NT
-
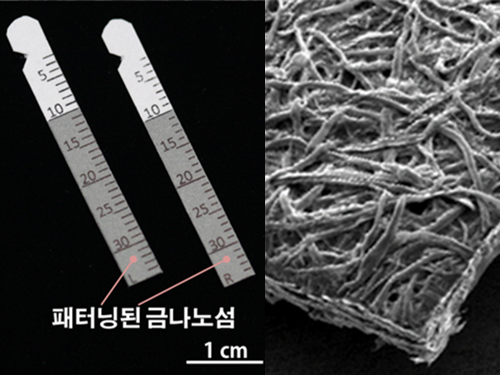 Gout Diagnostic Strip Using a Single Teardrop
A novel diagnostic strip for gout patients using a single teardrop has been announced by KAIST research team. This technology analyzes biological molecules in tears for a non-invasive diagnosis, significantly reducing the time and expense previously required for a diagnosis.
The research team under Professor Ki-Hun Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in developing an affordable and elaborate gout diagnostic strip by depositing metal nanoparticles on paper. This technology can not only be used in diagnostic medicine and drug testing, but also in various other areas such as field diagnoses that require prompt and accurate detection of a certain substance.
Gout induces pain in joints due to needle-shaped uric acid crystal build up. In general, therapeutic treatments exist to administer pain relief, stimulate uric acid discharge, and uric acid depressant. Such treatments work for temporary relief, but there have significant limitations. Thus, patients are required to regularly check uric acid concentrations, as well as control their diets. Therefore, simpler ways to measure uric acid would greatly benefit gout control and its prevention in a more affordable and convenient manner.
Existing gout diagnostic techniques include measuring uric acid concentrations from blood samples or observing uric acid crystals from joint synovial fluid under a microscope. These existing methods are invasive and time consuming. To overcome their limitations, the research team uniformly deposited gold nanoislands with nanoplasnomics properties on the surface of paper that can easily collect tears.
Nanoplasnomics techniques collect light on the surface of a metal nanostructure, and can be applied to disease and health diagnostic indicators as well as for genetic material detection. Further, metals such as gold absorb stronger light when it is irradiated, and thus can maximize light concentration on board surfaces while maintaining the properties of paper. The developed metal nanostructure production technology allows the flexible manufacturing of nanostructures on a large surface, which in turn allows flexible control of light concentrations.
The research team grafted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on paper diagnostic strips to allow uric acid concentration measurements in teardrops without additional indicators. The measured concentration in teardrops can be compared to blood uric acid concentrations for diagnosing gout.
Professor Jeong explained, “Based on these research results, our strip will make it possible to conduct low-cost, no indicator, supersensitive biological molecule analysis and fast field diagnosis using tears.” He continued, “Tears, as well as various other bodily fluids, can be used to contribute to disease diagnosis and physiological functional research.”
Ph.D. candidate Moonseong Park participated in the research as the first author of the paper that was published in the online edition of ACS Nano on December 14, 2016. Park said, “The strip will allow fast and simple field diagnosis, and can be produced on a large scale using the existing semiconductor process.”
(Figure 1. Optical image of paper gout diagnostic strip covered with gold)
(Figure 2. Scanning delectron microscopic image of paper gout diagnostic strip)
(Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope image of cellulos fiber coated with gold nanoislands)
(Figure 4. Gout diagnosis using tears)
2017.04.27 View 8791
Gout Diagnostic Strip Using a Single Teardrop
A novel diagnostic strip for gout patients using a single teardrop has been announced by KAIST research team. This technology analyzes biological molecules in tears for a non-invasive diagnosis, significantly reducing the time and expense previously required for a diagnosis.
The research team under Professor Ki-Hun Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in developing an affordable and elaborate gout diagnostic strip by depositing metal nanoparticles on paper. This technology can not only be used in diagnostic medicine and drug testing, but also in various other areas such as field diagnoses that require prompt and accurate detection of a certain substance.
Gout induces pain in joints due to needle-shaped uric acid crystal build up. In general, therapeutic treatments exist to administer pain relief, stimulate uric acid discharge, and uric acid depressant. Such treatments work for temporary relief, but there have significant limitations. Thus, patients are required to regularly check uric acid concentrations, as well as control their diets. Therefore, simpler ways to measure uric acid would greatly benefit gout control and its prevention in a more affordable and convenient manner.
Existing gout diagnostic techniques include measuring uric acid concentrations from blood samples or observing uric acid crystals from joint synovial fluid under a microscope. These existing methods are invasive and time consuming. To overcome their limitations, the research team uniformly deposited gold nanoislands with nanoplasnomics properties on the surface of paper that can easily collect tears.
Nanoplasnomics techniques collect light on the surface of a metal nanostructure, and can be applied to disease and health diagnostic indicators as well as for genetic material detection. Further, metals such as gold absorb stronger light when it is irradiated, and thus can maximize light concentration on board surfaces while maintaining the properties of paper. The developed metal nanostructure production technology allows the flexible manufacturing of nanostructures on a large surface, which in turn allows flexible control of light concentrations.
The research team grafted surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy on paper diagnostic strips to allow uric acid concentration measurements in teardrops without additional indicators. The measured concentration in teardrops can be compared to blood uric acid concentrations for diagnosing gout.
Professor Jeong explained, “Based on these research results, our strip will make it possible to conduct low-cost, no indicator, supersensitive biological molecule analysis and fast field diagnosis using tears.” He continued, “Tears, as well as various other bodily fluids, can be used to contribute to disease diagnosis and physiological functional research.”
Ph.D. candidate Moonseong Park participated in the research as the first author of the paper that was published in the online edition of ACS Nano on December 14, 2016. Park said, “The strip will allow fast and simple field diagnosis, and can be produced on a large scale using the existing semiconductor process.”
(Figure 1. Optical image of paper gout diagnostic strip covered with gold)
(Figure 2. Scanning delectron microscopic image of paper gout diagnostic strip)
(Figure 3. Scanning electron microscope image of cellulos fiber coated with gold nanoislands)
(Figure 4. Gout diagnosis using tears)
2017.04.27 View 8791 -
 Professor Duck-Joo Lee Awarded the 21st Century Grand Prize
Professor Duck-Joo Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering was awarded the 21st Century Grand Prize in the field of technology development by the New Industry Management Academy and the 21st Leaders Club on April 13.
Professor Lee was honored in recognition of his contribution to the helicopter industry. He played a part in domestic helicopter development projects including the KUH-1 Surion (Korean Attack Helicopter), a twin-engine, transport utility helicopter as well as LAH (Light Armed Helicopter) and LCH (Light Civil Helicopter) projects.
Since joining KAIST in 1988, Professor Lee supervised more than 26 PhDs and 27 MSs. He was responsible for hosting the 1st Asian-Australian Rotorcraft Forum and Exhibition and currently serves as vice president of the American Helicopter Society and the Korea Drone Industry Promotion Association. He also participated in open online courses on K-MOOC and Coursera.
(Caption: Professor Lee (second from left in the first row) poses after receiving the award.)
2017.04.26 View 7716
Professor Duck-Joo Lee Awarded the 21st Century Grand Prize
Professor Duck-Joo Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering was awarded the 21st Century Grand Prize in the field of technology development by the New Industry Management Academy and the 21st Leaders Club on April 13.
Professor Lee was honored in recognition of his contribution to the helicopter industry. He played a part in domestic helicopter development projects including the KUH-1 Surion (Korean Attack Helicopter), a twin-engine, transport utility helicopter as well as LAH (Light Armed Helicopter) and LCH (Light Civil Helicopter) projects.
Since joining KAIST in 1988, Professor Lee supervised more than 26 PhDs and 27 MSs. He was responsible for hosting the 1st Asian-Australian Rotorcraft Forum and Exhibition and currently serves as vice president of the American Helicopter Society and the Korea Drone Industry Promotion Association. He also participated in open online courses on K-MOOC and Coursera.
(Caption: Professor Lee (second from left in the first row) poses after receiving the award.)
2017.04.26 View 7716 -
 Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 9322
Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 9322 -
 KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 8852
KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 8852 -
 FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 8955
FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 8955 -
 Newdin Contents Donates 'Strikezon'
Newdin Contents, an online and mobile game maker, made a gift of ‘Strikezon' to KAIST on April 19. The screen game valued at 100 million KRW will be placed in the lobby of the School of Computing, enriching the diverse physical activity options for the KAIST community. The donation was made at a ceremony attended by KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the CEO of the Newdin, Hyo-Kyum Kim, and Head of the School of Computing Professor Myoung Ho Kim.
At the Strikezon, students can enjoy mini baseball games indoors including a batting challenge and a pitching mode indoors for free.
President Shin thanked Mr. Kim of Newdin Contents, saying the donation will be a stepping stone for possible mutual collaborations which will play a synergistic role for technological development. Mr. Kim noted, “We are very pleased to donate the program to KAIST, which is the alma mater of Joon-Mo Hwang, the developer of Strikezon.” He added that Newdin Contents will make every effort to produce advanced game products with state of the art technology.
(Photo caption:President Sung-Chul Shin hits the ball at the Strikezon on April 19.)
2017.04.19 View 4839
Newdin Contents Donates 'Strikezon'
Newdin Contents, an online and mobile game maker, made a gift of ‘Strikezon' to KAIST on April 19. The screen game valued at 100 million KRW will be placed in the lobby of the School of Computing, enriching the diverse physical activity options for the KAIST community. The donation was made at a ceremony attended by KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the CEO of the Newdin, Hyo-Kyum Kim, and Head of the School of Computing Professor Myoung Ho Kim.
At the Strikezon, students can enjoy mini baseball games indoors including a batting challenge and a pitching mode indoors for free.
President Shin thanked Mr. Kim of Newdin Contents, saying the donation will be a stepping stone for possible mutual collaborations which will play a synergistic role for technological development. Mr. Kim noted, “We are very pleased to donate the program to KAIST, which is the alma mater of Joon-Mo Hwang, the developer of Strikezon.” He added that Newdin Contents will make every effort to produce advanced game products with state of the art technology.
(Photo caption:President Sung-Chul Shin hits the ball at the Strikezon on April 19.)
2017.04.19 View 4839 -
 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 8297
2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 8297 -
 Professor Otfried Cheong Named as Distinguished Scientist by ACM
Professor Otfried Cheong (Schwarzkopf) of the School of Computing was named as a Distinguished Scientist of 2016 by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
The ACM recognized 45 Distinguished Members in the category of Distinguished Scientist, Educator, and Engineer for their individual contributions to the field of computing. Professor Cheong is the sole recipient from a Korean institution. The recipients were selected among the top 10 percent of ACM members with at least 15 years of professional experience and five years of continuous professional membership.
He is known as one of the authors of the widely used computational geometry textbook Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications and as the developer of Ipe, a vector graphics editor. Professor Cheong joined KAIST in 2005, after earning his doctorate from the Free University of Berlin in 1992. He previously taught at Ultrecht University, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Eindhoven University of Technology.
2017.04.17 View 7730
Professor Otfried Cheong Named as Distinguished Scientist by ACM
Professor Otfried Cheong (Schwarzkopf) of the School of Computing was named as a Distinguished Scientist of 2016 by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM).
The ACM recognized 45 Distinguished Members in the category of Distinguished Scientist, Educator, and Engineer for their individual contributions to the field of computing. Professor Cheong is the sole recipient from a Korean institution. The recipients were selected among the top 10 percent of ACM members with at least 15 years of professional experience and five years of continuous professional membership.
He is known as one of the authors of the widely used computational geometry textbook Computational Geometry: Algorithms and Applications and as the developer of Ipe, a vector graphics editor. Professor Cheong joined KAIST in 2005, after earning his doctorate from the Free University of Berlin in 1992. He previously taught at Ultrecht University, Pohang University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Eindhoven University of Technology.
2017.04.17 View 7730 -
 Improving Silver Nanowires for FTCEs with Flash Light Interactions
Flexible transparent conducting electrodes (FTCEs) are an essential element of flexible optoelectronics for next-generation wearable displays, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoTs). Silver nanowires (Ag NWs) have received a great deal of attention as future FTCEs due to their great flexibility, material stability, and large-scale productivity. Despite these advantages, Ag NWs have drawbacks such as high wire-to-wire contact resistance and poor adhesion to substrates, resulting in severe power consumption and the delamination of FTCEs.
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Hong-Jin Park from BSP Inc., has developed high-performance Ag NWs (sheet resistance ~ 5 Ω/sq, transmittance 90 % at λ = 550 nm) with strong adhesion on plastic (interfacial energy of 30.7 J∙m-2) using flash light-material interactions.
The broad ultraviolet (UV) spectrum of a flash light enables the localized heating at the junctions of nanowires (NWs), which results in the fast and complete welding of Ag NWs. Consequently, the Ag NWs demonstrate six times higher conductivity than that of the pristine NWs. In addition, the near-infrared (NIR) of the flash lamp melted the interface between the Ag NWs and a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate, dramatically enhancing the adhesion force of the Ag NWs to the PET by 310 %.
Professor Lee said, “Light interaction with nanomaterials is an important field for future flexible electronics since it can overcome thermal limit of plastics, and we are currently expanding our research into light-inorganic interactions.”
Meanwhile, BSP Inc., a laser manufacturing company and a collaborator of this work, has launched new flash lamp equipment for flexible applications based on the Professor Lee’s research.
The results of this work entitled “Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW Network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201603473)” were published in the February 2, 2017 issue of Advanced Materials as the cover article.
Professor Lee also contributed an invited review in the same journal of the April 3, 2017 online issue, “Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications (DOI:10.1002/adma.201606586),” overviewing the recent advances in light interactions with flexible nanomaterials.
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 2, 2017, Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201603473/epdf
[2] Advanced Materials, April 3, 2017, Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201606586/abstract
For further inquiries on research:
keonlee@kaist.ac.kr (Keon Jae Lee), hjpark@bsptech.co.kr (Hong-Jin Park)
Picture 1: Artistic Rendtition of Light Interaction with Nanomaterials
(This image shows flash-induced plasmonic interactions with nanowires to improve silver nanowires (Ag NWs).)
Picture 2: Ag NW/PET Film
(This picture shows the Ag NWs on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film after the flash-induced plasmonic thermal process.)
2017.04.05 View 10494
Improving Silver Nanowires for FTCEs with Flash Light Interactions
Flexible transparent conducting electrodes (FTCEs) are an essential element of flexible optoelectronics for next-generation wearable displays, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoTs). Silver nanowires (Ag NWs) have received a great deal of attention as future FTCEs due to their great flexibility, material stability, and large-scale productivity. Despite these advantages, Ag NWs have drawbacks such as high wire-to-wire contact resistance and poor adhesion to substrates, resulting in severe power consumption and the delamination of FTCEs.
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Hong-Jin Park from BSP Inc., has developed high-performance Ag NWs (sheet resistance ~ 5 Ω/sq, transmittance 90 % at λ = 550 nm) with strong adhesion on plastic (interfacial energy of 30.7 J∙m-2) using flash light-material interactions.
The broad ultraviolet (UV) spectrum of a flash light enables the localized heating at the junctions of nanowires (NWs), which results in the fast and complete welding of Ag NWs. Consequently, the Ag NWs demonstrate six times higher conductivity than that of the pristine NWs. In addition, the near-infrared (NIR) of the flash lamp melted the interface between the Ag NWs and a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate, dramatically enhancing the adhesion force of the Ag NWs to the PET by 310 %.
Professor Lee said, “Light interaction with nanomaterials is an important field for future flexible electronics since it can overcome thermal limit of plastics, and we are currently expanding our research into light-inorganic interactions.”
Meanwhile, BSP Inc., a laser manufacturing company and a collaborator of this work, has launched new flash lamp equipment for flexible applications based on the Professor Lee’s research.
The results of this work entitled “Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW Network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201603473)” were published in the February 2, 2017 issue of Advanced Materials as the cover article.
Professor Lee also contributed an invited review in the same journal of the April 3, 2017 online issue, “Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications (DOI:10.1002/adma.201606586),” overviewing the recent advances in light interactions with flexible nanomaterials.
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 2, 2017, Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201603473/epdf
[2] Advanced Materials, April 3, 2017, Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201606586/abstract
For further inquiries on research:
keonlee@kaist.ac.kr (Keon Jae Lee), hjpark@bsptech.co.kr (Hong-Jin Park)
Picture 1: Artistic Rendtition of Light Interaction with Nanomaterials
(This image shows flash-induced plasmonic interactions with nanowires to improve silver nanowires (Ag NWs).)
Picture 2: Ag NW/PET Film
(This picture shows the Ag NWs on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film after the flash-induced plasmonic thermal process.)
2017.04.05 View 10494 -
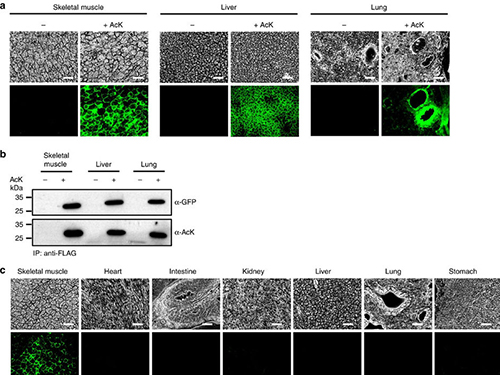 Expanding the Genetic Code of Mus Musculus
Professor Hee-Sung Park of the Department of Chemistry, who garnered attention for his novel strategy of installing authentic post-translational modifications into recombinant proteins, expanded his research portfolio to another level. Professor Park’s team was the first to report the generation of a mouse strain with an expanded genetic code, allowing site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids.
Professor Park published the research on the new chemical biology method for achieving selective chemical modifications in proteins in Science last September. The research team, this time in collaboration with Professor Chan Bae Park of the Department of Physiology at the Ajou University School of Medicine, demonstrated temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse using a recombinant green fluorescent protein as a model protein. This research was published in the online edition of Nature Communications on February 21.
This approach enables the rapid onset of position-specific acetylation of a target protein at any developmental stage, facilitating temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse. Such temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation will be of prime importance for investigating many essential biological processes and human diseases at the tissue and organism level.
Almost all human proteins, the products of about 25,000 genes, are known to undergo various post-translational modifications during and after synthesis. Post-translation modifications regulate the function of cellular proteins, playing a key role in many essential processes such as delivering signals and body growth. However, the unusual protein modifications, aroused from genetic and/or environmental factors, trigger severe diseases including cancer, dementia, and diabetes.
The team inserted transgenes into the mouse genome to allocate the site-specific addition of unnatural amino acids. The researchers inserted a modified version of lysine into the house mice, which allowed for the control of the acetylation. They used recombinant green fluorescent proteins from transgenic house mice as models for control of the acetylation.
The team was also able to regulate the acetylation of specific temporal and spatial frames in the mice, restraining the abnormality in proteins to certain organs such as the liver and kidneys. The research team said the strategy will provide a powerful tool for systematic in vivo study of cellular proteins in the most commonly used mammalian model organisms for human physiology and disease. Professor Park said, “This method can be easily extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains for further investigating diverse proteins of interest.” He added, “This method can be further extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains, opening a new paradigm for investigating anti-cancer and cerebral disease treatments.
This work was supported by grants from KAIST Systems Healthcare and the Medicinal Bioconvergence Research Center and the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of the Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
(Figure:Temporal and spatial control of in vivo protein acetylation)
(a) Temporal expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. The expression of GFPuv in skeletal muscle, liver, and lung tissues was detected only in the AcK-injected mouse. Scale bar, 200 µm. (b) Western blotting of anti-FLAG-immunoprecipitated proteins from tissues of the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was produced after AcK injection. (c) Spatial expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was observed only in skeletal muscle when AcK was directly delivered to the tissues. Sacle bar, 200 µm.
2017.03.27 View 9393
Expanding the Genetic Code of Mus Musculus
Professor Hee-Sung Park of the Department of Chemistry, who garnered attention for his novel strategy of installing authentic post-translational modifications into recombinant proteins, expanded his research portfolio to another level. Professor Park’s team was the first to report the generation of a mouse strain with an expanded genetic code, allowing site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids.
Professor Park published the research on the new chemical biology method for achieving selective chemical modifications in proteins in Science last September. The research team, this time in collaboration with Professor Chan Bae Park of the Department of Physiology at the Ajou University School of Medicine, demonstrated temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse using a recombinant green fluorescent protein as a model protein. This research was published in the online edition of Nature Communications on February 21.
This approach enables the rapid onset of position-specific acetylation of a target protein at any developmental stage, facilitating temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse. Such temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation will be of prime importance for investigating many essential biological processes and human diseases at the tissue and organism level.
Almost all human proteins, the products of about 25,000 genes, are known to undergo various post-translational modifications during and after synthesis. Post-translation modifications regulate the function of cellular proteins, playing a key role in many essential processes such as delivering signals and body growth. However, the unusual protein modifications, aroused from genetic and/or environmental factors, trigger severe diseases including cancer, dementia, and diabetes.
The team inserted transgenes into the mouse genome to allocate the site-specific addition of unnatural amino acids. The researchers inserted a modified version of lysine into the house mice, which allowed for the control of the acetylation. They used recombinant green fluorescent proteins from transgenic house mice as models for control of the acetylation.
The team was also able to regulate the acetylation of specific temporal and spatial frames in the mice, restraining the abnormality in proteins to certain organs such as the liver and kidneys. The research team said the strategy will provide a powerful tool for systematic in vivo study of cellular proteins in the most commonly used mammalian model organisms for human physiology and disease. Professor Park said, “This method can be easily extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains for further investigating diverse proteins of interest.” He added, “This method can be further extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains, opening a new paradigm for investigating anti-cancer and cerebral disease treatments.
This work was supported by grants from KAIST Systems Healthcare and the Medicinal Bioconvergence Research Center and the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of the Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
(Figure:Temporal and spatial control of in vivo protein acetylation)
(a) Temporal expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. The expression of GFPuv in skeletal muscle, liver, and lung tissues was detected only in the AcK-injected mouse. Scale bar, 200 µm. (b) Western blotting of anti-FLAG-immunoprecipitated proteins from tissues of the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was produced after AcK injection. (c) Spatial expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was observed only in skeletal muscle when AcK was directly delivered to the tissues. Sacle bar, 200 µm.
2017.03.27 View 9393 -
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8732
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 8732 -
 Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 10289
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim Receives the 2017 HSFP Award
The Human Frontier Science Program (HSFP), one of the most competitive research grants in life sciences, has funded researchers worldwide across and beyond the field since 1990. Each year, the program selects a handful of recipients who push the envelope of basic research in biology to bring breakthroughs from novel approaches. Among its 7,000 recipients thus far, 26 scientists have received the Nobel Prize. For that reason, HSFP grants are often referred to as “Nobel Prize Grants.”
Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of the Mathematical Sciences Department at KAIST and his international collaborators, Professor Robert Havekes from the University of Groningen, the Netherlands, Professor Sara Aton from the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor, the United States, and Professor Matias Zurbriggen from the University of Düsseldorf, Germany, won the Young Investigator Grants of the 2017 HSFP.
The 30 winning teams of the 2017 competition (in 9 Young Investigator Grants and 21 Program Grants) went through a rigorous year-long review process from a total of 1,073 applications submitted from more than 60 countries around the world. Each winning team will receive financial support averaging 110,000-125,000 USD per year for three years.
Although Professor Kim was trained as a mathematician, he has extended his research focus into biological sciences and attempted to solve some of the most difficult problems in biology by employing mathematical theories and applications including nonlinear dynamics, stochastic process, singular perturbation, and parameter estimation.
The project that won the Young Investigator Grants was a study on how a molecular circadian clock may affect sleep-regulated neurophysiology in mammals. Physiological and metabolic processes such as sleep, blood pressure, and hormone secretion exhibit circadian rhythms in mammals. Professor Kim used mathematical modeling and analysis to explain that the mammalian circadian clock is a hierarchical system, in which the master clock in the superchiasmatic nucleus, a tiny region in the brain that controls circadian rhythms, functions as a pacemaker and synchronizer of peripheral clocks to generate coherent systematic rhythms throughout the body.
Professor Kim said, “The mechanisms of our neuronal and hormonal activities regulating many of our bodily functions over a 24-hour cycle are not yet fully known. We go to sleep every night, but do not really know how it affects our brain functions. I hope my experience in mathematics, along with insights from biologists, can find meaningful answers to some of today’s puzzling problems in biological sciences, for example, revealing the complexities of our brains and showing how they work.”
“In the meantime, I hope collaborations between the fields of mathematics and biology, as yet a rare phenomenon in the Korean scientific community, will become more popular in the near future.”
Professor Kim received his doctoral degree in Applied and Interdisciplinary Mathematics in 2013 from the University of Michigan and joined KAIST in 2015. He has published numerous articles in reputable science journals such as Science, Molecular Cell, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, and Nature Communications.
Both the Program Grants and Young Investigator Grants support international teams with members from at least two countries for innovative and creative research. This year, the Program Grants were awarded to research topics ranging from the evolution of counting and the role of extracellular vesicles in breast cancer bone metastasis to the examination of obesity from a mechanobiological point of view.
The Young Investigator Grants are limited to teams that established their independent research within the last five years and received their doctoral degrees within the last decade. Besides Professor Kim’s study, such topics as the use of infrasound for navigation by seabirds and protein formation in photochemistry and photophysics were awarded in 2017.
Full lists of the 2017 HFSP winners are available at: http://www.hfsp.org/awardees/newly-awarded.
About the Human Frontier Science Program (HFSP):
The HFSP is a research funding program implemented by the International Human Frontier Science Program (HFSPO) based in Strasbourg, France. It promotes intercontinental collaboration and training in cutting-edge, interdisciplinary research specializing in life sciences. Founded in 1989, the HFSPO consists of the European Union and 14 other countries including the G7 nations and South Korea.
2017.03.21 View 10289