AND
-
 Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10960
Professor Hojong Chang’s Research Team Wins ISIITA 2020 Best Paper Award
The paper written by Professor Hojong Chang’s research team from KAIST Institute for IT Convergence won the best paper award from the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology Application (ISIITA) 2020, held this month at Ton Duc Thang University in Vietnam.
ISIITA is a networking symposium where leading researchers from various fields including information and communications, biotechnology, and computer systems come together and share on the convergence of technology.
Professor Chang’s team won the best paper award at this year’s symposium with its paper, “A Study of Single Photon Counting System for Quantitative Analysis of Luminescence”. The awarded paper discusses the realization of a signal processing system for silicon photomultipliers.
The silicon photomultiplier is the core of a urinalysis technique that tests for sodium and potassium in the body using simple chemical reactions. If our bodily sodium and potassium levels exceed a certain amount, it can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular problems, and kidney damage.
Through this research, the team has developed a core technique that quantifies the sodium and potassium discharged in the urine. When the reagent is injected into the urine, a very small amount of light is emitted as a result of the chemical reaction. However, if there is a large amount of sodium and potassium, they interrupt the reaction and reduce the emission. The key to this measurement technique is digitizing the strength of this very fine emission of light. Professor Chang’s team developed a system that uses a photomultiplier to measure the chemiluminescence.
Professor Chang said, “I look forward for this signal processing system greatly helping to prevent diseases caused by the excessive consumption of sodium and potassium through quick and easy detection.”
Researcher Byunghun Han who carried out the central research for the system design added, “We are planning to focus on miniaturizing the developed technique, so that anyone can carry our device around like a cellphone.”
The research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(END)
2020.02.27 View 10960 -
 Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11509
Professor Jong Chul Ye Appointed as Distinguished Lecturer of IEEE EMBS
Professor Jong Chul Ye from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was appointed as a distinguished lecturer by the International Association of Electrical and Electronic Engineers (IEEE) Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS). Professor Ye was invited to deliver a lecture on his leading research on artificial intelligence (AI) technology in medical video restoration. He will serve a term of two years beginning in 2020.
IEEE EMBS's distinguished lecturer program is designed to educate researchers around the world on the latest trends and technology in biomedical engineering. Sponsored by IEEE, its members can attend lectures on the distinguished professor's research subject.
Professor Ye said, "We are at a time where the importance of AI in medical imaging is increasing.” He added, “I am proud to be appointed as a distinguished lecturer of the IEEE EMBS in recognition of my contributions to this field.”
(END)
2020.02.27 View 11509 -
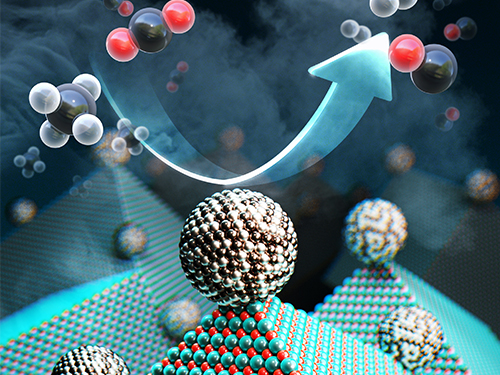 New Catalyst Recycles Greenhouse Gases into Fuel and Hydrogen Gas
< Professor Cafer T. Yavuz (left), PhD Candidate Youngdong Song (center), and Researcher Sreerangappa Ramesh (right) >
Scientists have taken a major step toward a circular carbon economy by developing a long-lasting, economical catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas, and other chemicals. The results could be revolutionary in the effort to reverse global warming, according to the researchers. The study was published on February 14 in Science.
“We set out to develop an effective catalyst that can convert large amounts of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane without failure,” said Cafer T. Yavuz, paper author and associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry at KAIST.
The catalyst, made from inexpensive and abundant nickel, magnesium, and molybdenum, initiates and speeds up the rate of reaction that converts carbon dioxide and methane into hydrogen gas. It can work efficiently for more than a month.
This conversion is called ‘dry reforming’, where harmful gases, such as carbon dioxide, are processed to produce more useful chemicals that could be refined for use in fuel, plastics, or even pharmaceuticals. It is an effective process, but it previously required rare and expensive metals such as platinum and rhodium to induce a brief and inefficient chemical reaction.
Other researchers had previously proposed nickel as a more economical solution, but carbon byproducts would build up and the surface nanoparticles would bind together on the cheaper metal, fundamentally changing the composition and geometry of the catalyst and rendering it useless.
“The difficulty arises from the lack of control on scores of active sites over the bulky catalysts surfaces because any refinement procedures attempted also change the nature of the catalyst itself,” Yavuz said.
The researchers produced nickel-molybdenum nanoparticles under a reductive environment in the presence of a single crystalline magnesium oxide. As the ingredients were heated under reactive gas, the nanoparticles moved on the pristine crystal surface seeking anchoring points. The resulting activated catalyst sealed its own high-energy active sites and permanently fixed the location of the nanoparticles — meaning that the nickel-based catalyst will not have a carbon build up, nor will the surface particles bind to one another.
“It took us almost a year to understand the underlying mechanism,” said first author Youngdong Song, a graduate student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. “Once we studied all the chemical events in detail, we were shocked.”
The researchers dubbed the catalyst Nanocatalysts on Single Crystal Edges (NOSCE). The magnesium-oxide nanopowder comes from a finely structured form of magnesium oxide, where the molecules bind continuously to the edge. There are no breaks or defects in the surface, allowing for uniform and predictable reactions.
“Our study solves a number of challenges the catalyst community faces,” Yavuz said. “We believe the NOSCE mechanism will improve other inefficient catalytic reactions and provide even further savings of greenhouse gas emissions.”
This work was supported, in part, by the Saudi-Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Other contributors include Ercan Ozdemir, Sreerangappa Ramesh, Aldiar Adishev, and Saravanan Subramanian, all of whom are affiliated with the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability at KAIST; Aadesh Harale, Mohammed Albuali, Bandar Abdullah Fadhel, and Aqil Jamal, all of whom are with the Research and Development Center in Saudi Arabia; and Dohyun Moon and Sun Hee Choi, both of whom are with the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. Ozdemir is also affiliated with the Institute of Nanotechnology at the Gebze Technical University in Turkey; Fadhel and Jamal are also affiliated with the Saudi-Armco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea.
<Newly developed catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas and other chemicals.>
Publication:
Song et al. (2020) Dry reforming of methane by stable Ni–Mo nanocatalysts on single-crystalline MgO. Science, Vol. 367, Issue 6479, pp. 777-781. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aav2412
Profile: Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, MA, PhD
yavuz@kaist.ac.kr
http://yavuz.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Oxide and Organic Nanomaterials for the Environment (ONE) Laboratory
Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Youngdong Song ydsong88@kaist.ac.kr
Ph.D. Candidate
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.17 View 18094
New Catalyst Recycles Greenhouse Gases into Fuel and Hydrogen Gas
< Professor Cafer T. Yavuz (left), PhD Candidate Youngdong Song (center), and Researcher Sreerangappa Ramesh (right) >
Scientists have taken a major step toward a circular carbon economy by developing a long-lasting, economical catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas, and other chemicals. The results could be revolutionary in the effort to reverse global warming, according to the researchers. The study was published on February 14 in Science.
“We set out to develop an effective catalyst that can convert large amounts of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane without failure,” said Cafer T. Yavuz, paper author and associate professor of chemical and biomolecular engineering and of chemistry at KAIST.
The catalyst, made from inexpensive and abundant nickel, magnesium, and molybdenum, initiates and speeds up the rate of reaction that converts carbon dioxide and methane into hydrogen gas. It can work efficiently for more than a month.
This conversion is called ‘dry reforming’, where harmful gases, such as carbon dioxide, are processed to produce more useful chemicals that could be refined for use in fuel, plastics, or even pharmaceuticals. It is an effective process, but it previously required rare and expensive metals such as platinum and rhodium to induce a brief and inefficient chemical reaction.
Other researchers had previously proposed nickel as a more economical solution, but carbon byproducts would build up and the surface nanoparticles would bind together on the cheaper metal, fundamentally changing the composition and geometry of the catalyst and rendering it useless.
“The difficulty arises from the lack of control on scores of active sites over the bulky catalysts surfaces because any refinement procedures attempted also change the nature of the catalyst itself,” Yavuz said.
The researchers produced nickel-molybdenum nanoparticles under a reductive environment in the presence of a single crystalline magnesium oxide. As the ingredients were heated under reactive gas, the nanoparticles moved on the pristine crystal surface seeking anchoring points. The resulting activated catalyst sealed its own high-energy active sites and permanently fixed the location of the nanoparticles — meaning that the nickel-based catalyst will not have a carbon build up, nor will the surface particles bind to one another.
“It took us almost a year to understand the underlying mechanism,” said first author Youngdong Song, a graduate student in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST. “Once we studied all the chemical events in detail, we were shocked.”
The researchers dubbed the catalyst Nanocatalysts on Single Crystal Edges (NOSCE). The magnesium-oxide nanopowder comes from a finely structured form of magnesium oxide, where the molecules bind continuously to the edge. There are no breaks or defects in the surface, allowing for uniform and predictable reactions.
“Our study solves a number of challenges the catalyst community faces,” Yavuz said. “We believe the NOSCE mechanism will improve other inefficient catalytic reactions and provide even further savings of greenhouse gas emissions.”
This work was supported, in part, by the Saudi-Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Other contributors include Ercan Ozdemir, Sreerangappa Ramesh, Aldiar Adishev, and Saravanan Subramanian, all of whom are affiliated with the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability at KAIST; Aadesh Harale, Mohammed Albuali, Bandar Abdullah Fadhel, and Aqil Jamal, all of whom are with the Research and Development Center in Saudi Arabia; and Dohyun Moon and Sun Hee Choi, both of whom are with the Pohang Accelerator Laboratory in Korea. Ozdemir is also affiliated with the Institute of Nanotechnology at the Gebze Technical University in Turkey; Fadhel and Jamal are also affiliated with the Saudi-Armco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea.
<Newly developed catalyst that recycles greenhouse gases into ingredients that can be used in fuel, hydrogen gas and other chemicals.>
Publication:
Song et al. (2020) Dry reforming of methane by stable Ni–Mo nanocatalysts on single-crystalline MgO. Science, Vol. 367, Issue 6479, pp. 777-781. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.aav2412
Profile: Prof. Cafer T. Yavuz, MA, PhD
yavuz@kaist.ac.kr
http://yavuz.kaist.ac.kr/
Associate Professor
Oxide and Organic Nanomaterials for the Environment (ONE) Laboratory
Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Youngdong Song ydsong88@kaist.ac.kr
Ph.D. Candidate
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.17 View 18094 -
 What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 15309
What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 15309 -
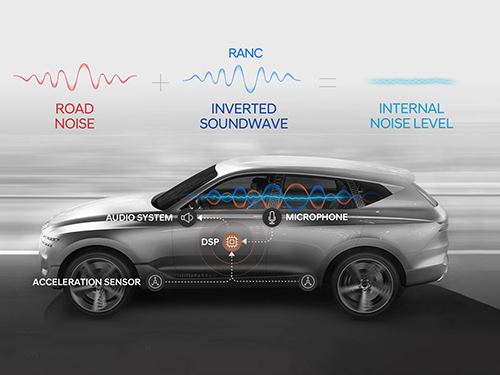 A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 12295
A System Controlling Road Active Noise to Hit the Road
The research team led by Professor Youngjin Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a road noise active noise control (RANC) system to be commercialized in partnership with Hyundai Motor Group.
On December 11, Hyundai Motor Group announced the successful development of the RANC system, which significantly reduces the road noise flowing into cars. The carmaker has completed the domestic and American patent applications for the location of sensors and the signal selection method, the core technology of RANC.
RANC is a technology for reducing road noise during driving. This system consists of an acceleration sensor, digital signal processor (the control computer to analyze sound signals), microphone, amplifier, and audio system. To make the system as simple as possible, the audio system utilizes the original audio system embedded in the car instead of a separate system.
The acceleration sensor first calculates the vibration from the road into the car. The location of the sensor is important for accurately identifying the vibration path. The research team was able to find the optimal sensor location through a number of tests.
The System Dynamics and Applied Control Laboratory of Professor Park researched ways to significantly reduce road noise with Hyundai Motor Group for four years from 1993 as a G7 national project and published the results in international journals. In 2002, the researchers published an article titled “Noise Quietens Driving” in Nature, where they announced the first success in reducing road noise in actual cars. The achievement did not lead to commercialization, however, due to the lack of auxiliary technologies at the time, digital amplifiers and DSP for cars for example, and pricing issues.
Since 2013, Professor Park’s research team has participated in one technology transfer and eight university-industry projects. Based on these efforts, the team was able to successfully develop the RANC system with domestic technology in partnership with Hyundai’s NVH Research Lab (Research Fellow, Dr. Gangdeok Lee; Ph.D. in aviation engineering, 1996), Optomech (Founder, Professor Gyeongsu Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1999), ARE (CEO Hyeonseok Kim; Ph.D. in mechanical engineering, 1998), WeAcom, and BurnYoung.
Professor Park’s team led the project by performing theory-based research during the commercialization stage in collaboration with Hyundai Motor Group.
For the commercialization of the RANC system, Hyundai Motor Group is planning to collaborate with the global car audio company Harman to increase the degree of completion and apply the RANC system to the GV 80, the first SUV model of the Genesis brand.
“I am very delighted as an engineer to see the research I worked on from my early days at KAIST be commercialized after 20 years,” noted Professor Park. “I am thrilled to make a contribution to such commercialization with my students in my lab.”
2019.12.27 View 12295 -
 KAIST GSAI and SNUBH Join Hands for AI in Healthcare
< Dean Song Chong (left) and Director Chang Wan Oh (right)
at the KAIST GSAI - SNUBH MOU Signing Ceremony >
The Graduate School of AI (GSAI) at KAIST and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to cooperate in AI education and research in the field of healthcare last month. The two institutions have agreed to collaborate on research and technology development through the implementation of academic and personnel exchange programs.
The GSAI, opened in August 2019 as Korea’s first AI graduate school, has been in the forefront of nurturing top-tier AI specialists in the era of Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school employs a two-track strategy that not only provides students with core AI-related courses on machine learning, data mining, computer vision, and natural language processing, but also a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies. Its faculty members are "the cream of the crop” in their early 40s, achieving world-class performance in their respective fields.
SNUBH opened the Healthcare Innovation Park in 2016, the first hospital-led convergence research complex among Korean medical institutions. It is leading future medical research in five specialized areas: medical devices, healthcare ICT, human genetics, nano-machines, and regenerative medicine.
The Dean of the GSAI, Song Chong, said, “We have set the stage for a cooperative platform for continuous and efficient joint education and research by the two institutions.” He expressed his excitement, saying, “Through this platform and our expertise in AI engineering and medicine, we will lead future AI-based medical technology.”
The Director of the SNUBH Research Division, Chang Wan Oh, stressed that “the mutual cooperation between the two institutions will become a crucial turning point in AI education and research, which is at the core of future healthcare.” He added, “Through a high level of cooperation, we will have the ability to bring about global competitiveness and innovation.”
(END)
2019.12.27 View 9113
KAIST GSAI and SNUBH Join Hands for AI in Healthcare
< Dean Song Chong (left) and Director Chang Wan Oh (right)
at the KAIST GSAI - SNUBH MOU Signing Ceremony >
The Graduate School of AI (GSAI) at KAIST and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital (SNUBH) signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) to cooperate in AI education and research in the field of healthcare last month. The two institutions have agreed to collaborate on research and technology development through the implementation of academic and personnel exchange programs.
The GSAI, opened in August 2019 as Korea’s first AI graduate school, has been in the forefront of nurturing top-tier AI specialists in the era of Fourth Industrial Revolution. The school employs a two-track strategy that not only provides students with core AI-related courses on machine learning, data mining, computer vision, and natural language processing, but also a multidisciplinary curriculum incorporating the five key fields of healthcare, autonomous vehicles, manufacturing, security, and emerging technologies. Its faculty members are "the cream of the crop” in their early 40s, achieving world-class performance in their respective fields.
SNUBH opened the Healthcare Innovation Park in 2016, the first hospital-led convergence research complex among Korean medical institutions. It is leading future medical research in five specialized areas: medical devices, healthcare ICT, human genetics, nano-machines, and regenerative medicine.
The Dean of the GSAI, Song Chong, said, “We have set the stage for a cooperative platform for continuous and efficient joint education and research by the two institutions.” He expressed his excitement, saying, “Through this platform and our expertise in AI engineering and medicine, we will lead future AI-based medical technology.”
The Director of the SNUBH Research Division, Chang Wan Oh, stressed that “the mutual cooperation between the two institutions will become a crucial turning point in AI education and research, which is at the core of future healthcare.” He added, “Through a high level of cooperation, we will have the ability to bring about global competitiveness and innovation.”
(END)
2019.12.27 View 9113 -
 Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 12034
Professor Junil Choi Receives Stephen O. Rice Prize
< Professor Junil Choi (second from the left) >
Professor Junil Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Stephen O. Rice Prize at the Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) hosted by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) in Hawaii on December 10, 2019.
The Stephen O. Rice Prize is awarded to only one paper of exceptional merit every year. The IEEE Communications Society evaluates all papers published in the IEEE Transactions on Communications journal within the last three years, and marks each paper by aggregating its scores on originality, the number of citations, impact, and peer evaluation.
Professor Choi won the prize for his research on one-bit analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for multiuser massive multiple-input and multiple-output (MIMO) antenna systems published in 2016. In his paper, Professor Choi proposed a technology that can drastically reduce the power consumption of the multiuser massive MIMO antenna systems, which are the core technology for 5G and future wireless communication. Professor Choi’s paper has been cited more than 230 times in various academic journals and conference papers since its publication, and multiple follow-up studies are actively ongoing.
In 2015, Professor Choi received the IEEE Signal Processing Society Best Paper Award, an award equals to the Stephen O. Rice Prize. He was also selected as the winner of the 15th Haedong Young Engineering Researcher Award presented by the Korean Institute of Communications and Information Sciences (KICS) on December 6, 2019 for his outstanding academic achievements, including 34 international journal publications and 26 US patent registrations.
(END)
2019.12.23 View 12034 -
 Professor Sung Yong Kim Elected as the Chair of PICES MONITOR
< Professor Sung Yong Kim >
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was elected as the chair of the Technical Committee on Monitoring (MONITOR) of the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES).
PICES is an intergovernmental marine science organization that was established in 1992 through a collaboration between six North Pacific nations including South Korea, Russia, the United States, Japan, China, and Canada to exchange and discuss research on the Pacific waters. Its headquarters is located in Canada and the organization consists of seven affiliated maritime science and marine technology committees.
Professor Kim was elected as the chair of the technical committee that focuses on monitoring and will be part of the Science Board as an ex-officio member. His term will last three years from November 2019.
Professor Kim was recognized for his academic excellence, expertise, and leadership among oceanographers both domestically and internationally.
Professor Kim will also participate as an academia civilian committee member of the Maritime and Fisheries Science and Technology Committee under the Korean Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries for two years from December 18, 2019.
He stated, “I will give my full efforts to broaden Korean oceanography research by participating in maritime leadership positions at home and abroad, and help South Korea become a maritime powerhouse.”
(END)
2019.12.22 View 10269
Professor Sung Yong Kim Elected as the Chair of PICES MONITOR
< Professor Sung Yong Kim >
Professor Sung Yong Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was elected as the chair of the Technical Committee on Monitoring (MONITOR) of the North Pacific Marine Science Organization (PICES).
PICES is an intergovernmental marine science organization that was established in 1992 through a collaboration between six North Pacific nations including South Korea, Russia, the United States, Japan, China, and Canada to exchange and discuss research on the Pacific waters. Its headquarters is located in Canada and the organization consists of seven affiliated maritime science and marine technology committees.
Professor Kim was elected as the chair of the technical committee that focuses on monitoring and will be part of the Science Board as an ex-officio member. His term will last three years from November 2019.
Professor Kim was recognized for his academic excellence, expertise, and leadership among oceanographers both domestically and internationally.
Professor Kim will also participate as an academia civilian committee member of the Maritime and Fisheries Science and Technology Committee under the Korean Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries for two years from December 18, 2019.
He stated, “I will give my full efforts to broaden Korean oceanography research by participating in maritime leadership positions at home and abroad, and help South Korea become a maritime powerhouse.”
(END)
2019.12.22 View 10269 -
 Professor Shin-Hyun Kim Receives the Young Scientist Award
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the Young Scientist Award from the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The Young Scientist Award is presented to a promising young Korean scientist under the age of 40 who shows significant potential, passion, and remarkable achievement.
Professor Kim was lauded for his research of intelligent soft materials. By applying his research, he developed a capsule sensor material that can not only be used for sensors, but also for displays, color aesthetics, anti-counterfeit technology, residual drug detection, and more.
The award ceremony took place on December 14 at the Gwacheon National Science Museum.
The Korean minister of Science and ICT delivered words of encouragement, reminding everyone that “the driving force behind creative performance of scientists is the provision of continuous support.” He added, “Researchers of Korea deserve greater public attention and support.”
(END)
2019.12.21 View 8549
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim Receives the Young Scientist Award
Professor Shin-Hyun Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the Young Scientist Award from the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
The Young Scientist Award is presented to a promising young Korean scientist under the age of 40 who shows significant potential, passion, and remarkable achievement.
Professor Kim was lauded for his research of intelligent soft materials. By applying his research, he developed a capsule sensor material that can not only be used for sensors, but also for displays, color aesthetics, anti-counterfeit technology, residual drug detection, and more.
The award ceremony took place on December 14 at the Gwacheon National Science Museum.
The Korean minister of Science and ICT delivered words of encouragement, reminding everyone that “the driving force behind creative performance of scientists is the provision of continuous support.” He added, “Researchers of Korea deserve greater public attention and support.”
(END)
2019.12.21 View 8549 -
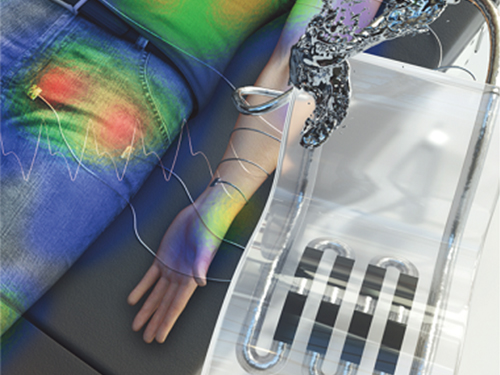 New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 15023
New Liquid Metal Wearable Pressure Sensor Created for Health Monitoring Applications
Soft pressure sensors have received significant research attention in a variety of fields, including soft robotics, electronic skin, and wearable electronics. Wearable soft pressure sensors have great potential for the real-time health monitoring and for the early diagnosis of diseases.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a highly sensitive wearable pressure sensor for health monitoring applications. This work was reported in Advanced Healthcare Materials on November 21 as a front cover article.
This technology is capable of sensitive, precise, and continuous measurement of physiological and physical signals and shows great potential for health monitoring applications and the early diagnosis of diseases.
A soft pressure sensor is required to have high compliance, high sensitivity, low cost, long-term performance stability, and environmental stability in order to be employed for continuous health monitoring. Conventional solid-state soft pressure sensors using functional materials including carbon nanotubes and graphene have showed great sensing performance. However, these sensors suffer from limited stretchability, signal drifting, and long-term instability due to the distance between the stretchable substrate and the functional materials.
To overcome these issues, liquid-state electronics using liquid metal have been introduced for various wearable applications. Of these materials, Galinstan, a eutectic metal alloy of gallium, indium, and tin, has great mechanical and electrical properties that can be employed in wearable applications. But today’s liquid metal-based pressure sensors have low-pressure sensitivity, limiting their applicability for health monitoring devices.
The research team developed a 3D-printed rigid microbump array-integrated, liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor. With the help of 3D printing, the integration of a rigid microbump array and the master mold for a liquid metal microchannel could be achieved simultaneously, reducing the complexity of the manufacturing process. Through the integration of the rigid microbump and the microchannel, the new pressure sensor has an extremely low detection limit and enhanced pressure sensitivity compared to previously reported liquid metal-based pressure sensors. The proposed sensor also has a negligible signal drift over 10,000 cycles of pressure, bending, and stretching and exhibited excellent stability when subjected to various environmental conditions.
These performance outcomes make it an excellent sensor for various health monitoring devices. First, the research team demonstrated a wearable wristband device that can continuously monitor one’s pulse during exercise and be employed in a noninvasive cuffless BP monitoring system based on PTT calculations. Then, they introduced a wireless wearable heel pressure monitoring system that integrates three 3D-BLiPS with a wireless communication module.
Professor Park said, “It was possible to measure health indicators including pulse and blood pressure continuously as well as pressure of body parts using our proposed soft pressure sensor. We expect it to be used in health care applications, such as the prevention and the monitoring of the pressure-driven diseases such as pressure ulcers in the near future. There will be more opportunities for future research including a whole-body pressure monitoring system related to other physical parameters.”
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 1. The front cover image of Advanced Healthcare Materials, Volume 8, Issue 22. >
< Figure 2. Highly sensitive liquid metal-based soft pressure sensor integrated with 3D-printed microbump array. >
< Figure 3. High pressure sensitivity and reliable sensing performances of the proposed sensor and wireless heel pressure monitoring application. >
-ProfileProfessor Inkyu ParkMicro/Nano Transducers Laboratoryhttp://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Mechanical EngineeringKAIST
2019.12.20 View 15023 -
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 10530
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 10530 -
 Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 11169
Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 11169