semiconductors
-
 KAIST Turns an Unprecedented Idea into Reality: Quantum Computing with Magnets
What started as an idea under KAIST’s Global Singularity Research Project—"Can we build a quantum computer using magnets?"—has now become a scientific reality. A KAIST-led international research team has successfully demonstrated a core quantum computing technology using magnetic materials (ferromagnets) for the first time in the world.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th of May that a team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), has developed a “photon-magnon hybrid chip” and successfully implemented real-time, multi-pulse interference using magnetic materials—marking a global first.
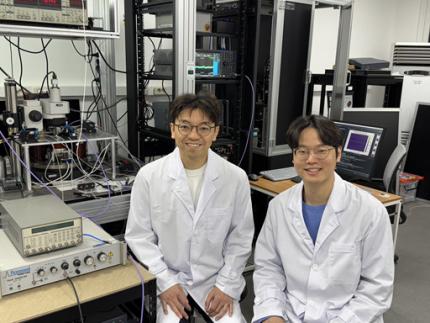
< Photo 1. Dr. Moojune Song (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim (right) of KAIST Department of Physics >
In simple terms, the researchers developed a special chip that synchronizes light and internal magnetic vibrations (magnons), enabling the transmission of phase information between distant magnets. They succeeded in observing and controlling interference between multiple signals in real time. This marks the first experimental evidence that magnets can serve as key components in quantum computing, serving as a pivotal step toward magnet-based quantum platforms.
The N and S poles of a magnet stem from the spin of electrons inside atoms. When many atoms align, their collective spin vibrations create a quantum particle known as a “magnon.”
Magnons are especially promising because of their nonreciprocal nature—they can carry information in only one direction, which makes them suitable for quantum noise isolation in compact quantum chips. They can also couple with both light and microwaves, enabling the potential for long-distance quantum communication over tens of kilometers.
Moreover, using special materials like antiferromagnets could allow quantum computers to operate at terahertz (THz) frequencies, far surpassing today’s hardware limitations, and possibly enabling room-temperature quantum computing without the need for bulky cryogenic equipment.
To build such a system, however, one must be able to transmit, measure, and control the phase information of magnons—the starting point and propagation of their waveforms—in real time. This had not been achieved until now.
< Figure 1. Superconducting Circuit-Based Magnon-Photon Hybrid System. (a) Schematic diagram of the device. A NbN superconducting resonator circuit fabricated on a silicon substrate is coupled with spherical YIG magnets (250 μm diameter), and magnons are generated and measured in real-time via a vertical antenna. (b) Photograph of the actual device. The distance between the two YIG spheres is 12 mm, a distance at which they cannot influence each other without the superconducting circuit. >
Professor Kim’s team used two tiny magnetic spheres made of Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) placed 12 mm apart with a superconducting resonator in between—similar to those used in quantum processors by Google and IBM. They input pulses into one magnet and successfully observed lossless transmission of magnon vibrations to the second magnet via the superconducting circuit.
They confirmed that from single nanosecond pulses to four microwave pulses, the magnon vibrations maintained their phase information and demonstrated predictable constructive or destructive interference in real time—known as coherent interference.
By adjusting the pulse frequencies and their intervals, the researchers could also freely control the interference patterns of magnons, effectively showing for the first time that electrical signals can be used to manipulate magnonic quantum states.
This work demonstrated that quantum gate operations using multiple pulses—a fundamental technique in quantum information processing—can be implemented using a hybrid system of magnetic materials and superconducting circuits. This opens the door for the practical use of magnet-based quantum devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental Data. (a) Measurement results of magnon-magnon band anticrossing via continuous wave measurement, showing the formation of a strong coupling hybrid system. (b) Magnon pulse exchange oscillation phenomenon between YIG spheres upon single pulse application. It can be seen that magnon information is coherently transmitted at regular time intervals through the superconducting circuit. (c,d) Magnon interference phenomenon upon dual pulse application. The magnon information state can be arbitrarily controlled by adjusting the time interval and carrier frequency between pulses. >
Professor Kab-Jin Kim stated, “This project began with a bold, even unconventional idea proposed to the Global Singularity Research Program: ‘What if we could build a quantum computer with magnets?’ The journey has been fascinating, and this study not only opens a new field of quantum spintronics, but also marks a turning point in developing high-efficiency quantum information processing devices.”
The research was co-led by postdoctoral researcher Moojune Song (KAIST), Dr. Yi Li and Dr. Valentine Novosad from Argonne National Lab, and Prof. Axel Hoffmann’s team at UIUC. The results were published in Nature Communications on April 17 and npj Spintronics on April 1, 2025.
Paper 1: Single-shot magnon interference in a magnon-superconducting-resonator hybrid circuit, Nat. Commun. 16, 3649 (2025)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58482-2
Paper 2: Single-shot electrical detection of short-wavelength magnon pulse transmission in a magnonic ultra-thin-film waveguide, npj Spintronics 3, 12 (2025)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44306-025-00072-5
The research was supported by KAIST’s Global Singularity Research Initiative, the National Research Foundation of Korea (including the Mid-Career Researcher, Leading Research Center, and Quantum Information Science Human Resource Development programs), and the U.S. Department of Energy.
2025.06.12 View 3469
KAIST Turns an Unprecedented Idea into Reality: Quantum Computing with Magnets
What started as an idea under KAIST’s Global Singularity Research Project—"Can we build a quantum computer using magnets?"—has now become a scientific reality. A KAIST-led international research team has successfully demonstrated a core quantum computing technology using magnetic materials (ferromagnets) for the first time in the world.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th of May that a team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Argonne National Laboratory and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign (UIUC), has developed a “photon-magnon hybrid chip” and successfully implemented real-time, multi-pulse interference using magnetic materials—marking a global first.
< Photo 1. Dr. Moojune Song (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim (right) of KAIST Department of Physics >
In simple terms, the researchers developed a special chip that synchronizes light and internal magnetic vibrations (magnons), enabling the transmission of phase information between distant magnets. They succeeded in observing and controlling interference between multiple signals in real time. This marks the first experimental evidence that magnets can serve as key components in quantum computing, serving as a pivotal step toward magnet-based quantum platforms.
The N and S poles of a magnet stem from the spin of electrons inside atoms. When many atoms align, their collective spin vibrations create a quantum particle known as a “magnon.”
Magnons are especially promising because of their nonreciprocal nature—they can carry information in only one direction, which makes them suitable for quantum noise isolation in compact quantum chips. They can also couple with both light and microwaves, enabling the potential for long-distance quantum communication over tens of kilometers.
Moreover, using special materials like antiferromagnets could allow quantum computers to operate at terahertz (THz) frequencies, far surpassing today’s hardware limitations, and possibly enabling room-temperature quantum computing without the need for bulky cryogenic equipment.
To build such a system, however, one must be able to transmit, measure, and control the phase information of magnons—the starting point and propagation of their waveforms—in real time. This had not been achieved until now.
< Figure 1. Superconducting Circuit-Based Magnon-Photon Hybrid System. (a) Schematic diagram of the device. A NbN superconducting resonator circuit fabricated on a silicon substrate is coupled with spherical YIG magnets (250 μm diameter), and magnons are generated and measured in real-time via a vertical antenna. (b) Photograph of the actual device. The distance between the two YIG spheres is 12 mm, a distance at which they cannot influence each other without the superconducting circuit. >
Professor Kim’s team used two tiny magnetic spheres made of Yttrium Iron Garnet (YIG) placed 12 mm apart with a superconducting resonator in between—similar to those used in quantum processors by Google and IBM. They input pulses into one magnet and successfully observed lossless transmission of magnon vibrations to the second magnet via the superconducting circuit.
They confirmed that from single nanosecond pulses to four microwave pulses, the magnon vibrations maintained their phase information and demonstrated predictable constructive or destructive interference in real time—known as coherent interference.
By adjusting the pulse frequencies and their intervals, the researchers could also freely control the interference patterns of magnons, effectively showing for the first time that electrical signals can be used to manipulate magnonic quantum states.
This work demonstrated that quantum gate operations using multiple pulses—a fundamental technique in quantum information processing—can be implemented using a hybrid system of magnetic materials and superconducting circuits. This opens the door for the practical use of magnet-based quantum devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental Data. (a) Measurement results of magnon-magnon band anticrossing via continuous wave measurement, showing the formation of a strong coupling hybrid system. (b) Magnon pulse exchange oscillation phenomenon between YIG spheres upon single pulse application. It can be seen that magnon information is coherently transmitted at regular time intervals through the superconducting circuit. (c,d) Magnon interference phenomenon upon dual pulse application. The magnon information state can be arbitrarily controlled by adjusting the time interval and carrier frequency between pulses. >
Professor Kab-Jin Kim stated, “This project began with a bold, even unconventional idea proposed to the Global Singularity Research Program: ‘What if we could build a quantum computer with magnets?’ The journey has been fascinating, and this study not only opens a new field of quantum spintronics, but also marks a turning point in developing high-efficiency quantum information processing devices.”
The research was co-led by postdoctoral researcher Moojune Song (KAIST), Dr. Yi Li and Dr. Valentine Novosad from Argonne National Lab, and Prof. Axel Hoffmann’s team at UIUC. The results were published in Nature Communications on April 17 and npj Spintronics on April 1, 2025.
Paper 1: Single-shot magnon interference in a magnon-superconducting-resonator hybrid circuit, Nat. Commun. 16, 3649 (2025)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-58482-2
Paper 2: Single-shot electrical detection of short-wavelength magnon pulse transmission in a magnonic ultra-thin-film waveguide, npj Spintronics 3, 12 (2025)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44306-025-00072-5
The research was supported by KAIST’s Global Singularity Research Initiative, the National Research Foundation of Korea (including the Mid-Career Researcher, Leading Research Center, and Quantum Information Science Human Resource Development programs), and the U.S. Department of Energy.
2025.06.12 View 3469 -
 ‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 16315
‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 16315 -
 Research Day Highlights Most Outstanding Research Achievements
Professor Byung Jin Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the Grand Research Prize Winner in recognition of his innovative research achievement in the fields of nano electric and flexible energy devices during the 2019 KAIST Research Day ceremony held on April 23 at the Chung Kunmo Conference Hall.
The ten most outstanding research achievements from the past year were also awarded in the three areas of Research, Innovation, Convergence Researches.
Professor Cho is an internationally recognized researcher in the field of future nano and energy device technology. Professor Cho’s team has continued to research on advanced CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductors). CMOS has become his key research topic over the past three decades.
In 2014, he developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator, which is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. It is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles. His wearable thermoelectric generator was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015.
He now is working on high-performance and ultra-flexible CMOS IC for biomedical applications, expanding his scope to thermal haptic technology in VR using graphene-CMOS hybrid integrated circuits; to self-powered wireless sensor nodes and self-powered ECG system using wearable thermoelectric generators .
In his special lecture at the ceremony, Professor Cho stressed the importance of collaboration in making scientific research and presented how he moved to future devices after focusing on scaling the devices.
“When I started the research on semiconductors, I focused on how to scale the device down as much as possible. For decades, we have conducted a number of procedures to produce tiny but efficient materials. Now we have shifted to develop flexible thermoelements and wearable devices,” said Professor Cho.
“We all thought the scaling down is the only way to create value-added technological breakthroughs. Now, the devices have been scaled down to 7nm and will go down to 5 nm soon. Over the past few years, I think we have gone through all the possible technological breakthroughs for reducing the size to 5nm. The semiconductor devices are made of more 1 billion transistors and go through 1,000 technological processes. So, there won’t be any possible way for a single genius to make a huge breakthrough. Without collaboration with others, it is nearly impossible to make any new technological breakthroughs.”
Professor Cho has published more than 240 papers in renowned academic journals and presented more than 300 papers at academic conferences. He has also registered approximately 50 patents in the field of semiconductor device technology.
The top ten research highlights of 2018 as follows:
- Rydberg-Atom Quantum Simulator Development by Professor Jaewook Ahn and Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics
- From C-H to C-C Bonds at Room Temperature by Professor Mu-Hyun Baik from the Department of Chemistry
- The Role of Rodlike Counterions on the Interactions of DNAs by Professor Yong Woon Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology
- The Medal Preoptic Area Induces Hunting-Like Behaviors to Target Objects and Prey by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences
- Identification of the Origin of Brain Tumors and New Therapeutic Strategy by Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
- The Linear Frequency Conversion of Light at a Spatiotemporal Boundary by Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering
- An Industrial Grade Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering
- The Detection and Clustering of Mixed-Type Defect Patterns in Wafer Bin Maps by Professor Heeyoung Kim from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
- The Development of a Reconfigurable Spin-Based Logic Device by Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Development of a Miniaturized X-Ray Tube Based on Carbon Nanotube and Electronic Brachytherapy Device by Professor Sung Oh Cho from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics and Professor In-Chel Park from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Research Award. For the Innovation Award, Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering was the recipient and the Convergence Research Awards was conferred to Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Sung Gap Im from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor SangHee Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering during the ceremony.
For more on KAIST’s Top Research Achievements and Highlight of 2018, please refer to the attached below. click.
2019.04.25 View 18525
Research Day Highlights Most Outstanding Research Achievements
Professor Byung Jin Cho from the School of Electrical Engineering was selected as the Grand Research Prize Winner in recognition of his innovative research achievement in the fields of nano electric and flexible energy devices during the 2019 KAIST Research Day ceremony held on April 23 at the Chung Kunmo Conference Hall.
The ten most outstanding research achievements from the past year were also awarded in the three areas of Research, Innovation, Convergence Researches.
Professor Cho is an internationally recognized researcher in the field of future nano and energy device technology. Professor Cho’s team has continued to research on advanced CMOS (complementary metal-oxide semiconductors). CMOS has become his key research topic over the past three decades.
In 2014, he developed a glass fabric-based thermoelectric generator, which is extremely light and flexible and produces electricity from the heat of the human body. It is so flexible that the allowable bending radius of the generator is as low as 20 mm. There are no changes in performance even if the generator bends upward and downward for up to 120 cycles. His wearable thermoelectric generator was selected as one of the top ten most promising digital technologies by the Netexplo Forum in 2015.
He now is working on high-performance and ultra-flexible CMOS IC for biomedical applications, expanding his scope to thermal haptic technology in VR using graphene-CMOS hybrid integrated circuits; to self-powered wireless sensor nodes and self-powered ECG system using wearable thermoelectric generators .
In his special lecture at the ceremony, Professor Cho stressed the importance of collaboration in making scientific research and presented how he moved to future devices after focusing on scaling the devices.
“When I started the research on semiconductors, I focused on how to scale the device down as much as possible. For decades, we have conducted a number of procedures to produce tiny but efficient materials. Now we have shifted to develop flexible thermoelements and wearable devices,” said Professor Cho.
“We all thought the scaling down is the only way to create value-added technological breakthroughs. Now, the devices have been scaled down to 7nm and will go down to 5 nm soon. Over the past few years, I think we have gone through all the possible technological breakthroughs for reducing the size to 5nm. The semiconductor devices are made of more 1 billion transistors and go through 1,000 technological processes. So, there won’t be any possible way for a single genius to make a huge breakthrough. Without collaboration with others, it is nearly impossible to make any new technological breakthroughs.”
Professor Cho has published more than 240 papers in renowned academic journals and presented more than 300 papers at academic conferences. He has also registered approximately 50 patents in the field of semiconductor device technology.
The top ten research highlights of 2018 as follows:
- Rydberg-Atom Quantum Simulator Development by Professor Jaewook Ahn and Heung-Sun Sim from the Department of Physics
- From C-H to C-C Bonds at Room Temperature by Professor Mu-Hyun Baik from the Department of Chemistry
- The Role of Rodlike Counterions on the Interactions of DNAs by Professor Yong Woon Kim of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology
- The Medal Preoptic Area Induces Hunting-Like Behaviors to Target Objects and Prey by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences
- Identification of the Origin of Brain Tumors and New Therapeutic Strategy by Professor Jeong Ho Lee from the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
- The Linear Frequency Conversion of Light at a Spatiotemporal Boundary by Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering
- An Industrial Grade Flexible Transparent Force Touch Sensor by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering
- The Detection and Clustering of Mixed-Type Defect Patterns in Wafer Bin Maps by Professor Heeyoung Kim from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
- The Development of a Reconfigurable Spin-Based Logic Device by Professor Byong-Guk Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering
- The Development of a Miniaturized X-Ray Tube Based on Carbon Nanotube and Electronic Brachytherapy Device by Professor Sung Oh Cho from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics and Professor In-Chel Park from the School of Electrical Engineering received the Research Award. For the Innovation Award, Professor Munchurl Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering was the recipient and the Convergence Research Awards was conferred to Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering, Professor Sung Gap Im from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, and Professor SangHee Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering during the ceremony.
For more on KAIST’s Top Research Achievements and Highlight of 2018, please refer to the attached below. click.
2019.04.25 View 18525 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 14313
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 14313