transistor
-
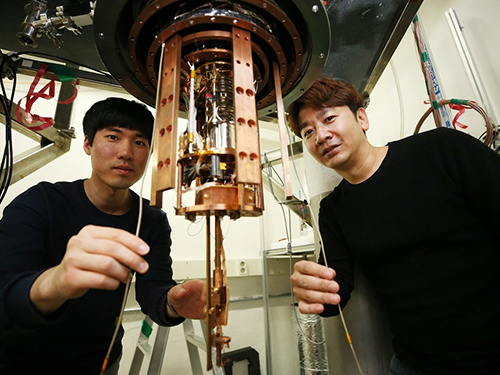 Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 13627
Black Phosphorous Tunnel Field-Effect Transistor as an Alternative Ultra-low Power Switch
Researchers have reported a black phosphorus transistor that can be used as an alternative ultra-low power switch. A research team led by Professor Sungjae Cho in the KAIST Department of Physics developed a thickness-controlled black phosphorous tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) that shows 10-times lower switching power consumption as well as 10,000-times lower standby power consumption than conventional complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) transistors.
The research team said they developed fast and low-power transistors that can replace conventional CMOS transistors. In particular, they solved problems that have degraded TFET operation speed and performance, paving the way to extend Moore’s Law.
In the study featured in Nature Nanotechnology last month, Professor Cho’s team reported a natural heterojunction TFET with spatially varying layer thickness in black phosphorous without interface problems. They achieved record-low average subthreshold swing values over 4-5 dec of current and record-high, on-state current, which allows the TFETs to operate as fast as conventional CMOS transistors with as much lower power consumption.
"We successfully developed the first transistor that achieved the essential criteria for fast, low-power switching. Our newly developed TFETs can replace CMOS transistors by solving a major issue regarding the performance degradation of TFETs,"Professor Cho said.
The continuous down-scaling of transistors has been the key to the successful development of current information technology. However, with Moore’s Law reaching its limits due to the increased power consumption, the development of new alternative transistor designs has emerged as an urgent need.
Reducing both switching and standby power consumption while further scaling transistors requires overcoming the thermionic limit of subthreshold swing, which is defined as the required voltage per ten-fold current increase in the subthreshold region. In order to reduce both the switching and standby power of CMOS circuits, it is critical to reduce the subthreshold swing of the transistors.
However, there is fundamental subthreshold swing limit of 60 mV/dec in CMOS transistors, which originates from thermal carrier injection. The International Roadmap for Devices and Systems has already predicted that new device geometries with new materials beyond CMOS will be required to address transistor scaling challenges in the near future. In particular, TFETs have been suggested as a major alternative to CMOS transistors, since the subthreshold swing in TFETs can be substantially reduced below the thermionic limit of 60 mV/dec. TFETs operate via quantum tunneling, which does not limit subthreshold swing as in thermal injection of CMOS transistors.
In particular, heterojunction TFETs hold significant promise for delivering both low subthreshold swing and high on-state current. High on-current is essential for the fast operation of transistors since charging a device to on state takes a longer time with lower currents. Unlike theoretical expectations, previously developed heterojunction TFETs show 100-100,000x lower on-state current (100-100,000x slower operation speeds) than CMOS transistors due to interface problems in the heterojunction. This low operation speed impedes the replacement of CMOS transistors with low-power TFETs.
Professor Cho said, “We have demonstrated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, TFET optimization for both fast and ultra-low-power operations, which is essential to replace CMOS transistors for low-power applications.” He said he is very delighted to extend Moore’s Law, which may eventually affect almost every aspect of life and society. This study (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7) was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Kim et al. (2020) Thickness-controlled black phosphorus tunnel field-effect transistor for low-power switches. Nature Nanotechnology. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0623-7
Profile:
Professor Sungjae Cho
sungjae.cho@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
Profile:
Seungho Kim, PhD Candidate
krksh21@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Physics
http://qtak.kaist.ac.kr/
KAIST
(END)
2020.02.21 View 13627 -
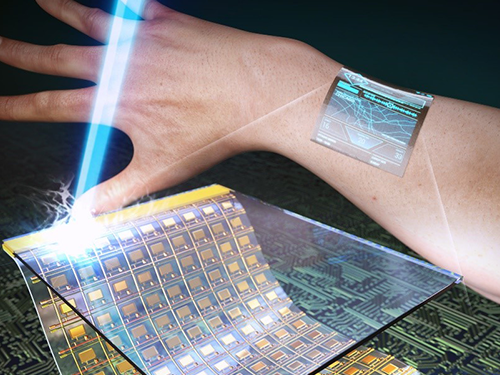 KAIST Develops Transparent Oxide Thin-Film Transistors
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) era, strong demand has grown for wearable and transparent displays that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR) and skin-like thin flexible devices. However, previous flexible transparent displays have posed real challenges to overcome, which are, among others, poor transparency and low electrical performance. To improve the transparency and performance, past research efforts have tried to use inorganic-based electronics, but the fundamental thermal instabilities of plastic substrates have hampered the high temperature process, an essential step necessary for the fabrication of high performance electronic devices.
As a solution to this problem, a research team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Sang-Hee Ko Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the KAIST has developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors (TFT) for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off (ILLO) method. Professor Lee’s team previously demonstrated the ILLO technology for energy-harvesting (Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014) and flexible memory (Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014) devices.
The research team fabricated a high-performance oxide TFT array on top of a sacrificial laser-reactive substrate. After laser irradiation from the backside of the substrate, only the oxide TFT arrays were separated from the sacrificial substrate as a result of reaction between laser and laser-reactive layer, and then subsequently transferred onto ultrathin plastics ( thickness). Finally, the transferred ultrathin-oxide driving circuit for the flexible display was attached conformally to the surface of human skin to demonstrate the possibility of the wearable application. The attached oxide TFTs showed high optical transparency of 83% and mobility of even under several cycles of severe bending tests.
Professor Lee said, “By using our ILLO process, the technological barriers for high performance transparent flexible displays have been overcome at a relatively low cost by removing expensive polyimide substrates. Moreover, the high-quality oxide semiconductor can be easily transferred onto skin-like or any flexible substrate for wearable application.”
These research results, entitled “Skin-Like Oxide Thin-Film Transistors for Transparent Displays,”
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201601296/abstract) were the lead article published in the July 2016 online issue of Wiley’s Advanced Functional Materials.
###
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014, Highly-efficient, Flexible Piezoelectric PZT Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201305659/abstract)
[2] Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014, Flexible Crossbar-structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substartes via Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract)
Picture 1: A Schamatic Image of Ultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This image shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors produced via the ILLO process.
Picture 2: Application of Uultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This picture shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors attached to a jumper sleeve and human skin.
2016.08.01 View 13398
KAIST Develops Transparent Oxide Thin-Film Transistors
With the advent of the Internet of Things (IoT) era, strong demand has grown for wearable and transparent displays that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR) and skin-like thin flexible devices. However, previous flexible transparent displays have posed real challenges to overcome, which are, among others, poor transparency and low electrical performance. To improve the transparency and performance, past research efforts have tried to use inorganic-based electronics, but the fundamental thermal instabilities of plastic substrates have hampered the high temperature process, an essential step necessary for the fabrication of high performance electronic devices.
As a solution to this problem, a research team led by Professors Keon Jae Lee and Sang-Hee Ko Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at the KAIST has developed ultrathin and transparent oxide thin-film transistors (TFT) for an active-matrix backplane of a flexible display by using the inorganic-based laser lift-off (ILLO) method. Professor Lee’s team previously demonstrated the ILLO technology for energy-harvesting (Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014) and flexible memory (Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014) devices.
The research team fabricated a high-performance oxide TFT array on top of a sacrificial laser-reactive substrate. After laser irradiation from the backside of the substrate, only the oxide TFT arrays were separated from the sacrificial substrate as a result of reaction between laser and laser-reactive layer, and then subsequently transferred onto ultrathin plastics ( thickness). Finally, the transferred ultrathin-oxide driving circuit for the flexible display was attached conformally to the surface of human skin to demonstrate the possibility of the wearable application. The attached oxide TFTs showed high optical transparency of 83% and mobility of even under several cycles of severe bending tests.
Professor Lee said, “By using our ILLO process, the technological barriers for high performance transparent flexible displays have been overcome at a relatively low cost by removing expensive polyimide substrates. Moreover, the high-quality oxide semiconductor can be easily transferred onto skin-like or any flexible substrate for wearable application.”
These research results, entitled “Skin-Like Oxide Thin-Film Transistors for Transparent Displays,”
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adfm.201601296/abstract) were the lead article published in the July 2016 online issue of Wiley’s Advanced Functional Materials.
###
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 12, 2014, Highly-efficient, Flexible Piezoelectric PZT Thin Film Nanogenerator on Plastic Substrates
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201305659/abstract)
[2] Advanced Materials, September 8, 2014, Flexible Crossbar-structured Resistive Memory Arrays on Plastic Substartes via Inorganic-based Laser Lift-off
(http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201402472/abstract)
Picture 1: A Schamatic Image of Ultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This image shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors produced via the ILLO process.
Picture 2: Application of Uultrathin, Flexible, and Transparent Oxide Thin-film Transistors
This picture shows ultrathin, flexible, and transparent oxide thin-film transistors attached to a jumper sleeve and human skin.
2016.08.01 View 13398 -
 KAIST Develops Ultrathin Polymer Insulators Key to Low-Power Soft Electronics
Using an initiated chemical vapor deposition technique, the research team created an ultrathin polymeric insulating layer essential in realizing transistors with flexibility and low power consumption. This advance is expected to accelerate the commercialization of wearable and soft electronics.
A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a high-performance ultrathin polymeric insulator for field-effect transistors (FETs). The researchers used vaporized monomers to form polymeric films grown conformally on various surfaces including plastics to produce a versatile insulator that meets a wide range of requirements for next-generation electronic devices. Their research results were published online in Nature Materials on March 9th, 2015.
FETs are an essential component for any modern electronic device used in our daily life from cell phones and computers, to flat-panel displays. Along with three electrodes (gate, source, and drain), FETs consist of an insulating layer and a semiconductor channel layer. The insulator in FETs plays an important role in controlling the conductance of the semiconductor channel and thus current flow within the translators. For reliable and low-power operation of FETs, electrically robust, ultrathin insulators are essential. Conventionally, such insulators are made of inorganic materials (e.g., oxides and nitrides) built on a hard surface such as silicon or glass due to their excellent insulating performance and reliability.
However, these insulators were difficult to implement into soft electronics due to their rigidity and high process temperature. In recent years, many researchers have studied polymers as promising insulating materials that are compatible with soft unconventional substrates and emerging semiconductor materials. The traditional technique employed in developing a polymer insulator, however, had the limitations of low surface coverage at ultra-low thickness, hindering FETs adopting polymeric insulators from operating at low voltage.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Sung Gap Im of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Professor Seunghyup Yoo and Professor Byung Jin Cho of the Electrical Engineering Department developed an insulating layer of organic polymers, “pV3D3,” that can be greatly scaled down, without losing its ideal insulating properties, to a thickness of less than 10 nanometers (nm) using the all-dry vapor-phase technique called the “initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD).”
The iCVD process allows gaseous monomers and initiators to react with each other in a low vacuum condition, and as a result, conformal polymeric films with excellent insulating properties are deposited on a substrate. Unlike the traditional technique, the surface-growing character of iCVD can overcome the problems associated with surface tension and produce highly uniform and pure ultrathin polymeric films over a large area with virtually no surface or substrate limitations. Furthermore, most iCVD polymers are created at room temperature, which lessens the strain exerted upon and damage done to the substrates.
With the pV3D3 insulator, the research team built low-power, high-performance FETs based on various semiconductor materials such as organics, graphene, and oxides, demonstrating the pV3D3 insulator’s wide range of material compatibility. They also manufactured a stick-on, removable electronic component using conventional packaging tape as a substrate. In collaboration with Professor Yong-Young Noh from Dongguk University in Korea, the team successfully developed a transistor array on a large-scale flexible substrate with the pV3D3 insulator.
Professor Im said, “The down-scalability and wide range of compatibility observed with iCVD-grown pV3D3 are unprecedented for polymeric insulators. Our iCVD pV3D3 polymeric films showed an insulating performance comparable to that of inorganic insulating layers, even when their thickness were scaled down to sub-10 nm. We expect our development will greatly benefit flexible or soft electronics, which will play a key role in the success of emerging electronic devices such as wearable computers.”
The title of the research paper is “Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapor deposition for low-power soft electronics” (Digital Object Identifier (DOI) number is 10.1038/nmat4237).
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how the initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) technique produces pV3D3 polymeric films: (i) introduction of vaporized monomers and initiators, (ii) activation of initiators to thermally dissociate into radicals, (iii) adsorption of monomers and initiator radicals onto a substrate, and (iv) transformation of free-radical polymerization into pV3D3 thin films.
Picture 2: This is a transistor array fabricated on a large scale, highly flexible substrate with pV3D3 polymeric films.
Picture 3: This photograph shows an electronic component fabricated on a conventional packaging tape, which is attachable or detachable, with pV3D3 polymeric films embedded.
2015.03.10 View 14507
KAIST Develops Ultrathin Polymer Insulators Key to Low-Power Soft Electronics
Using an initiated chemical vapor deposition technique, the research team created an ultrathin polymeric insulating layer essential in realizing transistors with flexibility and low power consumption. This advance is expected to accelerate the commercialization of wearable and soft electronics.
A group of researchers at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a high-performance ultrathin polymeric insulator for field-effect transistors (FETs). The researchers used vaporized monomers to form polymeric films grown conformally on various surfaces including plastics to produce a versatile insulator that meets a wide range of requirements for next-generation electronic devices. Their research results were published online in Nature Materials on March 9th, 2015.
FETs are an essential component for any modern electronic device used in our daily life from cell phones and computers, to flat-panel displays. Along with three electrodes (gate, source, and drain), FETs consist of an insulating layer and a semiconductor channel layer. The insulator in FETs plays an important role in controlling the conductance of the semiconductor channel and thus current flow within the translators. For reliable and low-power operation of FETs, electrically robust, ultrathin insulators are essential. Conventionally, such insulators are made of inorganic materials (e.g., oxides and nitrides) built on a hard surface such as silicon or glass due to their excellent insulating performance and reliability.
However, these insulators were difficult to implement into soft electronics due to their rigidity and high process temperature. In recent years, many researchers have studied polymers as promising insulating materials that are compatible with soft unconventional substrates and emerging semiconductor materials. The traditional technique employed in developing a polymer insulator, however, had the limitations of low surface coverage at ultra-low thickness, hindering FETs adopting polymeric insulators from operating at low voltage.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Sung Gap Im of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department and Professor Seunghyup Yoo and Professor Byung Jin Cho of the Electrical Engineering Department developed an insulating layer of organic polymers, “pV3D3,” that can be greatly scaled down, without losing its ideal insulating properties, to a thickness of less than 10 nanometers (nm) using the all-dry vapor-phase technique called the “initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD).”
The iCVD process allows gaseous monomers and initiators to react with each other in a low vacuum condition, and as a result, conformal polymeric films with excellent insulating properties are deposited on a substrate. Unlike the traditional technique, the surface-growing character of iCVD can overcome the problems associated with surface tension and produce highly uniform and pure ultrathin polymeric films over a large area with virtually no surface or substrate limitations. Furthermore, most iCVD polymers are created at room temperature, which lessens the strain exerted upon and damage done to the substrates.
With the pV3D3 insulator, the research team built low-power, high-performance FETs based on various semiconductor materials such as organics, graphene, and oxides, demonstrating the pV3D3 insulator’s wide range of material compatibility. They also manufactured a stick-on, removable electronic component using conventional packaging tape as a substrate. In collaboration with Professor Yong-Young Noh from Dongguk University in Korea, the team successfully developed a transistor array on a large-scale flexible substrate with the pV3D3 insulator.
Professor Im said, “The down-scalability and wide range of compatibility observed with iCVD-grown pV3D3 are unprecedented for polymeric insulators. Our iCVD pV3D3 polymeric films showed an insulating performance comparable to that of inorganic insulating layers, even when their thickness were scaled down to sub-10 nm. We expect our development will greatly benefit flexible or soft electronics, which will play a key role in the success of emerging electronic devices such as wearable computers.”
The title of the research paper is “Synthesis of ultrathin polymer insulating layers by initiated chemical vapor deposition for low-power soft electronics” (Digital Object Identifier (DOI) number is 10.1038/nmat4237).
Picture 1: A schematic image to show how the initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD) technique produces pV3D3 polymeric films: (i) introduction of vaporized monomers and initiators, (ii) activation of initiators to thermally dissociate into radicals, (iii) adsorption of monomers and initiator radicals onto a substrate, and (iv) transformation of free-radical polymerization into pV3D3 thin films.
Picture 2: This is a transistor array fabricated on a large scale, highly flexible substrate with pV3D3 polymeric films.
Picture 3: This photograph shows an electronic component fabricated on a conventional packaging tape, which is attachable or detachable, with pV3D3 polymeric films embedded.
2015.03.10 View 14507 -
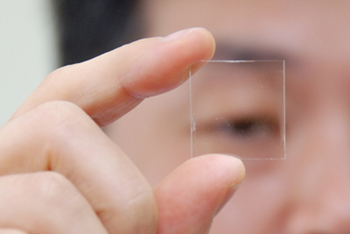 Home-Grown Transparent Thin Film Transistor Developed
KAIST, Aug. 6, 2008 -- A KAIST research team led by Profs. Jae-Woo Park and Seung-Hyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Division has developed a home-grown technology to create transparent thin film transistor using titanium dioxide., university authorities said.The KAIST team made the technological advance in collaboration with the LCD Division of Samsung Electronics and the Techno Semichem Co., a local LCD equipment maker. Transparent thin film transistor continues to enjoy a wealth of popularity and intensive research interest since it is used in producing operating circuits including transparent display, active-matrix OLED (AMOLED) display and flexible display.
The new technology is significant in that it is based on a titanium dioxide, the first such attempt in the world, while the technologies patented by the United States and Japan are based on ZnO.
Researchers will continue to work on securing technological reliability and developing a technology to mass-produce in a large-scale chemical vapor deposition equipment for the next couple of years.
"The development of technology to produce transparent thin film transistor will help Korean LCD makers reduce its dependence on foreign technologies, as well as maintain Korea"s status as a leader of the world"s display industry," said Prof. Park.
KAIST has applied for local patent registration of the technology and the process is expected to complete by this October or November. International patents have been also applied for in the U.S., Japan and Europe.
The new technology was introduced in the latest edition of the Electron Device Letters, a journal published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers or IEEE, a New York-based international non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related to electricity. It will be presented at the International Display Workshop 2008 on Dec. 5 in Niigata, Japan.
2008.08.07 View 17943
Home-Grown Transparent Thin Film Transistor Developed
KAIST, Aug. 6, 2008 -- A KAIST research team led by Profs. Jae-Woo Park and Seung-Hyup Yoo of the Electrical Engineering Division has developed a home-grown technology to create transparent thin film transistor using titanium dioxide., university authorities said.The KAIST team made the technological advance in collaboration with the LCD Division of Samsung Electronics and the Techno Semichem Co., a local LCD equipment maker. Transparent thin film transistor continues to enjoy a wealth of popularity and intensive research interest since it is used in producing operating circuits including transparent display, active-matrix OLED (AMOLED) display and flexible display.
The new technology is significant in that it is based on a titanium dioxide, the first such attempt in the world, while the technologies patented by the United States and Japan are based on ZnO.
Researchers will continue to work on securing technological reliability and developing a technology to mass-produce in a large-scale chemical vapor deposition equipment for the next couple of years.
"The development of technology to produce transparent thin film transistor will help Korean LCD makers reduce its dependence on foreign technologies, as well as maintain Korea"s status as a leader of the world"s display industry," said Prof. Park.
KAIST has applied for local patent registration of the technology and the process is expected to complete by this October or November. International patents have been also applied for in the U.S., Japan and Europe.
The new technology was introduced in the latest edition of the Electron Device Letters, a journal published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers or IEEE, a New York-based international non-profit, professional organization for the advancement of technology related to electricity. It will be presented at the International Display Workshop 2008 on Dec. 5 in Niigata, Japan.
2008.08.07 View 17943