Polymer
-
 KAIST Develops Glare-Free, Heat-Blocking 'Smart Window'... Applicable to Buildings and Vehicles
• Professor Hong Chul Moon of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering develops RECM, a next-generation smart window technology, expecting cooling energy savings and effective indoor thermal management.
• When using the developed RECM, a significantly superior temperature reduction effect is observed compared to conventional windows.
• With a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' design that eliminates glare by suppressing external reflections, it is expected to be adapted in architectural structures, transportation, and more.
< (From left) First author Hoy Jung Jo, Professor Hong Chul Moon >
In the building sector, which accounts for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, heat ingress through windows has been identified as a primary cause of wasted heating and cooling energy. Our research team has successfully developed a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' technology capable of not only reducing heating and cooling energy in urban buildings but also resolving the persistent issue of 'light pollution' in urban living.
On the 17th of June, Professor Hong Chul Moon's research team at KAIST's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering announced the development of a 'smart window technology' that allows users to control the light and heat entering through windows according to their intent, and effectively neutralize glare from external sources.
Recently, 'active smart window' technology, which enables free adjustment of light and heat based on user operation, has garnered significant attention. Unlike conventional windows that passively react to changes in temperature or light, this is a next-generation window system that can be controlled in real-time via electrical signals.
The next-generation smart window technology developed by the research team, RECM (Reversible Electrodeposition and Electrochromic Mirror), is a smart window system based on a single-structured *electrochromic device that can actively control the transmittance of visible light and near-infrared (heat).
*Electrochromic device: A device whose optical properties change in response to an electrical signal.
In particular, by effectively suppressing the glare phenomenon caused by external reflected light—a problem previously identified in traditional metal *deposition smart windows—through the combined application of electrochromic materials, a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' suitable for building facades has been realized.
*Deposition: A process involving the electrochemical reaction to coat metal ions, such as Ag+, onto an electrode surface in solid form.
The RECM system developed in this study operates in three modes depending on voltage control.
Mode I (Transparent Mode) is advantageous for allowing sunlight to enter the indoor space during winter, as it transmits both light and heat like ordinary glass.
In Mode II (Colored Mode), *Prussian Blue (PB) and **DHV+• chemical species are formed through a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction, causing the window to turn a deep blue color. In this state, light is absorbed, and only a portion of the heat is transmitted, allowing for privacy while enabling appropriate indoor temperature control.
*Prussian Blue: An electrochromic material that transitions between colorless and blue upon electrical stimulation.
**DHV+•: A radical state colored molecule generated upon electrical stimulation.
Mode III (Colored and Deposition Mode) involves the reduction and deposition of silver (Ag+) ions on the electrode surface, reflecting both light and heat. Concurrently, the colored material absorbs the reflected light, effectively blocking glare for external pedestrians.
The research team validated the practical indoor temperature reduction effect of the RECM technology through experiments utilizing a miniature model house. When a conventional glass window was installed, the indoor temperature rose to 58.7°C within 45 minutes. Conversely, when RECM was operated in Mode III, the temperature reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a temperature reduction effect of approximately 27.2°C.
Furthermore, since each state transition is achievable solely by electrical signals, it is regarded as an active smart technology capable of instantaneous response according to season, time, and intended use.
< Figure 1. Operation mechanism of the RECM smart window. The RECM system can switch among three states—transparent, colored, and colored & deposition—via electrical stimulation. At -1.6 V, DHV•+ and Prussian Blue (PB) are formed, blocking visible light to provide privacy protection and heat blocking. At -2.0 V, silver (Ag) is deposited on the electrode surface, reflecting light and heat, while DHV•+ and Prussian Blue absorb reflected light, effectively suppressing external glare. Through this mechanism, it functions as an active smart window that simultaneously controls light, heat, and glare. >
Professor Hong Chul Moon of KAIST, the corresponding author of this study, stated, "This research goes beyond existing smart window technologies limited to visible light control, presenting a truly smart window platform that comprehensively considers not only active indoor thermal control but also the visual safety of pedestrians." He added, "Various applications are anticipated, from urban buildings to vehicles and trains."
< Figure 2. Analysis of glare suppression effect of conventional reflective smart windows and RECM. This figure presents the results comparing the glare phenomenon occurring during silver (Ag) deposition between conventional reflective smart windows and RECM Mode III. Conventional reflective devices resulted in strong reflected light on the desk surface due to their high reflectivity. In contrast, RECM Mode III, where the colored material absorbed reflected light, showed a 33% reduction in reflected light intensity, and no reflected light was observed from outside. This highlights the RECM system's distinctiveness and practicality as a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' optimized for dense urban environments, extending beyond just heat blocking. >
The findings of this research were published on June 13, 2025, in Volume 10, Issue 6 of 'ACS Energy Letters'. The listed authors for this publication are Hoy Jung Jo, Yeon Jae Jang, Hyeon-Don Kim, Kwang-Seop Kim, and Hong Chul Moon.
※ Paper Title: Glare-Free, Energy-Efficient Smart Windows: A Pedestrian-Friendly System with Dynamically Tunable Light and Heat Regulation
※ DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00637
< Figure 3. Temperature reduction performance verification in a miniature model house. The actual heat blocking effect was evaluated by applying RECM devices to a model building. Under identical conditions, the indoor temperature with ordinary glass rose to 58.7°C, whereas with RECM in Mode III, it reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a maximum temperature reduction effect of 27.2°C. The indoor temperature difference was also visually confirmed through thermal images, which proves the potential for indoor temperature control in urban buildings. >
This research was supported by the Nano & Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the internal research program of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials.
2025.06.20 View 4231
KAIST Develops Glare-Free, Heat-Blocking 'Smart Window'... Applicable to Buildings and Vehicles
• Professor Hong Chul Moon of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering develops RECM, a next-generation smart window technology, expecting cooling energy savings and effective indoor thermal management.
• When using the developed RECM, a significantly superior temperature reduction effect is observed compared to conventional windows.
• With a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' design that eliminates glare by suppressing external reflections, it is expected to be adapted in architectural structures, transportation, and more.
< (From left) First author Hoy Jung Jo, Professor Hong Chul Moon >
In the building sector, which accounts for approximately 40% of global energy consumption, heat ingress through windows has been identified as a primary cause of wasted heating and cooling energy. Our research team has successfully developed a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' technology capable of not only reducing heating and cooling energy in urban buildings but also resolving the persistent issue of 'light pollution' in urban living.
On the 17th of June, Professor Hong Chul Moon's research team at KAIST's Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering announced the development of a 'smart window technology' that allows users to control the light and heat entering through windows according to their intent, and effectively neutralize glare from external sources.
Recently, 'active smart window' technology, which enables free adjustment of light and heat based on user operation, has garnered significant attention. Unlike conventional windows that passively react to changes in temperature or light, this is a next-generation window system that can be controlled in real-time via electrical signals.
The next-generation smart window technology developed by the research team, RECM (Reversible Electrodeposition and Electrochromic Mirror), is a smart window system based on a single-structured *electrochromic device that can actively control the transmittance of visible light and near-infrared (heat).
*Electrochromic device: A device whose optical properties change in response to an electrical signal.
In particular, by effectively suppressing the glare phenomenon caused by external reflected light—a problem previously identified in traditional metal *deposition smart windows—through the combined application of electrochromic materials, a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' suitable for building facades has been realized.
*Deposition: A process involving the electrochemical reaction to coat metal ions, such as Ag+, onto an electrode surface in solid form.
The RECM system developed in this study operates in three modes depending on voltage control.
Mode I (Transparent Mode) is advantageous for allowing sunlight to enter the indoor space during winter, as it transmits both light and heat like ordinary glass.
In Mode II (Colored Mode), *Prussian Blue (PB) and **DHV+• chemical species are formed through a redox (oxidation-reduction) reaction, causing the window to turn a deep blue color. In this state, light is absorbed, and only a portion of the heat is transmitted, allowing for privacy while enabling appropriate indoor temperature control.
*Prussian Blue: An electrochromic material that transitions between colorless and blue upon electrical stimulation.
**DHV+•: A radical state colored molecule generated upon electrical stimulation.
Mode III (Colored and Deposition Mode) involves the reduction and deposition of silver (Ag+) ions on the electrode surface, reflecting both light and heat. Concurrently, the colored material absorbs the reflected light, effectively blocking glare for external pedestrians.
The research team validated the practical indoor temperature reduction effect of the RECM technology through experiments utilizing a miniature model house. When a conventional glass window was installed, the indoor temperature rose to 58.7°C within 45 minutes. Conversely, when RECM was operated in Mode III, the temperature reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a temperature reduction effect of approximately 27.2°C.
Furthermore, since each state transition is achievable solely by electrical signals, it is regarded as an active smart technology capable of instantaneous response according to season, time, and intended use.
< Figure 1. Operation mechanism of the RECM smart window. The RECM system can switch among three states—transparent, colored, and colored & deposition—via electrical stimulation. At -1.6 V, DHV•+ and Prussian Blue (PB) are formed, blocking visible light to provide privacy protection and heat blocking. At -2.0 V, silver (Ag) is deposited on the electrode surface, reflecting light and heat, while DHV•+ and Prussian Blue absorb reflected light, effectively suppressing external glare. Through this mechanism, it functions as an active smart window that simultaneously controls light, heat, and glare. >
Professor Hong Chul Moon of KAIST, the corresponding author of this study, stated, "This research goes beyond existing smart window technologies limited to visible light control, presenting a truly smart window platform that comprehensively considers not only active indoor thermal control but also the visual safety of pedestrians." He added, "Various applications are anticipated, from urban buildings to vehicles and trains."
< Figure 2. Analysis of glare suppression effect of conventional reflective smart windows and RECM. This figure presents the results comparing the glare phenomenon occurring during silver (Ag) deposition between conventional reflective smart windows and RECM Mode III. Conventional reflective devices resulted in strong reflected light on the desk surface due to their high reflectivity. In contrast, RECM Mode III, where the colored material absorbed reflected light, showed a 33% reduction in reflected light intensity, and no reflected light was observed from outside. This highlights the RECM system's distinctiveness and practicality as a 'pedestrian-friendly smart window' optimized for dense urban environments, extending beyond just heat blocking. >
The findings of this research were published on June 13, 2025, in Volume 10, Issue 6 of 'ACS Energy Letters'. The listed authors for this publication are Hoy Jung Jo, Yeon Jae Jang, Hyeon-Don Kim, Kwang-Seop Kim, and Hong Chul Moon.
※ Paper Title: Glare-Free, Energy-Efficient Smart Windows: A Pedestrian-Friendly System with Dynamically Tunable Light and Heat Regulation
※ DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00637
< Figure 3. Temperature reduction performance verification in a miniature model house. The actual heat blocking effect was evaluated by applying RECM devices to a model building. Under identical conditions, the indoor temperature with ordinary glass rose to 58.7°C, whereas with RECM in Mode III, it reached 31.5°C, demonstrating a maximum temperature reduction effect of 27.2°C. The indoor temperature difference was also visually confirmed through thermal images, which proves the potential for indoor temperature control in urban buildings. >
This research was supported by the Nano & Material Technology Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the internal research program of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials.
2025.06.20 View 4231 -
 A KAIST Research Team Develops High-Performance Stretchable Solar Cells
With the market for wearable electric devices growing rapidly, stretchable solar cells that can function under strain have received considerable attention as an energy source. To build such solar cells, it is necessary that their photoactive layer, which converts light into electricity, shows high electrical performance while possessing mechanical elasticity. However, satisfying both of these two requirements is challenging, making stretchable solar cells difficult to develop.
On December 26, a KAIST research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE) led by Professor Bumjoon Kim announced the development of a new conductive polymer material that achieved both high electrical performance and elasticity while introducing the world’s highest-performing stretchable organic solar cell.
Organic solar cells are devices whose photoactive layer, which is responsible for the conversion of light into electricity, is composed of organic materials. Compared to existing non-organic material-based solar cells, they are lighter and flexible, making them highly applicable for wearable electrical devices. Solar cells as an energy source are particularly important for building electrical devices, but high-efficiency solar cells often lack flexibility, and their application in wearable devices have therefore been limited to this point.
The team led by Professor Kim conjugated a highly stretchable polymer to an electrically conductive polymer with excellent electrical properties through chemical bonding, and developed a new conductive polymer with both electrical conductivity and mechanical stretchability. This polymer meets the highest reported level of photovoltaic conversion efficiency (19%) using organic solar cells, while also showing 10 times the stretchability of existing devices. The team thereby built the world’s highest performing stretchable solar cell that can be stretched up to 40% during operation, and demonstrated its applicability for wearable devices.
< Figure 1. Chemical structure of the newly developed conductive polymer and performance of stretchable organic solar cells using the material. >
Professor Kim said, “Through this research, we not only developed the world’s best performing stretchable organic solar cell, but it is also significant that we developed a new polymer that can be applicable as a base material for various electronic devices that needs to be malleable and/or elastic.”
< Figure 2. Photovoltaic efficiency and mechanical stretchability of newly developed polymers compared to existing polymers. >
This research, conducted by KAIST researchers Jin-Woo Lee and Heung-Goo Lee as first co-authors in cooperation with teams led by Professor Taek-Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Sheng Li from the Department of CBE, was published in Joule on December 1 (Paper Title: Rigid and Soft Block-Copolymerized Conjugated Polymers Enable High-Performance Intrinsically-Stretchable Organic Solar Cells).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.01.04 View 10624
A KAIST Research Team Develops High-Performance Stretchable Solar Cells
With the market for wearable electric devices growing rapidly, stretchable solar cells that can function under strain have received considerable attention as an energy source. To build such solar cells, it is necessary that their photoactive layer, which converts light into electricity, shows high electrical performance while possessing mechanical elasticity. However, satisfying both of these two requirements is challenging, making stretchable solar cells difficult to develop.
On December 26, a KAIST research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE) led by Professor Bumjoon Kim announced the development of a new conductive polymer material that achieved both high electrical performance and elasticity while introducing the world’s highest-performing stretchable organic solar cell.
Organic solar cells are devices whose photoactive layer, which is responsible for the conversion of light into electricity, is composed of organic materials. Compared to existing non-organic material-based solar cells, they are lighter and flexible, making them highly applicable for wearable electrical devices. Solar cells as an energy source are particularly important for building electrical devices, but high-efficiency solar cells often lack flexibility, and their application in wearable devices have therefore been limited to this point.
The team led by Professor Kim conjugated a highly stretchable polymer to an electrically conductive polymer with excellent electrical properties through chemical bonding, and developed a new conductive polymer with both electrical conductivity and mechanical stretchability. This polymer meets the highest reported level of photovoltaic conversion efficiency (19%) using organic solar cells, while also showing 10 times the stretchability of existing devices. The team thereby built the world’s highest performing stretchable solar cell that can be stretched up to 40% during operation, and demonstrated its applicability for wearable devices.
< Figure 1. Chemical structure of the newly developed conductive polymer and performance of stretchable organic solar cells using the material. >
Professor Kim said, “Through this research, we not only developed the world’s best performing stretchable organic solar cell, but it is also significant that we developed a new polymer that can be applicable as a base material for various electronic devices that needs to be malleable and/or elastic.”
< Figure 2. Photovoltaic efficiency and mechanical stretchability of newly developed polymers compared to existing polymers. >
This research, conducted by KAIST researchers Jin-Woo Lee and Heung-Goo Lee as first co-authors in cooperation with teams led by Professor Taek-Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Sheng Li from the Department of CBE, was published in Joule on December 1 (Paper Title: Rigid and Soft Block-Copolymerized Conjugated Polymers Enable High-Performance Intrinsically-Stretchable Organic Solar Cells).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.01.04 View 10624 -
 Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 14956
Professor Bumjoon Kim Named Scientist of the Month
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering won January’s Scientist of the Month Award presented by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) on January 6. Professor Kim also received 10 million won in prize money.
Professor Kim was recognized for his research in the field of fuel cells. Since the first paper on fuel cells was published in 1839 by the German chemist Friedrich Schonbein, there has been an increase in the number of fields in which fuel cells are used, including national defense, aerospace engineering, and autonomous vehicles.
Professor Kim developed carbonized block copolymer particles with high durability and a high-performance fuel cell. Block copolymers are two different polymers cross-linked into a chain structure. Various nanostructures can be made effectively by using the attractive and repulsive forces between the chains.
Professor Kim used the membrane emulsification technique, employing a high-performance separation membrane to develop a platform that makes the mass production of highly durable carbonized particles possible, which he then used to develop high-performance energy devices like fuel cells.
The carbonized particles designed by Professor Kim and his research team were used to create the world’s more durable fuel cells that boast outstanding performance while using only five percent of the costly platinum needed for existing commercialized products.
The team’s research results were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society and Energy Environmental Science in May and July of last year.
“We have developed a fuel cell that ticks all the boxes including performance, durability, and cost,” said Professor Kim. “Related techniques will not be limited to fuel cells, but could also be applied to the development of various energy devices like solar cells and secondary cells,” he added.
(END)
2021.01.22 View 14956 -
 Universal Virus Detection Platform to Expedite Viral Diagnosis
Reactive polymer-based tester pre-screens dsRNAs of a wide range of viruses without their genome sequences
The prompt, precise, and massive detection of a virus is the key to combat infectious diseases such as Covid-19. A new viral diagnostic strategy using reactive polymer-grafted, double-stranded RNAs will serve as a pre-screening tester for a wide range of viruses with enhanced sensitivity.
Currently, the most widely using viral detection methodology is polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnosis, which amplifies and detects a piece of the viral genome. Prior knowledge of the relevant primer nucleic acids of the virus is quintessential for this test.
The detection platform developed by KAIST researchers identifies viral activities without amplifying specific nucleic acid targets. The research team, co-led by Professor Sheng Li and Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, constructed a universal virus detection platform by utilizing the distinct features of the PPFPA-grafted surface and double-stranded RNAs.
The key principle of this platform is utilizing the distinct feature of reactive polymer-grafted surfaces, which serve as a versatile platform for the immobilization of functional molecules. These activated surfaces can be used in a wide range of applications including separation, delivery, and detection. As long double-stranded RNAs are common byproducts of viral transcription and replication, these PPFPA-grafted surfaces can detect the presence of different kinds of viruses without prior knowledge of their genomic sequences.
“We employed the PPFPA-grafted silicon surface to develop a universal virus detection platform by immobilizing antibodies that recognize double-stranded RNAs,” said Professor Kim.
To increase detection sensitivity, the research team devised two-step detection process analogues to sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay where the bound double-stranded RNAs are then visualized using fluorophore-tagged antibodies that also recognize the RNAs’ double-stranded secondary structure.
By utilizing the developed platform, long double-stranded RNAs can be detected and visualized from an RNA mixture as well as from total cell lysates, which contain a mixture of various abundant contaminants such as DNAs and proteins.
The research team successfully detected elevated levels of hepatitis C and A viruses with this tool.
“This new technology allows us to take on virus detection from a new perspective. By targeting a common biomarker, viral double-stranded RNAs, we can develop a pre-screening platform that can quickly differentiate infected populations from non-infected ones,” said Professor Li.
“This detection platform provides new perspectives for diagnosing infectious diseases. This will provide fast and accurate diagnoses for an infected population and prevent the influx of massive outbreaks,” said Professor Kim.
This work is featured in Biomacromolecules. This work was supported by the Agency for Defense Development (Grant UD170039ID), the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03034660, NRF-2019R1C1C1006672), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project from the Ministry of Science and ICT (KAISTHEALTHCARE42).
Profile:-Professor Yoosik KimDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST-Professor Sheng LiDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://bcpolymer.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
Publication:Ku et al., 2020. Reactive Polymer Targeting dsRNA as Universal Virus Detection Platform with Enhanced Sensitivity. Biomacromolecules (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00379).
2020.06.01 View 21288
Universal Virus Detection Platform to Expedite Viral Diagnosis
Reactive polymer-based tester pre-screens dsRNAs of a wide range of viruses without their genome sequences
The prompt, precise, and massive detection of a virus is the key to combat infectious diseases such as Covid-19. A new viral diagnostic strategy using reactive polymer-grafted, double-stranded RNAs will serve as a pre-screening tester for a wide range of viruses with enhanced sensitivity.
Currently, the most widely using viral detection methodology is polymerase chain reaction (PCR) diagnosis, which amplifies and detects a piece of the viral genome. Prior knowledge of the relevant primer nucleic acids of the virus is quintessential for this test.
The detection platform developed by KAIST researchers identifies viral activities without amplifying specific nucleic acid targets. The research team, co-led by Professor Sheng Li and Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, constructed a universal virus detection platform by utilizing the distinct features of the PPFPA-grafted surface and double-stranded RNAs.
The key principle of this platform is utilizing the distinct feature of reactive polymer-grafted surfaces, which serve as a versatile platform for the immobilization of functional molecules. These activated surfaces can be used in a wide range of applications including separation, delivery, and detection. As long double-stranded RNAs are common byproducts of viral transcription and replication, these PPFPA-grafted surfaces can detect the presence of different kinds of viruses without prior knowledge of their genomic sequences.
“We employed the PPFPA-grafted silicon surface to develop a universal virus detection platform by immobilizing antibodies that recognize double-stranded RNAs,” said Professor Kim.
To increase detection sensitivity, the research team devised two-step detection process analogues to sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay where the bound double-stranded RNAs are then visualized using fluorophore-tagged antibodies that also recognize the RNAs’ double-stranded secondary structure.
By utilizing the developed platform, long double-stranded RNAs can be detected and visualized from an RNA mixture as well as from total cell lysates, which contain a mixture of various abundant contaminants such as DNAs and proteins.
The research team successfully detected elevated levels of hepatitis C and A viruses with this tool.
“This new technology allows us to take on virus detection from a new perspective. By targeting a common biomarker, viral double-stranded RNAs, we can develop a pre-screening platform that can quickly differentiate infected populations from non-infected ones,” said Professor Li.
“This detection platform provides new perspectives for diagnosing infectious diseases. This will provide fast and accurate diagnoses for an infected population and prevent the influx of massive outbreaks,” said Professor Kim.
This work is featured in Biomacromolecules. This work was supported by the Agency for Defense Development (Grant UD170039ID), the Ministry of Science and ICT (NRF-2017R1D1A1B03034660, NRF-2019R1C1C1006672), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project from the Ministry of Science and ICT (KAISTHEALTHCARE42).
Profile:-Professor Yoosik KimDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST-Professor Sheng LiDepartment of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineeringhttps://bcpolymer.kaist.ac.kr
KAIST
Publication:Ku et al., 2020. Reactive Polymer Targeting dsRNA as Universal Virus Detection Platform with Enhanced Sensitivity. Biomacromolecules (https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00379).
2020.06.01 View 21288 -
 The 10th KINC Fusion Research Awardees
The KAIST Institute for NanoCentury (KINC) recognized three distinguished researchers whose convergence studies made significant impacts. The KINC presented the 10th KINC Fusion Research Awards during a ceremony that took place at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon on May 19.
This year’s ‘best’ convergence research award went to a joint research group led by Professor Hee Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Their research, featured in the December 27 issue of Advanced Materials as a front cover article last year, introduced the world’s first high-energy efficiency, membraneless, flowless, zinc-bromine battery. This study, in which research professor Gyoung Hwa Jeong, postdoctoral researcher Yearin Byun, and PhD candidate Ju-Hyuck Lee took part as co-lead authors, is deemed as an example of a best practice in convergence research in which two groups’ respective expertise in the fields of carbon materials and electrochemical analysis created a synergistic effect.
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was also recognized for having published the most interdisciplinary research papers on polymer electronics and nanomaterials at home and abroad.
Professor Hee-Tae Jung, the Director of KINC and the host of the KINC Fusion Research Awards, said, “The KINC is happy to announce the 10th awardees in nano-fusion research this year. Since convergence is crucial for making revolutionary changes, the importance of convergence studies should be recognized. Our institute will spare no effort to create a research environment suitable for convergence studies, which will be crucial for making a significant difference.”
The KINC was established in June 2006 under the KAIST Institute with the mission of facilitating convergence studies by tearing down boarders among departments and carrying out interdisciplinary joint research. Currently, the institute is comprised of approximately 90 professors from 13 departments. It aims to become a hub of university institutes for nano-fusion research.
(END)
2020.05.19 View 17128
The 10th KINC Fusion Research Awardees
The KAIST Institute for NanoCentury (KINC) recognized three distinguished researchers whose convergence studies made significant impacts. The KINC presented the 10th KINC Fusion Research Awards during a ceremony that took place at KAIST’s main campus in Daejeon on May 19.
This year’s ‘best’ convergence research award went to a joint research group led by Professor Hee Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering. Their research, featured in the December 27 issue of Advanced Materials as a front cover article last year, introduced the world’s first high-energy efficiency, membraneless, flowless, zinc-bromine battery. This study, in which research professor Gyoung Hwa Jeong, postdoctoral researcher Yearin Byun, and PhD candidate Ju-Hyuck Lee took part as co-lead authors, is deemed as an example of a best practice in convergence research in which two groups’ respective expertise in the fields of carbon materials and electrochemical analysis created a synergistic effect.
Professor Bumjoon Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was also recognized for having published the most interdisciplinary research papers on polymer electronics and nanomaterials at home and abroad.
Professor Hee-Tae Jung, the Director of KINC and the host of the KINC Fusion Research Awards, said, “The KINC is happy to announce the 10th awardees in nano-fusion research this year. Since convergence is crucial for making revolutionary changes, the importance of convergence studies should be recognized. Our institute will spare no effort to create a research environment suitable for convergence studies, which will be crucial for making a significant difference.”
The KINC was established in June 2006 under the KAIST Institute with the mission of facilitating convergence studies by tearing down boarders among departments and carrying out interdisciplinary joint research. Currently, the institute is comprised of approximately 90 professors from 13 departments. It aims to become a hub of university institutes for nano-fusion research.
(END)
2020.05.19 View 17128 -
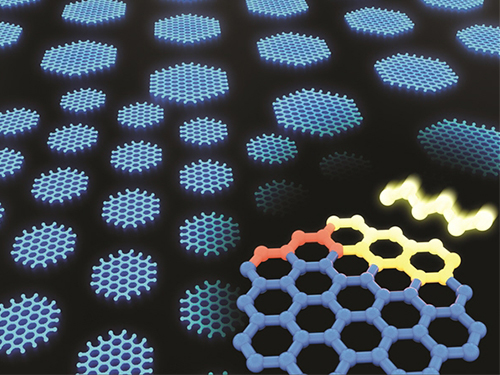 Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 36941
Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 36941 -
 Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park Won the IBA Technology Award 2018
(Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park)
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the IBA Technology Award from the International Battery Association (IBA).
IBA 2018 was held from March 11 to 16 on Jeju Island, which was the first time it was hosted in Korea. The conference was an excellent opportunity to let the world know the level of the Korean rechargeable battery industry and its technology.
Professor Park delivered his keynote speech titled Advances in Lithium Batteries in Korea at the conference and received the IBA Technology Award as the first Korean recipient.
Professor Park is a world-renowned scholar who was a groundbreaker in the rechargeable battery industry. He was recognized by the IBA Award Committee for his contributions carrying out research and development, fostering competent people, and enhancing the lithium rechargeable battery industry in Korea over the last 30 years.
Professor Park said, “It is my great honor to receive this award, which is the best international award in the field of rechargeable batteries. I would like to share this with my colleagues and students. As competition in the rechargeable industry intensifies, systemic cooperation among industries, academia, and government is needed for the continued development of the battery industry in Korea.
2018.03.19 View 9385
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park Won the IBA Technology Award 2018
(Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park)
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the IBA Technology Award from the International Battery Association (IBA).
IBA 2018 was held from March 11 to 16 on Jeju Island, which was the first time it was hosted in Korea. The conference was an excellent opportunity to let the world know the level of the Korean rechargeable battery industry and its technology.
Professor Park delivered his keynote speech titled Advances in Lithium Batteries in Korea at the conference and received the IBA Technology Award as the first Korean recipient.
Professor Park is a world-renowned scholar who was a groundbreaker in the rechargeable battery industry. He was recognized by the IBA Award Committee for his contributions carrying out research and development, fostering competent people, and enhancing the lithium rechargeable battery industry in Korea over the last 30 years.
Professor Park said, “It is my great honor to receive this award, which is the best international award in the field of rechargeable batteries. I would like to share this with my colleagues and students. As competition in the rechargeable industry intensifies, systemic cooperation among industries, academia, and government is needed for the continued development of the battery industry in Korea.
2018.03.19 View 9385 -
 Polymers with Highly Improved Light-transformation Efficiency
A joint Korean research team, led by Professor Bum-Joon Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Young-Woo Han of the Department of Nanofusion Engineering at Pusan National University, has developed a new type of electrically-conductive polymer for solar batteries with an improved light-transformation efficiency of up to 5%. The team considers it a viable replacement for existing plastic batteries for solar power which is viewed as the energy source of the future.
Polymer solar cells have greater structural stability and heat resistance compared to fullerene organic solar cells. However, they have lower light-transformation efficiency—below 4%—compared to 10% of the latter. The low efficiency is due to the failure of blending among the polymers that compose the active layer of the cell. This phenomenon deters the formation and movement of electrons and thus lowers light-transformation efficiency.
By manipulating the structure and concentration of conductive polymers, the team was able to effectively increase the polymer blending and increase light-transformation efficiency. The team was able to maximize the efficiency up to 6% which is the highest reported ratio.
Professor Kim said, “This research demonstrates that conductive polymer plastics can be used widely for solar cells and batteries for mobile devices.”
The research findings were published in the February 18th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Picture: Flexible Solar Cell Polymer Developed by the Research Team
2015.04.05 View 12900
Polymers with Highly Improved Light-transformation Efficiency
A joint Korean research team, led by Professor Bum-Joon Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Young-Woo Han of the Department of Nanofusion Engineering at Pusan National University, has developed a new type of electrically-conductive polymer for solar batteries with an improved light-transformation efficiency of up to 5%. The team considers it a viable replacement for existing plastic batteries for solar power which is viewed as the energy source of the future.
Polymer solar cells have greater structural stability and heat resistance compared to fullerene organic solar cells. However, they have lower light-transformation efficiency—below 4%—compared to 10% of the latter. The low efficiency is due to the failure of blending among the polymers that compose the active layer of the cell. This phenomenon deters the formation and movement of electrons and thus lowers light-transformation efficiency.
By manipulating the structure and concentration of conductive polymers, the team was able to effectively increase the polymer blending and increase light-transformation efficiency. The team was able to maximize the efficiency up to 6% which is the highest reported ratio.
Professor Kim said, “This research demonstrates that conductive polymer plastics can be used widely for solar cells and batteries for mobile devices.”
The research findings were published in the February 18th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS).
Picture: Flexible Solar Cell Polymer Developed by the Research Team
2015.04.05 View 12900 -
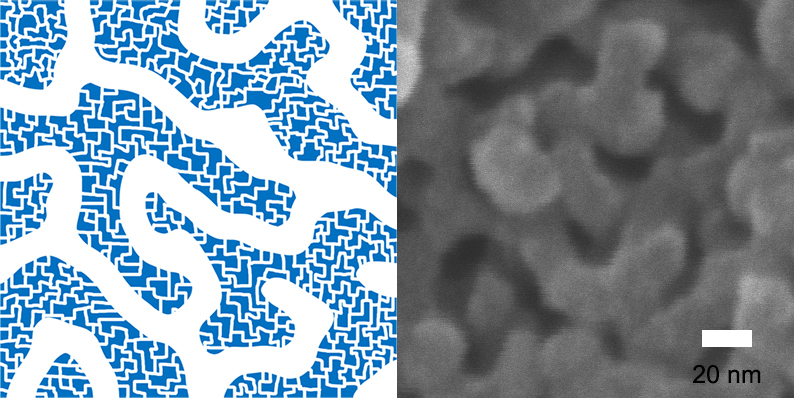 Hierarchically-Porous Polymers with Fast Absorption
KAIST's Professor Myungeun Seo and his research team from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology has developed a method to form micropores of less than 2 nanometers within porous polymers where 10 nanometers long mesopores connect like a net. The advantage of the porous polymers is fast absorption of molecules.
Porous polymers with micropores of less than 2 nanometers, like a zeolite, have a large surface area. They are used as a means to store hydrogen-based molecules or as a catalytic support that can be used as a surface to convert a material into a desired form. However, because the size of the pores in its path was too small for the molecules, it took a long time to spread into the pores and reach the surface.
To reach the surface efficiently, a lung cell or the vein of a leaf has a structure wherein the pores are subdivided into different sizes so that the molecule can spread throughout the organ. A technology that can create not only micropores but also bigger pores was necessary in order to create such structure.
The research team solved the issue by implementing a "self-assembly" of block polymers to easily form a net-like nanostructure from mesopores of 10 nanometers.
The team created hierarchically-porous polymers consisting of two different types of pores by using a hypercrosslinking reaction along with the "self-assembly" method. The reaction creates micropores within the chain after the polymer chain is confined by a chemical bond.
This porous polymer has micropores that are smaller than 2 nanometers on the walls of mesopores while 10 nanometers long mesopores forming 3-dimensional net structures. Because of the "self-assembly" method, the size of mesopores can be adjusted within the range of 6 to 15 nanometers.
This is the first case where a porous polymer has both well-defined mesopores and micropores. The research team verified the effect of hierarchically-porous structures on absorption of molecules by confirming that the porous polymer had faster absorption speeds than a polymer consisting only of micropores.
Professor Seo said, “The study has found a simple way to create different sizes of pores within a polymer.” He expected that the hierarchically-porous polymers can be used as a catalytic support in which fast diffusion of molecules is essential, or for molecule collection.
The research was sponsored by National Research Foundation of Korea and published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Figure 1 – Net-like Structure of Hierarchically-Porous Polymers with Mesopores and Micropores on the walls of Mesopores.
Figure 2 - Hierarchically-Porous Polymers
Figure 3 – Comparison of Porous-Polymers consisting of Mesopores only (left), and Mesopores and Micropores (right)
2015.01.13 View 10122
Hierarchically-Porous Polymers with Fast Absorption
KAIST's Professor Myungeun Seo and his research team from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology has developed a method to form micropores of less than 2 nanometers within porous polymers where 10 nanometers long mesopores connect like a net. The advantage of the porous polymers is fast absorption of molecules.
Porous polymers with micropores of less than 2 nanometers, like a zeolite, have a large surface area. They are used as a means to store hydrogen-based molecules or as a catalytic support that can be used as a surface to convert a material into a desired form. However, because the size of the pores in its path was too small for the molecules, it took a long time to spread into the pores and reach the surface.
To reach the surface efficiently, a lung cell or the vein of a leaf has a structure wherein the pores are subdivided into different sizes so that the molecule can spread throughout the organ. A technology that can create not only micropores but also bigger pores was necessary in order to create such structure.
The research team solved the issue by implementing a "self-assembly" of block polymers to easily form a net-like nanostructure from mesopores of 10 nanometers.
The team created hierarchically-porous polymers consisting of two different types of pores by using a hypercrosslinking reaction along with the "self-assembly" method. The reaction creates micropores within the chain after the polymer chain is confined by a chemical bond.
This porous polymer has micropores that are smaller than 2 nanometers on the walls of mesopores while 10 nanometers long mesopores forming 3-dimensional net structures. Because of the "self-assembly" method, the size of mesopores can be adjusted within the range of 6 to 15 nanometers.
This is the first case where a porous polymer has both well-defined mesopores and micropores. The research team verified the effect of hierarchically-porous structures on absorption of molecules by confirming that the porous polymer had faster absorption speeds than a polymer consisting only of micropores.
Professor Seo said, “The study has found a simple way to create different sizes of pores within a polymer.” He expected that the hierarchically-porous polymers can be used as a catalytic support in which fast diffusion of molecules is essential, or for molecule collection.
The research was sponsored by National Research Foundation of Korea and published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Figure 1 – Net-like Structure of Hierarchically-Porous Polymers with Mesopores and Micropores on the walls of Mesopores.
Figure 2 - Hierarchically-Porous Polymers
Figure 3 – Comparison of Porous-Polymers consisting of Mesopores only (left), and Mesopores and Micropores (right)
2015.01.13 View 10122 -
 Secondary, High Capacity Battery developed from Rice Husks
Rice husks, a waste product from rice polishing, has been successfully utilized as the silicon anode for use in high capacity lithium ion secondary batteries. The new silicon anode derived from rice husks exhibit superior output and lifespan.
Professor Choi Jang Wook (The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Park Seung Min (Department of Biochemistry) and their respective research teams separated naturally occurring, highly porous silica material within the rice husks and developed a 3-dimensional, highly porous silicon anode material.
The result of the research effort was published in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal, a world renowned journal in the field of natural sciences.
Silicon has attracted much attention as anode material for next generation lithium ion secondary batteries because it exhibits 3~5 times higher capacity than conventional graphene. The high capacity will pave the way to lithium secondary batteries with higher energy densities than conventional batteries. It is anticipated that the application of silicon batteries will yield electronic devices with a longer duration for use in addition to electronic vehicles boasting longer mileage.
The silicon anode is based on the 3-dimensional, highly porous structure of rice husks which remedies the problematic extreme volume expansion of conventional silicon anodes.
Utilization of inexpensive rice husks to create high value silicon anodes will cause a ripple effect on the industry and academia.
2013.08.23 View 12772
Secondary, High Capacity Battery developed from Rice Husks
Rice husks, a waste product from rice polishing, has been successfully utilized as the silicon anode for use in high capacity lithium ion secondary batteries. The new silicon anode derived from rice husks exhibit superior output and lifespan.
Professor Choi Jang Wook (The Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)) and Professor Park Seung Min (Department of Biochemistry) and their respective research teams separated naturally occurring, highly porous silica material within the rice husks and developed a 3-dimensional, highly porous silicon anode material.
The result of the research effort was published in the online edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) journal, a world renowned journal in the field of natural sciences.
Silicon has attracted much attention as anode material for next generation lithium ion secondary batteries because it exhibits 3~5 times higher capacity than conventional graphene. The high capacity will pave the way to lithium secondary batteries with higher energy densities than conventional batteries. It is anticipated that the application of silicon batteries will yield electronic devices with a longer duration for use in addition to electronic vehicles boasting longer mileage.
The silicon anode is based on the 3-dimensional, highly porous structure of rice husks which remedies the problematic extreme volume expansion of conventional silicon anodes.
Utilization of inexpensive rice husks to create high value silicon anodes will cause a ripple effect on the industry and academia.
2013.08.23 View 12772 -
 Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13497
Synthesis of a New Organic Supermolecule Succeeded
From left to right: Prof.Stoddart, Prof.Goddard and Prof.Jang Wook Choi
KAIST EEWS graduate school’s research team led by Prof. Stoddart, Prof. Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi has succeeded the synthesis of a new organic supermolecule that is stable in a radical condition under room temperature.
Prof. Stoddart, who mainly led this research, is the world’s great scholar on orgaic molecular structure especially on catenane with an interconnection of several ring structures. Catenane is originated from Latin “catenane” referring to “chain”. The brief structure of the synthesized catenane is as following:
Usually radicals are known to be unstable since they are electronically neutral and have very high reactivity. However, the radicals from this research showed air- and water- stability. It also showed a reversible change in oxidation number from o to +8 through chemical/electrochemical oxidation-reduction reaction. The phenomenon where paramagnetic and diamagnetic characteristics change according to the oxidation number has also been observed.
Thus, the research like this - on the molecules showing various characteristics with stable radical - is expected to give a new direction to the next-generation electromemory system, semiconductor and energy storage system research.
Meanwhile, this research, led by Prof.Stoddart team with Prof.Goddard and Prof. Jang Wook Choi’s team, is conducted under the support of Science and Technology’s World Class University project by Ministry of Education and published in ‘Science’ on 25th of Jan.
2013.02.24 View 13497 -
 Prof. Jang-Uk Choi develops Strong, Long-lasting Lithium-ion Battery
Lithium-ion secondary battery with high power, as well asmuch longer life span, has been developed using nanotechnology. Professor Jang-Uk Choi and his colleagues at KAIST University EEWS graduate school has succeeded in developing a new lithium-ion secondary battery that has more than five times the output and three times the life span of the conventional batteries.
The industry expects the new battery to significantly improve the acceleration performance and solve the drawbacks of slow electric cars, which occurred due to failure of battery performance to keep up with the output of the motors during acceleration.
It is also expected that the new battery could be utilized in various fields that require high power batteries such as Smart Grid, which is the next generation intelligent electrical grid, as well as electric tools and many others.
Currently, the most widely used commercial lithium ion batteries’ lithium-cobalt-based cathode material has the disadvantage of expensive cost, high toxicity, short life expectancy and long-charge/discharge time. Also, it has been difficult to apply in electric cars that require a large current density and are vulnerable to heat generated during charging/discharging.
On the other hand, Professor Choi and his colleagues’ lithium-manganese based cathode material is gaining popularity for having the advantages such as abundant raw materials, cheap prices, eco-friendliness and especially excellent high-temperature stability and high output, which are suitable for use as electrode material in electric cars.
The pure lithium manganese based cathode material has a critical drawback of a very short life expectancy, only lasting about average of 1-2 years, which is due to the elution when the melted manganese flows out into the electrolyte. There have been various studies to solve this problem; however, the unique crystal structure of the material remained as a challenge for many scientists.
Professor Choi’s team analyzed the structure of the crystal at the time shortly before manganese oxides were formed, while controlling the reaction temperature at the step of synthesizing nanomaterial. It has been found that, at 220℃, there are simultaneously existing two crystal faces, one that inhibits the dissolution of manganese ions and the other that enables lithium ions to move smoothly.
Each of these crystal faces improves both the life span and output, increasing the output more than five times and life expectancy over three times. In addition, the existing high temperature life span, that was known to be especially vulnerable, has improved ten-fold.
“By controlling the crystal face of lithium manganese anode material, which has previously existed in the battery as chunks of about 10 micro-meter particles, both output and life span has significantly improved,” said Professor Choi, “Domestic and international patent application for the regarding technology has been finished and we have plans to work with companies in the future for commercialization within 2-3 years.”
Professor Yi Cui of Stanford University, the world’s leading scholar on the secondary battery, has evaluated that “This research exemplifies how nanotechnology can innovatively develop the field of secondary battery.”
Meanwhile, the research led by Professor Jang-Uk Choi and participated by researcher Ju-Seong Kim has been published on the online edition (dated Nov 27th) of Nanoletters, the world’s leading authority on Nanoscience.
2012.12.21 View 11153
Prof. Jang-Uk Choi develops Strong, Long-lasting Lithium-ion Battery
Lithium-ion secondary battery with high power, as well asmuch longer life span, has been developed using nanotechnology. Professor Jang-Uk Choi and his colleagues at KAIST University EEWS graduate school has succeeded in developing a new lithium-ion secondary battery that has more than five times the output and three times the life span of the conventional batteries.
The industry expects the new battery to significantly improve the acceleration performance and solve the drawbacks of slow electric cars, which occurred due to failure of battery performance to keep up with the output of the motors during acceleration.
It is also expected that the new battery could be utilized in various fields that require high power batteries such as Smart Grid, which is the next generation intelligent electrical grid, as well as electric tools and many others.
Currently, the most widely used commercial lithium ion batteries’ lithium-cobalt-based cathode material has the disadvantage of expensive cost, high toxicity, short life expectancy and long-charge/discharge time. Also, it has been difficult to apply in electric cars that require a large current density and are vulnerable to heat generated during charging/discharging.
On the other hand, Professor Choi and his colleagues’ lithium-manganese based cathode material is gaining popularity for having the advantages such as abundant raw materials, cheap prices, eco-friendliness and especially excellent high-temperature stability and high output, which are suitable for use as electrode material in electric cars.
The pure lithium manganese based cathode material has a critical drawback of a very short life expectancy, only lasting about average of 1-2 years, which is due to the elution when the melted manganese flows out into the electrolyte. There have been various studies to solve this problem; however, the unique crystal structure of the material remained as a challenge for many scientists.
Professor Choi’s team analyzed the structure of the crystal at the time shortly before manganese oxides were formed, while controlling the reaction temperature at the step of synthesizing nanomaterial. It has been found that, at 220℃, there are simultaneously existing two crystal faces, one that inhibits the dissolution of manganese ions and the other that enables lithium ions to move smoothly.
Each of these crystal faces improves both the life span and output, increasing the output more than five times and life expectancy over three times. In addition, the existing high temperature life span, that was known to be especially vulnerable, has improved ten-fold.
“By controlling the crystal face of lithium manganese anode material, which has previously existed in the battery as chunks of about 10 micro-meter particles, both output and life span has significantly improved,” said Professor Choi, “Domestic and international patent application for the regarding technology has been finished and we have plans to work with companies in the future for commercialization within 2-3 years.”
Professor Yi Cui of Stanford University, the world’s leading scholar on the secondary battery, has evaluated that “This research exemplifies how nanotechnology can innovatively develop the field of secondary battery.”
Meanwhile, the research led by Professor Jang-Uk Choi and participated by researcher Ju-Seong Kim has been published on the online edition (dated Nov 27th) of Nanoletters, the world’s leading authority on Nanoscience.
2012.12.21 View 11153