KI
-
 Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
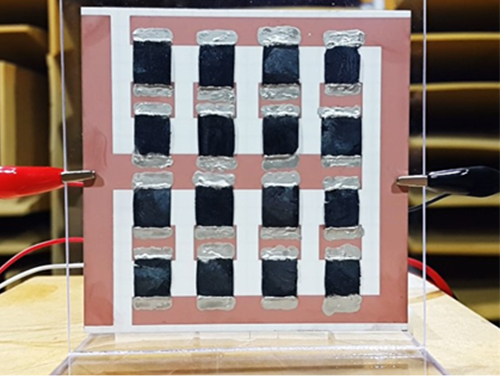
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 15089
Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 15089 -
 Continuous Roll-Process Technology for Transferring and Packaging Flexible Large-Scale Integrated Circuits
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from KAIST and by Dr. Jae-Hyun Kim from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) has jointly developed a continuous roll-processing technology that transfers and packages flexible large-scale integrated circuits (LSI), the key element in constructing the computer’s brain such as CPU, on plastics to realize flexible electronics.
Professor Lee previously demonstrated the silicon-based flexible LSIs using 0.18 CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) process in 2013 (ACS Nano, “In Vivo Silicon-based Flexible Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Monolithically Encapsulated with Biocompatible Liquid Crystal Polymers”) and presented the work in an invited talk of 2015 International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), the world’s premier semiconductor forum.
Highly productive roll-processing is considered a core technology for accelerating the commercialization of wearable computers using flexible LSI. However, realizing it has been a difficult challenge not only from the roll-based manufacturing perspective but also for creating roll-based packaging for the interconnection of flexible LSI with flexible displays, batteries, and other peripheral devices.
To overcome these challenges, the research team started fabricating NAND flash memories on a silicon wafer using conventional semiconductor processes, and then removed a sacrificial wafer leaving a top hundreds-nanometer-thick circuit layer. Next, they simultaneously transferred and interconnected the ultrathin device on a flexible substrate through the continuous roll-packaging technology using anisotropic conductive film (ACF). The final silicon-based flexible NAND memory successfully demonstrated stable memory operations and interconnections even under severe bending conditions. This roll-based flexible LSI technology can be potentially utilized to produce flexible application processors (AP), high-density memories, and high-speed communication devices for mass manufacture.
Professor Lee said, “Highly productive roll-process was successfully applied to flexible LSIs to continuously transfer and interconnect them onto plastics. For example, we have confirmed the reliable operation of our flexible NAND memory at the circuit level by programming and reading letters in ASCII codes. Out results may open up new opportunities to integrate silicon-based flexible LSIs on plastics with the ACF packing for roll-based manufacturing.”
Dr. Kim added, “We employed the roll-to-plate ACF packaging, which showed outstanding bonding capability for continuous roll-based transfer and excellent flexibility of interconnecting core and peripheral devices. This can be a key process to the new era of flexible computers combining the already developed flexible displays and batteries.”
The team’s results will be published on the front cover of Advanced Materials (August 31, 2016) in an article entitled “Simultaneous Roll Transfer and Interconnection of Silicon NAND Flash Memory.” (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201602339)
YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8OJjAEm27sw
Picture 1: This schematic image shows the flexible silicon NAND flash memory produced by the simultaneous roll-transfer and interconnection process.
Picture 2: The flexible silicon NAND flash memory is attached to a 7 mm diameter glass rod.
2016.09.01 View 12494
Continuous Roll-Process Technology for Transferring and Packaging Flexible Large-Scale Integrated Circuits
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from KAIST and by Dr. Jae-Hyun Kim from the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) has jointly developed a continuous roll-processing technology that transfers and packages flexible large-scale integrated circuits (LSI), the key element in constructing the computer’s brain such as CPU, on plastics to realize flexible electronics.
Professor Lee previously demonstrated the silicon-based flexible LSIs using 0.18 CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductor) process in 2013 (ACS Nano, “In Vivo Silicon-based Flexible Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Monolithically Encapsulated with Biocompatible Liquid Crystal Polymers”) and presented the work in an invited talk of 2015 International Electron Device Meeting (IEDM), the world’s premier semiconductor forum.
Highly productive roll-processing is considered a core technology for accelerating the commercialization of wearable computers using flexible LSI. However, realizing it has been a difficult challenge not only from the roll-based manufacturing perspective but also for creating roll-based packaging for the interconnection of flexible LSI with flexible displays, batteries, and other peripheral devices.
To overcome these challenges, the research team started fabricating NAND flash memories on a silicon wafer using conventional semiconductor processes, and then removed a sacrificial wafer leaving a top hundreds-nanometer-thick circuit layer. Next, they simultaneously transferred and interconnected the ultrathin device on a flexible substrate through the continuous roll-packaging technology using anisotropic conductive film (ACF). The final silicon-based flexible NAND memory successfully demonstrated stable memory operations and interconnections even under severe bending conditions. This roll-based flexible LSI technology can be potentially utilized to produce flexible application processors (AP), high-density memories, and high-speed communication devices for mass manufacture.
Professor Lee said, “Highly productive roll-process was successfully applied to flexible LSIs to continuously transfer and interconnect them onto plastics. For example, we have confirmed the reliable operation of our flexible NAND memory at the circuit level by programming and reading letters in ASCII codes. Out results may open up new opportunities to integrate silicon-based flexible LSIs on plastics with the ACF packing for roll-based manufacturing.”
Dr. Kim added, “We employed the roll-to-plate ACF packaging, which showed outstanding bonding capability for continuous roll-based transfer and excellent flexibility of interconnecting core and peripheral devices. This can be a key process to the new era of flexible computers combining the already developed flexible displays and batteries.”
The team’s results will be published on the front cover of Advanced Materials (August 31, 2016) in an article entitled “Simultaneous Roll Transfer and Interconnection of Silicon NAND Flash Memory.” (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201602339)
YouTube Link: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8OJjAEm27sw
Picture 1: This schematic image shows the flexible silicon NAND flash memory produced by the simultaneous roll-transfer and interconnection process.
Picture 2: The flexible silicon NAND flash memory is attached to a 7 mm diameter glass rod.
2016.09.01 View 12494 -
 KAIST Team Develops Semi-Transparent Solar Cells with Thermal Mirror Capability
A research team led by KAIST and Sungkyunkwan University professors has created semi-transparent perovskite solar cells that demonstrate high-power conversion efficiency and transmit visible light while blocking infrared light, making them great candidates for solar windows.
Modern architects prefer to build exteriors designed with glass mainly from artistic or cost perspectives. Scientists, however, go one step further and see opportunities from its potential ability to harness solar energy. Researchers have thus explored ways to make solar cells transparent or semi-transparent as a substitute material for glass, but this has proven to be a challenging task because solar cells need to absorb sunlight to generate electricity, and when they are transparent, it reduces their energy efficiency.
Typical solar cells today are made of crystalline silicon, but it is difficult to make them translucent. Semi-transparent solar cells under development use, for example, organic or dye-sensitized materials, but compared to crystalline silicon-based cells, their power-conversion efficiencies are relatively low. Perovskites are hybrid organic-inorganic halide-based photovoltaic materials, which are cheap to produce and easy to manufacture. They have recently received much attention as the efficiency of perovskite solar cells has rapidly increased to the level of silicon technologies in the past few years.
Using perovskites, a Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and Professor Nam-Gyu Park of the Chemical Engineering School at Sungkyunkwan University developed a semi-transparent solar cell that is highly efficient and, additionally, functions very effectively as a thermal-mirror.
The team has developed a top transparent electrode (TTE) that works well with perovskite solar cells. In most cases, a key to success in realizing semi-transparent solar cells is to find a TTE that is compatible with a given photoactive material system, which is also the case for perovskite solar cells. The proposed TTE is based on a multilayer stack consisting of a metal film sandwiched between a high refractive-index (high-index) layer and an interfacial buffer layer. This TTE, placed as a top-most layer, can be prepared without damaging ingredients used in perovskite solar cells. Unlike conventional transparent electrodes focusing only on transmitting visible light, the proposed TTE plays the dual role of passing through visible light while reflecting infrared rays. The semi-transparent solar cells made with the proposed TTEs exhibited average power conversion efficiency as high as 13.3% with 85.5% infrared rejection.
The team believes that if the semi-transparent perovskite solar cells are scaled up for practical applications, they can be used in solar windows for buildings and automobiles, which not only generate electrical energy but also enable the smart heat management for indoor environments, thereby utilizing solar energy more efficiently and effectively.
This result was published as a cover article in the July 20, 2016 issue of Advanced Energy Materials. The research paper is entitled “Empowering Semi-transparent Solar Cells with Thermal-mirror Functionality.” (DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502466)
The team designed the transparent electrode (TE) stack in three layers: A thin-film of silver (Ag) is placed in between the bottom interfacial layer of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) and the top high-index dielectric layer of zinc sulfide (ZnS). Such a tri-layer approach has been known as a means to increase the overall visible-light transmittance of metallic thin films via index matching technique, which is essentially the same technique used for anti-reflection coating of glasses except that the present case involves a metallic layer.
Traditionally, when a TE is based on a metal film, such as Ag, the film should be extremely thin, e.g., 7-12 nanometers (nm), to obtain transparency and, accordingly, to transmit visible light. However, the team took a different approach in this research. They made the Ag TE two or three times thicker (12-24 nm) than conventional metal films and, as a result, it reflected more infrared light. The high refractive index of the ZnS layer plays an essential role in keeping the visible light transmittance of the proposed TTE high even with the relatively thick Ag film when its thickness is carefully optimized for maximal destructive interference, leading to low reflectance (and thus high transmittance) within its visible light range.
The team confirmed the semi-transparent perovskite solar cell’s thermal-mirror function through an experiment in which a halogen lamp illuminated an object for five minutes through three mediums: a window of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and the proposed semi-transparent perovskite solar cell. An infrared (IR) camera took thermal images of the object as well as that of each window’s surface. The object’s temperature, when exposed through the glass window, rose to 36.8 Celsius degrees whereas both the tinting film and the cell allowed the object to remain below 27 Celsius degrees. The tinting film absorbs light to block solar energy, so the film’s surface became hot as it was continuously exposed to the lamp light, but the proposed semi-transparent solar cell stayed cool since it rejects solar heat energy by reflection, rather than by absorption. The total solar energy rejection (TSER) of the proposed cell was as high as 89.6%.
Professor Yoo of KAIST said, “The major contributions of this work are to find transparent electrode technology suitable for translucent perovskite cells and to provide a design approach to fully harness the potential it can further deliver as a heat mirror in addition to its main role as an electrode. The present work can be further fine-tuned to include colored solar cells and to incorporate flexible or rollable form factors, as they will allow for greater design freedom and thus offer more opportunities for them to be integrated into real-world objects and structures such as cars, buildings, and houses.”
The lead authors are Hoyeon Kim and Jaewon Ha, both Ph.D. candidates in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, and Hui-Seon Kim, a student in the School of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University. This research was supported mainly by the Climate Change Research Hub Program of KAIST.
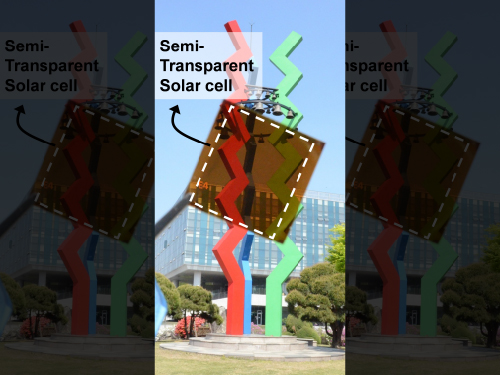
Picture 1: Semi-transparent Perovskite Solar Cell
This picture shows a prototype of a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell with thermal-mirror functionality.
Picture 2: A Heat Rejection Performance Comparison Experiment
This picture presents thermal images taken by an infrared camera for comparing the heat rejection performance of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell after being illuminated by a halogen lamp for five minutes.
2016.08.02 View 13369
KAIST Team Develops Semi-Transparent Solar Cells with Thermal Mirror Capability
A research team led by KAIST and Sungkyunkwan University professors has created semi-transparent perovskite solar cells that demonstrate high-power conversion efficiency and transmit visible light while blocking infrared light, making them great candidates for solar windows.
Modern architects prefer to build exteriors designed with glass mainly from artistic or cost perspectives. Scientists, however, go one step further and see opportunities from its potential ability to harness solar energy. Researchers have thus explored ways to make solar cells transparent or semi-transparent as a substitute material for glass, but this has proven to be a challenging task because solar cells need to absorb sunlight to generate electricity, and when they are transparent, it reduces their energy efficiency.
Typical solar cells today are made of crystalline silicon, but it is difficult to make them translucent. Semi-transparent solar cells under development use, for example, organic or dye-sensitized materials, but compared to crystalline silicon-based cells, their power-conversion efficiencies are relatively low. Perovskites are hybrid organic-inorganic halide-based photovoltaic materials, which are cheap to produce and easy to manufacture. They have recently received much attention as the efficiency of perovskite solar cells has rapidly increased to the level of silicon technologies in the past few years.
Using perovskites, a Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and Professor Nam-Gyu Park of the Chemical Engineering School at Sungkyunkwan University developed a semi-transparent solar cell that is highly efficient and, additionally, functions very effectively as a thermal-mirror.
The team has developed a top transparent electrode (TTE) that works well with perovskite solar cells. In most cases, a key to success in realizing semi-transparent solar cells is to find a TTE that is compatible with a given photoactive material system, which is also the case for perovskite solar cells. The proposed TTE is based on a multilayer stack consisting of a metal film sandwiched between a high refractive-index (high-index) layer and an interfacial buffer layer. This TTE, placed as a top-most layer, can be prepared without damaging ingredients used in perovskite solar cells. Unlike conventional transparent electrodes focusing only on transmitting visible light, the proposed TTE plays the dual role of passing through visible light while reflecting infrared rays. The semi-transparent solar cells made with the proposed TTEs exhibited average power conversion efficiency as high as 13.3% with 85.5% infrared rejection.
The team believes that if the semi-transparent perovskite solar cells are scaled up for practical applications, they can be used in solar windows for buildings and automobiles, which not only generate electrical energy but also enable the smart heat management for indoor environments, thereby utilizing solar energy more efficiently and effectively.
This result was published as a cover article in the July 20, 2016 issue of Advanced Energy Materials. The research paper is entitled “Empowering Semi-transparent Solar Cells with Thermal-mirror Functionality.” (DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502466)
The team designed the transparent electrode (TE) stack in three layers: A thin-film of silver (Ag) is placed in between the bottom interfacial layer of molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) and the top high-index dielectric layer of zinc sulfide (ZnS). Such a tri-layer approach has been known as a means to increase the overall visible-light transmittance of metallic thin films via index matching technique, which is essentially the same technique used for anti-reflection coating of glasses except that the present case involves a metallic layer.
Traditionally, when a TE is based on a metal film, such as Ag, the film should be extremely thin, e.g., 7-12 nanometers (nm), to obtain transparency and, accordingly, to transmit visible light. However, the team took a different approach in this research. They made the Ag TE two or three times thicker (12-24 nm) than conventional metal films and, as a result, it reflected more infrared light. The high refractive index of the ZnS layer plays an essential role in keeping the visible light transmittance of the proposed TTE high even with the relatively thick Ag film when its thickness is carefully optimized for maximal destructive interference, leading to low reflectance (and thus high transmittance) within its visible light range.
The team confirmed the semi-transparent perovskite solar cell’s thermal-mirror function through an experiment in which a halogen lamp illuminated an object for five minutes through three mediums: a window of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and the proposed semi-transparent perovskite solar cell. An infrared (IR) camera took thermal images of the object as well as that of each window’s surface. The object’s temperature, when exposed through the glass window, rose to 36.8 Celsius degrees whereas both the tinting film and the cell allowed the object to remain below 27 Celsius degrees. The tinting film absorbs light to block solar energy, so the film’s surface became hot as it was continuously exposed to the lamp light, but the proposed semi-transparent solar cell stayed cool since it rejects solar heat energy by reflection, rather than by absorption. The total solar energy rejection (TSER) of the proposed cell was as high as 89.6%.
Professor Yoo of KAIST said, “The major contributions of this work are to find transparent electrode technology suitable for translucent perovskite cells and to provide a design approach to fully harness the potential it can further deliver as a heat mirror in addition to its main role as an electrode. The present work can be further fine-tuned to include colored solar cells and to incorporate flexible or rollable form factors, as they will allow for greater design freedom and thus offer more opportunities for them to be integrated into real-world objects and structures such as cars, buildings, and houses.”
The lead authors are Hoyeon Kim and Jaewon Ha, both Ph.D. candidates in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, and Hui-Seon Kim, a student in the School of Chemical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University. This research was supported mainly by the Climate Change Research Hub Program of KAIST.
Picture 1: Semi-transparent Perovskite Solar Cell
This picture shows a prototype of a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell with thermal-mirror functionality.
Picture 2: A Heat Rejection Performance Comparison Experiment
This picture presents thermal images taken by an infrared camera for comparing the heat rejection performance of bare glass, automotive tinting film, and a semi-transparent perovskite solar cell after being illuminated by a halogen lamp for five minutes.
2016.08.02 View 13369 -
 Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
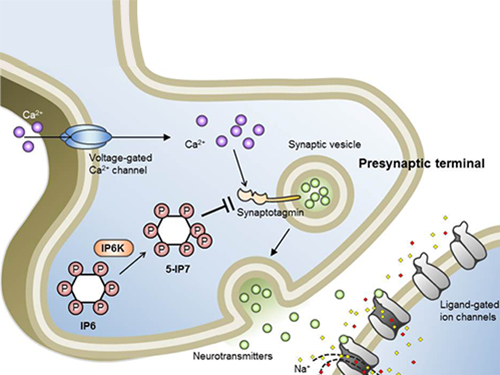
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12725
Professor Seyun Kim Identifies a Neuron Signal Controlling Molecule
A research team led by Professor Seyun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST has identified inositol pyrophosphates as the molecule that strongly controls neuron signaling via synaptotagmin.
Professors Tae-Young Yoon of Yonsei University’s Y-IBS and Sung-Hyun Kim of Kyung Hee University’s Department of Biomedical Science also joined the team.
The results were published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on June 30, 2016.
This interdisciplinary research project was conducted by six research teams from four different countries and covered a wide scope of academic fields, from neurobiology to super resolution optic imaging.
Inositol pyrophosphates such as 5-diphosphoinositol pentakisphos-phate (5-IP7), which naturally occur in corns and beans, are essential metabolites in the body. In particular, inositol hexakisphosphate (IP6) has anti-cancer properties and is thought to have an important role in cell signaling.
Inositol pentakisphosphate (IP7) differs from IP6 by having an additional phosphate group, which was first discovered 20 years ago. IP7 has recently been identified as playing a key role in diabetes and obesity.
Psychopathy and neurodegenerative diseases are known to result from the disrupted balance of inositol pyrophosphates. However, the role and the mechanism of action of IP7 in brain neurons and nerve transmission remained unknown.
Professor Kim’s team has worked on inositol pyrophosphates for several years and discovered that very small quantities of IP7 control cell-signaling transduction. Professor Yoon of Yonsei University identified IP7 as a much stronger inhibitor of neuron signaling compared to IP6. In particular, IP7 directly suppresses synaptotagmin, one of the key proteins in neuron signaling. Moreover, Professor Kim of Kyung Hee University observed IP7 inhibition in sea horse neurons.
Together, the joint research team identified inositol pyrophosphates as the key switch metabolite of brain-signaling transduction.
The researchers hope that future research on synaptotagmin and IP7 will reveal the mechanism of neuron-signal transduction and thus enable the treatment of neurological disorders.
These research findings were the result of cooperation of various science and technology institutes: KAIST, Yonsei-IBS (Institute for Basic Science), Kyung Hee University, Sungkyunkwan University, KIST, University of Zurich in Switzerland, and Albert-Ludwigs-University Freiburg in Germany.
Schematic Image of Controlling the Synaptic Exocytotic Pathway by 5-IP7 , Helping the Understanding of the Signaling Mechanisms of Inositol Pyrophosphates
2016.07.21 View 12725 -
 ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 9290
ICISTS Hosts the International Interdisciplinary Conference
A KAIST student organization, The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology and Society (ICISTS), will host ICISTS 2016 at the Hotel ICC in Daejeon from 3 to 7 August with the participation of around 300 Korean and international students.
ICISTS was first established in 2005 to provide an annual platform for delegates and speakers to discuss the integration and the convergence of science, technology, and society regardless of their academic backgrounds.
This year’s conference, with the theme of “Beyond the Center,” emphasizes the ways in which technological advancements can change central organizations in areas such as financial technology, healthcare, and global governance.
The keynote speakers include Dennis Hong, a developer of the first automobile for the blind and a professor of the Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering Department at UCLA, Dor Konforty, a founder and a CEO of SNS platform Synereo, and Marzena Rostek, a professor of Economics at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Other notable speakers include: Gi-Jung Jung, Head of the National Fusion Research Institute; Janos Barberis, Founder of FinTech HK; Tae-Hoon Kim, CEO and Founder of Rainist; Gulrez Shah Azhar, Assistant Policy Analyst at RAND Corporation; Thomas Concannon, Senior Policy Researcher at RAND Corporation; Leah Vriesman, Professor at the School of Public Health, UCLA; and Bjorn Cumps, Professor of Management Practice at Vlerick Business School in Belgium.
The conference consists of keynote speeches, panel discussions, open talks, experience sessions, team project presentations, a culture night, and a beer party, at which all participants will be encouraged to interact with speakers and delegates and to discuss the topics of their interest.
Han-Kyul Jung, ICISTS’s Head of Public Relations, said, “This conference will not only allow the delegates to understand the trends of future technology, but also be an opportunity for KAIST students to form valuable contacts with students from around the world.”
For more information, please go to www.icists.org.
2016.07.20 View 9290 -
 Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
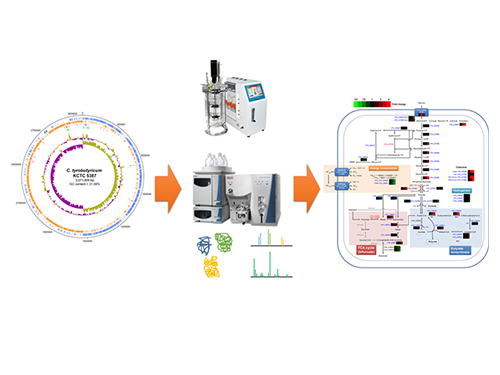
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 11484
Unveiling the Distinctive Features of Industrial Microorganism
KAIST researchers have sequenced the whole genome of Clostridium tyrobutyricum, which has a higher tolerance to toxic chemicals, such as 1-butanol, compared to other clostridial bacterial strains.
Clostridium tyrobutyricum, a Gram-positive, anaerobic spore-forming bacterium, is considered a promising industrial host strain for the production of various chemicals including butyric acid which has many applications in different industries such as a precursor to biofuels. Despite such potential, C. tyrobutyricum has received little attention, mainly due to a limited understanding of its genotypic and metabolic characteristics at the genome level.
A Korean research team headed by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) deciphered the genome sequence of C. tyrobutyricum and its proteome profiles during the course of batch fermentation. As a result, the research team learned that the bacterium is not only capable of producing a large amount of butyric acid but also can tolerate toxic compounds such as 1-butanol. The research results were published in mBio on June 14, 2016.
The team adopted a genoproteomic approach, combining genomics and proteomics, to investigate the metabolic features of C. tyrobutyricum. Unlike Clostridium acetobutylicum, the most widely used organism for 1-butanol production, C. tyrobutyricum has a novel butyrate-producing pathway and various mechanisms for energy conservation under anaerobic conditions. The expression of various metabolic genes, including those involved in butyrate formation, was analyzed using the “shotgun” proteome approach.
To date, the bio-based production of 1-butanol, a next-generation biofuel, has relied on several clostridial hosts including C. acetobutylicum and C. beijerinckii. However, these organisms have a low tolerance against 1-butanol even though they are naturally capable of producing it. C. tyrobutyricum cannot produce 1-butanol itself, but has a higher 1-butanol-tolerance and rapid uptake of monosaccharides, compared to those two species.
The team identified most of the genes involved in the central metabolism of C. tyrobutyricum from the whole-genome and shotgun proteome data, and this study will accelerate the bacterium’s engineering to produce useful chemicals including butyric acid and 1-butanol, replacing traditional bacterial hosts.
Professor Lee said,
“The unique metabolic features and energy conservation mechanisms of C. tyrobutyricum can be employed in the various microbial hosts we have previously developed to further improve their productivity and yield. Moreover, findings on C. tyrobutyricum revealed by this study will be the first step to directly engineer this bacterium.”
Director Jin-Woo Kim at the Platform Technology Division of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, who oversees the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change, said,
“Over the years, Professor Lee’s team has researched the development of a bio-refinery system to produce natural and non-natural chemicals with the systems metabolic engineering of microorganisms. They were able to design strategies for the development of diverse industrial microbial strains to produce useful chemicals from inedible biomass-based carbon dioxide fixation. We believe the efficient production of butyric acid using a metabolic engineering approach will play an important role in the establishment of a bioprocess for chemical production.”
The title of the research paper is “Deciphering Clostridium tyrobutyricum Metabolism Based on the Who-Genome Sequence and Proteome Analyses.” (DOI: 10.1128/mBio.00743-16)
The lead authors are Joungmin Lee, a post-doctoral fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working in CJ CheilJedang Research Institute; Yu-Sin Jang, a research fellow in the BioProcess Research Center at KAIST, currently working at Gyeongsang National University as an assistant professor; and Mee-Jung Han, an assistant professor in the Environmental Engineering and Energy Department at Dongyang University. Jin Young Kim, a senior researcher at the Korea Basic Science Institute, also participated in the research.
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change’s research project entitled “Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries” from the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556).
Schematic Diagram of C. tyrobutyricum’s Genome Sequence and Its Proteome Profiles
The picture below shows the complete genome sequence, global protein expression profiles, and the genome-based metabolic characteristics during batch fermentation of C. tyrobutyricum.
2016.06.20 View 11484 -
 Meditox Donates 600 Million KRW Scholarship
On February 17, a Korean biopharmaceutical company Meditox, headed by Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Hyun-Ho Jeong, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with KAIST to establish the “Meditox Fellowship” and donated a total of 600 million Korean won (KRW) to the university to assist in promoting more scientists in the field of biology.
Meditox CEO Hyun-Ho Jeong, KAIST President Steve Kang, Dean of Life Science and Bioengineering College Jung-Hoe Kim, and Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences Byung-Ha Oh participated in the agreement ceremony.
According to the MOU, Meditox will donate 60,000,000 KRW over a ten year period, from which KAIST can draw on to grant scholarships for master’s and doctoral students.
The “Meditox Fellowship” will support promising and enthusiastic students whose finances limit their studies. The first scholarship students for 2016 were: Kwang-Uk Min, In-suk Yeo, Sung-ryung- Lee, Si-on Lee, and Jung-hyun Kim.
Meditox CEO Jeong, who graduated from KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, said, "I felt it was important to start the Meditox Fellowship at my alma mater to contribute to the cultivation of outstanding scientists in the field of biological sciences."
He also said that he would plan to launch projects that aim to support not only those who receive the scholarship but also the development of Korea’s biological sciences in general.
President Steve Kang (right) and Chief Executive Officer Hyun-Ho Jeong (left) of Meditox hold the signed memorandum of understanding together.
2016.02.18 View 11427
Meditox Donates 600 Million KRW Scholarship
On February 17, a Korean biopharmaceutical company Meditox, headed by Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Hyun-Ho Jeong, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with KAIST to establish the “Meditox Fellowship” and donated a total of 600 million Korean won (KRW) to the university to assist in promoting more scientists in the field of biology.
Meditox CEO Hyun-Ho Jeong, KAIST President Steve Kang, Dean of Life Science and Bioengineering College Jung-Hoe Kim, and Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences Byung-Ha Oh participated in the agreement ceremony.
According to the MOU, Meditox will donate 60,000,000 KRW over a ten year period, from which KAIST can draw on to grant scholarships for master’s and doctoral students.
The “Meditox Fellowship” will support promising and enthusiastic students whose finances limit their studies. The first scholarship students for 2016 were: Kwang-Uk Min, In-suk Yeo, Sung-ryung- Lee, Si-on Lee, and Jung-hyun Kim.
Meditox CEO Jeong, who graduated from KAIST’s Department of Biological Sciences, said, "I felt it was important to start the Meditox Fellowship at my alma mater to contribute to the cultivation of outstanding scientists in the field of biological sciences."
He also said that he would plan to launch projects that aim to support not only those who receive the scholarship but also the development of Korea’s biological sciences in general.
President Steve Kang (right) and Chief Executive Officer Hyun-Ho Jeong (left) of Meditox hold the signed memorandum of understanding together.
2016.02.18 View 11427 -
 Symposium on Creative Education
KAIST and the Korea Society for Creativity and Application (KSCA) co-hosted a symposium on creative education on January 21, 2016 at the KAIST Business and Management College in Seoul. Along with the symposium, the two organizations also held the Korea "Theory of Inventive Problem Solving" (TRIZ) Festival 2016.
Around 200 experts from academia, industry, and research including Dong-Suk Kim, Dean of the KAIST College of Business and Management and Gui-Chan Park, Director of POSCO Group Academy, attended the symposium.
The event was organized to celebrate the foundation of KSCA and to increase social awareness of creative education and design-related thinking with a "TRIZ approach."
"TRIZ" stands for the “Theory of Inventive Problem Solving” in Russian. It is a problem-solving method based on logic and data, not intuition, which accelerates the project team’s ability to work out issues creatively. The "TRIZ approach" has been widely used among Korean companies including Samsung, LG, and POSCO as a means of boosting employees’ creativity.
The academic symposium was divided into a keynote speech, paper presentations from each field, and a poster fair.
Professor Dae-Sik Kim from KAIST delivered a keynote speech on “Neuroscience and Creativity,” offering a glimpse of the world from a neuroscience perspective. Jae-min Lee, a researcher at Samsung Electronics, provided an industrial case study, “Application of TRIZ for the Improvement of Refrigerator.” Professor Jung-Seok Hyun from Jeju University and Dr. Jung-Ho Shin from E-Triz System presented their application of TRIZ on “Limitless Imagination and Invention Class for the Elementary School Students.” Altogether, 36 other research papers and case studies were presented at the symposium.
Dr. Dong-ryul Yang, President of KSCA, said, “This academic symposium allows us to discuss a range of innovative case studies that utilize TRIZ in industrial and educational fields, from which we can learn good lessons and practices.”
2016.01.19 View 7357
Symposium on Creative Education
KAIST and the Korea Society for Creativity and Application (KSCA) co-hosted a symposium on creative education on January 21, 2016 at the KAIST Business and Management College in Seoul. Along with the symposium, the two organizations also held the Korea "Theory of Inventive Problem Solving" (TRIZ) Festival 2016.
Around 200 experts from academia, industry, and research including Dong-Suk Kim, Dean of the KAIST College of Business and Management and Gui-Chan Park, Director of POSCO Group Academy, attended the symposium.
The event was organized to celebrate the foundation of KSCA and to increase social awareness of creative education and design-related thinking with a "TRIZ approach."
"TRIZ" stands for the “Theory of Inventive Problem Solving” in Russian. It is a problem-solving method based on logic and data, not intuition, which accelerates the project team’s ability to work out issues creatively. The "TRIZ approach" has been widely used among Korean companies including Samsung, LG, and POSCO as a means of boosting employees’ creativity.
The academic symposium was divided into a keynote speech, paper presentations from each field, and a poster fair.
Professor Dae-Sik Kim from KAIST delivered a keynote speech on “Neuroscience and Creativity,” offering a glimpse of the world from a neuroscience perspective. Jae-min Lee, a researcher at Samsung Electronics, provided an industrial case study, “Application of TRIZ for the Improvement of Refrigerator.” Professor Jung-Seok Hyun from Jeju University and Dr. Jung-Ho Shin from E-Triz System presented their application of TRIZ on “Limitless Imagination and Invention Class for the Elementary School Students.” Altogether, 36 other research papers and case studies were presented at the symposium.
Dr. Dong-ryul Yang, President of KSCA, said, “This academic symposium allows us to discuss a range of innovative case studies that utilize TRIZ in industrial and educational fields, from which we can learn good lessons and practices.”
2016.01.19 View 7357 -
 Public Forum on the Development of High-Performance Supercomputing System
KAIST hosted a public forum on the development of high-performance supercomputing systems at the K Hotel in Seoul on December 17, 2015.
About 100 participants attended the forum, including Steve Kang, the President of KAIST; Jae-Moon Park, the Director General of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea; Sun-Hwa Hahn, the President of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information; Sang-Gyu Park, the Director of the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute; Soon-Chill Lee, the Dean of KAIST’s Natural Sciences College; Jangwoo Kim, the Professor of Computer Science and Engineering of Pohang University of Science and Technology; and Kyung-Hak Suh, the Director of Convergence Technology Division at the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Also attending the forum were representatives from the private sector, including Sung-Soon Park, the President of Gluesys; Myung-Chul Lee, the Director of IMB Korea; Jin-Hyun Choi, the President of Cray Korea; and Chung-Gun Yoo, the Director of HP Korea.
KAIST created the High-performance Computing Development Forum in July this year. Since then, the forum has held four conferences and workshops to discuss issues related to the growth of supercomputing power in Korea.
This public forum consisted of a keynote speech on the “Policy Proposal for the Development of Supercomputers” by Professor Hyuk-Jae Lee of the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at Seoul National University and panel discussions presided over by President Kang on the topic of “Development and Implementation Strategies to Build Korean Supercomputers.”
President Kang said, “I hope this public forum can serve as a place for designing the future of Korean supercomputers, and what we have discussed at the forum will be duly delivered to the government to help them develop policies necessary to build the computers.”
2015.12.16 View 8467
Public Forum on the Development of High-Performance Supercomputing System
KAIST hosted a public forum on the development of high-performance supercomputing systems at the K Hotel in Seoul on December 17, 2015.
About 100 participants attended the forum, including Steve Kang, the President of KAIST; Jae-Moon Park, the Director General of Science, ICT and Future Planning of the Republic of Korea; Sun-Hwa Hahn, the President of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information; Sang-Gyu Park, the Director of the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute; Soon-Chill Lee, the Dean of KAIST’s Natural Sciences College; Jangwoo Kim, the Professor of Computer Science and Engineering of Pohang University of Science and Technology; and Kyung-Hak Suh, the Director of Convergence Technology Division at the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Also attending the forum were representatives from the private sector, including Sung-Soon Park, the President of Gluesys; Myung-Chul Lee, the Director of IMB Korea; Jin-Hyun Choi, the President of Cray Korea; and Chung-Gun Yoo, the Director of HP Korea.
KAIST created the High-performance Computing Development Forum in July this year. Since then, the forum has held four conferences and workshops to discuss issues related to the growth of supercomputing power in Korea.
This public forum consisted of a keynote speech on the “Policy Proposal for the Development of Supercomputers” by Professor Hyuk-Jae Lee of the Electrical and Computer Engineering Department at Seoul National University and panel discussions presided over by President Kang on the topic of “Development and Implementation Strategies to Build Korean Supercomputers.”
President Kang said, “I hope this public forum can serve as a place for designing the future of Korean supercomputers, and what we have discussed at the forum will be duly delivered to the government to help them develop policies necessary to build the computers.”
2015.12.16 View 8467 -
 The Final Presentation of the 2015 Interdisciplinary Convergence Capstone Design Takes Place on Campus
The final presentation of the 2015 Interdisciplinary Convergence Capstone Design took place in the lobby of the Creative Lecture Hall on December 11, 2015.
Started in the spring of 2014, the capstone design course offers KAIST’s undergraduate students an opportunity to explore solutions, based on their learning from coursework, to real and important industry and engineering problems.
In the class, five students with different majors form a team to discuss and identify what are the problems of a certain company’s products, the causes, and possible design solutions for such problems. After reaching a conclusion, students then manufacture a prototype to address the problems.
In this presentation, six teams introduced their research topic and subsequently, demonstrated their trial products.
Sung-Hyun Cho, a student majoring in Mechanical Engineering, presented the “Designing a Robot System for Automatic Collection of Radio Maps,” and Jong-Yong Do, also majoring in Mechanical Engineering, showcased his “Sleeping Pattern Measurement Pad.” Topics such as noise measurement, haptic handles, wrinkle improvements by micro-needling, and fingerprint scanners were also discussed.
Students who developed these techniques have already finished patent applications, and interested companies are planning to commercialize the techniques after evaluating their marketability.
Recently, there were concerns in Korea that engineering students were overly interested in the publication of research papers due to the paper-based evaluation of research outcomes. In response, KAIST has emphasized a more field-centered education to help students gain insightful perspective to real issues in science and engineering.
Wan-Su Kim, a student in the Mechanical Engineering Department said that “this course provided me with an invaluable experience to apply engineering principles that I’ve learned from class to the actual field, while sharing ideas and solutions with other students.”
Professors Su-Kyung Park and Ik-Jin Lee of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, Professor Yu-Chun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Dong-Su Han of the School of Computing, and Professor Jun-Bo Youn of the School of Electrical Engineering participated in the course as advisers.
2015.12.11 View 7917
The Final Presentation of the 2015 Interdisciplinary Convergence Capstone Design Takes Place on Campus
The final presentation of the 2015 Interdisciplinary Convergence Capstone Design took place in the lobby of the Creative Lecture Hall on December 11, 2015.
Started in the spring of 2014, the capstone design course offers KAIST’s undergraduate students an opportunity to explore solutions, based on their learning from coursework, to real and important industry and engineering problems.
In the class, five students with different majors form a team to discuss and identify what are the problems of a certain company’s products, the causes, and possible design solutions for such problems. After reaching a conclusion, students then manufacture a prototype to address the problems.
In this presentation, six teams introduced their research topic and subsequently, demonstrated their trial products.
Sung-Hyun Cho, a student majoring in Mechanical Engineering, presented the “Designing a Robot System for Automatic Collection of Radio Maps,” and Jong-Yong Do, also majoring in Mechanical Engineering, showcased his “Sleeping Pattern Measurement Pad.” Topics such as noise measurement, haptic handles, wrinkle improvements by micro-needling, and fingerprint scanners were also discussed.
Students who developed these techniques have already finished patent applications, and interested companies are planning to commercialize the techniques after evaluating their marketability.
Recently, there were concerns in Korea that engineering students were overly interested in the publication of research papers due to the paper-based evaluation of research outcomes. In response, KAIST has emphasized a more field-centered education to help students gain insightful perspective to real issues in science and engineering.
Wan-Su Kim, a student in the Mechanical Engineering Department said that “this course provided me with an invaluable experience to apply engineering principles that I’ve learned from class to the actual field, while sharing ideas and solutions with other students.”
Professors Su-Kyung Park and Ik-Jin Lee of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae of the Department of Industrial Design, Professor Yu-Chun Kim of the Department of Biological Sciences, Professor Dong-Su Han of the School of Computing, and Professor Jun-Bo Youn of the School of Electrical Engineering participated in the course as advisers.
2015.12.11 View 7917 -
 KAIST Holds Its Fourth Public Art Exhibition
KAIST hosted an opening ceremony for the annual art exhibition on December 3, 2015 at the KAIST Institute building. The KAIST Art and Design Committee first organized the event in 2012 to promote the integration of art and technology.
This year’s event entitled “Understanding the Purpose of an Object” will display 20 art pieces under six themes. Artist Keumhong Lee, Haeyool Roh, Joon Kim, Kyung Lee, and Juhae Yang participated in the exhibition. The names of some of the art pieces include “Feedback Field” by Joon Kim, “Self Action” by Haeyool Roh, and “Net of Time” by Juhae Yang.
Juhae Yang believes that, in the digital age, an identity of an object is defined by the traces of light which we read in the information hidden in the barcodes. Based on this interpretation, she transforms the black bars and white spaces into a harmony of colors and sounds. The continuum of colors and sounds in her work arouses time-space synesthesia.
Professor Sangmin Bae of the Industrial Design Department, the Director of the KAIST Art and Design Committee, hopes that the exhibition will inspire novel scientific ideas and artistic spirits.
The exhibition will remain open to the public until December 20, 2015.
2015.12.03 View 9932
KAIST Holds Its Fourth Public Art Exhibition
KAIST hosted an opening ceremony for the annual art exhibition on December 3, 2015 at the KAIST Institute building. The KAIST Art and Design Committee first organized the event in 2012 to promote the integration of art and technology.
This year’s event entitled “Understanding the Purpose of an Object” will display 20 art pieces under six themes. Artist Keumhong Lee, Haeyool Roh, Joon Kim, Kyung Lee, and Juhae Yang participated in the exhibition. The names of some of the art pieces include “Feedback Field” by Joon Kim, “Self Action” by Haeyool Roh, and “Net of Time” by Juhae Yang.
Juhae Yang believes that, in the digital age, an identity of an object is defined by the traces of light which we read in the information hidden in the barcodes. Based on this interpretation, she transforms the black bars and white spaces into a harmony of colors and sounds. The continuum of colors and sounds in her work arouses time-space synesthesia.
Professor Sangmin Bae of the Industrial Design Department, the Director of the KAIST Art and Design Committee, hopes that the exhibition will inspire novel scientific ideas and artistic spirits.
The exhibition will remain open to the public until December 20, 2015.
2015.12.03 View 9932 -
 More Donations Arrive to Establish the New Medicine Research and Development Center on Campus
A raft of businesses continues to make donations to establish a new medicine research and development center on campus. The Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST is leading the fundraising campaign.
On November 9, 2015, Nikon Instruments Korea Co., Ltd. contributed USD 8,500 to the fundraising, followed by Carl Zeiss AG and Three-Shine Inc., which donated USD 12,800 and 8,500, respectively.
Bruno Lin, an Executive Director at Carl Zeiss AG in Korea, said, “I’m very glad to participate in this fundraising initiative for the Biological Sciences Department at KAIST, one rapidly reaching out to the world.”
From the left in the picture are Vice President Tae-Hoon Kim, Director Gyu-Hyeok Lee, and Executive Director Bruno Lin of Carl Zeiss AG, Byung-Ha Oh, Dean of the Biological Sciences Department, and Professor Eunjoon Kim.
From the left in the picture are Byung-Ha Oh, Dean of the Biological Sciences Department, President Chun-Gui Park of Three-Shine Inc., and Professor Daesoo Kim.
President Chun of Three-Shine Inc., said, “We hope that the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, aided by the construction of new research center, will produce practical research achievements and stand on the frontier of new medicine development research in Korea.”
The New Medicine Research and Development Center will be equipped with state-of-the-art, purpose-built research facilities to support convergent, interdisciplinary research in biomedicine.
2015.11.27 View 8535
More Donations Arrive to Establish the New Medicine Research and Development Center on Campus
A raft of businesses continues to make donations to establish a new medicine research and development center on campus. The Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST is leading the fundraising campaign.
On November 9, 2015, Nikon Instruments Korea Co., Ltd. contributed USD 8,500 to the fundraising, followed by Carl Zeiss AG and Three-Shine Inc., which donated USD 12,800 and 8,500, respectively.
Bruno Lin, an Executive Director at Carl Zeiss AG in Korea, said, “I’m very glad to participate in this fundraising initiative for the Biological Sciences Department at KAIST, one rapidly reaching out to the world.”
From the left in the picture are Vice President Tae-Hoon Kim, Director Gyu-Hyeok Lee, and Executive Director Bruno Lin of Carl Zeiss AG, Byung-Ha Oh, Dean of the Biological Sciences Department, and Professor Eunjoon Kim.
From the left in the picture are Byung-Ha Oh, Dean of the Biological Sciences Department, President Chun-Gui Park of Three-Shine Inc., and Professor Daesoo Kim.
President Chun of Three-Shine Inc., said, “We hope that the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, aided by the construction of new research center, will produce practical research achievements and stand on the frontier of new medicine development research in Korea.”
The New Medicine Research and Development Center will be equipped with state-of-the-art, purpose-built research facilities to support convergent, interdisciplinary research in biomedicine.
2015.11.27 View 8535