Royal+Society+of+Chemistry
-
 On-chip Drug Screening for Identifying Antibiotic Interactions in Eight Hours
(from left: Seunggyu Kimand Professor Jessie Sungyun Jeon)
A KAIST research team developed a microfluidic-based drug screening chip that identifies synergistic interactions between two antibiotics in eight hours. This chip can be a cell-based drug screening platform for exploring critical pharmacological patterns of antibiotic interactions, along with potential applications in screening other cell-type agents and guidance for clinical therapies.
Antibiotic susceptibility testing, which determines types and doses of antibiotics that can effectively inhibit bacterial growth, has become more critical in recent years with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria strains.
To overcome the antibiotic-resistant bacteria, combinatory therapy using two or more kinds of antibiotics has been gaining considerable attention. However, the major problem is that this therapy is not always effective; occasionally, unfavorable antibiotic pairs may worsen results, leading to suppressed antimicrobial effects. Therefore, combinatory testing is a crucial preliminary process to find suitable antibiotic pairs and their concentration range against unknown pathogens, but the conventional testing methods are inconvenient for concentration dilution and sample preparation, and they take more than 24 hours to produce the results.
To reduce time and enhance the efficiency of combinatory testing, Professor Jessie Sungyun Jeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences, developed a high-throughput drug screening chip that generates 121 pairwise concentrations between two antibiotics.
The team utilized a microfluidic chip with a sample volume of a few tens of microliters. This chip enabled 121 pairwise concentrations of two antibiotics to be automatically formed in only 35 minutes.
They loaded a mixture of bacterial samples and agarose into the microchannel and injected reagents with or without antibiotics into the surrounding microchannel. The diffusion of antibiotic molecules from the channel with antibiotics to the one without antibiotics resulted in the formation of two orthogonal concentration gradients of the two antibiotics on the bacteria-trapping agarose gel.
The team observed the inhibition of bacterial growth by the antibiotic orthogonal gradients over six hours with a microscope, and confirmed different patterns of antibiotic pairs, classifying the interaction types into either synergy or antagonism.
Professor Jeon said, “The feasibility of microfluidic-based drug screening chips is promising, and we expect our microfluidic chip to be commercialized and utilized in near future.”
This study, led by Seunggyu Kim, was published in Lab on a Chip (10.1039/c8lc01406j) on March 21, 2019.
Figure 1. Back cover image for the “Lab on a Chip”.
Figure 2. Examples of testing results using the microfluidic chips developed in this research.
2019.04.18 View 31112
On-chip Drug Screening for Identifying Antibiotic Interactions in Eight Hours
(from left: Seunggyu Kimand Professor Jessie Sungyun Jeon)
A KAIST research team developed a microfluidic-based drug screening chip that identifies synergistic interactions between two antibiotics in eight hours. This chip can be a cell-based drug screening platform for exploring critical pharmacological patterns of antibiotic interactions, along with potential applications in screening other cell-type agents and guidance for clinical therapies.
Antibiotic susceptibility testing, which determines types and doses of antibiotics that can effectively inhibit bacterial growth, has become more critical in recent years with the emergence of antibiotic-resistant pathogenic bacteria strains.
To overcome the antibiotic-resistant bacteria, combinatory therapy using two or more kinds of antibiotics has been gaining considerable attention. However, the major problem is that this therapy is not always effective; occasionally, unfavorable antibiotic pairs may worsen results, leading to suppressed antimicrobial effects. Therefore, combinatory testing is a crucial preliminary process to find suitable antibiotic pairs and their concentration range against unknown pathogens, but the conventional testing methods are inconvenient for concentration dilution and sample preparation, and they take more than 24 hours to produce the results.
To reduce time and enhance the efficiency of combinatory testing, Professor Jessie Sungyun Jeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences, developed a high-throughput drug screening chip that generates 121 pairwise concentrations between two antibiotics.
The team utilized a microfluidic chip with a sample volume of a few tens of microliters. This chip enabled 121 pairwise concentrations of two antibiotics to be automatically formed in only 35 minutes.
They loaded a mixture of bacterial samples and agarose into the microchannel and injected reagents with or without antibiotics into the surrounding microchannel. The diffusion of antibiotic molecules from the channel with antibiotics to the one without antibiotics resulted in the formation of two orthogonal concentration gradients of the two antibiotics on the bacteria-trapping agarose gel.
The team observed the inhibition of bacterial growth by the antibiotic orthogonal gradients over six hours with a microscope, and confirmed different patterns of antibiotic pairs, classifying the interaction types into either synergy or antagonism.
Professor Jeon said, “The feasibility of microfluidic-based drug screening chips is promising, and we expect our microfluidic chip to be commercialized and utilized in near future.”
This study, led by Seunggyu Kim, was published in Lab on a Chip (10.1039/c8lc01406j) on March 21, 2019.
Figure 1. Back cover image for the “Lab on a Chip”.
Figure 2. Examples of testing results using the microfluidic chips developed in this research.
2019.04.18 View 31112 -
 True-meaning Wearable Displays: Self-powered, Washable and Wearable
(Video: The washing process of wearing display module) When we think about clothes, they are usually formed with textiles and have to be both wearable and washable for daily use; however, smart clothing has had a problem with its power sources and moisture permeability, which causes the devices to malfunction. This problem has now been overcome by a KAIST research team, who developed a textile-based wearable display module technology that is washable and does not require an external power source.
To ease out the problem of external power sources and enhance the practicability of wearable displays, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated their wearing display modules on real textiles that integrated polymer solar cells (PSCs) with organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs).
PSCs have been one of the most promising candidates for a next-generation power source, especially for wearable and optoelectronic applications because they can provide stable power without an external power source, while OLEDs can be driven with milliwatts. However, the problem was that they are both very vulnerable to external moisture and oxygen. The encapsulation barrier is essential for their reliability. The conventional encapsulation barrier is sufficient for normal environments; however, it loses its characteristics in aqueous environments, such as water. It limits the commercialization of wearing displays that must operate even on rainy days or after washing.
To tackle this issue, the team employed a washable encapsulation barrier that can protect the device without losing its characteristics after washing through atomic layer deposition (ALD) and spin coating. With this encapsulation technology, the team confirmed that textile-based wearing display modules including PSCs, OLEDs, and the proposed encapsulation barrier exhibited little change in characteristics even after 20 washings with 10-minute cycles. Moreover, the encapsulated device operated stably with a low curvature radius of 3mm and boasted high reliability.
Finally, it exhibited no deterioration in properties over 30 days even after being subjected to both bending stress and washing. Since it uses a less stressful textile, compared to conventional wearable electronic devices that use traditional plastic substrates, this technology can accelerate the commercialization of wearing electronic devices. Importantly, this wearable electronic device in daily life can save energy through a self-powered system.
Professor Choi said, “I could say that this research realized a truly washable wearable electronic module in the sense that it uses daily wearable textiles instead of the plastic used in conventional wearable electronic devices. Saving energy with PSCs, it can be self-powered, using nature-friendly solar energy, and washed. I believe that it has paved the way for a ‘true-meaning wearable display’ that can be formed on textile, beyond the attachable form of wearable technology.”
This research, in collaboration with Professor Seok Ho Cho from Chonnam National University and led by Eun Gyo Jeong, was published in Energy and Environmental Science (10.1039/c8ee03271h) on January 18, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic and photo of a washable wearing display module
Figure 2. Cover page of Energy and Environmental Science
2019.03.21 View 31471
True-meaning Wearable Displays: Self-powered, Washable and Wearable
(Video: The washing process of wearing display module) When we think about clothes, they are usually formed with textiles and have to be both wearable and washable for daily use; however, smart clothing has had a problem with its power sources and moisture permeability, which causes the devices to malfunction. This problem has now been overcome by a KAIST research team, who developed a textile-based wearable display module technology that is washable and does not require an external power source.
To ease out the problem of external power sources and enhance the practicability of wearable displays, Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated their wearing display modules on real textiles that integrated polymer solar cells (PSCs) with organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs).
PSCs have been one of the most promising candidates for a next-generation power source, especially for wearable and optoelectronic applications because they can provide stable power without an external power source, while OLEDs can be driven with milliwatts. However, the problem was that they are both very vulnerable to external moisture and oxygen. The encapsulation barrier is essential for their reliability. The conventional encapsulation barrier is sufficient for normal environments; however, it loses its characteristics in aqueous environments, such as water. It limits the commercialization of wearing displays that must operate even on rainy days or after washing.
To tackle this issue, the team employed a washable encapsulation barrier that can protect the device without losing its characteristics after washing through atomic layer deposition (ALD) and spin coating. With this encapsulation technology, the team confirmed that textile-based wearing display modules including PSCs, OLEDs, and the proposed encapsulation barrier exhibited little change in characteristics even after 20 washings with 10-minute cycles. Moreover, the encapsulated device operated stably with a low curvature radius of 3mm and boasted high reliability.
Finally, it exhibited no deterioration in properties over 30 days even after being subjected to both bending stress and washing. Since it uses a less stressful textile, compared to conventional wearable electronic devices that use traditional plastic substrates, this technology can accelerate the commercialization of wearing electronic devices. Importantly, this wearable electronic device in daily life can save energy through a self-powered system.
Professor Choi said, “I could say that this research realized a truly washable wearable electronic module in the sense that it uses daily wearable textiles instead of the plastic used in conventional wearable electronic devices. Saving energy with PSCs, it can be self-powered, using nature-friendly solar energy, and washed. I believe that it has paved the way for a ‘true-meaning wearable display’ that can be formed on textile, beyond the attachable form of wearable technology.”
This research, in collaboration with Professor Seok Ho Cho from Chonnam National University and led by Eun Gyo Jeong, was published in Energy and Environmental Science (10.1039/c8ee03271h) on January 18, 2019.
Figure 1. Schematic and photo of a washable wearing display module
Figure 2. Cover page of Energy and Environmental Science
2019.03.21 View 31471 -
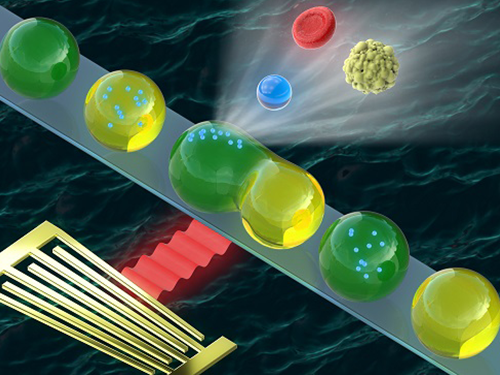 Washing and Enrichment of Micro-Particles Encapsulated in Droplets
Researchers developed microfluidic technology for the washing and enrichment of in-droplet micro-particles. They presented the technology using a microfluidic chip based on surface acoustic wave (SAW)-driven acoustic radiation force (ARF).
The team demonstrated the first instance of acoustic in-droplet micro-particle washing with a particle recovery rate of approximately 90 percent. They further extended the applicability of the proposed method to in-droplet particle enrichment with the unprecedented abilities to increase the in-droplet particle quantity and exchange the droplet dispersed phase.
This proposed method enabled on-chip, label-free, continuous, and selective in-droplet micro-particle manipulation. The team demonstrated the first instance of in-droplet micro-particle washing between two types of alternating droplets in a simple microchannel, proving that the method can increase the particle quantity, which has not been achieved by previously reported methods.
The study aimed to develop an in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment method based on SAW-driven ARF. When a droplet containing particles is exposed to an acoustic field, both the droplet and suspended particles experience ARF arising from inhomogeneous wave scattering at the liquid-liquid and liquid-solid interfaces. Unlike previous in-droplet particle manipulation methods, this method allows simultaneous and precise control over the droplets and suspended particles. Moreover, the proposed acoustic method does not require labelled particles, such as magnetic particles, and employs a simple microchannel geometry.
Microfluidic sample washing has emerged as an alternative to centrifugation because the limitations of centrifugation-based washing methods can be addressed using continuous washing processes. It also has considerable potential and importance in a variety of applications such as single-cell/particle assays, high-throughput screening of rare samples, and cell culture medium exchange.
Compared to continuous flow-based microfluidic methods, droplet-based microfluidic sample washing has been rarely explored due to technological difficulties. On-chip, in-droplet sample washing requires sample transfer across the droplet interface composed of two immiscible fluids. This process involves simultaneous and precise control over the encapsulated sample and droplet interface during the medium exchange of the in-droplet sample.
Sample encapsulation within individual microscale droplets offers isolated microenvironments for the samples. Experimental uncertainties due to cross-contamination and Taylor dispersion between multiple reagents can be reduced in droplet-based microfluidics.
This is the first research achievement made by the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare, the cross-generation collaborative lab KAIST opened in May. This novel approach pairs senior and junior faculty members for sustaining the research legacy even after the senior researcher retires. The research center, which paired Chair Professor Hyung Jin Sung and Professors Hyoungsoo Kim and Yeunwoo Cho, made a breakthrough in microfluidics along with PhD candidate Jinsoo Park. The study was featured as the cover of Lab on a Chip published by Royal Society of Chemistry.
Jinsoo Park, first author of the study, believes this technology will may serve as an in-droplet sample preparation platform with in-line integration of other droplet microfluidic components. Chair Professor Sung said, “The proposed acoustic method will offer new perspectives on sample washing and enrichment by performing the operation in microscale droplets.”
Figure 1. (a) A microfluidic device for in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment; (b) alternatingly produced droplets of two kinds at a double T-junction; (c) a droplet and encapsulated micro-particles exposed to surface acoustic wave-driven acoustic radiation force; (d-h) sequential processes of in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment operation.
2018.10.19 View 7850
Washing and Enrichment of Micro-Particles Encapsulated in Droplets
Researchers developed microfluidic technology for the washing and enrichment of in-droplet micro-particles. They presented the technology using a microfluidic chip based on surface acoustic wave (SAW)-driven acoustic radiation force (ARF).
The team demonstrated the first instance of acoustic in-droplet micro-particle washing with a particle recovery rate of approximately 90 percent. They further extended the applicability of the proposed method to in-droplet particle enrichment with the unprecedented abilities to increase the in-droplet particle quantity and exchange the droplet dispersed phase.
This proposed method enabled on-chip, label-free, continuous, and selective in-droplet micro-particle manipulation. The team demonstrated the first instance of in-droplet micro-particle washing between two types of alternating droplets in a simple microchannel, proving that the method can increase the particle quantity, which has not been achieved by previously reported methods.
The study aimed to develop an in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment method based on SAW-driven ARF. When a droplet containing particles is exposed to an acoustic field, both the droplet and suspended particles experience ARF arising from inhomogeneous wave scattering at the liquid-liquid and liquid-solid interfaces. Unlike previous in-droplet particle manipulation methods, this method allows simultaneous and precise control over the droplets and suspended particles. Moreover, the proposed acoustic method does not require labelled particles, such as magnetic particles, and employs a simple microchannel geometry.
Microfluidic sample washing has emerged as an alternative to centrifugation because the limitations of centrifugation-based washing methods can be addressed using continuous washing processes. It also has considerable potential and importance in a variety of applications such as single-cell/particle assays, high-throughput screening of rare samples, and cell culture medium exchange.
Compared to continuous flow-based microfluidic methods, droplet-based microfluidic sample washing has been rarely explored due to technological difficulties. On-chip, in-droplet sample washing requires sample transfer across the droplet interface composed of two immiscible fluids. This process involves simultaneous and precise control over the encapsulated sample and droplet interface during the medium exchange of the in-droplet sample.
Sample encapsulation within individual microscale droplets offers isolated microenvironments for the samples. Experimental uncertainties due to cross-contamination and Taylor dispersion between multiple reagents can be reduced in droplet-based microfluidics.
This is the first research achievement made by the Acousto-Microfluidics Research Center for Next-Generation Healthcare, the cross-generation collaborative lab KAIST opened in May. This novel approach pairs senior and junior faculty members for sustaining the research legacy even after the senior researcher retires. The research center, which paired Chair Professor Hyung Jin Sung and Professors Hyoungsoo Kim and Yeunwoo Cho, made a breakthrough in microfluidics along with PhD candidate Jinsoo Park. The study was featured as the cover of Lab on a Chip published by Royal Society of Chemistry.
Jinsoo Park, first author of the study, believes this technology will may serve as an in-droplet sample preparation platform with in-line integration of other droplet microfluidic components. Chair Professor Sung said, “The proposed acoustic method will offer new perspectives on sample washing and enrichment by performing the operation in microscale droplets.”
Figure 1. (a) A microfluidic device for in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment; (b) alternatingly produced droplets of two kinds at a double T-junction; (c) a droplet and encapsulated micro-particles exposed to surface acoustic wave-driven acoustic radiation force; (d-h) sequential processes of in-droplet micro-particle washing and enrichment operation.
2018.10.19 View 7850 -
 Undergrad's Paper Chosen as the Cover Article in Soft Matter
(from left: Research Professor KyuHan Kim and Undergrad Student Subeen Kim)
A KAIST undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, had his paper chosen as the cover article in an international journal during his senior year.
There have been an increasing number of undergraduate students who were published as the first author because the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation program allows more active research participation by undergraduate students.
Through URP, Kim successfully published his paper in the internationally-renowned journal, Soft Matter, which is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry, and it was chosen as the cover article of that journal in February 2018.
This publication means a lot to him because he designed the cover image himself, based on his imagination and observations.
His research is about controllable one-step double emulsion formation. Double emulsion is a system in which dispersed droplets contain additional immiscible liquid droplets.
Having great retention ability, double emulsion has been used in various applications in the food industry, in cosmetics, and for drug delivery. Nevertheless, two-step emulsification is a conventional approach to produce double emulsions that typically leads to partial destabilization of the emulsion formed during the initial stage. Hence, it does not ensure the stability of a double emulsion. On the other hand, a microfluidic approach with various flow-focusing techniques has been developed, but it has low production efficiency and thus limited industrial applications.
Kim’s results came from the process of phase inversion to solve this problem. He identified the instant formation of double emulsions during the process of phase inversion. Based on this finding, he proposed criteria to achieve high stability of double emulsion.
Through constant research, he developed a quite general method using a combination of an oil soluble poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hydrophobic silica nanoparticle (HDK H18). This new method enables one-step and stable production of double emersions in a stable manner. It also allows control of the number and the volume of inner oil droplets inside the outer water droplets by adjusting PMMA and HDK H18.
Kim enrolled at KAIST as a KAIST Presidential Fellowship and Presidential Science Scholarship in 2014. While studying both chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry he has been developing his hypothesis and conducting research.
He was able to begin conducting research because he has taken part in URP projects twice. In his sophomore year, he studied the formation of high internal phase double emulsions. After one year, he conducted research to produce superabsorbent resins, which are the base material for diapers, by using colloid particles. Using partial research outcomes, he published his paper in Nature Communications as a second author.
Kim said, “Double majoring the chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry has helped me producing this outcome. I hope that this research contributes to commercializing double emulsions. I will continue to identify accurate principles to produce chemicals that can be controlled exquisitely.”
Figure 1. The cover article of Soft Matter
2018.05.03 View 10988
Undergrad's Paper Chosen as the Cover Article in Soft Matter
(from left: Research Professor KyuHan Kim and Undergrad Student Subeen Kim)
A KAIST undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, had his paper chosen as the cover article in an international journal during his senior year.
There have been an increasing number of undergraduate students who were published as the first author because the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation program allows more active research participation by undergraduate students.
Through URP, Kim successfully published his paper in the internationally-renowned journal, Soft Matter, which is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry, and it was chosen as the cover article of that journal in February 2018.
This publication means a lot to him because he designed the cover image himself, based on his imagination and observations.
His research is about controllable one-step double emulsion formation. Double emulsion is a system in which dispersed droplets contain additional immiscible liquid droplets.
Having great retention ability, double emulsion has been used in various applications in the food industry, in cosmetics, and for drug delivery. Nevertheless, two-step emulsification is a conventional approach to produce double emulsions that typically leads to partial destabilization of the emulsion formed during the initial stage. Hence, it does not ensure the stability of a double emulsion. On the other hand, a microfluidic approach with various flow-focusing techniques has been developed, but it has low production efficiency and thus limited industrial applications.
Kim’s results came from the process of phase inversion to solve this problem. He identified the instant formation of double emulsions during the process of phase inversion. Based on this finding, he proposed criteria to achieve high stability of double emulsion.
Through constant research, he developed a quite general method using a combination of an oil soluble poly methyl methacrylate (PMMA) and hydrophobic silica nanoparticle (HDK H18). This new method enables one-step and stable production of double emersions in a stable manner. It also allows control of the number and the volume of inner oil droplets inside the outer water droplets by adjusting PMMA and HDK H18.
Kim enrolled at KAIST as a KAIST Presidential Fellowship and Presidential Science Scholarship in 2014. While studying both chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry he has been developing his hypothesis and conducting research.
He was able to begin conducting research because he has taken part in URP projects twice. In his sophomore year, he studied the formation of high internal phase double emulsions. After one year, he conducted research to produce superabsorbent resins, which are the base material for diapers, by using colloid particles. Using partial research outcomes, he published his paper in Nature Communications as a second author.
Kim said, “Double majoring the chemical and biomolecular engineering and chemistry has helped me producing this outcome. I hope that this research contributes to commercializing double emulsions. I will continue to identify accurate principles to produce chemicals that can be controlled exquisitely.”
Figure 1. The cover article of Soft Matter
2018.05.03 View 10988 -
 Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 8282
Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 8282 -
 Easier Way to Produce High Performing, Flexible Micro-Supercapacitor
(Professor Minyang Yang and PhD Student Jae Hak Lee)
Professor Minyang Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his team developed a high-energy, flexible micro-supercapacitor in a simple and cost-effective way.
Compared to conventional micro-batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, these new batteries, also called supercapacitors, are significantly faster to charge and semi-permanent.
Thin, flexible micro-supercapacitors can be a power source directly attached to wearable and flexible electronics.
However, fabrication of these micro-supercapacitors requires a complex patterning process, such as lithography techniques and vacuum evaporation. Hence, the process requires expensive instruments and toxic chemicals.
To simplify the fabrication of micro-supercapacitors in an eco-friendly manner, the team developed laser growth sintering technology. This technology manufactures superporous silver electrodes and applies them to the supercapacitors’ electrodes.
The team used a laser to form micro-patterns and generated nanoporous structures inside. This laser-induced growth sintering contributed to shortening the manufacturing process from ten steps to one.
Moreover, the team explored this unique laser growth sintering process –nucleation, growth, and sintering –by employing a particle-free, organometallic solution, which is not costly compared to typical laser-sintering methods for metallic nanoparticle solutions used in the printing of micro-electrodes.
Finally, unlike the typical supercapacitors comprised of a single substance, the team applied an asymmetric electrode configuration of nanoporous gold and manganese dioxide, which exhibits a highly-specific capacitance, to operate at a high voltage.
This method allows the team to develop energy storage with a high capacity. This developed micro-supercapacitor only requires four seconds to be charged and passed more than 5,000 durability tests.
Professor Yang said, “This research outcome can be used as energy storage installed in wearable and flexible electronic devices. Through this research, we are one step closer to realizing a complete version of flexible electronic devices by incorporating a power supply.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Jae Hak Lee, was selected as the cover of Journal of Materials Chemistry A on December 21, 2017.
Figure 1. Cover of the Journal Materials Chemistry A
Figure 2. Manufactured micro-supercapacitor and its performance
Figure 3. Laser growth sintering mechanism
Figure 4. Structural change of the silver conductor according to the irradiated laser energy
2018.01.18 View 7992
Easier Way to Produce High Performing, Flexible Micro-Supercapacitor
(Professor Minyang Yang and PhD Student Jae Hak Lee)
Professor Minyang Yang from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his team developed a high-energy, flexible micro-supercapacitor in a simple and cost-effective way.
Compared to conventional micro-batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, these new batteries, also called supercapacitors, are significantly faster to charge and semi-permanent.
Thin, flexible micro-supercapacitors can be a power source directly attached to wearable and flexible electronics.
However, fabrication of these micro-supercapacitors requires a complex patterning process, such as lithography techniques and vacuum evaporation. Hence, the process requires expensive instruments and toxic chemicals.
To simplify the fabrication of micro-supercapacitors in an eco-friendly manner, the team developed laser growth sintering technology. This technology manufactures superporous silver electrodes and applies them to the supercapacitors’ electrodes.
The team used a laser to form micro-patterns and generated nanoporous structures inside. This laser-induced growth sintering contributed to shortening the manufacturing process from ten steps to one.
Moreover, the team explored this unique laser growth sintering process –nucleation, growth, and sintering –by employing a particle-free, organometallic solution, which is not costly compared to typical laser-sintering methods for metallic nanoparticle solutions used in the printing of micro-electrodes.
Finally, unlike the typical supercapacitors comprised of a single substance, the team applied an asymmetric electrode configuration of nanoporous gold and manganese dioxide, which exhibits a highly-specific capacitance, to operate at a high voltage.
This method allows the team to develop energy storage with a high capacity. This developed micro-supercapacitor only requires four seconds to be charged and passed more than 5,000 durability tests.
Professor Yang said, “This research outcome can be used as energy storage installed in wearable and flexible electronic devices. Through this research, we are one step closer to realizing a complete version of flexible electronic devices by incorporating a power supply.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Jae Hak Lee, was selected as the cover of Journal of Materials Chemistry A on December 21, 2017.
Figure 1. Cover of the Journal Materials Chemistry A
Figure 2. Manufactured micro-supercapacitor and its performance
Figure 3. Laser growth sintering mechanism
Figure 4. Structural change of the silver conductor according to the irradiated laser energy
2018.01.18 View 7992 -
 Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 6937
Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 6937 -
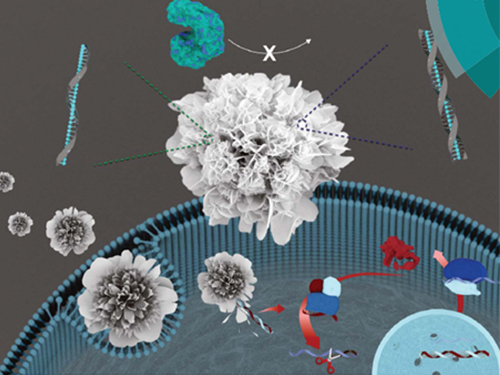 Nuclease-Resistant Hybrid Nanoflowers
An eco-friendly method to synthesize DNA-copper nanoflowers with high load efficiencies, low cytotoxicity, and strong resistance against nucleases has been developed by Professor Hyun Gyu Park in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his collaborators.
The research team successfully formed a flower-shaped nanostructure in an eco-friendly condition by using interactions between copper ions and DNA containing amide and amine groups. The resulting nanoflowers exhibit high DNA loading capacities in addition to low cytotoxicity.
Flower-shaped nanocrystals called nanoflowers have gained attention for their distinct features of high surface roughness and high surface area to volume ratios. The nanoflowers have been used in many areas including catalysis, electronics, and analytical chemistry.
Of late, research breakthroughs were made in the generation of hybrid inorganic-organic nanoflowers containing various enzymes as organic components. The hybridization with inorganic materials greatly enhanced enzymatic activity, stability, and durability compared to the corresponding free enzymes.
Generally, the formation of protein nanocrystals requires high heat treatment so it has limitations for achieving the high loading capacities of intact DNA.
The research team addressed the issue, focusing on the fact that nucleic acids with well-defined structures and selective recognition properties also contain amide and amine groups in their nucleobases. They proved that flower-like structures could be formed by using nucleic acids as a synthetic template, which paved the way to synthesize the hybrid nanoflowers containing DNA as an organic component in an eco-friendly condition.
The team also confirmed that this synthetic method can be universally applied to any DNA sequences containing amide and amine groups. They said their approach is quite unique considering that the majority of previous works focused on the utilization of DNA as a linker to assemble the nanomaterials. They said the method has several advantageous features. First, the ‘green’ synthetic procedure doesn’t involve any toxic chemicals, and shows low cytotoxicity and strong resistance against nucleases. Second, the obtained nanoflowers exhibit exceptionally high DNA loading capacities.
Above all, such superior features of hybrid nanoflowers enabled the sensitive detection of various molecules including phenol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. DNA-copper nanoflowers showed even higher peroxidase activity than those of protein-copper nanoflowers, which may be due to the larger surface area of the flower- shaped structures, creating a greater chance for applying them in the field of sensing of detection of hydrogen peroxide.
The research team expects that their research will create diverse applications in many areas including biosensors and will be further applied into therapeutic applications.
Professor Park said, “The inorganic component in the hybrid nanoflowers not only exhibits low cytotoxicity, but also protects the encapsulated DNA from being cleaved by endonuclease enzymes. Using this feature, the nanostructure will be applied into developing gene therapeutic carriers.”
This research was co-led by Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University and KAIST graduate Ki Soo Park, currently a professor at Konkuk University, is the first author. The research was featured as the front cover article of the Journal of Materials Chemistry B on March 28, Issue 12, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The research was funded by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Global Frontier Project of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
(Figure: (A) Schematic illustration of the formation of nuclease-resistant DNA–inorganic nanoflowers. (B) SEM images showing time-dependent growth of DNA-nanoflowers. The concentration of A-rich ssDNA (Table S1, ESI†) was 0.25 mM.)
2017.04.14 View 9367
Nuclease-Resistant Hybrid Nanoflowers
An eco-friendly method to synthesize DNA-copper nanoflowers with high load efficiencies, low cytotoxicity, and strong resistance against nucleases has been developed by Professor Hyun Gyu Park in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his collaborators.
The research team successfully formed a flower-shaped nanostructure in an eco-friendly condition by using interactions between copper ions and DNA containing amide and amine groups. The resulting nanoflowers exhibit high DNA loading capacities in addition to low cytotoxicity.
Flower-shaped nanocrystals called nanoflowers have gained attention for their distinct features of high surface roughness and high surface area to volume ratios. The nanoflowers have been used in many areas including catalysis, electronics, and analytical chemistry.
Of late, research breakthroughs were made in the generation of hybrid inorganic-organic nanoflowers containing various enzymes as organic components. The hybridization with inorganic materials greatly enhanced enzymatic activity, stability, and durability compared to the corresponding free enzymes.
Generally, the formation of protein nanocrystals requires high heat treatment so it has limitations for achieving the high loading capacities of intact DNA.
The research team addressed the issue, focusing on the fact that nucleic acids with well-defined structures and selective recognition properties also contain amide and amine groups in their nucleobases. They proved that flower-like structures could be formed by using nucleic acids as a synthetic template, which paved the way to synthesize the hybrid nanoflowers containing DNA as an organic component in an eco-friendly condition.
The team also confirmed that this synthetic method can be universally applied to any DNA sequences containing amide and amine groups. They said their approach is quite unique considering that the majority of previous works focused on the utilization of DNA as a linker to assemble the nanomaterials. They said the method has several advantageous features. First, the ‘green’ synthetic procedure doesn’t involve any toxic chemicals, and shows low cytotoxicity and strong resistance against nucleases. Second, the obtained nanoflowers exhibit exceptionally high DNA loading capacities.
Above all, such superior features of hybrid nanoflowers enabled the sensitive detection of various molecules including phenol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. DNA-copper nanoflowers showed even higher peroxidase activity than those of protein-copper nanoflowers, which may be due to the larger surface area of the flower- shaped structures, creating a greater chance for applying them in the field of sensing of detection of hydrogen peroxide.
The research team expects that their research will create diverse applications in many areas including biosensors and will be further applied into therapeutic applications.
Professor Park said, “The inorganic component in the hybrid nanoflowers not only exhibits low cytotoxicity, but also protects the encapsulated DNA from being cleaved by endonuclease enzymes. Using this feature, the nanostructure will be applied into developing gene therapeutic carriers.”
This research was co-led by Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University and KAIST graduate Ki Soo Park, currently a professor at Konkuk University, is the first author. The research was featured as the front cover article of the Journal of Materials Chemistry B on March 28, Issue 12, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The research was funded by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Global Frontier Project of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
(Figure: (A) Schematic illustration of the formation of nuclease-resistant DNA–inorganic nanoflowers. (B) SEM images showing time-dependent growth of DNA-nanoflowers. The concentration of A-rich ssDNA (Table S1, ESI†) was 0.25 mM.)
2017.04.14 View 9367 -
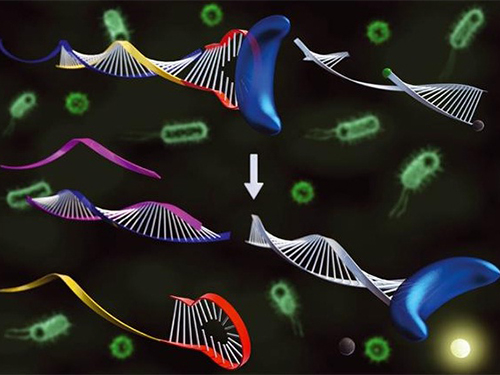 Affordable Genetic Diagnostic Technique for Target DNA Analysis Developed
Professor Hyun-Gyu Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a technique to analyze various target DNAs using an aptamer, a DNA fragment that can recognize and bind to a specific protein or enzyme. This technique will allow the development of affordable genetic diagnoses for new bacteria or virus, such as Middle Ease Respiratory Syndrome (MERS). The research findings were published in the June issue of Chemical Communications, issued by the Royal Society of Chemistry in the United Kingdom. The paper was selected as a lead article of the journal.
The existing genetic diagnosis technique, based on molecular beacon probes, requires a new beacon probe whenever a target DNA mutates. As a result, it was costly to analyze various target DNA fragments. To address this problem, Professor Park’s team designed an aptamer that binds and deactivates DNA polymerase. The technique was used in reverse, so that the aptemer did not bind to the polymerase, maintaining its activated state, only if the target DNA was present. These probes are called TagMan probes.
The controlled activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase enables nucleic acid to elongate or dwindle, making it possible to measure fluorescence signals coming from TaqMan probes. This same probe can be used to detect various target DNAs, leading to the development of a new and sensitive genetic diagnostic technique.
Unlike the existing molecular beacon probe technique which requires a new probe for every target DNA, this new technique uses the same fluorescent TaqMan probe, which is cheaper and easier to detect a number of different target nucleic acid fragments. The application of this technique will make the process of identifying and detecting foreign DNAs from pathogens such as virus and bacteria more affordable and simple.
Professor Park said, “This technique will enable us to develop simpler diagnostic kits for new pathogens, such as MERS, allowing a faster response to various diseases. Our technology can also be applied widely in the field of genetic diagnostics.”
Picture: A schematic image of target nucleic acid extracted through the activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase
2015.07.31 View 10501
Affordable Genetic Diagnostic Technique for Target DNA Analysis Developed
Professor Hyun-Gyu Park of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has developed a technique to analyze various target DNAs using an aptamer, a DNA fragment that can recognize and bind to a specific protein or enzyme. This technique will allow the development of affordable genetic diagnoses for new bacteria or virus, such as Middle Ease Respiratory Syndrome (MERS). The research findings were published in the June issue of Chemical Communications, issued by the Royal Society of Chemistry in the United Kingdom. The paper was selected as a lead article of the journal.
The existing genetic diagnosis technique, based on molecular beacon probes, requires a new beacon probe whenever a target DNA mutates. As a result, it was costly to analyze various target DNA fragments. To address this problem, Professor Park’s team designed an aptamer that binds and deactivates DNA polymerase. The technique was used in reverse, so that the aptemer did not bind to the polymerase, maintaining its activated state, only if the target DNA was present. These probes are called TagMan probes.
The controlled activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase enables nucleic acid to elongate or dwindle, making it possible to measure fluorescence signals coming from TaqMan probes. This same probe can be used to detect various target DNAs, leading to the development of a new and sensitive genetic diagnostic technique.
Unlike the existing molecular beacon probe technique which requires a new probe for every target DNA, this new technique uses the same fluorescent TaqMan probe, which is cheaper and easier to detect a number of different target nucleic acid fragments. The application of this technique will make the process of identifying and detecting foreign DNAs from pathogens such as virus and bacteria more affordable and simple.
Professor Park said, “This technique will enable us to develop simpler diagnostic kits for new pathogens, such as MERS, allowing a faster response to various diseases. Our technology can also be applied widely in the field of genetic diagnostics.”
Picture: A schematic image of target nucleic acid extracted through the activation and deactivation of DNA polymerase
2015.07.31 View 10501 -
 Prof. Sang-Ouk Kim Featured on the Cover of Emerging Investigator Special Issue
KAIST Prof. Sang-Ouk Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was featured on the cover of the Emerging Investigator Special Issue published by Britain"s Royal Society of Chemistry on June 21, university authorities said on Monday (June 22).
The special issue shed spotlight on 18 up-and-coming scientists who have been selected through the recommendation and rigorous screening process of the editorial and advisory boards of the Royal Society of Chemistry. The 18 scientists consist of six from the American continent, 10 from Europe, one from Japan and one from Korea.
The journal introduced Prof. Kim"s paper, titled "Highly entangled carbon nanotube (CNT) scaffolds by self-organized aqueous droplets." Kim explained in the paper that the cellular CNT demonstrated high electrical conductivity and field-emission properties, which is potentially useful for various applications in electronics and energy storage devices.
2009.06.24 View 13793
Prof. Sang-Ouk Kim Featured on the Cover of Emerging Investigator Special Issue
KAIST Prof. Sang-Ouk Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was featured on the cover of the Emerging Investigator Special Issue published by Britain"s Royal Society of Chemistry on June 21, university authorities said on Monday (June 22).
The special issue shed spotlight on 18 up-and-coming scientists who have been selected through the recommendation and rigorous screening process of the editorial and advisory boards of the Royal Society of Chemistry. The 18 scientists consist of six from the American continent, 10 from Europe, one from Japan and one from Korea.
The journal introduced Prof. Kim"s paper, titled "Highly entangled carbon nanotube (CNT) scaffolds by self-organized aqueous droplets." Kim explained in the paper that the cellular CNT demonstrated high electrical conductivity and field-emission properties, which is potentially useful for various applications in electronics and energy storage devices.
2009.06.24 View 13793