Science
-
 International Student Conference (ICISTS-KAIST) to be Held in August
- 300 participants including university students worldwide and renowned speakers expected to gather
- Ideal coexistence of science & technology and society explored under the theme of “Perfect Alliance”
Science & technology and society are at the core of 21st century’s development. ICISTS-KAIST 2013, international conference for university students, seeks ways for the two to coexist harmoniously and is to be held from August 5 to 9 on KAIST campus as well as at Daejeon Convention Center.
ICISTS stands for International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society. ICISTS-KAIST is a non-profit organization run by KAIST students who are directly engaged in the coordination, planning, finance, public relations, and management of this academic event. The upcoming ninth annual event of ICISTS (www.icists.org) 2013 is centered around the theme, “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society.” The conference will last for four nights and five days; scholars and students across various academic backgrounds gather to narrow the gap between fields of study and discuss possible solutions to the problems in today’s society.
The annual conference, ICISTS-KAIST attracts hundreds of participants from all over the world to KAIST, Daejeon and its most recent event last year witnessed discussions among some 300 students from 22 countries hearing the lectures from 40 academics and scholars. This year’s event will welcome the 16-year old inventor, scientist, and cancer researcher Jack Thomas Andraka, the founder of the “One Laptop Per Child” project Walter Bender, Chemistry Nobel Prize laureate Harold Walter Kroto, and many more.
The application period for ICISTS-KAIST 2013 runs from May 20 to July 12, and applications are received through the website at www.icists.org.
ICISTS-KAIST 2013 Promgram Summary
Event Title: International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society 2013 (ICISTS-KAIST 2013)
Theme: Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society
Date and Venue: 2013 Aug. 5 (Mon.) ~ Aug. 9 (Fri.), KAIST Campus and Daejeon Convention Center
Host and Organizer: ICISTS KAIST
Sponsor: Korean National Commission for UNESCO, Korea Tourism Organization, Korea Ministry of Education, Science & Technology, KOFST
Session Description:
Keynote Speech - Keynote address on fundamental approach to coexistence
Parallel Session - Multiple simultaneous lecture of delegates’ choice
Group Discussion - Small group discussions among delegates and speakers
Panel Discussion - In-depth and thought-revealing discussion among speakers
Experience Session - First-person experience on relevant technology
Team Project & Poster Fair - Team mission, poster exhibition and evaluation
Subtopics:
- New Values from Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
- Synergetic Resolution via Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
- Essential Communication for Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
Notable Speakers:
- Gretchen Kalonji: Assistant to Director-General at UNESCO
- Sheila Jasanoff: Director of STS Program at Harvard Kennedy School
- Walter Bender: Former Director of MIT Media Lab and One Laptop Per Child- Jack Andraka: 16-year old Cancer Resesarcher
2013.05.31 View 10876
International Student Conference (ICISTS-KAIST) to be Held in August
- 300 participants including university students worldwide and renowned speakers expected to gather
- Ideal coexistence of science & technology and society explored under the theme of “Perfect Alliance”
Science & technology and society are at the core of 21st century’s development. ICISTS-KAIST 2013, international conference for university students, seeks ways for the two to coexist harmoniously and is to be held from August 5 to 9 on KAIST campus as well as at Daejeon Convention Center.
ICISTS stands for International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society. ICISTS-KAIST is a non-profit organization run by KAIST students who are directly engaged in the coordination, planning, finance, public relations, and management of this academic event. The upcoming ninth annual event of ICISTS (www.icists.org) 2013 is centered around the theme, “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society.” The conference will last for four nights and five days; scholars and students across various academic backgrounds gather to narrow the gap between fields of study and discuss possible solutions to the problems in today’s society.
The annual conference, ICISTS-KAIST attracts hundreds of participants from all over the world to KAIST, Daejeon and its most recent event last year witnessed discussions among some 300 students from 22 countries hearing the lectures from 40 academics and scholars. This year’s event will welcome the 16-year old inventor, scientist, and cancer researcher Jack Thomas Andraka, the founder of the “One Laptop Per Child” project Walter Bender, Chemistry Nobel Prize laureate Harold Walter Kroto, and many more.
The application period for ICISTS-KAIST 2013 runs from May 20 to July 12, and applications are received through the website at www.icists.org.
ICISTS-KAIST 2013 Promgram Summary
Event Title: International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society 2013 (ICISTS-KAIST 2013)
Theme: Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society
Date and Venue: 2013 Aug. 5 (Mon.) ~ Aug. 9 (Fri.), KAIST Campus and Daejeon Convention Center
Host and Organizer: ICISTS KAIST
Sponsor: Korean National Commission for UNESCO, Korea Tourism Organization, Korea Ministry of Education, Science & Technology, KOFST
Session Description:
Keynote Speech - Keynote address on fundamental approach to coexistence
Parallel Session - Multiple simultaneous lecture of delegates’ choice
Group Discussion - Small group discussions among delegates and speakers
Panel Discussion - In-depth and thought-revealing discussion among speakers
Experience Session - First-person experience on relevant technology
Team Project & Poster Fair - Team mission, poster exhibition and evaluation
Subtopics:
- New Values from Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
- Synergetic Resolution via Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
- Essential Communication for Coexistence of Science & Technology and Society
Notable Speakers:
- Gretchen Kalonji: Assistant to Director-General at UNESCO
- Sheila Jasanoff: Director of STS Program at Harvard Kennedy School
- Walter Bender: Former Director of MIT Media Lab and One Laptop Per Child- Jack Andraka: 16-year old Cancer Resesarcher
2013.05.31 View 10876 -
 Popular Science May 2013: Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) Introduced as Part of Smart Roads
Popular Science (PopSci), a famous American monthly magazine publishing popular science articles for general readers on science and technology subjects, introduced KAIST’s Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) in its latest issue of May 2013. For the article, please see the attachment.
2013.04.25 View 8628
Popular Science May 2013: Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) Introduced as Part of Smart Roads
Popular Science (PopSci), a famous American monthly magazine publishing popular science articles for general readers on science and technology subjects, introduced KAIST’s Online Electric Vehicle (OLEV) in its latest issue of May 2013. For the article, please see the attachment.
2013.04.25 View 8628 -
 The new era of personalized cancer diagnosis and treatment
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Succeeded in observing carcinogenic protein at the molecular level
- “Paved the way to customized cancer treatment through accurate analysis of carcinogenic protein”
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professor Won Do Huh of the Department of Biological Sciences have developed the technology to monitor characteristics of carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue – for the first time in the world.
The technology makes it possible to analyse the mechanism of cancer development through a small amount of carcinogenic protein from a cancer patient. Therefore, a personalised approach to diagnosis and treatment using the knowledge of the specific mechanism of cancer development in the patient may be possible in the future.
Until recently, modern medicine could only speculate on the cause of cancer through statistics. Although developed countries, such as the United States, are known to use a large sequencing technology that analyses the patient’s DNA, identification of the interactions between proteins responsible for causing cancer remained an unanswered question for a long time in medicine.
Firstly, Professor Yoon’s research team has developed a fluorescent microscope that can observe even a single molecule. Then, the “Immunoprecipitation method”, a technology to extract a specific protein exploiting the high affinity between antigens and antibodies was developed. Using this technology and the microscope, “Real-Time Single Molecule co-Immunoprecipitation Method” was created. In this way, the team succeeded in observing the interactions between carcinogenic and other proteins at a molecular level, in real time.
To validate the developed technology, the team investigated Ras, a carcinogenic protein; its mutation statistically is known to cause around 30% of cancers.
The experimental results confirmed that 30-50% of Ras protein was expressed in mouse tumour and human cancer cells. In normal cells, less than 5% of Ras protein was expressed. Thus, the experiment showed that unusual increase in activation of Ras protein induces cancer.
The increase in the ratio of active Ras protein can be inferred from existing research data but the measurement of specific numerical data has never been done before.
The team suggested a new molecular level diagnosis technique of identifying the progress of cancer in patients through measuring the percentage of activated carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue.
Professor Yoon Tae-young said, “This newly developed technology does not require a separate procedure of protein expression or refining, hence the existing proteins in real biological tissues or cancer cells can be observed directly.” He also said, “Since carcinogenic protein can be analyzed accurately, it has opened up the path to customized cancer treatment in the future.”
“Since the observation is possible on a molecular level, the technology confers the advantage that researchers can carry out various examinations on a small sample of the cancer patient.” He added, “The clinical trial will start in December 2012 and in a few years customized cancer diagnosis and treatment will be possible.”
Meanwhile, the research has been published in Nature Communications (February 19). Many researchers from various fields have participated, regardless of the differences in their speciality, and successfully produced interdisciplinary research. Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professors Dae Sik Lim and Won Do Huh of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Professor Chang Bong Hyun of Computational Science of KIAS contributed to developing the technique.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of observed interactions at the molecular level in real time using fluorescent microscope. The carcinogenic protein from a mouse tumour is fixed on the microchip, and its molecular characteristics are observed live.
Figure 2: Molecular interaction data using a molecular level fluorescent microscope. A signal in the form of spike is shown when two proteins combine. This is monitored live using an Electron Multiplying Charge Coupled Device (EMCCD). It shows signal results in bright dots.
An organism has an immune system as a defence mechanism to foreign intruders. The immune system is activated when unwanted pathogens or foreign protein are in the body. Antibodies form in recognition of the specific antigen to protect itself. Organisms evolved to form antibodies with high specificity to a certain antigen. Antibodies only react to its complementary antigens. The field of molecular biology uses the affinity between antigens and antibodies to extract specific proteins; a technology called immunoprecipitation. Even in a mixture of many proteins, the protein sought can be extracted using antibodies. Thus immunoprecipitation is widely used to detect pathogens or to extract specific proteins.
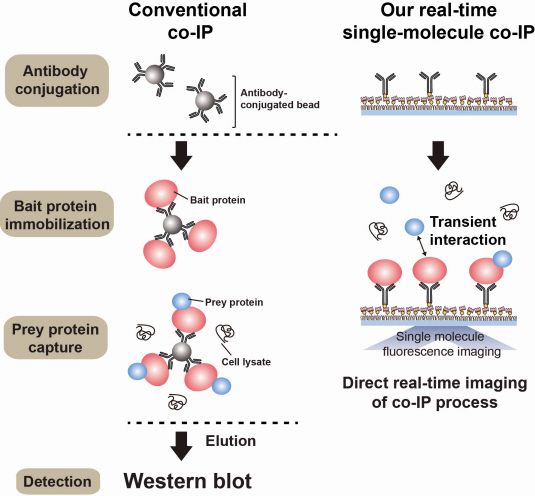
Technology co-IP is a well-known example that uses immunoprecipitation. The research on interactions between proteins uses co-IP in general. The basis of fixing the antigen on the antibody to extract antigen protein is the same as immunoprecipitation. Then, researchers inject and observe its reaction with the partner protein to observe the interactions and precipitate the antibodies. If the reaction occurs, the partner protein will be found with the antibodies in the precipitations. If not, then the partner protein will not be found. This shows that the two proteins interact.
However, the traditional co-IP can be used to infer the interactions between the two proteins although the information of the dynamics on how the reaction occurs is lost. To overcome these shortcomings, the Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP Method enables observation on individual protein level in real time. Therefore, the significance of the new technique is in making observation of interactions more direct and quantitative.
Additional Figure 1: Comparison between Conventional co-IP and Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP
2013.04.01 View 22336
The new era of personalized cancer diagnosis and treatment
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Succeeded in observing carcinogenic protein at the molecular level
- “Paved the way to customized cancer treatment through accurate analysis of carcinogenic protein”
The joint KAIST research team of Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professor Won Do Huh of the Department of Biological Sciences have developed the technology to monitor characteristics of carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue – for the first time in the world.
The technology makes it possible to analyse the mechanism of cancer development through a small amount of carcinogenic protein from a cancer patient. Therefore, a personalised approach to diagnosis and treatment using the knowledge of the specific mechanism of cancer development in the patient may be possible in the future.
Until recently, modern medicine could only speculate on the cause of cancer through statistics. Although developed countries, such as the United States, are known to use a large sequencing technology that analyses the patient’s DNA, identification of the interactions between proteins responsible for causing cancer remained an unanswered question for a long time in medicine.
Firstly, Professor Yoon’s research team has developed a fluorescent microscope that can observe even a single molecule. Then, the “Immunoprecipitation method”, a technology to extract a specific protein exploiting the high affinity between antigens and antibodies was developed. Using this technology and the microscope, “Real-Time Single Molecule co-Immunoprecipitation Method” was created. In this way, the team succeeded in observing the interactions between carcinogenic and other proteins at a molecular level, in real time.
To validate the developed technology, the team investigated Ras, a carcinogenic protein; its mutation statistically is known to cause around 30% of cancers.
The experimental results confirmed that 30-50% of Ras protein was expressed in mouse tumour and human cancer cells. In normal cells, less than 5% of Ras protein was expressed. Thus, the experiment showed that unusual increase in activation of Ras protein induces cancer.
The increase in the ratio of active Ras protein can be inferred from existing research data but the measurement of specific numerical data has never been done before.
The team suggested a new molecular level diagnosis technique of identifying the progress of cancer in patients through measuring the percentage of activated carcinogenic protein in cancer tissue.
Professor Yoon Tae-young said, “This newly developed technology does not require a separate procedure of protein expression or refining, hence the existing proteins in real biological tissues or cancer cells can be observed directly.” He also said, “Since carcinogenic protein can be analyzed accurately, it has opened up the path to customized cancer treatment in the future.”
“Since the observation is possible on a molecular level, the technology confers the advantage that researchers can carry out various examinations on a small sample of the cancer patient.” He added, “The clinical trial will start in December 2012 and in a few years customized cancer diagnosis and treatment will be possible.”
Meanwhile, the research has been published in Nature Communications (February 19). Many researchers from various fields have participated, regardless of the differences in their speciality, and successfully produced interdisciplinary research. Professor Tae Young Yoon of the Department of Physics and Professors Dae Sik Lim and Won Do Huh of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Professor Chang Bong Hyun of Computational Science of KIAS contributed to developing the technique.
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of observed interactions at the molecular level in real time using fluorescent microscope. The carcinogenic protein from a mouse tumour is fixed on the microchip, and its molecular characteristics are observed live.
Figure 2: Molecular interaction data using a molecular level fluorescent microscope. A signal in the form of spike is shown when two proteins combine. This is monitored live using an Electron Multiplying Charge Coupled Device (EMCCD). It shows signal results in bright dots.
An organism has an immune system as a defence mechanism to foreign intruders. The immune system is activated when unwanted pathogens or foreign protein are in the body. Antibodies form in recognition of the specific antigen to protect itself. Organisms evolved to form antibodies with high specificity to a certain antigen. Antibodies only react to its complementary antigens. The field of molecular biology uses the affinity between antigens and antibodies to extract specific proteins; a technology called immunoprecipitation. Even in a mixture of many proteins, the protein sought can be extracted using antibodies. Thus immunoprecipitation is widely used to detect pathogens or to extract specific proteins.
Technology co-IP is a well-known example that uses immunoprecipitation. The research on interactions between proteins uses co-IP in general. The basis of fixing the antigen on the antibody to extract antigen protein is the same as immunoprecipitation. Then, researchers inject and observe its reaction with the partner protein to observe the interactions and precipitate the antibodies. If the reaction occurs, the partner protein will be found with the antibodies in the precipitations. If not, then the partner protein will not be found. This shows that the two proteins interact.
However, the traditional co-IP can be used to infer the interactions between the two proteins although the information of the dynamics on how the reaction occurs is lost. To overcome these shortcomings, the Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP Method enables observation on individual protein level in real time. Therefore, the significance of the new technique is in making observation of interactions more direct and quantitative.
Additional Figure 1: Comparison between Conventional co-IP and Real-Time Single Molecule co-IP
2013.04.01 View 22336 -
 Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13511
Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13511 -
 Online Article on President Sung-Mo 'Steve' Kang by California Council on Science and Technology (CCST)
The California Council on Science and Technology (CCST), an independent, not-for-profit organization established by the mandate of California Legislature in 1988, is designed to offer expert advice to the California state government and recommend solutions to science and technology-related policy issues.
Over the past three years, President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang has served as a member of CCST Council, an assembly of corporate CEOs, academicians, scientists, and scholars of the highest distinction.
On February 21, 2013, CCST posted on its website the announcement of Council Member Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang as President of KAIST along with his personal comments on his move to KAIST and its presidency. For the online article, please visit: http://www.ccst.us/news/2013/0221KAIST.php
2013.02.23 View 9650
Online Article on President Sung-Mo 'Steve' Kang by California Council on Science and Technology (CCST)
The California Council on Science and Technology (CCST), an independent, not-for-profit organization established by the mandate of California Legislature in 1988, is designed to offer expert advice to the California state government and recommend solutions to science and technology-related policy issues.
Over the past three years, President Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang has served as a member of CCST Council, an assembly of corporate CEOs, academicians, scientists, and scholars of the highest distinction.
On February 21, 2013, CCST posted on its website the announcement of Council Member Sung-Mo “Steve” Kang as President of KAIST along with his personal comments on his move to KAIST and its presidency. For the online article, please visit: http://www.ccst.us/news/2013/0221KAIST.php
2013.02.23 View 9650 -
 Professor Hwang Kyu Young and Professor Yang Dong Yeol Receives Engineer of Korea Award
Emeritus Professor Hwang Kyu Young (Department of Computer Sciences) and Professor Yang Dong Yeol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) were named as the 2012 Engineer of Korea by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology and Korea Science Foundation.
The Engineer of Korea Award is awarded biannually to scientists and engineers that have contributed to the development of Korea’s science and technology and national economy.
Professor Hwang’s work with DBMS and close coupling architecture of information search and overall new theories and application technology development in the field of database system has aided the opening and expansion of IT software industry development and the advent of internet information culture era.
Professor Yang is a word renowned scholar in the field of net shape manufacturing and is considered to have opened a new page in the field of nano-molding technique.
In addition, Professor Eum Sang Il (Department of Mathematical Science) has been selected as the 2012 Young Scientist Award.
2013.01.22 View 14556
Professor Hwang Kyu Young and Professor Yang Dong Yeol Receives Engineer of Korea Award
Emeritus Professor Hwang Kyu Young (Department of Computer Sciences) and Professor Yang Dong Yeol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) were named as the 2012 Engineer of Korea by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology and Korea Science Foundation.
The Engineer of Korea Award is awarded biannually to scientists and engineers that have contributed to the development of Korea’s science and technology and national economy.
Professor Hwang’s work with DBMS and close coupling architecture of information search and overall new theories and application technology development in the field of database system has aided the opening and expansion of IT software industry development and the advent of internet information culture era.
Professor Yang is a word renowned scholar in the field of net shape manufacturing and is considered to have opened a new page in the field of nano-molding technique.
In addition, Professor Eum Sang Il (Department of Mathematical Science) has been selected as the 2012 Young Scientist Award.
2013.01.22 View 14556 -
 Professor Lee Jeong Yong Receives 2012 'KAISTian of the Year' Award
Professor Lee Jeong Yong (Department of Material Science and Engineering) received the 2012 ‘KAISTian of the Year’ Award.
Professor Lee had successfully developed a technique that allowed the observation and analysis of liquid in atomic scale.
The technique is expected to have great impact on nano-material synthesis in solution, explaining electrode and electrolyte reaction, liquid and catalysis reaction research, and etc. and was therefore named as the best experimental accomplishment in KAIST in 2012.
Professor Lee and his team’s finding has been published in the April edition of Science magazine and has had attracted the attention of the world. In addition, BBC News, and Science & Environment reported on the findings as their respective top articles.
The optical microscope is incapable of atomic scale observation and the electron microscopes are capable but because of the vacuum state all liquids undergo evaporation making it impossible to observe liquids in an atomic scale.
Professor Lee’s team wrapped the liquid with a layer of grapheme to prevent evaporation and successfully observed real time the platinum growth process in solution.
Professor Lee’s findings were introduced as an example of exemplar research case in the Presidential address for ‘Science Day’ in April.
2013.01.22 View 11218
Professor Lee Jeong Yong Receives 2012 'KAISTian of the Year' Award
Professor Lee Jeong Yong (Department of Material Science and Engineering) received the 2012 ‘KAISTian of the Year’ Award.
Professor Lee had successfully developed a technique that allowed the observation and analysis of liquid in atomic scale.
The technique is expected to have great impact on nano-material synthesis in solution, explaining electrode and electrolyte reaction, liquid and catalysis reaction research, and etc. and was therefore named as the best experimental accomplishment in KAIST in 2012.
Professor Lee and his team’s finding has been published in the April edition of Science magazine and has had attracted the attention of the world. In addition, BBC News, and Science & Environment reported on the findings as their respective top articles.
The optical microscope is incapable of atomic scale observation and the electron microscopes are capable but because of the vacuum state all liquids undergo evaporation making it impossible to observe liquids in an atomic scale.
Professor Lee’s team wrapped the liquid with a layer of grapheme to prevent evaporation and successfully observed real time the platinum growth process in solution.
Professor Lee’s findings were introduced as an example of exemplar research case in the Presidential address for ‘Science Day’ in April.
2013.01.22 View 11218 -
 KAIST Alumni Association Selects 'Proud Alums'
KAIST Alumni Association selected ‘Proud Alums’ who have contributed to the development of Korea and society and brought honor to KAIST.
The Alums selected were: CEO of Hyundai Heavy Industry Lee Jae Seong, Vice President of SK Hynix Park Sang Hoon, President of Samsung Display Kim Ki Nam, Director of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Kang Dae Lim, and President of Dawonsys Park Sun Soon.
Lee Jae Song (Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, M.S. 3rd) has led Hyundai Heavy Industries through innovation and had contributed in the development of Korea and oversaw the growth of Hyundai Heavy Industries to number 1 in Shipbuilding.
Park Sang Hoon (Biological and Chemical Engineering, M.S. 5th) has led SK Hynix in the fields of energy, chemical and biological medicine and oversaw the development of world class R&D and production technologies to aid the development of Korea.
Kim Ki Nam (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 9th) has led the development of innovative semiconductor technologies thereby helping strengthening the competitiveness of Korean semiconductor industry.
Kang Dae Lim (Mechanical Engineering, Ph.D. 1994 graduate) has helped in the development of Korean science and technology by leading the field of measurement standardization as Chairman of International Measurement Confederation and Chairman of Korea Association of Standards & Testing Organizations.
Park Sun Soon (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 12th) has succeeded in advancing the field of electronics by pioneering the field of creative technology.
2013.01.22 View 12124
KAIST Alumni Association Selects 'Proud Alums'
KAIST Alumni Association selected ‘Proud Alums’ who have contributed to the development of Korea and society and brought honor to KAIST.
The Alums selected were: CEO of Hyundai Heavy Industry Lee Jae Seong, Vice President of SK Hynix Park Sang Hoon, President of Samsung Display Kim Ki Nam, Director of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science Kang Dae Lim, and President of Dawonsys Park Sun Soon.
Lee Jae Song (Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, M.S. 3rd) has led Hyundai Heavy Industries through innovation and had contributed in the development of Korea and oversaw the growth of Hyundai Heavy Industries to number 1 in Shipbuilding.
Park Sang Hoon (Biological and Chemical Engineering, M.S. 5th) has led SK Hynix in the fields of energy, chemical and biological medicine and oversaw the development of world class R&D and production technologies to aid the development of Korea.
Kim Ki Nam (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 9th) has led the development of innovative semiconductor technologies thereby helping strengthening the competitiveness of Korean semiconductor industry.
Kang Dae Lim (Mechanical Engineering, Ph.D. 1994 graduate) has helped in the development of Korean science and technology by leading the field of measurement standardization as Chairman of International Measurement Confederation and Chairman of Korea Association of Standards & Testing Organizations.
Park Sun Soon (Electrical and Electronic Engineering, M.S. 12th) has succeeded in advancing the field of electronics by pioneering the field of creative technology.
2013.01.22 View 12124 -
 Op-Ed by Prof. David Helfman: Global Science and Education in the 21st Century
Professor David Helfman from the Department of Biological Sciences and Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology(https://sites.google.com/site/cellsignalinglaboratory/home) recently wrote an Op-Ed in the January 2013 issue of Journal of Happy Scientists and Engineers that ispublished by the Ministry of Science, Education and Technology, the Republic of Korea. In the article entitled “Global Science and Education in the 21st Century,” Professor Helfman addressed three important issues in science and education, which will have a great impact for the development of world-leading universities in Korea. For the article, please see the attachment.
2013.01.22 View 14791
Op-Ed by Prof. David Helfman: Global Science and Education in the 21st Century
Professor David Helfman from the Department of Biological Sciences and Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology(https://sites.google.com/site/cellsignalinglaboratory/home) recently wrote an Op-Ed in the January 2013 issue of Journal of Happy Scientists and Engineers that ispublished by the Ministry of Science, Education and Technology, the Republic of Korea. In the article entitled “Global Science and Education in the 21st Century,” Professor Helfman addressed three important issues in science and education, which will have a great impact for the development of world-leading universities in Korea. For the article, please see the attachment.
2013.01.22 View 14791 -
 KAIST Professors win 2012 Korea Engineering Award
Distinguished Professor Hwang Gyu Young (Department of Computer Science) and Professor Yang Dong Yol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) from KAIST received the 2012 ‘Korea Engineering Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korea Research Foundation.
The ‘Korea Engineering Award’ is given biennially to researchers who have accomplished world class research and have contributed greatly to Korea’s development in the field of Science and Technology. The award started in 1994 and a total of 24 recipients were recognized in various fields such as electronics, mechanics, chemistry, construction, etc. The recipients of the award areawarded the Presidential award as well as 50million won as prize money.
Professor Hwang was recognized for his research on DBMS close-coupling architecture as well as other new data base system theories, contributing to the development of the IT software industry in Korea. Professor Yang was praised for his work in precision shape creation and manufacturing, especially for his work in the nano-stereolithography process.
In addition, Professor Oum Sang-il from the Deparment of Mathematical Science received the 2012 ‘Young Scientist Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The ceremony for ‘Korea Engineering Award’ and the ‘Young Scientist Award’ was held in Seoul Press Center Press Club on the 21st of December.
2012.12.26 View 16668
KAIST Professors win 2012 Korea Engineering Award
Distinguished Professor Hwang Gyu Young (Department of Computer Science) and Professor Yang Dong Yol (Department of Mechanical Engineering) from KAIST received the 2012 ‘Korea Engineering Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korea Research Foundation.
The ‘Korea Engineering Award’ is given biennially to researchers who have accomplished world class research and have contributed greatly to Korea’s development in the field of Science and Technology. The award started in 1994 and a total of 24 recipients were recognized in various fields such as electronics, mechanics, chemistry, construction, etc. The recipients of the award areawarded the Presidential award as well as 50million won as prize money.
Professor Hwang was recognized for his research on DBMS close-coupling architecture as well as other new data base system theories, contributing to the development of the IT software industry in Korea. Professor Yang was praised for his work in precision shape creation and manufacturing, especially for his work in the nano-stereolithography process.
In addition, Professor Oum Sang-il from the Deparment of Mathematical Science received the 2012 ‘Young Scientist Award’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The ceremony for ‘Korea Engineering Award’ and the ‘Young Scientist Award’ was held in Seoul Press Center Press Club on the 21st of December.
2012.12.26 View 16668 -
 Professor Cho Young-ho wins 'E2 Star' award
Professor Cho Young-ho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST was chosen as the ‘E2 Star’ at the ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ in academics. The ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology was held to display outstanding research results and to conceptualize the future of science education.
The ‘E2 star’ award is given to renowned figures in industry, academia and society. A total of 35 candidates were recommended for the 3 fields and Professor Cho received the first place in the online voting.
Professor Cho received high marks for his work in engineering education, research development and increasing the communication between academia and industry, as well as the commercialization of science and technology. Professor Cho was especially praised for the specialization of engineering education in integrated fields and the joint research with US and Swiss universities.
Professor Cho Young-ho(Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST)
2012.12.26 View 12910
Professor Cho Young-ho wins 'E2 Star' award
Professor Cho Young-ho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST was chosen as the ‘E2 Star’ at the ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ in academics. The ‘2012 Engineering Education Festa’ hosted by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology was held to display outstanding research results and to conceptualize the future of science education.
The ‘E2 star’ award is given to renowned figures in industry, academia and society. A total of 35 candidates were recommended for the 3 fields and Professor Cho received the first place in the online voting.
Professor Cho received high marks for his work in engineering education, research development and increasing the communication between academia and industry, as well as the commercialization of science and technology. Professor Cho was especially praised for the specialization of engineering education in integrated fields and the joint research with US and Swiss universities.
Professor Cho Young-ho(Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST)
2012.12.26 View 12910 -
 Midam Scholarship Society Receives Minister of Education, Science, and Technology Prize for Education Donation
Midam Scholarship Society, consisting of KAIST students, has been awarded the First Korea Education Donation Grand Prize from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
The Education Donation Prize has been created in order to encourage those university clubs that have been increasing awareness of education donation and at the same time donating educational services themselves.
Midam Scholarship Society was established by KAIST students in 2009 to provide educational services to those students from low income families. Currently over 200 students from six different universities (KAIST, UNIST, Pusan University, Chonnam University, Kyungpook National University, Kumoh Engineering University) are involved in the Midam Scholarship Society.
Approximately 70 students participate in the KAIST Midam Scholarship Society. The classes take place in the classrooms every week for three hours over a period of three months. The classes are offered to over 1,000 high school students in and near DaeJeon.
2012.12.21 View 11610
Midam Scholarship Society Receives Minister of Education, Science, and Technology Prize for Education Donation
Midam Scholarship Society, consisting of KAIST students, has been awarded the First Korea Education Donation Grand Prize from the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
The Education Donation Prize has been created in order to encourage those university clubs that have been increasing awareness of education donation and at the same time donating educational services themselves.
Midam Scholarship Society was established by KAIST students in 2009 to provide educational services to those students from low income families. Currently over 200 students from six different universities (KAIST, UNIST, Pusan University, Chonnam University, Kyungpook National University, Kumoh Engineering University) are involved in the Midam Scholarship Society.
Approximately 70 students participate in the KAIST Midam Scholarship Society. The classes take place in the classrooms every week for three hours over a period of three months. The classes are offered to over 1,000 high school students in and near DaeJeon.
2012.12.21 View 11610