. With this award, Professor Sim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2021.07.12 View 9415
Professor Heung-Sun Sim the MSIT Scientist of July
Professor Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics was selected as the Scientist of July by the Ministry of Science and ICT. Professor Sim was recognized for his research of the Kondo effect, which opened a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. His research revealed that the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This phenomenon is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed. The research was reported in Nature in March 2020. With this award, Professor Sim received 10 million KRW in prize money.
2021.07.12 View 9415 -
 Quantum Laser Turns Energy Loss into Gain
A new laser that generates quantum particles can recycle lost energy for highly efficient, low threshold laser applications
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
The researchers found another unique and counter-intuitive feature of this design. Normally, energy is lost during laser operation. But in this system, as energy loss increased, the amount of energy needed to induce lasing decreased. Exploiting this phenomenon could lead to the development of high efficiency, low threshold lasers for future quantum optical devices.
“This system applies a concept of quantum physics known as parity-time reversal symmetry,” explains Professor Cho. “This is an important platform that allows energy loss to be used as gain. It can be used to reduce laser threshold energy for classical optical devices and sensors, as well as quantum devices and controlling the direction of light.”
The key is the design and materials. The hexagonal microcavity divides light particles into two different modes: one that passes through the upward-facing triangle of the hexagon and another that passes through its downward-facing triangle. Both modes of light particles have the same energy and path but don’t interact with each other.
However, the light particles do interact with other particles called excitons, provided by the hexagonal microcavity, which is made of semiconductors. This interaction leads to the generation of new quantum particles called polaritons that then interact with each other to generate the polariton laser. By controlling the degree of loss between the microcavity and the semiconductor substrate, an intriguing phenomenon arises, with the threshold energy becoming smaller as energy loss increases. This research was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and Korea’s National Research Foundation.
-PublicationSong,H.G, Choi, M, Woo, K.Y. Yong-Hoon Cho Room-temperature polaritonic non-Hermitian system with single microcavityNature Photonics (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00820-z)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.07 View 12328
Quantum Laser Turns Energy Loss into Gain
A new laser that generates quantum particles can recycle lost energy for highly efficient, low threshold laser applications
Scientists at KAIST have fabricated a laser system that generates highly interactive quantum particles at room temperature. Their findings, published in the journal Nature Photonics, could lead to a single microcavity laser system that requires lower threshold energy as its energy loss increases.
The system, developed by KAIST physicist Yong-Hoon Cho and colleagues, involves shining light through a single hexagonal-shaped microcavity treated with a loss-modulated silicon nitride substrate. The system design leads to the generation of a polariton laser at room temperature, which is exciting because this usually requires cryogenic temperatures.
The researchers found another unique and counter-intuitive feature of this design. Normally, energy is lost during laser operation. But in this system, as energy loss increased, the amount of energy needed to induce lasing decreased. Exploiting this phenomenon could lead to the development of high efficiency, low threshold lasers for future quantum optical devices.
“This system applies a concept of quantum physics known as parity-time reversal symmetry,” explains Professor Cho. “This is an important platform that allows energy loss to be used as gain. It can be used to reduce laser threshold energy for classical optical devices and sensors, as well as quantum devices and controlling the direction of light.”
The key is the design and materials. The hexagonal microcavity divides light particles into two different modes: one that passes through the upward-facing triangle of the hexagon and another that passes through its downward-facing triangle. Both modes of light particles have the same energy and path but don’t interact with each other.
However, the light particles do interact with other particles called excitons, provided by the hexagonal microcavity, which is made of semiconductors. This interaction leads to the generation of new quantum particles called polaritons that then interact with each other to generate the polariton laser. By controlling the degree of loss between the microcavity and the semiconductor substrate, an intriguing phenomenon arises, with the threshold energy becoming smaller as energy loss increases. This research was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation and Korea’s National Research Foundation.
-PublicationSong,H.G, Choi, M, Woo, K.Y. Yong-Hoon Cho Room-temperature polaritonic non-Hermitian system with single microcavityNature Photonics (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41566-021-00820-z)
-ProfileProfessor Yong-Hoon ChoQuantum & Nanobio Photonics Laboratoryhttp://qnp.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of PhysicsKAIST
2021.07.07 View 12328 -
 Defining the Hund Physics Landscape of Two-Orbital Systems
Researchers identify exotic metals in unexpected quantum systems
Electrons are ubiquitous among atoms, subatomic tokens of energy that can independently change how a system behaves—but they also can change each other. An international research collaboration found that collectively measuring electrons revealed unique and unanticipated findings. The researchers published their results on May 17 in Physical Review Letters.
“It is not feasible to obtain the solution just by tracing the behavior of each individual electron,” said paper author Myung Joon Han, professor of physics at KAIST. “Instead, one should describe or track all the entangled electrons at once. This requires a clever way of treating this entanglement.”
Professor Han and the researchers used a recently developed “many-particle” theory to account for the entangled nature of electrons in solids, which approximates how electrons locally interact with one another to predict their global activity.
Through this approach, the researchers examined systems with two orbitals — the space in which electrons can inhabit. They found that the electrons locked into parallel arrangements within atom sites in solids. This phenomenon, known as Hund’s coupling, results in a Hund’s metal. This metallic phase, which can give rise to such properties as superconductivity, was thought only to exist in three-orbital systems.
“Our finding overturns a conventional viewpoint that at least three orbitals are needed for Hund’s metallicity to emerge,” Professor Han said, noting that two-orbital systems have not been a focus of attention for many physicists. “In addition to this finding of a Hund’s metal, we identified various metallic regimes that can naturally occur in generic, correlated electron materials.”
The researchers found four different correlated metals. One stems from the proximity to a Mott insulator, a state of a solid material that should be conductive but actually prevents conduction due to how the electrons interact. The other three metals form as electrons align their magnetic moments — or phases of producing a magnetic field — at various distances from the Mott insulator. Beyond identifying the metal phases, the researchers also suggested classification criteria to define each metal phase in other systems.
“This research will help scientists better characterize and understand the deeper nature of so-called ‘strongly correlated materials,’ in which the standard theory of solids breaks down due to the presence of strong Coulomb interactions between electrons,” Professor Han said, referring to the force with which the electrons attract or repel each other. These interactions are not typically present in solid materials but appear in materials with metallic phases.
The revelation of metals in two-orbital systems and the ability to determine whole system electron behavior could lead to even more discoveries, according to Professor Han.
“This will ultimately enable us to manipulate and control a variety of electron correlation phenomena,” Professor Han said.
Co-authors include Siheon Ryee from KAIST and Sangkook Choi from the Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory in the United States. Korea’s National Research Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences, supported this work.
-PublicationSiheon Ryee, Myung Joon Han, and SangKook Choi, 2021.Hund Physics Landscape of Two-Orbital Systems, Physical Review Letters, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.206401
-ProfileProfessor Myung Joon HanDepartment of PhysicsCollege of Natural ScienceKAIST
2021.06.17 View 11375
Defining the Hund Physics Landscape of Two-Orbital Systems
Researchers identify exotic metals in unexpected quantum systems
Electrons are ubiquitous among atoms, subatomic tokens of energy that can independently change how a system behaves—but they also can change each other. An international research collaboration found that collectively measuring electrons revealed unique and unanticipated findings. The researchers published their results on May 17 in Physical Review Letters.
“It is not feasible to obtain the solution just by tracing the behavior of each individual electron,” said paper author Myung Joon Han, professor of physics at KAIST. “Instead, one should describe or track all the entangled electrons at once. This requires a clever way of treating this entanglement.”
Professor Han and the researchers used a recently developed “many-particle” theory to account for the entangled nature of electrons in solids, which approximates how electrons locally interact with one another to predict their global activity.
Through this approach, the researchers examined systems with two orbitals — the space in which electrons can inhabit. They found that the electrons locked into parallel arrangements within atom sites in solids. This phenomenon, known as Hund’s coupling, results in a Hund’s metal. This metallic phase, which can give rise to such properties as superconductivity, was thought only to exist in three-orbital systems.
“Our finding overturns a conventional viewpoint that at least three orbitals are needed for Hund’s metallicity to emerge,” Professor Han said, noting that two-orbital systems have not been a focus of attention for many physicists. “In addition to this finding of a Hund’s metal, we identified various metallic regimes that can naturally occur in generic, correlated electron materials.”
The researchers found four different correlated metals. One stems from the proximity to a Mott insulator, a state of a solid material that should be conductive but actually prevents conduction due to how the electrons interact. The other three metals form as electrons align their magnetic moments — or phases of producing a magnetic field — at various distances from the Mott insulator. Beyond identifying the metal phases, the researchers also suggested classification criteria to define each metal phase in other systems.
“This research will help scientists better characterize and understand the deeper nature of so-called ‘strongly correlated materials,’ in which the standard theory of solids breaks down due to the presence of strong Coulomb interactions between electrons,” Professor Han said, referring to the force with which the electrons attract or repel each other. These interactions are not typically present in solid materials but appear in materials with metallic phases.
The revelation of metals in two-orbital systems and the ability to determine whole system electron behavior could lead to even more discoveries, according to Professor Han.
“This will ultimately enable us to manipulate and control a variety of electron correlation phenomena,” Professor Han said.
Co-authors include Siheon Ryee from KAIST and Sangkook Choi from the Condensed Matter Physics and Materials Science Department, Brookhaven National Laboratory in the United States. Korea’s National Research Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science, Basic Energy Sciences, supported this work.
-PublicationSiheon Ryee, Myung Joon Han, and SangKook Choi, 2021.Hund Physics Landscape of Two-Orbital Systems, Physical Review Letters, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.206401
-ProfileProfessor Myung Joon HanDepartment of PhysicsCollege of Natural ScienceKAIST
2021.06.17 View 11375 -
 Observing Individual Atoms in 3D Nanomaterials and Their Surfaces
Atoms are the basic building blocks for all materials. To tailor functional properties, it is essential to accurately determine their atomic structures. KAIST researchers observed the 3D atomic structure of a nanoparticle at the atom level via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography.
Using a platinum nanoparticle as a model system, a research team led by Professor Yongsoo Yang demonstrated that an atomicity-based deep learning approach can reliably identify the 3D surface atomic structure with a precision of 15 picometers (only about 1/3 of a hydrogen atom’s radius). The atomic displacement, strain, and facet analysis revealed that the surface atomic structure and strain are related to both the shape of the nanoparticle and the particle-substrate interface.
Combined with quantum mechanical calculations such as density functional theory, the ability to precisely identify surface atomic structure will serve as a powerful key for understanding catalytic performance and oxidation effect.
“We solved the problem of determining the 3D surface atomic structure of nanomaterials in a reliable manner. It has been difficult to accurately measure the surface atomic structures due to the ‘missing wedge problem’ in electron tomography, which arises from geometrical limitations, allowing only part of a full tomographic angular range to be measured. We resolved the problem using a deep learning-based approach,” explained Professor Yang.
The missing wedge problem results in elongation and ringing artifacts, negatively affecting the accuracy of the atomic structure determined from the tomogram, especially for identifying the surface structures. The missing wedge problem has been the main roadblock for the precise determination of the 3D surface atomic structures of nanomaterials.
The team used atomic electron tomography (AET), which is basically a very high-resolution CT scan for nanomaterials using transmission electron microscopes. AET allows individual atom level 3D atomic structural determination.
“The main idea behind this deep learning-based approach is atomicity—the fact that all matter is composed of atoms. This means that true atomic resolution electron tomogram should only contain sharp 3D atomic potentials convolved with the electron beam profile,” said Professor Yang.
“A deep neural network can be trained using simulated tomograms that suffer from missing wedges as inputs, and the ground truth 3D atomic volumes as targets. The trained deep learning network effectively augments the imperfect tomograms and removes the artifacts resulting from the missing wedge problem.”
The precision of 3D atomic structure can be enhanced by nearly 70% by applying the deep learning-based augmentation. The accuracy of surface atom identification was also significantly improved.
Structure-property relationships of functional nanomaterials, especially the ones that strongly depend on the surface structures, such as catalytic properties for fuel-cell applications, can now be revealed at one of the most fundamental scales: the atomic scale.
Professor Yang concluded, “We would like to fully map out the 3D atomic structure with higher precision and better elemental specificity. And not being limited to atomic structures, we aim to measure the physical, chemical, and functional properties of nanomaterials at the 3D atomic scale by further advancing electron tomography techniques.”
This research, reported at Nature Communications, was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research M3I3 Project.
-Publication
Juhyeok Lee, Chaehwa Jeong & Yongsoo Yang
“Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography”
Nature Communications
-Profile
Professor Yongsoo Yang
Department of Physics
Multi-Dimensional Atomic Imaging Lab (MDAIL)
http://mdail.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.05.12 View 14746
Observing Individual Atoms in 3D Nanomaterials and Their Surfaces
Atoms are the basic building blocks for all materials. To tailor functional properties, it is essential to accurately determine their atomic structures. KAIST researchers observed the 3D atomic structure of a nanoparticle at the atom level via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography.
Using a platinum nanoparticle as a model system, a research team led by Professor Yongsoo Yang demonstrated that an atomicity-based deep learning approach can reliably identify the 3D surface atomic structure with a precision of 15 picometers (only about 1/3 of a hydrogen atom’s radius). The atomic displacement, strain, and facet analysis revealed that the surface atomic structure and strain are related to both the shape of the nanoparticle and the particle-substrate interface.
Combined with quantum mechanical calculations such as density functional theory, the ability to precisely identify surface atomic structure will serve as a powerful key for understanding catalytic performance and oxidation effect.
“We solved the problem of determining the 3D surface atomic structure of nanomaterials in a reliable manner. It has been difficult to accurately measure the surface atomic structures due to the ‘missing wedge problem’ in electron tomography, which arises from geometrical limitations, allowing only part of a full tomographic angular range to be measured. We resolved the problem using a deep learning-based approach,” explained Professor Yang.
The missing wedge problem results in elongation and ringing artifacts, negatively affecting the accuracy of the atomic structure determined from the tomogram, especially for identifying the surface structures. The missing wedge problem has been the main roadblock for the precise determination of the 3D surface atomic structures of nanomaterials.
The team used atomic electron tomography (AET), which is basically a very high-resolution CT scan for nanomaterials using transmission electron microscopes. AET allows individual atom level 3D atomic structural determination.
“The main idea behind this deep learning-based approach is atomicity—the fact that all matter is composed of atoms. This means that true atomic resolution electron tomogram should only contain sharp 3D atomic potentials convolved with the electron beam profile,” said Professor Yang.
“A deep neural network can be trained using simulated tomograms that suffer from missing wedges as inputs, and the ground truth 3D atomic volumes as targets. The trained deep learning network effectively augments the imperfect tomograms and removes the artifacts resulting from the missing wedge problem.”
The precision of 3D atomic structure can be enhanced by nearly 70% by applying the deep learning-based augmentation. The accuracy of surface atom identification was also significantly improved.
Structure-property relationships of functional nanomaterials, especially the ones that strongly depend on the surface structures, such as catalytic properties for fuel-cell applications, can now be revealed at one of the most fundamental scales: the atomic scale.
Professor Yang concluded, “We would like to fully map out the 3D atomic structure with higher precision and better elemental specificity. And not being limited to atomic structures, we aim to measure the physical, chemical, and functional properties of nanomaterials at the 3D atomic scale by further advancing electron tomography techniques.”
This research, reported at Nature Communications, was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research M3I3 Project.
-Publication
Juhyeok Lee, Chaehwa Jeong & Yongsoo Yang
“Single-atom level determination of 3-dimensional surface atomic structure via neural network-assisted atomic electron tomography”
Nature Communications
-Profile
Professor Yongsoo Yang
Department of Physics
Multi-Dimensional Atomic Imaging Lab (MDAIL)
http://mdail.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.05.12 View 14746 -
 Professor Jae Kyoung Kim to Lead a New Mathematical Biology Research Group at IBS
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences was appointed as the third Chief Investigator (CI) of the Pioneer Research Center (PRC) for Mathematical and Computational Sciences at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Professor Kim will launch and lead a new research group that will be devoted to resolving various biological conundrums from a mathematical perspective. His appointment began on March 1, 2021.
Professor Kim, a rising researcher in the field of mathematical biology, has received attention from both the mathematical and biological communities at the international level. Professor Kim puts novel and unremitting efforts into understanding biological systems such as cell-to-cell interactions mathematically and designing mathematical models for identifying causes of diseases and developing therapeutic medicines.
Through active joint research with biologists, mathematician Kim has addressed many challenges that have remained unsolved in biology and published papers in a number of leading international journals in related fields. His notable works based on mathematical modelling include having designed a biological circuit that can maintain a stable circadian rhythm (Science, 2015) and unveiling the principles of how the biological clock in the body maintains a steady speed for the first time in over 60 years (Molecular Cell, 2015). Recently, through a joint research project with Pfizer, Professor Kim identified what causes the differences between animal and clinical test results during drug development explaining why drugs have different efficacies in different people (Molecular Systems Biology, 2019).
The new IBS biomedical mathematics research group led by Professor Kim will further investigate the causes of unstable circadian rhythms and sleeping patterns. The team will aim to present a new paradigm in treatments for sleep disorders.
Professor Kim said, “We are all so familiar with sleep behaviors, but the exact mechanisms behind how such behaviors occur are still unknown. Through cooperation with biomedical scientists, our group will do its best to discover the complicated, fundamental mechanisms of sleep, and investigate the causes and cures of sleep disorders.”
Every year, the IBS selects young and promising researchers and appoints them as CIs. A maximum of five selected CIs can form each independent research group within the IBS PRC, and receive research funds of 1 billion to 1.5 billion KRW over five years.
(END)
2021.03.18 View 11726
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim to Lead a New Mathematical Biology Research Group at IBS
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences was appointed as the third Chief Investigator (CI) of the Pioneer Research Center (PRC) for Mathematical and Computational Sciences at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Professor Kim will launch and lead a new research group that will be devoted to resolving various biological conundrums from a mathematical perspective. His appointment began on March 1, 2021.
Professor Kim, a rising researcher in the field of mathematical biology, has received attention from both the mathematical and biological communities at the international level. Professor Kim puts novel and unremitting efforts into understanding biological systems such as cell-to-cell interactions mathematically and designing mathematical models for identifying causes of diseases and developing therapeutic medicines.
Through active joint research with biologists, mathematician Kim has addressed many challenges that have remained unsolved in biology and published papers in a number of leading international journals in related fields. His notable works based on mathematical modelling include having designed a biological circuit that can maintain a stable circadian rhythm (Science, 2015) and unveiling the principles of how the biological clock in the body maintains a steady speed for the first time in over 60 years (Molecular Cell, 2015). Recently, through a joint research project with Pfizer, Professor Kim identified what causes the differences between animal and clinical test results during drug development explaining why drugs have different efficacies in different people (Molecular Systems Biology, 2019).
The new IBS biomedical mathematics research group led by Professor Kim will further investigate the causes of unstable circadian rhythms and sleeping patterns. The team will aim to present a new paradigm in treatments for sleep disorders.
Professor Kim said, “We are all so familiar with sleep behaviors, but the exact mechanisms behind how such behaviors occur are still unknown. Through cooperation with biomedical scientists, our group will do its best to discover the complicated, fundamental mechanisms of sleep, and investigate the causes and cures of sleep disorders.”
Every year, the IBS selects young and promising researchers and appoints them as CIs. A maximum of five selected CIs can form each independent research group within the IBS PRC, and receive research funds of 1 billion to 1.5 billion KRW over five years.
(END)
2021.03.18 View 11726 -
 Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10746
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik Honored with the POSCO TJ Park Prize
Professor Mu-Hyun Baik at the Department of Chemistry was honored to be the recipient of the 2021 POSCO TJ Park Prize in Science. The POSCO TJ Park Foundation awards every year the individual or organization which made significant contribution in science, education, community development, philanthropy, and technology.
Professor Baik, a renowned computational chemist in analyzing complicated chemical reactions to understand how molecules behave and how they change. Professor Baik was awarded in recognition of his pioneering research in designing numerous organometallic catalysts with using computational molecular modelling. In 2016, he published in Science on the catalytic borylation of methane that showed how chemical reactions can be carried out using the natural gas methane as a substrate.
In 2020, he reported in Science that electrodes can be used as functional groups with adjustable inductive effects to change the chemical reactivity of molecules that are attached to them, closely mimicking the inductive effect of conventional functional groups. This constitutes a potentially powerful new way of controlling chemical reactions, offering an alternative to preparing derivatives to install electron-withdrawing functional groups.
Joined at KAIST in 2015, Professor Baik also serves as associate director at the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalization at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) since 2015. Among the many recognitions and awards that he received include the Kavli Fellowship by the Kavli Foundation and the National Academy of Science in the US in 2019 and the 2018 Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation in Germany.
2021.03.11 View 10746 -
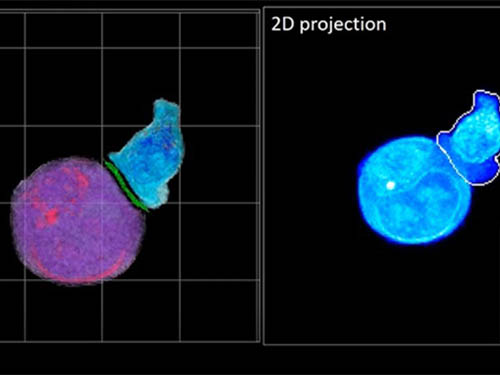 Deep-Learning and 3D Holographic Microscopy Beats Scientists at Analyzing Cancer Immunotherapy
Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate a key process in cancer immunotherapy “live” as it takes place. The AI transformed work that, if performed manually by scientists, would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive and time-consuming into one that is not only effortless but done better than they could have done it themselves. The research, conducted by the team of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, appeared in the journal eLife last December.
A critical stage in the development of the human immune system’s ability to respond not just generally to any invader (such as pathogens or cancer cells) but specifically to that particular type of invader and remember it should it attempt to invade again is the formation of a junction between an immune cell called a T-cell and a cell that presents the antigen, or part of the invader that is causing the problem, to it. This process is like when a picture of a suspect is sent to a police car so that the officers can recognize the criminal they are trying to track down. The junction between the two cells, called the immunological synapse, or IS, is the key process in teaching the immune system how to recognize a specific type of invader.
Since the formation of the IS junction is such a critical step for the initiation of an antigen-specific immune response, various techniques allowing researchers to observe the process as it happens have been used to study its dynamics. Most of these live imaging techniques rely on fluorescence microscopy, where genetic tweaking causes part of a protein from a cell to fluoresce, in turn allowing the subject to be tracked via fluorescence rather than via the reflected light used in many conventional microscopy techniques.
However, fluorescence-based imaging can suffer from effects such as photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, preventing the assessment of dynamic changes in the IS junction process over the long term. Fluorescence-based imaging still involves illumination, whereupon the fluorophores (chemical compounds that cause the fluorescence) emit light of a different color. Photo-bleaching or photo-toxicity occur when the subject is exposed to too much illumination, resulting in chemical alteration or cellular damage.
One recent option that does away with fluorescent labelling and thereby avoids such problems is 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography (HT). In this technique, the refractive index (the way that light changes direction when encountering a substance with a different density—why a straw looks like it bends in a glass of water) is recorded in 3D as a hologram.
Until now, HT has been used to study single cells, but never cell-cell interactions involved in immune responses. One of the main reasons is the difficulty of “segmentation,” or distinguishing the different parts of a cell and thus distinguishing between the interacting cells; in other words, deciphering which part belongs to which cell.
Manual segmentation, or marking out the different parts manually, is one option, but it is difficult and time-consuming, especially in three dimensions. To overcome this problem, automatic segmentation has been developed in which simple computer algorithms perform the identification.
“But these basic algorithms often make mistakes,” explained Professor YongKeun Park, “particularly with respect to adjoining segmentation, which of course is exactly what is occurring here in the immune response we’re most interested in.”
So, the researchers applied a deep learning framework to the HT segmentation problem. Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which artificial neural networks based on the human brain recognize patterns in a way that is similar to how humans do this. Regular machine learning requires data as an input that has already been labelled. The AI “learns” by understanding the labeled data and then recognizes the concept that has been labelled when it is fed novel data. For example, AI trained on a thousand images of cats labelled “cat” should be able to recognize a cat the next time it encounters an image with a cat in it. Deep learning involves multiple layers of artificial neural networks attacking much larger, but unlabeled datasets, in which the AI develops its own ‘labels’ for concepts it encounters.
In essence, the deep learning framework that KAIST researchers developed, called DeepIS, came up with its own concepts by which it distinguishes the different parts of the IS junction process. To validate this method, the research team applied it to the dynamics of a particular IS junction formed between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and target cancer cells. They then compared the results to what they would normally have done: the laborious process of performing the segmentation manually. They found not only that DeepIS was able to define areas within the IS with high accuracy, but that the technique was even able to capture information about the total distribution of proteins within the IS that may not have been easily measured using conventional techniques.
“In addition to allowing us to avoid the drudgery of manual segmentation and the problems of photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, we found that the AI actually did a better job,” Professor Park added.
The next step will be to combine the technique with methods of measuring how much physical force is applied by different parts of the IS junction, such as holographic optical tweezers or traction force microscopy.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Department of Physics
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.02.24 View 14688
Deep-Learning and 3D Holographic Microscopy Beats Scientists at Analyzing Cancer Immunotherapy
Live tracking and analyzing of the dynamics of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells targeting cancer cells can open new avenues for the development of cancer immunotherapy. However, imaging via conventional microscopy approaches can result in cellular damage, and assessments of cell-to-cell interactions are extremely difficult and labor-intensive. When researchers applied deep learning and 3D holographic microscopy to the task, however, they not only avoided these difficultues but found that AI was better at it than humans were.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is helping researchers decipher images from a new holographic microscopy technique needed to investigate a key process in cancer immunotherapy “live” as it takes place. The AI transformed work that, if performed manually by scientists, would otherwise be incredibly labor-intensive and time-consuming into one that is not only effortless but done better than they could have done it themselves. The research, conducted by the team of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, appeared in the journal eLife last December.
A critical stage in the development of the human immune system’s ability to respond not just generally to any invader (such as pathogens or cancer cells) but specifically to that particular type of invader and remember it should it attempt to invade again is the formation of a junction between an immune cell called a T-cell and a cell that presents the antigen, or part of the invader that is causing the problem, to it. This process is like when a picture of a suspect is sent to a police car so that the officers can recognize the criminal they are trying to track down. The junction between the two cells, called the immunological synapse, or IS, is the key process in teaching the immune system how to recognize a specific type of invader.
Since the formation of the IS junction is such a critical step for the initiation of an antigen-specific immune response, various techniques allowing researchers to observe the process as it happens have been used to study its dynamics. Most of these live imaging techniques rely on fluorescence microscopy, where genetic tweaking causes part of a protein from a cell to fluoresce, in turn allowing the subject to be tracked via fluorescence rather than via the reflected light used in many conventional microscopy techniques.
However, fluorescence-based imaging can suffer from effects such as photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, preventing the assessment of dynamic changes in the IS junction process over the long term. Fluorescence-based imaging still involves illumination, whereupon the fluorophores (chemical compounds that cause the fluorescence) emit light of a different color. Photo-bleaching or photo-toxicity occur when the subject is exposed to too much illumination, resulting in chemical alteration or cellular damage.
One recent option that does away with fluorescent labelling and thereby avoids such problems is 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography (HT). In this technique, the refractive index (the way that light changes direction when encountering a substance with a different density—why a straw looks like it bends in a glass of water) is recorded in 3D as a hologram.
Until now, HT has been used to study single cells, but never cell-cell interactions involved in immune responses. One of the main reasons is the difficulty of “segmentation,” or distinguishing the different parts of a cell and thus distinguishing between the interacting cells; in other words, deciphering which part belongs to which cell.
Manual segmentation, or marking out the different parts manually, is one option, but it is difficult and time-consuming, especially in three dimensions. To overcome this problem, automatic segmentation has been developed in which simple computer algorithms perform the identification.
“But these basic algorithms often make mistakes,” explained Professor YongKeun Park, “particularly with respect to adjoining segmentation, which of course is exactly what is occurring here in the immune response we’re most interested in.”
So, the researchers applied a deep learning framework to the HT segmentation problem. Deep learning is a type of machine learning in which artificial neural networks based on the human brain recognize patterns in a way that is similar to how humans do this. Regular machine learning requires data as an input that has already been labelled. The AI “learns” by understanding the labeled data and then recognizes the concept that has been labelled when it is fed novel data. For example, AI trained on a thousand images of cats labelled “cat” should be able to recognize a cat the next time it encounters an image with a cat in it. Deep learning involves multiple layers of artificial neural networks attacking much larger, but unlabeled datasets, in which the AI develops its own ‘labels’ for concepts it encounters.
In essence, the deep learning framework that KAIST researchers developed, called DeepIS, came up with its own concepts by which it distinguishes the different parts of the IS junction process. To validate this method, the research team applied it to the dynamics of a particular IS junction formed between chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cells and target cancer cells. They then compared the results to what they would normally have done: the laborious process of performing the segmentation manually. They found not only that DeepIS was able to define areas within the IS with high accuracy, but that the technique was even able to capture information about the total distribution of proteins within the IS that may not have been easily measured using conventional techniques.
“In addition to allowing us to avoid the drudgery of manual segmentation and the problems of photo-bleaching and photo-toxicity, we found that the AI actually did a better job,” Professor Park added.
The next step will be to combine the technique with methods of measuring how much physical force is applied by different parts of the IS junction, such as holographic optical tweezers or traction force microscopy.
-Profile
Professor YongKeun Park
Department of Physics
Biomedical Optics Laboratory
http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
2021.02.24 View 14688 -
 Mystery Solved with Math: Cytoplasmic Traffic Jam Disrupts Sleep-Wake Cycles
KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators at Florida State University have identified the principle of how aging and diseases like dementia and obesity cause sleep disorders. A combination of mathematical modelling and experiments demonstrated that the cytoplasmic congestion caused by aging, dementia, and/or obesity disrupts the circadian rhythms in the human body and leads to irregular sleep-wake cycles. This finding suggests new treatment strategies for addressing unstable sleep-wake cycles.
Human bodies adjust sleep schedules in accordance with the ‘circadian rhythms’, which are regulated by our time keeping system, the ‘circadian clock’. This clock tells our body when to rest by generating the 24-hour rhythms of a protein called PERIOD (PER) (See Figure 1).
The amount of the PER protein increases for half of the day and then decreases for the remaining half. The principle is that the PER protein accumulating in the cytoplasm for several hours enters the cell nucleus all at once, hindering the transcription of PER genes and thereby reducing the amount of PER.
However, it has remained a mystery how thousands of PER molecules can simultaneously enter into the nucleus in a complex cell environment where a variety of materials co-exist and can interfere with the motion of PER. This would be like finding a way for thousands of employees from all over New York City to enter an office building at the same time every day.
A group of researchers led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences solved the mystery by developing a spatiotemporal and probabilistic model that describes the motion of PER molecules in a cell environment.
This study was conducted in collaboration with Professor Choogon Lee’s group from Florida State University, where the experiments were carried out, and the results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) last month.
The joint research team’s spatial stochastic model (See Figure 2) described the motion of PER molecules in cells and demonstrated that the PER molecule should be sufficiently condensed around the cell nucleus to be phosphorylated simultaneously and enter the nucleus together (See Figure 3 Left). Thanks to this phosphorylation synchronization switch, thousands of PER molecules can enter the nucleus at the same time every day and maintain stable circadian rhythms.
However, when aging and/or diseases including dementia and obesity cause the cytoplasm to become congested with increased cytoplasmic obstacles such as protein aggregates and fat vacuoles, it hinders the timely condensation of PER molecules around the cell nucleus (See Figure 3 Right). As a result, the phosphorylation synchronization switch does not work and PER proteins enter into the nucleus at irregular times, making the circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles unstable, the study revealed.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of new treatment strategies that can improve the lives of so many patients who suffer from irregular sleep-wake cycles. Taking these findings as an opportunity, I hope to see more active interchanges of ideas and collaboration between mathematical and biological sciences.”
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation in the US, and the International Human Frontiers Science Program Organization and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Beesley, S. and Kim, D. W, et al. (2020) Wake-sleep cycles are severely disrupted by diseases affecting cytoplasmic homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 45, 28402-28411. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003524117
Profile:
Jae Kyoung Kim, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
@umichkim on Twitter
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Choogon Lee, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
clee@neuro.fsu.edu
https://med.fsu.edu/biosci/lee-lab
Department of Biomedical Sciences
Florida State University
Florida, USA
(END)
2020.12.11 View 12698
Mystery Solved with Math: Cytoplasmic Traffic Jam Disrupts Sleep-Wake Cycles
KAIST mathematicians and their collaborators at Florida State University have identified the principle of how aging and diseases like dementia and obesity cause sleep disorders. A combination of mathematical modelling and experiments demonstrated that the cytoplasmic congestion caused by aging, dementia, and/or obesity disrupts the circadian rhythms in the human body and leads to irregular sleep-wake cycles. This finding suggests new treatment strategies for addressing unstable sleep-wake cycles.
Human bodies adjust sleep schedules in accordance with the ‘circadian rhythms’, which are regulated by our time keeping system, the ‘circadian clock’. This clock tells our body when to rest by generating the 24-hour rhythms of a protein called PERIOD (PER) (See Figure 1).
The amount of the PER protein increases for half of the day and then decreases for the remaining half. The principle is that the PER protein accumulating in the cytoplasm for several hours enters the cell nucleus all at once, hindering the transcription of PER genes and thereby reducing the amount of PER.
However, it has remained a mystery how thousands of PER molecules can simultaneously enter into the nucleus in a complex cell environment where a variety of materials co-exist and can interfere with the motion of PER. This would be like finding a way for thousands of employees from all over New York City to enter an office building at the same time every day.
A group of researchers led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences solved the mystery by developing a spatiotemporal and probabilistic model that describes the motion of PER molecules in a cell environment.
This study was conducted in collaboration with Professor Choogon Lee’s group from Florida State University, where the experiments were carried out, and the results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) last month.
The joint research team’s spatial stochastic model (See Figure 2) described the motion of PER molecules in cells and demonstrated that the PER molecule should be sufficiently condensed around the cell nucleus to be phosphorylated simultaneously and enter the nucleus together (See Figure 3 Left). Thanks to this phosphorylation synchronization switch, thousands of PER molecules can enter the nucleus at the same time every day and maintain stable circadian rhythms.
However, when aging and/or diseases including dementia and obesity cause the cytoplasm to become congested with increased cytoplasmic obstacles such as protein aggregates and fat vacuoles, it hinders the timely condensation of PER molecules around the cell nucleus (See Figure 3 Right). As a result, the phosphorylation synchronization switch does not work and PER proteins enter into the nucleus at irregular times, making the circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles unstable, the study revealed.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help enable the advancement of new treatment strategies that can improve the lives of so many patients who suffer from irregular sleep-wake cycles. Taking these findings as an opportunity, I hope to see more active interchanges of ideas and collaboration between mathematical and biological sciences.”
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation in the US, and the International Human Frontiers Science Program Organization and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Beesley, S. and Kim, D. W, et al. (2020) Wake-sleep cycles are severely disrupted by diseases affecting cytoplasmic homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 45, 28402-28411. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2003524117
Profile:
Jae Kyoung Kim, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr
http://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
@umichkim on Twitter
Department of Mathematical Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Choogon Lee, Ph.D.
Associate Professor
clee@neuro.fsu.edu
https://med.fsu.edu/biosci/lee-lab
Department of Biomedical Sciences
Florida State University
Florida, USA
(END)
2020.12.11 View 12698 -
 Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 13433
Drawing the Line to Answer Art’s Big Questions
- KAIST scientists show how statistical physics can reveal art trends across time and culture. -
Algorithms have shown that the compositional structure of Western landscape paintings changed “suspiciously” smoothly between 1500 and 2000 AD, potentially indicating a selection bias by art curators or in art historical literature, physicists from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and colleagues report in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
KAIST statistical physicist Hawoong Jeong worked with statisticians, digital analysts and art historians in Korea, Estonia and the US to clarify whether computer algorithms could help resolve long-standing questions about design principles used in landscape paintings, such as the placement of the horizon and other primary features.
“A foundational question among art historians is whether artwork contains organizing principles that transcend culture and time and, if yes, how these principles evolved over time,” explains Jeong. “We developed an information-theoretic approach that can capture compositional proportion in landscape paintings and found that the preferred compositional proportion systematically evolved over time.”
Digital versions of almost 15,000 canonical landscape paintings from the Western renaissance in the 1500s to the more recent contemporary art period were run through a computer algorithm. The algorithm progressively divides artwork into horizontal and vertical lines depending on the amount of information in each subsequent partition. It allows scientists to evaluate how artists and various art styles compose landscape artwork, in terms of placement of a piece’s most important components, in addition to how high or low the landscape’s horizon is placed.
The scientists started by analysing the first two partitioning lines identified by the algorithm in the paintings and found they could be categorized into four groups: an initial horizontal line followed by a second horizontal line (H-H); an initial horizontal line followed by a second vertical line (H-V); a vertical followed by horizontal line (V-H); or a vertical followed by a vertical line (V-V) (see image 1 and 2). They then looked at the categorizations over time.
They found that before the mid-nineteenth century, H-V was the dominant composition type, followed by H-H, V-H, and V-V. The mid-nineteenth century then brought change, with the H-V composition style decreasing in popularity with a rise in the H-H composition style. The other two styles remained relatively stable.
The scientists also looked at how the horizon line, which separates sky from land, changed over time. In the 16th century, the dominant horizon line of the painting was above the middle of the canvas, but it gradually descended to the lower middle of the canvas by the 17th century, where it remained until the mid-nineteenth century. After that, the horizon line began gradually rising again.
Interestingly, the algorithm showed that these findings were similar across cultures and artistic periods, even through periods dominated by a diversity in art styles. This similarity may well be a function, then, of a bias in the dataset.
“In recent decades, art historians have prioritized the argument that there is great diversity in the evolution of artistic expression rather than offering a relatively smoother consensus story in Western art,” Jeong says. “This study serves as a reminder that the available large-scale datasets might be perpetuating severe biases.”
The scientists next aim to broaden their analyses to include more diverse artwork, as this particular dataset was ultimately Western and male biased. Future analyses should also consider diagonal compositions in paintings, they say.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Lee, B, et al. (2020) Dissecting landscape art history with information theory. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), Vol. 117, No. 43, 26580-26590. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2011927117
Profile:
Hawoong Jeong, Ph.D.
Professor
hjeong@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.11.13 View 13433 -
 X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 17793
X-ray Scattering Shines Light on Protein Folding
- Multiple forms of a non-functional, unfolded protein follow different pathways and timelines to reach its folded, functional state, a study reveals. -
KAIST researchers have used an X-ray method to track how proteins fold, which could improve computer simulations of this process, with implications for understanding diseases and improving drug discovery. Their findings were reported in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30.
When proteins are translated from their DNA codes, they quickly transform from a non-functional, unfolded state into their folded, functional state. Problems in folding can lead to diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Protein folding is one of the most important biological processes, as it forms the functioning 3D protein structure,” explained the physical chemist Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. Dr. Tae Wu Kim, the lead author of this research from Ihee’s group, added, “Understanding the mechanisms of protein folding is important, and could pave the way for disease study and drug development.”
Ihee’s team developed an approach using an X-ray scattering technique to uncover how the protein cytochrome c folds from its initial unfolded state. This protein is composed of a chain of 104 amino acids with an iron-containing heme molecule. It is often used for protein folding studies.
The researchers placed the protein in a solution and shined ultraviolet light on it. This process provides electrons to cytochrome c, reducing the iron within it from the ferric to the ferrous form, which initiates folding. As this was happening, the researchers beamed X-rays at very short intervals onto the sample. The X-rays scattered off all the atomic pairs in the sample and a detector continuously recorded the X-ray scattering patterns. The X-ray scattering patterns provided direct information regarding the 3D protein structure and the changes made in these patterns over time showed real-time motion of the protein during the folding process.
The team found cytochrome c proteins initially exist in a wide variety of unfolded states. Once the folding process is triggered, they stop by a group of intermediates within 31.6 microseconds, and then those intermediates follow different pathways with different folding times to reach an energetically stable folded state.
“We don’t know if this diversity in folding paths can be generalized to other proteins,” Ihee confessed. He continued, “However, we believe that our approach can be used to study other protein folding systems.”
Ihee hopes this approach can improve the accuracy of models that simulate protein interactions by including information on their unstructured states. These simulations are important as they can help identify barriers to proper folding and predict a protein’s folded state given its amino acid sequence. Ultimately, the models could help clarify how some diseases develop and how drugs interact with various protein structures.
Ihee’s group collaborated with Professor Young Min Rhee at the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and this work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS).
Figure. The scientists found that non-functional unfolded forms of the protein cytochrome c follow different pathways and timelines to reach a stable functional folded state.
Publications:
Kim, T. W., et al. (2020) ‘Protein folding from heterogeneous unfolded state revealed by time-resolved X-ray solution scattering’. PNAS. Volume 117. Issue 26. Page 14996-15005. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1913442117
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Young Min Rhee, Ph.D.
Professor
ymrhee@kaist.ac.kr
http://singlet.kaist.ac.kr
Rhee Research Group
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.07.09 View 17793 -
 Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 20874
Every Moment of Ultrafast Chemical Bonding Now Captured on Film
- The emerging moment of bond formation, two separate bonding steps, and subsequent vibrational motions were visualized. -
< Emergence of molecular vibrations and the evolution to covalent bonds observed in the research. Video Credit: KEK IMSS >
A team of South Korean researchers led by Professor Hyotcherl Ihee from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST reported the direct observation of the birthing moment of chemical bonds by tracking real-time atomic positions in the molecule. Professor Ihee, who also serves as Associate Director of the Center for Nanomaterials and Chemical Reactions at the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), conducted this study in collaboration with scientists at the Institute of Materials Structure Science of High Energy Accelerator Research Organization (KEK IMSS, Japan), RIKEN (Japan), and Pohang Accelerator Laboratory (PAL, South Korea). This work was published in Nature on June 24.
Targeted cancer drugs work by striking a tight bond between cancer cell and specific molecular targets that are involved in the growth and spread of cancer. Detailed images of such chemical bonding sites or pathways can provide key information necessary for maximizing the efficacy of oncogene treatments. However, atomic movements in a molecule have never been captured in the middle of the action, not even for an extremely simple molecule such as a triatomic molecule, made of only three atoms.
Professor Ihee's group and their international collaborators finally succeeded in capturing the ongoing reaction process of the chemical bond formation in the gold trimer. "The femtosecond-resolution images revealed that such molecular events took place in two separate stages, not simultaneously as previously assumed," says Professor Ihee, the corresponding author of the study. "The atoms in the gold trimer complex atoms remain in motion even after the chemical bonding is complete. The distance between the atoms increased and decreased periodically, exhibiting the molecular vibration. These visualized molecular vibrations allowed us to name the characteristic motion of each observed vibrational mode." adds Professor Ihee.
Atoms move extremely fast at a scale of femtosecond (fs) ― quadrillionths (or millionths of a billionth) of a second. Its movement is minute in the level of angstrom equal to one ten-billionth of a meter. They are especially elusive during the transition state where reaction intermediates are transitioning from reactants to products in a flash. The KAIST-IBS research team made this experimentally challenging task possible by using femtosecond x-ray liquidography (solution scattering). This experimental technique combines laser photolysis and x-ray scattering techniques. When a laser pulse strikes the sample, X-rays scatter and initiate the chemical bond formation reaction in the gold trimer complex. Femtosecond x-ray pulses obtained from a special light source called an x-ray free-electron laser (XFEL) were used to interrogate the bond-forming process. The experiments were performed at two XFEL facilities (4th generation linear accelerator) that are PAL-XFEL in South Korea and SACLA in Japan, and this study was conducted in collaboration with researchers from KEK IMSS, PAL, RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI).
Scattered waves from each atom interfere with each other and thus their x-ray scattering images are characterized by specific travel directions. The KAIST-IBS research team traced real-time positions of the three gold atoms over time by analyzing x-ray scattering images, which are determined by a three-dimensional structure of a molecule. Structural changes in the molecule complex resulted in multiple characteristic scattering images over time. When a molecule is excited by a laser pulse, multiple vibrational quantum states are simultaneously excited. The superposition of several excited vibrational quantum states is called a wave packet. The researchers tracked the wave packet in three-dimensional nuclear coordinates and found that the first half round of chemical bonding was formed within 35 fs after photoexcitation. The second half of the reaction followed within 360 fs to complete the entire reaction dynamics.
They also accurately illustrated molecular vibration motions in both temporal- and spatial-wise. This is quite a remarkable feat considering that such an ultrafast speed and a minute length of motion are quite challenging conditions for acquiring precise experimental data.
In this study, the KAIST-IBS research team improved upon their 2015 study published by Nature. In the previous study in 2015, the speed of the x-ray camera (time resolution) was limited to 500 fs, and the molecular structure had already changed to be linear with two chemical bonds within 500 fs. In this study, the progress of the bond formation and bent-to-linear structural transformation could be observed in real time, thanks to the improvement time resolution down to 100 fs. Thereby, the asynchronous bond formation mechanism in which two chemical bonds are formed in 35 fs and 360 fs, respectively, and the bent-to-linear transformation completed in 335 fs were visualized. In short, in addition to observing the beginning and end of chemical reactions, they reported every moment of the intermediate, ongoing rearrangement of nuclear configurations with dramatically improved experimental and analytical methods.
They will push this method of 'real-time tracking of atomic positions in a molecule and molecular vibration using femtosecond x-ray scattering' to reveal the mechanisms of organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and reactions involving proteins in the human body. "By directly tracking the molecular vibrations and real-time positions of all atoms in a molecule in the middle of reaction, we will be able to uncover mechanisms of various unknown organic and inorganic catalytic reactions and biochemical reactions," notes Dr. Jong Goo Kim, the lead author of the study.
Publications:
Kim, J. G., et al. (2020) ‘Mapping the emergence of molecular vibrations mediating bond formation’. Nature. Volume 582. Page 520-524. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2417-3
Profile: Hyotcherl Ihee, Ph.D.
Professor
hyotcherl.ihee@kaist.ac.kr
http://time.kaist.ac.kr/
Ihee Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
(END)
2020.06.24 View 20874 -
 Highly Efficient Charge-to-Spin Interconversion in Graphene Heterostructures
Researchers present a new route for designing a graphene-based active spintronic component
KAIST physicists described a route to design the energy-efficient generation, manipulation and detection of spin currents using nonmagnetic two-dimensional materials. The research team, led by Professor Sungjae Cho, observed highly efficient charge-to-spin interconversion via the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstien effect (REE) in graphene heterostructures.
This research paves the way for the application of graphene as an active spintronic component for generating, controlling, and detecting spin current without ferromagnetic electrodes or magnetic fields.
Graphene is a promising spintronic component owing to its long spin diffusion length. However, its small spin-orbit coupling limits the potential of graphene in spintronic applications since graphene cannot be used to generate, control, or detect spin current.
“We successfully increased the spin-orbit coupling of graphene by stacking graphene on top of 2H-TaS2, which is one of the transition metal dichalcogenide materials with the largest spin-orbit coupling. Graphene now can be used to generate, control, and detect spin current,” Professor Cho said.
The Rashba-Edelstein effect is a physical mechanism that enables charge current-to-spin current interconversion by spin-dependent band structure induced by the Rashba effect, a momentum-dependent splitting of spin bands in low-dimensional condensed matter systems.
Professor Cho’s group demonstrated the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstein effect in a multilayer graphene for the first time. The Rahsba-Edelstein effect allows the two-dimensional conduction electrons of graphene to be magnetized by an applied charge current and form a spin current. Furthermore, as the Fermi level of graphene, tuned by gate voltage, moves from the valence to conduction band, the spin current generated by graphene reversed its spin direction.
This spin reversal is useful in the design of low-power-consumption transistors utilizing spins in that it provides the carrier “On” state with spin up holes (or spin down electrons) and the "Off" state with zero net spin polarization at so called “charge neutrality point” where numbers of electrons and holes are equal.
“Our work is the first demonstration of charge-to-spin interconversion in a metallic TMD (transition-metal dichalcogenides) and graphene heterostructure with a spin polarization state controlled by a gate. We expect that the all-electrical spin-switching effect and the reversal of non-equilibrium spin polarization by the application of gate voltage is applicable for the energy-efficient generation and manipulation of spin currents using nonmagnetic van der Waals materials,” explained Professor Cho.
This study (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Lijun Li, Jin Zhang, Gyuho Myeong, Wongil Shin, Hongsik Lim, Boram Kim, Seungho Kim, Taehyeok Jin, Stuart Cavill, Beom Seo Kim, Changyoung Kim, Johannes Lischner, Aires Ferreira, and Sungjae Cho, Gate-Tunable Reversible Rashba−Edelstein Effect in a Few-Layer Graphene/2H-TaS2 Heterostructure at Room Temperature. ACS Nano 2020. Link to download the paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho, PhD
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
2020.05.18 View 11795
Highly Efficient Charge-to-Spin Interconversion in Graphene Heterostructures
Researchers present a new route for designing a graphene-based active spintronic component
KAIST physicists described a route to design the energy-efficient generation, manipulation and detection of spin currents using nonmagnetic two-dimensional materials. The research team, led by Professor Sungjae Cho, observed highly efficient charge-to-spin interconversion via the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstien effect (REE) in graphene heterostructures.
This research paves the way for the application of graphene as an active spintronic component for generating, controlling, and detecting spin current without ferromagnetic electrodes or magnetic fields.
Graphene is a promising spintronic component owing to its long spin diffusion length. However, its small spin-orbit coupling limits the potential of graphene in spintronic applications since graphene cannot be used to generate, control, or detect spin current.
“We successfully increased the spin-orbit coupling of graphene by stacking graphene on top of 2H-TaS2, which is one of the transition metal dichalcogenide materials with the largest spin-orbit coupling. Graphene now can be used to generate, control, and detect spin current,” Professor Cho said.
The Rashba-Edelstein effect is a physical mechanism that enables charge current-to-spin current interconversion by spin-dependent band structure induced by the Rashba effect, a momentum-dependent splitting of spin bands in low-dimensional condensed matter systems.
Professor Cho’s group demonstrated the gate-tunable Rashba-Edelstein effect in a multilayer graphene for the first time. The Rahsba-Edelstein effect allows the two-dimensional conduction electrons of graphene to be magnetized by an applied charge current and form a spin current. Furthermore, as the Fermi level of graphene, tuned by gate voltage, moves from the valence to conduction band, the spin current generated by graphene reversed its spin direction.
This spin reversal is useful in the design of low-power-consumption transistors utilizing spins in that it provides the carrier “On” state with spin up holes (or spin down electrons) and the "Off" state with zero net spin polarization at so called “charge neutrality point” where numbers of electrons and holes are equal.
“Our work is the first demonstration of charge-to-spin interconversion in a metallic TMD (transition-metal dichalcogenides) and graphene heterostructure with a spin polarization state controlled by a gate. We expect that the all-electrical spin-switching effect and the reversal of non-equilibrium spin polarization by the application of gate voltage is applicable for the energy-efficient generation and manipulation of spin currents using nonmagnetic van der Waals materials,” explained Professor Cho.
This study (https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Lijun Li, Jin Zhang, Gyuho Myeong, Wongil Shin, Hongsik Lim, Boram Kim, Seungho Kim, Taehyeok Jin, Stuart Cavill, Beom Seo Kim, Changyoung Kim, Johannes Lischner, Aires Ferreira, and Sungjae Cho, Gate-Tunable Reversible Rashba−Edelstein Effect in a Few-Layer Graphene/2H-TaS2 Heterostructure at Room Temperature. ACS Nano 2020. Link to download the paper: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsnano.0c01037
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho, PhD
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
2020.05.18 View 11795