ANS
-
 A KAIST research team develops a washable, transparent, and flexible OLED with MXene nanotechnology
Transparent and flexible displays, which have received a lot of attention in various fields including automobile displays, bio-healthcare, military, and fashion, are in fact known to break easily when experiencing small deformations. To solve this problem, active research is being conducted on many transparent and flexible conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, silver nanowires, and conductive polymers.
On June 13, a joint research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Dr. Yonghee Lee from the National Nano Fab Center (NNFC) announced the successful development of a water-resistant, transparent, and flexible OLED using MXene nanotechnology. The material can emit and transmit light even when exposed to water.
MXene is a 2D material with high electrical conductivity and optical transmittance, and it can be produced on a large scale through solution processes. However, despite these attractive properties, MXene’s applications were limited as a long-term electrical device due to its electrical properties being degraded easily by atmospheric moisture and water. The material was therefore unable to be systemized into the form of a matrix that can display information.
Professor Choi’s research team used an encapsulation tactic that can protect materials from oxidation caused by moisture and oxygen to develop a MXene-based OLED with a long lifespan and high stability against external environmental factors. The research team first focused on analyzing the degradation mechanism of MXene’s electrical conductivity, and then concentrated on designing an encapsulation membrane. The team blocked moisture and provided flexibility through residual stress offset, ultimately producing a double-layered encapsulation membrane. In addition, a thin plastic film with a thickness of a few micrometers was attached to the top layer to allow washing in water without degradation.
< Figure 1. (a) Transparent passive-matrix display made of MXene-based OLED, (b) Cross-sectional image of MXene-based OLED observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM), (c) Electro-optical characteristic graph of red, green, and blue MXene-based OLED >
Through this study, the research team developed a MXene-based red(R)/green(G)/blue(B) OLED that emits a brightness of over 1,000 cd/m2 that is detectable by the naked eye even under sunlight, thereby meeting the conditions for outdoor displays. As for the red MXene-based OLED, the researchers confirmed a standby storage life of 2,000 hours (under 70% luminescence), a standby operation life of 1,500 hours (under 60% luminescence), and a flexibility withstanding 1,000 cycles under a low curvature of under 1.5mm. In addition, they showed that its performance was maintained even after six hours of immersion under water (under 80% luminescence). Furthermore, a patterning technique was used to produce the MXene-based OLED in the form of a passive matrix, and the team demonstrated its use as a transparent display by displaying letters and shapes.
Ph.D. candidate So Yeong Jeong, who led this study, said, “To improve the reliability of MXene OLED, we focused on producing an adequate encapsulation structure and a suitable process design.” She added, “By producing a matrix-type MXene OLED and displaying simple letters and shapes, we have laid the foundations for MXene’s application in the field of transparent displays.”
< Image 1. Cover of ACS Nano Front Cover (Conceptual diagram of MXene-based OLED display) >
Professor Choi said, “This research will become the guideline for applying MXene in electrical devices, but we expect for it to also be applied in other fields that require flexible and transparent displays like automobiles, fashion, and functional clothing. And to widen the gap with China’s OLED technology, these new OLED convergence technologies must continue to be developed.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea. It was published as a front cover story of ACS Nano under the title, “Highly Air-Stable, Flexible, and Water-Resistive 2D Titanium Carbide MXene-Based RGB Organic Light-Emitting Diode Displays for Transparent Free-Form Electronics” on June 13.
2023.07.10 View 7776
A KAIST research team develops a washable, transparent, and flexible OLED with MXene nanotechnology
Transparent and flexible displays, which have received a lot of attention in various fields including automobile displays, bio-healthcare, military, and fashion, are in fact known to break easily when experiencing small deformations. To solve this problem, active research is being conducted on many transparent and flexible conductive materials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, silver nanowires, and conductive polymers.
On June 13, a joint research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering and Dr. Yonghee Lee from the National Nano Fab Center (NNFC) announced the successful development of a water-resistant, transparent, and flexible OLED using MXene nanotechnology. The material can emit and transmit light even when exposed to water.
MXene is a 2D material with high electrical conductivity and optical transmittance, and it can be produced on a large scale through solution processes. However, despite these attractive properties, MXene’s applications were limited as a long-term electrical device due to its electrical properties being degraded easily by atmospheric moisture and water. The material was therefore unable to be systemized into the form of a matrix that can display information.
Professor Choi’s research team used an encapsulation tactic that can protect materials from oxidation caused by moisture and oxygen to develop a MXene-based OLED with a long lifespan and high stability against external environmental factors. The research team first focused on analyzing the degradation mechanism of MXene’s electrical conductivity, and then concentrated on designing an encapsulation membrane. The team blocked moisture and provided flexibility through residual stress offset, ultimately producing a double-layered encapsulation membrane. In addition, a thin plastic film with a thickness of a few micrometers was attached to the top layer to allow washing in water without degradation.
< Figure 1. (a) Transparent passive-matrix display made of MXene-based OLED, (b) Cross-sectional image of MXene-based OLED observed by transmission electron microscope (TEM), (c) Electro-optical characteristic graph of red, green, and blue MXene-based OLED >
Through this study, the research team developed a MXene-based red(R)/green(G)/blue(B) OLED that emits a brightness of over 1,000 cd/m2 that is detectable by the naked eye even under sunlight, thereby meeting the conditions for outdoor displays. As for the red MXene-based OLED, the researchers confirmed a standby storage life of 2,000 hours (under 70% luminescence), a standby operation life of 1,500 hours (under 60% luminescence), and a flexibility withstanding 1,000 cycles under a low curvature of under 1.5mm. In addition, they showed that its performance was maintained even after six hours of immersion under water (under 80% luminescence). Furthermore, a patterning technique was used to produce the MXene-based OLED in the form of a passive matrix, and the team demonstrated its use as a transparent display by displaying letters and shapes.
Ph.D. candidate So Yeong Jeong, who led this study, said, “To improve the reliability of MXene OLED, we focused on producing an adequate encapsulation structure and a suitable process design.” She added, “By producing a matrix-type MXene OLED and displaying simple letters and shapes, we have laid the foundations for MXene’s application in the field of transparent displays.”
< Image 1. Cover of ACS Nano Front Cover (Conceptual diagram of MXene-based OLED display) >
Professor Choi said, “This research will become the guideline for applying MXene in electrical devices, but we expect for it to also be applied in other fields that require flexible and transparent displays like automobiles, fashion, and functional clothing. And to widen the gap with China’s OLED technology, these new OLED convergence technologies must continue to be developed.”
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea. It was published as a front cover story of ACS Nano under the title, “Highly Air-Stable, Flexible, and Water-Resistive 2D Titanium Carbide MXene-Based RGB Organic Light-Emitting Diode Displays for Transparent Free-Form Electronics” on June 13.
2023.07.10 View 7776 -
 A KAIST research team unveils new path for dense photonic integration
Integrated optical semiconductor (hereinafter referred to as optical semiconductor) technology is a next-generation semiconductor technology for which many researches and investments are being made worldwide because it can make complex optical systems such as LiDAR and quantum sensors and computers into a single small chip. In the existing semiconductor technology, the key was how small it was to make it in units of 5 nanometers or 2 nanometers, but increasing the degree of integration in optical semiconductor devices can be said to be a key technology that determines performance, price, and energy efficiency.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th that a research team led by Professor Sangsik Kim of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering discovered a new optical coupling mechanism that can increase the degree of integration of optical semiconductor devices by more than 100 times.
The degree of the number of elements that can be configured per chip is called the degree of integration. However, it is very difficult to increase the degree of integration of optical semiconductor devices, because crosstalk occurs between photons between adjacent devices due to the wave nature of light.
In previous studies, it was possible to reduce crosstalk of light only in specific polarizations, but in this study, the research team developed a method to increase the degree of integration even under polarization conditions, which were previously considered impossible, by discovering a new light coupling mechanism.
This study, led by Professor Sangsik Kim as a corresponding author and conducted with students he taught at Texas Tech University, was published in the international journal 'Light: Science & Applications' [IF=20.257] on June 2nd. done. (Paper title: Anisotropic leaky-like perturbation with subwavelength gratings enables zero crosstalk).
Professor Sangsik Kim said, "The interesting thing about this study is that it paradoxically eliminated the confusion through leaky waves (light tends to spread sideways), which was previously thought to increase the crosstalk." He went on to add, “If the optical coupling method using the leaky wave revealed in this study is applied, it will be possible to develop various optical semiconductor devices that are smaller and that has less noise.”
Professor Sangsik Kim is a researcher recognized for his expertise and research in optical semiconductor integration. Through his previous research, he developed an all-dielectric metamaterial that can control the degree of light spreading laterally by patterning a semiconductor structure at a size smaller than the wavelength, and proved this through experiments to improve the degree of integration of optical semiconductors. These studies were reported in ‘Nature Communications’ (Vol. 9, Article 1893, 2018) and ‘Optica’ (Vol. 7, pp. 881-887, 2020). In recognition of these achievements, Professor Kim has received the NSF Career Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Young Scientist Award from the Association of Korean-American Scientists and Engineers.
Meanwhile, this research was carried out with the support from the New Research Project of Excellence of the National Research Foundation of Korea and and the National Science Foundation of the US.
< Figure 1. Illustration depicting light propagation without crosstalk in the waveguide array of the developed metamaterial-based optical semiconductor >
2023.06.21 View 8397
A KAIST research team unveils new path for dense photonic integration
Integrated optical semiconductor (hereinafter referred to as optical semiconductor) technology is a next-generation semiconductor technology for which many researches and investments are being made worldwide because it can make complex optical systems such as LiDAR and quantum sensors and computers into a single small chip. In the existing semiconductor technology, the key was how small it was to make it in units of 5 nanometers or 2 nanometers, but increasing the degree of integration in optical semiconductor devices can be said to be a key technology that determines performance, price, and energy efficiency.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th that a research team led by Professor Sangsik Kim of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering discovered a new optical coupling mechanism that can increase the degree of integration of optical semiconductor devices by more than 100 times.
The degree of the number of elements that can be configured per chip is called the degree of integration. However, it is very difficult to increase the degree of integration of optical semiconductor devices, because crosstalk occurs between photons between adjacent devices due to the wave nature of light.
In previous studies, it was possible to reduce crosstalk of light only in specific polarizations, but in this study, the research team developed a method to increase the degree of integration even under polarization conditions, which were previously considered impossible, by discovering a new light coupling mechanism.
This study, led by Professor Sangsik Kim as a corresponding author and conducted with students he taught at Texas Tech University, was published in the international journal 'Light: Science & Applications' [IF=20.257] on June 2nd. done. (Paper title: Anisotropic leaky-like perturbation with subwavelength gratings enables zero crosstalk).
Professor Sangsik Kim said, "The interesting thing about this study is that it paradoxically eliminated the confusion through leaky waves (light tends to spread sideways), which was previously thought to increase the crosstalk." He went on to add, “If the optical coupling method using the leaky wave revealed in this study is applied, it will be possible to develop various optical semiconductor devices that are smaller and that has less noise.”
Professor Sangsik Kim is a researcher recognized for his expertise and research in optical semiconductor integration. Through his previous research, he developed an all-dielectric metamaterial that can control the degree of light spreading laterally by patterning a semiconductor structure at a size smaller than the wavelength, and proved this through experiments to improve the degree of integration of optical semiconductors. These studies were reported in ‘Nature Communications’ (Vol. 9, Article 1893, 2018) and ‘Optica’ (Vol. 7, pp. 881-887, 2020). In recognition of these achievements, Professor Kim has received the NSF Career Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) and the Young Scientist Award from the Association of Korean-American Scientists and Engineers.
Meanwhile, this research was carried out with the support from the New Research Project of Excellence of the National Research Foundation of Korea and and the National Science Foundation of the US.
< Figure 1. Illustration depicting light propagation without crosstalk in the waveguide array of the developed metamaterial-based optical semiconductor >
2023.06.21 View 8397 -
 'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 9440
'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 9440 -
 Using light to throw and catch atoms to open up a new chapter for quantum computing
The technology to move and arrange atoms, the most basic component of a quantum computer, is very important to Rydberg quantum computing research. However, to place the atoms at the desired location, the atoms must be captured and transported one by one using a highly focused laser beam, commonly referred to as an optical tweezer. and, the quantum information of the atoms is likely to change midway.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th that a research team led by Professor Jaewook Ahn of the Department of Physics developed a technology to throw and receive rubidium atoms one by one using a laser beam.
The research team developed a method to throw and receive atoms which would minimize the time the optical tweezers are in contact with the atoms in which the quantum information the atoms carry may change. The research team used the characteristic that the rubidium atoms, which are kept at a very low temperature of 40μK below absolute zero, move very sensitively to the electromagnetic force applied by light along the focal point of the light tweezers.
The research team accelerated the laser of an optical tweezer to give an optical kick to an atom to send it to a target, then caught the flying atom with another optical tweezer to stop it. The atom flew at a speed of 65 cm/s, and traveled up to 4.2 μm. Compared to the existing technique of guiding the atoms with the optical tweezers, the technique of throwing and receiving atoms eliminates the need to calculate the transporting path for the tweezers, and makes it easier to fix the defects in the atomic arrangement. As a result, it is effective in generating and maintaining a large number of atomic arrangements, and when the technology is used to throw and receive flying atom qubits, it will be used in studying new and more powerful quantum computing methods that presupposes the structural changes in quantum arrangements.
"This technology will be used to develop larger and more powerful Rydberg quantum computers," says Professor Jaewook Ahn. “In a Rydberg quantum computer,” he continues, “atoms are arranged to store quantum information and interact with neighboring atoms through electromagnetic forces to perform quantum computing. The method of throwing an atom away for quick reconstruction the quantum array can be an effective way to fix an error in a quantum computer that requires a removal or replacement of an atom.”
The research, which was conducted by doctoral students Hansub Hwang and Andrew Byun of the Department of Physics at KAIST and Sylvain de Léséleuc, a researcher at the National Institute of Natural Sciences in Japan, was published in the international journal, Optica, 0n March 9th. (Paper title: Optical tweezers throw and catch single atoms).
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
<Figure 1> A schematic diagram of the atom catching and throwing technique. The optical tweezer on the left kicks the atom to throw it into a trajectory to have the tweezer on the right catch it to stop it.
2023.03.28 View 7892
Using light to throw and catch atoms to open up a new chapter for quantum computing
The technology to move and arrange atoms, the most basic component of a quantum computer, is very important to Rydberg quantum computing research. However, to place the atoms at the desired location, the atoms must be captured and transported one by one using a highly focused laser beam, commonly referred to as an optical tweezer. and, the quantum information of the atoms is likely to change midway.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th that a research team led by Professor Jaewook Ahn of the Department of Physics developed a technology to throw and receive rubidium atoms one by one using a laser beam.
The research team developed a method to throw and receive atoms which would minimize the time the optical tweezers are in contact with the atoms in which the quantum information the atoms carry may change. The research team used the characteristic that the rubidium atoms, which are kept at a very low temperature of 40μK below absolute zero, move very sensitively to the electromagnetic force applied by light along the focal point of the light tweezers.
The research team accelerated the laser of an optical tweezer to give an optical kick to an atom to send it to a target, then caught the flying atom with another optical tweezer to stop it. The atom flew at a speed of 65 cm/s, and traveled up to 4.2 μm. Compared to the existing technique of guiding the atoms with the optical tweezers, the technique of throwing and receiving atoms eliminates the need to calculate the transporting path for the tweezers, and makes it easier to fix the defects in the atomic arrangement. As a result, it is effective in generating and maintaining a large number of atomic arrangements, and when the technology is used to throw and receive flying atom qubits, it will be used in studying new and more powerful quantum computing methods that presupposes the structural changes in quantum arrangements.
"This technology will be used to develop larger and more powerful Rydberg quantum computers," says Professor Jaewook Ahn. “In a Rydberg quantum computer,” he continues, “atoms are arranged to store quantum information and interact with neighboring atoms through electromagnetic forces to perform quantum computing. The method of throwing an atom away for quick reconstruction the quantum array can be an effective way to fix an error in a quantum computer that requires a removal or replacement of an atom.”
The research, which was conducted by doctoral students Hansub Hwang and Andrew Byun of the Department of Physics at KAIST and Sylvain de Léséleuc, a researcher at the National Institute of Natural Sciences in Japan, was published in the international journal, Optica, 0n March 9th. (Paper title: Optical tweezers throw and catch single atoms).
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
<Figure 1> A schematic diagram of the atom catching and throwing technique. The optical tweezer on the left kicks the atom to throw it into a trajectory to have the tweezer on the right catch it to stop it.
2023.03.28 View 7892 -
 KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 11514
KAIST team develops smart immune system that can pin down on malignant tumors
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kyoon Choi of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Professor Jong-Eun Park of the KAIST Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering (GSMSE) announced the development of the key technologies to treat cancers using smart immune cells designed based on AI and big data analysis. This technology is expected to be a next-generation immunotherapy that allows precision targeting of tumor cells by having the chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) operate through a logical circuit. Professor Hee Jung An of CHA Bundang Medical Center and Professor Hae-Ock Lee of the Catholic University of Korea also participated in this research to contribute joint effort.
Professor Jung Kyoon Choi’s team built a gene expression database from millions of cells, and used this to successfully develop and verify a deep-learning algorithm that could detect the differences in gene expression patterns between tumor cells and normal cells through a logical circuit. CAR immune cells that were fitted with the logic circuits discovered through this methodology could distinguish between tumorous and normal cells as a computer would, and therefore showed potentials to strike only on tumor cells accurately without causing unwanted side effects.
This research, conducted by co-first authors Dr. Joonha Kwon of the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering and Ph.D. candidate Junho Kang of KAIST GSMSE, was published by Nature Biotechnology on February 16, under the title Single-cell mapping of combinatorial target antigens for CAR switches using logic gates.
An area in cancer research where the most attempts and advances have been made in recent years is immunotherapy. This field of treatment, which utilizes the patient’s own immune system in order to overcome cancer, has several methods including immune checkpoint inhibitors, cancer vaccines and cellular treatments. Immune cells like CAR-T or CAR-NK equipped with chimera antigen receptors, in particular, can recognize cancer antigens and directly destroy cancer cells.
Starting with its success in blood cancer treatment, scientists have been trying to expand the application of CAR cell therapy to treat solid cancer. But there have been difficulties to develop CAR cells with effective killing abilities against solid cancer cells with minimized side effects. Accordingly, in recent years, the development of smarter CAR engineering technologies, i.e., computational logic gates such as AND, OR, and NOT, to effectively target cancer cells has been underway.
At this point in time, the research team built a large-scale database for cancer and normal cells to discover the exact genes that are expressed only from cancer cells at a single-cell level. The team followed this up by developing an AI algorithm that could search for a combination of genes that best distinguishes cancer cells from normal cells. This algorithm, in particular, has been used to find a logic circuit that can specifically target cancer cells through cell-level simulations of all gene combinations. CAR-T cells equipped with logic circuits discovered through this methodology are expected to distinguish cancerous cells from normal cells like computers, thereby minimizing side effects and maximizing the effects of chemotherapy.
Dr. Joonha Kwon, who is the first author of this paper, said, “this research suggests a new method that hasn’t been tried before. What’s particularly noteworthy is the process in which we found the optimal CAR cell circuit through simulations of millions of individual tumors and normal cells.” He added, “This is an innovative technology that can apply AI and computer logic circuits to immune cell engineering. It would contribute greatly to expanding CAR therapy, which is being successfully used for blood cancer, to solid cancers as well.”
This research was funded by the Original Technology Development Project and Research Program for Next Generation Applied Omic of the Korea Research Foundation.
Figure 1. A schematic diagram of manufacturing and administration process of CAR therapy and of cancer cell-specific dual targeting using CAR.
Figure 2. Deep learning (convolutional neural networks, CNNs) algorithm for selection of dual targets based on gene combination (left) and algorithm for calculating expressing cell fractions by gene combination according to logical circuit (right).
2023.03.09 View 11514 -
 KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 19155
KAIST presents a fundamental technology to remove metastatic traits from lung cancer cells
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on January 30th that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in using systems biology research to change the properties of carcinogenic cells in the lungs and eliminate both drug resistance and their ability to proliferate out to other areas of the body.
As the incidences of cancer increase within aging populations, cancer has become the most lethal disease threatening healthy life. Fatality rates are especially high when early detection does not happen in time and metastasis has occurred in various organs. In order to resolve this problem, a series of attempts were made to remove or lower the ability of cancer cells to spread, but they resulted in cancer cells in the intermediate state becoming more unstable and even more malignant, which created serious treatment challenges.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team simulated various cancer cell states in the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) of lung cancer cells, between epithelial cells without metastatic ability and mesenchymal cells with metastatic ability. A mathematical model of molecular network was established, and key regulators that could reverse the state of invasive and drug resistant mesenchymal cells back to the epithelial state were discovered through computer simulation analysis and molecular cell experiments. In particular, this process succeeded in properly reverting the mesenchymal lung cancer cells to a state where they were sensitive to chemotherapy treatment while avoiding the unstable EMT hybrid cell state in the middle process, which had remained a difficult problem.
The results of this research, in which KAIST Ph.D. student Namhee Kim, Dr. Chae Young Hwang, Researcher Taeyoung Kim, and Ph.D. student Hyunjin Kim participated, were published as an online paper in the international journal “Cancer Research” published by the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) on January 30th. (Paper title: A cell fate reprogramming strategy reverses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of lung cancer cells while avoiding hybrid states)
Cells in an EMT hybrid state, which are caused by incomplete transitions during the EMT process in cancer cells, have the characteristics of both epithelial cells and mesenchymal cells, and are known to have high drug resistance and metastatic potential by acquiring high stem cell capacity. In particular, EMT is further enhanced through factors such as transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β) secreted from the tumor microenvironment (TME) and, as a result, various cell states with high plasticity appear. Due to the complexity of EMT, it has been very difficult to completely reverse the transitional process of the mesenchymal cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are eliminated while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state with high metastatic ability and drug resistance.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a mathematical model of the gene regulation network that governs the complex process of EMT, and then applied large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology to identify and verify 'p53', 'SMAD4', and 'ERK1' and 'ERK 2' (collectively ERKs) through molecular cell experiments as the three key molecular targets that can transform lung cancer cells in the mesenchymal cell state, reversed back to an epithelial cell state that no longer demonstrates the ability to metastasize, while avoiding the EMT hybrid cell state.
In particular, by analyzing the molecular regulatory mechanism of the complex EMT process at the system level, the key pathways were identified that were linked to the positive feedback that plays an important role in completely returning cancer cells to an epithelial cell state in which metastatic ability and drug resistance are removed.
This discovery is significant in that it proved that mesenchymal cells can be reverted to the state of epithelial cells under conditions where TGF-β stimulation are present, like they are in the actual environment where cancer tissue forms in the human body.
Abnormal EMT in cancer cells leads to various malignant traits such as the migration and invasion of cancer cells, changes in responsiveness to chemotherapy treatment, enhanced stem cell function, and the dissemination of cancer. In particular, the acquisition of the metastatic ability of cancer cells is a key determinant factor for the prognosis of cancer patients. The EMT reversal technology in lung cancer cells developed in this research is a new anti-cancer treatment strategy that reprograms cancer cells to eliminate their high plasticity and metastatic potential and increase their responsiveness to chemotherapy.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "By succeeding in reversing the state of lung cancer cells that acquired high metastatic traits and resistance to drugs and reverting them to a treatable epithelial cell state with renewed sensitivity to chemotherapy, the research findings propose a new strategy for treatments that can improve the prognosis of cancer patients.”
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team was the first to present the principle of reversal treatment to revert cancer cells to normal cells, following through with the announcement of the results of their study that reverted colon cancer cells to normal colon cells in January of 2020, and also presenting successful re-programming research where the most malignant basal type breast cancer cells turned into less-malignant luminal type breast cancer cells that were treatable with hormonal therapies in January of 2022. This latest research result is the third in the development of reversal technology where lung cancer cells that had acquired metastatic traits returned to a state in which their metastatic ability was removed and drug sensitivity was enhanced.
This research was carried out with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea's Basic Research in Science & Engineering Program for Mid-Career Researchers.
< Figure 1. Construction of the mathematical model of the regulatory network to represent the EMT phenotype based on the interaction between various molecules related to EMT.
(A) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team investigated numerous literatures and databases related to complex EMT, and based on comparative analysis of cell line data showing epithelial and mesenchymal cell conditions, they extracted key signaling pathways related to EMT and built a mathematical model of regulatory network (B) By comparing the results of computer simulation analysis and the molecular cell experiments, it was verified how well the constructed mathematical model simulated the actual cellular phenomena. >
< Figure 2. Understanding of various EMT phenotypes through large-scale computer simulation analysis and complex system network control technology.
(A) Through computer simulation analysis and experiments, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team found that complete control of EMT is impossible with single-molecule control alone. In particular, through comparison of the relative stability of attractors, it was revealed that the cell state exhibiting EMT hybrid characteristics has unstable properties. (B), (C) Based on these results, Prof. Cho’s team identified two feedbacks (positive feedback consisting of Snail-miR-34 and ZEB1-miR-200) that play an important role in avoiding the EMT hybrid state that appeared in the TGF-β-ON state. It was found through computer simulation analysis that the two feedbacks restore relatively high stability when the excavated p53 and SMAD4 are regulated. In addition, molecular cell experiments demonstrated that the expression levels of E-cad and ZEB1, which are representative phenotypic markers of EMT, changed similarly to the expression profile in the epithelial cell state, despite the TGF-β-ON state. >
< Figure 3. Complex molecular network analysis and discovery of reprogramming molecular targets for intact elimination of EMT hybrid features.
(A) Controlling the expression of p53 and SMAD4 in lung cancer cell lines was expected to overcome drug resistance, but contrary to expectations, chemotherapy responsiveness was not restored. (B) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team additionally analyzed computer simulations, genome data, and experimental results and found that high expression levels of TWIST1 and EPCAM were related to drug resistance. (C) Prof. Cho’s team identified three key molecular targets: p53, SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2. (D), (E) Furthermore, they identified a key pathway that plays an important role in completely reversing into epithelial cells while avoiding EMT hybrid characteristics, and confirmed through network analysis and attractor analysis that high stability of the key pathway was restored when the proposed molecular target was controlled. >
< Figure 4. Verification through experiments with lung cancer cell lines.
When p53 was activated and SMAD4 and ERK1/2 were inhibited in lung cancer cell lines, (A), (B) E-cad protein expression increased and ZEB1 protein expression decreased, and (C) mesenchymal cell status including TWIST1 and EPCAM and gene expression of markers related to stem cell potential characteristics were completely inhibited. In addition, (D) it was confirmed that resistance to chemotherapy treatment was also overcome as the cell state was reversed by the regulated target. >
< Figure 5. A schematic representation of the research results.
Prof. Cho’s research team identified key molecular regulatory pathways to avoid high plasticity formed by abnormal EMT of cancer cells and reverse it to an epithelial cell state through systems biology research. From this analysis, a reprogramming molecular target that can reverse the state of mesenchymal cells with acquired invasiveness and drug resistance to the state of epithelial cells with restored drug responsiveness was discovered.
For lung cancer cells, when a drug that enhances the expression of p53, one of the molecular targets discovered, and inhibits the expression of SMAD4 and ERK1 & ERK2 is administered, the molecular network of genes in the state of mesenchymal cells is modified, eventually eliminating metastatic ability and it is reprogrammed to turn into epithelial cells without the resistance to chemotherapy treatments. >
2023.01.30 View 19155 -
 KAIST Offers Hope to Musicians with Dystonia
< Photo 1. Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins before the Recital at the Carnegie Hall preparing with his bionic gloves >
KAIST’s neuroscientist and professor, Dr. Daesoo Kim attended the “Conference for Musicians with Dystonia” supported by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Carnegie Hall concert of legendary pianist João Carlos Martins, who is also a dystonia patient, to announce his team’s recent advancements toward finding a cure for dystonia.
On November 19, 2022, a “miracle concert” was held in Carnegie Hall. João Carlos Martins was a renowned world-class pianist in the 70s and 80s, but he had to put an end to his musical career due to focal dystonia in his fingers. But in 2020, he began using a bionic glove developed by industrial designer Ubiratã Bizarro Costa and after years of hard work he was back in Carnegie Hall as an 82-year-old man.
During the concert, he conducted the NOVUS NY orchestra in a performance of Bach, and later even played the piano himself. In particular, between his performances, he gave shout-outs to scientists studying dystonia including KAIST Professor Daesoo Kim, asking them to continue working towards curing rare diseases for musicians.
< Photo 2. Professor Daesoo Kim with Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins >
Musician’s dystonia affects 1-3% of musicians around the world and musicians make up approximately 5% of the total number of dystonia patients. Musicians who are no longer able to practice music due to the disease often experience stress and depression, which may even lead to suicide in extreme cases. Musicians are known to be particularly prone to such diseases due to excessive practice regimens, perfectionism, and even genetics. Currently, botulinum toxin (Botox) is used to suppress abnormal muscles, but muscle function suppression ultimately means that the musician is no longer able to play the instrument. João Carlos Martins himself underwent several Botox procedures and three brain surgeries, but saw no therapeutic results. This is why a new treatment was necessary.
Professor Daesoo Kim’s research team at KAIST took note of the fact that abnormal muscle tension is caused by excessive stress, and developed NT-1, a treatment that blocks the development of the symptoms of dystonia from the brain, allowing patients to use their muscles as they normally would. The research team published their findings in Science Advances in 2021, and João Carlos Martins invited Professor Daesoo Kim to the UN conference and his concert after reading this paper.
< Photo 3. Professor Daesoo Kim (3rd from the left) photographed with other guests at the recital including Dr. Dévora Kestel, the Director of the Mental Health and Substance Use at WHO, sharing the center with Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins >
During the UN conference held the day prior to the Carnegie Hall concert, Dr. Dévora Kestel, Director of the Mental Health and Substance Use at WHO, said, “Although dystonia is not as well-known, it is a common disease around the world, and needs our society’s attention and the devotion of many researchers.” Professor Daesoo Kim said, “NT-1 is a drug that blocks the cause of dystonia in the brain, and will allow musicians to continue practicing music. We aim to attain clinical approval in Korea by 2024.”
NT-1 is currently under development by NeuroTobe, a faculty-led start-up company at KAIST, headed by Professor Daesoo Kim as the CEO. The synthesis of the drug for clinical testing has been successfully completed, and it has shown excellent efficacy and safety through various rounds of animal testing. Unlike Botox, which takes a few days to show its therapeutic effects after receiving the procedure from a hospital, NT-1 shows its therapeutic effects within an hour after taking it. As a so-called “edible Botox”, it is expected to help treat various muscular diseases and ailments.
2022.12.27 View 12368
KAIST Offers Hope to Musicians with Dystonia
< Photo 1. Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins before the Recital at the Carnegie Hall preparing with his bionic gloves >
KAIST’s neuroscientist and professor, Dr. Daesoo Kim attended the “Conference for Musicians with Dystonia” supported by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Carnegie Hall concert of legendary pianist João Carlos Martins, who is also a dystonia patient, to announce his team’s recent advancements toward finding a cure for dystonia.
On November 19, 2022, a “miracle concert” was held in Carnegie Hall. João Carlos Martins was a renowned world-class pianist in the 70s and 80s, but he had to put an end to his musical career due to focal dystonia in his fingers. But in 2020, he began using a bionic glove developed by industrial designer Ubiratã Bizarro Costa and after years of hard work he was back in Carnegie Hall as an 82-year-old man.
During the concert, he conducted the NOVUS NY orchestra in a performance of Bach, and later even played the piano himself. In particular, between his performances, he gave shout-outs to scientists studying dystonia including KAIST Professor Daesoo Kim, asking them to continue working towards curing rare diseases for musicians.
< Photo 2. Professor Daesoo Kim with Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins >
Musician’s dystonia affects 1-3% of musicians around the world and musicians make up approximately 5% of the total number of dystonia patients. Musicians who are no longer able to practice music due to the disease often experience stress and depression, which may even lead to suicide in extreme cases. Musicians are known to be particularly prone to such diseases due to excessive practice regimens, perfectionism, and even genetics. Currently, botulinum toxin (Botox) is used to suppress abnormal muscles, but muscle function suppression ultimately means that the musician is no longer able to play the instrument. João Carlos Martins himself underwent several Botox procedures and three brain surgeries, but saw no therapeutic results. This is why a new treatment was necessary.
Professor Daesoo Kim’s research team at KAIST took note of the fact that abnormal muscle tension is caused by excessive stress, and developed NT-1, a treatment that blocks the development of the symptoms of dystonia from the brain, allowing patients to use their muscles as they normally would. The research team published their findings in Science Advances in 2021, and João Carlos Martins invited Professor Daesoo Kim to the UN conference and his concert after reading this paper.
< Photo 3. Professor Daesoo Kim (3rd from the left) photographed with other guests at the recital including Dr. Dévora Kestel, the Director of the Mental Health and Substance Use at WHO, sharing the center with Conductor and Pianist João Carlos Martins >
During the UN conference held the day prior to the Carnegie Hall concert, Dr. Dévora Kestel, Director of the Mental Health and Substance Use at WHO, said, “Although dystonia is not as well-known, it is a common disease around the world, and needs our society’s attention and the devotion of many researchers.” Professor Daesoo Kim said, “NT-1 is a drug that blocks the cause of dystonia in the brain, and will allow musicians to continue practicing music. We aim to attain clinical approval in Korea by 2024.”
NT-1 is currently under development by NeuroTobe, a faculty-led start-up company at KAIST, headed by Professor Daesoo Kim as the CEO. The synthesis of the drug for clinical testing has been successfully completed, and it has shown excellent efficacy and safety through various rounds of animal testing. Unlike Botox, which takes a few days to show its therapeutic effects after receiving the procedure from a hospital, NT-1 shows its therapeutic effects within an hour after taking it. As a so-called “edible Botox”, it is expected to help treat various muscular diseases and ailments.
2022.12.27 View 12368 -
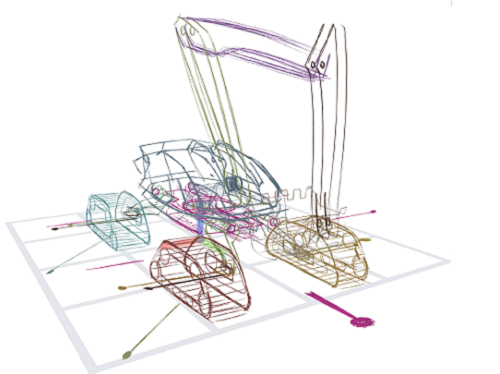 “3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 11751
“3D sketch” Your Ideas and Bring Them to Life, Instantly!
Professor Seok-Hyung Bae’s research team at the Department of Industrial Design developed a novel 3D sketching system that rapidly creates animated 3D concepts through simple user interactions like sketching on a piece of paper or playing a toy.
Foldable drones, transforming vehicles, and multi-legged robots from sci-fi movies are now becoming commonplace thanks to technological progress. However, designing them remains a difficult challenge even for skilled experts, because complex design decisions must be made regarding not only their form, but also the structure, poses, and motions, which are interdependent on one another.
Creating a 3D concept comprising of multiple moving parts connected by different types of joints using a traditional 3D CAD tool, which is more suited for processing precise and elaborate modeling, is a painstaking and time-consuming process. This presents a major bottleneck for the workflow during the early stage of design, in which it is preferred that as many ideas are tried and discarded out as quickly as possible in order to explore a wide range of possibilities in the shortest amount of time.
A research team led by Professor Bae has focused on designers’ freehand sketches drew up with a pen on a paper that serve as the starting point for virtually all design projects. This led them to develop their 3D sketching technology to generate desired 3D curves from the rough but expressive 2D strokes drawn with a digital stylus on a digital tablet.
Their latest research helps designers bring their 3D sketches to life almost instantly. Using the intuitive set of multi-touch gestures the team successfully designed and implemented, designers can handle the 3D sketches they are working on with their fingers as if they are playing with toys and put them into animation in no time.
< Figure 1. A novel 3D sketching system for rapidly designing articulated 3D concepts with a small set of coherent pen and multi-touch gestures. (a) Sketching: A 3D sketch curve is created by marking a pen stroke that is projected onto a sketch plane widget. (b) Segmenting: Entire or partial sketch curves are added to separate parts that serve as links in the kinematic chain. (c) Rigging: Repeatedly demonstrating the desired motion of a part leaves behind a trail, from which the system infers a joint. (d) Posing: Desired poses can be achieved through actuating joints via forward or inverse kinematics. (e) Filming: A sequence of keyframes specifying desired poses and viewpoints is connected as a smooth motion. >
< Figure 2. (a) Concept drawing of an autonomous excavator. It features (b, c) four caterpillars that swivel for high maneuverability, (d) an extendable boom and a bucket connected by multiple links, and (e) a rotating platform. The concept’s designer, who had 8 years of work experience, estimated that it would take 1-2 weeks to express and communicate such a complex articulated object with existing tools. With the proposed system, it took only 2 hours and 52 minutes. >
The major findings of their work were published under the title “Rapid Design of Articulated Objects” in ACM Transactions on Graphics (impact factor: 7.403), the top international journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 (h5-index: 103), the world’s largest international academic conference in the field, which was held back in August in Vancouver, Canada with Joon Hyub Lee, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design as the first author.
The ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 conference was reportedly attended by over 10,000 participants including researchers, artists, and developers from world-renowned universities; film, animation, and game studies, such as Marvel, Pixar, and Blizzard; high-tech manufacturers, such as Lockheed Martin and Boston Dynamics; and metaverse platform companies, such as Meta and Roblox.
< Figure 3. The findings of Professor Bae’s research team were published in ACM Transactions on Graphics, the top international academic journal in the field of computer graphics, and presented at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022, the largest international academic conference held in conjunction early August in Vancouver, Canada. The team’s live demo at the Emerging Technologies program was highly praised by numerous academics and industry officials and received an Honorable Mention. >
The team was also invited to present their technical paper as a demo and a special talk at the Emerging Technologies program at ACM SIGGRAPH 2022 as one of the top-three impactful technologies. The live performance, in which Hanbit Kim, a Ph.D. student of the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST and a co-author, sketched and animated a sophisticated animal-shaped robot from scratch in a matter of a few minutes, wowed the audience and won the Honorable Mention Award from the jury.
Edwin Catmull, the co-founder of Pixar and a keynote speaker at the SIGGRAPH conference, praised the team’s research on 3D sketching as “really excellent work” and “a kind of tool that would be useful to Pixar's creative model designers.”
This technology, which became virally popular in Japan after featuring in an online IT media outlet and attracting more than 600K views, received a special award from the Digital Content Association of Japan (DCAJ) and was invited and exhibited for three days at Tokyo in November, as a part of Inter BEE 2022, the largest broadcasting and media expo in Japan.
“The more we come to understand how designers think and work, the more effective design tools can be built around that understanding,” said Professor Bae, explaining that “the key is to integrate different algorithms into a harmonious system as intuitive interactions.” He added that “this work wouldn’t have been possible if it weren’t for the convergent research environment cultivated by the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST, in which all students see themselves not only as aspiring creative designers, but also as practical engineers.”
By enabling designers to produce highly expressive animated 3D concepts far more quickly and easily in comparison to using existing methods, this new tool is expected to revolutionize design practices and processes in the content creation, manufacturing, and metaverse-related industries.
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
More info: https://sketch.kaist.ac.kr/publications/2022_siggraph_rapid_design
Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rsBl0QvSDqI
< Figure 4. From left to right: Ph.D. students Hanbit Kim, and Joon Hyub Lee and Professor Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, KAIST >
2022.11.23 View 11751 -
 KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum Held
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) held the 'KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum' at the Korea Press Center in the morning of October 28th, 2022.
This forum was held in continuation to discuss the objectives of the 'Digital Vision Forum' that was hosted by New York University (NYU) back in September in the United States, and is the first public event to be held through joint efforts by KAIST and NYU since the signage of the 'KAIST-NYU Joint Campus' was presented at the New York forum.
< Signage of KAIST-NYU Joint Campus >
This forum was promoted based on the consensus of the two universities to create an international forum of solidarity to solve global challenges and seek new governance in the era of digital transformation.
Digital innovation technology is expected to bring economic and industrial benefits as well as political, social and ethical risks such as accelerating the digital divide, among others. In particular, in a time of global digital transformation, as the competition for digital and AI supremacy based on technology nationalism catches fire, there is an emergent need for a global governance system in which digital innovation and the value of freedom co-exist. With the consensus formed through this forum with NYU, KAIST plans to focus on detailing the vision for future digital cooperation that encompasses various stakeholders in our society.
To this end, President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST and President Andrew Hamilton of NYU led the forum with keynote addresses with President Hamilton taking part virtually, followed by NYU Professor Matthew Liao, a world-renowned scholar specialized in the ethics in the field of science and technology, and Jason Allford, Special Representative of the World Bank Group to Korea, presenting on relevant topics for discussion.
From KAIST, Professor Kyung Ryul Park of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and Director So Young Kim of the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, followed with their presentations. A panel discussion on governance in the period of digital transformation was also held, led by Professor Dongman Lee, the Dean of the College of Engineering.
To kick things off, Professor Matthew Liao of NYU proposed a normative system that can harmonize technology and social ethics while explaining various ethical issues following the technological development of artificial intelligence.
Jason Allford, Special Representative of the World Bank Group to Korea, outlined the changing roles of government in the digital era from the perspective of transparency and government efficiency and explained global development strategies through various cases of digital innovations by international organizations.
Professor Kyung Ryul Park of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy at KAIST emphasized that the core of new digital governance is not only innovative technology but also the participation and harmony of various stakeholders at home at abroad and brought up the importance of multi-dimensional international solidarity based on digital transformation that goes beyond the flat ‘technological geopolitics.’
Professor So Young Kim, the Director of the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution at KAIST, commented on the current government's digital platform strategy and emphasized the need for a leading digital transformation strategy that goes beyond the governance of the existing government.
Edward Mermelstein, the Commissioner for International Affairs of New York City, said, “The City of New York, shall also provide active support for the cooperative governance initiative organized by KAIST in Korea. As the conversation progresses further, we can draw up plans to organize international organizations to support the effort, likely to be named ‘Digitization for Good’, and we can go on to consider future collaboration,” to express the city’s willingness and anticipation for active cooperation.
Andrew Hamilton, the President of NYU, said "NYU is thrilled by the partnership we are embarking upon with KAIST, which goes hand in hand with our global tradition, and is based upon our bedrock commitment to the free movement of people and ideas.” He added that “As data-driven software, AI, and social networks become even more essential parts of our daily lives, I am confident that today’s discussions will lead to new and promising insights.”
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST said, “It is significant that we are to cooperate with New York University to prepare a venue to assess the changes of the forth coming era at a time in which digital technology, government platforms, and public data are attracting attention as a medium that can create various social and economic value.”
President Lee added, “KAIST and NYU, the two institutions in cross-continental partnership to lead innovations in higher education via the creation of a joint campus, have joined forces to host this forum to create an opportunity to envision the future of a cooperative governance that is inclusive of key players like the government, businesses, the civil societies, academia, and international organizations.”
The 'KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum' was broadcast live on KAIST’s Official YouTube Channel from 9:30 am on the 28th of October (Korea Standard Time) with simultaneous interpretation provided in both Korean and English. A recording of the video is available online for everyone to watch free of charge.
KAIST’s YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/KAISTofficial
Forum Recording with English interpretation: https://youtu.be/Vs31i7BtfEw
2022.10.28 View 8137
KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum Held
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) held the 'KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum' at the Korea Press Center in the morning of October 28th, 2022.
This forum was held in continuation to discuss the objectives of the 'Digital Vision Forum' that was hosted by New York University (NYU) back in September in the United States, and is the first public event to be held through joint efforts by KAIST and NYU since the signage of the 'KAIST-NYU Joint Campus' was presented at the New York forum.
< Signage of KAIST-NYU Joint Campus >
This forum was promoted based on the consensus of the two universities to create an international forum of solidarity to solve global challenges and seek new governance in the era of digital transformation.
Digital innovation technology is expected to bring economic and industrial benefits as well as political, social and ethical risks such as accelerating the digital divide, among others. In particular, in a time of global digital transformation, as the competition for digital and AI supremacy based on technology nationalism catches fire, there is an emergent need for a global governance system in which digital innovation and the value of freedom co-exist. With the consensus formed through this forum with NYU, KAIST plans to focus on detailing the vision for future digital cooperation that encompasses various stakeholders in our society.
To this end, President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST and President Andrew Hamilton of NYU led the forum with keynote addresses with President Hamilton taking part virtually, followed by NYU Professor Matthew Liao, a world-renowned scholar specialized in the ethics in the field of science and technology, and Jason Allford, Special Representative of the World Bank Group to Korea, presenting on relevant topics for discussion.
From KAIST, Professor Kyung Ryul Park of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and Director So Young Kim of the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, followed with their presentations. A panel discussion on governance in the period of digital transformation was also held, led by Professor Dongman Lee, the Dean of the College of Engineering.
To kick things off, Professor Matthew Liao of NYU proposed a normative system that can harmonize technology and social ethics while explaining various ethical issues following the technological development of artificial intelligence.
Jason Allford, Special Representative of the World Bank Group to Korea, outlined the changing roles of government in the digital era from the perspective of transparency and government efficiency and explained global development strategies through various cases of digital innovations by international organizations.
Professor Kyung Ryul Park of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy at KAIST emphasized that the core of new digital governance is not only innovative technology but also the participation and harmony of various stakeholders at home at abroad and brought up the importance of multi-dimensional international solidarity based on digital transformation that goes beyond the flat ‘technological geopolitics.’
Professor So Young Kim, the Director of the Korea Policy Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution at KAIST, commented on the current government's digital platform strategy and emphasized the need for a leading digital transformation strategy that goes beyond the governance of the existing government.
Edward Mermelstein, the Commissioner for International Affairs of New York City, said, “The City of New York, shall also provide active support for the cooperative governance initiative organized by KAIST in Korea. As the conversation progresses further, we can draw up plans to organize international organizations to support the effort, likely to be named ‘Digitization for Good’, and we can go on to consider future collaboration,” to express the city’s willingness and anticipation for active cooperation.
Andrew Hamilton, the President of NYU, said "NYU is thrilled by the partnership we are embarking upon with KAIST, which goes hand in hand with our global tradition, and is based upon our bedrock commitment to the free movement of people and ideas.” He added that “As data-driven software, AI, and social networks become even more essential parts of our daily lives, I am confident that today’s discussions will lead to new and promising insights.”
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST said, “It is significant that we are to cooperate with New York University to prepare a venue to assess the changes of the forth coming era at a time in which digital technology, government platforms, and public data are attracting attention as a medium that can create various social and economic value.”
President Lee added, “KAIST and NYU, the two institutions in cross-continental partnership to lead innovations in higher education via the creation of a joint campus, have joined forces to host this forum to create an opportunity to envision the future of a cooperative governance that is inclusive of key players like the government, businesses, the civil societies, academia, and international organizations.”
The 'KAIST-NYU Digital Governance Forum' was broadcast live on KAIST’s Official YouTube Channel from 9:30 am on the 28th of October (Korea Standard Time) with simultaneous interpretation provided in both Korean and English. A recording of the video is available online for everyone to watch free of charge.
KAIST’s YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/KAISTofficial
Forum Recording with English interpretation: https://youtu.be/Vs31i7BtfEw
2022.10.28 View 8137 -
 KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 12718
KAIST develops biocompatible adhesive applicable to hair transplants
Aside from being used as a new medical adhesive, the new material can be applied to developing a new method of hair transplants, which cannot be repeated multiple times using current method of implanting the wholly intact follicles into the skin.
Medical adhesives are materials that can be applied to various uses such as wound healing, hemostasis, vascular anastomosis, and tissue engineering, and is expected to contribute greatly to the development of minimally invasive surgery and organ transplants. However, adhesives with high adhesion, low toxicity, and capable of decomposing in the body are rare. Adhesives based on natural proteins, such as fibrin and collagen, have high biocompatibility but insufficient adhesive strength. Synthetic polymer adhesives based on urethane or acrylic have greater adhesion but do not decompose well and may cause an inflammatory reaction in the body.
A joint research team led by Professor Myungeun Seo and Professor Haeshin Lee from the KAIST Department of Chemistry developed a bio-friendly adhesive from biocompatible polymers using tannic acid, the source of astringency in wine.
The research team focused on tannic acid, a natural polyphenolic product. Tannic acid is a polyphenol present in large amounts in fruit peels, nuts, and cacao. It has a high affinity and coating ability on other substances, and we sense the astringent taste in wine when tannic acid sticks to the surface of our tongue. When tannic acid is mixed with hydrophilic polymers, they form coacervates, or small droplets of jelly-like fluids that sink. If the polymers used are biocompatible, the mixture can be applied as a medical adhesive with low toxicity. However, coacervates are fundamentally fluid-like and cannot withstand large forces, which limits their adhesive capabilities. Thus, while research to utilize it as an adhesive has been actively discussed, a biodegradable material exhibiting strong adhesion due to its high shear strength has not yet been developed.
The research team figured out a way to enhance adhesion by mixing two biocompatible FDA-approved polymers, polyethylene glycol (PEG) and polylactic acid (PLA). While PEG, which is used widely in eyedrops and cream, is hydrophilic, PLA, a well-known bioplastic derived from lactic acid, is insoluble in water. The team combined the two into a block copolymer, which forms hydrophilic PLA aggregates in water with PEG blocks surrounding them. A coacervate created by mixing the micelles and tannic acid would behave like a solid due to the hard PLA components, and show an elastic modulus improved by a thousand times compared to PEG, enabling it to withstand much greater force as an adhesive.
Figure 1. (Above) Principle of biodegradable adhesive made by mixing poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(lactic acid) diblock copolymer and tannic acid in water. Yellow coacervate is precipitated through hydrogen bonding between the block copolymer micelles and tannic acid, and exhibits adhesion. After heat treatment, hydrogen bonds are rearranged to further improve adhesion. (Bottom) Adhesion comparison. Compared to using poly(ethylene glycol) polymer (d), it can support 10 times more weight when using block copolymer (e) and 60 times more weight after heat treatment (f). The indicated G' values represent the elastic modulus of the material.
Furthermore, the research team observed that the material’s mechanical properties can be improved by over a hundred times through a heating and cooling process that is used to heat-treat metals. They also discovered that this is due to the enforced interactions between micelle and tannic acid arrays.
The research team used the fact that the material shows minimal irritation to the skin and decomposes well in the body to demonstrate its possible application as an adhesive for hair transplantation through an animal experiment. Professor Haeshin Lee, who has pioneered various application fields including medical adhesives, hemostatic agents, and browning shampoo, focused on the adhesive capacities and low toxicity of polyphenols like tannic acid, and now looks forward to it improving the limitations of current hair transplant methods, which still involve follicle transfer and are difficult to be repeated multiple times.
Figure 2. (a) Overview of a hair transplantation method using a biodegradable adhesive (right) compared to a conventional hair transplantation method (left) that transplants hair containing hair follicles. After applying an adhesive to the tip of the hair, it is fixed to the skin by implanting it through a subcutaneous injection, and repeated treatment is possible. (b) Initial animal test results. One day after 15 hair transplantation, 12 strands of hair remain. If you pull the 3 strands of hair, you can see that the whole body is pulled up, indicating that it is firmly implanted into the skin. All strands of hair applied without the new adhesive material fell off, and in the case of adhesive without heat treatment, the efficiency was 1/7.
This research was conducted by first co-authors Dr. Jongmin Park (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology) from Professor Myeongeun Seo’s team and Dr. Eunsook Park from Professor Haeshin Lee’s team in the KAIST Department of Chemistry, and through joint research with the teams led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Siyoung Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. The research was published online on August 22 in the international journal Au (JACS Au) under the title Biodegradable Block Copolymer-Tannic Acid Glue.
This study was funded by the Support Research Under Protection Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF), Leading Research Center Support Project (Research Center for Multiscale Chiral Structure), Biodegradable Plastics Commercialization and Demonstration Project by the Ministry of Trade and Industry, and institutional funding from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology.
2022.10.07 View 12718 -
 KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 16006
KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition.
A KAIST research team in the Department of Chemistry led by professor Mi Hee Lim took on a lead to discovered a new role for somatostatin, a protein-based neurotransmitter, in reducing the toxicity caused in the pathogenic mechanism taken towards development of Alzheimer’s disease. The study was published in the July issue of Nature Chemistry under the title, “Conformational and functional changes of the native neuropeptide somatostatin occur in the presence of copper and amyloid-β”.
According to the amyloid hypothesis, the abnormal deposition of Aβ proteins causes death of neuronal cells. While Aβ agglomerations make up most of the aged plaques through fibrosis, in recent studies, high concentrations of transitional metal were found in the plaques from Alzheimer’s patients.
This suggests a close interaction between metallic ions and Aβ, which accelerates the fibrosis of proteins. Copper in particular is a redox-activating transition metal that can produce large amounts of oxygen and cause serious oxidative stress on cell organelles. Aβ proteins and transition metals can closely interact with neurotransmitters at synapses, but the direct effects of such abnormalities on the structure and function of neurotransmitters are yet to be understood.
Figure 1. Functional shift of somatostatin (SST) by factors in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.
Figure 2. Somatostatin’s loss-of-function as neurotransmitter. a. Schematic diagram of SST auto-aggregation due to Alzheimer's pathological factors. b. SST’s aggregation by copper ions. c. Coordination-prediction structure and N-terminal folding of copper-SST. d. Inhibition of SST receptor binding specificity by metals.
In their research, Professor Lim’s team discovered that when somatostatin, the protein-based neurotransmitter, is met with copper, Aβ, and metal-Aβ complexes, self-aggregates and ceases to perform its innate function of transmitting neural signals, but begins to attenuate the toxicity and agglomeration of metal-Aβ complexes.
Figure 3. Gain-of-function of somatostatin (SST) in the dementia setting. a. Prediction of docking of SST and amyloid beta. b. SST making metal-amyloid beta aggregates into an amorphous form. c. Cytotoxic mitigation effect of SST. d. SST mitigating the interaction between amyloid beta protein with the cell membrane.
This research, by Dr. Jiyeon Han et al. from the KAIST Department of Chemistry, revealed the coordination structure between copper and somatostatin at a molecular level through which it suggested the agglomeration mechanism, and discovered the effects of somatostatin on Aβ agglomeration path depending on the presence or absence of metals. The team has further confirmed somatostatin’s receptor binding, interactions with cell membranes, and effects on cell toxicity for the first time to receive international attention.
Professor Mi Hee Lim said, “This research has great significance in having discovered a new role of neurotransmitters in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease.” “We expect this research to contribute to defining the pathogenic network of neurodegenerative diseases caused by aging, and to the development of future biomarkers and medicine,” she added.
This research was conducted jointly by Professor Seung-Hee Lee’s team of KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Kiyoung Park’s Team of KAIST Department of Chemistry, and Professor Yulong Li’s team of Peking University.
The research was funded by Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and KAIST.
For more information about the research team, visit the website: https://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab/1-professor-mi-hee-lim.
2022.07.29 View 16006 -
 Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 8951
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang Named the 2022 Ho-Am Laureate
Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry was named the awardee of the Ho-Am Prize in the fields of chemistry and life sciences. The award has recognized the most distinguished scholars, individuals, and organizations in physics and mathematics, chemistry and life sciences, engineering, medicine, arts, and community service in honor of the late founder of Samsung Group Byong-Chul Lee, whose penname is Ho-Am. The awards ceremony will be held on May 31 and awardees will receive 300 million KRW in prize money.
Professor Chang became the fourth KAIST Ho-Am laureate following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in engineering in 2014, Distinguished Professor Jun Ho Oh in engineering in 2016, and Distinguished Professor Gou Young Koh in medicine in 2018.
Professor Chang is a renowned chemist who has made pioneering research in the area of transition metal catalysis for organic transformations. Professor Chang is also one of the Highly Cited Researchers who rank in the top 1% of citations by field and publication year in the Web of Science citation index. He has made the list seven years in a row from 2016.
Professor Chang has developed a range of new and impactful C-H bond functionalization reactions. By using his approaches, value-added molecules can be readily produced from chemical feedstocks, representatively hydrocarbons and (hetero)arenes. His research team elucidated fundamental key mechanistic aspects in the course of the essential C-H bond activation process of unreactive starting materials. He was able to utilize the obtained mechanistic understanding for the subsequent catalyst design to develop more efficient and highly (stereo)selective catalytic reactions.
Among the numerous contributions he made, the design of new mechanistic approaches toward metal nitrenoid transfers are of especially high impact to the chemical community. Indeed, a series of important transition metal catalyst systems were developed by Professor Chang to enable the direct and selective C-H amidation of unreactive organic compounds, thereby producing aminated compounds that have important applicability in synthetic, medicinal, and materials science. He has also pioneered in the area of asymmetric C-H amination chemistry by creatively devising various types of chiral transition metal catalyst systems, and his team proved for the first time that chiral lactam compounds can be obtained at an excellent level of stereoselectivity.
Another significant contribution of Professor. Chang was the introduction of dioxazolones as a robust but highly reactive source of acyl nitrenoids for the catalytic C-H amidation reactions, and this reagent is now broadly utilized in synthetic chemistry worldwide.
Professor Chang also leads a research group in the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute for Basic Science.
2022.04.06 View 8951