AI
-
 Vietnamese Alumni of Korean S&T Universities Gather in Hanoi
(Vietnamese KAIST alumni gather in Hanoi on November 24.)
(Dr.Huong Minh Nguyen at the Institute of Biotechnology in the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). She is the representative of Vietnamese KAIST alumni.)
Some came from Ho Chi Minh and some even flew in from Singapore. For those KAIST alumni who gathered in Hanoi, the trip was well worth it. More than 100 Vietnamese alumni of KAIST, GIST, and UST attended the reunion in Hanoi on November 24. Presidents and vice president from three universities welcomed them and celebrated their successful careers after returning home or starting careers in other countries.
The reunion was co-hosted by KAIST, UST, and GIST in an effort to make a platform for continued networking for scientists who have studied at Korea’s science and technology universities. This joint reunion will be expected to include other science and technology universities and institutes in the future.
Among 1,873 international KAIST alumni from 106 countries, the number of Vietnamese graduates is the most dominant with 262 alumni, 14% of the total international alumni. Welcoming them, KAIST Vice President Soohyun Kim said that he was very impressed that all of the alumni are making a very impressive stride in their fields.
“You will be a big asset to make your country grow. You will also be a bridge for future collaborations with your institutions and KAIST and Korea. Vietnam holds great potential for future prosperity especially in science and technology and we look forward to seeing this network continue to benefit both countries.” Vice President Kim said all of the presidents shared the idea to make this gathering a regular event. “Other S&T universities will join to hold joint reunions in other countries in the future,” he added.
Dr. Huong Minh Nguyen at the Institute of Biotechnology in the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST) is one of 22 KAIST alumni who joined the reunion and supported the idea. She is also the representative of Vietnamese KAIST alumni. Dr. Nguyen, who earned her MS and PhD in the Department of Biological Sciences in 2013, spent five and half years at KAIST. “All the members at the lab were taking care of each other. When I joined the lab back then, they treated me as a ‘baby sister’ in a family and our relationship grew like a sister and brotherhood. I still appreciate the bonding relationship we could make with our colleagues.”
She cites a supporting culture, a competent educational system that places a focus on practicality, and rich resources that help researchers try whatever they want as the distinct advantages of a KAIST education.
“I never heard my professor saying “No” to any of my suggestions in conducting research. Professors and lab members put all their efforts, resources, and facilities to getting my research started. They helped me obtain all the resources that I needed. It was a huge encouragement to me,” she added.
She started her Masters, along with four Vietnamese colleagues, right after graduating from the Hanoi University of Natural Sciences, a top science university in Vietnam. Their experience at KAIST during a 4-week exchange program during undergraduates made them decide their academic destination without any doubt. All of them finished their PhDs in 2013. Two of them moved back home and the two others are now in the US and Germany as postdoctoral fellows.
“At that time, I could go to other countries for my further studies. But I already experienced KAIST for a month when I was an undergraduate, so I was not hesitant to go to KAIST. All of the classes are in English so, for students who do not speak in Korean, language does not bring any problems in studying and conducting research.”
She said that KAIST alumni are enjoying very successful careers in Vietnam and many foreign countries. “We do not have any problems choosing our careers back home and other countries we wanted to work in.”
However, like many PhD candidates who feel pressure about their studies and an uncertain future, her days at KAIST also included challenging times while adjusting to Korean culture. She took Korean classes for three semesters voluntarily at the KAIST Language Center to better understand Korea and her lab members. Her efforts paid off well. She could easily communicate with her colleagues and felt she became a real part of the inner group. But the stress remained to prove herself in research and she still had to deal with some bias.
“I know some people think Vietnam is behind Korea. Many people think that we are not as good as Korean students because we are from Vietnam. I desperately wanted to prove that I am as good as my peers.” Studying together with Korean and other international PhD candidates, she realized that everyone has their own purposes and pressures. “Even though there are minor differences, every PhD candidate has the same issues with their uncertain futures. It was quite comforting when we shared that it’s not only my problem. To understand that it’s a problem we all share comforts us a lot and we came to support each other.
To better help students release such pressure and stress, she said the university needs to create more diverse institutional channels to communicate with them. “Looking back, I was younger and less competent to speak up about when we were stressed and needed to ask for help. I hope students can begin to release their pressure and stress through diverse channels and resolve the problems,” she said.
Asked about her future plans, she replied, “I don’t think I can do anything better than what I am doing now. I enjoy what I am doing now at my institute. But in the near very future, I want to visit Korea and KAIST again.”
2018.11.27 View 3980
Vietnamese Alumni of Korean S&T Universities Gather in Hanoi
(Vietnamese KAIST alumni gather in Hanoi on November 24.)
(Dr.Huong Minh Nguyen at the Institute of Biotechnology in the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST). She is the representative of Vietnamese KAIST alumni.)
Some came from Ho Chi Minh and some even flew in from Singapore. For those KAIST alumni who gathered in Hanoi, the trip was well worth it. More than 100 Vietnamese alumni of KAIST, GIST, and UST attended the reunion in Hanoi on November 24. Presidents and vice president from three universities welcomed them and celebrated their successful careers after returning home or starting careers in other countries.
The reunion was co-hosted by KAIST, UST, and GIST in an effort to make a platform for continued networking for scientists who have studied at Korea’s science and technology universities. This joint reunion will be expected to include other science and technology universities and institutes in the future.
Among 1,873 international KAIST alumni from 106 countries, the number of Vietnamese graduates is the most dominant with 262 alumni, 14% of the total international alumni. Welcoming them, KAIST Vice President Soohyun Kim said that he was very impressed that all of the alumni are making a very impressive stride in their fields.
“You will be a big asset to make your country grow. You will also be a bridge for future collaborations with your institutions and KAIST and Korea. Vietnam holds great potential for future prosperity especially in science and technology and we look forward to seeing this network continue to benefit both countries.” Vice President Kim said all of the presidents shared the idea to make this gathering a regular event. “Other S&T universities will join to hold joint reunions in other countries in the future,” he added.
Dr. Huong Minh Nguyen at the Institute of Biotechnology in the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology (VAST) is one of 22 KAIST alumni who joined the reunion and supported the idea. She is also the representative of Vietnamese KAIST alumni. Dr. Nguyen, who earned her MS and PhD in the Department of Biological Sciences in 2013, spent five and half years at KAIST. “All the members at the lab were taking care of each other. When I joined the lab back then, they treated me as a ‘baby sister’ in a family and our relationship grew like a sister and brotherhood. I still appreciate the bonding relationship we could make with our colleagues.”
She cites a supporting culture, a competent educational system that places a focus on practicality, and rich resources that help researchers try whatever they want as the distinct advantages of a KAIST education.
“I never heard my professor saying “No” to any of my suggestions in conducting research. Professors and lab members put all their efforts, resources, and facilities to getting my research started. They helped me obtain all the resources that I needed. It was a huge encouragement to me,” she added.
She started her Masters, along with four Vietnamese colleagues, right after graduating from the Hanoi University of Natural Sciences, a top science university in Vietnam. Their experience at KAIST during a 4-week exchange program during undergraduates made them decide their academic destination without any doubt. All of them finished their PhDs in 2013. Two of them moved back home and the two others are now in the US and Germany as postdoctoral fellows.
“At that time, I could go to other countries for my further studies. But I already experienced KAIST for a month when I was an undergraduate, so I was not hesitant to go to KAIST. All of the classes are in English so, for students who do not speak in Korean, language does not bring any problems in studying and conducting research.”
She said that KAIST alumni are enjoying very successful careers in Vietnam and many foreign countries. “We do not have any problems choosing our careers back home and other countries we wanted to work in.”
However, like many PhD candidates who feel pressure about their studies and an uncertain future, her days at KAIST also included challenging times while adjusting to Korean culture. She took Korean classes for three semesters voluntarily at the KAIST Language Center to better understand Korea and her lab members. Her efforts paid off well. She could easily communicate with her colleagues and felt she became a real part of the inner group. But the stress remained to prove herself in research and she still had to deal with some bias.
“I know some people think Vietnam is behind Korea. Many people think that we are not as good as Korean students because we are from Vietnam. I desperately wanted to prove that I am as good as my peers.” Studying together with Korean and other international PhD candidates, she realized that everyone has their own purposes and pressures. “Even though there are minor differences, every PhD candidate has the same issues with their uncertain futures. It was quite comforting when we shared that it’s not only my problem. To understand that it’s a problem we all share comforts us a lot and we came to support each other.
To better help students release such pressure and stress, she said the university needs to create more diverse institutional channels to communicate with them. “Looking back, I was younger and less competent to speak up about when we were stressed and needed to ask for help. I hope students can begin to release their pressure and stress through diverse channels and resolve the problems,” she said.
Asked about her future plans, she replied, “I don’t think I can do anything better than what I am doing now. I enjoy what I am doing now at my institute. But in the near very future, I want to visit Korea and KAIST again.”
2018.11.27 View 3980 -
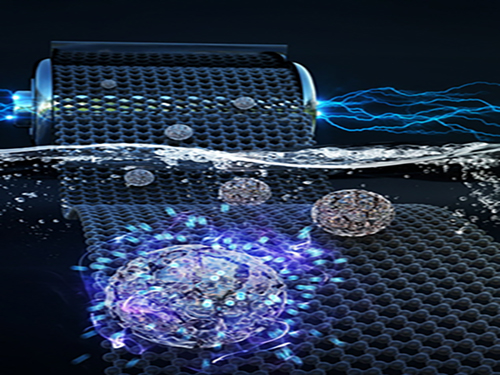 Faster and More Powerful Aqueous Hybrid Capacitor
(Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Graduate School of EEWS)
A KAIST research team made it one step closer to realizing safe energy storage with high energy density, high power density, and a longer cycle life. This hybrid storage alternative shows power density 100 times faster than conventional batteries, allowing it to be charged within a few seconds. Hence, it is suitable for small portable electronic devices.
Conventional electrochemical energy storage systems, including lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), have a high voltage range and energy density, but are subject to safety issues raised by flammable organic electrolytes, which are used to ensure the beneficial properties. Additionally, they suffer from slow electrochemical reaction rates, which lead to a poor charging rate and low power density with a capacity that fades quickly, resulting in a short cycle life.
On the other hand, capacitors based on aqueous electrolytes are receiving a great deal of attention because they are considered to be safe and environmentally friendly alternatives. However, aqueous electrolytes lag behind energy storage systems based on organic electrolytes in terms of energy density due to their limited voltage range and low capacitance.
Hence, developing aqueous energy storage with high energy density and a long cycle life in addition to the high power density that enables fast charging is the most challenging task for advancing next-generation electrochemical energy storage devices.
Here, Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team developed an aqueous hybrid capacitor (AHC) that boasts high energy density, high power, and excellent cycle stability by synthesizing two types of porous metal oxide nanoclusters on graphene to create positive and negative electrodes for AHCs.
The porous metal oxide nanoparticles are composed of nanoclusters as small as two to three nanometers and have mesopores that are smaller than five nanometers. In these porous structures, ions can be rapidly transferred to the material surfaces and a large number of ions can be stored inside the metal oxide particles very quickly due to their small particle size and large surface area.
The team applied porous manganese oxide on graphene for positive electrodes and porous iron oxide on graphene for negative electrodes to design an aqueous hybrid capacitor that can operate at an extended voltage range of 2V.
Professor Kang said, “This newly developed AHC with high capacity and power density driven from porous metal oxide electrodes will contribute to commercializing a new type of energy storage system. This technology allows ultra-fast charging within several seconds, making it suitable as a power source for mobile devices or electric vehicles where solar energy is directly stored as electricity.”
This research, co-led by Professor Hyung Mo Jeong from Kangwon National University, was published in Advanced Functional Materials on August 15, 2018.
Figure 1. Image that shows properties of porous metal oxide nanoparticles formed on graphene in the aqueous hybrid capacitor
2018.11.09 View 7682
Faster and More Powerful Aqueous Hybrid Capacitor
(Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Graduate School of EEWS)
A KAIST research team made it one step closer to realizing safe energy storage with high energy density, high power density, and a longer cycle life. This hybrid storage alternative shows power density 100 times faster than conventional batteries, allowing it to be charged within a few seconds. Hence, it is suitable for small portable electronic devices.
Conventional electrochemical energy storage systems, including lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), have a high voltage range and energy density, but are subject to safety issues raised by flammable organic electrolytes, which are used to ensure the beneficial properties. Additionally, they suffer from slow electrochemical reaction rates, which lead to a poor charging rate and low power density with a capacity that fades quickly, resulting in a short cycle life.
On the other hand, capacitors based on aqueous electrolytes are receiving a great deal of attention because they are considered to be safe and environmentally friendly alternatives. However, aqueous electrolytes lag behind energy storage systems based on organic electrolytes in terms of energy density due to their limited voltage range and low capacitance.
Hence, developing aqueous energy storage with high energy density and a long cycle life in addition to the high power density that enables fast charging is the most challenging task for advancing next-generation electrochemical energy storage devices.
Here, Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team developed an aqueous hybrid capacitor (AHC) that boasts high energy density, high power, and excellent cycle stability by synthesizing two types of porous metal oxide nanoclusters on graphene to create positive and negative electrodes for AHCs.
The porous metal oxide nanoparticles are composed of nanoclusters as small as two to three nanometers and have mesopores that are smaller than five nanometers. In these porous structures, ions can be rapidly transferred to the material surfaces and a large number of ions can be stored inside the metal oxide particles very quickly due to their small particle size and large surface area.
The team applied porous manganese oxide on graphene for positive electrodes and porous iron oxide on graphene for negative electrodes to design an aqueous hybrid capacitor that can operate at an extended voltage range of 2V.
Professor Kang said, “This newly developed AHC with high capacity and power density driven from porous metal oxide electrodes will contribute to commercializing a new type of energy storage system. This technology allows ultra-fast charging within several seconds, making it suitable as a power source for mobile devices or electric vehicles where solar energy is directly stored as electricity.”
This research, co-led by Professor Hyung Mo Jeong from Kangwon National University, was published in Advanced Functional Materials on August 15, 2018.
Figure 1. Image that shows properties of porous metal oxide nanoparticles formed on graphene in the aqueous hybrid capacitor
2018.11.09 View 7682 -
 KAIST Thanks Supporters for Building KAIST of Today
KAIST hosted its first Fundraising Gala on October 26, 2018. It was organized to demonstrate deep gratitude to those who have made contributions to KAIST, making it possible to progress every year.
The KAIST Development Foundation (KDF) endeavored to make a meaningful and inclusive event by collecting archives that show the history of donations while sending invitatio ns to all the members of KAIST, including donors and potential donors as well as professors and student representatives.
Approximately 200 distinguished guests attended the gala, including major donors, Chairperson of KDF Soo Young Lee and Chairman Beang Ho Kim, Former Minister of Science Dr. Geun Mo Jung, Former Minister of Science and Technology Woo Sik Kim, and KAIST alumni including the first Korean astronaut So-Yeon Yi.
(Student cheer leading club, ELKA)
At the gala, KAIST shared its 47 years of funding and an expenditure summary with major performances achieved from the year it was founded. According to the summary, KAIST has received more than 323.1 billion won since 1971. The total number of donors was 12,906 while the number of contribution reached 77,710.
Among the total funding (323.1 billion won), corporate gifts made up 43.1% of the total and individual gifts stood at 39.1%, showing that KAIST has received and is receiving support evenly from companies and individuals.
Taking a close look at the major donors, there is an interesting fact about KAIST’s fundraising culture. There has been continuous support from individuals who did not have any personal or academic ties with KAIST before donating. However, they have made large gifts to KAIST so that the best students in the fields of science and technology can be fostered for the sake of national development. The major donors included Young Han Kim (1999), Moon Soul Chung (2001), Byiung Joon Park (2007), Keun Chul Ryu (2008), Beong Ho Kim (2009), Chun Shik Cho and E won Oh (2010), Soo Young Lee (2012), Tae-won Chey (2014), Jeong Ja Cho (2015), and Chang Kun Sohn (2017).
Especially, M. S. Chung, B. H. Kim, C. S. Cho and S. Y. Lee made additional mega-gifts to KAIST, showing continuous support for KAIST’s development.
Nevertheless, the KAIST fundraising culture could not be created with major donors only. Among the total number of donors (12,906), alumni showed the strong engagement standing at 40.4% while parents and students were at 26.1% and 12.7% respectively. The contribution numbers follow the order of alumni (34.8%), parents (20.3%), staff (20%), professors (13.3%), and students (5.7%). These statistics imply that individual’s constant donations play a significant part in the fundraising culture of KAIST.
Additionally, engagement continues to rise every year, and it reached 12,039 gifts in 2017, which increased 5.7 times over ten years.
(from left: Executive Director of KDF Young-gul Kim KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
These valuable gifts are the vital fuel for KAIST’s progress. As of 2018, KAIST has spent 205.8 billion won: 81.9 billion won for construction and facilities operation, 79.7 billion won for academics and research, 39 billion won for academic management, and 5.2 billion won for scholarships.
The construction and facilities operation fund aided the evolution of physical infrastructure. KAIST endowed the ChungMoonSoul Building for promoting convergence between information and biotechnology, the Yang Bun Soon Building for bio and brain engineering studies, and the Chunghi & Byiung Jun Park KI Building for multi and interdisciplinary research. Their generous gifts built the foundation for KAIST taking off towards becoming a global leading university.
Meanwhile, the academic and research funds provided opportunities to professors and students to carry out creative research and academic missions. The academic management fund helped open new departments (i.e. The Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy) and their programs, for which their names came from the major donors.
(The first Korean astronaut So-Yeon Yi)
At the gala, special events were held for two exclusive moments that contributed to promoting and making a better image for KAIST to the public. One was the 10th anniversary of the space exploration of the first Korean astronaut Dr. Yi. The other was the 20th anniversary of the TV drama series, called ‘KAIST’ which was aired from 1999 to 2000. The writer and main casting crew members joined the event. They said that it was their first time to gather in one place after the show last aired and this event would be memorable for them as well.
President Sung-Chul Shin said, “These gifts play the role of seed money that helps KAIST obtain competence in a global scenario. I hope people have more interest in supporting KAIST through this event.”
1 Total Amount of Gift
2 Total Donors
3 Expenditure Number of Contribution
4 Expenditure
2018.10.29 View 7808
KAIST Thanks Supporters for Building KAIST of Today
KAIST hosted its first Fundraising Gala on October 26, 2018. It was organized to demonstrate deep gratitude to those who have made contributions to KAIST, making it possible to progress every year.
The KAIST Development Foundation (KDF) endeavored to make a meaningful and inclusive event by collecting archives that show the history of donations while sending invitatio ns to all the members of KAIST, including donors and potential donors as well as professors and student representatives.
Approximately 200 distinguished guests attended the gala, including major donors, Chairperson of KDF Soo Young Lee and Chairman Beang Ho Kim, Former Minister of Science Dr. Geun Mo Jung, Former Minister of Science and Technology Woo Sik Kim, and KAIST alumni including the first Korean astronaut So-Yeon Yi.
(Student cheer leading club, ELKA)
At the gala, KAIST shared its 47 years of funding and an expenditure summary with major performances achieved from the year it was founded. According to the summary, KAIST has received more than 323.1 billion won since 1971. The total number of donors was 12,906 while the number of contribution reached 77,710.
Among the total funding (323.1 billion won), corporate gifts made up 43.1% of the total and individual gifts stood at 39.1%, showing that KAIST has received and is receiving support evenly from companies and individuals.
Taking a close look at the major donors, there is an interesting fact about KAIST’s fundraising culture. There has been continuous support from individuals who did not have any personal or academic ties with KAIST before donating. However, they have made large gifts to KAIST so that the best students in the fields of science and technology can be fostered for the sake of national development. The major donors included Young Han Kim (1999), Moon Soul Chung (2001), Byiung Joon Park (2007), Keun Chul Ryu (2008), Beong Ho Kim (2009), Chun Shik Cho and E won Oh (2010), Soo Young Lee (2012), Tae-won Chey (2014), Jeong Ja Cho (2015), and Chang Kun Sohn (2017).
Especially, M. S. Chung, B. H. Kim, C. S. Cho and S. Y. Lee made additional mega-gifts to KAIST, showing continuous support for KAIST’s development.
Nevertheless, the KAIST fundraising culture could not be created with major donors only. Among the total number of donors (12,906), alumni showed the strong engagement standing at 40.4% while parents and students were at 26.1% and 12.7% respectively. The contribution numbers follow the order of alumni (34.8%), parents (20.3%), staff (20%), professors (13.3%), and students (5.7%). These statistics imply that individual’s constant donations play a significant part in the fundraising culture of KAIST.
Additionally, engagement continues to rise every year, and it reached 12,039 gifts in 2017, which increased 5.7 times over ten years.
(from left: Executive Director of KDF Young-gul Kim KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
These valuable gifts are the vital fuel for KAIST’s progress. As of 2018, KAIST has spent 205.8 billion won: 81.9 billion won for construction and facilities operation, 79.7 billion won for academics and research, 39 billion won for academic management, and 5.2 billion won for scholarships.
The construction and facilities operation fund aided the evolution of physical infrastructure. KAIST endowed the ChungMoonSoul Building for promoting convergence between information and biotechnology, the Yang Bun Soon Building for bio and brain engineering studies, and the Chunghi & Byiung Jun Park KI Building for multi and interdisciplinary research. Their generous gifts built the foundation for KAIST taking off towards becoming a global leading university.
Meanwhile, the academic and research funds provided opportunities to professors and students to carry out creative research and academic missions. The academic management fund helped open new departments (i.e. The Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation and the Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy) and their programs, for which their names came from the major donors.
(The first Korean astronaut So-Yeon Yi)
At the gala, special events were held for two exclusive moments that contributed to promoting and making a better image for KAIST to the public. One was the 10th anniversary of the space exploration of the first Korean astronaut Dr. Yi. The other was the 20th anniversary of the TV drama series, called ‘KAIST’ which was aired from 1999 to 2000. The writer and main casting crew members joined the event. They said that it was their first time to gather in one place after the show last aired and this event would be memorable for them as well.
President Sung-Chul Shin said, “These gifts play the role of seed money that helps KAIST obtain competence in a global scenario. I hope people have more interest in supporting KAIST through this event.”
1 Total Amount of Gift
2 Total Donors
3 Expenditure Number of Contribution
4 Expenditure
2018.10.29 View 7808 -
 Skin Hardness to Estimate Better Human Thermal Status
(Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher Sunghyun Yoon)
Under the same temperature and humidity, human thermal status may vary due to individual body constitution and climatic environment. A KAIST research team previously developed a wearable sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring. Furthering the development, this time they proposed skin hardness as an additional, independent physiological sign to estimate human thermal status more accurately. This novel approach can be applied to developing systems incorporating human-machine interaction, which requires accurate information about human thermal status.
Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had previously studied skin temperature and sweat rate to determine human thermal comfort, and developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor that accurately and steadily detects thermal comfort last February (title: Wearable Sweat Rate Sensors for Human Thermal Comfort Monitoring ).
However, skin temperature and sweat rate are still not enough to estimate exact human thermal comfort. Hence, an additional indicator is required for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the estimation and the team selected skin hardness. When people feel hot or cold, arrector pili muscles connected to hair follicles contract and expand, and skin hardness comes from this contraction and relaxation of the muscles. Based on the phenomenon of changing skin hardness, the team proposed skin hardness as a new indicator for measuring human thermal sensation.
With this new estimation model using three physiological signs for estimating human thermal status, the team conducted human experiments and verified that skin hardness is effective and independent from the two conventional physiological signs. Adding skin hardness to the conventional model can reduce errors by 23.5%, which makes its estimation more reliable.
The team will develop a sensor that detects skin hardness and applies it to cognitive air-conditioning and heating systems that better interact with humans than existing systems.
Professor Cho said, “Introducing this new indicator, skin hardness, elevates the reliability of measuring human thermal comfort regardless of individual body constitution and climatic environment. Based on this method, we can develop a personalized air conditioning and heating system that will allow affective interaction between humans and machines by sharing both physical and mental health conditions and emotions.”
This research, led by researchers Sunghyun Yoon and Jai Kyoung Sim, was published in Scientific Reports, Vol.8, Article No.12027 on August 13, 2018. (pp.1-6)
Figure 1. Measuring human thermal status through skin hardness
Figure 2. The instrument used for measuring human thermal status through skin hardness
2018.10.17 View 6521
Skin Hardness to Estimate Better Human Thermal Status
(Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher Sunghyun Yoon)
Under the same temperature and humidity, human thermal status may vary due to individual body constitution and climatic environment. A KAIST research team previously developed a wearable sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring. Furthering the development, this time they proposed skin hardness as an additional, independent physiological sign to estimate human thermal status more accurately. This novel approach can be applied to developing systems incorporating human-machine interaction, which requires accurate information about human thermal status.
Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had previously studied skin temperature and sweat rate to determine human thermal comfort, and developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor that accurately and steadily detects thermal comfort last February (title: Wearable Sweat Rate Sensors for Human Thermal Comfort Monitoring ).
However, skin temperature and sweat rate are still not enough to estimate exact human thermal comfort. Hence, an additional indicator is required for enhancing the accuracy and reliability of the estimation and the team selected skin hardness. When people feel hot or cold, arrector pili muscles connected to hair follicles contract and expand, and skin hardness comes from this contraction and relaxation of the muscles. Based on the phenomenon of changing skin hardness, the team proposed skin hardness as a new indicator for measuring human thermal sensation.
With this new estimation model using three physiological signs for estimating human thermal status, the team conducted human experiments and verified that skin hardness is effective and independent from the two conventional physiological signs. Adding skin hardness to the conventional model can reduce errors by 23.5%, which makes its estimation more reliable.
The team will develop a sensor that detects skin hardness and applies it to cognitive air-conditioning and heating systems that better interact with humans than existing systems.
Professor Cho said, “Introducing this new indicator, skin hardness, elevates the reliability of measuring human thermal comfort regardless of individual body constitution and climatic environment. Based on this method, we can develop a personalized air conditioning and heating system that will allow affective interaction between humans and machines by sharing both physical and mental health conditions and emotions.”
This research, led by researchers Sunghyun Yoon and Jai Kyoung Sim, was published in Scientific Reports, Vol.8, Article No.12027 on August 13, 2018. (pp.1-6)
Figure 1. Measuring human thermal status through skin hardness
Figure 2. The instrument used for measuring human thermal status through skin hardness
2018.10.17 View 6521 -
 Trigger of the Hyperactivation of Fibrosis Identified
(Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
Scientists have been investigating the negative effects that the hyperactivation of fibrosis has on fibrotic diseases and cancer. A KAIST research team unveiled a positive feedback loop that bi-stably activates fibroblasts in collaboration with Samsung Medical Center. This finding will contribute to developing therapeutic targets for both fibrosis and cancer.
Human fibroblasts are dormant in normal tissue, but show radical activation during wound healing. However, the principle that induces their explosive activation has not yet been identified.
Here, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Seok-Hyung Kim from Samsung Medical Center, discovered the principle of a circuit that continuously activates fibroblasts.
They constructed a positive feedback loops (PFLs) where Twist1, Prrx1, and Tenascin-C (TNC) molecules consecutively activate fibroblasts. They confirmed that these are the main inducers of fibroblast activation by conducting various experiments, including molecular biological tests, mathematical modeling, animal testing, and computer simulations to conclude that they are the main inducers of fibroblast activation.
According to their research, Twist 1 is a key regulator of cancer-associated fibroblasts, which directly upregulates Prrx1 and then triggers TNC, which also increases Twist1 expression. This circuit consequently forms a Twist-Prrx1-TNC positive feedback loop.
Activated fibroblasts need to be deactivated after wounds are healed. However, if the PFLs continue, the fibroblasts become the major cause of worsening fibrotic diseases and cancers.
Therefore, the team expects that Twist1-Prrx1-TNC positive PFLs will be applied for novel and effective therapeutic targeting of fibrotic diseases and cancers.
This research was published in Nature Communications on August 1, 2018.
Figure 1. Twist1 increases tenascin-c expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Twist1 is a potent but indirect inducer of tenascin-c (TNC), which is essential for maintaining Twist1 expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs).
Figure 2. Summary of the study. The Twist1-Prrx1-TNC positive feedback regulation provides clues for understanding the activation of fibroblasts during wound healing under normal conditions, as well as abnormally activated fibroblasts in pathological conditions such as cancerous and fibrotic diseases. Under normal conditions, the PFL acts as a reversible bistable switch by which the activation of fibroblasts is “ON" above a sufficient level of stimulation and “OFF" for the withdrawal of the stimulus. However, this switch can be permanently turned on under pathologic conditions by continued activation of the PFL, resulting in sustained proliferation of fibroblasts.
2018.10.11 View 6542
Trigger of the Hyperactivation of Fibrosis Identified
(Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering)
Scientists have been investigating the negative effects that the hyperactivation of fibrosis has on fibrotic diseases and cancer. A KAIST research team unveiled a positive feedback loop that bi-stably activates fibroblasts in collaboration with Samsung Medical Center. This finding will contribute to developing therapeutic targets for both fibrosis and cancer.
Human fibroblasts are dormant in normal tissue, but show radical activation during wound healing. However, the principle that induces their explosive activation has not yet been identified.
Here, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Seok-Hyung Kim from Samsung Medical Center, discovered the principle of a circuit that continuously activates fibroblasts.
They constructed a positive feedback loops (PFLs) where Twist1, Prrx1, and Tenascin-C (TNC) molecules consecutively activate fibroblasts. They confirmed that these are the main inducers of fibroblast activation by conducting various experiments, including molecular biological tests, mathematical modeling, animal testing, and computer simulations to conclude that they are the main inducers of fibroblast activation.
According to their research, Twist 1 is a key regulator of cancer-associated fibroblasts, which directly upregulates Prrx1 and then triggers TNC, which also increases Twist1 expression. This circuit consequently forms a Twist-Prrx1-TNC positive feedback loop.
Activated fibroblasts need to be deactivated after wounds are healed. However, if the PFLs continue, the fibroblasts become the major cause of worsening fibrotic diseases and cancers.
Therefore, the team expects that Twist1-Prrx1-TNC positive PFLs will be applied for novel and effective therapeutic targeting of fibrotic diseases and cancers.
This research was published in Nature Communications on August 1, 2018.
Figure 1. Twist1 increases tenascin-c expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Twist1 is a potent but indirect inducer of tenascin-c (TNC), which is essential for maintaining Twist1 expression in cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs).
Figure 2. Summary of the study. The Twist1-Prrx1-TNC positive feedback regulation provides clues for understanding the activation of fibroblasts during wound healing under normal conditions, as well as abnormally activated fibroblasts in pathological conditions such as cancerous and fibrotic diseases. Under normal conditions, the PFL acts as a reversible bistable switch by which the activation of fibroblasts is “ON" above a sufficient level of stimulation and “OFF" for the withdrawal of the stimulus. However, this switch can be permanently turned on under pathologic conditions by continued activation of the PFL, resulting in sustained proliferation of fibroblasts.
2018.10.11 View 6542 -
 Permanent, Wireless Self-charging System Using NIR Band
(Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability)
As wearable devices are emerging, there are numerous studies on wireless charging systems. Here, a KAIST research team has developed a permanent, wireless self-charging platform for low-power wearable electronics by converting near-infrared (NIR) band irradiation to electrical energy. This novel technology can be applied to flexible, wearable charging systems without needing any attachments.
Colloidal-quantum-dots (CQDs) are promising materials for manufacturing semiconductors; in particular, PbS-based CQDs have facile optical tunability from the visible to infrared wavelength region. Hence, they can be applied to various devices, such as lighting, photovoltaics (PVs), and photodetectors.
Continuous research on CQD-based optoelectronic devices has increased their power conversion efficiency (PCE) to 12%; however, applicable fields have not yet been found for them. Meanwhile, wearable electronic devices commonly face the problem of inconvenient charging systems because users have to constantly charge batteries attached to an energy source.
A joint team led by Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and Jang Wok Choi from Seoul National University decided to apply CQD PVs, which have high quantum efficiency in NIR band to self-charging systems on wearable devices.
They employed a stable and efficient NIR energy conversion strategy. The system was comprised of a PbS CQD-based PV module, a flexible interdigitated lithium-ion battery, and various types of NIR-transparent films.
The team removed the existing battery from the already commercialized wearable healthcare bracelet and replaced it with the proposed self-charging system. They confirmed that the system can be applied to a low power wearable device via the NIR band.
There have been numerous platforms using solar irradiation, but the newly developed platform has more advantages because it allows conventional devices to be much more comfortable to wear and charged easily in everyday life using various irradiation sources for constant charging.
With this aspect, the proposed platform facilitates more flexible designs, which are the important component for actual commercialization. It also secures higher photostability and efficient than existing structures.
Professor Lee said, “By using the NIR band, we proposed a new approach to solve charging system issues of wearable devices. I believe that this platform will be a novel platform for energy conversion and that its application can be further extended to various fields, including mobiles, IoTs, and drones.”
This research, led by PhD Se-Woong Baek and M.S. candidate Jungmin Cho, was published in Advanced Materials on May 11.
Figure 1. a) Conceptual NIR-driven self-charging system including a flexible CQD PVs module and an interdigitatedly structured LIB. b) Photographic images of a conventional wearable healthcare bracelet and a self-charging system-integrated wearable device.
Figure 2. Illustration of the CQD PVs structure and performance of the wireless self-charging platform.
2018.10.08 View 8476
Permanent, Wireless Self-charging System Using NIR Band
(Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability)
As wearable devices are emerging, there are numerous studies on wireless charging systems. Here, a KAIST research team has developed a permanent, wireless self-charging platform for low-power wearable electronics by converting near-infrared (NIR) band irradiation to electrical energy. This novel technology can be applied to flexible, wearable charging systems without needing any attachments.
Colloidal-quantum-dots (CQDs) are promising materials for manufacturing semiconductors; in particular, PbS-based CQDs have facile optical tunability from the visible to infrared wavelength region. Hence, they can be applied to various devices, such as lighting, photovoltaics (PVs), and photodetectors.
Continuous research on CQD-based optoelectronic devices has increased their power conversion efficiency (PCE) to 12%; however, applicable fields have not yet been found for them. Meanwhile, wearable electronic devices commonly face the problem of inconvenient charging systems because users have to constantly charge batteries attached to an energy source.
A joint team led by Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and Jang Wok Choi from Seoul National University decided to apply CQD PVs, which have high quantum efficiency in NIR band to self-charging systems on wearable devices.
They employed a stable and efficient NIR energy conversion strategy. The system was comprised of a PbS CQD-based PV module, a flexible interdigitated lithium-ion battery, and various types of NIR-transparent films.
The team removed the existing battery from the already commercialized wearable healthcare bracelet and replaced it with the proposed self-charging system. They confirmed that the system can be applied to a low power wearable device via the NIR band.
There have been numerous platforms using solar irradiation, but the newly developed platform has more advantages because it allows conventional devices to be much more comfortable to wear and charged easily in everyday life using various irradiation sources for constant charging.
With this aspect, the proposed platform facilitates more flexible designs, which are the important component for actual commercialization. It also secures higher photostability and efficient than existing structures.
Professor Lee said, “By using the NIR band, we proposed a new approach to solve charging system issues of wearable devices. I believe that this platform will be a novel platform for energy conversion and that its application can be further extended to various fields, including mobiles, IoTs, and drones.”
This research, led by PhD Se-Woong Baek and M.S. candidate Jungmin Cho, was published in Advanced Materials on May 11.
Figure 1. a) Conceptual NIR-driven self-charging system including a flexible CQD PVs module and an interdigitatedly structured LIB. b) Photographic images of a conventional wearable healthcare bracelet and a self-charging system-integrated wearable device.
Figure 2. Illustration of the CQD PVs structure and performance of the wireless self-charging platform.
2018.10.08 View 8476 -
 AI |QC ITRC Opens at KAIST
(from left: Dean of College of Engineering Jong-Hwan Kim, Director of AI│QC ITRC June-Koo Rhee, Vice President for R&DB Heekyung Park and Director General for Industrial Policy Hong Taek Yong)
Artificial Intelligence|The Quantum Computing Information Technology Research Center (AI|QC ITRC) opened at KAIST on October 2.
AI|QC ITRC, established with government funding, is the first institute specializing in quantum computing. Three universities (Seoul National University, Korea University, and Kyung Hee University), and four corporations, KT, Homomicus, Actusnetworks, and Mirae Tech are jointly participating in the center. Over four years, the institute will receive 3.2 billion KRW of research funds.
Last April, KAIST selected quantum technology as one of its flagship research areas. AI|QC ITRC will dedicate itself to developing quantum computing technology that provides the computability required for human-level artificial intelligence. It will also foster leaders in related industries by introducing industry-academic educational programs in graduate schools.
QC is receiving a great deal of attention for transcending current digital computers in terms of computability. World-class IT companies like IBM, Google, and Intel and ventures including D-Wave, Rigetti, and IonQ are currently leading the industry and investing heavily in securing source technologies.
Starting from the establishment of the ITRC, KAIST will continue to plan strategies to foster the field of QC. KAIST will carry out two-track strategies; one is to secure source technology of first-generation QC technology, and the other is to focus on basic research that can preoccupy next-generation QC technology.
Professor June-Koo Rhee, the director of AI│QC ITRC said, “I believe that QC will be the imperative technology that enables the realization of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. AIQC ITRC will foster experts required for domestic academia and industries and build a foundation to disseminate the technology to industries.”
Vice President for R&DB Heekyung Park, Director General for Industrial Policy Hong Taek Yong from the Ministry of Science and ICT, Seung Pyo Hong from the Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion, Head of Technology Strategy Jinhyon Youn from KT, and participating companies attended and celebrated the opening of the AI│QC ITRC.
2018.10.05 View 6948
AI |QC ITRC Opens at KAIST
(from left: Dean of College of Engineering Jong-Hwan Kim, Director of AI│QC ITRC June-Koo Rhee, Vice President for R&DB Heekyung Park and Director General for Industrial Policy Hong Taek Yong)
Artificial Intelligence|The Quantum Computing Information Technology Research Center (AI|QC ITRC) opened at KAIST on October 2.
AI|QC ITRC, established with government funding, is the first institute specializing in quantum computing. Three universities (Seoul National University, Korea University, and Kyung Hee University), and four corporations, KT, Homomicus, Actusnetworks, and Mirae Tech are jointly participating in the center. Over four years, the institute will receive 3.2 billion KRW of research funds.
Last April, KAIST selected quantum technology as one of its flagship research areas. AI|QC ITRC will dedicate itself to developing quantum computing technology that provides the computability required for human-level artificial intelligence. It will also foster leaders in related industries by introducing industry-academic educational programs in graduate schools.
QC is receiving a great deal of attention for transcending current digital computers in terms of computability. World-class IT companies like IBM, Google, and Intel and ventures including D-Wave, Rigetti, and IonQ are currently leading the industry and investing heavily in securing source technologies.
Starting from the establishment of the ITRC, KAIST will continue to plan strategies to foster the field of QC. KAIST will carry out two-track strategies; one is to secure source technology of first-generation QC technology, and the other is to focus on basic research that can preoccupy next-generation QC technology.
Professor June-Koo Rhee, the director of AI│QC ITRC said, “I believe that QC will be the imperative technology that enables the realization of the Fourth Industrial Revolution. AIQC ITRC will foster experts required for domestic academia and industries and build a foundation to disseminate the technology to industries.”
Vice President for R&DB Heekyung Park, Director General for Industrial Policy Hong Taek Yong from the Ministry of Science and ICT, Seung Pyo Hong from the Institute for Information & communications Technology Promotion, Head of Technology Strategy Jinhyon Youn from KT, and participating companies attended and celebrated the opening of the AI│QC ITRC.
2018.10.05 View 6948 -
 Improved Efficiency of CQD Solar Cells Using an Organic Thin Film
(from left: Professor Jung-Yong Lee and Dr. Se-Woong Baek)
Recently, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of colloidal quantum dot (CQD)-based solar cells has been enhanced, paving the way for their commercialization in various fields; nevertheless, they are still a long way from being commercialized due to their efficiency not matching their stability. In this research, a KAIST team achieved highly stable and efficient CQD-based solar cells by using an amorphous organic layer to block oxygen and water permeation.
CQD-based solar cells are light-weight, flexible, and they boost light harvesting by absorbing near-infrared lights. Especially, they draw special attention for their optical properties controlled efficiently by changing the quantum dot sizes. However, they are still incompatible with existing solar cells in terms of efficiency, stability, and cost. Therefore, there is great demand for a novel technology that can simultaneously improve both PCE and stability while using an inexpensive electrode material.
Responding to this demand, Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team introduced a technology to improve the efficiency and stability of CQD-based solar cells.
The team found that an amorphous organic thin film has a strong resistance to oxygen and water. Using these properties, they employed this doped organic layer as a top-hole selective layer (HSL) for the PbS CQD solar cells, and confirmed that the hydro/oxo-phobic properties of the layer efficiently protected the PbS layer. According to the molecular dynamics simulations, the layer significantly postponed the oxygen and water permeation into the PbS layer. Moreover, the efficient injection of the holes in the layer reduced interfacial resistance and improved performance.
With this technology, the team finally developed CQD-based solar cells with excellent stability. The PCE of their device stood at 11.7% and maintained over 90% of its initial performance when stored for one year under ambient conditions.
Professor Lee said, “This technology can be also applied to QD LEDs and Perovskite devices. I hope this technology can hasten the commercialization of CQD-based solar cells.”
This research, led by Dr. Se-Woong Baek and a Ph.D. student, Sang-Hoon Lee, was published in Energy & Environmental Science on May 10.
Figure 1. The schematic of the equilibrated structure of the amorphous organic film
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of CQD-based solar cells and graphs showing their performance
2018.08.27 View 8280
Improved Efficiency of CQD Solar Cells Using an Organic Thin Film
(from left: Professor Jung-Yong Lee and Dr. Se-Woong Baek)
Recently, the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of colloidal quantum dot (CQD)-based solar cells has been enhanced, paving the way for their commercialization in various fields; nevertheless, they are still a long way from being commercialized due to their efficiency not matching their stability. In this research, a KAIST team achieved highly stable and efficient CQD-based solar cells by using an amorphous organic layer to block oxygen and water permeation.
CQD-based solar cells are light-weight, flexible, and they boost light harvesting by absorbing near-infrared lights. Especially, they draw special attention for their optical properties controlled efficiently by changing the quantum dot sizes. However, they are still incompatible with existing solar cells in terms of efficiency, stability, and cost. Therefore, there is great demand for a novel technology that can simultaneously improve both PCE and stability while using an inexpensive electrode material.
Responding to this demand, Professor Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team introduced a technology to improve the efficiency and stability of CQD-based solar cells.
The team found that an amorphous organic thin film has a strong resistance to oxygen and water. Using these properties, they employed this doped organic layer as a top-hole selective layer (HSL) for the PbS CQD solar cells, and confirmed that the hydro/oxo-phobic properties of the layer efficiently protected the PbS layer. According to the molecular dynamics simulations, the layer significantly postponed the oxygen and water permeation into the PbS layer. Moreover, the efficient injection of the holes in the layer reduced interfacial resistance and improved performance.
With this technology, the team finally developed CQD-based solar cells with excellent stability. The PCE of their device stood at 11.7% and maintained over 90% of its initial performance when stored for one year under ambient conditions.
Professor Lee said, “This technology can be also applied to QD LEDs and Perovskite devices. I hope this technology can hasten the commercialization of CQD-based solar cells.”
This research, led by Dr. Se-Woong Baek and a Ph.D. student, Sang-Hoon Lee, was published in Energy & Environmental Science on May 10.
Figure 1. The schematic of the equilibrated structure of the amorphous organic film
Figure 2. Schematic illustration of CQD-based solar cells and graphs showing their performance
2018.08.27 View 8280 -
 Computer Simulation Identifies a Key Principle for Next-generation Carbon Fibers
(from left: Professor Yong-Hoon Kim and PhD candidate Juho Lee)
Performing state-of-the-art computer simulations, a KAIST research team identified an atomistic design principle to produce high-quality, next-generation carbon fibers.
Carbon fibers are light-weight yet excellent in mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Boasting these properties, they can be diversely applied in high-technology sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and nuclear engineering.
They are produced from a polymer precursor through a series of spinning, stabilization, and carbonization processes. However, there is a major obstacle to producing high-quality carbon fibers. That is, when there exist ill-defined regions within the polymer matrixes, they result in disorder and defects within the produced carbon fibers.
As a solution to this problem, it was proposed that the introduction of carbon nanotubes (CNT) could enhance polymer orientation and crystallization. However, although the alignment geometry of the CNT-polymer interface apparently affects the quality of produced fibers, the atomistic understanding of the CNT-polymer interface has been so far lacking, hindering further developments.
To clarify the nature of CNT-polymer interactions, Professor Yong-Hoon Kim from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team employed a multiscale approach that combines first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculations and force-fields molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and revealed the unique structural and electronic characteristics of polymer-CNT interfaces.
Here, they studied polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-CNT hybrid structures as a representative case of polymer-CNT composites. PAN is the most common polymer precursor, taking more than 90% of carbon fiber production.
Based on their DFT calculations, the team showed that the lying-down PAN configurations give a larger PAN-CNT binding energy than their standing-up counterparts. Moreover, maximizing the lying-down PAN configuration was shown to allow linear alignments of PANs on CNT, enabling the desirable ordered long-range PAN-PAN packing.
They also identified the CNT curvature as another significant factor, giving the largest PAN-CNT binding energy in the zero-curvature graphene limit. Conducting large-scale MD simulations, they then demonstrated that graphene nanoribbons are a promising carbon nano-reinforcement candidate by explicitly showing its strong propensity to induce linear alignments of PANs adsorbed on them.
Professor Kim said, “This research can be an exemplary case where the quantum mechanical simulations identify basic principles for developing advanced materials. Computer simulation studies will play an increasingly greater role thanks to the advances in the simulation theory and computer performance.”
This research, carried out by the PhD candidate Juho Lee, was published in the inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials on April 11.
Figure 1. Inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials
Figure 2. Research outline
2018.08.03 View 8508
Computer Simulation Identifies a Key Principle for Next-generation Carbon Fibers
(from left: Professor Yong-Hoon Kim and PhD candidate Juho Lee)
Performing state-of-the-art computer simulations, a KAIST research team identified an atomistic design principle to produce high-quality, next-generation carbon fibers.
Carbon fibers are light-weight yet excellent in mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Boasting these properties, they can be diversely applied in high-technology sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and nuclear engineering.
They are produced from a polymer precursor through a series of spinning, stabilization, and carbonization processes. However, there is a major obstacle to producing high-quality carbon fibers. That is, when there exist ill-defined regions within the polymer matrixes, they result in disorder and defects within the produced carbon fibers.
As a solution to this problem, it was proposed that the introduction of carbon nanotubes (CNT) could enhance polymer orientation and crystallization. However, although the alignment geometry of the CNT-polymer interface apparently affects the quality of produced fibers, the atomistic understanding of the CNT-polymer interface has been so far lacking, hindering further developments.
To clarify the nature of CNT-polymer interactions, Professor Yong-Hoon Kim from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team employed a multiscale approach that combines first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculations and force-fields molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and revealed the unique structural and electronic characteristics of polymer-CNT interfaces.
Here, they studied polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-CNT hybrid structures as a representative case of polymer-CNT composites. PAN is the most common polymer precursor, taking more than 90% of carbon fiber production.
Based on their DFT calculations, the team showed that the lying-down PAN configurations give a larger PAN-CNT binding energy than their standing-up counterparts. Moreover, maximizing the lying-down PAN configuration was shown to allow linear alignments of PANs on CNT, enabling the desirable ordered long-range PAN-PAN packing.
They also identified the CNT curvature as another significant factor, giving the largest PAN-CNT binding energy in the zero-curvature graphene limit. Conducting large-scale MD simulations, they then demonstrated that graphene nanoribbons are a promising carbon nano-reinforcement candidate by explicitly showing its strong propensity to induce linear alignments of PANs adsorbed on them.
Professor Kim said, “This research can be an exemplary case where the quantum mechanical simulations identify basic principles for developing advanced materials. Computer simulation studies will play an increasingly greater role thanks to the advances in the simulation theory and computer performance.”
This research, carried out by the PhD candidate Juho Lee, was published in the inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials on April 11.
Figure 1. Inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials
Figure 2. Research outline
2018.08.03 View 8508 -
 Taming AI: Engineering, Ethics, and Policy
(Professor Lee, Professor Koene, Professor Walsh, and Professor Ema (from left))
Can AI-powered robotics could be adequate companions for humans? Will the good faith of users and developers work for helping AI-powered robots become the new tribe of the digital future?
AI’s efficiency is creating new socio-economic opportunities in the global market. Despite the opportunities, challenges still remain. It is said that efficiency-enforcing algorithms through deep learning will take an eventual toll on human dignity and safety, bringing out the disastrous fiascos featured in the Terminator movies.
A research group at the Korean Flagship AI Project for Emotional Digital Companionship at KAIST Institute for AI (KI4AI) and the Fourth Industrial Intelligence Center at KAIST Institute co-hosted a seminar, “Taming AI: Engineering, Ethics, and Policy” last week to discuss ways to better employ AI technologies in ways that upholds human values.
The KI4AI has been conducting this flagship project from the end of 2016 with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
The seminar brought together three speakers from Australia, Japan, and the UK to better fathom the implications of the new technology emergence from the ethical perspectives of engineering and discuss policymaking for the responsible usage of technology.
Professor Toby Walsh, an anti-autonomous weapon activist from New South Wales University in Australia continued to argue the possible risk that AI poses to malfunction. He said that an independent ethics committee or group usually monitors academic institutions’ research activities in order to avoid any possible mishaps.
However, he said there is no independent group or committee monitoring the nature of corporations’ engagement of such technologies, while its possible threats against humanity are alleged to be growing. He mentioned that Google’s and Amazon’s information collecting also pose a potent threat. He said that ethical standards similar to academic research integrity should be established to avoid the possible restricting of the dignity of humans and mass destruction. He hoped that KAIST and Google would play a leading role in establishing an international norm toward this compelling issue.
Professor Arisa Ema from the University of Tokyo provided very compelling arguments for thinking about the duplicity of technology and how technology should serve the public interest without any bias against gender, race, and social stratum. She pointed out the information dominated by several Western corporations like Google. She said that such algorithms for deep learning of data provided by several Western corporations will create very biased information, only applicable to limited races and classes.
Meanwhile, Professor Ansgar Koene from the University of Nottingham presented the IEEE’s global initiative on the ethics of autonomous and intelligence systems. He shared the cases of industry standards and ethically-aligned designs made by the IEEE Standards Association. He said more than 250 global cross-disciplinary thought leaders from around the world joined to develop ethical guidelines called Ethically Aligned Design (EAD) V2. EAD V2 includes methodologies to guide ethical research and design, embedding values into autonomous intelligence systems among others. For the next step beyond EAD V2, the association is now working for IEEE P70xx Standards Projects, detailing more technical approaches.
Professor Soo Young Lee at KAIST argued that the eventual goal of complete AI is to have human-like emotions, calling it a new paradigm for the relationship between humans and AI-robots. According to Professor Lee, AI-powered robots will serve as a good companion for humans. “Especially in aging societies affecting the globe, this will be a very viable and practical option,” he said.
He pointed out, “Kids learn from parents’ morality and social behavior. Users should have AI-robots learn morality as well. Their relationships should be based on good faith and trust, no longer that of master and slave. He said that liability issues for any mishap will need to be discussed further, but basically each user and developer should have their own responsibility when dealing with these issues.
2018.06.26 View 9103
Taming AI: Engineering, Ethics, and Policy
(Professor Lee, Professor Koene, Professor Walsh, and Professor Ema (from left))
Can AI-powered robotics could be adequate companions for humans? Will the good faith of users and developers work for helping AI-powered robots become the new tribe of the digital future?
AI’s efficiency is creating new socio-economic opportunities in the global market. Despite the opportunities, challenges still remain. It is said that efficiency-enforcing algorithms through deep learning will take an eventual toll on human dignity and safety, bringing out the disastrous fiascos featured in the Terminator movies.
A research group at the Korean Flagship AI Project for Emotional Digital Companionship at KAIST Institute for AI (KI4AI) and the Fourth Industrial Intelligence Center at KAIST Institute co-hosted a seminar, “Taming AI: Engineering, Ethics, and Policy” last week to discuss ways to better employ AI technologies in ways that upholds human values.
The KI4AI has been conducting this flagship project from the end of 2016 with the support of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
The seminar brought together three speakers from Australia, Japan, and the UK to better fathom the implications of the new technology emergence from the ethical perspectives of engineering and discuss policymaking for the responsible usage of technology.
Professor Toby Walsh, an anti-autonomous weapon activist from New South Wales University in Australia continued to argue the possible risk that AI poses to malfunction. He said that an independent ethics committee or group usually monitors academic institutions’ research activities in order to avoid any possible mishaps.
However, he said there is no independent group or committee monitoring the nature of corporations’ engagement of such technologies, while its possible threats against humanity are alleged to be growing. He mentioned that Google’s and Amazon’s information collecting also pose a potent threat. He said that ethical standards similar to academic research integrity should be established to avoid the possible restricting of the dignity of humans and mass destruction. He hoped that KAIST and Google would play a leading role in establishing an international norm toward this compelling issue.
Professor Arisa Ema from the University of Tokyo provided very compelling arguments for thinking about the duplicity of technology and how technology should serve the public interest without any bias against gender, race, and social stratum. She pointed out the information dominated by several Western corporations like Google. She said that such algorithms for deep learning of data provided by several Western corporations will create very biased information, only applicable to limited races and classes.
Meanwhile, Professor Ansgar Koene from the University of Nottingham presented the IEEE’s global initiative on the ethics of autonomous and intelligence systems. He shared the cases of industry standards and ethically-aligned designs made by the IEEE Standards Association. He said more than 250 global cross-disciplinary thought leaders from around the world joined to develop ethical guidelines called Ethically Aligned Design (EAD) V2. EAD V2 includes methodologies to guide ethical research and design, embedding values into autonomous intelligence systems among others. For the next step beyond EAD V2, the association is now working for IEEE P70xx Standards Projects, detailing more technical approaches.
Professor Soo Young Lee at KAIST argued that the eventual goal of complete AI is to have human-like emotions, calling it a new paradigm for the relationship between humans and AI-robots. According to Professor Lee, AI-powered robots will serve as a good companion for humans. “Especially in aging societies affecting the globe, this will be a very viable and practical option,” he said.
He pointed out, “Kids learn from parents’ morality and social behavior. Users should have AI-robots learn morality as well. Their relationships should be based on good faith and trust, no longer that of master and slave. He said that liability issues for any mishap will need to be discussed further, but basically each user and developer should have their own responsibility when dealing with these issues.
2018.06.26 View 9103 -
 Printed Thermo-Plasmonic Heat Patterns for Neurological Disorder Treatment
(Professor Nam and Dr. Kang, right)
A KAIST team presented a highly customizable neural stimulation method. The research team developed a technology that can print the heat pattern on a micron scale to enable the control of biological activities remotely.
The researchers integrated a precision inkjet printing technology with bio-functional thermo-plasmonic nanoparticles to achieve a ‘selective nano-photothermal neural stimulation method.’
The research team of Professor Yoonkey Nam at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering expects this will serve as an enabling technology for personalized precision neuromodulation therapy for patients with neurological disorders.
The nano-photothermal neural stimulation method uses the thermo-plasmonic effect of metal nanoparticles to modulate the activities of neuronal networks. With the thermo-plasmonic effect, metal nanoparticles can absorb specific wavelength of illuminated light to efficiently generate localized heat. The research team discovered the inhibitory behavior of spontaneous activities of neurons upon photothermal stimulation four years ago. Since then, they have developed this technology to control hyperactive behaviors of neurons and neural circuits, which is often found in neurological disorders such as epilepsy.
In order to overcome the limitation on the spatial selectivity and resolution of the previously developed nano-photothermal method, the team adopted an inkjet printing technology to micro pattern the plasmonic nanoparticles (a few tens of microns), and successfully demonstrated that the nano-photothermal stimulation can be selectively applied according to the printed patterns.
The researchers applied a polyelectrolyte layer-by-layer coating method to printing substrates in a way to improve the pattern fidelity and achieve the uniform assembly of nanoparticles. The electrostatic attraction between the printed nanoparticles and the coated printing substrate also helped the stability of the attached nanoparticles. Because the polyelectrolyte coating is biocompatible, biological experiments including cell culture are possible with the technology developed in this work.
Using printed gold nanorod particles in a few tens of microns resolution over a several centimeters area, the researchers showed that highly complex heat patterns can be precisely formed upon light illumination according to the printing image.
Lastly, the team confirmed that the printed heat patterns can selectively and instantaneously inhibit the activities of cultured hippocampal neurons upon near-infrared light illumination. Because the printing process is applicable to thin and flexible substrates, the technology can be easily applied to implantable neurological disorder treatment devices and wearable devices. By selectively applying the heat patterns to only the desired cellular areas, customized and personalized photothermal neuromodulation therapy can be applied to patients.
“The fact that any desired heat patterns can be simply ‘printed’ anywhere broadens the applicability of this technology in many engineering fields. In bioengineering, it can be applied to neural interfaces using light and heat to modulate physiological functions. As another engineering application, for example, printed heat patterns can be used as a new concept of anti-counterfeit applications,” said the principal investigator, Yoonkey Nam at KAIST. This work, led mainly by Dr. Hongki Kang, was published in ACS Nano on February 5th 2018.
2018.04.06 View 7115
Printed Thermo-Plasmonic Heat Patterns for Neurological Disorder Treatment
(Professor Nam and Dr. Kang, right)
A KAIST team presented a highly customizable neural stimulation method. The research team developed a technology that can print the heat pattern on a micron scale to enable the control of biological activities remotely.
The researchers integrated a precision inkjet printing technology with bio-functional thermo-plasmonic nanoparticles to achieve a ‘selective nano-photothermal neural stimulation method.’
The research team of Professor Yoonkey Nam at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering expects this will serve as an enabling technology for personalized precision neuromodulation therapy for patients with neurological disorders.
The nano-photothermal neural stimulation method uses the thermo-plasmonic effect of metal nanoparticles to modulate the activities of neuronal networks. With the thermo-plasmonic effect, metal nanoparticles can absorb specific wavelength of illuminated light to efficiently generate localized heat. The research team discovered the inhibitory behavior of spontaneous activities of neurons upon photothermal stimulation four years ago. Since then, they have developed this technology to control hyperactive behaviors of neurons and neural circuits, which is often found in neurological disorders such as epilepsy.
In order to overcome the limitation on the spatial selectivity and resolution of the previously developed nano-photothermal method, the team adopted an inkjet printing technology to micro pattern the plasmonic nanoparticles (a few tens of microns), and successfully demonstrated that the nano-photothermal stimulation can be selectively applied according to the printed patterns.
The researchers applied a polyelectrolyte layer-by-layer coating method to printing substrates in a way to improve the pattern fidelity and achieve the uniform assembly of nanoparticles. The electrostatic attraction between the printed nanoparticles and the coated printing substrate also helped the stability of the attached nanoparticles. Because the polyelectrolyte coating is biocompatible, biological experiments including cell culture are possible with the technology developed in this work.
Using printed gold nanorod particles in a few tens of microns resolution over a several centimeters area, the researchers showed that highly complex heat patterns can be precisely formed upon light illumination according to the printing image.
Lastly, the team confirmed that the printed heat patterns can selectively and instantaneously inhibit the activities of cultured hippocampal neurons upon near-infrared light illumination. Because the printing process is applicable to thin and flexible substrates, the technology can be easily applied to implantable neurological disorder treatment devices and wearable devices. By selectively applying the heat patterns to only the desired cellular areas, customized and personalized photothermal neuromodulation therapy can be applied to patients.
“The fact that any desired heat patterns can be simply ‘printed’ anywhere broadens the applicability of this technology in many engineering fields. In bioengineering, it can be applied to neural interfaces using light and heat to modulate physiological functions. As another engineering application, for example, printed heat patterns can be used as a new concept of anti-counterfeit applications,” said the principal investigator, Yoonkey Nam at KAIST. This work, led mainly by Dr. Hongki Kang, was published in ACS Nano on February 5th 2018.
2018.04.06 View 7115 -
 Aqueous Storage Device Needs Only 20 Seconds to Go
(from left: PhD candidate Il Woo Ock and Professor Jeung Ku Kang)
A KAIST research team developed a new hybrid energy storage device that can be charged in less than half a minute. It employs aqueous electrolytes instead of flammable organic solvents, so it is both environmentally friendly and safe. It also facilitates a boosting charge with high energy density, which makes it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability developed this hybrid energy storage with high energy and power densities along over a long cycle life by assembling fibre-like polymer chain anodes and sub-nanoscale metal oxide cathodes on graphene.
Conventional aqueous electrolyte-based energy storage devices have a limitation for boosting charges and high energy density due to low driving voltage and a shortage of anode materials.
Energy storage device capacity is determined by the two electrodes, and the balance between cathode and anode leads to high stability. In general, two electrodes show differences in electrical properties and differ in ion storage mechanism processes, resulting in poor storage and stability from the imbalance.
The research team came up with new structures and materials to facilitate rapid speed in energy exchange on the surfaces of the electrodes and minimize the energy loss between the two electrodes.
The team made anodes with graphene-based polymer chain materials. The web-like structure of graphene leads to a high surface area, thereby allowing higher capacitance.
For cathode materials, the team used metal oxide in sub-nanoscale structures to elevate atom-by-ion redox reactions. This method realized higher energy density and faster energy exchange while minimizing energy loss.
The developed device can be charged within 20 to 30 seconds using a low-power charging system, such as a USB switching charger or a flexible photovoltaic cell. The developed aqueous hybrid energy device shows more than 100-fold higher power density compared to conventional aqueous batteries and can be rapidly recharged. Further, the device showed high stability with its capacity maintained at 100% at a high charge/discharge current.
Professor Kang said, “This eco-friendly technology can be easily manufactured and is highly applicable. In particular, its high capacity and high stability, compared to existing technologies, could contribute to the commercialization of aqueous capacitors. The device can be rapidly charged using a low-power charging system, and thus can be applied to portable electronic device.”
This research, led by a PhD candidate Il Woo Ock, was published in Advanced Energy Materials on January 15.
Figure 1. Switching wearable LED kit with two AHCs in series charged by a flexible photovoltaic cell
Figure 2. Schematic diagram for aqueous hybrid capacitors
Figure 3. TEM images of anode and cathode
2018.02.28 View 12786
Aqueous Storage Device Needs Only 20 Seconds to Go
(from left: PhD candidate Il Woo Ock and Professor Jeung Ku Kang)
A KAIST research team developed a new hybrid energy storage device that can be charged in less than half a minute. It employs aqueous electrolytes instead of flammable organic solvents, so it is both environmentally friendly and safe. It also facilitates a boosting charge with high energy density, which makes it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability developed this hybrid energy storage with high energy and power densities along over a long cycle life by assembling fibre-like polymer chain anodes and sub-nanoscale metal oxide cathodes on graphene.
Conventional aqueous electrolyte-based energy storage devices have a limitation for boosting charges and high energy density due to low driving voltage and a shortage of anode materials.
Energy storage device capacity is determined by the two electrodes, and the balance between cathode and anode leads to high stability. In general, two electrodes show differences in electrical properties and differ in ion storage mechanism processes, resulting in poor storage and stability from the imbalance.
The research team came up with new structures and materials to facilitate rapid speed in energy exchange on the surfaces of the electrodes and minimize the energy loss between the two electrodes.
The team made anodes with graphene-based polymer chain materials. The web-like structure of graphene leads to a high surface area, thereby allowing higher capacitance.
For cathode materials, the team used metal oxide in sub-nanoscale structures to elevate atom-by-ion redox reactions. This method realized higher energy density and faster energy exchange while minimizing energy loss.
The developed device can be charged within 20 to 30 seconds using a low-power charging system, such as a USB switching charger or a flexible photovoltaic cell. The developed aqueous hybrid energy device shows more than 100-fold higher power density compared to conventional aqueous batteries and can be rapidly recharged. Further, the device showed high stability with its capacity maintained at 100% at a high charge/discharge current.
Professor Kang said, “This eco-friendly technology can be easily manufactured and is highly applicable. In particular, its high capacity and high stability, compared to existing technologies, could contribute to the commercialization of aqueous capacitors. The device can be rapidly charged using a low-power charging system, and thus can be applied to portable electronic device.”
This research, led by a PhD candidate Il Woo Ock, was published in Advanced Energy Materials on January 15.
Figure 1. Switching wearable LED kit with two AHCs in series charged by a flexible photovoltaic cell
Figure 2. Schematic diagram for aqueous hybrid capacitors
Figure 3. TEM images of anode and cathode
2018.02.28 View 12786