AR
-
 KAIST, First to Win the Cube Satellite Competition
Professor Hyochoong Bang from the Department of Aerospace Engineering and his team received the Minister of Science and ICT Award at the 1st Cube Satellite Competition.
The team actually participated in the competition in 2012, but it took several years for the awarding ceremony since it took years for the satellites to be designed, produced, and launched.
The KAIST team successfully developed a cube satellite, named ‘Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST (LINK)’ and completed its launch in April 2017.
LINK (size: 20cmx10cmx10cm, weight: 2kg) mounted mass spectrometry and Langmuir probe for Earth observation. The Langmuir probe was developed by Professor Kyoung Wook Min from the Department of Physics, KAIST.
Yeerang Lim, a PhD student from the Department of Aerospace Engineering said, “I still remember the feeling that I had on the day when LINK launched into orbit and sent back signals. I hope that space exploration is not something far away but attainable for us in near future.”
2018.02.22 View 11223
KAIST, First to Win the Cube Satellite Competition
Professor Hyochoong Bang from the Department of Aerospace Engineering and his team received the Minister of Science and ICT Award at the 1st Cube Satellite Competition.
The team actually participated in the competition in 2012, but it took several years for the awarding ceremony since it took years for the satellites to be designed, produced, and launched.
The KAIST team successfully developed a cube satellite, named ‘Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST (LINK)’ and completed its launch in April 2017.
LINK (size: 20cmx10cmx10cm, weight: 2kg) mounted mass spectrometry and Langmuir probe for Earth observation. The Langmuir probe was developed by Professor Kyoung Wook Min from the Department of Physics, KAIST.
Yeerang Lim, a PhD student from the Department of Aerospace Engineering said, “I still remember the feeling that I had on the day when LINK launched into orbit and sent back signals. I hope that space exploration is not something far away but attainable for us in near future.”
2018.02.22 View 11223 -
 Professor Il-Doo Kim Recevies the Song-gok Award
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST received the 20th Song-gok Science and Technology Award from Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KSIT).
The Song-gok Science and Technology Award was established to praise the accomplishments of the first president, Hyung-seop Choi, whose penname is Song-gok. The award selects a recipient in the field of materials and technology every other year.
Professor Kim, in recognition of his outstanding research and contributions to materials science in Korea, received the award during the 52nd anniversary ceremony of KIST on February 9.
Professor Kim focuses on developing nanofiber gas sensors for diagnosing disease in advance by analyzing exhaled biomarkers with electrospinning technology.
He has published more than 211 papers and has recorded more than 9,650 citations and 50 h-index.
Professor Kim has registered 107 patents and applied 38 patents in Korea while registering 29 patents and applying 16 patents overseas. Also, he transferred four technologies in 2017.
Professor Kim is recognized as one of the researchers who is leading nanofiber technology. On January 17, he made a keynote speech at the 5th International Conference on Electrospinning, which was his fourth keynote speech at that conference.
Moreover, he received the Technology Innovation Award at the College of Engineering, KAIST on December 19, 2017.
Professor Kim said, “It is my great honor to receive the Song-gok Science and Technology Award. I would like to bring distinction to KAIST by taking the lead in the commercializing a nanofiber-based highly sensitive nanosensors, diversifying and commercializing technology using nanofiber.”
2018.02.13 View 8578
Professor Il-Doo Kim Recevies the Song-gok Award
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST received the 20th Song-gok Science and Technology Award from Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KSIT).
The Song-gok Science and Technology Award was established to praise the accomplishments of the first president, Hyung-seop Choi, whose penname is Song-gok. The award selects a recipient in the field of materials and technology every other year.
Professor Kim, in recognition of his outstanding research and contributions to materials science in Korea, received the award during the 52nd anniversary ceremony of KIST on February 9.
Professor Kim focuses on developing nanofiber gas sensors for diagnosing disease in advance by analyzing exhaled biomarkers with electrospinning technology.
He has published more than 211 papers and has recorded more than 9,650 citations and 50 h-index.
Professor Kim has registered 107 patents and applied 38 patents in Korea while registering 29 patents and applying 16 patents overseas. Also, he transferred four technologies in 2017.
Professor Kim is recognized as one of the researchers who is leading nanofiber technology. On January 17, he made a keynote speech at the 5th International Conference on Electrospinning, which was his fourth keynote speech at that conference.
Moreover, he received the Technology Innovation Award at the College of Engineering, KAIST on December 19, 2017.
Professor Kim said, “It is my great honor to receive the Song-gok Science and Technology Award. I would like to bring distinction to KAIST by taking the lead in the commercializing a nanofiber-based highly sensitive nanosensors, diversifying and commercializing technology using nanofiber.”
2018.02.13 View 8578 -
 First Female Grand Prize Awardee of Samsung Humantech
Yeunhee Huh, PhD candidate (Professor Gyu-Hyeong Cho) from the School of Electrical Engineering received the grand prize of the 24th Humantech Paper Award. She is the first female recipient of this prize since its establishment in 1994. The Humantech Paper Award is hosted by Samsung Electronics and sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT with JoongAng Daily Newspaper. Her paper is titled, ‘A Hybrid Structure Dual-Path Step-Down Converter with 96.2% Peak Efficiency using 250mΩ Large-DCR Inductor’. Electronic devices require numerous chips and have a power converter to supply energy adequately. She proposed a new structure to enhance energy efficiency by combining inductors and capacitors. Enhancing energy efficiency can reduce energy loss, which prolongs battery hours and solves overheating of devices; for instance, energy loss leads to the overheating issue affecting phone chargers. This technology can be applied to various electronic devices, such as cell phones, laptops, and drones. Huh said, “Power has to go up in order to meet customers’ needs; however the overheating problem emerges during this process. This problem affects surrounding circuits and causes other issues, such as malfunctions of electronic devices. This technology may vary according to the conditions, but it can enhance energy efficiency up to 4%.”During the ceremony, about eight hundred million KRW worth cash prizes was conferred to 119 papers. KAIST (44 papers) and Gyeonggi Science High School (6 papers) received special awards given to the schools.
2018.02.12 View 9265
First Female Grand Prize Awardee of Samsung Humantech
Yeunhee Huh, PhD candidate (Professor Gyu-Hyeong Cho) from the School of Electrical Engineering received the grand prize of the 24th Humantech Paper Award. She is the first female recipient of this prize since its establishment in 1994. The Humantech Paper Award is hosted by Samsung Electronics and sponsored by the Ministry of Science and ICT with JoongAng Daily Newspaper. Her paper is titled, ‘A Hybrid Structure Dual-Path Step-Down Converter with 96.2% Peak Efficiency using 250mΩ Large-DCR Inductor’. Electronic devices require numerous chips and have a power converter to supply energy adequately. She proposed a new structure to enhance energy efficiency by combining inductors and capacitors. Enhancing energy efficiency can reduce energy loss, which prolongs battery hours and solves overheating of devices; for instance, energy loss leads to the overheating issue affecting phone chargers. This technology can be applied to various electronic devices, such as cell phones, laptops, and drones. Huh said, “Power has to go up in order to meet customers’ needs; however the overheating problem emerges during this process. This problem affects surrounding circuits and causes other issues, such as malfunctions of electronic devices. This technology may vary according to the conditions, but it can enhance energy efficiency up to 4%.”During the ceremony, about eight hundred million KRW worth cash prizes was conferred to 119 papers. KAIST (44 papers) and Gyeonggi Science High School (6 papers) received special awards given to the schools.
2018.02.12 View 9265 -
 Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 8143
Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 8143 -
 Finding Human Thermal Comfort with a Watch-type Sweat Rate Sensor
(from left: Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher SungHyun Yoon)
KAIST developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor. This subminiature device can detect human thermal comfort accurately and steadily by measuring an individual’s sweat rate.
It is natural to sweat more in the summer and less in the winter; however, an individual’s sweat rate may vary in a given environment. Therefore, sweat can be an excellent proxy for sensing core body temperature.
Conventional sweat rate sensors using natural ventilation require bulky external devices, such as pumps and ice condensers. They are usually for physiological experiments, hence they need a manual ventilation process or high power, bulky thermos-pneumatic actuators to lift sweat rate detection chambers above skin for continuous measurement. There is also a small sweat rate sensor, but it needs a long recovery period.
To overcome these problems, Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed a lightweight, watch-type sweat sensor. The team integrated miniaturized thermos-pneumatic actuators for automatic natural ventilation, which allows sweat to be measured continuously.
This watch-type sensor measures sweat rate with the humidity rising rate when the chamber is closed during skin contact. Since the team integrated thermos-pneumatic actuators, the chamber no longer needs to be separated manually from skin after each measurement in order for the chamber to ventilate the collected humidity.
Moreover, this sensor is wind-resistant enough to be used for portable and wearable devices. The team identified that the sensor operates steadily with air velocity ranging up to 1.5m/s, equivalent to the average human walking speed.
Although this subminiature sensor (35mm x 25mm) only weighs 30 grams, it operates continuously for more than four hours using the conventional wrist watch batteries.
The team plans to utilize this technology for developing a new concept of cognitive air-conditioning systems recognizing Human thermal status directly; while the conventional air-conditioning systems measuring air temperature and humidity.
Professor Cho said, “Our sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring can be applied to customized or smart air conditioners. Furthermore, there will be more demands for both physical and mental healthcare, hence this technology will serve as a new platform for personalized emotional communion between humans and devices.”
This research, led by researchers Jai Kyoung Sim and SungHyun Yoon, was published in Scientific Reports on January 19, 2018.
Figure1. The fabricated watch-type sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring
Figure 2. Views of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
Figure 3. Operation of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
2018.02.08 View 8596
Finding Human Thermal Comfort with a Watch-type Sweat Rate Sensor
(from left: Professor Young-Ho Cho and Researcher SungHyun Yoon)
KAIST developed a watch-type sweat rate sensor. This subminiature device can detect human thermal comfort accurately and steadily by measuring an individual’s sweat rate.
It is natural to sweat more in the summer and less in the winter; however, an individual’s sweat rate may vary in a given environment. Therefore, sweat can be an excellent proxy for sensing core body temperature.
Conventional sweat rate sensors using natural ventilation require bulky external devices, such as pumps and ice condensers. They are usually for physiological experiments, hence they need a manual ventilation process or high power, bulky thermos-pneumatic actuators to lift sweat rate detection chambers above skin for continuous measurement. There is also a small sweat rate sensor, but it needs a long recovery period.
To overcome these problems, Professor Young-Ho Cho and his team from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering developed a lightweight, watch-type sweat sensor. The team integrated miniaturized thermos-pneumatic actuators for automatic natural ventilation, which allows sweat to be measured continuously.
This watch-type sensor measures sweat rate with the humidity rising rate when the chamber is closed during skin contact. Since the team integrated thermos-pneumatic actuators, the chamber no longer needs to be separated manually from skin after each measurement in order for the chamber to ventilate the collected humidity.
Moreover, this sensor is wind-resistant enough to be used for portable and wearable devices. The team identified that the sensor operates steadily with air velocity ranging up to 1.5m/s, equivalent to the average human walking speed.
Although this subminiature sensor (35mm x 25mm) only weighs 30 grams, it operates continuously for more than four hours using the conventional wrist watch batteries.
The team plans to utilize this technology for developing a new concept of cognitive air-conditioning systems recognizing Human thermal status directly; while the conventional air-conditioning systems measuring air temperature and humidity.
Professor Cho said, “Our sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring can be applied to customized or smart air conditioners. Furthermore, there will be more demands for both physical and mental healthcare, hence this technology will serve as a new platform for personalized emotional communion between humans and devices.”
This research, led by researchers Jai Kyoung Sim and SungHyun Yoon, was published in Scientific Reports on January 19, 2018.
Figure1. The fabricated watch-type sweat rate sensor for human thermal comfort monitoring
Figure 2. Views of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
Figure 3. Operation of the watch-type sweat rate sensor
2018.02.08 View 8596 -
 Professor Jungwon Kim Wins Haerim Optics and Photonics Award
(Professor Jungwon Kim)
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the 8th Haerim Optics and Photonics Award from the Optical Society of Korea (OSK).
He was recognized for his dedication to pioneering the field of microwave photonics by developing ultra-low noise fiber photonics lasers.
The Haerim Optics and Photonics Award is given to an outstanding researcher who has made academic contributions in the field of optics and photonics for the last five years.
The name of the award (Haerim) comes from the pen-name of the renowned scholar, Professor Un-Chul Paek, because it is maintained using funds he contributed to the OSK.
The OSK will confer the award on February 8 during the 29th OSK Annual Meeting and Winter Conference of 2018.
2018.02.07 View 7586
Professor Jungwon Kim Wins Haerim Optics and Photonics Award
(Professor Jungwon Kim)
Professor Jungwon Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering received the 8th Haerim Optics and Photonics Award from the Optical Society of Korea (OSK).
He was recognized for his dedication to pioneering the field of microwave photonics by developing ultra-low noise fiber photonics lasers.
The Haerim Optics and Photonics Award is given to an outstanding researcher who has made academic contributions in the field of optics and photonics for the last five years.
The name of the award (Haerim) comes from the pen-name of the renowned scholar, Professor Un-Chul Paek, because it is maintained using funds he contributed to the OSK.
The OSK will confer the award on February 8 during the 29th OSK Annual Meeting and Winter Conference of 2018.
2018.02.07 View 7586 -
 KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 9086
KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 9086 -
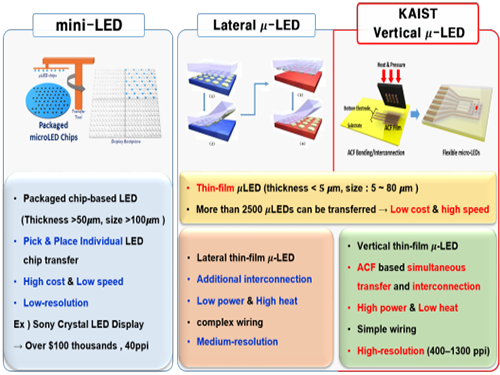 Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 13258
Developing Flexible Vertical Micro LED
A KAIST research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences has developed flexible vertical micro LEDs (f-VLEDs) using anisotropic conductive film (ACF)-based transfer and interconnection technology. The team also succeeded in controlling animal behavior via optogenetic stimulation of the f-VLEDs.
Flexible micro LEDs have become a strong candidate for the next-generation display due to their ultra-low power consumption, fast response speed, and excellent flexibility. However, the previous micro LED technology had critical issues such as poor device efficiency, low thermal reliability, and the lack of interconnection technology for high-resolution micro LED displays.
The research team has designed new transfer equipment and fabricated a f-VLED array (50ⅹ50) using simultaneous transfer and interconnection through the precise alignment of ACF bonding process. These f-VLEDs (thickness: 5 ㎛, size: below 80 ㎛) achieved optical power density (30 mW/mm2) three times higher than that of lateral micro LEDs, improving thermal reliability and lifetime by reducing heat generation within the thin film LEDs.
These f-VLEDs can be applied to optogenetics for controlling the behavior of neuron cells and brains. In contrast to the electrical stimulation that activates all of the neurons in brain, optogenetics can stimulate specific excitatory or inhibitory neurons within the localized cortical areas of the brain, which facilitates precise analysis, high-resolution mapping, and neuron modulation of animal brains. (Refer to the author’s previous ACS Nano paper of “Optogenetic Mapping of Functional Connectivity in Freely Moving Mice via Insertable Wrapping Electrode Array Beneath the Skull.” )
In this work, they inserted the innovative f-VLEDs into the narrow space between the skull and the brain surface and succeeded in controlling mouse behavior by illuminating motor neurons on two-dimensional cortical areas located deep below the brain surface.
Professor Lee said, “The flexible vertical micro LED can be used in low-power smart watches, mobile displays, and wearable lighting. In addition, these flexible optoelectronic devices are suitable for biomedical applications such as brain science, phototherapeutic treatment, and contact lens biosensors.”
He recently established a startup company ( FRONICS Inc. ) based on micro LED technology and is looking for global partnerships for commercialization. This result entitled “ Optogenetic Control of Body Movements via Flexible Vertical Light-Emitting Diodes on Brain Surface ” was published in the February 2018 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1. Comparison of μ-LEDs Technology
2018.01.29 View 13258 -
 Plasma, an Excellent Sterilizer to Remove Harmful Bacteria
(PhD candidate Joo Young Park, Professor Wonho Choe and PhD researcher Sanghoo Park)
KAIST researchers are using plasma to remove bacteria that are stuck to surfaces of plastic bottles and food. This novel technology will contribute to disinfection in medical settings as well as food and agricultural industries.
Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Physics developed a technology that removes biofilm, which is comprised of microorganisms, by using plasma as a non-thermal sterilization method.
Plasma contains multiple bactericidal agents, including reactive species. In particular, the chemicals formed in aqueous solution during plasma exposure have the potential for high antibacterial activity against various bacterial infections.
The team treated water with plasma to see how effectively bactericidal agents in the plasma water can remove biofilm comprised of harmful microorganism such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Listeria.
The team identified that reactive species, including hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide, ozone, nitrite, and superoxide produced during plasma treatment, showed considerable ability to remove the biofilm. Hydrogen peroxide showed the strongest effect removing the biofilm; however, the hydroxyl radical also played a significant role in removing biofilm. Despite having a concentration 100 to 10,000 times lower than other reactive species, the hydroxyl radical showed a high biofilm removal efficacy owing to its strong oxidative power.
These findings reveal that plasma can be used as a no-residual and safe sterilization process alternative to conventional methods. With these outcomes, the team is planning to develop and commercialize a technology that can produce hydroxyl radicals with plasma.
Professor Choe has registered a patent for flexible packaging materials that facilitate plasma and completed the technology transfer to the startup company, named ‘Plasmapp’, which focuses on commercializing bactericidal technology.
“This research outcome will be the foundation for understanding plasma control technology and physicochemical interactions between plasma and microorganisms. It will also become an accelerator for utilizing plasma technology in the medical, food, and agricultural fields,” said Professor Choe.
This research, led by PhD candidate Joo Young Park and PhD researcher Sanghoo Park in collaboration with Professor Cheorun Jo’s team from Seoul National University, was published in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces on December 20, 2017.
Figure 1. Flexible packaging materials that facilitate plasma
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of biofilm treatment with plasma
Figure 3. Concept of plasma application and evaluation result of reactive species' efficacy
Figure 4. STERPACK, the product launched by Plasmapp
2018.01.25 View 9728
Plasma, an Excellent Sterilizer to Remove Harmful Bacteria
(PhD candidate Joo Young Park, Professor Wonho Choe and PhD researcher Sanghoo Park)
KAIST researchers are using plasma to remove bacteria that are stuck to surfaces of plastic bottles and food. This novel technology will contribute to disinfection in medical settings as well as food and agricultural industries.
Professor Wonho Choe and his team from the Department of Physics developed a technology that removes biofilm, which is comprised of microorganisms, by using plasma as a non-thermal sterilization method.
Plasma contains multiple bactericidal agents, including reactive species. In particular, the chemicals formed in aqueous solution during plasma exposure have the potential for high antibacterial activity against various bacterial infections.
The team treated water with plasma to see how effectively bactericidal agents in the plasma water can remove biofilm comprised of harmful microorganism such as Escherichia coli, Salmonella, and Listeria.
The team identified that reactive species, including hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide, ozone, nitrite, and superoxide produced during plasma treatment, showed considerable ability to remove the biofilm. Hydrogen peroxide showed the strongest effect removing the biofilm; however, the hydroxyl radical also played a significant role in removing biofilm. Despite having a concentration 100 to 10,000 times lower than other reactive species, the hydroxyl radical showed a high biofilm removal efficacy owing to its strong oxidative power.
These findings reveal that plasma can be used as a no-residual and safe sterilization process alternative to conventional methods. With these outcomes, the team is planning to develop and commercialize a technology that can produce hydroxyl radicals with plasma.
Professor Choe has registered a patent for flexible packaging materials that facilitate plasma and completed the technology transfer to the startup company, named ‘Plasmapp’, which focuses on commercializing bactericidal technology.
“This research outcome will be the foundation for understanding plasma control technology and physicochemical interactions between plasma and microorganisms. It will also become an accelerator for utilizing plasma technology in the medical, food, and agricultural fields,” said Professor Choe.
This research, led by PhD candidate Joo Young Park and PhD researcher Sanghoo Park in collaboration with Professor Cheorun Jo’s team from Seoul National University, was published in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces on December 20, 2017.
Figure 1. Flexible packaging materials that facilitate plasma
Figure 2. Schematic diagram of biofilm treatment with plasma
Figure 3. Concept of plasma application and evaluation result of reactive species' efficacy
Figure 4. STERPACK, the product launched by Plasmapp
2018.01.25 View 9728 -
 Cellular Mechanism for Severe Viral Hepatitis Identified
(Professor Shin(left) and Professor Jung)
KAIST medical scientists identified a cellular mechanism causing inflammatory changes in regulatory T cells that can lead to severe viral hepatitis. Research on this mechanism will help further understand the nature of various inflammatory diseases and lead to the development of relevant clinical treatments.
It is known that activated immune cells of patients with viral hepatitis destroy hepatocyte, but its regulatory mechanism has not yet been described.
Regulatory T cells inhibit activation of other immune cells and thus are important for homeostasis of the immune system. However, recent studies contradictorily show that immune inhibitory functions of regulatory T cells weaken in inflammatory conditions and the cells secrete inflammatory cytokines in response. Meanwhile, such a phenomenon was not observed in viral hepatitis including types A, B and C.
The team focused on changes in regulatory T cells in patients with viral hepatitis and discovered that regulatory T cells undergo inflammatory changes to secrete inflammatory cytokines (protein secreted by immune cells) called TNF. They also proved regulatory T cells that secrete TNF contribute to the progression of viral hepatitis.
The team confirmed that regulatory T cells of acute hepatitis A patients have reduced immune-inhibitory functions. Instead, their regulatory T cells secrete TNF. Through this research, the team identified a molecular mechanism for changes in regulatory T cells and identified the transcription factor regulating the process. Furthermore, the team found similar changes to be also present in hepatitis B and C patients.
A KAIST immunology research team led by Professors Eui-Cheol Shin and Min Kyung Jung at the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering conducted this translational research with teams from Chungnam National University and Yonsei University to identify the mechanism in humans, instead of using animal models. The research was described in Gastroenterology last December.
Professor Shin said, “This is the first research on regulatory T cells that contributes to hepatocyte damage in viral hepatitis.” He continued, “It is significant for identifying the cells and the molecules that can be used as effective treatment targets for viral hepatitis in the future. This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation.
(Figure1: Treg cells from acute hepatitis A (AHA) patients produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) andhave reduced suppressive activity. These changes are due to a decrease in FoxP3 transcription factor and an increase in RORγt transcription factor. TNF-producing Treg cells are associated with severe liver injury in AHA patients.)
(Figure 2: A higher proportion of Treg cells from patients with acute hepatitis A, compared with healthy controls, produced TNF upon stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD2. This study reports the presence and the significance of TNF-producing Treg cells for the first time in human patients.)
2018.01.18 View 8577
Cellular Mechanism for Severe Viral Hepatitis Identified
(Professor Shin(left) and Professor Jung)
KAIST medical scientists identified a cellular mechanism causing inflammatory changes in regulatory T cells that can lead to severe viral hepatitis. Research on this mechanism will help further understand the nature of various inflammatory diseases and lead to the development of relevant clinical treatments.
It is known that activated immune cells of patients with viral hepatitis destroy hepatocyte, but its regulatory mechanism has not yet been described.
Regulatory T cells inhibit activation of other immune cells and thus are important for homeostasis of the immune system. However, recent studies contradictorily show that immune inhibitory functions of regulatory T cells weaken in inflammatory conditions and the cells secrete inflammatory cytokines in response. Meanwhile, such a phenomenon was not observed in viral hepatitis including types A, B and C.
The team focused on changes in regulatory T cells in patients with viral hepatitis and discovered that regulatory T cells undergo inflammatory changes to secrete inflammatory cytokines (protein secreted by immune cells) called TNF. They also proved regulatory T cells that secrete TNF contribute to the progression of viral hepatitis.
The team confirmed that regulatory T cells of acute hepatitis A patients have reduced immune-inhibitory functions. Instead, their regulatory T cells secrete TNF. Through this research, the team identified a molecular mechanism for changes in regulatory T cells and identified the transcription factor regulating the process. Furthermore, the team found similar changes to be also present in hepatitis B and C patients.
A KAIST immunology research team led by Professors Eui-Cheol Shin and Min Kyung Jung at the Graduate School of Medical Science & Engineering conducted this translational research with teams from Chungnam National University and Yonsei University to identify the mechanism in humans, instead of using animal models. The research was described in Gastroenterology last December.
Professor Shin said, “This is the first research on regulatory T cells that contributes to hepatocyte damage in viral hepatitis.” He continued, “It is significant for identifying the cells and the molecules that can be used as effective treatment targets for viral hepatitis in the future. This research was funded by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation.
(Figure1: Treg cells from acute hepatitis A (AHA) patients produce tumor necrosis factor (TNF) andhave reduced suppressive activity. These changes are due to a decrease in FoxP3 transcription factor and an increase in RORγt transcription factor. TNF-producing Treg cells are associated with severe liver injury in AHA patients.)
(Figure 2: A higher proportion of Treg cells from patients with acute hepatitis A, compared with healthy controls, produced TNF upon stimulation with anti-CD3 and anti-CD2. This study reports the presence and the significance of TNF-producing Treg cells for the first time in human patients.)
2018.01.18 View 8577 -
 Three Professors Named KAST Fellows
(Professor Dan Keun Sung at the center)
(Professor Y.H. Cho at the center)
(Professor K.H. Cho at the center)
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) inducted three KAIST professors as fellows at the New Year’s ceremony held at KAST on January 12. They were among the 24 newly elected fellows of the most distinguished academy in Korea. The new fellows are Professor Dan Keun Sung of the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics.
Professor Sung was recognized for his lifetime academic achievements in fields related with network protocols and energy ICT. He also played a crucial role in launching the Korean satellites KITSAT-1,2,3 and the establishment of the Satellite Technology Research Center at KAIST.
Professor Y.H.Cho has been a pioneer in the field of low-dimensional semiconductor-powered quantum photonics that enables quantum optical research in solid state. He has been recognized as a renowned scholar in this field internationally.
Professor K.H.Cho has conducted original research that combines IT and BT in systems biology and has applied novel technologies of electronic modeling and computer simulation analysis for investigating complex life sciences. Professor Cho, who is in his 40s, is the youngest fellow among the newly inducted fellows.
2018.01.16 View 14104
Three Professors Named KAST Fellows
(Professor Dan Keun Sung at the center)
(Professor Y.H. Cho at the center)
(Professor K.H. Cho at the center)
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) inducted three KAIST professors as fellows at the New Year’s ceremony held at KAST on January 12. They were among the 24 newly elected fellows of the most distinguished academy in Korea. The new fellows are Professor Dan Keun Sung of the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, and Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics.
Professor Sung was recognized for his lifetime academic achievements in fields related with network protocols and energy ICT. He also played a crucial role in launching the Korean satellites KITSAT-1,2,3 and the establishment of the Satellite Technology Research Center at KAIST.
Professor Y.H.Cho has been a pioneer in the field of low-dimensional semiconductor-powered quantum photonics that enables quantum optical research in solid state. He has been recognized as a renowned scholar in this field internationally.
Professor K.H.Cho has conducted original research that combines IT and BT in systems biology and has applied novel technologies of electronic modeling and computer simulation analysis for investigating complex life sciences. Professor Cho, who is in his 40s, is the youngest fellow among the newly inducted fellows.
2018.01.16 View 14104 -
 Harnessing the Strength of KAIST Alumni: New Head of KAA Inaugurated
KAIST alumni gathered in Seoul on January 13 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAIST Alumni Association (KAA). More than 300 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, joined the gala event held at the Lotte Hotel.
Photo: Ki-Chul Cha(left) and Jung Sik Koh(right)
The KAA inaugurated its new president, Ki-Chul Cha, who was preceded by Jung Sik Koh, the former CEO at the Korea Resources Corporation. His term starts from January 2018 to December 2020.
Cha is the CEO of Inbody Co Ltd., a global company specializing in developing and selling medical instruments, such as a body composition analyzers, and medical solutions. He is also an adjunct professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University. Cha obtained a master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering at KAIST in 1980, and a Ph.D. in Bioengineering at the University of Utah, before finishing his post-doc fellowship at Harvard Medical School.
Cha plans to explore the idea that alumni engagement, saying, “KAIST stays as a home in the memories of 60,000 alumni. I will dedicate myself to stimulating the alumni association to make KAISTians proud.”
At the gala event, the KAA awarded the Alumni of the Year honor to six alumni who distinguished themselves in the areas of professional achievement, humanitarianism, and public service. They are the Director of Startup KAIST Professor Byoung Yoon Kim; President of LG Chem Ltd and Head of Battery Research and Development Myung Hwan Kim; Director of INNOX Advanced Materials Co., Ltd Kyung Ho Chang; Vice President of the Korea International Trade Association Jung-Kwan Kim; CEO of Samsung Electro-Mechanics Yun-Tae Lee; and CEO of ENF Technology Jinbae Jung.
Photo: President Shin(far right) poses with six awardees of the Distinguished Alumni Award and the former President of KAA, Koh(far left)
2018.01.16 View 10699
Harnessing the Strength of KAIST Alumni: New Head of KAA Inaugurated
KAIST alumni gathered in Seoul on January 13 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAIST Alumni Association (KAA). More than 300 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, joined the gala event held at the Lotte Hotel.
Photo: Ki-Chul Cha(left) and Jung Sik Koh(right)
The KAA inaugurated its new president, Ki-Chul Cha, who was preceded by Jung Sik Koh, the former CEO at the Korea Resources Corporation. His term starts from January 2018 to December 2020.
Cha is the CEO of Inbody Co Ltd., a global company specializing in developing and selling medical instruments, such as a body composition analyzers, and medical solutions. He is also an adjunct professor in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Yonsei University. Cha obtained a master’s degree in Mechanical Engineering at KAIST in 1980, and a Ph.D. in Bioengineering at the University of Utah, before finishing his post-doc fellowship at Harvard Medical School.
Cha plans to explore the idea that alumni engagement, saying, “KAIST stays as a home in the memories of 60,000 alumni. I will dedicate myself to stimulating the alumni association to make KAISTians proud.”
At the gala event, the KAA awarded the Alumni of the Year honor to six alumni who distinguished themselves in the areas of professional achievement, humanitarianism, and public service. They are the Director of Startup KAIST Professor Byoung Yoon Kim; President of LG Chem Ltd and Head of Battery Research and Development Myung Hwan Kim; Director of INNOX Advanced Materials Co., Ltd Kyung Ho Chang; Vice President of the Korea International Trade Association Jung-Kwan Kim; CEO of Samsung Electro-Mechanics Yun-Tae Lee; and CEO of ENF Technology Jinbae Jung.
Photo: President Shin(far right) poses with six awardees of the Distinguished Alumni Award and the former President of KAA, Koh(far left)
2018.01.16 View 10699