TR
-
 Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 7501
Coordination Chemistry and Alzheimer’s Disease
It has become evident recently that the interactions between copper and amyloid-b neurotoxically impact the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. KAIST researchers have reported a new strategy to alter the neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease by using a rationally designed chemical reagent.
This strategy, developed by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry, can modify the coordination sphere of copper bound to amyloid-b, effectively inhibiting copper’s binding to amyloid-b and altering its aggregation and toxicity. Their study was featured in PNAS last month.
The researchers developed a small molecule that is able to directly interact with the coordination sphere of copper–amyloid-b complexes followed by modifications via either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both under aerobic conditions. The research team simply utilized copper–dioxygen chemistry to design a chemical reagent.
Answering how peptide modifications by a small molecule occur remains very challenging. The system includes transition metals and amyloidogenic proteins and is quite heterogeneous, since they are continuously being changed. It is critical to carefully check the multiple variables such as the presence of dioxygen and the type of transition metal ions and amyloidogenic proteins in order to identify the underlying mechanisms and target specificity of the chemical reagent.
The research team employed various biophysical and biochemical methods to determine the mechanisms for modifications on the coordination sphere of copper–Aꞵ complexes. Among them, peptide modifications were mainly analyzed using electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry.
Mass spectrometry (MS) has been applied to verify such peptide modifications by calculating the shift in exact mass. The research team also performed collision-induced dissociation (CID) of the target ion detected by MS to pinpoint which amino acid residue is specifically modified. The CID fragmentizes the amide bond located between the amino acid residues. This fragmental analysis allows us to identify the specific sites of peptide modifications.
The copper and amyloid-b complexes represent a pathological connection between metal ions and amyloid-b in Alzheimer’s disease. Recent findings indicate that copper and amyloid-b can directly contribute toward neurodegeneration by producing toxic amyloid-b oligomers and reactive oxygen species.
Professor Lim said, “This study illustrates the first experimental evidence that the 14th histidine residue in copper–amyloid-b complexes can be specifically modified through either covalent conjugation, oxidation, or both. Considering the neurotoxic implications of the interactions between copper and amyloid-b, such modifications at the coordination sphere of copper in amyloid-b could effectively alter its properties and toxicity.”
“This multidisciplinary study with an emphasis on approaches, reactivities, and mechanisms looks forward to opening a new way to develop candidates of anti-neurodegenerative diseases,” she added. The National Research Foundation of Korea funded this research.
2020.03.03 View 7501 -
 Stress-Relief Substrate Helps OLED Stretch Two-Dimensionally
Highly functional and free-form displays are critical components to complete the technological prowess of wearable electronics, robotics, and human-machine interfaces.
A KAIST team created stretchable OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes) that are compliant and maintain their performance under high-strain deformation. Their stress-relief substrates have a unique structure and utilize pillar arrays to reduce the stress on the active areas of devices when strain is applied.
Traditional intrinsically stretchable OLEDs have commercial limitations due to their low efficiency in the electrical conductivity of the electrodes. In addition, previous geometrically stretchable OLEDs laminated to the elastic substrates with thin film devices lead to different pixel emissions of the devices from different peak sizes of the buckles.
To solve these problems, a research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi designed a stretchable substrate system with surface relief island structures that relieve the stress at the locations of bridges in the devices. Their stretchable OLED devices contained an elastic substrate structure comprising bonded elastic pillars and bridges. A patterned upper substrate with bridges makes the rigid substrate stretchable, while the pillars decentralize the stress on the device.
Although various applications using micropillar arrays have been reported, it has not yet been reported how elastic pillar arrays can affect substrates by relieving the stress applied to those substrates upon stretching. Compared to results using similar layouts with conventional free-standing, flat substrates or island structures, their results with elastic pillar arrays show relatively low stress levels at both the bridges and plates when stretching the devices. They achieved stretchable RGB (red, green, blue) OLEDs and had no difficulties with material selection as practical processes were conducted with stress-relief substrates.
Their stretchable OLEDs were mechanically stable and have two-dimensional stretchability, which is superior to only one-direction stretchable electronics, opening the way for practical applications like wearable electronics and health monitoring systems.
Professor Choi said, “Our substrate design will impart flexibility into electronics technology development including semiconductor and circuit technologies. We look forward this new stretchable OLED lowering the barrier for entering the stretchable display market.”
This research was published in Nano Letters titled Two-Dimensionally Stretchable Organic Light-Emitting Diode with Elastic Pillar Arrays for Stress Relief. (https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03657). This work was supported by the Engineering Research Center of Excellence Program supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Profile
Professor Kyung Cheol Choi
kyungcc@kaist.ac.kr
http://adnc.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.02.27 View 9062
Stress-Relief Substrate Helps OLED Stretch Two-Dimensionally
Highly functional and free-form displays are critical components to complete the technological prowess of wearable electronics, robotics, and human-machine interfaces.
A KAIST team created stretchable OLEDs (Organic Light-Emitting Diodes) that are compliant and maintain their performance under high-strain deformation. Their stress-relief substrates have a unique structure and utilize pillar arrays to reduce the stress on the active areas of devices when strain is applied.
Traditional intrinsically stretchable OLEDs have commercial limitations due to their low efficiency in the electrical conductivity of the electrodes. In addition, previous geometrically stretchable OLEDs laminated to the elastic substrates with thin film devices lead to different pixel emissions of the devices from different peak sizes of the buckles.
To solve these problems, a research team led by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi designed a stretchable substrate system with surface relief island structures that relieve the stress at the locations of bridges in the devices. Their stretchable OLED devices contained an elastic substrate structure comprising bonded elastic pillars and bridges. A patterned upper substrate with bridges makes the rigid substrate stretchable, while the pillars decentralize the stress on the device.
Although various applications using micropillar arrays have been reported, it has not yet been reported how elastic pillar arrays can affect substrates by relieving the stress applied to those substrates upon stretching. Compared to results using similar layouts with conventional free-standing, flat substrates or island structures, their results with elastic pillar arrays show relatively low stress levels at both the bridges and plates when stretching the devices. They achieved stretchable RGB (red, green, blue) OLEDs and had no difficulties with material selection as practical processes were conducted with stress-relief substrates.
Their stretchable OLEDs were mechanically stable and have two-dimensional stretchability, which is superior to only one-direction stretchable electronics, opening the way for practical applications like wearable electronics and health monitoring systems.
Professor Choi said, “Our substrate design will impart flexibility into electronics technology development including semiconductor and circuit technologies. We look forward this new stretchable OLED lowering the barrier for entering the stretchable display market.”
This research was published in Nano Letters titled Two-Dimensionally Stretchable Organic Light-Emitting Diode with Elastic Pillar Arrays for Stress Relief. (https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b03657). This work was supported by the Engineering Research Center of Excellence Program supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
-Profile
Professor Kyung Cheol Choi
kyungcc@kaist.ac.kr
http://adnc.kaist.ac.kr/
School of Electrical Engineering
KAIST
2020.02.27 View 9062 -
 Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10173
Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10173 -
 Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 11870
Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 11870 -
 New Graphene-Based Metasurface Capable of Independent Amplitude and Phase Control of Light
Researchers described a new strategy of designing metamolecules that incorporates two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. This two-parametric control of the metamolecule secures the complete control of both amplitude and the phase of light.
A KAIST research team in collaboration with the University of Wisconsin-Madison theoretically suggested a graphene-based active metasurface capable of independent amplitude and phase control of mid-infrared light. This research gives a new insight into modulating the mid-infrared wavefront with high resolution by solving the problem of the independent control of light amplitude and phase, which has remained a long-standing challenge.
Light modulation technology is essential for developing future optical devices such as holography, high-resolution imaging, and optical communication systems. Liquid crystals and a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) have previously been utilized to modulate light. However, both methods suffer from significantly limited driving speeds and unit pixel sizes larger than the diffraction limit, which consequently prevent their integration into photonic systems.
The metasurface platform is considered a strong candidate for the next generation of light modulation technology. Metasurfaces have optical properties that natural materials cannot have, and can overcome the limitations of conventional optical systems, such as forming a high-resolution image beyond the diffraction limit. In particular, the active metasurface is regarded as a technology with a wide range of applications due to its tunable optical characteristics with an electrical signal.
However, the previous active metasurfaces suffered from the inevitable correlation between light amplitude control and phase control. This problem is caused by the modulation mechanism of conventional metasurfaces. Conventional metasurfaces have been designed such that a metaatom only has one resonance condition, but a single resonant design inherently lacks the degrees of freedom to independently control the amplitude and phase of light.
The research team made a metaunit by combining two independently controllable metaatoms, dramatically improving the modulation range of active metasurfaces. The proposed metasurface can control the amplitude and phase of the mid-infrared light independently with a resolution beyond the diffraction limit, thus allowing complete control of the optical wavefront.
The research team theoretically confirmed the performance of the proposed active metasurface and the possibility of wavefront shaping using this design method. Furthermore, they developed an analytical method that can approximate the optical properties of metasurfaces without complex electromagnetic simulations. This analytical platform proposes a more intuitive and comprehensively applicable metasurface design guideline.
The proposed technology is expected to enable accurate wavefront shaping with a much higher spatial resolution than existing wavefront shaping technologies, which will be applied to active optical systems such as mid-infrared holography, high-speed beam steering devices that can be applied for LiDAR, and variable focus infrared lenses.
Professor Min Seok Jang commented, "This study showed the independent control amplitude and phase of light, which has been a long-standing quest in light modulator technology. The development of optical devices using complex wavefront control is expected to become more active in the future."
MS candidate Sangjun Han and Dr. Seyoon Kim of the University of Wisconsin-Madison are the co-first authors of the research, which was published and selected as the front cover of the January 28 edition of ACS Nano titled “Complete complex amplitude modulation with electronically tunable graphene plasmonic metamolecules.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology.
Publication:
Han et al. (2020) Complete Complex Amplitude Modulation with Electronically Tunable Graphene Plasmonic Metamolecules. ACS Nano, Vol. 14, Issue 1, pp. 1166-1175. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b09277
Profile: Prof. Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Sangjun Han
sangjun.han@kaist.ac.kr
MS Candidate
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.20 View 9240
New Graphene-Based Metasurface Capable of Independent Amplitude and Phase Control of Light
Researchers described a new strategy of designing metamolecules that incorporates two independently controllable subwavelength meta-atoms. This two-parametric control of the metamolecule secures the complete control of both amplitude and the phase of light.
A KAIST research team in collaboration with the University of Wisconsin-Madison theoretically suggested a graphene-based active metasurface capable of independent amplitude and phase control of mid-infrared light. This research gives a new insight into modulating the mid-infrared wavefront with high resolution by solving the problem of the independent control of light amplitude and phase, which has remained a long-standing challenge.
Light modulation technology is essential for developing future optical devices such as holography, high-resolution imaging, and optical communication systems. Liquid crystals and a microelectromechanical system (MEMS) have previously been utilized to modulate light. However, both methods suffer from significantly limited driving speeds and unit pixel sizes larger than the diffraction limit, which consequently prevent their integration into photonic systems.
The metasurface platform is considered a strong candidate for the next generation of light modulation technology. Metasurfaces have optical properties that natural materials cannot have, and can overcome the limitations of conventional optical systems, such as forming a high-resolution image beyond the diffraction limit. In particular, the active metasurface is regarded as a technology with a wide range of applications due to its tunable optical characteristics with an electrical signal.
However, the previous active metasurfaces suffered from the inevitable correlation between light amplitude control and phase control. This problem is caused by the modulation mechanism of conventional metasurfaces. Conventional metasurfaces have been designed such that a metaatom only has one resonance condition, but a single resonant design inherently lacks the degrees of freedom to independently control the amplitude and phase of light.
The research team made a metaunit by combining two independently controllable metaatoms, dramatically improving the modulation range of active metasurfaces. The proposed metasurface can control the amplitude and phase of the mid-infrared light independently with a resolution beyond the diffraction limit, thus allowing complete control of the optical wavefront.
The research team theoretically confirmed the performance of the proposed active metasurface and the possibility of wavefront shaping using this design method. Furthermore, they developed an analytical method that can approximate the optical properties of metasurfaces without complex electromagnetic simulations. This analytical platform proposes a more intuitive and comprehensively applicable metasurface design guideline.
The proposed technology is expected to enable accurate wavefront shaping with a much higher spatial resolution than existing wavefront shaping technologies, which will be applied to active optical systems such as mid-infrared holography, high-speed beam steering devices that can be applied for LiDAR, and variable focus infrared lenses.
Professor Min Seok Jang commented, "This study showed the independent control amplitude and phase of light, which has been a long-standing quest in light modulator technology. The development of optical devices using complex wavefront control is expected to become more active in the future."
MS candidate Sangjun Han and Dr. Seyoon Kim of the University of Wisconsin-Madison are the co-first authors of the research, which was published and selected as the front cover of the January 28 edition of ACS Nano titled “Complete complex amplitude modulation with electronically tunable graphene plasmonic metamolecules.”
This research was funded by the Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center for Future Technology.
Publication:
Han et al. (2020) Complete Complex Amplitude Modulation with Electronically Tunable Graphene Plasmonic Metamolecules. ACS Nano, Vol. 14, Issue 1, pp. 1166-1175. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.9b09277
Profile: Prof. Min Seok Jang, MS, PhD
jang.minseok@kaist.ac.kr
http://jlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Jang Research Group
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Sangjun Han
sangjun.han@kaist.ac.kr
MS Candidate
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.20 View 9240 -
 What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 13894
What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 13894 -
 New KAA President Chilhee Chung Calls Alumni Engagement a Top Priority
The KAIST Alumni Association (KAA) inaugurated Advisor Chilhee Chung of Samsung Electronics as its new president. President Chung was preceded by Ki-Chul Cha, the CEO of Inbody Co. Ltd. His term as the 25th president starts from February 2020 and ends in January 2022.
President Chung received his master’s degree from KAIST's Department of Physics in 1979 and joined Samsung Electronics the same year. He also holds a doctorate in physics from Michigan State University in the United States.
President Chung devoted himself to helping Samsung Electronics and Korea's system semiconductor and memory device technologies achieve global dominance for more than 40 years. He led future technology development at Samsung Electronics in the fields of quantum dot and neural processing from various leadership positions, including the head of the Semiconductor R&D Center, and the president of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT).
President Chung is currently an advisor to SAIT, a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology (PACST), and the chairman of the 2045 National Future Strategy Committee and the Nano Technology Research Association (NTRA).
President Chung said, “KAIST, throughout its history of half a century, has been working tirelessly to become the world’s best, beyond being the best in Korea. We, the alumni of KAIST, have the commensurate duty as well as the privilege of being proud members of KAIST, as the university's global stature grows.”
“Recently, 46 alumni made 535 million won in donations, and established a scholarship to encourage entrepreneurial spirit in members of the KAIST community. This fund was dedicated to supporting 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students participating in the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 that was held in Las Vegas last month. Moreover, another alumnus of ours Byeong-Gyu Chang, the CSO of the KRAFTON Inc., donated 10 billion won to KAIST in hopes of opening up more opportunities that may lead KAIST students to success. Mr. Chang’s donation is by far the largest that has been made by KAIST alumni. I feel grateful to see more alumni getting involved in shaping the future of KAIST these days, and my top priority as the new president of the KAA will be to stimulate the alumni association and engagement in the spirit of ‘Team KAIST’,” he added.
More than 900 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, gathered in Seoul on January 18 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAA.
(END)
2020.02.03 View 7257
New KAA President Chilhee Chung Calls Alumni Engagement a Top Priority
The KAIST Alumni Association (KAA) inaugurated Advisor Chilhee Chung of Samsung Electronics as its new president. President Chung was preceded by Ki-Chul Cha, the CEO of Inbody Co. Ltd. His term as the 25th president starts from February 2020 and ends in January 2022.
President Chung received his master’s degree from KAIST's Department of Physics in 1979 and joined Samsung Electronics the same year. He also holds a doctorate in physics from Michigan State University in the United States.
President Chung devoted himself to helping Samsung Electronics and Korea's system semiconductor and memory device technologies achieve global dominance for more than 40 years. He led future technology development at Samsung Electronics in the fields of quantum dot and neural processing from various leadership positions, including the head of the Semiconductor R&D Center, and the president of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology (SAIT).
President Chung is currently an advisor to SAIT, a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology (PACST), and the chairman of the 2045 National Future Strategy Committee and the Nano Technology Research Association (NTRA).
President Chung said, “KAIST, throughout its history of half a century, has been working tirelessly to become the world’s best, beyond being the best in Korea. We, the alumni of KAIST, have the commensurate duty as well as the privilege of being proud members of KAIST, as the university's global stature grows.”
“Recently, 46 alumni made 535 million won in donations, and established a scholarship to encourage entrepreneurial spirit in members of the KAIST community. This fund was dedicated to supporting 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students participating in the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 that was held in Las Vegas last month. Moreover, another alumnus of ours Byeong-Gyu Chang, the CSO of the KRAFTON Inc., donated 10 billion won to KAIST in hopes of opening up more opportunities that may lead KAIST students to success. Mr. Chang’s donation is by far the largest that has been made by KAIST alumni. I feel grateful to see more alumni getting involved in shaping the future of KAIST these days, and my top priority as the new president of the KAA will be to stimulate the alumni association and engagement in the spirit of ‘Team KAIST’,” he added.
More than 900 alumni, including President Sung-Chul Shin who is also an alumnus of KAIST, gathered in Seoul on January 18 to celebrate the New Year and the newly-elected leadership of the KAA.
(END)
2020.02.03 View 7257 -
 Transformative Electronics Systems to Broaden Wearable Applications
Imagine a handheld electronic gadget that can soften and deform when attached to our skin. This will be the future of electronics we all dreamed of. A research team at KAIST says their new platform called 'Transformative Electronics Systems' will open a new class of electronics, allowing reconfigurable electronic interfaces to be optimized for a variety of applications.
A team working under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST has invented a multifunctional electronic platform that can mechanically transform its shape, flexibility, and stretchability. This platform, which was reported in Science Advances, allows users to seamlessly and precisely tune its stiffness and shape.
"This new class of electronics will not only offer robust, convenient interfaces for use in both tabletop or handheld setups, but also allow seamless integration with the skin when applied onto our bodies," said Professor Jeong.
The transformative electronics consist of a special gallium metal structure, hermetically encapsulated and sealed within a soft silicone material, combined with electronics that are designed to be flexible and stretchable. The mechanical transformation of the electronic systems is specifically triggered by temperature change events controlled by the user.
"Gallium is an interesting key material. It is biocompatible, has high rigidity in solid form, and melts at a temperature comparable to the skin's temperature," said lead author Sang-Hyuk Byun, a researcher at KAIST.
Once the transformative electronic platform comes in contact with a human body, the gallium metal encapsulated inside the silicone changes to a liquid state and softens the whole electronic structure, making it stretchable, flexible, and wearable. The gallium metal then solidifies again once the structure is peeled off the skin, making the electronic circuits stiff and stable. When flexible electronic circuits were integrated onto these transformative platforms, it empowered them with the ability to become either flexible and stretchable or rigid.
"This technology could not have been achieved without interdisciplinary efforts," said co-lead author Joo Yong Sim, who is a researcher with ETRI. "We worked together with electrical, mechanical, and biomedical engineers, as well as material scientists and neuroscientists to make this breakthrough."
This universal electronics platform allowed researchers to demonstrate applications that were highly adaptable and customizable, such as a multi-purpose personal electronics with variable stiffness and stretchability, a pressure sensor with tuneable bandwidth and sensitivity, and a neural probe that softens upon implantation into brain tissue.
Applicable for both traditional and emerging electronics technologies, this breakthrough can potentially reshape the consumer electronics industry, especially in the biomedical and robotic domains. The researchers believe that with further development, this novel electronics technology can significantly impact the way we use electronics in our daily life.
< Transformative electronics in soft mode,which becomes wearable for outdoor applications.>
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/im0J18TfShk
Publication: Sang-Hyuk Byun, Joo Yong Sim, Zhanan Zhou, Juhyun Lee, Raza Qazi, Marie C. Walicki, Kyle E. Parker, Matthew P. Haney, Su Hwan Choi, Ahnsei Shon, Graydon B. Gereau, John Bilbily, Shuo Li, Yuhao Liu, Woon-Hong Yeo, Jordan G. McCall, Jianliang Xiao, and Jae-Woong Jeong. 2019. Mechanically transformative electronics, sensors, and implantable devices. Science Advances. Volume 5. No. 11. 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay0418
Link to download the full-text paper: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/advances/5/11/eaay0418.full.pdf
Profile: Prof. Jae-Woong Jeong, PhD jjeong1@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
Professor
Bio-Integrated Electronics and Systems Laboratory
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sang-Hyuk Byun, PhD Candidate
shbun95@kaist.ac.kr
(END)
2020.01.31 View 7181
Transformative Electronics Systems to Broaden Wearable Applications
Imagine a handheld electronic gadget that can soften and deform when attached to our skin. This will be the future of electronics we all dreamed of. A research team at KAIST says their new platform called 'Transformative Electronics Systems' will open a new class of electronics, allowing reconfigurable electronic interfaces to be optimized for a variety of applications.
A team working under Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST has invented a multifunctional electronic platform that can mechanically transform its shape, flexibility, and stretchability. This platform, which was reported in Science Advances, allows users to seamlessly and precisely tune its stiffness and shape.
"This new class of electronics will not only offer robust, convenient interfaces for use in both tabletop or handheld setups, but also allow seamless integration with the skin when applied onto our bodies," said Professor Jeong.
The transformative electronics consist of a special gallium metal structure, hermetically encapsulated and sealed within a soft silicone material, combined with electronics that are designed to be flexible and stretchable. The mechanical transformation of the electronic systems is specifically triggered by temperature change events controlled by the user.
"Gallium is an interesting key material. It is biocompatible, has high rigidity in solid form, and melts at a temperature comparable to the skin's temperature," said lead author Sang-Hyuk Byun, a researcher at KAIST.
Once the transformative electronic platform comes in contact with a human body, the gallium metal encapsulated inside the silicone changes to a liquid state and softens the whole electronic structure, making it stretchable, flexible, and wearable. The gallium metal then solidifies again once the structure is peeled off the skin, making the electronic circuits stiff and stable. When flexible electronic circuits were integrated onto these transformative platforms, it empowered them with the ability to become either flexible and stretchable or rigid.
"This technology could not have been achieved without interdisciplinary efforts," said co-lead author Joo Yong Sim, who is a researcher with ETRI. "We worked together with electrical, mechanical, and biomedical engineers, as well as material scientists and neuroscientists to make this breakthrough."
This universal electronics platform allowed researchers to demonstrate applications that were highly adaptable and customizable, such as a multi-purpose personal electronics with variable stiffness and stretchability, a pressure sensor with tuneable bandwidth and sensitivity, and a neural probe that softens upon implantation into brain tissue.
Applicable for both traditional and emerging electronics technologies, this breakthrough can potentially reshape the consumer electronics industry, especially in the biomedical and robotic domains. The researchers believe that with further development, this novel electronics technology can significantly impact the way we use electronics in our daily life.
< Transformative electronics in soft mode,which becomes wearable for outdoor applications.>
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/im0J18TfShk
Publication: Sang-Hyuk Byun, Joo Yong Sim, Zhanan Zhou, Juhyun Lee, Raza Qazi, Marie C. Walicki, Kyle E. Parker, Matthew P. Haney, Su Hwan Choi, Ahnsei Shon, Graydon B. Gereau, John Bilbily, Shuo Li, Yuhao Liu, Woon-Hong Yeo, Jordan G. McCall, Jianliang Xiao, and Jae-Woong Jeong. 2019. Mechanically transformative electronics, sensors, and implantable devices. Science Advances. Volume 5. No. 11. 12 pages. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aay0418
Link to download the full-text paper: https://advances.sciencemag.org/content/advances/5/11/eaay0418.full.pdf
Profile: Prof. Jae-Woong Jeong, PhD jjeong1@kaist.ac.kr
https://www.jeongresearch.org/
Professor
Bio-Integrated Electronics and Systems Laboratory
School of Electrical Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sang-Hyuk Byun, PhD Candidate
shbun95@kaist.ac.kr
(END)
2020.01.31 View 7181 -
 KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 11589
KAIST Showcases Advanced Technologies at CES 2020
< President Sung-Chul Shin experiencing cooling gaming headset developed by TEGWAY >
KAIST Pavilion showcased 12 KAIST startups and alumni companies’ technologies at the International Consumer Electronics Show (CES) 2020 held in Las Vegas last month. Especially four companies, TEGWAY, THE.WAVE.TALK, Sherpa Space, and LiBEST won the CES 2020 Innovation Awards presented by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA). The CTA selects the most innovative items from among all submissions.
TEGWAY spinned off by KAIST Professor Byung Jin Cho already made international headlines for their flexible, wearable, and temperature immersive thermoelectric device. The device was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015, and has been expanded into VR, AR, and games.
THE.WAVE.TALK has developed their first home appliance product in collaboration with ID+IM Design Laboratory of KAIST in which Professor Sang-Min Bae heads as creative director. Their real-time bacteria analysis with smart IoT sensor won the home appliances section.
Sherpa Space and LiBEST are the alumni companies. Sherpa Space’s lighting for plants won the sustainability, eco-design, and smart energy section, and LiBEST’s full-range flexible battery won the section for technology for a better world.
KAIST’s Alumni Association, Development Foundation, and the Office of University-Industry Cooperation (OUIC) made every effort to present KAIST technologies to the global market. President Sung-Chul Shin led the delegation comprising of 70 faculty, researchers, and young entrepreneurs. The KAIST Alumni Association fully funded the traveling costs of 30 alumni entrepreneurs and students, establishing scholarship for the CES participation. Ten young entrepreneurs were selected through the KAIST Startup Awards, and 20 current students preparing to start their own companies were selected via recommendation from the respective departments.
Associate Vice President of the OUIC Kyung Cheol Choi said in excitement, “We received many offers for joint research and investment from leading companies around the world,” adding, “We will continue doing our best to generate global value by developing the innovative technologies obtained from education and research into businesses.”
The KAIST pavilion at CES 2020 showcased:
1. flexible thermoelectric device ThermoReal and cooling gaming headset from TEGWAY,
2. wearable flexible battery from LiBEST,
3. applications such as conductive transparent electrode film and transparent heating film from J-Micro,
4. on-device AI solution based on deep learning model compression technology from Nota,
5. portable high resolution brain imaging device from OBELAB,
6. real-time bacteria analysis technology from THE.WAVE.TALK,
7. conversation-based AI-1 radio service platform from Timecode Archive,
8. light source solutions for different stages in a plant’s life cycle from Sherpa Space,
9. skin attached micro-LED patch and flexible piezoelectric acoustic sensor from FRONICS,
10. real-time cardiovascular measurement device from Healthrian,
11. block chain based mobile research documentation system from ReDWit, and
12. student-developed comprehensive healthcare device using a smart mirror.
(END)
2020.01.13 View 11589 -
 Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 10127
Scientists Discover the Mechanism of DNA High-Order Structure Formation
(Molecular structures of Abo1 in different energy states (left), Demonstration of an Abo1-assisted histone loading onto DNA by the DNA curtain assay. )
The genetic material of our cells—DNA—exists in a high-order structure called “chromatin”. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins and efficiently packs DNA into a small volume. Moreover, using a spool and thread analogy, chromatin allows DNA to be locally wound or unwound, thus enabling genes to be enclosed or exposed. The misregulation of chromatin structures results in aberrant gene expression and can ultimately lead to developmental disorders or cancers. Despite the importance of DNA high-order structures, the complexity of the underlying machinery has circumvented molecular dissection.
For the first time, molecular biologists have uncovered how one particular mechanism uses energy to ensure proper histone placement onto DNA to form chromatin. They published their results on Dec. 17 in Nature Communications.
The study focused on proteins called histone chaperones. Histone chaperones are responsible for adding and removing specific histones at specific times during the DNA packaging process. The wrong histone at the wrong time and place could result in the misregulation of gene expression or aberrant DNA replication. Thus, histone chaperones are key players in the assembly and disassembly of chromatin.
“In order to carefully control the assembly and disassembly of chromatin units, histone chaperones act as molecular escorts that prevent histone aggregation and undesired interactions,” said Professor Ji-Joon Song in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST. “We set out to understand how a unique histone chaperone uses chemical energy to assemble or disassemble chromatin.”
Song and his team looked to Abo1, the only known histone chaperone that utilizes cellular energy (ATP). While Abo1 is found in yeast, it has an analogous partner in other organisms, including humans, called ATAD2. Both use ATP, which is produced through a cellular process where enzymes break down a molecule’s phosphate bond. ATP energy is typically used to power other cellular processes, but it is a rare partner for histone chaperones.
“This was an interesting problem in the field because all other histone chaperones studied to date do not use ATP,” Song said.
By imaging Abo1 with a single-molecule fluorescence imaging technique known as the DNA curtain assay, the researchers could examine the protein interactions at the single-molecule level. The technique allows scientists to arrange the DNA molecules and proteins on a single layer of a microfluidic chamber and examine the layer with fluorescence microscopy.
The researchers found through real-time observation that Abo1 is ring-shaped and changes its structure to accommodate a specific histone and deposit it on DNA. Moreover, they found that the accommodating structural changes are powered by ADP.
“We discovered a mechanism by which Abo1 accommodates histone substrates, ultimately allowing it to function as a unique energy-dependent histone chaperone,” Song said. “We also found that despite looking like a protein disassembly machine, Abo1 actually loads histone substrates onto DNA to facilitate chromatin assembly.”
The researchers plan to continue exploring how energy-dependent histone chaperones bind and release histones, with the ultimate goal of developing therapeutics that can target cancer-causing misbehavior by Abo1’s analogous human counterpart, ATAD2.
-Profile
Professor Ji-Joon Song
Department of Biological Sciences KI for the BioCentury (https://kis.kaist.ac.kr/index.php?mid=KIB_O) KAIST
2020.01.07 View 10127 -
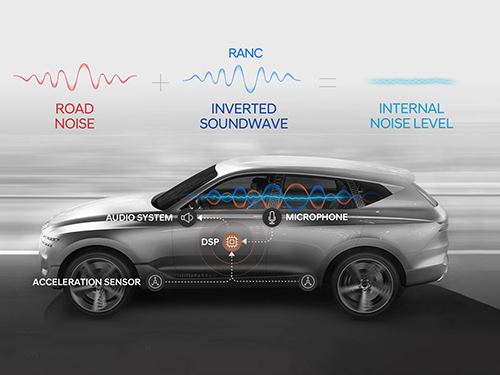 A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 11329
A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 11329 -
 Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 10883
Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 10883