OT
-
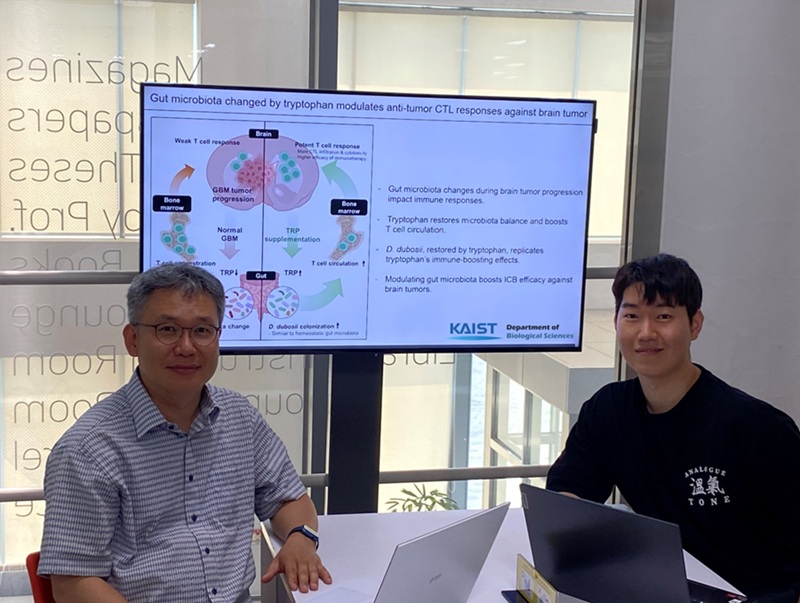 KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut Microbiota
< Photo 1.(From left) Prof. Heung Kyu Lee, Department of Biological Sciences,
and Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim>
Advanced treatments, known as immunotherapies that activate T cells—our body's immune cells—to eliminate cancer cells, have shown limited efficacy as standalone therapies for glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain tumor. This is due to their minimal response to glioblastoma and high resistance to treatment.
Now, a KAIST research team has now demonstrated a new therapeutic strategy that can enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy for brain tumors by utilizing gut microbes and their metabolites. This also opens up possibilities for developing microbiome-based immunotherapy supplements in the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July 1 that a research team led by Professor Heung Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences discovered and demonstrated a method to significantly improve the efficiency of glioblastoma immunotherapy by focusing on changes in the gut microbial ecosystem.
The research team noted that as glioblastoma progresses, the concentration of ‘tryptophan’, an important amino acid in the gut, sharply decreases, leading to changes in the gut microbial ecosystem. They discovered that by supplementing tryptophan to restore microbial diversity, specific beneficial strains activate CD8 T cells (a type of immune cell) and induce their infiltration into tumor tissues. Through a mouse model of glioblastoma, the research team confirmed that tryptophan supplementation enhanced the response of cancer-attacking T cells (especially CD8 T cells), leading to their increased migration to tumor sites such as lymph nodes and the brain.
In this process, they also revealed that ‘Duncaniella dubosii’, a beneficial commensal bacterium present in the gut, plays a crucial role. This bacterium helped T cells effectively redistribute within the body, and survival rates significantly improved when used in combination with immunotherapy (anti-PD-1).
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that even when this commensal bacterium was administered alone to germ-free mice (mice without any commensal microbes), the survival rate for glioblastoma increased. This is because the bacterium utilizes tryptophan to regulate the gut environment, and the metabolites produced in this process strengthen the ability of CD8 T cells to attack cancer cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This research is a meaningful achievement, showing that even in intractable brain tumors where immune checkpoint inhibitors had no effect, a combined strategy utilizing gut microbes can significantly enhance treatment response."
Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim of KAIST (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute for Biological Sciences) participated as the first author. The research findings were published online in Cell Reports, an international journal in the life sciences, on June 26.
This research was conducted as part of the Basic Research Program and Bio & Medical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
※Paper Title: Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by brain tumor modulates the efficacy of immunotherapy
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115825
2025.07.02 View 126
KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut Microbiota
< Photo 1.(From left) Prof. Heung Kyu Lee, Department of Biological Sciences,
and Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim>
Advanced treatments, known as immunotherapies that activate T cells—our body's immune cells—to eliminate cancer cells, have shown limited efficacy as standalone therapies for glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain tumor. This is due to their minimal response to glioblastoma and high resistance to treatment.
Now, a KAIST research team has now demonstrated a new therapeutic strategy that can enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy for brain tumors by utilizing gut microbes and their metabolites. This also opens up possibilities for developing microbiome-based immunotherapy supplements in the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July 1 that a research team led by Professor Heung Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences discovered and demonstrated a method to significantly improve the efficiency of glioblastoma immunotherapy by focusing on changes in the gut microbial ecosystem.
The research team noted that as glioblastoma progresses, the concentration of ‘tryptophan’, an important amino acid in the gut, sharply decreases, leading to changes in the gut microbial ecosystem. They discovered that by supplementing tryptophan to restore microbial diversity, specific beneficial strains activate CD8 T cells (a type of immune cell) and induce their infiltration into tumor tissues. Through a mouse model of glioblastoma, the research team confirmed that tryptophan supplementation enhanced the response of cancer-attacking T cells (especially CD8 T cells), leading to their increased migration to tumor sites such as lymph nodes and the brain.
In this process, they also revealed that ‘Duncaniella dubosii’, a beneficial commensal bacterium present in the gut, plays a crucial role. This bacterium helped T cells effectively redistribute within the body, and survival rates significantly improved when used in combination with immunotherapy (anti-PD-1).
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that even when this commensal bacterium was administered alone to germ-free mice (mice without any commensal microbes), the survival rate for glioblastoma increased. This is because the bacterium utilizes tryptophan to regulate the gut environment, and the metabolites produced in this process strengthen the ability of CD8 T cells to attack cancer cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This research is a meaningful achievement, showing that even in intractable brain tumors where immune checkpoint inhibitors had no effect, a combined strategy utilizing gut microbes can significantly enhance treatment response."
Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim of KAIST (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute for Biological Sciences) participated as the first author. The research findings were published online in Cell Reports, an international journal in the life sciences, on June 26.
This research was conducted as part of the Basic Research Program and Bio & Medical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
※Paper Title: Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by brain tumor modulates the efficacy of immunotherapy
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115825
2025.07.02 View 126 -
 KAIST Invites World-Renowned Scholars, Elevating Global Competitiveness
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor John Rogers, Professor Gregg Rothermel, Dr. Sang H. Choi >
KAIST announced on June 27th that it has appointed three world-renowned scholars, including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University, USA, as Invited Distinguished Professors in key departments such as Materials Science and Engineering.
Professor John A. Rogers (Northwestern University, USA) will be working with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering from July 2025 to June 2028 with Professor Gregg Rothermel (North Carolina State University, USA) working with the School of Computing from August 2025 to July 2026, and Dr. Sang H. Choi (NASA Langley Research Center, USA) with the Department of Aerospace Engineering from May 2025 to April 2028.
Professor John A. Rogers, a person of global authority in the field of bio-integrated electronics, has been leading advanced convergence technologies such as flexible electronics, smart skin, and implantable sensors. His significant impact on academia and industry is evident through over 900 papers published in top-tier academic journals like Science, Nature, and Cell, and he comes in an H-index of 240*. His research group, the Rogers Research Group at Northwestern University, focuses on "Science that brings Solutions to Society," encompassing areas such as bio-integrated microsystems and unconventional nanofabrication techniques. He is the founding Director of the Querrey-Simpson Institute of Bioelectronics at Northwestern University.
* H-index 240: An H-index is a measurement used to assess the research productivity and impact of an individual authors. H-index 240 means that 240 or more papers have been cited at least 240 times each, indicating a significant impact and the presumable status as a world-class scholar.
The Department of Materials Science and Engineering plans to further enhance its research capabilities in next-generation bio-implantable materials and wearable devices and boost its global competitiveness through the invitation of Professor Rogers. In particular, it aims to create strong research synergies by linking with the development of bio-convergence interface materials, a core task of the Leading Research Center (ERC, total research budget of 13.5 billion KRW over 7 years) led by Professor Kun-Jae Lee.
Professor Gregg Rothermel, a world-renowned scholar in software engineering, was ranked second among the top 50 global researchers by Communications of the ACM. For over 30 years, he has conducted practical research to improve software reliability and quality. He has achieved influential research outcomes through collaborations with global companies such as Boeing, Microsoft, and Lockheed Martin. Dr. Rothermel's research at North Carolina State University focuses on software engineering and program analysis, with significant contributions through initiatives like the ESQuaReD Laboratory and the Software-Artifact Infrastructure Repository (SIR).
The School of Computing plans to strengthen its research capabilities in software engineering and conduct collaborative research on software design and testing to enhance the reliability and safety of AI-based software systems through the invitation of Professor Gregg Rothermel. In particular, he is expected to participate in the Big Data Edge-Cloud Service Research Center (ITRC, total research budget of 6.7 billion KRW over 8 years) led by Professor In-Young Ko of the School of Computing, and the Research on Improving Complex Mobility Safety (SafetyOps, Digital Columbus Project, total research budget of 3.5 billion KRW over 8 years), contributing to resolving uncertainties in machine learning-based AI software and advancing technology.
Dr. Sang H. Choi, a global expert in space exploration and energy harvesting, has worked at NASA Langley Research Center for over 40 years, authoring over 200 papers and reports, holding 45 patents, and receiving 71 awards from NASA. In 2022, he was inducted into the 'Inventors Hall of Fame' as part of NASA's Technology Transfer Program. This is a rare honor, recognizing researchers who have contributed to the private sector dissemination of space exploration technology, with only 35 individuals worldwide selected to date. Dr. Choi's extensive work at NASA includes research on advanced electronic and energetic materials, satellite sensors, and various nano-technologies.
Dr. Choi plans to collaborate with Associate Professor Hyun-Jung Kim (former NASA Research Scientist, 2009-2024), who joined the Department of Aerospace Engineering in September of 2024, to lead the development of core technologies for lunar exploration (energy sources, sensing, in-situ resource utilization ISRU).
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee stated, "It is very meaningful to be able to invite these world-class scholars. Through these appointments, KAIST will further strengthen its global competitiveness in research in the fields of advanced convergence technology such as bio-convergence electronics, AI software engineering, and space exploration, securing our position as the leader of global innovations."
2025.06.27 View 583
KAIST Invites World-Renowned Scholars, Elevating Global Competitiveness
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor John Rogers, Professor Gregg Rothermel, Dr. Sang H. Choi >
KAIST announced on June 27th that it has appointed three world-renowned scholars, including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University, USA, as Invited Distinguished Professors in key departments such as Materials Science and Engineering.
Professor John A. Rogers (Northwestern University, USA) will be working with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering from July 2025 to June 2028 with Professor Gregg Rothermel (North Carolina State University, USA) working with the School of Computing from August 2025 to July 2026, and Dr. Sang H. Choi (NASA Langley Research Center, USA) with the Department of Aerospace Engineering from May 2025 to April 2028.
Professor John A. Rogers, a person of global authority in the field of bio-integrated electronics, has been leading advanced convergence technologies such as flexible electronics, smart skin, and implantable sensors. His significant impact on academia and industry is evident through over 900 papers published in top-tier academic journals like Science, Nature, and Cell, and he comes in an H-index of 240*. His research group, the Rogers Research Group at Northwestern University, focuses on "Science that brings Solutions to Society," encompassing areas such as bio-integrated microsystems and unconventional nanofabrication techniques. He is the founding Director of the Querrey-Simpson Institute of Bioelectronics at Northwestern University.
* H-index 240: An H-index is a measurement used to assess the research productivity and impact of an individual authors. H-index 240 means that 240 or more papers have been cited at least 240 times each, indicating a significant impact and the presumable status as a world-class scholar.
The Department of Materials Science and Engineering plans to further enhance its research capabilities in next-generation bio-implantable materials and wearable devices and boost its global competitiveness through the invitation of Professor Rogers. In particular, it aims to create strong research synergies by linking with the development of bio-convergence interface materials, a core task of the Leading Research Center (ERC, total research budget of 13.5 billion KRW over 7 years) led by Professor Kun-Jae Lee.
Professor Gregg Rothermel, a world-renowned scholar in software engineering, was ranked second among the top 50 global researchers by Communications of the ACM. For over 30 years, he has conducted practical research to improve software reliability and quality. He has achieved influential research outcomes through collaborations with global companies such as Boeing, Microsoft, and Lockheed Martin. Dr. Rothermel's research at North Carolina State University focuses on software engineering and program analysis, with significant contributions through initiatives like the ESQuaReD Laboratory and the Software-Artifact Infrastructure Repository (SIR).
The School of Computing plans to strengthen its research capabilities in software engineering and conduct collaborative research on software design and testing to enhance the reliability and safety of AI-based software systems through the invitation of Professor Gregg Rothermel. In particular, he is expected to participate in the Big Data Edge-Cloud Service Research Center (ITRC, total research budget of 6.7 billion KRW over 8 years) led by Professor In-Young Ko of the School of Computing, and the Research on Improving Complex Mobility Safety (SafetyOps, Digital Columbus Project, total research budget of 3.5 billion KRW over 8 years), contributing to resolving uncertainties in machine learning-based AI software and advancing technology.
Dr. Sang H. Choi, a global expert in space exploration and energy harvesting, has worked at NASA Langley Research Center for over 40 years, authoring over 200 papers and reports, holding 45 patents, and receiving 71 awards from NASA. In 2022, he was inducted into the 'Inventors Hall of Fame' as part of NASA's Technology Transfer Program. This is a rare honor, recognizing researchers who have contributed to the private sector dissemination of space exploration technology, with only 35 individuals worldwide selected to date. Dr. Choi's extensive work at NASA includes research on advanced electronic and energetic materials, satellite sensors, and various nano-technologies.
Dr. Choi plans to collaborate with Associate Professor Hyun-Jung Kim (former NASA Research Scientist, 2009-2024), who joined the Department of Aerospace Engineering in September of 2024, to lead the development of core technologies for lunar exploration (energy sources, sensing, in-situ resource utilization ISRU).
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee stated, "It is very meaningful to be able to invite these world-class scholars. Through these appointments, KAIST will further strengthen its global competitiveness in research in the fields of advanced convergence technology such as bio-convergence electronics, AI software engineering, and space exploration, securing our position as the leader of global innovations."
2025.06.27 View 583 -
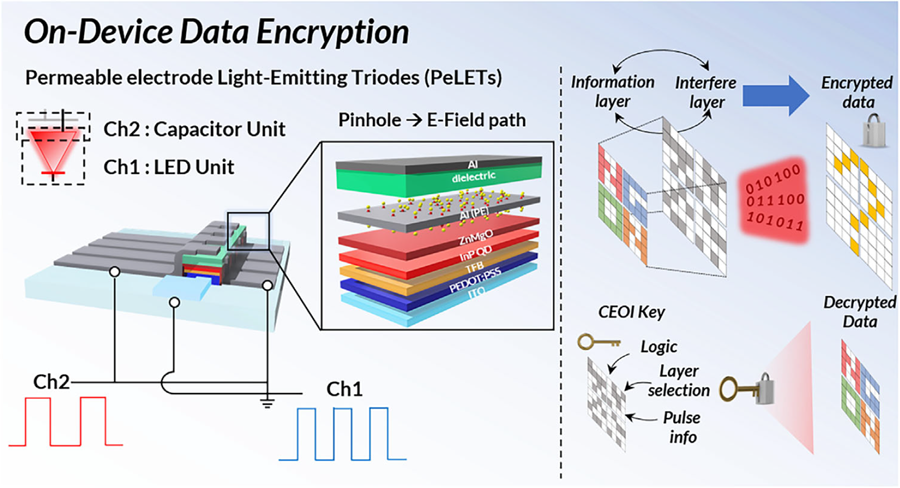 KAIST's Li-Fi - Achieves 100 Times Faster Speed and Enhanced Security of Wi-Fi
- KAIST-KRISS Develop 'On-Device Encryption Optical Transmitter' Based on Eco-Friendly Quantum Dots
- New Li-Fi Platform Technology Achieves High Performance with 17.4% Device Efficiency and 29,000 nit Brightness, Simultaneously Improving Transmission Speed and Security
- Presents New Methodology for High-Speed and Encrypted Communication Through Single-Device-Based Dual-Channel Optical Modulation
< Photo 1. (Front row from left) Seungmin Shin, First Author; Professor Himchan Cho; (Back row from left) Hyungdoh Lee, Seungwoo Lee, Wonbeom Lee; (Top left) Dr. Kyung-geun Lim >
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a wireless communication technology that utilizes the visible light spectrum (400-800 THz), similar to LED light, offering speeds up to 100 times faster than existing Wi-Fi (up to 224 Gbps). While it has fewer limitations in available frequency allocation and less radio interference, it is relatively vulnerable to security breaches as anyone can access it. Korean researchers have now proposed a new Li-Fi platform that overcomes the limitations of conventional optical communication devices and can simultaneously enhance both transmission speed and security.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that Professor Himchan Cho's research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Ho-Seong Lee) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young-Sik Kim), has developed 'on-device encryption optical communication device' technology for the utilization of 'Li-Fi,' which is attracting attention as a next-generation ultra-high-speed data communication.
Professor Cho's team created high-efficiency light-emitting triode devices using eco-friendly quantum dots (low-toxicity and sustainable materials). The device developed by the research team is a mechanism that generates light using an electric field. Specifically, the electric field is concentrated in 'tiny holes (pinholes) in the permeable electrode' and transmitted beyond the electrode. This device utilizes this principle to simultaneously process two input data streams.
Using this principle, the research team developed a technology called 'on-device encryption optical transmitter.' The core of this technology is that the device itself converts information into light and simultaneously encrypts it. This means that enhanced security data transmission is possible without the need for complex, separate equipment.
External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) is an indicator of how efficiently electricity is converted into light, with a general commercialization standard of about 20%. The newly developed device recorded an EQE of 17.4%, and its luminance was 29,000 nit, significantly exceeding the maximum brightness of a smartphone OLED screen, which is 2,000 nit, demonstrating a brightness more than 10 times higher.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the device structure developed by the research team and encrypted communication >
Furthermore, to more accurately understand how this device converts information into light, the research team used a method called 'transient electroluminescence analysis.' They analyzed the light-emitting characteristics generated by the device when voltage was instantaneously applied for very short durations (hundreds of nanoseconds = billionths of a second). Through this analysis, they investigated the movement of charges within the device at hundreds of nanoseconds, elucidating the operating mechanism of dual-channel optical modulation implemented within a single device.
Professor Himchan Cho of KAIST stated, "This research overcomes the limitations of existing optical communication devices and proposes a new communication platform that can both increase transmission speed and enhance security."
< Photo 2. Professor Himchan Cho, Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
He added, "This technology, which strengthens security without additional equipment and simultaneously enables encryption and transmission, can be widely applied in various fields where security is crucial in the future."
This research, with Seungmin Shin, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participating as the first author, and Professor Himchan Cho and Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of KRISS as co-corresponding authors, was published in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on May 30th and was selected as an inside front cover paper.※ Paper Title: High-Efficiency Quantum Dot Permeable electrode Light-Emitting Triodes for Visible-Light Communications and On-Device Data Encryption※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202503189
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST), and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.24 View 943
KAIST's Li-Fi - Achieves 100 Times Faster Speed and Enhanced Security of Wi-Fi
- KAIST-KRISS Develop 'On-Device Encryption Optical Transmitter' Based on Eco-Friendly Quantum Dots
- New Li-Fi Platform Technology Achieves High Performance with 17.4% Device Efficiency and 29,000 nit Brightness, Simultaneously Improving Transmission Speed and Security
- Presents New Methodology for High-Speed and Encrypted Communication Through Single-Device-Based Dual-Channel Optical Modulation
< Photo 1. (Front row from left) Seungmin Shin, First Author; Professor Himchan Cho; (Back row from left) Hyungdoh Lee, Seungwoo Lee, Wonbeom Lee; (Top left) Dr. Kyung-geun Lim >
Li-Fi (Light Fidelity) is a wireless communication technology that utilizes the visible light spectrum (400-800 THz), similar to LED light, offering speeds up to 100 times faster than existing Wi-Fi (up to 224 Gbps). While it has fewer limitations in available frequency allocation and less radio interference, it is relatively vulnerable to security breaches as anyone can access it. Korean researchers have now proposed a new Li-Fi platform that overcomes the limitations of conventional optical communication devices and can simultaneously enhance both transmission speed and security.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th that Professor Himchan Cho's research team from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of the Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS, President Ho-Seong Lee) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young-Sik Kim), has developed 'on-device encryption optical communication device' technology for the utilization of 'Li-Fi,' which is attracting attention as a next-generation ultra-high-speed data communication.
Professor Cho's team created high-efficiency light-emitting triode devices using eco-friendly quantum dots (low-toxicity and sustainable materials). The device developed by the research team is a mechanism that generates light using an electric field. Specifically, the electric field is concentrated in 'tiny holes (pinholes) in the permeable electrode' and transmitted beyond the electrode. This device utilizes this principle to simultaneously process two input data streams.
Using this principle, the research team developed a technology called 'on-device encryption optical transmitter.' The core of this technology is that the device itself converts information into light and simultaneously encrypts it. This means that enhanced security data transmission is possible without the need for complex, separate equipment.
External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) is an indicator of how efficiently electricity is converted into light, with a general commercialization standard of about 20%. The newly developed device recorded an EQE of 17.4%, and its luminance was 29,000 nit, significantly exceeding the maximum brightness of a smartphone OLED screen, which is 2,000 nit, demonstrating a brightness more than 10 times higher.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the device structure developed by the research team and encrypted communication >
Furthermore, to more accurately understand how this device converts information into light, the research team used a method called 'transient electroluminescence analysis.' They analyzed the light-emitting characteristics generated by the device when voltage was instantaneously applied for very short durations (hundreds of nanoseconds = billionths of a second). Through this analysis, they investigated the movement of charges within the device at hundreds of nanoseconds, elucidating the operating mechanism of dual-channel optical modulation implemented within a single device.
Professor Himchan Cho of KAIST stated, "This research overcomes the limitations of existing optical communication devices and proposes a new communication platform that can both increase transmission speed and enhance security."
< Photo 2. Professor Himchan Cho, Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
He added, "This technology, which strengthens security without additional equipment and simultaneously enables encryption and transmission, can be widely applied in various fields where security is crucial in the future."
This research, with Seungmin Shin, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, participating as the first author, and Professor Himchan Cho and Dr. Kyung-geun Lim of KRISS as co-corresponding authors, was published in the international journal 'Advanced Materials' on May 30th and was selected as an inside front cover paper.※ Paper Title: High-Efficiency Quantum Dot Permeable electrode Light-Emitting Triodes for Visible-Light Communications and On-Device Data Encryption※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202503189
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST), and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.24 View 943 -
 ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ Launched to Lead AI Convergence Innovation
KAIST announced on the 16th of June that it has launched the ‘InnoCORE (Innovation-Core) Research Group,’ which will lead advanced strategic research in AI convergence (AI+S&T), in cooperation with the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Yoo Sang-im, hereinafter referred to as MSIT) and DGIST, GIST, and UNIST*. Through this, the group plans to actively recruit up to 200 world-class postdoctoral researchers.
DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science & Technology), UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology)
The ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ aims to foster core research personnel who will lead innovation in the field of AI convergence, focusing on nurturing and attracting high-level research talent in AI+Science & Technology. This is a strategic response to prevent brain drain of domestic talent and attract excellent overseas talent amidst the accelerating global competition for AI talent.
Through this initiative, our university plans to accelerate AI-based science and technology innovation and disseminate research achievements across industries and the economy by supporting top domestic and international postdoctoral researchers to dedicate themselves to developing AI convergence technologies in an advanced collaborative research environment.
The InnoCORE project for advanced AI+S&T convergence research and global talent attraction is jointly promoted by four science and technology institutes, including KAIST. It is structured around AI core technologies (such as hyper-scale language models, AI semiconductors) and AI convergence technologies (such as bio, manufacturing, energy, and aerospace).
As the leading institution, our university operates the following four research groups:
Hyper-scale Language Model Innovation Research Group: Advancement of LLM technology and research on generative AI, multimodal AI, and ensuring reliability.
AI-based Intelligent Design-Manufacturing Integration Research Group: Establishment of an AI platform for the entire lifecycle of the manufacturing industry and innovation in design and processes.
AI-Innovation Drug Research Group: Securing AI-based drug development technologies across the entire lifecycle and overcoming intractable diseases.
AI-Transformed Aerospace Research Group: AI transformation of aerospace systems throughout their lifecycle and development of new technologies such as autonomous flight and space communication.
< Poster on the InnoCORE Global Jobfair for Recruitment of Postdoctoral Researchers >
In addition, a total of eight research groups are formed to promote global collaborative convergence research, including those led by DGIST, GIST, and UNIST: ▲Bio-Integrated Physical AI, ▲Early Diagnosis of Brain Diseases AI+Nano Convergence, ▲Intelligent Hydrogen Technology Innovation, and ▲AI-Space Solar Power Research Group.
Starting in 2025, the four science and technology institutes, including KAIST, will officially begin recruiting 400 postdoctoral researchers in the AI+S&T fields. Selected postdoctoral researchers will be guaranteed high-level treatment with an annual salary of over 90 million KRW, and additional support through matching with companies and research projects is also planned.
In particular, global recruitment fairs will be held in major US regions to expand the attraction of excellent overseas talent. Local recruitment fairs will be held in Boston (Harvard, MIT), New York (NYU), and Silicon Valley (Stanford) in June, along with promotions through global academic journals such as Nature and Science, and LinkedIn.
KAIST plans to provide multiple mentor programs, global joint research opportunities, and excellent infrastructure (such as supercomputers, semiconductor fabs, and AI research platforms) within the research groups to enable postdoctoral researchers to collaborate with experts from various academic and industrial fields.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, “Through this InnoCORE project, KAIST will leap forward as a Global Hub for AI+S&T convergence research. Young researchers from around the world will challenge themselves and grow at KAIST, and our country will play a pivotal role in establishing itself as a leading nation in global AI convergence research and industry. To achieve this, we will spare no effort in providing the best research environment and active support.”
KAIST plans to actively pursue the InnoCORE project to secure global competitiveness in AI convergence research and contribute to the development of advanced industries. The eight selected research groups will finalize their detailed research plans by the end of June and commence full-scale research in July.
2025.06.19 View 1146
‘InnoCORE Research Group’ Launched to Lead AI Convergence Innovation
KAIST announced on the 16th of June that it has launched the ‘InnoCORE (Innovation-Core) Research Group,’ which will lead advanced strategic research in AI convergence (AI+S&T), in cooperation with the Ministry of Science and ICT (Minister Yoo Sang-im, hereinafter referred to as MSIT) and DGIST, GIST, and UNIST*. Through this, the group plans to actively recruit up to 200 world-class postdoctoral researchers.
DGIST (Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science & Technology), GIST (Gwangju Institute of Science & Technology), UNIST (Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology)
The ‘InnoCORE Research Group’ aims to foster core research personnel who will lead innovation in the field of AI convergence, focusing on nurturing and attracting high-level research talent in AI+Science & Technology. This is a strategic response to prevent brain drain of domestic talent and attract excellent overseas talent amidst the accelerating global competition for AI talent.
Through this initiative, our university plans to accelerate AI-based science and technology innovation and disseminate research achievements across industries and the economy by supporting top domestic and international postdoctoral researchers to dedicate themselves to developing AI convergence technologies in an advanced collaborative research environment.
The InnoCORE project for advanced AI+S&T convergence research and global talent attraction is jointly promoted by four science and technology institutes, including KAIST. It is structured around AI core technologies (such as hyper-scale language models, AI semiconductors) and AI convergence technologies (such as bio, manufacturing, energy, and aerospace).
As the leading institution, our university operates the following four research groups:
Hyper-scale Language Model Innovation Research Group: Advancement of LLM technology and research on generative AI, multimodal AI, and ensuring reliability.
AI-based Intelligent Design-Manufacturing Integration Research Group: Establishment of an AI platform for the entire lifecycle of the manufacturing industry and innovation in design and processes.
AI-Innovation Drug Research Group: Securing AI-based drug development technologies across the entire lifecycle and overcoming intractable diseases.
AI-Transformed Aerospace Research Group: AI transformation of aerospace systems throughout their lifecycle and development of new technologies such as autonomous flight and space communication.
< Poster on the InnoCORE Global Jobfair for Recruitment of Postdoctoral Researchers >
In addition, a total of eight research groups are formed to promote global collaborative convergence research, including those led by DGIST, GIST, and UNIST: ▲Bio-Integrated Physical AI, ▲Early Diagnosis of Brain Diseases AI+Nano Convergence, ▲Intelligent Hydrogen Technology Innovation, and ▲AI-Space Solar Power Research Group.
Starting in 2025, the four science and technology institutes, including KAIST, will officially begin recruiting 400 postdoctoral researchers in the AI+S&T fields. Selected postdoctoral researchers will be guaranteed high-level treatment with an annual salary of over 90 million KRW, and additional support through matching with companies and research projects is also planned.
In particular, global recruitment fairs will be held in major US regions to expand the attraction of excellent overseas talent. Local recruitment fairs will be held in Boston (Harvard, MIT), New York (NYU), and Silicon Valley (Stanford) in June, along with promotions through global academic journals such as Nature and Science, and LinkedIn.
KAIST plans to provide multiple mentor programs, global joint research opportunities, and excellent infrastructure (such as supercomputers, semiconductor fabs, and AI research platforms) within the research groups to enable postdoctoral researchers to collaborate with experts from various academic and industrial fields.
President Kwang Hyung Lee emphasized, “Through this InnoCORE project, KAIST will leap forward as a Global Hub for AI+S&T convergence research. Young researchers from around the world will challenge themselves and grow at KAIST, and our country will play a pivotal role in establishing itself as a leading nation in global AI convergence research and industry. To achieve this, we will spare no effort in providing the best research environment and active support.”
KAIST plans to actively pursue the InnoCORE project to secure global competitiveness in AI convergence research and contribute to the development of advanced industries. The eight selected research groups will finalize their detailed research plans by the end of June and commence full-scale research in July.
2025.06.19 View 1146 -
 KAIST Successfully Develops High-Performance Water Electrolysis Without Platinum, Bringing Hydrogen Economy Closer
< Photo 1. (Front row, from left) Jeesoo Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Professor Hee-Tak Kim (Back row, from left) Kyunghwa Seok (Ph.D. Candidate), Dr. Gisu Doo, Euntaek Oh (Ph.D. Candidate) >
Hydrogen is gaining attention as a clean energy source that emits no carbon. Among various methods, water electrolysis, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, is recognized as an eco-friendly hydrogen production method. Specifically, proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE) is considered a next-generation hydrogen production technology due to its ability to produce high-purity hydrogen at high pressure. However, existing PEMWE technology has faced limitations in commercialization due to its heavy reliance on expensive precious metal catalysts and coating materials. Korean researchers have now proposed a new solution to address these technical and economic bottlenecks.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 11th that a research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, in a joint study with Dr. Gisu Doo of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER, President Chang-keun Lee), has developed a next-generation water electrolysis technology that achieves high performance without the need for expensive platinum (Pt) coating.
The research team focused on the primary reason why 'iridium oxide (IrOx),' a highly active catalyst for water electrolysis electrodes, fails to perform optimally. They found that this is due to inefficient electron transfer and, for the first time in the world, demonstrated that performance can be maximized simply by controlling the catalyst particle size.
In this study, it was revealed that the reason iridium oxide catalysts do not exhibit excellent performance without platinum coating is due to 'electron transport resistance' that occurs at the interface between the catalyst, the ion conductor (hereinafter referred to as ionomer), and the Ti (titanium) substrate—core components inherently used together in water electrolysis electrodes.
Specifically, they identified that the 'pinch-off' phenomenon, where the electron pathway is blocked between the catalyst, ionomer, and titanium substrate, is the critical cause of reduced conductivity. The ionomer has properties close to an electron insulator, thereby hindering electron flow when it surrounds catalyst particles. Furthermore, when the ionomer comes into contact with the titanium substrate, an electron barrier forms on the surface oxide layer of the titanium substrate, significantly increasing resistance.
< Figure 1. Infographic related to electron transport resistance at the catalyst layer/diffusion layer interface >
To address this, the research team fabricated and compared catalysts of various particle sizes. Through single-cell evaluation and multiphysics simulations, they demonstrated, for the first time globally, that when iridium oxide catalyst particles with a size of 20 nanometers (nm) or larger are used, the ionomer mixed region decreases, ensuring an electron pathway and restoring conductivity.
Moreover, they successfully optimized the interfacial structure through precise design, simultaneously ensuring both reactivity and electron transport. This achievement demonstrated that the previously unavoidable trade-off between catalyst activity and conductivity can be overcome through meticulous interfacial design.
This breakthrough is expected to be a significant milestone not only for the development of high-performance catalyst materials but also for the future commercialization of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis systems that can achieve high efficiency while drastically reducing the amount of precious metals used.
Professor Hee-Tak Kim stated, "This research presents a new interface design strategy that can resolve the interfacial conductivity problem, which was a bottleneck in high-performance water electrolysis technology." He added, "By securing high performance even without expensive materials like platinum, it will be a stepping stone closer to realizing a hydrogen economy."
This research, with Jeesoo Park, a Ph.D. student from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, as the first author, was published on June 7th in 'Energy & Environmental Science' (IF: 32.4, 2025), a leading international journal in the energy and environmental fields, and was recognized for its innovativeness and impact. (Paper title: On the interface electron transport problem of highly active IrOx catalysts, DOI: 10.1039/D4EE05816J).
This research was supported by the New and Renewable Energy Core Technology Development Project of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
2025.06.11 View 1820
KAIST Successfully Develops High-Performance Water Electrolysis Without Platinum, Bringing Hydrogen Economy Closer
< Photo 1. (Front row, from left) Jeesoo Park (Ph.D. Candidate), Professor Hee-Tak Kim (Back row, from left) Kyunghwa Seok (Ph.D. Candidate), Dr. Gisu Doo, Euntaek Oh (Ph.D. Candidate) >
Hydrogen is gaining attention as a clean energy source that emits no carbon. Among various methods, water electrolysis, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using electricity, is recognized as an eco-friendly hydrogen production method. Specifically, proton exchange membrane water electrolysis (PEMWE) is considered a next-generation hydrogen production technology due to its ability to produce high-purity hydrogen at high pressure. However, existing PEMWE technology has faced limitations in commercialization due to its heavy reliance on expensive precious metal catalysts and coating materials. Korean researchers have now proposed a new solution to address these technical and economic bottlenecks.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 11th that a research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, in a joint study with Dr. Gisu Doo of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER, President Chang-keun Lee), has developed a next-generation water electrolysis technology that achieves high performance without the need for expensive platinum (Pt) coating.
The research team focused on the primary reason why 'iridium oxide (IrOx),' a highly active catalyst for water electrolysis electrodes, fails to perform optimally. They found that this is due to inefficient electron transfer and, for the first time in the world, demonstrated that performance can be maximized simply by controlling the catalyst particle size.
In this study, it was revealed that the reason iridium oxide catalysts do not exhibit excellent performance without platinum coating is due to 'electron transport resistance' that occurs at the interface between the catalyst, the ion conductor (hereinafter referred to as ionomer), and the Ti (titanium) substrate—core components inherently used together in water electrolysis electrodes.
Specifically, they identified that the 'pinch-off' phenomenon, where the electron pathway is blocked between the catalyst, ionomer, and titanium substrate, is the critical cause of reduced conductivity. The ionomer has properties close to an electron insulator, thereby hindering electron flow when it surrounds catalyst particles. Furthermore, when the ionomer comes into contact with the titanium substrate, an electron barrier forms on the surface oxide layer of the titanium substrate, significantly increasing resistance.
< Figure 1. Infographic related to electron transport resistance at the catalyst layer/diffusion layer interface >
To address this, the research team fabricated and compared catalysts of various particle sizes. Through single-cell evaluation and multiphysics simulations, they demonstrated, for the first time globally, that when iridium oxide catalyst particles with a size of 20 nanometers (nm) or larger are used, the ionomer mixed region decreases, ensuring an electron pathway and restoring conductivity.
Moreover, they successfully optimized the interfacial structure through precise design, simultaneously ensuring both reactivity and electron transport. This achievement demonstrated that the previously unavoidable trade-off between catalyst activity and conductivity can be overcome through meticulous interfacial design.
This breakthrough is expected to be a significant milestone not only for the development of high-performance catalyst materials but also for the future commercialization of proton exchange membrane water electrolysis systems that can achieve high efficiency while drastically reducing the amount of precious metals used.
Professor Hee-Tak Kim stated, "This research presents a new interface design strategy that can resolve the interfacial conductivity problem, which was a bottleneck in high-performance water electrolysis technology." He added, "By securing high performance even without expensive materials like platinum, it will be a stepping stone closer to realizing a hydrogen economy."
This research, with Jeesoo Park, a Ph.D. student from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, as the first author, was published on June 7th in 'Energy & Environmental Science' (IF: 32.4, 2025), a leading international journal in the energy and environmental fields, and was recognized for its innovativeness and impact. (Paper title: On the interface electron transport problem of highly active IrOx catalysts, DOI: 10.1039/D4EE05816J).
This research was supported by the New and Renewable Energy Core Technology Development Project of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy.
2025.06.11 View 1820 -
 KAIST Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives Global IEEE Robotics Journal Best Paper Award
- Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu of Civil and Environmental Engineering receives the Best Paper Award from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics Journal, officially presented at ICRA, a world-renowned robotics conference.
- This is the highest level of international recognition, awarded to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024.
- Securing a new working channel technology for soft growing robots expands the practicality and application possibilities in the field of soft robotics.
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu (left), Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate (right) from the KAIST Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and KAIST Robotics Program >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering received the 2024 Best Paper Award from the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), a premier journal under the IEEE, at the '2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)' held in Atlanta, USA, on May 22nd.
This Best Paper Award is a prestigious honor presented to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024, boasting high international competition and authority.
The award-winning paper by Professor Ryu proposes a novel working channel securing mechanism that significantly expands the practicality and application possibilities of 'Soft Growing Robots,' which are based on soft materials that move or perform tasks through a growing motion similar to plant roots.
< IEEE Robotics Journal Award Ceremony >
Existing soft growing robots move by inflating or contracting their bodies through increasing or decreasing internal pressure, which can lead to blockages in their internal passages. In contrast, the newly developed soft growing robot achieves a growing function while maintaining the internal passage pressure equal to the external atmospheric pressure, thereby successfully securing an internal passage while retaining the robot's flexible and soft characteristics.
This structure allows various materials or tools to be freely delivered through the internal passage (working channel) within the robot and offers the advantage of performing multi-purpose tasks by flexibly replacing equipment according to the working environment.
The research team fabricated a prototype to prove the effectiveness of this technology and verified its performance through various experiments. Specifically, in the slide plate experiment, they confirmed whether materials or equipment could pass through the robot's internal channel without obstruction, and in the pipe pulling experiment, they verified if a long pipe-shaped tool could be pulled through the internal channel.
< Figure 1. Overall hardware structure of the proposed soft growing robot (left) and a cross-sectional view composing the inflatable structure (right) >
Experimental results demonstrated that the internal channel remained stable even while the robot was growing, serving as a key basis for supporting the technology's practicality and scalability.
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu stated, "This award is very meaningful as it signifies the global recognition of Korea's robotics technology and academic achievements. Especially, it holds great significance in achieving technical progress that can greatly expand the practicality and application fields of soft growing robots. This achievement was possible thanks to the dedication and collaboration of the research team, and I will continue to contribute to the development of robotics technology through innovative research."
< Figure 2. Material supplying mechanism of the Soft Growing Robot >
This research was co-authored by Dongoh Seo, Ph.D. Candidate in Civil and Environmental Engineering, and Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate in Robotics. It was published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters on September 1, 2024.
(Paper Title: Inflatable-Structure-Based Working-Channel Securing Mechanism for Soft Growing Robots, DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3426322)
This project was supported simultaneously by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Future Promising Convergence Technology Pioneer Research Project and Mid-career Researcher Project.
2025.06.09 View 1898
KAIST Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives Global IEEE Robotics Journal Best Paper Award
- Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu of Civil and Environmental Engineering receives the Best Paper Award from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics Journal, officially presented at ICRA, a world-renowned robotics conference.
- This is the highest level of international recognition, awarded to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024.
- Securing a new working channel technology for soft growing robots expands the practicality and application possibilities in the field of soft robotics.
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu (left), Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate (right) from the KAIST Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and KAIST Robotics Program >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering received the 2024 Best Paper Award from the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), a premier journal under the IEEE, at the '2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)' held in Atlanta, USA, on May 22nd.
This Best Paper Award is a prestigious honor presented to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024, boasting high international competition and authority.
The award-winning paper by Professor Ryu proposes a novel working channel securing mechanism that significantly expands the practicality and application possibilities of 'Soft Growing Robots,' which are based on soft materials that move or perform tasks through a growing motion similar to plant roots.
< IEEE Robotics Journal Award Ceremony >
Existing soft growing robots move by inflating or contracting their bodies through increasing or decreasing internal pressure, which can lead to blockages in their internal passages. In contrast, the newly developed soft growing robot achieves a growing function while maintaining the internal passage pressure equal to the external atmospheric pressure, thereby successfully securing an internal passage while retaining the robot's flexible and soft characteristics.
This structure allows various materials or tools to be freely delivered through the internal passage (working channel) within the robot and offers the advantage of performing multi-purpose tasks by flexibly replacing equipment according to the working environment.
The research team fabricated a prototype to prove the effectiveness of this technology and verified its performance through various experiments. Specifically, in the slide plate experiment, they confirmed whether materials or equipment could pass through the robot's internal channel without obstruction, and in the pipe pulling experiment, they verified if a long pipe-shaped tool could be pulled through the internal channel.
< Figure 1. Overall hardware structure of the proposed soft growing robot (left) and a cross-sectional view composing the inflatable structure (right) >
Experimental results demonstrated that the internal channel remained stable even while the robot was growing, serving as a key basis for supporting the technology's practicality and scalability.
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu stated, "This award is very meaningful as it signifies the global recognition of Korea's robotics technology and academic achievements. Especially, it holds great significance in achieving technical progress that can greatly expand the practicality and application fields of soft growing robots. This achievement was possible thanks to the dedication and collaboration of the research team, and I will continue to contribute to the development of robotics technology through innovative research."
< Figure 2. Material supplying mechanism of the Soft Growing Robot >
This research was co-authored by Dongoh Seo, Ph.D. Candidate in Civil and Environmental Engineering, and Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate in Robotics. It was published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters on September 1, 2024.
(Paper Title: Inflatable-Structure-Based Working-Channel Securing Mechanism for Soft Growing Robots, DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3426322)
This project was supported simultaneously by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Future Promising Convergence Technology Pioneer Research Project and Mid-career Researcher Project.
2025.06.09 View 1898 -
 RAIBO Runs over Walls with Feline Agility... Ready for Effortless Search over Mountaineous and Rough Terrains
< Photo 1. Research Team Photo (Professor Jemin Hwangbo, second from right in the front row) >
KAIST's quadrupedal robot, RAIBO, can now move at high speed across discontinuous and complex terrains such as stairs, gaps, walls, and debris. It has demonstrated its ability to run on vertical walls, leap over 1.3-meter-wide gaps, sprint at approximately 14.4 km/h over stepping stones, and move quickly and nimbly on terrain combining 30° slopes, stairs, and stepping stones. RAIBO is expected to be deployed soon for practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at our university announced on June 3rd that they have developed a quadrupedal robot navigation framework capable of high-speed locomotion at 14.4 km/h (4m/s) even on discontinuous and complex terrains such as walls, stairs, and stepping stones.
The research team developed a quadrupedal navigation system that enables the robot to reach its target destination quickly and safely in complex and discontinuous terrain.
To achieve this, they approached the problem by breaking it down into two stages: first, developing a planner for planning foothold positions, and second, developing a tracker to accurately follow the planned foothold positions.
First, the planner module quickly searches for physically feasible foothold positions using a sampling-based optimization method with neural network-based heuristics and verifies the optimal path through simulation rollouts.
While existing methods considered various factors such as contact timing and robot posture in addition to foothold positions, this research significantly reduced computational complexity by setting only foothold positions as the search space. Furthermore, inspired by the walking method of cats, the introduction of a structure where the hind feet step on the same spots as the front feet further significantly reduced computational complexity.
< Figure 1. High-speed navigation across various discontinuous terrains >
Second, the tracker module is trained to accurately step on planned positions, and tracking training is conducted through a generative model that competes in environments of appropriate difficulty.
The tracker is trained through reinforcement learning to accurately step on planned plots, and during this process, a generative model called the 'map generator' provides the target distribution.
This generative model is trained simultaneously and adversarially with the tracker to allow the tracker to progressively adapt to more challenging difficulties. Subsequently, a sampling-based planner was designed to generate feasible foothold plans that can reflect the characteristics and performance of the trained tracker.
This hierarchical structure showed superior performance in both planning speed and stability compared to existing techniques, and experiments proved its high-speed locomotion capabilities across various obstacles and discontinuous terrains, as well as its general applicability to unseen terrains.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo stated, "We approached the problem of high-speed navigation in discontinuous terrain, which previously required a significantly large amount of computation, from the simple perspective of how to select the footprint positions. Inspired by the placements of cat's paw, allowing the hind feet to step where the front feet stepped drastically reduced computation. We expect this to significantly expand the range of discontinuous terrain that walking robots can overcome and enable them to traverse it at high speeds, contributing to the robot's ability to perform practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches."
This research achievement was published in the May 2025 issue of the international journal Science Robotics.
Paper Title: High-speed control and navigation for quadrupedal robots on complex and discrete terrain, (https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.ads6192)YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/EZbM594T3c4?si=kfxLF2XnVUvYVIyk
2025.06.04 View 2679
RAIBO Runs over Walls with Feline Agility... Ready for Effortless Search over Mountaineous and Rough Terrains
< Photo 1. Research Team Photo (Professor Jemin Hwangbo, second from right in the front row) >
KAIST's quadrupedal robot, RAIBO, can now move at high speed across discontinuous and complex terrains such as stairs, gaps, walls, and debris. It has demonstrated its ability to run on vertical walls, leap over 1.3-meter-wide gaps, sprint at approximately 14.4 km/h over stepping stones, and move quickly and nimbly on terrain combining 30° slopes, stairs, and stepping stones. RAIBO is expected to be deployed soon for practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo's research team in the Department of Mechanical Engineering at our university announced on June 3rd that they have developed a quadrupedal robot navigation framework capable of high-speed locomotion at 14.4 km/h (4m/s) even on discontinuous and complex terrains such as walls, stairs, and stepping stones.
The research team developed a quadrupedal navigation system that enables the robot to reach its target destination quickly and safely in complex and discontinuous terrain.
To achieve this, they approached the problem by breaking it down into two stages: first, developing a planner for planning foothold positions, and second, developing a tracker to accurately follow the planned foothold positions.
First, the planner module quickly searches for physically feasible foothold positions using a sampling-based optimization method with neural network-based heuristics and verifies the optimal path through simulation rollouts.
While existing methods considered various factors such as contact timing and robot posture in addition to foothold positions, this research significantly reduced computational complexity by setting only foothold positions as the search space. Furthermore, inspired by the walking method of cats, the introduction of a structure where the hind feet step on the same spots as the front feet further significantly reduced computational complexity.
< Figure 1. High-speed navigation across various discontinuous terrains >
Second, the tracker module is trained to accurately step on planned positions, and tracking training is conducted through a generative model that competes in environments of appropriate difficulty.
The tracker is trained through reinforcement learning to accurately step on planned plots, and during this process, a generative model called the 'map generator' provides the target distribution.
This generative model is trained simultaneously and adversarially with the tracker to allow the tracker to progressively adapt to more challenging difficulties. Subsequently, a sampling-based planner was designed to generate feasible foothold plans that can reflect the characteristics and performance of the trained tracker.
This hierarchical structure showed superior performance in both planning speed and stability compared to existing techniques, and experiments proved its high-speed locomotion capabilities across various obstacles and discontinuous terrains, as well as its general applicability to unseen terrains.
Professor Jemin Hwangbo stated, "We approached the problem of high-speed navigation in discontinuous terrain, which previously required a significantly large amount of computation, from the simple perspective of how to select the footprint positions. Inspired by the placements of cat's paw, allowing the hind feet to step where the front feet stepped drastically reduced computation. We expect this to significantly expand the range of discontinuous terrain that walking robots can overcome and enable them to traverse it at high speeds, contributing to the robot's ability to perform practical missions such as disaster site exploration and mountain searches."
This research achievement was published in the May 2025 issue of the international journal Science Robotics.
Paper Title: High-speed control and navigation for quadrupedal robots on complex and discrete terrain, (https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/scirobotics.ads6192)YouTube Link: https://youtu.be/EZbM594T3c4?si=kfxLF2XnVUvYVIyk
2025.06.04 View 2679 -
 Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 2702
Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 2702 -
 KAIST-UIUC researchers develop a treatment platform to disable the ‘biofilm’ shield of superbugs
< (From left) Ph.D. Candidate Joo Hun Lee (co-author), Professor Hyunjoon Kong (co-corresponding author) and Postdoctoral Researcher Yujin Ahn (co-first author) from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Ju Yeon Chung (co-first author) from the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program, and Professor Hyun Jung Chung (co-corresponding author) from the Department of Biological Sciences of KAIST >
A major cause of hospital-acquired infections, the super bacteria Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), not only exhibits strong resistance to existing antibiotics but also forms a dense biofilm that blocks the effects of external treatments. To meet this challenge, KAIST researchers, in collaboration with an international team, successfully developed a platform that utilizes microbubbles to deliver gene-targeted nanoparticles capable of break ing down the biofilms, offering an innovative solution for treating infections resistant to conventional antibiotics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on May 29 that a research team led by Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences, in collaboration with Professor Hyunjoon Kong's team at the University of Illinois, has developed a microbubble-based nano-gene delivery platform (BTN MB) that precisely delivers gene suppressors into bacteria to effectively remove biofilms formed by MRSA.
The research team first designed short DNA oligonucleotides that simultaneously suppress three major MRSA genes, related to—biofilm formation (icaA), cell division (ftsZ), and antibiotic resistance (mecA)—and engineered nanoparticles (BTN) to effectively deliver them into the bacteria.
< Figure 1. Effective biofilm treatment using biofilm-targeting nanoparticles controlled by microbubbler system. Schematic illustration of BTN delivery with microbubbles (MB), enabling effective permeation of ASOs targeting bacterial genes within biofilms infecting skin wounds. Gene silencing of targets involved in biofilm formation, bacterial proliferation, and antibiotic resistance leads to effective biofilm removal and antibacterial efficacy in vivo. >
In addition, microbubbles (MB) were used to increase the permeability of the microbial membrane, specifically the biofilm formed by MRSA. By combining these two technologies, the team implemented a dual-strike strategy that fundamentally blocks bacterial growth and prevents resistance acquisition.
This treatment system operates in two stages. First, the MBs induce pressure changes within the bacterial biofilm, allowing the BTNs to penetrate. Then, the BTNs slip through the gaps in the biofilm and enter the bacteria, delivering the gene suppressors precisely. This leads to gene regulation within MRSA, simultaneously blocking biofilm regeneration, cell proliferation, and antibiotic resistance expression.
In experiments conducted in a porcine skin model and a mouse wound model infected with MRSA biofilm, the BTN MB treatment group showed a significant reduction in biofilm thickness, as well as remarkable decreases in bacterial count and inflammatory responses.
< Figure 2. (a) Schematic illustration on the evaluation of treatment efficacy of BTN-MB gene therapy. (b) Reduction in MRSA biofilm mass via simultaneous inhibition of multiple genes. (c, d) Antibacterial efficacy of BTN-MB over time in a porcine skin infection biofilm model. (e) Schematic of the experimental setup to verify antibacterial efficacy in a mouse skin wound infection model. (f) Wound healing effects in mice. (g) Antibacterial effects at the wound site. (h) Histological analysis results. >
These results are difficult to achieve with conventional antibiotic monotherapy and demonstrate the potential for treating a wide range of resistant bacterial infections.
Professor Hyun Jung Chung of KAIST, who led the research, stated, “This study presents a new therapeutic solution that combines nanotechnology, gene suppression, and physical delivery strategies to address superbug infections that existing antibiotics cannot resolve. We will continue our research with the aim of expanding its application to systemic infections and various other infectious diseases.”
< (From left) Ju Yeon Chung from the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program, and Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences >
The study was co-first authored by Ju Yeon Chung, a graduate student in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Dr. Yujin Ahn from the University of Illinois. The study was published online on May 19 in the journal, Advanced Functional Materials.
※ Paper Title: Microbubble-Controlled Delivery of Biofilm-Targeting Nanoparticles to Treat MRSA Infection ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202508291
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation and the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea; and the National Science Foundation and National Institutes of Health, USA.
2025.05.29 View 1988
KAIST-UIUC researchers develop a treatment platform to disable the ‘biofilm’ shield of superbugs
< (From left) Ph.D. Candidate Joo Hun Lee (co-author), Professor Hyunjoon Kong (co-corresponding author) and Postdoctoral Researcher Yujin Ahn (co-first author) from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Ju Yeon Chung (co-first author) from the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program, and Professor Hyun Jung Chung (co-corresponding author) from the Department of Biological Sciences of KAIST >
A major cause of hospital-acquired infections, the super bacteria Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), not only exhibits strong resistance to existing antibiotics but also forms a dense biofilm that blocks the effects of external treatments. To meet this challenge, KAIST researchers, in collaboration with an international team, successfully developed a platform that utilizes microbubbles to deliver gene-targeted nanoparticles capable of break ing down the biofilms, offering an innovative solution for treating infections resistant to conventional antibiotics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on May 29 that a research team led by Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences, in collaboration with Professor Hyunjoon Kong's team at the University of Illinois, has developed a microbubble-based nano-gene delivery platform (BTN MB) that precisely delivers gene suppressors into bacteria to effectively remove biofilms formed by MRSA.
The research team first designed short DNA oligonucleotides that simultaneously suppress three major MRSA genes, related to—biofilm formation (icaA), cell division (ftsZ), and antibiotic resistance (mecA)—and engineered nanoparticles (BTN) to effectively deliver them into the bacteria.
< Figure 1. Effective biofilm treatment using biofilm-targeting nanoparticles controlled by microbubbler system. Schematic illustration of BTN delivery with microbubbles (MB), enabling effective permeation of ASOs targeting bacterial genes within biofilms infecting skin wounds. Gene silencing of targets involved in biofilm formation, bacterial proliferation, and antibiotic resistance leads to effective biofilm removal and antibacterial efficacy in vivo. >
In addition, microbubbles (MB) were used to increase the permeability of the microbial membrane, specifically the biofilm formed by MRSA. By combining these two technologies, the team implemented a dual-strike strategy that fundamentally blocks bacterial growth and prevents resistance acquisition.
This treatment system operates in two stages. First, the MBs induce pressure changes within the bacterial biofilm, allowing the BTNs to penetrate. Then, the BTNs slip through the gaps in the biofilm and enter the bacteria, delivering the gene suppressors precisely. This leads to gene regulation within MRSA, simultaneously blocking biofilm regeneration, cell proliferation, and antibiotic resistance expression.
In experiments conducted in a porcine skin model and a mouse wound model infected with MRSA biofilm, the BTN MB treatment group showed a significant reduction in biofilm thickness, as well as remarkable decreases in bacterial count and inflammatory responses.
< Figure 2. (a) Schematic illustration on the evaluation of treatment efficacy of BTN-MB gene therapy. (b) Reduction in MRSA biofilm mass via simultaneous inhibition of multiple genes. (c, d) Antibacterial efficacy of BTN-MB over time in a porcine skin infection biofilm model. (e) Schematic of the experimental setup to verify antibacterial efficacy in a mouse skin wound infection model. (f) Wound healing effects in mice. (g) Antibacterial effects at the wound site. (h) Histological analysis results. >
These results are difficult to achieve with conventional antibiotic monotherapy and demonstrate the potential for treating a wide range of resistant bacterial infections.
Professor Hyun Jung Chung of KAIST, who led the research, stated, “This study presents a new therapeutic solution that combines nanotechnology, gene suppression, and physical delivery strategies to address superbug infections that existing antibiotics cannot resolve. We will continue our research with the aim of expanding its application to systemic infections and various other infectious diseases.”
< (From left) Ju Yeon Chung from the Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program, and Professor Hyun Jung Chung from the Department of Biological Sciences >
The study was co-first authored by Ju Yeon Chung, a graduate student in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and Dr. Yujin Ahn from the University of Illinois. The study was published online on May 19 in the journal, Advanced Functional Materials.
※ Paper Title: Microbubble-Controlled Delivery of Biofilm-Targeting Nanoparticles to Treat MRSA Infection ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202508291
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation and the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea; and the National Science Foundation and National Institutes of Health, USA.
2025.05.29 View 1988 -
 KAIST Develops Virtual Staining Technology for 3D Histopathology
Moving beyond traditional methods of observing thinly sliced and stained cancer tissues, a collaborative international research team led by KAIST has successfully developed a groundbreaking technology. This innovation uses advanced optical techniques combined with an artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithm to create realistic, virtually stained 3D images of cancer tissue without the need for serial sectioning nor staining. This breakthrough is anticipated to pave the way for next-generation non-invasive pathological diagnosis.
< Photo 1. (From left) Juyeon Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Physics), Professor YongKeun Park (Department of Physics) (Top left) Professor Su-Jin Shin (Gangnam Severance Hospital), Professor Tae Hyun Hwang (Vanderbilt University School of Medicine) >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Professor Su-Jin Shin's team at Yonsei University Gangnam Severance Hospital, Professor Tae Hyun Hwang's team at Mayo Clinic, and Tomocube's AI research team, has developed an innovative technology capable of vividly displaying the 3D structure of cancer tissues without separate staining.
For over 200 years, conventional pathology has relied on observing cancer tissues under a microscope, a method that only shows specific cross-sections of the 3D cancer tissue. This has limited the ability to understand the three-dimensional connections and spatial arrangements between cells.
To overcome this, the research team utilized holotomography (HT), an advanced optical technology, to measure the 3D refractive index information of tissues. They then integrated an AI-based deep learning algorithm to successfully generate virtual H&E* images.* H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin): The most widely used staining method for observing pathological tissues. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, and eosin stains cytoplasm pink.
The research team quantitatively demonstrated that the images generated by this technology are highly similar to actual stained tissue images. Furthermore, the technology exhibited consistent performance across various organs and tissues, proving its versatility and reliability as a next-generation pathological analysis tool.
< Figure 1. Comparison of conventional 3D tissue pathology procedure and the 3D virtual H&E staining technology proposed in this study. The traditional method requires preparing and staining dozens of tissue slides, while the proposed technology can reduce the number of slides by up to 10 times and quickly generate H&E images without the staining process. >
Moreover, by validating the feasibility of this technology through joint research with hospitals and research institutions in Korea and the United States, utilizing Tomocube's holotomography equipment, the team demonstrated its potential for full-scale adoption in real-world pathological research settings.
Professor YongKeun Park stated, "This research marks a major advancement by transitioning pathological analysis from conventional 2D methods to comprehensive 3D imaging. It will greatly enhance biomedical research and clinical diagnostics, particularly in understanding cancer tumor boundaries and the intricate spatial arrangements of cells within tumor microenvironments."
< Figure 2. Results of AI-based 3D virtual H&E staining and quantitative analysis of pathological tissue. The virtually stained images enabled 3D reconstruction of key pathological features such as cell nuclei and glandular lumens. Based on this, various quantitative indicators, including cell nuclear distribution, volume, and surface area, could be extracted. >
This research, with Juyeon Park, a student of the Integrated Master’s and Ph.D. Program at KAIST, as the first author, was published online in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on May 22.
(Paper title: Revealing 3D microanatomical structures of unlabeled thick cancer tissues using holotomography and virtual H&E staining.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59820-0]
This study was supported by the Leader Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Global Industry Technology Cooperation Center Project of the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology, and the Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
2025.05.26 View 2894
KAIST Develops Virtual Staining Technology for 3D Histopathology
Moving beyond traditional methods of observing thinly sliced and stained cancer tissues, a collaborative international research team led by KAIST has successfully developed a groundbreaking technology. This innovation uses advanced optical techniques combined with an artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithm to create realistic, virtually stained 3D images of cancer tissue without the need for serial sectioning nor staining. This breakthrough is anticipated to pave the way for next-generation non-invasive pathological diagnosis.
< Photo 1. (From left) Juyeon Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Physics), Professor YongKeun Park (Department of Physics) (Top left) Professor Su-Jin Shin (Gangnam Severance Hospital), Professor Tae Hyun Hwang (Vanderbilt University School of Medicine) >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Professor Su-Jin Shin's team at Yonsei University Gangnam Severance Hospital, Professor Tae Hyun Hwang's team at Mayo Clinic, and Tomocube's AI research team, has developed an innovative technology capable of vividly displaying the 3D structure of cancer tissues without separate staining.
For over 200 years, conventional pathology has relied on observing cancer tissues under a microscope, a method that only shows specific cross-sections of the 3D cancer tissue. This has limited the ability to understand the three-dimensional connections and spatial arrangements between cells.
To overcome this, the research team utilized holotomography (HT), an advanced optical technology, to measure the 3D refractive index information of tissues. They then integrated an AI-based deep learning algorithm to successfully generate virtual H&E* images.* H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin): The most widely used staining method for observing pathological tissues. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, and eosin stains cytoplasm pink.
The research team quantitatively demonstrated that the images generated by this technology are highly similar to actual stained tissue images. Furthermore, the technology exhibited consistent performance across various organs and tissues, proving its versatility and reliability as a next-generation pathological analysis tool.
< Figure 1. Comparison of conventional 3D tissue pathology procedure and the 3D virtual H&E staining technology proposed in this study. The traditional method requires preparing and staining dozens of tissue slides, while the proposed technology can reduce the number of slides by up to 10 times and quickly generate H&E images without the staining process. >
Moreover, by validating the feasibility of this technology through joint research with hospitals and research institutions in Korea and the United States, utilizing Tomocube's holotomography equipment, the team demonstrated its potential for full-scale adoption in real-world pathological research settings.
Professor YongKeun Park stated, "This research marks a major advancement by transitioning pathological analysis from conventional 2D methods to comprehensive 3D imaging. It will greatly enhance biomedical research and clinical diagnostics, particularly in understanding cancer tumor boundaries and the intricate spatial arrangements of cells within tumor microenvironments."
< Figure 2. Results of AI-based 3D virtual H&E staining and quantitative analysis of pathological tissue. The virtually stained images enabled 3D reconstruction of key pathological features such as cell nuclei and glandular lumens. Based on this, various quantitative indicators, including cell nuclear distribution, volume, and surface area, could be extracted. >
This research, with Juyeon Park, a student of the Integrated Master’s and Ph.D. Program at KAIST, as the first author, was published online in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on May 22.
(Paper title: Revealing 3D microanatomical structures of unlabeled thick cancer tissues using holotomography and virtual H&E staining.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59820-0]
This study was supported by the Leader Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Global Industry Technology Cooperation Center Project of the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology, and the Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
2025.05.26 View 2894 -
 <Big Coins> Exhibition: Where Coins and Imagination Collide - Held at SUPEX Hall, KAIST Seoul Campus
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 19th the opening of the solo exhibition, “Big Coins,” by photographer and media artist Hojun Ji (Adjunct Professor, Department of Industrial Design) at the SUPEX Hall in the Business School of the Seoul Campus. The exhibition will run from May 19th to the end of February of the following year.
This exhibition at the KAIST Seoul Campus Business School presents artworks with an insightful perspective, inviting diverse interpretations from the audience. Notable pieces include ‘Priced,’ which juxtaposes Leonardo da Vinci's ‘Salvator Mundi,’ sold for approximately 450 million US dollars at a 2017 auction, with a Vatican coin bearing the image of Pope John XXIII. Another work, ‘Ciphered,’ superimposes a code used by the German army during World War II onto a Swiss coin featuring Helvetia.
< Priced, 150x150cm, 2025 >
Currently, Hojun Ji, an Adjunct Professor in KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design (and a student at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology), creates his art using images captured by observing everyday objects through optical or electron microscopes.
He has garnered particular attention for his unique artistic world, which combines enlarged microscopic photographs of coins from across the globe with significant news articles from modern and contemporary history.
Yeo-sun Yoon, Dean of the College of Business Administration, commented, “While the KAIST Art Museum is located at the main campus in Daejeon, the College of Business Administration here on the Seoul Campus also regularly hosts exhibitions curated by the museum. I am delighted to encounter a new realm of art through this solo exhibition by Artist Hojun Ji.”
< Ciphered, 150x150cm, 2025 >
Hyeon-Jeong Suk, Director of the Art Museum and a Full Professor in KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, remarked, “Professor Hojun Ji's experimental imagination is remarkably unique and eccentric. As a graduate student, he connected data from his observations of his lab dog’s droppings with Jeong Seon's <Geumgang Jeondo>. Such imaginative thinking exemplifies the direction KAIST is pursuing.”
Artist Hojun Ji stated, “The coins I examined through optical and electron microscopes were not merely a form of payment but rather portraits of humanity etched with time and power. The history and memories embedded in their fine cracks and textures resonated with me as a singular sculpture. I aim to unlock the vast world of imagination concealed within these small pieces of metal.”
< Geumgang Byeondo: a Variation of the View of Mt. Geumgang (a twist of Geumgang Jeondo - a Complete View of Geumgangsan Mountain, 1734), 80x120cm, 2009 >
Ji has presented experimental works that transcend the boundaries of science and art through numerous exhibitions both domestically and internationally. His work has also been featured on the cover of the international academic journal Digital Creativity and is increasingly recognized for its artistic merit, with pieces housed in the Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Turkey, the Seoul Museum of Art, and the 9/11 Memorial Center in the United States.
This solo exhibition, which will continue until the end of February of next year, is open to KAIST members and external visitors free of charge.
2025.05.20 View 2076
<Big Coins> Exhibition: Where Coins and Imagination Collide - Held at SUPEX Hall, KAIST Seoul Campus
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 19th the opening of the solo exhibition, “Big Coins,” by photographer and media artist Hojun Ji (Adjunct Professor, Department of Industrial Design) at the SUPEX Hall in the Business School of the Seoul Campus. The exhibition will run from May 19th to the end of February of the following year.
This exhibition at the KAIST Seoul Campus Business School presents artworks with an insightful perspective, inviting diverse interpretations from the audience. Notable pieces include ‘Priced,’ which juxtaposes Leonardo da Vinci's ‘Salvator Mundi,’ sold for approximately 450 million US dollars at a 2017 auction, with a Vatican coin bearing the image of Pope John XXIII. Another work, ‘Ciphered,’ superimposes a code used by the German army during World War II onto a Swiss coin featuring Helvetia.
< Priced, 150x150cm, 2025 >
Currently, Hojun Ji, an Adjunct Professor in KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design (and a student at the KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology), creates his art using images captured by observing everyday objects through optical or electron microscopes.
He has garnered particular attention for his unique artistic world, which combines enlarged microscopic photographs of coins from across the globe with significant news articles from modern and contemporary history.
Yeo-sun Yoon, Dean of the College of Business Administration, commented, “While the KAIST Art Museum is located at the main campus in Daejeon, the College of Business Administration here on the Seoul Campus also regularly hosts exhibitions curated by the museum. I am delighted to encounter a new realm of art through this solo exhibition by Artist Hojun Ji.”
< Ciphered, 150x150cm, 2025 >
Hyeon-Jeong Suk, Director of the Art Museum and a Full Professor in KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, remarked, “Professor Hojun Ji's experimental imagination is remarkably unique and eccentric. As a graduate student, he connected data from his observations of his lab dog’s droppings with Jeong Seon's <Geumgang Jeondo>. Such imaginative thinking exemplifies the direction KAIST is pursuing.”
Artist Hojun Ji stated, “The coins I examined through optical and electron microscopes were not merely a form of payment but rather portraits of humanity etched with time and power. The history and memories embedded in their fine cracks and textures resonated with me as a singular sculpture. I aim to unlock the vast world of imagination concealed within these small pieces of metal.”
< Geumgang Byeondo: a Variation of the View of Mt. Geumgang (a twist of Geumgang Jeondo - a Complete View of Geumgangsan Mountain, 1734), 80x120cm, 2009 >
Ji has presented experimental works that transcend the boundaries of science and art through numerous exhibitions both domestically and internationally. His work has also been featured on the cover of the international academic journal Digital Creativity and is increasingly recognized for its artistic merit, with pieces housed in the Embassy of the Republic of Korea in Turkey, the Seoul Museum of Art, and the 9/11 Memorial Center in the United States.
This solo exhibition, which will continue until the end of February of next year, is open to KAIST members and external visitors free of charge.
2025.05.20 View 2076 -
 Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 2970
Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 2970