TR
-
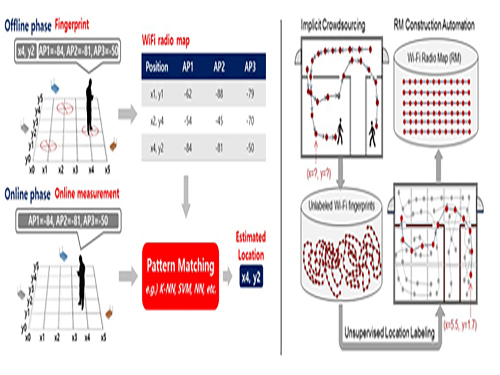 Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 9829
Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 9829 -
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 9003
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 9003 -
 A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 9418
A Transport Technology for Nanowires Thermally Treated at 700 Celsius Degrees
Professor Jun-Bo Yoon and his research team of the Department of Electrical Engineering at KAIST developed a technology for transporting thermally treated nanowires to a flexible substrate and created a high performance device for collecting flexible energy by using the new technology.
Mr. Min-Ho Seo, a Ph.D. candidate, participated in this study as the first author. The results were published online on January 30th in ACS Nano, an international journal in the field of nanoscience and engineering. (“Versatile Transfer of an Ultralong and Seamless Nanowire Array Crystallized at High Temperature for Use in High-performance Flexible Devices,” DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.6b06842)
Nanowires are one of the most representative nanomaterials. They have wire structures with dimensions in nanometers. The nanowires are widely used in the scientific and engineering fields due to their prominent physical and chemical properties that depend on a one-dimensional structure, and their high applicability.
Nanowires have much higher performance if their structure has unique features such as an excellent arrangement and a longer-than-average length. Many researchers are thus actively participating in the research for making nanowires without much difficulty, analyzing them, and developing them for high performance application devices.
Scientists have recently favored a research topic on making nanowires chemically and physically on a flexible substrate and applies the nanowires to a flexible electric device such as a high performance wearable sensor.
The existing technology, however, mixed nanowires from a chemical synthesis with a solution and spread the mixture on a flexible substrate. The resultant distribution was random, and it was difficult to produce a high performance device based on the structural advantages of nanowires. In addition, the technology used a cutting edge nano-process and flexible materials, but this was not economically beneficial. The production of stable materials at a temperature of 700 Celsius degrees or higher is unattainable, a great challenge for the application.
To solve this problem, the research team developed a new nano-transfer technology that combines a silicon nano-grating board with a large surface area and a nano-sacrificial layer process. A nano-sacrificial layer exists between nanowires and a nano-grating board, which acts as the mold for the nano-transfer. The new technology allows the device undergo thermal treatment. After this, the layer disappears when the nanowires are transported to a flexible substrate.
This technology also permits the stable production of nanowires with secured properties at an extremely high temperature. In this case, the nanowires are neatly organized on a flexible substrate. The research team used the technology to manufacture barium carbonate nanowires on top of the flexible substrate. The wires secured their properties at a temperature of 700℃ or above. The team employed the collection of wearable energy to obtain much higher electrical energy than that of an energy collecting device designed based on regular barium titanate nanowires.
The researchers said that their technology is built upon a semiconductor process, known as Physical Vapor Deposition that allows various materials such as ceramics and semiconductors to be used for flexible substrates of nanowires. They expected that high performance flexible electric devices such as flexible transistors and thermoelectric elements can be produced with this method.
Mr. Seo said, “In this study, we transported nanowire materials with developed properties on a flexible substrate and showed an increase in device performance. Our technology will be fundamental to the production of various nanowires on a flexible substrate as well as the feasibility of making high performance wearable electric devices.”
This research was supported by the Leap Research Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Fig. 1. Transcription process of new, developed nanowires (a) and a fundamental mimetic diagram of a nano-sacrificial layer (b)
Fig. 2. Transcription results from using gold (AU) nanowires. The categories of the results were (a) optical images, (b) physical signals, (c) cross-sectional images from a scanning electron microscope (SEM), and (d-f) an electric verification of whether the perfectly arranged nanowires were made on a large surface.
Fig. 3. Transcription from using barium titanate (BaTiO3) nanowires. The results were (a) optical images, (b-e) top images taken from an SEM in various locations, and (f, g) property analysis.
Fig. 4. Mimetic diagram of the energy collecting device from using a BaTiO3 nanowire substrate and an optical image of the experiment for the miniature energy collecting device attached to an index finger.
2017.03.22 View 9418 -
 Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 10448
Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 10448 -
 Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 11004
Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 11004 -
 13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 17895
13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 17895 -
 Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11448
Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 11448 -
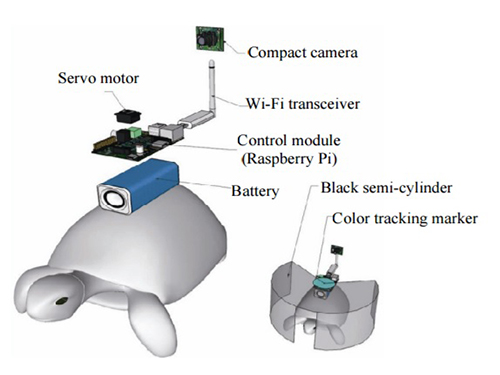 Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 15122
Controlling Turtle Motion with Human Thought
KAIST researchers have developed a technology that can remotely control an animal’s movement with human thought.
In the 2009 blockbuster “Avatar,” a human remotely controls the body of an alien. It does so by injecting human intelligence into a remotely located, biological body. Although still in the realm of science fiction, researchers are nevertheless developing so-called ‘brain-computer interfaces’ (BCIs) following recent advances in electronics and computing. These technologies can ‘read’ and use human thought to control machines, for example, humanoid robots.
New research has demonstrated the possibility of combining a BCI with a device that transmits information from a computer to a brain, or known as a ‘computer-to-brain interface’ (CBI). The combination of these devices could be used to establish a functional link between the brains of different species. Now, researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) have developed a human-turtle interaction system in which a signal originating from a human brain can affect where a turtle moves.
Unlike previous research that has tried to control animal movement by applying invasive methods, most notably in insects, Professors Phill-Seung Lee of the Mechanical Engineering Department and Sungho Jo of the Computing School propose a conceptual system that can guide an animal’s moving path by controlling its instinctive escape behavior. They chose a turtle because of its cognitive abilities as well as its ability to distinguish different wavelengths of light. Specifically, turtles can recognize a white light source as an open space and so move toward it. They also show specific avoidance behavior to things that might obstruct their view. Turtles also move toward and away from obstacles in their environment in a predictable manner. It was this instinctive, predictable behavior that the researchers induced using the BCI.
The entire human-turtle setup is as follows: A head-mounted display (HMD) is combined with a BCI to immerse the human user in the turtle’s environment. The human operator wears the BCI-HMD system, while the turtle has a 'cyborg system'—consisting of a camera, Wi-Fi transceiver, computer control module, and battery—all mounted on the turtle’s upper shell. Also included on the turtle’s shell is a black semi-cylinder with a slit, which forms the ‘stimulation device.’ This can be turned ±36 degrees via the BCI.
The entire process works like this: the human operator receives images from the camera mounted on the turtle. These real-time video images allow the human operator to decide where the turtle should move. The human provides thought commands that are recognized by the wearable BCI system as electroencephalography (EEG) signals. The BCI can distinguish between three mental states: left, right, and idle. The left and right commands activate the turtle’s stimulation device via Wi-Fi, turning it so that it obstructs the turtle’s view. This invokes its natural instinct to move toward light and change its direction. Finally, the human acquires updated visual feedback from the camera mounted on the shell and in this way continues to remotely navigate the turtle’s trajectory.
The research demonstrates that the animal guiding scheme via BCI can be used in a variety of environments with turtles moving indoors and outdoors on many different surfaces, like gravel and grass, and tackling a range of obstacles, such as shallow water and trees. This technology could be developed to integrate positioning systems and improved augmented and virtual reality techniques, enabling various applications, including devices for military reconnaissance and surveillance.
***
Reference: “Remote Navigation of Turtle by Controlling Instinct Behavior via Human Brain-computer Interface,” Journal of Bionic Engineering, July 2016 (DOI: 10.1016/S1672-6529(16)60322-0)
Depiction of Cyborg System
A human controller influences the turtle’s escape behavior by sending left and right signals via Wi-Fi to a control system on the back of the turtle.
2017.02.21 View 15122 -
 KAIST Celebrates the 2017 Commencement
KAIST hosted its 2017 Commencement, awarding diplomas to 2,767 members of the Class of 2017 during a ceremony on February 17. President Sung-Mo Kang, Minister Yang-hee Choi of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Jang-Moo Lee joined the ceremony along with the graduates and their family and friends at the Ryu Keun Chul Sports Complex.
The graduating class included 638 Ph.D. degrees, 1,335 Master’s degrees, and 794 Bachelor’s degrees being conferred. Among them, Young-Ki Song from the Department of Electric Engineering was honored to win the Minister’s Award, the highest award bestowed to an undergraduate. The KAIST Presidential Award went to Min-Jae Park of the Department of Mathematical Sciences and the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairman’s Award was presented to Jae-Hyung Cho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Including this year’s graduating class, KAIST has turned out more than 59,000 highly educated science and technology talents including 11,731 Ph.D.s since its foundation in 1971. This year, 24-year-old Seo-Hee Oh earned her Ph.D. in chemistry as the youngest Ph.D. of the year after completing her Master’s and Ph.D. combined course in three years.
President Sung-Mo Kang praised the creativity of this graduating class and their excellent ability in his charge, saying, “As future leaders of our society, you are expected to develop a sense of compassion and outstanding professionalism to contribute to the advancement of not only Korea but also the whole world.’
For full text of President Kang’s charge to the graduates, please click.
2017.02.17 View 9170
KAIST Celebrates the 2017 Commencement
KAIST hosted its 2017 Commencement, awarding diplomas to 2,767 members of the Class of 2017 during a ceremony on February 17. President Sung-Mo Kang, Minister Yang-hee Choi of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, and Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Jang-Moo Lee joined the ceremony along with the graduates and their family and friends at the Ryu Keun Chul Sports Complex.
The graduating class included 638 Ph.D. degrees, 1,335 Master’s degrees, and 794 Bachelor’s degrees being conferred. Among them, Young-Ki Song from the Department of Electric Engineering was honored to win the Minister’s Award, the highest award bestowed to an undergraduate. The KAIST Presidential Award went to Min-Jae Park of the Department of Mathematical Sciences and the KAIST Board of Trustee Chairman’s Award was presented to Jae-Hyung Cho from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Including this year’s graduating class, KAIST has turned out more than 59,000 highly educated science and technology talents including 11,731 Ph.D.s since its foundation in 1971. This year, 24-year-old Seo-Hee Oh earned her Ph.D. in chemistry as the youngest Ph.D. of the year after completing her Master’s and Ph.D. combined course in three years.
President Sung-Mo Kang praised the creativity of this graduating class and their excellent ability in his charge, saying, “As future leaders of our society, you are expected to develop a sense of compassion and outstanding professionalism to contribute to the advancement of not only Korea but also the whole world.’
For full text of President Kang’s charge to the graduates, please click.
2017.02.17 View 9170 -
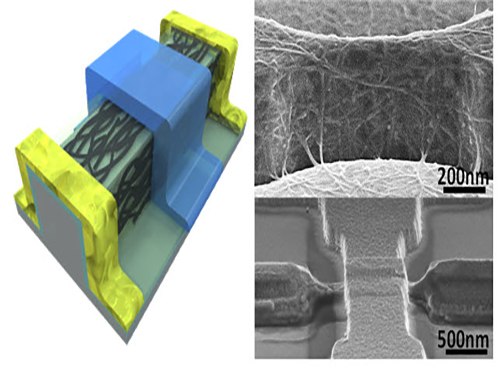 An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 11064
An Improved Carbon Nanotube Semiconductor
Professor Yang-Kyu Choi and his research team of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST collaborated with Professor Sung-Jin Choi of Kookmin University to develop a large-scale carbon nanotube semiconductor by using a 3-D fin-gate structure with carbon nanotubes on its top.
Dong Il Lee, a postdoctoral researcher at KAIST’s Electrical Engineering School, participated in this study as the first author. It was published in ACS Nano on November 10, 2016, and was entitled “Three-Dimensional Fin-Structured Semiconducting Carbon Nanotube Network Transistor.”
A semiconductor made with carbon nanotubes operates faster than a silicon semiconductor and requires less energy, yielding higher performance.
Most electronic equipment and devices, however, use silicon semiconductors because it is difficult to fabricate highly purified and densely packed semiconductors with carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
To date, the performance of CNTs was limited due to their low density. Their purity was also low, so it was impossible to make products that had a constant yield on a large-surface wafer or substrate. These characteristics made the mass production of semiconducting CNTs difficult.
To solve these difficulties, the research team used a 3-D fin-gate to vapor-deposit carbon nanotubes on its top. They developed a semiconductor that had a high current density with a width less than 50 nm.
The three-dimensional fin structure was able to vapor-deposit 600 carbon nanotubes per micrometer. This structure could have 20 times more nanotubes than the two dimensional structure, which could only vapor-deposit thirty in the same 1 micrometer width.
In addition, the research team used semi-conductive carbon nanotubes having a purity rating higher than 99.9% from a previous study to obtain a high yield semiconductor.
The semiconductor from the research group has a high current density even with a width less than 50 μm. The new semiconductor is expected to be five times faster than a silicon-based semiconductor and will require five times less electricity during operation.
Furthermore, the new semiconductor can be made by or will be compatible with the equipment for producing silicon-based semiconductors, so there will be no additional costs.
Researcher Lee said, “As a next generation semiconductor, the carbon nanotube semiconductor will have better performance, and its effectiveness will be higher.” He also added, “Hopefully, the new semiconductor will replace the silicon-based semiconductors in ten years.”
This study received support from the Center for Integrated Smart Sensors funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning of Korea as the Global Frontier Project, and from the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) THz Technology Convergence Center of the Pioneer Research Center Program sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Picture 1: 3D Diagram of the Carbon Nanotube Electronic Device and Its Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Image
Picture 2: 3D Transistor Device on an 8-inch Base and the SEM Image of Its Cross Section
2017.02.16 View 11064 -
 Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6760
Dr.M Drives Smart Healthcare Industry in Partnership with Hancom
President Sung-Mo Kang signed an agreement on January 25 with Hancom Group Chairman Sang Chul Kim to establish a smart healthcare complex in Gapyeong, Kyonggido. With the Gapyeong complex launch, KAIST will come to commercialize Dr. M system along with other Dr.M consortium members as a new growth engine to drive the smart health industry.
Dr. M is a smart healthcare platform developed by the Health Science Research Institute at KAIST in 2014. Dr. M is capable of analyzing and predicting diseases, as well as prescribing, by incorporating ICT and medical technologies. Dr. M applies diverse technologies such as healthcare sensors, wearable devices, low-power communications technology, and cloud and big data collection platforms.
Hancom Group, a leading computer software company in Korea, has participated in the project since 2015 for advancing the smart healthcare market by developing mobile healthcare software program. Hancom joined the Dr.M consortium launched last November.
(President Kang (left) poses with Hancom Chairman Kim after signing.)
2017.02.03 View 6760 -
 KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8380
KAIST Intensive Science Camp for Middle-High School Students
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education (Director: Dong-Soo Kwon) invited around 90 middle and high school students for an advanced science intensive camp from January 22 to 24.
This camp targeted middle and high school students in community centers or child-care institutions. It aims to increase students’ interest in science and engineering, and assist them with their career paths through programs such as special lectures on science, advanced science projects, and career mentoring.
Participating students were divided into groups of seven or eight with a KAIST student as a mentor to conduct advanced science projects such as VR controller production and robot arm programming. The camp included exploring future career options and science and engineering college admission counselling.
Jiyoung Ryu, Research Professor for the KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education, said, “KAIST started the science and engineering career experience program in 2016 with the Ministry of Education and Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training (KRIVET). So far, 6000 middle and high school students from around the country have participated. The camp is more meaningful since it educates students in social responsibility, in addition to the fields of science and engineering, both of which are missions and goals that KAIST strives for.” She continued to say, “We plan to continue to expand the program in the future.”
The KAIST Global Institute of Talented Education is actively conducting research and projects on national education for talented youth such as policy research concerning gifted education, science and engineering career education, advanced science camps, training for gifted education teachers, and cyber gifted education programs.
2017.02.01 View 8380