Korea+University
-
 Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University Named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University in the UK was named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Award recipient. PhD candidate Kyu-Sob Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Master’s candidate from Korea University Kon-Hee Chang, Jae-Woo Chang from Kongju National University High School were also selected.
Professor Shin, a PhD graduate from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2016 works at Cranfield University. Professor Shin, whose main research focus covers guidance, navigation, and control, conducts research on information-based control. He has published 66 articles in SCI journals and presented approximately 70 papers at academic conference with more than 12 patent registrations. He is known for his expertise in areas related to unmanned aerospace systems and urban aero traffic automation. Professor Shin is participating in various aerospace engineering development projects run by the UK government.
The award recognizes promising young scientists who have made significant achievements in the field of aerospace engineering in honor of Jeong Hun Cho, the former PhD candidate in KAIST’s Department of Aerospace Engineering. Cho died in a lab accident in May 2003. Cho’s family endowed the award and scholarship to honor him and a recipient from each of his three alma maters (Kongju National High School, Korea University, and KAIST) are selected every year.
Professor Shin was awarded 25 million KRW in prize money. KAIST student Kim and Korea University student Chang received four million KRW while Kongju National University High School student Chang received three million KRW.
2022.05.16 View 8634
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University Named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
Professor Hyo-Sang Shin at Cranfield University in the UK was named the 18th Jeong Hun Cho Award recipient. PhD candidate Kyu-Sob Kim from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Master’s candidate from Korea University Kon-Hee Chang, Jae-Woo Chang from Kongju National University High School were also selected.
Professor Shin, a PhD graduate from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2016 works at Cranfield University. Professor Shin, whose main research focus covers guidance, navigation, and control, conducts research on information-based control. He has published 66 articles in SCI journals and presented approximately 70 papers at academic conference with more than 12 patent registrations. He is known for his expertise in areas related to unmanned aerospace systems and urban aero traffic automation. Professor Shin is participating in various aerospace engineering development projects run by the UK government.
The award recognizes promising young scientists who have made significant achievements in the field of aerospace engineering in honor of Jeong Hun Cho, the former PhD candidate in KAIST’s Department of Aerospace Engineering. Cho died in a lab accident in May 2003. Cho’s family endowed the award and scholarship to honor him and a recipient from each of his three alma maters (Kongju National High School, Korea University, and KAIST) are selected every year.
Professor Shin was awarded 25 million KRW in prize money. KAIST student Kim and Korea University student Chang received four million KRW while Kongju National University High School student Chang received three million KRW.
2022.05.16 View 8634 -
 Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho at KARI Receives the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho, a senior researcher at the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), was honored as the recipient of the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering.
Dr. Cho earned his MS and PhD degrees from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2012, and served as a researcher at the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, before joining the Future Convergence Research Division at KARI. He won this year’s award and received 25 million KRW in prize money.
Jeong Hun Cho, who was a PhD candidate in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, passed away in a tragic lab accident in May 2003 and was awarded an honorary doctorate posthumously. His family endowed the award and scholarship in his memory. Since 2005, the scholarship has selected three young scholars every year who specialize in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho was selected as this year’s awardee in recognition of his studies on the development and operation of KARISMA, a comprehensive software package for space debris collision risk management. Dr. Cho built a terrestrial testbed and produced a model for the development of a space debris elimination algorithm. He published six papers in SCI-level journals and wrote 35 symposium papers in the field of space development. He also applied or registered approximately 40 patents both in Korea and internationally.
The Award Committee also selected three students as scholarship recipients: PhD candidate Yongtae Yun from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST received 4 million KRW, MS-PhD candidate Haun-Min Lee from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University received 4 million KRW, and Seonju Yim from Kongju National University High School received 3 million KRW.
(END)
2020.05.13 View 13261
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho at KARI Receives the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho, a senior researcher at the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), was honored as the recipient of the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering.
Dr. Cho earned his MS and PhD degrees from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2012, and served as a researcher at the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, before joining the Future Convergence Research Division at KARI. He won this year’s award and received 25 million KRW in prize money.
Jeong Hun Cho, who was a PhD candidate in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, passed away in a tragic lab accident in May 2003 and was awarded an honorary doctorate posthumously. His family endowed the award and scholarship in his memory. Since 2005, the scholarship has selected three young scholars every year who specialize in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho was selected as this year’s awardee in recognition of his studies on the development and operation of KARISMA, a comprehensive software package for space debris collision risk management. Dr. Cho built a terrestrial testbed and produced a model for the development of a space debris elimination algorithm. He published six papers in SCI-level journals and wrote 35 symposium papers in the field of space development. He also applied or registered approximately 40 patents both in Korea and internationally.
The Award Committee also selected three students as scholarship recipients: PhD candidate Yongtae Yun from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST received 4 million KRW, MS-PhD candidate Haun-Min Lee from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University received 4 million KRW, and Seonju Yim from Kongju National University High School received 3 million KRW.
(END)
2020.05.13 View 13261 -
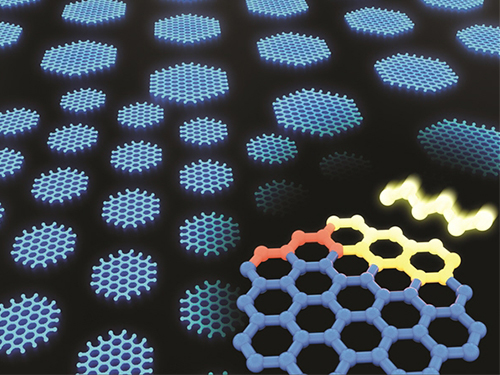 Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 36951
Synthesizing Single-Crystalline Hexagonal Graphene Quantum Dots
(Figure: Uniformly ordered single-crystalline graphene quantum dots of various sizes synthesized through solution chemistry.)
A KAIST team has designed a novel strategy for synthesizing single-crystalline graphene quantum dots, which emit stable blue light. The research team confirmed that a display made of their synthesized graphene quantum dots successfully emitted blue light with stable electric pressure, reportedly resolving the long-standing challenges of blue light emission in manufactured displays. The study, led by Professor O Ok Park in the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, was featured online in Nano Letters on July 5.
Graphene has gained increased attention as a next-generation material for its heat and electrical conductivity as well as its transparency. However, single and multi-layered graphene have characteristics of a conductor so that it is difficult to apply into semiconductor. Only when downsized to the nanoscale, semiconductor’s distinct feature of bandgap will be exhibited to emit the light in the graphene. This illuminating featuring of dot is referred to as a graphene quantum dot.
Conventionally, single-crystalline graphene has been fabricated by chemical vapor deposition (CVD) on copper or nickel thin films, or by peeling graphite physically and chemically. However, graphene made via chemical vapor deposition is mainly used for large-surface transparent electrodes. Meanwhile, graphene made by chemical and physical peeling carries uneven size defects.
The research team explained that their graphene quantum dots exhibited a very stable single-phase reaction when they mixed amine and acetic acid with an aqueous solution of glucose. Then, they synthesized single-crystalline graphene quantum dots from the self-assembly of the reaction intermediate. In the course of fabrication, the team developed a new separation method at a low-temperature precipitation, which led to successfully creating a homogeneous nucleation of graphene quantum dots via a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park and his colleagues have developed solution phase synthesis technology that allows for the creation of the desired crystal size for single nanocrystals down to 100 nano meters. It is reportedly the first synthesis of the homogeneous nucleation of graphene through a single-phase reaction.
Professor Park said, "This solution method will significantly contribute to the grafting of graphene in various fields. The application of this new graphene will expand the scope of its applications such as for flexible displays and varistors.”
This research was a joint project with a team from Korea University under Professor Sang Hyuk Im from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering, and was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program from the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI), KAIST EEWS, and the BK21+ project from the Korean government.
2019.08.02 View 36951 -
 New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 12004
New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 12004 -
 Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 12245
Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 12245 -
 A New Spin Current Generating Material Developed
(Professor Park(left) and Ph.D. candidate Kim)
Magnetic random-access memory (MRAM) is a non-volatile device made of thin magnetic film that can maintain information without an external power supply, in contrast to conventional silicon-based semiconductor memory. It also has the potential for high-density integration and high-speed operation.
The operation of MRAM involves the control of the magnetization direction by exerting spin current-induced torque on a magnetic material. Spin current is generated using electricity in conventional MRAM, but this study developed materials technology that generates spin current using heat.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Byong-Guk Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a material that generates spin current from heat, which can be utilized for a new operation principle for MRAM.
There have been theoretical reports on the spin Nernst effect, the phenomenon of the thermal generation of spin current, but is yet to have been experimentally proven due to technological limitations. However, the research team introduced a spin Nernst magnetoresistance measurement method using tungsten (W) and platinum (Pt) with high spin orbit coupling which allows for the experimental identification of the spin Nernst effect. They also demonstrated that the efficiency of spin current generation from heat is similar to that of spin current generated from electricity.
Professor Park said, “This research has great significance in experimentally proving spin current generation from heat, a new physical phenomenon. We aim to develop the technology as a new operational method for MRAM through further research. This can lower power consumption, and is expected to contribute to the advancement of electronics requiring low power requirement such as wearable, mobile, and IOT devices”.
This research was conducted as a joint research project with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University and Professor Jong-Ryul Jeong at Chungnam National University. It was published in Nature Communications online on November 9 titled “Observation of transverse spin Nernst magnetoresistance induced by thermal spin current in ferromagnet/non-magnet bilayers.” Ph.D. candidate Dong-Jun Kim at KAIST is the first author. This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Schematic diagram of spin Nernst magnetoresistance)
(Research result of new spin current generating materials)
2017.12.08 View 9661
A New Spin Current Generating Material Developed
(Professor Park(left) and Ph.D. candidate Kim)
Magnetic random-access memory (MRAM) is a non-volatile device made of thin magnetic film that can maintain information without an external power supply, in contrast to conventional silicon-based semiconductor memory. It also has the potential for high-density integration and high-speed operation.
The operation of MRAM involves the control of the magnetization direction by exerting spin current-induced torque on a magnetic material. Spin current is generated using electricity in conventional MRAM, but this study developed materials technology that generates spin current using heat.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Byong-Guk Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a material that generates spin current from heat, which can be utilized for a new operation principle for MRAM.
There have been theoretical reports on the spin Nernst effect, the phenomenon of the thermal generation of spin current, but is yet to have been experimentally proven due to technological limitations. However, the research team introduced a spin Nernst magnetoresistance measurement method using tungsten (W) and platinum (Pt) with high spin orbit coupling which allows for the experimental identification of the spin Nernst effect. They also demonstrated that the efficiency of spin current generation from heat is similar to that of spin current generated from electricity.
Professor Park said, “This research has great significance in experimentally proving spin current generation from heat, a new physical phenomenon. We aim to develop the technology as a new operational method for MRAM through further research. This can lower power consumption, and is expected to contribute to the advancement of electronics requiring low power requirement such as wearable, mobile, and IOT devices”.
This research was conducted as a joint research project with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University and Professor Jong-Ryul Jeong at Chungnam National University. It was published in Nature Communications online on November 9 titled “Observation of transverse spin Nernst magnetoresistance induced by thermal spin current in ferromagnet/non-magnet bilayers.” Ph.D. candidate Dong-Jun Kim at KAIST is the first author. This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Schematic diagram of spin Nernst magnetoresistance)
(Research result of new spin current generating materials)
2017.12.08 View 9661 -
 High-Speed Motion Core Technology for Magnetic Memory
(Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics)
A joint research team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics, KAIST and Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University developed technology to dramatically enhance the speed of next generation domain wall-based magnetic memory. This research was published online in Nature Materials on September 25.
Currently-used memory materials, D-RAM and S-RAM, are fast but volatile, leading to memory loss when the power is switched off. Flash memory is non-volatile but slow, while hard disk drives (HDD) have greater storage but are high in energy usage and weak in physical shock tolerance.
To overcome the limitations of existing memory materials, ‘domain wall-based, magnetic memory’ is being researched. The core mechanism of domain wall magnetic memory is the movement of a domain wall by the current. Non-volatility is secured by using magnetic nanowires and the lack of mechanical rotation reduced power usage. This is a new form of high density, low power next-generation memory.
However, previous studies showed the speed limit of domain wall memory to be hundreds m/s at maximum due to the ‘Walker breakdown phenomenon’, which refers to velocity breakdown from the angular precession of a domain wall. Therefore, there was a need to develop core technology to remove the Walker breakdown phenomenon and increase the speed for the commercialization of domain wall memory.
Most domain wall memory studies used ferromagnetic bodies, which cannot overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon. The team discovered that the use of ‘ferrimagnetic‘ GdFeCo at certain conditions could overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon and using this mechanism they could increase domain wall speed to over 2Km/s at room temperature.
Domain wall memory is high-density, low-power, and non-volatile memory. The memory could be the leading next-generation memory with the addition of the high speed property discovered in this research.
Professor Kim said, “This research is significant in discovering a new physical phenomenon at the point at which the angular momentum of a ferrimagnetic body is 0 and it is expected to advance the implementation of next-generation memory in the future.”
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) (No. 2017R1C1B2009686, NRF-2016R1A5A1008184) and by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BT-02).
(Figure 1. Concept Map of Domain Wall Memory Material using Ferrimagnetic Body)
(Figure 2. Scheme and Experimental Results of Domain Wall Speed Measurements)
2017.10.30 View 10010
High-Speed Motion Core Technology for Magnetic Memory
(Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics)
A joint research team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics, KAIST and Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University developed technology to dramatically enhance the speed of next generation domain wall-based magnetic memory. This research was published online in Nature Materials on September 25.
Currently-used memory materials, D-RAM and S-RAM, are fast but volatile, leading to memory loss when the power is switched off. Flash memory is non-volatile but slow, while hard disk drives (HDD) have greater storage but are high in energy usage and weak in physical shock tolerance.
To overcome the limitations of existing memory materials, ‘domain wall-based, magnetic memory’ is being researched. The core mechanism of domain wall magnetic memory is the movement of a domain wall by the current. Non-volatility is secured by using magnetic nanowires and the lack of mechanical rotation reduced power usage. This is a new form of high density, low power next-generation memory.
However, previous studies showed the speed limit of domain wall memory to be hundreds m/s at maximum due to the ‘Walker breakdown phenomenon’, which refers to velocity breakdown from the angular precession of a domain wall. Therefore, there was a need to develop core technology to remove the Walker breakdown phenomenon and increase the speed for the commercialization of domain wall memory.
Most domain wall memory studies used ferromagnetic bodies, which cannot overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon. The team discovered that the use of ‘ferrimagnetic‘ GdFeCo at certain conditions could overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon and using this mechanism they could increase domain wall speed to over 2Km/s at room temperature.
Domain wall memory is high-density, low-power, and non-volatile memory. The memory could be the leading next-generation memory with the addition of the high speed property discovered in this research.
Professor Kim said, “This research is significant in discovering a new physical phenomenon at the point at which the angular momentum of a ferrimagnetic body is 0 and it is expected to advance the implementation of next-generation memory in the future.”
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) (No. 2017R1C1B2009686, NRF-2016R1A5A1008184) and by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BT-02).
(Figure 1. Concept Map of Domain Wall Memory Material using Ferrimagnetic Body)
(Figure 2. Scheme and Experimental Results of Domain Wall Speed Measurements)
2017.10.30 View 10010 -
 Dr. Zi Jing Wong Named 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(Photo caption: The 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship recipients pose with President Shin (left photo) and Dr. Zi Jing Wong, the recipient of the 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Award)
Dr. Zi Jing Wong, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley was named the 2017 recipient of the Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient receives a 20 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Wong who earned his MS at KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering is a rising scholar in the fields of optic meta materials, photonics, imaging, among others. He has published five papers on the realization of a zero refractive index and the control of a refractive index, as well as the realization of a 3D invisibility cloak in Science and Nature Photonics in 2014 and 2015. Dr. Wong also swept the best paper awards from many international academic societies including the US Materials Research Society, IEEE, SPIE, and Metamaterials Congress in 2015. He finished his Ph.D. at the University of California, Berkeley.
The Award Committee also named three recipients of the Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship: Ph.D. candidate Hyon-Tak Kim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Ph.D. candidate Ho-Song Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Hyong-Jin Choi of Kongju National University High School.
The award was endowed by the family of the late Ph.D. candidate Jeong Hun Cho who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In memory of Cho, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship.’ The scholarship annually selects three young scholars from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
2017.05.12 View 13901
Dr. Zi Jing Wong Named 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(Photo caption: The 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship recipients pose with President Shin (left photo) and Dr. Zi Jing Wong, the recipient of the 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Award)
Dr. Zi Jing Wong, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley was named the 2017 recipient of the Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient receives a 20 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Wong who earned his MS at KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering is a rising scholar in the fields of optic meta materials, photonics, imaging, among others. He has published five papers on the realization of a zero refractive index and the control of a refractive index, as well as the realization of a 3D invisibility cloak in Science and Nature Photonics in 2014 and 2015. Dr. Wong also swept the best paper awards from many international academic societies including the US Materials Research Society, IEEE, SPIE, and Metamaterials Congress in 2015. He finished his Ph.D. at the University of California, Berkeley.
The Award Committee also named three recipients of the Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship: Ph.D. candidate Hyon-Tak Kim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Ph.D. candidate Ho-Song Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Hyong-Jin Choi of Kongju National University High School.
The award was endowed by the family of the late Ph.D. candidate Jeong Hun Cho who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In memory of Cho, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship.’ The scholarship annually selects three young scholars from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
2017.05.12 View 13901 -
 KAIST Holds a Ceremony to Present the Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award
Doctor Gyu-Tae Kim from General Electric (GE) received the eleventh Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award. The award ceremony took place in the main conference room of the administration building on campus on May 13, 2015.
Dr. Kim, a graduate of KAIST, conducts research in the field of instable swirl combustion of gas turbines and has contributed to the development of aircraft engines. He earned his name as a researcher by identifying, for the first time in the world, the correlation between the thermoacoustic instability of gas turbine engines and the complex response of swirl flames.
Along with Dr. Kim, Shin-Jae Kang of the Aerospace Engineering Department, KAIST, Yong-Gyun Bae of the Mechanical Engineering Department, Korea University, and Ji-Won Kim from Kongju National University High School, received the Cho Jeong-Hoon scholarship.
The award was created in commemoration of Cho Jeong-Hoon who was killed in an explosion during his research at the KAIST Rocket Laboratory on May 13, 2003. Cho’s parents donated USD 450,000 to KAIST in his memory. Since 2005, a total of four students from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, all of which the late Honorary Doctor Cho attended, have received the scholarship.
2015.05.19 View 9738
KAIST Holds a Ceremony to Present the Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award
Doctor Gyu-Tae Kim from General Electric (GE) received the eleventh Cho Jeong-Hoon Academic Award. The award ceremony took place in the main conference room of the administration building on campus on May 13, 2015.
Dr. Kim, a graduate of KAIST, conducts research in the field of instable swirl combustion of gas turbines and has contributed to the development of aircraft engines. He earned his name as a researcher by identifying, for the first time in the world, the correlation between the thermoacoustic instability of gas turbine engines and the complex response of swirl flames.
Along with Dr. Kim, Shin-Jae Kang of the Aerospace Engineering Department, KAIST, Yong-Gyun Bae of the Mechanical Engineering Department, Korea University, and Ji-Won Kim from Kongju National University High School, received the Cho Jeong-Hoon scholarship.
The award was created in commemoration of Cho Jeong-Hoon who was killed in an explosion during his research at the KAIST Rocket Laboratory on May 13, 2003. Cho’s parents donated USD 450,000 to KAIST in his memory. Since 2005, a total of four students from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, all of which the late Honorary Doctor Cho attended, have received the scholarship.
2015.05.19 View 9738 -
 Dr. Sung-Gu Kim of KARI receives the 10th KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award
KAIST President Steve Kang awarded the 10th "KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award" to Dr. Sung-Gu Kim of Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) along with Byeong-Sup Park, a graduate student of KAIST Aerospace Engineering, Hee-Won Chae of Korea University, and Jin-Hyung Noh of Kongju National University High School on May 13, 2014.
Dr. Sung-Gu Kim was recognized for his development of a 30-ton class reproduction cooling burner and the securing of essential factor technology for liquid-fuel rocket engines on the Naro project.
The KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award was established to commemorate Jung-Hun Cho who was killed while researching in the rocket laboratory on May 13, 2003. From 2005, young scientists from the Aerospace Engineering field have been recognized every year. One student each from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, where the honorary doctorate Dr. Cho attended, has been chosen as a scholarship recipient.
The KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award was established with USD 460,000 in funds donated from Cho's family.
2014.05.17 View 11640
Dr. Sung-Gu Kim of KARI receives the 10th KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award
KAIST President Steve Kang awarded the 10th "KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award" to Dr. Sung-Gu Kim of Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI) along with Byeong-Sup Park, a graduate student of KAIST Aerospace Engineering, Hee-Won Chae of Korea University, and Jin-Hyung Noh of Kongju National University High School on May 13, 2014.
Dr. Sung-Gu Kim was recognized for his development of a 30-ton class reproduction cooling burner and the securing of essential factor technology for liquid-fuel rocket engines on the Naro project.
The KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award was established to commemorate Jung-Hun Cho who was killed while researching in the rocket laboratory on May 13, 2003. From 2005, young scientists from the Aerospace Engineering field have been recognized every year. One student each from KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School, where the honorary doctorate Dr. Cho attended, has been chosen as a scholarship recipient.
The KAIST Jung-Hun Cho Academic Award was established with USD 460,000 in funds donated from Cho's family.
2014.05.17 View 11640 -
 6th TEDxKAIST Held on May 11, 2013
The sixth TEDxKAIST (https://www.facebook.com/TEDxKAIST?fref=ts) took place on May 11, 2013. The event was held under the theme, “Choice between Birth and Death,” and the slogan, “B-C-D,” which was inspired from Jean Paul Satre’s quote, “Life is a choice between birth and death.”
The following speakers gave talks on the choices they have made and the impacts on their lives: Sonya S. Kwak, Professor of the Industrial Design Department at Ehwa Women’s University; Meoung-Seok Oh, a college student majoring in dental technology and business at Korea University; SooA Yeo, CEO of “Chalk,” a social venture company that offers talent donations; and Jeong-Won Lee, a senior researcher at Medical Imaging Laboratory, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI).
According to the speakers, every day we make decisions, and these decisions affect not only our own lives, but also our society as a whole. Speakers and participants explored the underlying relations between the choices being made and the outcome resulted therefrom. Attendees also shared their experiences and ideas that helped them to make the right decision and stressed the importance of choices we make in our lives.
TEDxKAIST is an event operating under the official license of TED to hold TEDx programs based on TED’s slogan “Ideas Worth Spreading.” Since the first event took place under the theme “Science for Happiness, Happiness for Science” on September 2010, TEDxKAIST has brought together over 300 participants through five successful events.
2013.05.31 View 9255
6th TEDxKAIST Held on May 11, 2013
The sixth TEDxKAIST (https://www.facebook.com/TEDxKAIST?fref=ts) took place on May 11, 2013. The event was held under the theme, “Choice between Birth and Death,” and the slogan, “B-C-D,” which was inspired from Jean Paul Satre’s quote, “Life is a choice between birth and death.”
The following speakers gave talks on the choices they have made and the impacts on their lives: Sonya S. Kwak, Professor of the Industrial Design Department at Ehwa Women’s University; Meoung-Seok Oh, a college student majoring in dental technology and business at Korea University; SooA Yeo, CEO of “Chalk,” a social venture company that offers talent donations; and Jeong-Won Lee, a senior researcher at Medical Imaging Laboratory, Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI).
According to the speakers, every day we make decisions, and these decisions affect not only our own lives, but also our society as a whole. Speakers and participants explored the underlying relations between the choices being made and the outcome resulted therefrom. Attendees also shared their experiences and ideas that helped them to make the right decision and stressed the importance of choices we make in our lives.
TEDxKAIST is an event operating under the official license of TED to hold TEDx programs based on TED’s slogan “Ideas Worth Spreading.” Since the first event took place under the theme “Science for Happiness, Happiness for Science” on September 2010, TEDxKAIST has brought together over 300 participants through five successful events.
2013.05.31 View 9255 -
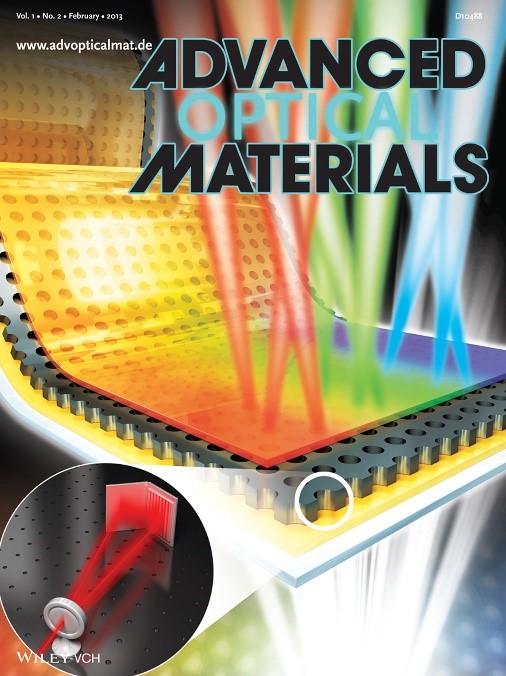 New Technology Will Enable the Commercialization of Plasmon Displays
-- Enhancements in the penetration ratios of color filters are expected by applying nano-surface plasmon effects. --
-- Color filter technology will be applicable to large-area OLED and LCD. --
The fabrication technology to commercialize display color filters using plasmon effects has been discovered.
A joint research team headed by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering of the Korea Advanced Institute for Science and Technology and Prof. Byeong-Kwon Ju from the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University has developed the technology to design and produce a display color filter by applying nano-surface plasmon effects.
Color filters are core components used to express colors in CMOS image sensors found in LCD/OLED displays or digital cameras. The current color filters have penetration ratios of 20~30%, but the objective of the joint research team is to raise this penetration ratio by over 40% to facilitate the mass production of energy-efficient plasmonic displays.
Currently available plasmonic color filters are limited to applications on micrometer scales. However, outcomes of the newest research extend the size of the applications up to 2.5 cm by using laser interference lithography. The academic and industrial sectors agree that it is now possible to mass-produce displays using plasmonic color filters.
The researchers built a nanohole array to large scale by using laser interference lithography, a technology that forms nanostructures with laser light interferences. They also suggested a new manufacturing process that can optimize the features of color filters while compensating for defects arising from the fabrication stages.
The new manufacturing process of applying laser interference lithography is expected to overcome the shortcomings of traditional color filters by simplifying production and, enabling them to be produced at lower costs.
“There were limitations to industrial applications of plasmon effect due to production costs, time, and yields,” explained Yun Seon Do, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering of KAIST. “The new technology can reduce fabrication time and cost to the extent that it would be advisable to replace dye-based and pigment-based color filter technology."
“This research can be applied to large-scale displays, such as TV screens, by using laser-interference lithography,” said Jung-Ho Park, a Ph. D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University. “The research outcome is expected to be widely applied in advanced nano-manufacturing processes as it does not restrict the types of circuit boards."
The research outcome, led by doctoral candidates Do and Park, appeared on the front cover of the second issue of Advanced Optical Materials, a highly regarded academic journal in the field of nanotechnologies, and the team has applied for six related patents.
2013.03.13 View 10644
New Technology Will Enable the Commercialization of Plasmon Displays
-- Enhancements in the penetration ratios of color filters are expected by applying nano-surface plasmon effects. --
-- Color filter technology will be applicable to large-area OLED and LCD. --
The fabrication technology to commercialize display color filters using plasmon effects has been discovered.
A joint research team headed by Professor Kyung Cheol Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering of the Korea Advanced Institute for Science and Technology and Prof. Byeong-Kwon Ju from the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University has developed the technology to design and produce a display color filter by applying nano-surface plasmon effects.
Color filters are core components used to express colors in CMOS image sensors found in LCD/OLED displays or digital cameras. The current color filters have penetration ratios of 20~30%, but the objective of the joint research team is to raise this penetration ratio by over 40% to facilitate the mass production of energy-efficient plasmonic displays.
Currently available plasmonic color filters are limited to applications on micrometer scales. However, outcomes of the newest research extend the size of the applications up to 2.5 cm by using laser interference lithography. The academic and industrial sectors agree that it is now possible to mass-produce displays using plasmonic color filters.
The researchers built a nanohole array to large scale by using laser interference lithography, a technology that forms nanostructures with laser light interferences. They also suggested a new manufacturing process that can optimize the features of color filters while compensating for defects arising from the fabrication stages.
The new manufacturing process of applying laser interference lithography is expected to overcome the shortcomings of traditional color filters by simplifying production and, enabling them to be produced at lower costs.
“There were limitations to industrial applications of plasmon effect due to production costs, time, and yields,” explained Yun Seon Do, a Ph. D. candidate in the Department of Electrical Engineering of KAIST. “The new technology can reduce fabrication time and cost to the extent that it would be advisable to replace dye-based and pigment-based color filter technology."
“This research can be applied to large-scale displays, such as TV screens, by using laser-interference lithography,” said Jung-Ho Park, a Ph. D. candidate in the School of Electrical Engineering of Korea University. “The research outcome is expected to be widely applied in advanced nano-manufacturing processes as it does not restrict the types of circuit boards."
The research outcome, led by doctoral candidates Do and Park, appeared on the front cover of the second issue of Advanced Optical Materials, a highly regarded academic journal in the field of nanotechnologies, and the team has applied for six related patents.
2013.03.13 View 10644