CES
-
 Using light to throw and catch atoms to open up a new chapter for quantum computing
The technology to move and arrange atoms, the most basic component of a quantum computer, is very important to Rydberg quantum computing research. However, to place the atoms at the desired location, the atoms must be captured and transported one by one using a highly focused laser beam, commonly referred to as an optical tweezer. and, the quantum information of the atoms is likely to change midway.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th that a research team led by Professor Jaewook Ahn of the Department of Physics developed a technology to throw and receive rubidium atoms one by one using a laser beam.
The research team developed a method to throw and receive atoms which would minimize the time the optical tweezers are in contact with the atoms in which the quantum information the atoms carry may change. The research team used the characteristic that the rubidium atoms, which are kept at a very low temperature of 40μK below absolute zero, move very sensitively to the electromagnetic force applied by light along the focal point of the light tweezers.
The research team accelerated the laser of an optical tweezer to give an optical kick to an atom to send it to a target, then caught the flying atom with another optical tweezer to stop it. The atom flew at a speed of 65 cm/s, and traveled up to 4.2 μm. Compared to the existing technique of guiding the atoms with the optical tweezers, the technique of throwing and receiving atoms eliminates the need to calculate the transporting path for the tweezers, and makes it easier to fix the defects in the atomic arrangement. As a result, it is effective in generating and maintaining a large number of atomic arrangements, and when the technology is used to throw and receive flying atom qubits, it will be used in studying new and more powerful quantum computing methods that presupposes the structural changes in quantum arrangements.
"This technology will be used to develop larger and more powerful Rydberg quantum computers," says Professor Jaewook Ahn. “In a Rydberg quantum computer,” he continues, “atoms are arranged to store quantum information and interact with neighboring atoms through electromagnetic forces to perform quantum computing. The method of throwing an atom away for quick reconstruction the quantum array can be an effective way to fix an error in a quantum computer that requires a removal or replacement of an atom.”
The research, which was conducted by doctoral students Hansub Hwang and Andrew Byun of the Department of Physics at KAIST and Sylvain de Léséleuc, a researcher at the National Institute of Natural Sciences in Japan, was published in the international journal, Optica, 0n March 9th. (Paper title: Optical tweezers throw and catch single atoms).
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
<Figure 1> A schematic diagram of the atom catching and throwing technique. The optical tweezer on the left kicks the atom to throw it into a trajectory to have the tweezer on the right catch it to stop it.
2023.03.28 View 7849
Using light to throw and catch atoms to open up a new chapter for quantum computing
The technology to move and arrange atoms, the most basic component of a quantum computer, is very important to Rydberg quantum computing research. However, to place the atoms at the desired location, the atoms must be captured and transported one by one using a highly focused laser beam, commonly referred to as an optical tweezer. and, the quantum information of the atoms is likely to change midway.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th that a research team led by Professor Jaewook Ahn of the Department of Physics developed a technology to throw and receive rubidium atoms one by one using a laser beam.
The research team developed a method to throw and receive atoms which would minimize the time the optical tweezers are in contact with the atoms in which the quantum information the atoms carry may change. The research team used the characteristic that the rubidium atoms, which are kept at a very low temperature of 40μK below absolute zero, move very sensitively to the electromagnetic force applied by light along the focal point of the light tweezers.
The research team accelerated the laser of an optical tweezer to give an optical kick to an atom to send it to a target, then caught the flying atom with another optical tweezer to stop it. The atom flew at a speed of 65 cm/s, and traveled up to 4.2 μm. Compared to the existing technique of guiding the atoms with the optical tweezers, the technique of throwing and receiving atoms eliminates the need to calculate the transporting path for the tweezers, and makes it easier to fix the defects in the atomic arrangement. As a result, it is effective in generating and maintaining a large number of atomic arrangements, and when the technology is used to throw and receive flying atom qubits, it will be used in studying new and more powerful quantum computing methods that presupposes the structural changes in quantum arrangements.
"This technology will be used to develop larger and more powerful Rydberg quantum computers," says Professor Jaewook Ahn. “In a Rydberg quantum computer,” he continues, “atoms are arranged to store quantum information and interact with neighboring atoms through electromagnetic forces to perform quantum computing. The method of throwing an atom away for quick reconstruction the quantum array can be an effective way to fix an error in a quantum computer that requires a removal or replacement of an atom.”
The research, which was conducted by doctoral students Hansub Hwang and Andrew Byun of the Department of Physics at KAIST and Sylvain de Léséleuc, a researcher at the National Institute of Natural Sciences in Japan, was published in the international journal, Optica, 0n March 9th. (Paper title: Optical tweezers throw and catch single atoms).
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
<Figure 1> A schematic diagram of the atom catching and throwing technique. The optical tweezer on the left kicks the atom to throw it into a trajectory to have the tweezer on the right catch it to stop it.
2023.03.28 View 7849 -
 KAIST research team develops clathrin assembly for targeted protein delivery to cancer cells
In order to effectively treat cancer without additional side effects, we need a way to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. Protein assemblies have been widely used for drug delivery in the field of cancer treatment, but to use them for drug delivery they must first be functionalized, meaning they must be bound to the protein that recognizes the target tumor cell and deliver a drug that kills it. However, the functionalization process of protein assemblies is very complex, inefficient, and limited to small-sized chemical drugs, which limits their real-life applicability.
On March 14, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences reported the development of a clathrin assembly that can specifically deliver drugs to cancer cells.
Clathrin assemblies transport materials efficiently through endocytosis in living organisms. They are formed by the self-assembly of triskelion units, which are composed of three heavy chains bonded with three light chains. Inspired by this mechanism, the research team designed a clathrin chain to facilitate the functionalization of tumor cell recognition proteins and toxin proteins in order to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. From this, the team created a new type of clathrin assembly.
Figure 1. (Upper) Schematic diagram of the development of a new clathrin assembly that simultaneously functionalizes two types of proteins (cancer cell recognition protein and toxin protein) on heavy and light chains of clathrin in a one-pot reaction (bottom, left) Electron microscopy image of clathrin assembly: formation of an assembly with a diameter of about 28 nanometers (bottom, right) Cancer cell killing effect of CLA: CLA functionalized with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) recognition protein and toxin protein kills only the cancer cells that overexpress EGFR.
The newly developed clathrin assembly requires a one-pot reaction, meaning both the toxin and tumor-recognition proteins can be functionalized simultaneously and show high efficiency. As a result, this technique is expected to be used in a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and medicine including drug delivery, vaccine development, and diagnosing illnesses.
In this research, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a common tumor marker, was used as the recognition protein, allowing drug delivery only to tumor cells. The clathrin assemblies that were functionalized to recognize EGFR showed a bonding strength 900-times stronger than it normally would due to the avidity effect. Based on this finding, the research team confirmed that treatment with toxin-functionalized clathrin assembly led to effective cell death for tumor cells, while it showed no such effect on healthy cells.
This research by Dr. Hong-Sik Kim and his colleagues was published in Small volume 19, issue 8 on February 22 under the title, "Construction and Functionalization of a Clathrin Assembly for a Targeted Protein Delivery", and it was selected as the cover paper.
Figure 2. Cover Paper: This study was published in the international journal 'Small' on February 22nd, Volume 19, No. 8, and was selected as the cover paper.
First author Dr. Hong-Sik Kim said, “Clathrin is difficult to functionalize, and since it is extracted from mammals, realistic applications have been limited.” He added, “But the new clathrin assembly we designed for this research can be functionalized with two different types of proteins through a single-step reaction, and can be produced from E. coli, meaning it can become an applicable protein assembly technology for a wide range of biomedical fields.”
This research was funded by the Global Ph.D. Fellowship and the Mid-career Researcher Grant of the National Research Foundation.
2023.03.22 View 7242
KAIST research team develops clathrin assembly for targeted protein delivery to cancer cells
In order to effectively treat cancer without additional side effects, we need a way to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. Protein assemblies have been widely used for drug delivery in the field of cancer treatment, but to use them for drug delivery they must first be functionalized, meaning they must be bound to the protein that recognizes the target tumor cell and deliver a drug that kills it. However, the functionalization process of protein assemblies is very complex, inefficient, and limited to small-sized chemical drugs, which limits their real-life applicability.
On March 14, a KAIST research team led by Professor Hak-Sung Kim from the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences reported the development of a clathrin assembly that can specifically deliver drugs to cancer cells.
Clathrin assemblies transport materials efficiently through endocytosis in living organisms. They are formed by the self-assembly of triskelion units, which are composed of three heavy chains bonded with three light chains. Inspired by this mechanism, the research team designed a clathrin chain to facilitate the functionalization of tumor cell recognition proteins and toxin proteins in order to deliver drugs specifically to tumor cells. From this, the team created a new type of clathrin assembly.
Figure 1. (Upper) Schematic diagram of the development of a new clathrin assembly that simultaneously functionalizes two types of proteins (cancer cell recognition protein and toxin protein) on heavy and light chains of clathrin in a one-pot reaction (bottom, left) Electron microscopy image of clathrin assembly: formation of an assembly with a diameter of about 28 nanometers (bottom, right) Cancer cell killing effect of CLA: CLA functionalized with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) recognition protein and toxin protein kills only the cancer cells that overexpress EGFR.
The newly developed clathrin assembly requires a one-pot reaction, meaning both the toxin and tumor-recognition proteins can be functionalized simultaneously and show high efficiency. As a result, this technique is expected to be used in a wide variety of applications in the fields of biology and medicine including drug delivery, vaccine development, and diagnosing illnesses.
In this research, an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a common tumor marker, was used as the recognition protein, allowing drug delivery only to tumor cells. The clathrin assemblies that were functionalized to recognize EGFR showed a bonding strength 900-times stronger than it normally would due to the avidity effect. Based on this finding, the research team confirmed that treatment with toxin-functionalized clathrin assembly led to effective cell death for tumor cells, while it showed no such effect on healthy cells.
This research by Dr. Hong-Sik Kim and his colleagues was published in Small volume 19, issue 8 on February 22 under the title, "Construction and Functionalization of a Clathrin Assembly for a Targeted Protein Delivery", and it was selected as the cover paper.
Figure 2. Cover Paper: This study was published in the international journal 'Small' on February 22nd, Volume 19, No. 8, and was selected as the cover paper.
First author Dr. Hong-Sik Kim said, “Clathrin is difficult to functionalize, and since it is extracted from mammals, realistic applications have been limited.” He added, “But the new clathrin assembly we designed for this research can be functionalized with two different types of proteins through a single-step reaction, and can be produced from E. coli, meaning it can become an applicable protein assembly technology for a wide range of biomedical fields.”
This research was funded by the Global Ph.D. Fellowship and the Mid-career Researcher Grant of the National Research Foundation.
2023.03.22 View 7242 -
 KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8626
KAIST researchers develops a tech to enable production of ultrahigh-resolution LED with sub-micrometer scale pixels
Ultrahigh-resolution displays are an essential element for developing next-generation electronic products such as virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and smart watches, and can be applied not only to head-mounted displays, but also to smart glasses and smart lenses. The technology developed through this research is expected to be used to make such next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and other various sub-micro optoelectronic devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd that Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team of KAIST Department of Physics developed the core technology for an ultrahigh resolution light-emitting diode (LED) display that can realize 0.5 micron-scale pixels smaller than 1/100 of the average hair thickness (about 100 microns) using focused ion beams.
Commonly, pixelation of ultrahigh-resolution LED displays usually relies on the etching method that physically cuts the area around the pixel, but as the pixel becomes smaller due to the occurrence of various defects around it, leading to side-effects of having leakage of current increased and light-emission efficiency decreased. In addition, various complex processes such as patterning for pixelation and post-processing for prevention of leakage current are required.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho's research team developed a technology that can create pixels down to the size of a microscale without the complicated pre- and post-processing using a focused ion beam. This method has the advantage of being able to freely set the shape of the emitting pixel without causing any structural deformation on the material surface by controlling the intensity of the focused ion beam.
The focused ion beam technology has been widely used for ultrahigh-magnification imaging and nanostructure fabrication in fields such as materials engineering and biology. However, when a focused ion beam is used on a light emitting body such as an LED, light emission of a portion hit by the beam and a surrounding area rapidly decreases, which has been a barrier to fabricating a nano-scale light emitting structure. Upon facing this issue, Professor Cho's research team began the research on the idea that if they turned things around to use these problematic phenomena, they can be used in ultra-fine pixelation method on a sub-micron scale.
The research team used a focused ion beam whose intensity was softened to the extent that the surface was not shaved, and found that not only the light-emission rapidly decreased in the area hit by the focused ion beam, but also the local resistance greatly increased. As a result, while the surface of the LED is kept flat, the portion hit by the focused ion beam is optically and electrically isolated, enabling pixelation for independent operation.
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, who led the research, said, “We have newly developed a technology that can create sub-micron-scale pixels without complicated processes using a focused ion beam, which will be a base technology that can be applied to next-generation ultrahigh-resolution displays and nano-photoelectronic devices.”
This research in which the Master's student Ji-Hwan Moon and the Ph.D. student Baul Kim of KAIST Department of Physics participated as co-first authors, was carried out with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea's Support Program for Mid-Career Researchers and the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation. It was published online in 'Advanced Materials' on February 13, and was also selected as the internal cover of the next offline edition. (Title: Electrically Driven Sub-Micron Light-Emitting Diode Arrays Using Maskless and Etching-Free Pixelation)
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the technology for ultrahigh density sub-micron-sized pixels through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation on an LED device
Figure 2. Ultra-high-density pixelation technology of micro light-emitting diodes (μLED) through He focused ion beam (FIB) irradiation
Figure 3. Rectangular pixels of different sizes (surface structure picture and luminescence picture) realized by a focused ion beam. Luminescence pictures of pixel arrays ranging in size from 20 µm x 20 µm to 0.5 µm x 0.5 µm, with surface flatness maintained.
2023.03.08 View 8626 -
 Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
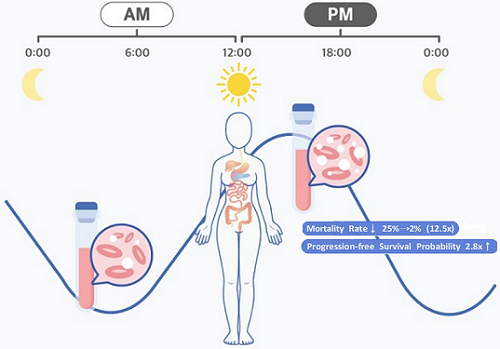
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 7951
Afternoon chemotherapy proved to deliver more desirable results for female lymphoma patients
Chemotherapy is a commonly used regimen for cancer treatment, but it is also a double-edged sword. While the drugs are highly effective at killing cancer cells, they are also notorious for killing healthy cells in the body. As such, minimizing the drug’s damage to the patient’s body is necessary for improving the prognosis of chemotherapy.
Recently, “chrono-chemotherapy” have been gaining interest in the research community. As the name suggests, the aim is timing the delivery of the drugs when the body is least vulnerable to their harmful effects and while the cancer cells are at their most vulnerable.
< Figure 1. Chrono-chemotherapy considering circadian rhythm >
Chrono-chemotherapy exploits the fact that human physiological processes, including cell proliferation and differentiation, are regulated by an endogenous timer called the circadian clock. However, this has not been widely exploited in real-world clinical settings because, as of now, there is no systematic method for finding the optimal chemotherapy delivery time.
This problem was tackled by an interdisciplinary team of researchers from South Korea. They were led by principal investigators Jae Kyoung Kim (a mathematician from the Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science) and Youngil Koh (an oncologist at Seoul National University Hospital). The researchers studied a group of patients suffering from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL).
Terminology
* Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL): Lymphoma is a type of blood cancer caused by the malignant transformation of lymphoid tissue cells. Lymphoma is divided into Hodgkin's lymphoma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (malignant lymphoma), and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma accounts for about 30 to 40% of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
The research team noticed that DLBCL patients at Seoul National University Hospital received chemotherapy on two different schedules, with some patients receiving morning treatment (8:30 a.m.) and others taking the drugs in the afternoon (2:30 p.m.). All patients received the same cancer treatment (R-CHOP), which is a combination of targeted therapy and chemotherapy, four to six times in the morning or afternoon at intervals of about three weeks.
They analyzed 210 patients to investigate whether there was any difference between morning and afternoon treatments. It was found that female patients who received the afternoon treatment had a 12.5 times reduced mortality rate (25% to 2%), while the cancer recurrence after 60 months decreased by 2.8 times (37% to 13%). In addition, chemotherapy side effects such as neutropenia were more common in female patients who received the morning treatment.
Surprisingly, there was no differences found in treatment efficiency depending on the treatment schedule in the cases of male patients.
To understand the cause of the gender differences, the research team analyzed upto 14,000 blood samples from the Seoul National University Hospital Health Examination Center. It was found that in females, white blood cell counts tended to decrease in the morning and increase in the afternoon. This indicates that the bone marrow proliferation rate was higher in the morning than in the afternoon because there is a upto 12 hour delay between bone marrow proliferation and blood cell production.
This means that if a female patient receives chemotherapy in the morning when bone marrow is actively producing blood cells, the possibility of adverse side effects becomes greater. These results are consistent with the findings from recent randomized clinical trials that showed female colorectal cancer patients treated with irinotecan in the morning suffered from higher drug toxicities.
One confounding variable was the drug dose. Since the morning female patients suffered from greater adverse side effects, oftentimes the dose had to be reduced for these patients. On average, the drug dose was reduced by upto 10% compared to the dose intensity given to female patients receiving the afternoon treatment.
Unlike the female patients, it was found that male patients did not show a significant difference in white blood cell count and bone marrow cell proliferation activity throughout the day, which explains why the timing of the treatment had no impact.
Professor Youngil Koh said, “We plan to verify the conclusions of this study again with a large-scale follow-up study that completely controls for the confounding variables, and to confirm whether chrono-chemotherapy has similar effects on other cancers.”
CI Jae Kyoung Kim said, “Because the time of the internal circadian clock can vary greatly depending on the individual's sleep-wake patterns, we are currently developing a technology to estimate a patient’s circadian clock from their sleep pattern. We hope that this can be used to develop an individualized anti-cancer chronotherapy schedule.”
< Figure 2. Chemotherapy in the afternoon can improve treatment outcomes. >
The daily fluctuation of proliferative activity of bone marrow is larger in females than in males, and it becomes higher in the morning (left). Thus, chemotherapy in the morning strongly inhibits proliferative activity in female lymphoma patients, resulting in a higher incidence of adverse events such as neutropenia and infections. This forced the clinicians to reduce the dose intensity (center). Consequently, female patients undergoing the morning treatment showed a lower survival probability than those undergoing the afternoon treatment (right). Specifically, only ~13% of female patients treated in the afternoon had a worse outcome and ~2% of them died while ~37% of female patients treated in the morning had a worse outcome and ~25% of them died. Male patients did not show any difference in treatment outcomes depending on the chemotherapy delivery time.
2023.01.27 View 7951 -
 Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 14516
Scientists re-writes FDA-recommended equation to improve estimation of drug-drug interaction
Drugs absorbed into the body are metabolized and thus removed by enzymes from several organs like the liver. How fast a drug is cleared out of the system can be affected by other drugs that are taken together because added substance can increase the amount of enzyme secretion in the body. This dramatically decreases the concentration of a drug, reducing its efficacy, often leading to the failure of having any effect at all. Therefore, accurately predicting the clearance rate in the presence of drug-drug interaction* is critical in the process of drug prescription and development of a new drug in order to ensure its efficacy and/or to avoid unwanted side-effects.
*Drug-drug interaction: In terms of metabolism, drug-drug interaction is a phenomenon in which one drug changes the metabolism of another drug to promote or inhibit its excretion from the body when two or more drugs are taken together. As a result, it increases the toxicity of medicines or causes loss of efficacy.
Since it is practically impossible to evaluate all interactions between new drug candidates and all marketed drugs during the development process, the FDA recommends indirect evaluation of drug interactions using a formula suggested in their guidance, first published in 1997, revised in January of 2020, in order to evaluate drug interactions and minimize side effects of having to use more than one type of drugs at once.
The formula relies on the 110-year-old Michaelis-Menten (MM) model, which has a fundamental limit of making a very broad and groundless assumption on the part of the presence of the enzymes that metabolizes the drug. While MM equation has been one of the most widely known equations in biochemistry used in more than 220,000 published papers, the MM equation is accurate only when the concentration of the enzyme that metabolizes the drug is almost non-existent, causing the accuracy of the equation highly unsatisfactory – only 38 percent of the predictions had less than two-fold errors.
“To make up for the gap, researcher resorted to plugging in scientifically unjustified constants into the equation,” Professor Jung-woo Chae of Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy said. “This is comparable to having to have the epicyclic orbits introduced to explain the motion of the planets back in the days in order to explain the now-defunct Ptolemaic theory, because it was 'THE' theory back then.”
< (From left) Ph.D. student Yun Min Song (KAIST, co-first authors), Professor Sang Kyum Kim (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Jae Kyoung Kim, CI (KAIST, co-corresponding author), Professor Jung-woo Chae (Chungnam National University, co-corresponding author), Ph.D. students Quyen Thi Tran and Ngoc-Anh Thi Vu (Chungnam National University, co-first authors) >
A joint research team composed of mathematicians from the Biomedical Mathematics Group within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS) and the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and pharmacological scientists from the Chungnam National University reported that they identified the major causes of the FDA-recommended equation’s inaccuracies and presented a solution.
When estimating the gut bioavailability (Fg), which is the key parameter of the equation, the fraction absorbed from the gut lumen (Fa) is usually assumed to be 1. However, many experiments have shown that Fa is less than 1, obviously since it can’t be expected that all of the orally taken drugs to be completely absorbed by the intestines. To solve this problem, the research team used an “estimated Fa” value based on factors such as the drug’s transit time, intestine radius, and permeability values and used it to re-calculate Fg.
Also, taking a different approach from the MM equation, the team used an alternative model they derived in a previous study back in 2020, which can more accurately predict the drug metabolism rate regardless of the enzyme concentration. Combining these changes, the modified equation with re-calculated Fg had a dramatically increased accuracy of the resulting estimate. The existing FDA formula predicted drug interactions within a 2-fold margin of error at the rate of 38%, whereas the accuracy rate of the revised formula reached 80%.
“Such drastic improvement in drug-drug interaction prediction accuracy is expected to make great contribution to increasing the success rate of new drug development and drug efficacy in clinical trials. As the results of this study were published in one of the top clinical pharmacology journal, it is expected that the FDA guidance will be revised according to the results of this study.” said Professor Sang Kyum Kim from Chungnam National University College of Pharmacy.
Furthermore, this study highlights the importance of collaborative research between research groups in vastly different disciplines, in a field that is as dynamic as drug interactions.
“Thanks to the collaborative research between mathematics and pharmacy, we were able to recify the formula that we have accepted to be the right answer for so long to finally grasp on the leads toward healthier life for mankind.,” said Professor Jae Kyung Kim. He continued, “I hope seeing a ‘K-formula’ entered into the US FDA guidance one day.”
The results of this study were published in the online edition of Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics (IF 7.051), an authoritative journal in the field of clinical pharmacology, on December 15, 2022 (Korean time).
Thesis Title: Beyond the Michaelis-Menten: Accurate Prediction of Drug Interactions through Cytochrome P450 3A4 Induction (doi: 10.1002/cpt.2824)
< Figure 1. The formula proposed by the FDA guidance for predicting drug-drug interactions (top) and the formula newly derived by the researchers (bottom). AUCR (the ratio of substrate area under the plasma concentration-time curve) represents the rate of change in drug concentration due to drug interactions. The research team more than doubled the accuracy of drug interaction prediction compared to the existing formula. >
< Figure 2. Existing FDA formulas tend to underestimate the extent of drug-drug interactions (gray dots) than the actual measured values. On the other hand, the newly derived equation (red dot) has a prediction rate that is within the error range of 2 times (0.5 to 2 times) of the measured value, and is more than twice as high as the existing equation. The solid line in the figure represents the predicted value that matches the measured value. The dotted line represents the predicted value with an error of 0.5 to 2 times. >
For further information or to request media assistance, please contact Jae Kyoung Kim at Biomedical Mathematics Group, Institute for Basic Science (IBS) (jaekkim@ibs.re.kr) or William I. Suh at the IBS Communications Team (willisuh@ibs.re.kr).
- About the Institute for Basic Science (IBS)
IBS was founded in 2011 by the government of the Republic of Korea with the sole purpose of driving forward the development of basic science in South Korea. IBS has 4 research institutes and 33 research centers as of January 2023. There are eleven physics, three mathematics, five chemistry, nine life science, two earth science, and three interdisciplinary research centers.
2023.01.18 View 14516 -
 KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 15933
KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 15933 -
 Success in Real-Time Observation of the Formation Process of Topological Solitons, a Core Technology for Next-Generation Information Transfer
< From left) Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Yun-Seok Choi (Ph.D.), Professor Dong Ki Yoon, and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) of the Department of Chemistry >
Professor Dong Ki Yoon's research team in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST announced on the 11th that they have succeeded in controlling the formation of topological solitons in a regular, large-area manner through the self-assembly of chiral liquid crystal materials and observing their formation process in real-time.
A soliton refers to a phenomenon where a specific wave persists without dissipating through interaction with its surroundings. In particular, even when a wave is transmitted over long distances, it retains its unique information until it reaches the desired destination. Therefore, in today's digital society, which is susceptible to hacking, solitons are highly anticipated to be the core of future communication due to their inherent high stability. Furthermore, topological solitons created using organic liquid crystal molecules are expected to be utilized as next-generation anti-counterfeiting devices and memory elements due to their unique spin directionality.
Professor Yoon's team specifically revealed the formation process of topological solitons in this study, which had not been observable in real-time under mild conditions such as room temperature until now. This was made possible by using self-assembling chiral liquid crystal materials in a confined space created by air pillars.
This research, in which Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Chemistry) and Dr. Ahram Suh participated as co-first authors, and Dr. Yun-Seok Choi and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) from the same group also participated, was published online in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on June 5th and is scheduled to be featured as the back cover of the July issue. (Paper title: "Fabrication of Arrays of Topological Solitons in Patterned Chiral Liquid Crystals for Real-Time Observation of Morphogenesis")
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research>
< Figure 2. Real-time observation of topological soliton formation using liquid crystals>
In this study, Professor Yoon's team implemented topological soliton structures at approximately 30 degrees Celsius, similar to room temperature, using chiral (asymmetric) liquid crystal materials instead of the conventional liquid crystal molecules widely used as core materials in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Generally, complex equipment is required to control the formation of topological solitons, and their formation time is very short, which has hindered research into their formation process until now.
To achieve regular formation and control of topological solitons formed by chiral liquid crystal molecules, Professor Yoon's team precisely controlled a combination of vertical alignment layers, which can orient molecules vertically, and air pillars. Specifically, they prepared concave patterns based on circular silicon material, several micrometers (one-millionth of a meter) in size, coated with a vertical alignment layer, and a glass substrate. By adjusting the gap to several micrometers and injecting chiral liquid crystal material, air pillars were spontaneously formed on the concave patterns. Subsequently, the liquid crystal molecules were vertically aligned on all substrates, inevitably causing regular distortions between the substrates, and between the substrate and the air pillars, thus developing a system where chiral molecular structures, i.e., topological solitons, could be formed.
The key to the formation and control of topological solitons lies in controlling the thermal phase transition to occur regularly as desired when cooling from the isotropic phase temperature (approximately 40 degrees Celsius) to the liquid crystal phase temperature (approximately 30 degrees Celsius), where the liquid crystal material near the air pillars is cooler than the liquid crystal material between the glass substrate and the silicon patterned parts. This is consistent with the everyday wisdom of eating steamed eggs from a 'Ttukbaegi' (earthen pot) by starting from the relatively cooler part exposed to the air (near the air pillars) rather than the hot pot part (silicon or glass substrate part).
Through real-time analysis, the research team elucidated that topological defects are formed by the naturally formed air pillars through controlled thermal phase transition, and topological solitons are formed only at the locations of these defects. This analysis technique has the potential for application in various fields, including the interpretation of topological soliton formation found in other physical phenomena such as skyrmion particles in electromagnetism.
< Figure 3. Snapshots during the formation process of regularly arranged topological solitons>
Professor Dong Ki Yoon stated, "General topological solitons are known to be highly stable, capable only of generation or annihilation. Through the results of this research, we can understand the formation process of solitons in more detail, and they can be used as spintronics application technology, considered a next-generation semiconductor device for storing and recording information."
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Ivan Smalyukh's laboratory at the University of Colorado, Department of Physics, and was supported by the Multiscale Chiral Structures Research Center and strategic projects of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2022.07.11 View 511
Success in Real-Time Observation of the Formation Process of Topological Solitons, a Core Technology for Next-Generation Information Transfer
< From left) Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Yun-Seok Choi (Ph.D.), Professor Dong Ki Yoon, and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) of the Department of Chemistry >
Professor Dong Ki Yoon's research team in the Department of Chemistry at KAIST announced on the 11th that they have succeeded in controlling the formation of topological solitons in a regular, large-area manner through the self-assembly of chiral liquid crystal materials and observing their formation process in real-time.
A soliton refers to a phenomenon where a specific wave persists without dissipating through interaction with its surroundings. In particular, even when a wave is transmitted over long distances, it retains its unique information until it reaches the desired destination. Therefore, in today's digital society, which is susceptible to hacking, solitons are highly anticipated to be the core of future communication due to their inherent high stability. Furthermore, topological solitons created using organic liquid crystal molecules are expected to be utilized as next-generation anti-counterfeiting devices and memory elements due to their unique spin directionality.
Professor Yoon's team specifically revealed the formation process of topological solitons in this study, which had not been observable in real-time under mild conditions such as room temperature until now. This was made possible by using self-assembling chiral liquid crystal materials in a confined space created by air pillars.
This research, in which Geonhyeong Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Chemistry) and Dr. Ahram Suh participated as co-first authors, and Dr. Yun-Seok Choi and Changjae Lee (Ph.D. Candidate) from the same group also participated, was published online in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on June 5th and is scheduled to be featured as the back cover of the July issue. (Paper title: "Fabrication of Arrays of Topological Solitons in Patterned Chiral Liquid Crystals for Real-Time Observation of Morphogenesis")
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the research>
< Figure 2. Real-time observation of topological soliton formation using liquid crystals>
In this study, Professor Yoon's team implemented topological soliton structures at approximately 30 degrees Celsius, similar to room temperature, using chiral (asymmetric) liquid crystal materials instead of the conventional liquid crystal molecules widely used as core materials in liquid crystal displays (LCDs). Generally, complex equipment is required to control the formation of topological solitons, and their formation time is very short, which has hindered research into their formation process until now.
To achieve regular formation and control of topological solitons formed by chiral liquid crystal molecules, Professor Yoon's team precisely controlled a combination of vertical alignment layers, which can orient molecules vertically, and air pillars. Specifically, they prepared concave patterns based on circular silicon material, several micrometers (one-millionth of a meter) in size, coated with a vertical alignment layer, and a glass substrate. By adjusting the gap to several micrometers and injecting chiral liquid crystal material, air pillars were spontaneously formed on the concave patterns. Subsequently, the liquid crystal molecules were vertically aligned on all substrates, inevitably causing regular distortions between the substrates, and between the substrate and the air pillars, thus developing a system where chiral molecular structures, i.e., topological solitons, could be formed.
The key to the formation and control of topological solitons lies in controlling the thermal phase transition to occur regularly as desired when cooling from the isotropic phase temperature (approximately 40 degrees Celsius) to the liquid crystal phase temperature (approximately 30 degrees Celsius), where the liquid crystal material near the air pillars is cooler than the liquid crystal material between the glass substrate and the silicon patterned parts. This is consistent with the everyday wisdom of eating steamed eggs from a 'Ttukbaegi' (earthen pot) by starting from the relatively cooler part exposed to the air (near the air pillars) rather than the hot pot part (silicon or glass substrate part).
Through real-time analysis, the research team elucidated that topological defects are formed by the naturally formed air pillars through controlled thermal phase transition, and topological solitons are formed only at the locations of these defects. This analysis technique has the potential for application in various fields, including the interpretation of topological soliton formation found in other physical phenomena such as skyrmion particles in electromagnetism.
< Figure 3. Snapshots during the formation process of regularly arranged topological solitons>
Professor Dong Ki Yoon stated, "General topological solitons are known to be highly stable, capable only of generation or annihilation. Through the results of this research, we can understand the formation process of solitons in more detail, and they can be used as spintronics application technology, considered a next-generation semiconductor device for storing and recording information."
This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Ivan Smalyukh's laboratory at the University of Colorado, Department of Physics, and was supported by the Multiscale Chiral Structures Research Center and strategic projects of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2022.07.11 View 511 -
 New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 9869
New Polymer Mesophase Structure Discovered
Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymer sequence
Polymers, large molecules made up of repeating smaller molecules called monomers, are found in nearly everything we use in our day-to-day lives. Polymers can be natural or created synthetically. Natural polymers, also called biopolymers, include DNA, proteins, and materials like silk, gelatin, and collagen. Synthetic polymers make up many different kinds of materials, including plastic, that are used in constructing everything from toys to industrial fiber cables to brake pads.
As polymers are formed through a process called polymerization, the monomers are connected through a chain. As the chain develops, the structure of the polymer determines its unique physical and chemical properties. Researchers are continually studying polymers, how they form, how they are structured, and how they develop these unique properties. By understanding this information, scientists can develop new uses for polymers and create new materials that can be used in a wide variety of industries.
In a paper published in Nature Communications on May 4, researchers describe a new structure found in an aqueous solution of an amphiphilic copolymer, called a bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase, that has been discovered through a random copolymer sequence.
“A new mesophase is an important discovery as it shows a new way for molecules to self-organize,” said Professor Myungeun Seo at the Department of Chemistry at KAIST. “We were particularly thrilled to identify this bilayer-folded lamellar phase because pure bilayer membranes are difficult to fold thermodynamically.”
Researchers think that this mesophase structure comes from the sequence of the monomers within the copolymer. The way the different monomers arrange themselves in the chain that makes up a copolymer is important and can have implications for what the copolymer can do. Many copolymers are random, which means that their structure relies on how the monomers interact with each other. In this case, the interaction between the hydrophobic monomers associates the copolymer chains to conceal the hydrophobic domain from water. As the structure gets more complex, researchers have found that a visible order develops so that monomers can be matched up with the right pair.
“While we tend to think random means disorder, here we showed that a periodic order can spontaneously arise from the random copolymer sequence based on their collective behavior,” said Professor Seo. “We believe this comes from the sequence matching problem: finding a perfectly complementary pair for a long sequence is nearly impossible.”
This is what creates the unique structure of this newly discovered mesophase. The copolymer spontaneously folds and creates a multilamellar structure that is separated by water. A multilamellar structure refers to plate-like folds and the folded layers stack on top of each other. The resulting mesophase is birefringent, meaning light refracts through it, it is similar to liquid crystalline, and viscoelastic, which means that it is both viscous and elastic at the same time.
Looking ahead, researchers hope to learn more about this new mesophase and figure out how to control the outcome. Once more is understood about the mesophase and how it is formed, it’s possible that new mesophases could be discovered as more sequences are researched. “One of the obvious questions for us is how to control the folding frequency and adjust the folded height, which we are currently working to address. Ultimately, we want to understand how different multinary sequences can associate with another to create order and apply the knowledge to develop new materials,” said Professor Seo. The National Research Foundation, the Ministry of Education, and the Ministry of Science and ICT of Korea funded this research.
-PublicationMinjoong Shin, Hayeon Kim, Geonhyeong Park, Jongmin Park, Hyungju Ahn, Dong Ki Yoon, Eunji Lee, Myungeun Seo, “Bilayer-folded lamellar mesophase induced by random polymersequence,” May 4, 2022, Nature Communications (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-30122-z)
-ProfileProfessor Myungeun SeoMacromolecular Materials Chemistry Lab (https://nanopsg.kaist.ac.kr/)Department of ChemistryCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.06.17 View 9869 -
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 8916
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 8916 -
 Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 11428
Mathematicians Identify a Key Source of Cell-to-Cell Variability in Cell Signaling
Systematic inferences identify a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics
Why do genetically identical cells respond differently to the same external stimuli, such as antibiotics? This long-standing mystery has been solved by KAIST and IBS mathematicians who have developed a new framework for analyzing cell responses to some stimuli. The team found that the cell-to-cell variability in antibiotic stress response increases as the effective length of the cell signaling pathway (i.e., the number of rate-limiting steps) increases. This finding could identify more effective chemotherapies to overcome the fractional killing of cancer cells caused by cell-to-cell variability.
Cells in the human body contain signal transduction systems that respond to various external stimuli such as antibiotics and changes in osmotic pressure. When an external stimulus is detected, various biochemical reactions occur sequentially. This leads to the expression of relevant genes, allowing the cells to respond to the perturbed external environment. Furthermore, signal transduction leads to a drug response (e.g., antibiotic resistance genes are expressed when antibiotic drugs are given).
However, even when the same external stimuli are detected, the responses of individual cells are greatly heterogeneous. This leads to the emergence of persister cells that are highly resistant to drugs. To identify potential sources of this cell-to cell variability, many studies have been conducted. However, most of the intermediate signal transduction reactions are unobservable with current experimental techniques.
A group of researchers including Dae Wook Kim and Hyukpyo Hong and led by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim from the KAIST Department of Mathematical Sciences and IBS Biomedical Mathematics Group solved the mystery by exploiting queueing theory and Bayesian inference methodology. They proposed a queueing process that describes the signal transduction system in cells. Based on this, they developed Bayesian inference computational software using MBI (the Moment-based Bayesian Inference method). This enables the analysis of the signal transduction system without a direct observation of the intermediate steps. This study was published in Science Advances.
By analyzing experimental data from Escherichia coli using MBI, the research team found that cell-to-cell variability increases as the number of rate-limiting steps in the signaling pathway increases.
The rate-limiting steps denote the slowest steps (i.e., bottlenecks) in sequential biochemical reaction steps composing cell signaling pathways and thus dominates most of the signaling time. As the number of the rate-limiting steps increases, the intensity of the transduced signal becomes greatly heterogeneous even in a population of genetically identical cells. This finding is expected to provide a new paradigm for studying the heterogeneous antibiotic resistance of cells, which is a big challenge in cancer medicine.
Professor Kim said, “As a mathematician, I am excited to help advance the understanding of cell-to-cell variability in response to external stimuli. I hope this finding facilitates the development of more effective chemotherapies.”
This work was supported by the Samsung Science and Technology Foundation, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Institute for Basic Science.
-Publication:Dae Wook Kim, Hyukpyo Hong, and Jae Kyoung Kim (2022) “Systematic inference identifies a major source of heterogeneity in cell signaling dynamics: the rate-limiting step number,”Science Advances March 18, 2022 (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abl4598)
-Profile:Professor Jae Kyoung Kimhttp://mathsci.kaist.ac.kr/~jaekkim
jaekkim@kaist.ac.kr@umichkim on TwitterDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.03.29 View 11428 -
 Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 9494
Tomographic Measurement of Dielectric Tensors
Dielectric tensor tomography allows the direct measurement of the 3D dielectric tensors of optically anisotropic structures
A research team reported the direct measurement of dielectric tensors of anisotropic structures including the spatial variations of principal refractive indices and directors. The group also demonstrated quantitative tomographic measurements of various nematic liquid-crystal structures and their fast 3D nonequilibrium dynamics using a 3D label-free tomographic method. The method was described in Nature Materials.
Light-matter interactions are described by the dielectric tensor. Despite their importance in basic science and applications, it has not been possible to measure 3D dielectric tensors directly. The main challenge was due to the vectorial nature of light scattering from a 3D anisotropic structure. Previous approaches only addressed 3D anisotropic information indirectly and were limited to two-dimensional, qualitative, strict sample conditions or assumptions.
The research team developed a method enabling the tomographic reconstruction of 3D dielectric tensors without any preparation or assumptions. A sample is illuminated with a laser beam with various angles and circularly polarization states. Then, the light fields scattered from a sample are holographically measured and converted into vectorial diffraction components. Finally, by inversely solving a vectorial wave equation, the 3D dielectric tensor is reconstructed.
Professor YongKeun Park said, “There were a greater number of unknowns in direct measuring than with the conventional approach. We applied our approach to measure additional holographic images by slightly tilting the incident angle.”
He said that the slightly tilted illumination provides an additional orthogonal polarization, which makes the underdetermined problem become the determined problem. “Although scattered fields are dependent on the illumination angle, the Fourier differentiation theorem enables the extraction of the same dielectric tensor for the slightly tilted illumination,” Professor Park added.
His team’s method was validated by reconstructing well-known liquid crystal (LC) structures, including the twisted nematic, hybrid aligned nematic, radial, and bipolar configurations. Furthermore, the research team demonstrated the experimental measurements of the non-equilibrium dynamics of annihilating, nucleating, and merging LC droplets, and the LC polymer network with repeating 3D topological defects.
“This is the first experimental measurement of non-equilibrium dynamics and 3D topological defects in LC structures in a label-free manner. Our method enables the exploration of inaccessible nematic structures and interactions in non-equilibrium dynamics,” first author Dr. Seungwoo Shin explained.
-PublicationSeungwoo Shin, Jonghee Eun, Sang Seok Lee, Changjae Lee, Herve Hugonnet, Dong Ki Yoon, Shin-Hyun Kim, Jongwoo Jeong, YongKeun Park, “Tomographic Measurement ofDielectric Tensors at Optical Frequency,” Nature Materials March 02, 2022 (https://doi.org/10/1038/s41563-022-01202-8)
-ProfileProfessor YongKeun ParkBiomedical Optics Laboratory (http://bmol.kaist.ac.kr)Department of PhysicsCollege of Natural SciencesKAIST
2022.03.22 View 9494 -
 Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11426
Scientist Discover How Circadian Rhythm Can Be Both Strong and Flexible
Study reveals that master and slave oscillators function via different molecular mechanisms
From tiny fruit flies to human beings, all animals on Earth maintain their daily rhythms based on their internal circadian clock. The circadian clock enables organisms to undergo rhythmic changes in behavior and physiology based on a 24-hour circadian cycle. For example, our own biological clock tells our brain to release melatonin, a sleep-inducing hormone, at night time.
The discovery of the molecular mechanism of the circadian clock was bestowed the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2017. From what we know, no one centralized clock is responsible for our circadian cycles. Instead, it operates in a hierarchical network where there are “master pacemaker” and “slave oscillator”.
The master pacemaker receives various input signals from the environment such as light. The master then drives the slave oscillator that regulates various outputs such as sleep, feeding, and metabolism. Despite the different roles of the pacemaker neurons, they are known to share common molecular mechanisms that are well conserved in all lifeforms. For example, interlocked systems of multiple transcriptional-translational feedback loops (TTFLs) composed of core clock proteins have been deeply studied in fruit flies.
However, there is still much that we need to learn about our own biological clock. The hierarchically-organized nature of master and slave clock neurons leads to a prevailing belief that they share an identical molecular clockwork. At the same time, the different roles they serve in regulating bodily rhythms also raise the question of whether they might function under different molecular clockworks.
Research team led by Professor Kim Jae Kyoung from the Department of Mathematical Sciences, a chief investigator at the Biomedical Mathematics Group at the Institute for Basic Science, used a combination of mathematical and experimental approaches using fruit flies to answer this question. The team found that the master clock and the slave clock operate via different molecular mechanisms.
In both master and slave neurons of fruit flies, a circadian rhythm-related protein called PER is produced and degraded at different rates depending on the time of the day. Previously, the team found that the master clock neuron (sLNvs) and the slave clock neuron (DN1ps) have different profiles of PER in wild-type and Clk-Δ mutant Drosophila. This hinted that there might be a potential difference in molecular clockworks between the master and slave clock neurons.
However, due to the complexity of the molecular clockwork, it was challenging to identify the source of such differences. Thus, the team developed a mathematical model describing the molecular clockworks of the master and slave clocks. Then, all possible molecular differences between the master and slave clock neurons were systematically investigated by using computer simulations. The model predicted that PER is more efficiently produced and then rapidly degraded in the master clock compared to the slave clock neurons. This prediction was then confirmed by the follow-up experiments using animal.
Then, why do the master clock neurons have such different molecular properties from the slave clock neurons? To answer this question, the research team again used the combination of mathematical model simulation and experiments. It was found that the faster rate of synthesis of PER in the master clock neurons allows them to generate synchronized rhythms with a high level of amplitude. Generation of such a strong rhythm with high amplitude is critical to delivering clear signals to slave clock neurons.
However, such strong rhythms would typically be unfavorable when it comes to adapting to environmental changes. These include natural causes such as different daylight hours across summer and winter seasons, up to more extreme artificial cases such as jet lag that occurs after international travel. Thanks to the distinct property of the master clock neurons, it is able to undergo phase dispersion when the standard light-dark cycle is disrupted, drastically reducing the level of PER. The master clock neurons can then easily adapt to the new diurnal cycle. Our master pacemaker’s plasticity explains how we can quickly adjust to the new time zones after international flights after just a brief period of jet lag.
It is hoped that the findings of this study can have future clinical implications when it comes to treating various disorders that affect our circadian rhythm. Professor Kim notes, “When the circadian clock loses its robustness and flexibility, the circadian rhythms sleep disorders can occur. As this study identifies the molecular mechanism that generates robustness and flexibility of the circadian clock, it can facilitate the identification of the cause of and treatment strategy for the circadian rhythm sleep disorders.” This work was supported by the Human Frontier Science Program.
-PublicationEui Min Jeong, Miri Kwon, Eunjoo Cho, Sang Hyuk Lee, Hyun Kim, Eun Young Kim, and Jae Kyoung Kim, “Systematic modeling-driven experiments identify distinct molecularclockworks underlying hierarchically organized pacemaker neurons,” February 22, 2022, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
-ProfileProfessor Jae Kyoung KimDepartment of Mathematical SciencesKAIST
2022.02.23 View 11426