rate
-
 An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 11542
An AI-based, Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated (IOI) GPS System to Bring Seismic Waves in the Terrains of Positioning Technology
KAIST breaks new grounds in positioning technology with an AI-integrated GPS board that works both indoors and out
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 8th that Professor Dong-Soo Han's research team (Intelligent Service Integration Lab) from the School of Computing has developed a GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors with quality precision regardless of the environment.
This Indoor/Outdoor-Integrated GPS System, or IOI GPS System, for short, uses the GPS signals outdoors and estimates locations indoors using signals from multiple sources like an inertial sensor, pressure sensors, geomagnetic sensors, and light sensors. To this end, the research team developed techniques to detect environmental changes such as entering a building, and methods to detect entrances, ground floors, stairs, elevators and levels of buildings by utilizing artificial intelligence techniques. Various landmark detecting techniques were also incorporated with pedestrian dead reckoning (PDR), a navigation tool for pedestrians, to devise the so-called “Sensor-Fusion Positioning Algorithm”.
To date, it was common to estimate locations based on wireless LAN signals or base station signals in a space where the GPS signal could not reach. However, the IOI GPS enables positioning even in buildings without signals nor indoor maps.
The algorithm developed by the research team can provide accurate floor information within a building where even big tech companies like Google and Apple's positioning services do not provide. Unlike other positioning methods that rely on visual data, geomagnetic positioning techniques, or wireless LAN, this system also has the advantage of not requiring any prior preparation. In other words, the foundation to enable the usage of a universal GPS system that works both indoors and outdoors anywhere in the world is now ready.
The research team also produced a circuit board for the purpose of operating the IOI GPS System, mounted with chips to receive and process GPS, Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth signals, along with an inertial sensor, a barometer, a magnetometer, and a light sensor. The sensor-fusion positioning algorithm the lab has developed is also incorporated in the board.
When the accuracy of the IOI GPS board was tested in the N1 building of KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon, it achieved an accuracy of about 95% in floor estimation and an accuracy of about 3 to 6 meters in distance estimation. As for the indoor/outdoor transition, the navigational mode change was completed in about 0.3 seconds. When it was combined with the PDR technique, the estimation accuracy improved further down to a scope of one meter.
The research team is now working on assembling a tag with a built-in positioning board and applying it to location-based docent services for visitors at museums, science centers, and art galleries. The IOI GPS tag can be used for the purpose of tracking children and/or the elderly, and it can also be used to locate people or rescue workers lost in disaster-ridden or hazardous sites. On a different note, the sensor-fusion positioning algorithm and positioning board for vehicles are also under development for the tracking of vehicles entering indoor areas like underground parking lots.
When the IOI GPS board for vehicles is manufactured, the research team will work to collaborate with car manufacturers and car rental companies, and will also develop a sensor-fusion positioning algorithm for smartphones. Telecommunication companies seeking to diversify their programs in the field of location-based services will also be interested in the use the IOI GPS.
Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing, who leads the research team, said, “This is the first time to develop an indoor/outdoor integrated GPS system that can pinpoint locations in a building where there is no wireless signal or an indoor map, and there are an infinite number of areas it can be applied to. When the integration with the Korea Augmentation Satellite System (KASS) and the Korean GPS (KPS) System that began this year, is finally completed, Korea can become the leader in the field of GPS both indoors and outdoors, and we also have plans to manufacture semi-conductor chips for the IOI GPS System to keep the tech-gap between Korea and the followers.”
He added, "The guidance services at science centers, museums, and art galleries that uses IOI GPS tags can provide a set of data that would be very helpful for analyzing the visitors’ viewing traces. It is an essential piece of information required when the time comes to decide when to organize the next exhibit. We will be working on having it applied to the National Science Museum, first.”
The projects to develop the IOI GPS system and the trace analysis system for science centers were supported through Science, Culture, Exhibits and Services Capability Enhancement Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Profile: Dong-Soo Han, Ph.D.Professorddsshhan@kaist.ac.krhttp://isilab.kaist.ac.kr
Intelligent Service Integration Lab.School of Computing
http://kaist.ac.kr/en/
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.13 View 11542 -
 The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 12243
The 1st Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp bridges KAIST and Silicon Valley, US
Twenty KAIST students gave a go at selling their business ideas to investors at Silicon Valley on the “Pitch Day” at 2022 Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp.
From Tuesday, June 21 to Monday, July 4, 2022, KAIST held the first Global Entrepreneurship Summer Camp (GESC).
The 2022 GESC, which was organized in collaboration with Stanford Technology Ventures Program (STVP), KOTRA Silicon Valley IT Center, and KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, was a pilot program that offered opportunities of experiencing and learning about the cases of startup companies in Silicon Valley and a chance to expand businesses to Silicon Valley through networking.
Twenty KAIST students, including pre-startup entrepreneurs and students interested in global entrepreneurship with less than one year of business experience were selected. The first week of the program was organized by Startup KAIST while the second week program was organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning (GSP) at KAIST in collaboration with the Stanford Technology Venture Program (STVP), KAIST Alumni at Silicon Valley, and KOTRA at Silicon Valley.
Dr. Mo-Yun Lei Fong, the Executive Director of STVP, said, “The program offered an opportunity for us to realize our vision of empowering aspiring entrepreneurs to become global citizens who create and scale responsible innovation. By collaborating with KAIST and offering entrepreneurial insights to Korean students, we are able to have a positive impact on a global scale.” Mo added, “The program also enabled STVP to build bridges, learn from the students, and refine our culturally relevant curriculum by understanding Korean culture and ideas.”
On the “Pitch Day” on July 1, following a special talk by Dr. Chong-Moon Lee, the Chairman of AmBex Venture Partners, the students presented their team business ideas such as an AI-assisted, noise-canceling pillow devised for better sleep, a metaverse dating application, an XR virtual conferencing system, and an AI language tutoring application to the entice global investors’ curiosity. The invited investors, majorly based in Silicon Valley, commented that all the presentation was very exciting, and the level of pitches was beyond the expectation considering that the students have given only two weeks.
Ms. Seunghee Lee of the team “Bored KAIST Yacht Club”, which was awarded the first prize, explained, “our item, called ‘Meta-Everland’, is a service that offers real-time dating experiences similar to off-line dates. The GESC taught me that anybody can launch a startup as long as they are willing. Developing a business model from ideation and taking it to the actual pitching was challenging, but it was a very thrilling experience at the same time.” Lee added, “Most importantly, over the course of the program and the final pitch, I found out that an interesting idea can attract investors interest even at a very early stage of the launching.”
Mr. Byunghoon Hwang, a student who attended the program said, “Having learned the thoughts and attitudes the people at the front line of Silicon Valley, my views on career and launching of a start-up have been expanded a lot.”
Ms. Marina Mondragon, another attendee at the program, also said that the program was very meaningful because she was able to learn the difference between the ecosystem for the new start-up businesses at Korea and at Silicon Valley through her talks with the CEOs at Silicon Valley.
The program was co-organized by the Center for Global Strategies and Planning at KAIST International Office and Startup of KAIST. Dr. Man-Sung Yim, the Associate Vice President for KAIST International Office, who guided students in Silicon Valley, said, “I believe the GESC program broadened the views and entrepreneurial mindset of students. After joining this program, students stepped forward to become a founder of startups.” In addition, Dr. Young-Tae Kim, the Associate Vice President of the Institute for Startup KAIST, addressed “Startup KAIST will support business items founded via the program through various other programs in order to enhance their competitiveness in the global market.”
The GSP and Startup KAIST will continuously revamp the program by selecting distinguished fellows to join the program and coming up with innovative startup items.
Profile:
Sooa Lee, Ph.D.
Research Assistant Professor
slee900@kaist.ac.kr
Center for Global Strategies and Planning
Office of Global Initiatives
KAIST International Office
https://io.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2022.07.05 View 12243 -
 Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 11870
Quantum Technology: the Next Game Changer?
The 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute Forum explores how quantum technology has evolved into a new growth engine for the future
The participants of the 6th KAIST Global Strategy Institute (GSI) Forum on April 20 agreed that the emerging technology of quantum computing will be a game changer of the future. As KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks, the future is quantum and that future is rapidly approaching. Keynote speakers and panelists presented their insights on the disruptive innovations we are already experiencing.
The three keynote speakers included Dr. Jerry M. Chow, IBM fellow and director of quantum infrastructure, Professor John Preskill from Caltech, and Professor Jungsang Kim from Duke University. They discussed the academic impact and industrial applications of quantum technology, and its prospects for the future.
Dr. Chow leads IBM Quantum’s hardware system development efforts, focusing on research and system deployment. Professor Preskill is one of the leading quantum information science and quantum computation scholars. He coined the term “quantum supremacy.” Professor Kim is the co-founder and CTO of IonQ Inc., which develops general-purpose trapped ion quantum computers and software to generate, optimize, and execute quantum circuits.
Two leading quantum scholars from KAIST, Professor June-Koo Kevin Rhee and Professor Youngik Sohn, and Professor Andreas Heinrich from the IBS Center for Quantum Nanoscience also participated in the forum as panelists. Professor Rhee is the founder of the nation’s first quantum computing software company and leads the AI Quantum Computing IT Research Center at KAIST.
During the panel session, Professor Rhee said that although it is undeniable the quantum computing will be a game changer, there are several challenges. For instance, the first actual quantum computer is NISQ (Noisy intermediate-scale quantum era), which is still incomplete. However, it is expected to outperform a supercomputer. Until then, it is important to advance the accuracy of quantum computation in order to offer super computation speeds.
Professor Sohn, who worked at PsiQuantum, detailed how quantum computers will affect our society. He said that PsiQuantum is developing silicon photonics that will control photons. We can’t begin to imagine how silicon photonics will transform our society. Things will change slowly but the scale would be massive.
The keynote speakers presented how quantum cryptography communications and its sensing technology will serve as disruptive innovations. Dr. Chow stressed that to realize the potential growth and innovation, additional R&D is needed. More research groups and scholars should be nurtured. Only then will the rich R&D resources be able to create breakthroughs in quantum-related industries. Lastly, the commercialization of quantum computing must be advanced, which will enable the provision of diverse services. In addition, more technological and industrial infrastructure must be built to better accommodate quantum computing.
Professor Preskill believes that quantum computing will benefit humanity. He cited two basic reasons for his optimistic prediction: quantum complexity and quantum error corrections. He explained why quantum computing is so powerful: quantum computer can easily solve the problems classically considered difficult, such as factorization. In addition, quantum computer has the potential to efficiently simulate all of the physical processes taking place in nature.
Despite such dramatic advantages, why does it seem so difficult? Professor Preskill believes this is because we want qubits (quantum bits or ‘qubits’ are the basic unit of quantum information) to interact very strongly with each other. Because computations can fail, we don’t want qubits to interact with the environment unless we can control and predict them.
As for quantum computing in the NISQ era, he said that NISQ will be an exciting tool for exploring physics. Professor Preskill does not believe that NISQ will change the world alone, rather it is a step forward toward more powerful quantum technologies in the future. He added that a potentially transformable, scalable quantum computer could still be decades away.
Professor Preskill said that a large number of qubits, higher accuracy, and better quality will require a significant investment. He said if we expand with better ideas, we can make a better system. In the longer term, quantum technology will bring significant benefits to the technological sectors and society in the fields of materials, physics, chemistry, and energy production.
Professor Kim from Duke University presented on the practical applications of quantum computing, especially in the startup environment. He said that although there is no right answer for the early applications of quantum computing, developing new approaches to solve difficult problems and raising the accessibility of the technology will be important for ensuring the growth of technology-based startups.
2022.04.21 View 11870 -
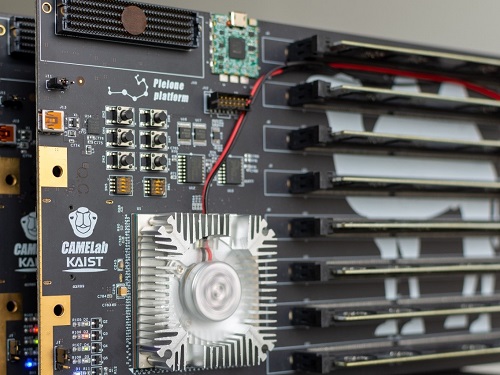 CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 23019
CXL-Based Memory Disaggregation Technology Opens Up a New Direction for Big Data Solution Frameworks
A KAIST team’s compute express link (CXL) provides new insights on memory disaggregation and ensures direct access and high-performance capabilities
A team from the Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL) at KAIST presented a new compute express link (CXL) solution whose directly accessible, and high-performance memory disaggregation opens new directions for big data memory processing. Professor Myoungsoo Jung said the team’s technology significantly improves performance compared to existing remote direct memory access (RDMA)-based memory disaggregation.
CXL is a peripheral component interconnect-express (PCIe)-based new dynamic multi-protocol made for efficiently utilizing memory devices and accelerators. Many enterprise data centers and memory vendors are paying attention to it as the next-generation multi-protocol for the era of big data.
Emerging big data applications such as machine learning, graph analytics, and in-memory databases require large memory capacities. However, scaling out the memory capacity via a prior memory interface like double data rate (DDR) is limited by the number of the central processing units (CPUs) and memory controllers. Therefore, memory disaggregation, which allows connecting a host to another host’s memory or memory nodes, has appeared.
RDMA is a way that a host can directly access another host’s memory via InfiniBand, the commonly used network protocol in data centers. Nowadays, most existing memory disaggregation technologies employ RDMA to get a large memory capacity. As a result, a host can share another host’s memory by transferring the data between local and remote memory.
Although RDMA-based memory disaggregation provides a large memory capacity to a host, two critical problems exist. First, scaling out the memory still needs an extra CPU to be added. Since passive memory such as dynamic random-access memory (DRAM), cannot operate by itself, it should be controlled by the CPU. Second, redundant data copies and software fabric interventions for RDMA-based memory disaggregation cause longer access latency. For example, remote memory access latency in RDMA-based memory disaggregation is multiple orders of magnitude longer than local memory access.
To address these issues, Professor Jung’s team developed the CXL-based memory disaggregation framework, including CXL-enabled customized CPUs, CXL devices, CXL switches, and CXL-aware operating system modules. The team’s CXL device is a pure passive and directly accessible memory node that contains multiple DRAM dual inline memory modules (DIMMs) and a CXL memory controller. Since the CXL memory controller supports the memory in the CXL device, a host can utilize the memory node without processor or software intervention. The team’s CXL switch enables scaling out a host’s memory capacity by hierarchically connecting multiple CXL devices to the CXL switch allowing more than hundreds of devices. Atop the switches and devices, the team’s CXL-enabled operating system removes redundant data copy and protocol conversion exhibited by conventional RDMA, which can significantly decrease access latency to the memory nodes.
In a test comparing loading 64B (cacheline) data from memory pooling devices, CXL-based memory disaggregation showed 8.2 times higher data load performance than RDMA-based memory disaggregation and even similar performance to local DRAM memory. In the team’s evaluations for a big data benchmark such as a machine learning-based test, CXL-based memory disaggregation technology also showed a maximum of 3.7 times higher performance than prior RDMA-based memory disaggregation technologies.
“Escaping from the conventional RDMA-based memory disaggregation, our CXL-based memory disaggregation framework can provide high scalability and performance for diverse datacenters and cloud service infrastructures,” said Professor Jung. He went on to stress, “Our CXL-based memory disaggregation research will bring about a new paradigm for memory solutions that will lead the era of big data.”
-Profile: Professor Myoungsoo Jung Computer Architecture and Memory Systems Laboratory (CAMEL)http://camelab.org School of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2022.03.16 View 23019 -
 Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 10209
Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2022
Third online commencement ceremony since the pandemic outbreak celebrates 2741 graduates
The 2022 commencement ceremony convened online on February 18 to celebrate and award degrees to the Class of 2022. The graduating class of 2022 included 663 PhDs, 1,383 Masters, and 695 Bachelors. The limited number of attendees included 86 graduate representatives and approximately 20 faculty members in senior leadership, as well as Korea’s Minister of Science and ICT Hyesook Lim. The ceremony was livestreamed on KAIST’s YouTube channel.
Valedictorian Ji-Young Lee from the Department of Physics received the Minister of Science and ICT’s Award. Yu-Jin Bang from the School of Business and Technology Management was the Awardee of the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees and the KAIST Presidential Awardee was Jong-Hwan Lee from the Department of Mathematical Sciences.
KAIST conferred honorary doctorates to Honorary Chairman Jae-Chul Kim of Dongwon Group and Chairman Sung-Hwan Chang of Samsung Brush. Chairman Kim, whose donation funded the establishment of the Kim Jae-Chul Graduate School of AI, was awarded an honorary doctorate of science technology. Chairman Chang was awarded an honorary doctorate of business administration in recognition of his funding in the fields of medical science and engineering at KAIST.
This year’s undergraduate commencement speaker was Hye-Lin Park from the School of Computing. She has severe cerebral palsy and was the first student admitted to KAIST with a severe physical handicap.
“I loved mathematics and wanted to become a mathematician. When I learned programming in my second year, I was so mesmerized by it that I transferred to the School of Computing,” said Park, who plans to continue studying programming languages in graduate school at KAIST.
“I spent my entire life of 24 years in this beautiful wheelchair. Without the support and help of my parents, friends, and my special teachers who helped me move and study at the campus, I would not have made it this far,” said Park. For easier access to classrooms and facilities, KAIST started to remodel its facilities to make the entrance of buildings more wheelchair-friendly. Park made many suggestions to the Office of Student Life and the Facilities Management Office on how to ease mobility for handicapped people on campus. The physical education course that was required for graduation was also revised to stipulate exceptions.
Minister Lim stressed the role of young scientists and researchers in these times of digital transformation dominated by AI and the metaverse. She encouraged the graduates to carry out their dreams with warm hearts and challenging spirits.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee also stressed the power of dreams, calling for graduates to dream big even in times of uncertainty.
“Humanity stands at an inflection point in history. The fourth industrial revolution and outbreak of Covid-19 have unfolded the grand global transformation. Although the future gives us new opportunities, it also comes with anxiety regarding the uncertainties ahead.”
“Dreams make your heart race and push us to live life to the fullest. Dreams will help you keep moving forward even in the face of adversity,” he said.
2022.02.18 View 10209 -
 A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 9717
A Study Shows Reactive Electrolyte Additives Improve Lithium Metal Battery Performance
Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives provide an opportunity to improve high-performance lithium metal batteries
A research team showed that electrolyte additives increase the lifetime of lithium metal batteries and remarkably improve the performance of fast charging and discharging. Professor Nam-Soon Choi’s team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST hierarchized the solid electrolyte interphase to make a dual-layer structure and showed groundbreaking run times for lithium metal batteries.
The team applied two electrolyte additives that have different reduction and adsorption properties to improve the functionality of the dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase. In addition, the team has confirmed that the structural stability of the nickel-rich cathode was achieved through the formation of a thin protective layer on the cathode. This study was reported in Energy Storage Materials.
Securing high-energy-density lithium metal batteries with a long lifespan and fast charging performance is vital for realizing their ubiquitous use as superior power sources for electric vehicles. Lithium metal batteries comprise a lithium metal anode that delivers 10 times higher capacity than the graphite anodes in lithium-ion batteries. Therefore, lithium metal is an indispensable anode material for realizing high-energy rechargeable batteries. However, undesirable reactions among the electrolytes with lithium metal anodes can reduce the power and this remains an impediment to achieving a longer battery lifespan. Previous studies only focused on the formation of the solid electrolyte interphase on the surface of the lithium metal anode.
The team designed a way to create a dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase to resolve the instability of the lithium metal anode by using electrolyte additives, depending on their electron accepting ability and adsorption tendencies. This hierarchical structure of the solid electrolyte interphase on the lithium metal anode has the potential to be further applied to lithium-alloy anodes, lithium storage structures, and anode-free technology to meet market expectations for electrolyte technology.
The batteries with lithium metal anodes and nickel-rich cathodes represented 80.9% of the initial capacity after 600 cycles and achieved a high Coulombic efficiency of 99.94%. These remarkable results contributed to the development of protective dual-layer solid electrolyte interphase technology for lithium metal anodes.
Professor Choi said that the research suggests a new direction for the development of electrolyte additives to regulate the unstable lithium metal anode-electrolyte interface, the biggest hurdle in research on lithium metal batteries.
She added that anode-free secondary battery technology is expected to be a game changer in the secondary battery market and electrolyte additive technology will contribute to the enhancement of anode-free secondary batteries through the stabilization of lithium metal anodes.
This research was funded by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change of the National Research Foundation in Korea funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Technology Innovation Program funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy, and Hyundai Motor Company.
- PublicationSaehun Kim, Sung O Park, Min-Young Lee, Jeong-A Lee, Imanuel Kristanto, Tae Kyung Lee, Daeyeon Hwang, Juyoung Kim, Tae-Ung Wi, Hyun-Wook Lee, Sang Kyu Kwak, and NamSoon Choi, “Stable electrode-electrolyte interfaces constructed by fluorine- and nitrogen-donating ionic additives for high-performance lithium metal batteries,” Energy Storage Materials,45, 1-13 (2022), (doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ensm.2021.10.031)
- ProfileProfessor Nam-Soon ChoiEnergy Materials LaboratoryDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2021.12.16 View 9717 -
 Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 15632
Scientists Develop Wireless Networks that Allow Brain Circuits to Be Controlled Remotely through the Internet
Wireless implantable devices and IoT could manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world due to their minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility
A new study shows that researchers can remotely control the brain circuits of numerous animals simultaneously and independently through the internet. The scientists believe this newly developed technology can speed up brain research and various neuroscience studies to uncover basic brain functions as well as the underpinnings of various neuropsychiatric and neurological disorders.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers at KAIST, Washington University in St. Louis, and the University of Colorado, Boulder, created a wireless ecosystem with its own wireless implantable devices and Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure to enable high-throughput neuroscience experiments over the internet. This innovative technology could enable scientists to manipulate the brains of animals from anywhere around the world. The study was published in the journal Nature Biomedical Engineering on November 25
“This novel technology is highly versatile and adaptive. It can remotely control numerous neural implants and laboratory tools in real-time or in a scheduled way without direct human interactions,” said Professor Jae-Woong Jeong of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST and a senior author of the study. “These wireless neural devices and equipment integrated with IoT technology have enormous potential for science and medicine.”
The wireless ecosystem only requires a mini-computer that can be purchased for under $45, which connects to the internet and communicates with wireless multifunctional brain probes or other types of conventional laboratory equipment using IoT control modules. By optimally integrating the versatility and modular construction of both unique IoT hardware and software within a single ecosystem, this wireless technology offers new applications that have not been demonstrated before by a single standalone technology. This includes, but is not limited to minimalistic hardware, global remote access, selective and scheduled experiments, customizable automation, and high-throughput scalability.
“As long as researchers have internet access, they are able to trigger, customize, stop, validate, and store the outcomes of large experiments at any time and from anywhere in the world. They can remotely perform large-scale neuroscience experiments in animals deployed in multiple countries,” said one of the lead authors, Dr. Raza Qazi, a researcher with KAIST and the University of Colorado, Boulder. “The low cost of this system allows it to be easily adopted and can further fuel innovation across many laboratories,” Dr. Qazi added.
One of the significant advantages of this IoT neurotechnology is its ability to be mass deployed across the globe due to its minimalistic hardware, low setup cost, ease of use, and customizable versatility. Scientists across the world can quickly implement this technology within their existing laboratories with minimal budget concerns to achieve globally remote access, scalable experimental automation, or both, thus potentially reducing the time needed to unravel various neuroscientific challenges such as those associated with intractable neurological conditions.
Another senior author on the study, Professor Jordan McCall from the Department of Anesthesiology and Center for Clinical Pharmacology at Washington University in St. Louis, said this technology has the potential to change how basic neuroscience studies are performed. “One of the biggest limitations when trying to understand how the mammalian brain works is that we have to study these functions in unnatural conditions. This technology brings us one step closer to performing important studies without direct human interaction with the study subjects.”
The ability to remotely schedule experiments moves toward automating these types of experiments. Dr. Kyle Parker, an instructor at Washington University in St. Louis and another lead author on the study added, “This experimental automation can potentially help us reduce the number of animals used in biomedical research by reducing the variability introduced by various experimenters. This is especially important given our moral imperative to seek research designs that enable this reduction.”
The researchers believe this wireless technology may open new opportunities for many applications including brain research, pharmaceuticals, and telemedicine to treat diseases in the brain and other organs remotely. This remote automation technology could become even more valuable when many labs need to shut down, such as during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This work was supported by grants from the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program, the National Research Foundation of Korea, the United States National Institute of Health, and Oak Ridge Associated Universities.
-PublicationRaza Qazi, Kyle Parker, Choong Yeon Kim, Jordan McCall, Jae-Woong Jeong et al. “Scalable and modular wireless-network infrastructure for large-scale behavioral neuroscience,” Nature Biomedical Engineering, November 25 2021 (doi.org/10.1038/s41551-021-00814-w)
-ProfileProfessor Jae-Woong JeongBio-Integrated Electronics and Systems LabSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.11.29 View 15632 -
 Marien Buissonniere Awarded the 9th Grand Award for Future Strategy
Global healthcare and humanitarian activist honored by the Grand Award for Future Strategy
The Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy awarded the 9th Grand Award for Future Strategy to Marine Buissonniere, an independent advisor and practitioner in the fields of global health and humanitarian action. She currently works as a senior advisor to the Prevent Epidemics team at Resolve to Save Lives. She also co-chairs Doctors Without Borders’ Transformational Investment Capacity.
Buissonniere was recognized for designing and implementing global response strategies in global strife and disaster stricken areas over the 25 years while serving as secretary general of Doctors Without Borders. She has been working with various government agencies around the world including Resolve to Save Lives to respond to the Covid-19 pandemic and preparing global future strategies for the post-pandemic era.
The Grand Award for Future Strategy recognizes individual and organization who have contributed to the nation and humanity through future research and strategies in the fields of science and technology, economy and industry, society and culture, politics and governance, and resources and environment.
The selection committee place particular emphasis on her humanitarian efforts toward North Korea. She was in charge of the task force for resuming the health project in North Korea and facilitated the North Korean program in 2002. She also played a significant role in raising awareness of North Korea’s humanitarian issues in the international community by lecturing at Columbia and Princeton.
Buissonniere said during the awards ceremony held online on November 5, “I am very grateful to receive this award from KAIST, a world’s top-flight university as well as from South Korea related to the Korean Peninsula and North Korea, where I have spent most of my life. What makes this award even more special is it is about the international medical relief activities and system innovations that I’ve devoted my life to over the last 25 years. I am going to continue this journey to help many people in difficult situations. Eventually, I would like to make it possible for those people in need to make their own future by themselves.”
2021.11.11 View 6888
Marien Buissonniere Awarded the 9th Grand Award for Future Strategy
Global healthcare and humanitarian activist honored by the Grand Award for Future Strategy
The Moon Soul Graduate School of Future Strategy awarded the 9th Grand Award for Future Strategy to Marine Buissonniere, an independent advisor and practitioner in the fields of global health and humanitarian action. She currently works as a senior advisor to the Prevent Epidemics team at Resolve to Save Lives. She also co-chairs Doctors Without Borders’ Transformational Investment Capacity.
Buissonniere was recognized for designing and implementing global response strategies in global strife and disaster stricken areas over the 25 years while serving as secretary general of Doctors Without Borders. She has been working with various government agencies around the world including Resolve to Save Lives to respond to the Covid-19 pandemic and preparing global future strategies for the post-pandemic era.
The Grand Award for Future Strategy recognizes individual and organization who have contributed to the nation and humanity through future research and strategies in the fields of science and technology, economy and industry, society and culture, politics and governance, and resources and environment.
The selection committee place particular emphasis on her humanitarian efforts toward North Korea. She was in charge of the task force for resuming the health project in North Korea and facilitated the North Korean program in 2002. She also played a significant role in raising awareness of North Korea’s humanitarian issues in the international community by lecturing at Columbia and Princeton.
Buissonniere said during the awards ceremony held online on November 5, “I am very grateful to receive this award from KAIST, a world’s top-flight university as well as from South Korea related to the Korean Peninsula and North Korea, where I have spent most of my life. What makes this award even more special is it is about the international medical relief activities and system innovations that I’ve devoted my life to over the last 25 years. I am going to continue this journey to help many people in difficult situations. Eventually, I would like to make it possible for those people in need to make their own future by themselves.”
2021.11.11 View 6888 -
 GSI Forum Highlights Global Collaboration Toward a Sustainable Global Economy
The forum stresses global collaboration to make the global value chain more resilient
Speakers at the 5th Global Strategy Institute International Forum on October 28 stressed the importance of global collaboration for rebuilding the global economy and making innovations in national science and technology governance in order to enhance national competitiveness. The forum entitled “Grand Strategic Shift under Global Techno-Geopolitical Paradigm” examined strategies for making the global supply chain more resilient and rebuild the global economy as well as how Korea could advance in the technology race.
Speakers concurred that technology has become an issue of national security. The global supply chain has been disrupted amid the global pandemic and intense conflict between the U.S. and China. Speakers presented a common solution: global collaboration and innovations in science and technology governance.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks that the future ‘world map’ may turn out very differently depending on how we prepare and what we envision for the future. He also stressed the importance of technology sovereignty, adding that only those who can create their own new technology independently will be the future leaders.
Prime Minister Boo Kyum Kim and Vice Minister of Science and ICT Hongtaek Yong delivered congratulatory remarks. Keynote speakers included Professor Scott Stern from the MIT Sloan School of Management, Professor Aaron Chatterji from the Fuqua School of Business at Duke University, Professor Sarah Kreps from the Department of Government at Cornell University, SK Group Chairperson Tae-Won Chey, President Woo Il Lee of the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies, Professor Young Kwan Yoon at Seoul National University, President Eun Mee Kim of Ewha Womans University, and President Ieehwan Kim of the University of Science and Technology.
During the first session, Professor Chatterji stressed that how to make supply chains resilience will be the key for making long-term strategy with relevant government policy. He said that AI has become a general purpose technology (GPT) and Korea ranked 4th in AI innovation in the world, but how to translate this innovativeness into national strategic leadership will be a new challenge for Korea. He suggested that Korea strengthen its strategic partnerships with allies such as the U.S. and provide opportunities not only for established players but start-ups and entrepreneurs. Meanwhile, Professor Kreps said that industrial policy should also leverage trust and innovations for building technology alliances with a more longer-term approach, without antagonizing certain groups of nations.
Vice President for Planning and Budget Bowon Kim who joined the forum as a discussant pointed out that in this hyper-connected era, nothing can be manufactured in a single company and country without the global supply chain. “In longer-term policy and strategies, we should embrace China as a global economy partner and include all nations around the world.”
Chairman Chey from SK said that the clear role among universities, industry, and the government doesn’t exist any longer. Now, universities are working hard for the commercialization of technology from their labs. Industry is nurturing the talents inept for future industry, and the government is trying to introduce a more private-sector approach. As such, universities, the government, and industry should embrace all-inclusive approaches encompassing global politics and trade to lead on the global stage.
Meanwhile in the second session, all of the speakers stressed innovation in science and technology governance in order to adopt to the new industrial paradigm. They agreed to make prompt innovations and solid collaborative systems among the government ministries to ensure national competitiveness, especially in the field of science and technology.
President Lee from KOFST said Korea should adopt a first mover strategy and the government should adopt a mission-oriented projects and deregulate more. He pointed out that when mandating more autonomy in decision making, scientists and students can make more creative outcomes.
Professor Yoon at SNU stressed the close alliance with the U.S. in the technology race, but suggested that Korea should also seek ways to help minimize the technology gap between advanced and developing countries. Universities should also be allowed more autonomy in running creative curriculum and academic affairs to in order boost the competitiveness of science and technology.
President Kim from Ewha pointed out the role of education as a public good. In some countries, strengthening science and technology can be accomplished with wider educational opportunities in middle and high schools. President Kim also stressed expanding strategic partnerships. She said Korea should expand its alliances and partnerships, not only with the U.S. but with European countries and other niche countries where certain technologies are superior.
President Kim of UST stressed a new science and technology leadership is required to build technology sovereignty and the government should spearhead the deregulations of the government policy.
This GSI forum was co-hosted by two think-tanks at KAIST, the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) and the Innovation Strategy and Policy Institute (ISPI).
2021.10.28 View 9407
GSI Forum Highlights Global Collaboration Toward a Sustainable Global Economy
The forum stresses global collaboration to make the global value chain more resilient
Speakers at the 5th Global Strategy Institute International Forum on October 28 stressed the importance of global collaboration for rebuilding the global economy and making innovations in national science and technology governance in order to enhance national competitiveness. The forum entitled “Grand Strategic Shift under Global Techno-Geopolitical Paradigm” examined strategies for making the global supply chain more resilient and rebuild the global economy as well as how Korea could advance in the technology race.
Speakers concurred that technology has become an issue of national security. The global supply chain has been disrupted amid the global pandemic and intense conflict between the U.S. and China. Speakers presented a common solution: global collaboration and innovations in science and technology governance.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee said in his opening remarks that the future ‘world map’ may turn out very differently depending on how we prepare and what we envision for the future. He also stressed the importance of technology sovereignty, adding that only those who can create their own new technology independently will be the future leaders.
Prime Minister Boo Kyum Kim and Vice Minister of Science and ICT Hongtaek Yong delivered congratulatory remarks. Keynote speakers included Professor Scott Stern from the MIT Sloan School of Management, Professor Aaron Chatterji from the Fuqua School of Business at Duke University, Professor Sarah Kreps from the Department of Government at Cornell University, SK Group Chairperson Tae-Won Chey, President Woo Il Lee of the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies, Professor Young Kwan Yoon at Seoul National University, President Eun Mee Kim of Ewha Womans University, and President Ieehwan Kim of the University of Science and Technology.
During the first session, Professor Chatterji stressed that how to make supply chains resilience will be the key for making long-term strategy with relevant government policy. He said that AI has become a general purpose technology (GPT) and Korea ranked 4th in AI innovation in the world, but how to translate this innovativeness into national strategic leadership will be a new challenge for Korea. He suggested that Korea strengthen its strategic partnerships with allies such as the U.S. and provide opportunities not only for established players but start-ups and entrepreneurs. Meanwhile, Professor Kreps said that industrial policy should also leverage trust and innovations for building technology alliances with a more longer-term approach, without antagonizing certain groups of nations.
Vice President for Planning and Budget Bowon Kim who joined the forum as a discussant pointed out that in this hyper-connected era, nothing can be manufactured in a single company and country without the global supply chain. “In longer-term policy and strategies, we should embrace China as a global economy partner and include all nations around the world.”
Chairman Chey from SK said that the clear role among universities, industry, and the government doesn’t exist any longer. Now, universities are working hard for the commercialization of technology from their labs. Industry is nurturing the talents inept for future industry, and the government is trying to introduce a more private-sector approach. As such, universities, the government, and industry should embrace all-inclusive approaches encompassing global politics and trade to lead on the global stage.
Meanwhile in the second session, all of the speakers stressed innovation in science and technology governance in order to adopt to the new industrial paradigm. They agreed to make prompt innovations and solid collaborative systems among the government ministries to ensure national competitiveness, especially in the field of science and technology.
President Lee from KOFST said Korea should adopt a first mover strategy and the government should adopt a mission-oriented projects and deregulate more. He pointed out that when mandating more autonomy in decision making, scientists and students can make more creative outcomes.
Professor Yoon at SNU stressed the close alliance with the U.S. in the technology race, but suggested that Korea should also seek ways to help minimize the technology gap between advanced and developing countries. Universities should also be allowed more autonomy in running creative curriculum and academic affairs to in order boost the competitiveness of science and technology.
President Kim from Ewha pointed out the role of education as a public good. In some countries, strengthening science and technology can be accomplished with wider educational opportunities in middle and high schools. President Kim also stressed expanding strategic partnerships. She said Korea should expand its alliances and partnerships, not only with the U.S. but with European countries and other niche countries where certain technologies are superior.
President Kim of UST stressed a new science and technology leadership is required to build technology sovereignty and the government should spearhead the deregulations of the government policy.
This GSI forum was co-hosted by two think-tanks at KAIST, the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution (KPC4IR) and the Innovation Strategy and Policy Institute (ISPI).
2021.10.28 View 9407 -
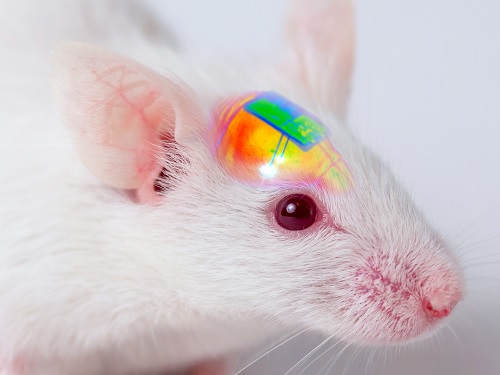 Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 26575
Wirelessly Rechargeable Soft Brain Implant Controls Brain Cells
Researchers have invented a smartphone-controlled soft brain implant that can be recharged wirelessly from outside the body. It enables long-term neural circuit manipulation without the need for periodic disruptive surgeries to replace the battery of the implant. Scientists believe this technology can help uncover and treat psychiatric disorders and neurodegenerative diseases such as addiction, depression, and Parkinson’s.
A group of KAIST researchers and collaborators have engineered a tiny brain implant that can be wirelessly recharged from outside the body to control brain circuits for long periods of time without battery replacement. The device is constructed of ultra-soft and bio-compliant polymers to help provide long-term compatibility with tissue. Geared with micrometer-sized LEDs (equivalent to the size of a grain of salt) mounted on ultrathin probes (the thickness of a human hair), it can wirelessly manipulate target neurons in the deep brain using light.
This study, led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong, is a step forward from the wireless head-mounted implant neural device he developed in 2019. That previous version could indefinitely deliver multiple drugs and light stimulation treatment wirelessly by using a smartphone. For more, Manipulating Brain Cells by Smartphone.
For the new upgraded version, the research team came up with a fully implantable, soft optoelectronic system that can be remotely and selectively controlled by a smartphone. This research was published on January 22, 2021 in Nature Communications.
The new wireless charging technology addresses the limitations of current brain implants. Wireless implantable device technologies have recently become popular as alternatives to conventional tethered implants, because they help minimize stress and inflammation in freely-moving animals during brain studies, which in turn enhance the lifetime of the devices. However, such devices require either intermittent surgeries to replace discharged batteries, or special and bulky wireless power setups, which limit experimental options as well as the scalability of animal experiments.
“This powerful device eliminates the need for additional painful surgeries to replace an exhausted battery in the implant, allowing seamless chronic neuromodulation,” said Professor Jeong. “We believe that the same basic technology can be applied to various types of implants, including deep brain stimulators, and cardiac and gastric pacemakers, to reduce the burden on patients for long-term use within the body.”
To enable wireless battery charging and controls, researchers developed a tiny circuit that integrates a wireless energy harvester with a coil antenna and a Bluetooth low-energy chip. An alternating magnetic field can harmlessly penetrate through tissue, and generate electricity inside the device to charge the battery. Then the battery-powered Bluetooth implant delivers programmable patterns of light to brain cells using an “easy-to-use” smartphone app for real-time brain control.
“This device can be operated anywhere and anytime to manipulate neural circuits, which makes it a highly versatile tool for investigating brain functions,” said lead author Choong Yeon Kim, a researcher at KAIST.
Neuroscientists successfully tested these implants in rats and demonstrated their ability to suppress cocaine-induced behaviour after the rats were injected with cocaine. This was achieved by precise light stimulation of relevant target neurons in their brains using the smartphone-controlled LEDs. Furthermore, the battery in the implants could be repeatedly recharged while the rats were behaving freely, thus minimizing any physical interruption to the experiments.
“Wireless battery re-charging makes experimental procedures much less complicated,” said the co-lead author Min Jeong Ku, a researcher at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine.
“The fact that we can control a specific behaviour of animals, by delivering light stimulation into the brain just with a simple manipulation of smartphone app, watching freely moving animals nearby, is very interesting and stimulates a lot of imagination,” said Jeong-Hoon Kim, a professor of physiology at Yonsei University’s College of Medicine. “This technology will facilitate various avenues of brain research.”
The researchers believe this brain implant technology may lead to new opportunities for brain research and therapeutic intervention to treat diseases in the brain and other organs.
This work was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea and the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program.
-Profile
Professor Jae-Woong Jeong
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2021.01.26 View 26575 -
 Life After COVID-19: Big Questions on Medical and Bio-Engineering
KAIST GSI forum explores big questions in the medical and bio-engineering revolution caused by the COVID-19 in fight against infectious diseases and life quality
On September 9, the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST will delve into innovative future strategies for the medical and bio-engineering sectors that have been disrupted by COVID-19. The forum will live stream via YouTube, KTV, and Naver TV from 9:00 am Korean time.
The online forum features a speaker lineup of world-renowned scholars who will discuss an array of bio-engineering technologies that will improve our quality of life and even extend our life span. This is the GSI’s third online forum since the first one in April that covered the socio-economic implications of the global pandemic and the second one in June focusing on the education sector.
In hosting the third round of the GSI Forum series, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed the power of science and technology saying, “In this world full of uncertainties, one thing for sure is that only the advancement of science and technology will deliver us from this crisis.” Korean Prime Minister Sye-Kyun Chung will also deliver a speech explaining the government’s response to COVID-19 and vaccine development strategies.
The President of the National Academy of Medicine in the US will share ideal policies to back up the bio-engineering and medical sectors and Futurist Thomas Frey from the Davinci Institute will present his distinct perspectives on our future lives after COVID-19. His thought-provoking insights on advancements in the bioengineering sector will examine whether humanity can put an end to infectious diseases and find new ways to lengthen our lives.
Two distinguished professors in the field of genetic engineering technology will share their latest breakthroughs. Professor George McDonald Church from Harvard Medical School who developed genome sequencing will deliver a keynote speech on how the advancement of gene editing and genome technology will overcome diseases and contribute to extending human life spans.
Professor Kwang-Soo Kim, a KAIST alumnus from Harvard Medical School who recently reported new discoveries for Parkinson’s disease treatment by reprogramming a patient’s own skin cells to replace cells in the brain, will introduce the latest clinical cell treatment technologies based on personalized therapeutics.
Senior Vice President and Chief Product Officer of Illumina Susan Tousi, a leading genome sequencing solution provider, will describe genome analysis technology and explore the potential for disease prevention.
KAIST medical scientist Jeong Ho Lee, who was the first to identify the causes of intractable epilepsies and has identified the genes responsible for several developmental brain disorders. Professor Jin-Hyung Lee from Stanford University and Dr. David B. Resnik from the National Institute of Environmental Health Science will also join the speaker lineup to discuss genetics-based personalized solutions to extend human life spans.
The forum will also invite about 50 young scientists and medical researchers from around the world to participate in an online panel session. They will engage in a Q&A session and a discussion with the speakers.
(END)
2020.09.04 View 10958
Life After COVID-19: Big Questions on Medical and Bio-Engineering
KAIST GSI forum explores big questions in the medical and bio-engineering revolution caused by the COVID-19 in fight against infectious diseases and life quality
On September 9, the Global Strategy Institute at KAIST will delve into innovative future strategies for the medical and bio-engineering sectors that have been disrupted by COVID-19. The forum will live stream via YouTube, KTV, and Naver TV from 9:00 am Korean time.
The online forum features a speaker lineup of world-renowned scholars who will discuss an array of bio-engineering technologies that will improve our quality of life and even extend our life span. This is the GSI’s third online forum since the first one in April that covered the socio-economic implications of the global pandemic and the second one in June focusing on the education sector.
In hosting the third round of the GSI Forum series, KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed the power of science and technology saying, “In this world full of uncertainties, one thing for sure is that only the advancement of science and technology will deliver us from this crisis.” Korean Prime Minister Sye-Kyun Chung will also deliver a speech explaining the government’s response to COVID-19 and vaccine development strategies.
The President of the National Academy of Medicine in the US will share ideal policies to back up the bio-engineering and medical sectors and Futurist Thomas Frey from the Davinci Institute will present his distinct perspectives on our future lives after COVID-19. His thought-provoking insights on advancements in the bioengineering sector will examine whether humanity can put an end to infectious diseases and find new ways to lengthen our lives.
Two distinguished professors in the field of genetic engineering technology will share their latest breakthroughs. Professor George McDonald Church from Harvard Medical School who developed genome sequencing will deliver a keynote speech on how the advancement of gene editing and genome technology will overcome diseases and contribute to extending human life spans.
Professor Kwang-Soo Kim, a KAIST alumnus from Harvard Medical School who recently reported new discoveries for Parkinson’s disease treatment by reprogramming a patient’s own skin cells to replace cells in the brain, will introduce the latest clinical cell treatment technologies based on personalized therapeutics.
Senior Vice President and Chief Product Officer of Illumina Susan Tousi, a leading genome sequencing solution provider, will describe genome analysis technology and explore the potential for disease prevention.
KAIST medical scientist Jeong Ho Lee, who was the first to identify the causes of intractable epilepsies and has identified the genes responsible for several developmental brain disorders. Professor Jin-Hyung Lee from Stanford University and Dr. David B. Resnik from the National Institute of Environmental Health Science will also join the speaker lineup to discuss genetics-based personalized solutions to extend human life spans.
The forum will also invite about 50 young scientists and medical researchers from around the world to participate in an online panel session. They will engage in a Q&A session and a discussion with the speakers.
(END)
2020.09.04 View 10958 -
 Virtual Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2020
The KAIST community gathered online to celebrate the 2020 graduating class. The blended ceremony conferred their hard-earned degrees on August 28. The belated celebration, which was postponed from February 21 due to the COVID-19 outbreak, honored the 2846 graduates with live streaming on YouTube beginning at 2:00 pm. The graduates include 721 PhDs and 1399 master’s degree holders.
The government raised its social distancing guidelines to level two out of three on August 23 as the second wave of the virus hit the nation. Level two guidelines prohibit the gathering of more than 50 persons indoors or 100 persons outdoors.
For the virtual ceremony, the Office of Student Affairs and Policy announced a list of 67 graduates who signed up to participate in the graduation ceremony. Graduates were divided into three groups to attend at three different places and watch the ceremony via Zoom. No family and friends of the graduates were allowed to participate at the campus.
This year’s valedictorian, Kon-Yong Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, received the Award of Minister of Science and Technology. Salutorian Hee-Kwang Roh from the Department of Chemistry received the Award of the KAIST Board of Trustees, while the recipient of the KAIST Presidential Award was Hong Jae-Min from the School of Computing.
President Sung-Chul Shin, Chairman of the Board of Trustees Woo-Sik Kim, former Minister of Science and Technology and former Provost at KAIST Dr. KunMo Chung, and a very limited number of faculty and staff members officiated the commencement ceremony from the KAIST auditorium.
President Shin in his commencement speech applauded the graduates’ hard work and dedication and delivered a very special congratulatory message to them. He encouraged the new graduates to be courageous enough to deal with these new challenges as well as future uncertainties, during the greatest transformation brought about by COVID-19.
“Instead of following behind others as a fast follower, we should take the initiative and walk down new paths as a first mover.” He also stressed, “We can transform this crisis into an opportunity by practicing the C3 values KAIST pursues: Challenging, Creating, and Caring.”
As new alumni of Korea’s top science and technology university, he said, “Our graduates should focus on creating the world’s best, first, or only one in their research or their work.” However, he also pointed out the importance of a caring mind for others when working together.
At the ceremony, KAIST conferred an honorary doctorate degree to Dr. Younghoon David Kim, CEO and Chairman of Daesung Group, in recognition of his lifetime dedication to making innovations in the energy industry.
Daesung Group is a leading energy company in Korea which manufactures and supplies natural gas for industries and home users. Dr. Kim is committed to making efficient energy sources by advancing cutting-energy sciences and disruptive technologies. He has served as chairman of the World Energy Council since 2016.
In his acceptance speech, Kim stressed the Grand Energy Transition as a new driving force in the future energy industry for maximizing energy efficiency.
“Since energy is the most basic foundation for all industries, improvements in energy efficiency translate into benefits for all related industries in terms of its efficiency and productivity.”
“The Grand Energy Transition is progressing widely and rapidly across the entire value chain of energy production, distribution, and consumption with decarbonization, decentralization, and digitalization serving as its driving force.”
He went on, “We should regard energy efficiency not as the fifth fuel but the first primary fuel.”
(END)
2020.08.28 View 12098
Virtual Commencement Ceremony Honors the Class of 2020
The KAIST community gathered online to celebrate the 2020 graduating class. The blended ceremony conferred their hard-earned degrees on August 28. The belated celebration, which was postponed from February 21 due to the COVID-19 outbreak, honored the 2846 graduates with live streaming on YouTube beginning at 2:00 pm. The graduates include 721 PhDs and 1399 master’s degree holders.
The government raised its social distancing guidelines to level two out of three on August 23 as the second wave of the virus hit the nation. Level two guidelines prohibit the gathering of more than 50 persons indoors or 100 persons outdoors.
For the virtual ceremony, the Office of Student Affairs and Policy announced a list of 67 graduates who signed up to participate in the graduation ceremony. Graduates were divided into three groups to attend at three different places and watch the ceremony via Zoom. No family and friends of the graduates were allowed to participate at the campus.
This year’s valedictorian, Kon-Yong Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, received the Award of Minister of Science and Technology. Salutorian Hee-Kwang Roh from the Department of Chemistry received the Award of the KAIST Board of Trustees, while the recipient of the KAIST Presidential Award was Hong Jae-Min from the School of Computing.
President Sung-Chul Shin, Chairman of the Board of Trustees Woo-Sik Kim, former Minister of Science and Technology and former Provost at KAIST Dr. KunMo Chung, and a very limited number of faculty and staff members officiated the commencement ceremony from the KAIST auditorium.
President Shin in his commencement speech applauded the graduates’ hard work and dedication and delivered a very special congratulatory message to them. He encouraged the new graduates to be courageous enough to deal with these new challenges as well as future uncertainties, during the greatest transformation brought about by COVID-19.
“Instead of following behind others as a fast follower, we should take the initiative and walk down new paths as a first mover.” He also stressed, “We can transform this crisis into an opportunity by practicing the C3 values KAIST pursues: Challenging, Creating, and Caring.”
As new alumni of Korea’s top science and technology university, he said, “Our graduates should focus on creating the world’s best, first, or only one in their research or their work.” However, he also pointed out the importance of a caring mind for others when working together.
At the ceremony, KAIST conferred an honorary doctorate degree to Dr. Younghoon David Kim, CEO and Chairman of Daesung Group, in recognition of his lifetime dedication to making innovations in the energy industry.
Daesung Group is a leading energy company in Korea which manufactures and supplies natural gas for industries and home users. Dr. Kim is committed to making efficient energy sources by advancing cutting-energy sciences and disruptive technologies. He has served as chairman of the World Energy Council since 2016.
In his acceptance speech, Kim stressed the Grand Energy Transition as a new driving force in the future energy industry for maximizing energy efficiency.
“Since energy is the most basic foundation for all industries, improvements in energy efficiency translate into benefits for all related industries in terms of its efficiency and productivity.”
“The Grand Energy Transition is progressing widely and rapidly across the entire value chain of energy production, distribution, and consumption with decarbonization, decentralization, and digitalization serving as its driving force.”
He went on, “We should regard energy efficiency not as the fifth fuel but the first primary fuel.”
(END)
2020.08.28 View 12098