National+Academy+of+Sciences
-
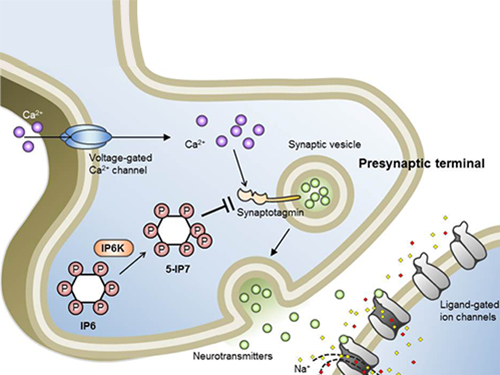 Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12318
Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12318 -
 Artificial Antibody-based Therapeutic Candidate for Lung Cancer Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of Biological Sciences at KAIST publishes a cover article on artificial antibody in "Molecular Therapy".
Repebody-based lung cancer therapeutic drug candidate developed Repebody-based protein demonstrates the possibility of the development of a new drug
KAIST Biological Sciences Department’s Professor Hak-Sung Kim, in collaboration with Professor Eun-Kyung Cho from the College of Medicine at Chungnam National University, has successfully developed an artificial antibody-based, or repebody, cancer therapeutic candidate. These research results were published as a cover paper of the July edition of Molecular Therapy.
The repebody developed by Professor Kim and his team strongly binds to interleukin-6, a cancer-causing factor. It has also been confirmed that the repebody can significantly inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells in non-small-cell lung cancer animal model.
Numerous multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies have invested astronomical amounts of money in research for the development of protein therapeutics with low side effects and high efficacy. More than 20 kinds of such therapeutics are currently under clinical trials, and over 100 drugs are under clinical demonstration. Among these, the majority is antibody-based therapeutics, and most of the investments are heavily concentrated in this field. However, antibody production cost is very high because it has large molecular weights and complex structural properties, and this makes it difficult to engineer. Consequently, the development costs a great deal of time and money.
In order to overcome the existing limitations of antibody-based therapeutics, Professor Kim and his team have developed a new artificial antibody, or repebody, which was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) in 2012. Based on this research, they have succeeded in developing a therapeutic candidate for treating non-small-cell lung cancer with a specifically strong cohesion to the cancer-causing factor, interleukin-6.
Interleukin-6 is a crucial substance within the body that is involved in immune and inflammatory-related signals. When abnormally expressed, it activates various carcinogenic pathways and promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Because of its importance, multinational pharmaceutical companies are heavily investing in developing therapeutics that can inhibit the signaling of interleukin-6.
In this study, Professor Kim and his team observed that a repebody consists of repeated modules, and they conceived a module-based affinity amplification technology that can effectively increase the binding affinity with the disease target. The developed therapeutic candidate has been confirmed in cell and animal experiments to show low immunogenicity, as well as to strongly inhibit the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Furthermore, by investigating the complex structure of the repebody with interleukin-6, Professor Kim has identified its mechanism, which demonstrated the potential for therapeutic development. The researchers are currently carrying out pre-clinical trials for acquiring permission to perform clinical trials on animals with non-small-cell lung cancer. The repebody can be developed into a new protein drug after demonstrating its safety and efficacy.
Professor Hak-Sung Kim and his team have confirmed that the repebody can be utilized as a new protein drug, and this will be a significant contribution to Korea’s protein drugs and biotechnology industry development.
The research was supported by the Future Pioneer Industry project and sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure 1. Professor Kim’s article published as the cover article of July edition of Molecular Therapy
Figure 2. Clinical proof of the repebody’s inhibition of cancer growth using animal models
2014.07.14 View 13811
Artificial Antibody-based Therapeutic Candidate for Lung Cancer Developed
Professor Hak-Sung Kim of Biological Sciences at KAIST publishes a cover article on artificial antibody in "Molecular Therapy".
Repebody-based lung cancer therapeutic drug candidate developed Repebody-based protein demonstrates the possibility of the development of a new drug
KAIST Biological Sciences Department’s Professor Hak-Sung Kim, in collaboration with Professor Eun-Kyung Cho from the College of Medicine at Chungnam National University, has successfully developed an artificial antibody-based, or repebody, cancer therapeutic candidate. These research results were published as a cover paper of the July edition of Molecular Therapy.
The repebody developed by Professor Kim and his team strongly binds to interleukin-6, a cancer-causing factor. It has also been confirmed that the repebody can significantly inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells in non-small-cell lung cancer animal model.
Numerous multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies have invested astronomical amounts of money in research for the development of protein therapeutics with low side effects and high efficacy. More than 20 kinds of such therapeutics are currently under clinical trials, and over 100 drugs are under clinical demonstration. Among these, the majority is antibody-based therapeutics, and most of the investments are heavily concentrated in this field. However, antibody production cost is very high because it has large molecular weights and complex structural properties, and this makes it difficult to engineer. Consequently, the development costs a great deal of time and money.
In order to overcome the existing limitations of antibody-based therapeutics, Professor Kim and his team have developed a new artificial antibody, or repebody, which was published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) in 2012. Based on this research, they have succeeded in developing a therapeutic candidate for treating non-small-cell lung cancer with a specifically strong cohesion to the cancer-causing factor, interleukin-6.
Interleukin-6 is a crucial substance within the body that is involved in immune and inflammatory-related signals. When abnormally expressed, it activates various carcinogenic pathways and promotes tumor growth and metastasis. Because of its importance, multinational pharmaceutical companies are heavily investing in developing therapeutics that can inhibit the signaling of interleukin-6.
In this study, Professor Kim and his team observed that a repebody consists of repeated modules, and they conceived a module-based affinity amplification technology that can effectively increase the binding affinity with the disease target. The developed therapeutic candidate has been confirmed in cell and animal experiments to show low immunogenicity, as well as to strongly inhibit the proliferation of non-small-cell lung cancer.
Furthermore, by investigating the complex structure of the repebody with interleukin-6, Professor Kim has identified its mechanism, which demonstrated the potential for therapeutic development. The researchers are currently carrying out pre-clinical trials for acquiring permission to perform clinical trials on animals with non-small-cell lung cancer. The repebody can be developed into a new protein drug after demonstrating its safety and efficacy.
Professor Hak-Sung Kim and his team have confirmed that the repebody can be utilized as a new protein drug, and this will be a significant contribution to Korea’s protein drugs and biotechnology industry development.
The research was supported by the Future Pioneer Industry project and sponsored by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
Figure 1. Professor Kim’s article published as the cover article of July edition of Molecular Therapy
Figure 2. Clinical proof of the repebody’s inhibition of cancer growth using animal models
2014.07.14 View 13811 -
 Materials Developed for Sodium Rechargeable Battery by EEWS
The research group of Professor William Goddard III, You-Sung Jung, and Jang-Wook Choi from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) at KAIST has developed a new sodium-ion rechargeable battery which operates at a high voltage, can be charged, and stably discharges over 10,000 cycles. The research results were published in the online version of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on December 30, 2013.
Since the material costs of sodium rechargeable batteries is 30 to 40 times lower than lithium batteries, it has received attention as an energy saving tool for smart grids and as the next generation of lithium rechargeable batteries. Until now, sodium-ion rechargeable batteries have had issues with stability when charging and discharging. The research group developed a vanadium-based electrode to solve these problems.
The group said follow-up research will be continued to develop advanced technology on sodium rechargeable batteries as it is still currently in the beginning stages.
The research team: From left to right is Professors William Goddard, You-Sung Jung, and Jang-Wook Choi
2014.01.13 View 11779
Materials Developed for Sodium Rechargeable Battery by EEWS
The research group of Professor William Goddard III, You-Sung Jung, and Jang-Wook Choi from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) at KAIST has developed a new sodium-ion rechargeable battery which operates at a high voltage, can be charged, and stably discharges over 10,000 cycles. The research results were published in the online version of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on December 30, 2013.
Since the material costs of sodium rechargeable batteries is 30 to 40 times lower than lithium batteries, it has received attention as an energy saving tool for smart grids and as the next generation of lithium rechargeable batteries. Until now, sodium-ion rechargeable batteries have had issues with stability when charging and discharging. The research group developed a vanadium-based electrode to solve these problems.
The group said follow-up research will be continued to develop advanced technology on sodium rechargeable batteries as it is still currently in the beginning stages.
The research team: From left to right is Professors William Goddard, You-Sung Jung, and Jang-Wook Choi
2014.01.13 View 11779 -
 Quantum Mechanical Calculation Theory Developed
An Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory, based on the widely used quantum mechanical principles and yet accurate and with shortened calculation period, was developed by Korean research team.
*Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory: Theory that proves that it is possible to calculate energy and properties with only simple wave equations and electron densities.
The research was conducted by Professor Jeong Yoo Sung (Graduate School of EEWS) and Professor William Goddard with support from WCU Foster Project initiated by Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and Korea Research Foundation. The result was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Journal.
The research team corrected the error when performing quantum calculations that arises from the length of calculation time and incorrect assumptions and developed a theory and algorithm that is more accurate and faster. The use of wave equations in quantum mechanical calculations results in high accuracy but there is a rapid increase in calculation time and is therefore difficult to implement in large molecules with hundreds, or thousands of atoms. By implementing a low electron density variable with relatively less calculation work, the size of calculable molecule increases but the accuracy decreases.
The team focused on the interaction between electrons with different spins to improve upon the speed of calculation in the conventional accurate calculation. The team used the fact that the interaction between electrons with different spins increases as it comes closer together in accordance with the Pauli’s Exclusion Principle.
In addition the interaction between electrons are local and therefore can ignore the interactions between far away electrons and still get the total energy value. The team also took advantage of this fact and developed the algorithm that decreased calculation time hundredth fold.
Professor Jeong commented that, “So far most of the domestic achievements were made by focusing on integrative researches by calculation science and material design communities but these involved short time frames. In areas that required lengthy time frames like fundamentals and software development, there was no competitive advantage. However this research is significant in that a superior solution was developed domestically”.
2012.01.31 View 12300
Quantum Mechanical Calculation Theory Developed
An Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory, based on the widely used quantum mechanical principles and yet accurate and with shortened calculation period, was developed by Korean research team.
*Electron Density Functional Calculation Theory: Theory that proves that it is possible to calculate energy and properties with only simple wave equations and electron densities.
The research was conducted by Professor Jeong Yoo Sung (Graduate School of EEWS) and Professor William Goddard with support from WCU Foster Project initiated by Ministry of Education, Science and Technology and Korea Research Foundation. The result was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Journal.
The research team corrected the error when performing quantum calculations that arises from the length of calculation time and incorrect assumptions and developed a theory and algorithm that is more accurate and faster. The use of wave equations in quantum mechanical calculations results in high accuracy but there is a rapid increase in calculation time and is therefore difficult to implement in large molecules with hundreds, or thousands of atoms. By implementing a low electron density variable with relatively less calculation work, the size of calculable molecule increases but the accuracy decreases.
The team focused on the interaction between electrons with different spins to improve upon the speed of calculation in the conventional accurate calculation. The team used the fact that the interaction between electrons with different spins increases as it comes closer together in accordance with the Pauli’s Exclusion Principle.
In addition the interaction between electrons are local and therefore can ignore the interactions between far away electrons and still get the total energy value. The team also took advantage of this fact and developed the algorithm that decreased calculation time hundredth fold.
Professor Jeong commented that, “So far most of the domestic achievements were made by focusing on integrative researches by calculation science and material design communities but these involved short time frames. In areas that required lengthy time frames like fundamentals and software development, there was no competitive advantage. However this research is significant in that a superior solution was developed domestically”.
2012.01.31 View 12300 -
 Bioengineers develop a new strategy for accurate prediction of cellular metabolic fluxes
A team of pioneering South Korean scientists has developed a new strategy for accurately predicting cellular metabolic fluxes under various genotypic and environmental conditions. This groundbreaking research is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS) on August 2, 2010.
To understand cellular metabolism and predict its metabolic capability at systems-level, systems biological analysis by modeling and simulation of metabolic network plays an important role. The team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, focused their research on the development of a new strategy for more accurate prediction of cellular metabolism.
“For strain improvement, biologists have made every effort to understand the global picture of biological systems and investigate the changes of all metabolic fluxes of the system under changing genotypic and environmental conditions,” said Lee. The accumulation of omics data, including genome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and fluxome, provides an opportunity to understand the cellular physiology and metabolic characteristics at systems-level. With the availability of the fully annotated genome sequence, the genome-scale in silico (means “performed on computer or via computer simulation.”) metabolic models for a number of organisms have been successfully developed to improve our understanding on these biological systems. With these advances, the development of new simulation methods to analyze and integrate systematically large amounts of biological data and predict cellular metabolic capability for systems biological analysis is important.
Information used to reconstruct the genome-scale in silico cell is not yet complete, which can make the simulation results different from the physiological performances of the real cell. Thus, additional information and procedures, such as providing additional constraints (constraint: a term to exclude incorrect metabolic fluxes by restricting the solution space of in silico cell) to the model, are often incorporated to improve the accuracy of the in silico cell.
By employing information generated from the genome sequence and annotation, the KAIST team developed a new set of constraints, called Grouping Reaction (GR) constraints, to accurately predict metabolic fluxes. Based on the genomic information, functionally related reactions were organized into different groups. These groups were considered for the generation of GR constraints, as condition- and objective function- independent constraints. Since the method developed in this study does not require complex information but only the genome sequence and annotation, this strategy can be applied to any organism with a completely annotated genome sequence.
“As we become increasingly concerned with environmental problems and the limits of fossil resources, bio-based production of chemicals from renewable biomass has been receiving great attention. Systems biological analysis by modeling and simulation of biological systems, to understand cellular metabolism and identify the targets for the strain improvement, has provided a new paradigm for developing successful bioprocesses,” concluded Lee. This new strategy for predicting cellular metabolism is expected to contribute to more accurate determination of cellular metabolic characteristics, and consequently to the development of metabolic engineering strategies for the efficient production of important industrial products and identification of new drug targets in pathogens.”
2010.08.05 View 15210
Bioengineers develop a new strategy for accurate prediction of cellular metabolic fluxes
A team of pioneering South Korean scientists has developed a new strategy for accurately predicting cellular metabolic fluxes under various genotypic and environmental conditions. This groundbreaking research is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS) on August 2, 2010.
To understand cellular metabolism and predict its metabolic capability at systems-level, systems biological analysis by modeling and simulation of metabolic network plays an important role. The team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, focused their research on the development of a new strategy for more accurate prediction of cellular metabolism.
“For strain improvement, biologists have made every effort to understand the global picture of biological systems and investigate the changes of all metabolic fluxes of the system under changing genotypic and environmental conditions,” said Lee. The accumulation of omics data, including genome, transcriptome, proteome, metabolome, and fluxome, provides an opportunity to understand the cellular physiology and metabolic characteristics at systems-level. With the availability of the fully annotated genome sequence, the genome-scale in silico (means “performed on computer or via computer simulation.”) metabolic models for a number of organisms have been successfully developed to improve our understanding on these biological systems. With these advances, the development of new simulation methods to analyze and integrate systematically large amounts of biological data and predict cellular metabolic capability for systems biological analysis is important.
Information used to reconstruct the genome-scale in silico cell is not yet complete, which can make the simulation results different from the physiological performances of the real cell. Thus, additional information and procedures, such as providing additional constraints (constraint: a term to exclude incorrect metabolic fluxes by restricting the solution space of in silico cell) to the model, are often incorporated to improve the accuracy of the in silico cell.
By employing information generated from the genome sequence and annotation, the KAIST team developed a new set of constraints, called Grouping Reaction (GR) constraints, to accurately predict metabolic fluxes. Based on the genomic information, functionally related reactions were organized into different groups. These groups were considered for the generation of GR constraints, as condition- and objective function- independent constraints. Since the method developed in this study does not require complex information but only the genome sequence and annotation, this strategy can be applied to any organism with a completely annotated genome sequence.
“As we become increasingly concerned with environmental problems and the limits of fossil resources, bio-based production of chemicals from renewable biomass has been receiving great attention. Systems biological analysis by modeling and simulation of biological systems, to understand cellular metabolism and identify the targets for the strain improvement, has provided a new paradigm for developing successful bioprocesses,” concluded Lee. This new strategy for predicting cellular metabolism is expected to contribute to more accurate determination of cellular metabolic characteristics, and consequently to the development of metabolic engineering strategies for the efficient production of important industrial products and identification of new drug targets in pathogens.”
2010.08.05 View 15210 -
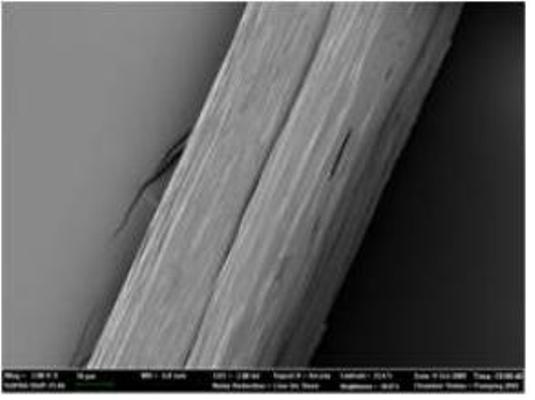 Native-like Spider Silk Produced in Metabolically Engineered Bacterium
Microscopic picture of 285 kilodalton recombinant spider silk fiber
Researchers have long envied spiders’ ability to manufacture silk that is light-weighted while as strong and tough as steel or Kevlar. Indeed, finer than human hair, five times stronger by weight than steel, and three times tougher than the top quality man-made fiber Kevlar, spider dragline silk is an ideal material for numerous applications. Suggested industrial applications have ranged from parachute cords and protective clothing to composite materials in aircrafts. Also, many biomedical applications are envisioned due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Unfortunately, natural dragline silk cannot be conveniently obtained by farming spiders because they are highly territorial and aggressive. To develop a more sustainable process, can scientists mass-produce artificial silk while maintaining the amazing properties of native silk? That is something Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, and his collaborators, Professor Young Hwan Park at Seoul National University and Professor David Kaplan at Tufts University, wanted to figure out. Their method is very similar to what spiders essentially do: first, expression of recombinant silk proteins; second, making the soluble silk proteins into water-insoluble fibers through spinning.
For the successful expression of high molecular weight spider silk protein, Professor Lee and his colleagues pieced together the silk gene from chemically synthesized oligonucleotides, and then inserted it into the expression host (in this case, an industrially safe bacterium Escherichia coli which is normally found in our gut). Initially, the bacterium refused to the challenging task of producing high molecular weight spider silk protein due to the unique characteristics of the protein, such as extremely large size, repetitive nature of the protein structure, and biased abundance of a particular amino acid glycine. “To make E. coli synthesize this ultra high molecular weight (as big as 285 kilodalton) spider silk protein having highly repetitive amino acid sequence, we helped E. coli overcome the difficulties by systems metabolic engineering,” says Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of KAIST, who led this project. His team boosted the pool of glycyl-tRNA, the major building block of spider silk protein synthesis. “We could obtain appreciable expression of the 285 kilodalton spider silk protein, which is the largest recombinant silk protein ever produced in E. coli. That was really incredible.” says Dr. Xia.
But this was only step one. The KAIST team performed high-cell-density cultures for mass production of the recombinant spider silk protein. Then, the team developed a simple, easy to scale-up purification process for the recombinant spider silk protein. The purified spider silk protein could be spun into beautiful silk fiber. To study the mechanical properties of the artificial spider silk, the researchers determined tenacity, elongation, and Young’s modulus, the three critical mechanical parameters that represent a fiber’s strength, extensibility, and stiffness. Importantly, the artificial fiber displayed the tenacity, elongation, and Young’s modulus of 508 MPa, 15%, and 21 GPa, respectively, which are comparable to those of the native spider silk.
“We have offered an overall platform for mass production of native-like spider dragline silk. This platform would enable us to have broader industrial and biomedical applications for spider silk. Moreover, many other silk-like biomaterials such as elastin, collagen, byssus, resilin, and other repetitive proteins have similar features to spider silk protein. Thus, our platform should also be useful for their efficient bio-based production and applications,” concludes Professor Lee.
This work is published on July 26 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online.
2010.07.28 View 19584
Native-like Spider Silk Produced in Metabolically Engineered Bacterium
Microscopic picture of 285 kilodalton recombinant spider silk fiber
Researchers have long envied spiders’ ability to manufacture silk that is light-weighted while as strong and tough as steel or Kevlar. Indeed, finer than human hair, five times stronger by weight than steel, and three times tougher than the top quality man-made fiber Kevlar, spider dragline silk is an ideal material for numerous applications. Suggested industrial applications have ranged from parachute cords and protective clothing to composite materials in aircrafts. Also, many biomedical applications are envisioned due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability.
Unfortunately, natural dragline silk cannot be conveniently obtained by farming spiders because they are highly territorial and aggressive. To develop a more sustainable process, can scientists mass-produce artificial silk while maintaining the amazing properties of native silk? That is something Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) in Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, and his collaborators, Professor Young Hwan Park at Seoul National University and Professor David Kaplan at Tufts University, wanted to figure out. Their method is very similar to what spiders essentially do: first, expression of recombinant silk proteins; second, making the soluble silk proteins into water-insoluble fibers through spinning.
For the successful expression of high molecular weight spider silk protein, Professor Lee and his colleagues pieced together the silk gene from chemically synthesized oligonucleotides, and then inserted it into the expression host (in this case, an industrially safe bacterium Escherichia coli which is normally found in our gut). Initially, the bacterium refused to the challenging task of producing high molecular weight spider silk protein due to the unique characteristics of the protein, such as extremely large size, repetitive nature of the protein structure, and biased abundance of a particular amino acid glycine. “To make E. coli synthesize this ultra high molecular weight (as big as 285 kilodalton) spider silk protein having highly repetitive amino acid sequence, we helped E. coli overcome the difficulties by systems metabolic engineering,” says Sang Yup Lee, Distinguished Professor of KAIST, who led this project. His team boosted the pool of glycyl-tRNA, the major building block of spider silk protein synthesis. “We could obtain appreciable expression of the 285 kilodalton spider silk protein, which is the largest recombinant silk protein ever produced in E. coli. That was really incredible.” says Dr. Xia.
But this was only step one. The KAIST team performed high-cell-density cultures for mass production of the recombinant spider silk protein. Then, the team developed a simple, easy to scale-up purification process for the recombinant spider silk protein. The purified spider silk protein could be spun into beautiful silk fiber. To study the mechanical properties of the artificial spider silk, the researchers determined tenacity, elongation, and Young’s modulus, the three critical mechanical parameters that represent a fiber’s strength, extensibility, and stiffness. Importantly, the artificial fiber displayed the tenacity, elongation, and Young’s modulus of 508 MPa, 15%, and 21 GPa, respectively, which are comparable to those of the native spider silk.
“We have offered an overall platform for mass production of native-like spider dragline silk. This platform would enable us to have broader industrial and biomedical applications for spider silk. Moreover, many other silk-like biomaterials such as elastin, collagen, byssus, resilin, and other repetitive proteins have similar features to spider silk protein. Thus, our platform should also be useful for their efficient bio-based production and applications,” concludes Professor Lee.
This work is published on July 26 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) online.
2010.07.28 View 19584 -
 Scaling Laws between Population and Facility Densities Found
A research team led by Prof. Ha-Woong Jeong of the Department of Physics, KAIST, has found a positive correlation between facilities and population densities, university authorities said on Tuesday (Sept. 2). The research was conducted in the cooperation with a research team of Prof. Beom-Jun Kim at Sungkyunkwan University.
The researchers investigated the ideal relation between the population and the facilities within the framework of an economic mechanism governing microdynamics.
In previous studies based on the global optimization of facility positions in minimizing the overall travel distance between people and facilities, the relation between population and facilities should follow a simple law. The new empirical analysis, however, determined that the law is not a fixed value but spreads in a broad range depending on facility types.
To explain this discrepancy, the researchers proposed a model based on economic mechanism that mimics the competitive balance between the profit of the facilities and the social opportunity cost for population.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States on Aug. 25.
2009.09.04 View 14354
Scaling Laws between Population and Facility Densities Found
A research team led by Prof. Ha-Woong Jeong of the Department of Physics, KAIST, has found a positive correlation between facilities and population densities, university authorities said on Tuesday (Sept. 2). The research was conducted in the cooperation with a research team of Prof. Beom-Jun Kim at Sungkyunkwan University.
The researchers investigated the ideal relation between the population and the facilities within the framework of an economic mechanism governing microdynamics.
In previous studies based on the global optimization of facility positions in minimizing the overall travel distance between people and facilities, the relation between population and facilities should follow a simple law. The new empirical analysis, however, determined that the law is not a fixed value but spreads in a broad range depending on facility types.
To explain this discrepancy, the researchers proposed a model based on economic mechanism that mimics the competitive balance between the profit of the facilities and the social opportunity cost for population.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States on Aug. 25.
2009.09.04 View 14354 -
 Maximum Yield Amino Acid-Producing Microorganism Developed with use of System Biotechnology
Maximum Yield Amino Acid-Producing Microorganism Developed with use of System Biotechnology
A team led by Sang-Yup Lee, a distinguished professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and chair professor of LG Chemical, has succeeded in developing maximum yield L-valine-producing microorganism by using System Biotechnology methods. The research results will be published at the April fourth week (April 23 - 27) edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) of the USA.
Prof. Lee’s team has developed maximum yield amino acid-producing microorganism (target substance of L-valine, an essential amino-acid) by using microorganism E cell system and simulation methods.
His team produced initial producing microorganism by selectively operating necessary parts in colon bacillus genome and excavated preliminary target gene which is to newly be operated through transcriptome analysis using DNA chips. Then they performed a great amount of gene deletion experiment on computer by using MBEL979, E-cells of colon bacillus, and excavated secondary engineering targets. And they finally succeeded in developing maximum yield valine-producing microorganism that can extract 37.8 grams of valine from 100 grams of glucose by applying experiment results to the actual development of microorganism so as to achieve the optimization of metabolic flux in cells,
Prof. Lee said, “Since successfully used for the development of microorganism on a systematic system level, system biotechnology methods are expected to significantly contribute to the development of all biotechnology-relevant industries. At the beginning, we had huge obstacles in fusing IT and BT, but my team mates cleverly overcame such obstacles, hence I’m very proud of them.” The producing microorganism and its developing methods are pending international applications (PCT).
2007.04.26 View 15825
Maximum Yield Amino Acid-Producing Microorganism Developed with use of System Biotechnology
Maximum Yield Amino Acid-Producing Microorganism Developed with use of System Biotechnology
A team led by Sang-Yup Lee, a distinguished professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and chair professor of LG Chemical, has succeeded in developing maximum yield L-valine-producing microorganism by using System Biotechnology methods. The research results will be published at the April fourth week (April 23 - 27) edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) of the USA.
Prof. Lee’s team has developed maximum yield amino acid-producing microorganism (target substance of L-valine, an essential amino-acid) by using microorganism E cell system and simulation methods.
His team produced initial producing microorganism by selectively operating necessary parts in colon bacillus genome and excavated preliminary target gene which is to newly be operated through transcriptome analysis using DNA chips. Then they performed a great amount of gene deletion experiment on computer by using MBEL979, E-cells of colon bacillus, and excavated secondary engineering targets. And they finally succeeded in developing maximum yield valine-producing microorganism that can extract 37.8 grams of valine from 100 grams of glucose by applying experiment results to the actual development of microorganism so as to achieve the optimization of metabolic flux in cells,
Prof. Lee said, “Since successfully used for the development of microorganism on a systematic system level, system biotechnology methods are expected to significantly contribute to the development of all biotechnology-relevant industries. At the beginning, we had huge obstacles in fusing IT and BT, but my team mates cleverly overcame such obstacles, hence I’m very proud of them.” The producing microorganism and its developing methods are pending international applications (PCT).
2007.04.26 View 15825 -
 Professor Seong-Ihl Woo Develops New High-Speed Research Method
Professor Seong-Ihl Woo Develops New High-Speed Research Method
Reduce research periods and expenses for thin film materials several ten times
Posted on the online version of Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on January 9
A team led by Seong-Ihl Woo, a professor of KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering and the director of the Center for Ultramicrochemical Process Systems, has developed a high-speed research method that can maximize research performances and posted the relevant contents on the online version of Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), a distinguished scientific journal, on January 9, 2007.
Professor Woo’s team has developed a high-speed research method that can fabricate several tens or several thousands of thin films with different compositions (mixing ratio) at the same time and carry out structural analysis and performance evaluation more than ten times faster and accurately, which leads to the shortening of the research processes of thin film materials. This is an epoch-making method that can reduce research periods and expenses several ten times or more, compared to the previous methods.
The qualities of final products of electronic materials, displays, and semi-conductors depend on the features of thin film materials. Averagely, it takes about two weeks or longer to fabricate a functional thin film and analyze and evaluate its performances. In order to fabricate thin film materials in need successfully, more than several thousand times of tests are required.
The existing thin film-fabricating equipment is expensive one demanding high-degree vacuum, such as chemical vapor deposition, sputtering, physical vapor deposition, laser evaporation, and so on. In order to fabricate thin films of various compositions with this equipment, a several million won-worth target (solid-state raw material) and precursors (volatile organic metal compound) pricing several hundreds won per gram are required. Therefore, huge amount of experiment expense is demanded for fabrication of several ten thousands of thin films with various compositions.
Professor Woo’s team has developed ‘combinatorial droplet chemical deposition’ equipment, which does not demand high-degree vacuum and is automated by computers and robots, by using a new high-speed research measure. The equipment is priced at about 1/5 of the existing equipment and easy for maintenance.
This equipment uses cheap reagents, instead of expensive raw materials. Reagents necessary to form required compositions are dissolved in water or proper solvents, and then applied by high frequencies to make several micrometer-scaled droplets (fine liquid droplet). Theses droplets are moved by nitrogen and dropped onto a substrate, which is to be fabricated into a thin film, and then subsequent thermal treatment is applied to the substrate to fabricate a thin film of required composition. At this moment, several tens or several hundreds of thin films with various compositions can be fabricated at the same time by reducing the size of thin film specimens into millimeter scale with the use of shade mask and adjusting vaporization time with masks, the moving speed of which can be adjusted. The expenses for materials necessary for the fabrication of thin films with this equipment amount to several ten thousands won per 100 grams, which is in the range of 1/100 and 1/10 of the previous methods, and the research period can be shortened into one of several tenth.
“If this new method is applied to the development of elements in the fields of core energy, material and health, which have not been discovered by the existing research methods so far, as well as researches in thin film material field, substantial effects will be brought,” said Professor Woo.
‘Combinatorial droplet chemical vaporization’ equipment is pending a domestic patent application and international patent applications at Japan and Germany. This equipment will be produced by order and provided to general researchers.
2007.02.02 View 18305
Professor Seong-Ihl Woo Develops New High-Speed Research Method
Professor Seong-Ihl Woo Develops New High-Speed Research Method
Reduce research periods and expenses for thin film materials several ten times
Posted on the online version of Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on January 9
A team led by Seong-Ihl Woo, a professor of KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering and the director of the Center for Ultramicrochemical Process Systems, has developed a high-speed research method that can maximize research performances and posted the relevant contents on the online version of Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS), a distinguished scientific journal, on January 9, 2007.
Professor Woo’s team has developed a high-speed research method that can fabricate several tens or several thousands of thin films with different compositions (mixing ratio) at the same time and carry out structural analysis and performance evaluation more than ten times faster and accurately, which leads to the shortening of the research processes of thin film materials. This is an epoch-making method that can reduce research periods and expenses several ten times or more, compared to the previous methods.
The qualities of final products of electronic materials, displays, and semi-conductors depend on the features of thin film materials. Averagely, it takes about two weeks or longer to fabricate a functional thin film and analyze and evaluate its performances. In order to fabricate thin film materials in need successfully, more than several thousand times of tests are required.
The existing thin film-fabricating equipment is expensive one demanding high-degree vacuum, such as chemical vapor deposition, sputtering, physical vapor deposition, laser evaporation, and so on. In order to fabricate thin films of various compositions with this equipment, a several million won-worth target (solid-state raw material) and precursors (volatile organic metal compound) pricing several hundreds won per gram are required. Therefore, huge amount of experiment expense is demanded for fabrication of several ten thousands of thin films with various compositions.
Professor Woo’s team has developed ‘combinatorial droplet chemical deposition’ equipment, which does not demand high-degree vacuum and is automated by computers and robots, by using a new high-speed research measure. The equipment is priced at about 1/5 of the existing equipment and easy for maintenance.
This equipment uses cheap reagents, instead of expensive raw materials. Reagents necessary to form required compositions are dissolved in water or proper solvents, and then applied by high frequencies to make several micrometer-scaled droplets (fine liquid droplet). Theses droplets are moved by nitrogen and dropped onto a substrate, which is to be fabricated into a thin film, and then subsequent thermal treatment is applied to the substrate to fabricate a thin film of required composition. At this moment, several tens or several hundreds of thin films with various compositions can be fabricated at the same time by reducing the size of thin film specimens into millimeter scale with the use of shade mask and adjusting vaporization time with masks, the moving speed of which can be adjusted. The expenses for materials necessary for the fabrication of thin films with this equipment amount to several ten thousands won per 100 grams, which is in the range of 1/100 and 1/10 of the previous methods, and the research period can be shortened into one of several tenth.
“If this new method is applied to the development of elements in the fields of core energy, material and health, which have not been discovered by the existing research methods so far, as well as researches in thin film material field, substantial effects will be brought,” said Professor Woo.
‘Combinatorial droplet chemical vaporization’ equipment is pending a domestic patent application and international patent applications at Japan and Germany. This equipment will be produced by order and provided to general researchers.
2007.02.02 View 18305