sustainable
-
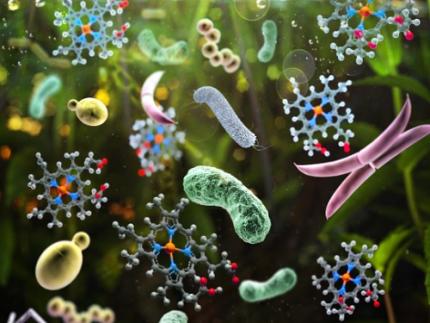 KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 7916
KAIST introduces microbial food as a strategy food production of the future
The global food crisis is increasing due to rapid population growth and declining food productivity to climate change. Moreover, today's food production and supply system emit a huge amount of carbon dioxide, reaching 30% of the total amount emitted by humanity, aggravating climate change. Sustainable and nutritious microbial food is attracting attention as a key to overcoming this impasse.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on April 12th that Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi of the BioProcess Engineering Research Center and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering published a paper that proposes a direction of research on ‘microbial food production from sustainable raw materials.’
Microbial food refers to various foods and food ingredients produced using microorganisms. Microbial biomass contains a large amount of protein per unit in dry mass, comparable to that of meat, and emits the smallest amount of carbon dioxide and is required to produce a unit mass compared to various livestock, fish, shellfish, and crops. Since the amount of water and space requirement is small, it can be an eco-friendly, sustainable and highly nutritious food resource.
Fermented foods are the most readily available microbial foods around us. Although the proportion of microbial biomass in fermented foods is small, compounds with relatively low nutritional value, such as carbohydrates, are consumed during the fermentation process, and as microorganisms proliferate, the content of nutrients with higher nutritional value, such as proteins and vitamins, increases.
Various food compounds isolated and purified from biomass or culture media obtained through microbial culture are also a branch of microbial food. Examples that can be found around us include various amino acids, including monosodium glutamate, food proteins, enzymes, flavoring compounds, food colorings, and bioactive substances.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram portraying various microbial biomass production strategies utlizing sustainable feedstocks >
Lastly, the most ultimate and fundamental form of microbial food can be said to be microbial biomass or extracts produced through microbial culture and foods cooked using them. A representative example is single-cell protein, which collectively refers to microbial biomass or microbial proteins extracted from it.
In this paper, the researchers comprehensively covered various non-edible raw materials and strategies for using them that can be used to produce microbial food in a more sustainable way. Furthermore, it covers various microbial foods that are actually produced in the industry using the relevant raw materials and their characteristics, as well as prospects for the production and generalization of sustainable microbial foods.
Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi, the first author of this paper, said, “Microbial foods produced from various sustainable raw materials will soon be commonly encountered at our tables.” Second author Seok Yeong Jung, a doctoral student, also said, “Microbial foods of the future will not be limited foods consumed only out of a sense of obligation to the environment, but will be complete foods that are consumed by choice because of their nutritional value and taste.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “It is time for the industry and academia, as well as the public and private sectors, to cooperate more closely so that more diverse microbial foods can be developed and supplied in order to create a sustainable society for ourselves and our descendants.”
< Figure 2. Compositions and environmental footprints of animal, plant and microbial biomass. >
This paper was published online on April 9 in ‘Nature Microbiology’ published by Nature.
※ Paper title: From sustainable feedstocks to microbial foods
※ Author information: Kyeong Rok Choi (first author), Seok Yeong Jung (second author) and Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author)
This research was conducted under the development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project (project leader KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee) supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project leader KAIST Research Professor Kyeong Rok Choi) of the Agricultural Microbiology Project Group (Director, Professor Pahn-Shick Chang) supported by the Rural Development Administration.
2024.04.12 View 7916 -
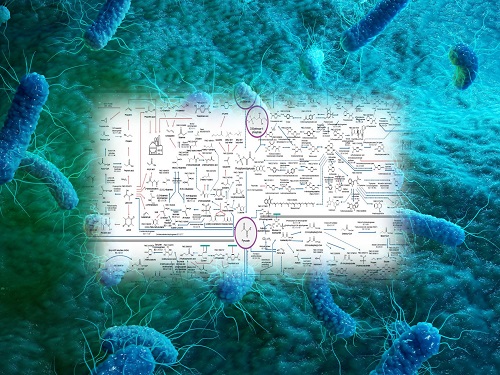 Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 16433
Interactive Map of Metabolical Synthesis of Chemicals
An interactive map that compiled the chemicals produced by biological, chemical and combined reactions has been distributed on the web
- A team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, organized and distributed an all-inclusive listing of chemical substances that can be synthesized using microorganisms
- It is expected to be used by researchers around the world as it enables easy assessment of the synthetic pathway through the web.
A research team comprised of Woo Dae Jang, Gi Bae Kim, and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported an interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals. Their research paper “An interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals” was published online in Trends in Biotechnology on August 10, 2022.
As a response to rapid climate change and environmental pollution, research on the production of petrochemical products using microorganisms is receiving attention as a sustainable alternative to existing methods of productions. In order to synthesize various chemical substances, materials, and fuel using microorganisms, it is necessary to first construct the biosynthetic pathway toward desired product by exploration and discovery and introduce them into microorganisms. In addition, in order to efficiently synthesize various chemical substances, it is sometimes necessary to employ chemical methods along with bioengineering methods using microorganisms at the same time. For the production of non-native chemicals, novel pathways are designed by recruiting enzymes from heterologous sources or employing enzymes designed though rational engineering, directed evolution, or ab initio design.
The research team had completed a map of chemicals which compiled all available pathways of biological and/or chemical reactions that lead to the production of various bio-based chemicals back in 2019 and published the map in Nature Catalysis. The map was distributed in the form of a poster to industries and academia so that the synthesis paths of bio-based chemicals could be checked at a glance.
The research team has expanded the bio-based chemicals map this time in the form of an interactive map on the web so that anyone with internet access can quickly explore efficient paths to synthesize desired products. The web-based map provides interactive visual tools to allow interactive visualization, exploration, and analysis of complex networks of biological and/or chemical reactions toward the desired products. In addition, the reported paper also discusses the production of natural compounds that are used for diverse purposes such as food and medicine, which will help designing novel pathways through similar approaches or by exploiting the promiscuity of enzymes described in the map. The published bio-based chemicals map is also available at http://systemsbiotech.co.kr.
The co-first authors, Dr. Woo Dae Jang and Ph.D. student Gi Bae Kim, said, “We conducted this study to address the demand for updating the previously distributed chemicals map and enhancing its versatility.” “The map is expected to be utilized in a variety of research and in efforts to set strategies and prospects for chemical production incorporating bio and chemical methods that are detailed in the map.”
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee said, “The interactive bio-based chemicals map is expected to help design and optimization of the metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of target chemicals together with the strategies of chemical conversions, serving as a blueprint for developing further ideas on the production of desired chemicals through biological and/or chemical reactions.”
The interactive metabolic map of bio-based chemicals.
2022.08.11 View 16433 -
 Hydrogen-Natural Gas Hydrates Harvested by Natural Gas
A hydrogen-natural gas blend (HNGB) can be a game changer only if it can be stored safely and used as a sustainable clean energy resource. A recent study has suggested a new strategy for stably storing hydrogen, using natural gas as a stabilizer. The research proposed a practical gas phase modulator based synthesis of HNGB without generating chemical waste after dissociation for the immediate service.
The research team of Professor Jae Woo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in collaboration with the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) demonstrated that the natural gas modulator based synthesis leads to significantly reduced synthesis pressure simultaneously with the formation of hydrogen clusters in the confined nanoporous cages of clathrate hydrates. This approach minimizes the environmental impact and reduces operation costs since clathrate hydrates do not generate any chemical waste in both the synthesis and decomposition processes.
For the efficient storage and transportation of hydrogen, numerous materials have been investigated. Among others, clathrate hydrates offer distinct benefits. Clathrate hydrates are nanoporous inclusion compounds composed of a 3D network of polyhedral cages made of hydrogen-bonded ‘host’ water molecules and captured ‘guest’ gas or liquid molecules.
In this study, the research team used two gases, methane and ethane, which have lower equilibrium conditions compared to hydrogen as thermodynamic stabilizers. As a result, they succeeded in stably storing the hydrogen-natural gas compound in hydrates. According to the composition ratio of methane and ethane, structure I or II hydrates can be formed, both of which can stably store hydrogen-natural gas in low-pressure conditions.
The research team found that two hydrogen molecules are stored in small cages in tuned structure I hydrates, while up to three hydrogen molecules can be stored in both small and large cages in tuned structure II hydrates. Hydrates can store gas up to about 170-times its volume and the natural gas used as thermodynamic stabilizers in this study can also be used as an energy source.
The research team developed technology to produce hydrates from ice, produced hydrogen-natural gas hydrates by substitution, and successfully observed that the tuning phenomenon only occurs when hydrogen is involved in hydrate formation from the start for both structures of hydrates.
They expect that the findings can be applied to not only an energy-efficient gas storage material, but also a smart platform to utilize hydrogen natural gas blends, which can serve as a new alternative energy source with targeted hydrogen contents by designing synthetic pathways of mixed gas hydrates.
The research was published online in Energy Storage Materials on June 6, with the title ‘One-step formation of hydrogen clusters in clathrate hydrates stabilized via natural gas blending’.
Professor Lee said, “HNGB will utilize the existing natural gas infrastructure for transportation, so it is very likely that we can commercialize this hydrate system. We are investigating the kinetic performance through a follow-up strategy to increase the volume of gas storage.
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and BK21 plus program.
(Figure1. Schematics showing the storage method for hydrogen in a natural gas hydrate using a substitution method and storage method directly from ice to a hydrogen-natural gas hydrate.)
(Figure 2. Artificially synthesized and dissociated hydrogen-natural gas hydrates. The Raman spectra of tuned sI and sII hydrate showing the hydrogen clusters in each cage.)
2019.06.21 View 42736
Hydrogen-Natural Gas Hydrates Harvested by Natural Gas
A hydrogen-natural gas blend (HNGB) can be a game changer only if it can be stored safely and used as a sustainable clean energy resource. A recent study has suggested a new strategy for stably storing hydrogen, using natural gas as a stabilizer. The research proposed a practical gas phase modulator based synthesis of HNGB without generating chemical waste after dissociation for the immediate service.
The research team of Professor Jae Woo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering in collaboration with the Gwangju Institute of Science and Technology (GIST) demonstrated that the natural gas modulator based synthesis leads to significantly reduced synthesis pressure simultaneously with the formation of hydrogen clusters in the confined nanoporous cages of clathrate hydrates. This approach minimizes the environmental impact and reduces operation costs since clathrate hydrates do not generate any chemical waste in both the synthesis and decomposition processes.
For the efficient storage and transportation of hydrogen, numerous materials have been investigated. Among others, clathrate hydrates offer distinct benefits. Clathrate hydrates are nanoporous inclusion compounds composed of a 3D network of polyhedral cages made of hydrogen-bonded ‘host’ water molecules and captured ‘guest’ gas or liquid molecules.
In this study, the research team used two gases, methane and ethane, which have lower equilibrium conditions compared to hydrogen as thermodynamic stabilizers. As a result, they succeeded in stably storing the hydrogen-natural gas compound in hydrates. According to the composition ratio of methane and ethane, structure I or II hydrates can be formed, both of which can stably store hydrogen-natural gas in low-pressure conditions.
The research team found that two hydrogen molecules are stored in small cages in tuned structure I hydrates, while up to three hydrogen molecules can be stored in both small and large cages in tuned structure II hydrates. Hydrates can store gas up to about 170-times its volume and the natural gas used as thermodynamic stabilizers in this study can also be used as an energy source.
The research team developed technology to produce hydrates from ice, produced hydrogen-natural gas hydrates by substitution, and successfully observed that the tuning phenomenon only occurs when hydrogen is involved in hydrate formation from the start for both structures of hydrates.
They expect that the findings can be applied to not only an energy-efficient gas storage material, but also a smart platform to utilize hydrogen natural gas blends, which can serve as a new alternative energy source with targeted hydrogen contents by designing synthetic pathways of mixed gas hydrates.
The research was published online in Energy Storage Materials on June 6, with the title ‘One-step formation of hydrogen clusters in clathrate hydrates stabilized via natural gas blending’.
Professor Lee said, “HNGB will utilize the existing natural gas infrastructure for transportation, so it is very likely that we can commercialize this hydrate system. We are investigating the kinetic performance through a follow-up strategy to increase the volume of gas storage.
This study was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea and BK21 plus program.
(Figure1. Schematics showing the storage method for hydrogen in a natural gas hydrate using a substitution method and storage method directly from ice to a hydrogen-natural gas hydrate.)
(Figure 2. Artificially synthesized and dissociated hydrogen-natural gas hydrates. The Raman spectra of tuned sI and sII hydrate showing the hydrogen clusters in each cage.)
2019.06.21 View 42736 -
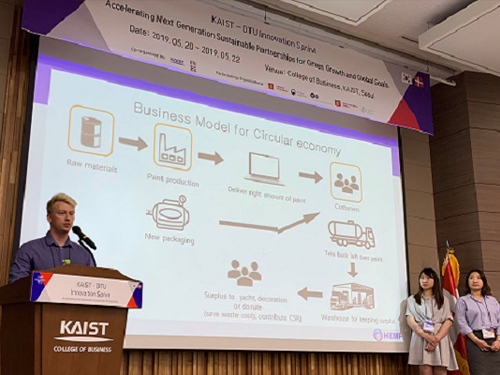 'Think Out of the Box,' Team Circos Wins the P4G Innovation Sprint
<The winning team of the P4G Innovation Sprint poses with the Crown Prince of Denmark (sixth from the left in the first row) and President Shin (fifth from the left in the first row) during the awarding ceremony.>
Team Circos from KAIST and Denmark made a new sustainable business model for Hempel, a global coating supplier group in Denmark, and won the first prize at the P4G (the Partnership for Green Growth and Global Goals) Innovation Sprint held at KAIST’s Seoul campus on May 22. The six-member team was awarded one million KRW in prize money by the Crown Prince of Denmark. Two of winning team members have the privilege of traveling to visit Hempel in Denmark.
The winning team thought outside the box, inspired by box wine which reduced the sales price from traditional bottled wine. Six teams made up of members from different academic disciplines spent two nights and three days brainstorming ways to resolve the challenges of corporations such as Velux and Hempel from Denmark and SK from Korea.
The P4G Innovation Sprint is one of the events co-hosted by KAIST and Technological University of Denmark in celebration of the 60th anniversary of diplomatic relations establishment between Denmark and Korea and the 8th anniversary of the Green Growth Alliance between the two countries. The Crown Prince Couple also made a royal visit to Korea in honor of the 60th anniversary celebration and Green Growth Alliance between the two countries.
This Innovation Sprint aimed to develop young academics’ perspectives, skills, and talents for the next generation to better research the Sustainable Development Goals set by UN.
Three teams made their final five-minute pitches before the Crown Prince and President Sung-Chul
Shin and responded to questions from the four-member jury.
The Crown Prince of Denmark and President Shin both agreed that the collaborative and convergent ideas will address global problems.
The Crown Prince stressed in his congratulatory remarks the importance of partnership in this polarizing world to achieve sustainable improvements saying, “Partnerships are only possible to sustain through collaboration and hard work while staying curious, creative, and critical. " He also shared the special relationship with KAIST. His father-in-law Professor John Donaldson used to be a visiting professor of applied mathmatics at KAIST back in 2003.
President Shin added, “Collaboration across boundaries is most critical for responding to these issues. In that sense, this P4G Innovation Sprint is a shining example for demonstrating the collaborative efforts between teammates from diverse disciplines. When we work together and build convergent ideas, we will be more innovative and go further.”
<Winning team member Nicolai Thorball from DTU pitches at the final in the presence of the Crown Prince of Denmark and KAIST President Shin.>
“The canned packaging in the paint industry results in 40 times more carbon emission in the course of production. However, when using aluminum packaging which is recyclable, the waste amount will be cut dramatically,” pitched Nicolai Thorball from DTU on exchange at Seoul National University. Nicolai, whose major is environmental engineering, is one of two Danish students including Thomsen Xandra Flyvbjerg from the University of Southern Denmark. Flyvbjergy, majoring in business, is now on exchange at Sungkynkwan University.
“I am very glad to have the chance to understand the concept of the circular economy and green growth at the sprint. It was also very challenging to make ideation from so many ideas brainstormed,” said Dong-Eun Lee, a KAIST undergraduate from the Department of Biological Sciences. He said that he learned a lot from his two other teammates who are from the Program of Green Business & Policy at KAIST College of Business, Jae-Hee Park and Kyung-Hyun Kim. Juho Park majoring in mechanical engineering at KAIST was one of the team.
Circos’ solution for a sustainable model received acclaim from the jury members. DTU Senior Vice President Marianne Thellerson, one of jurors, claimed their model has very high market feasibility, saying, “Their idea could be commercialized right now into the market.” Professor Hee-Kyung Park from KAIST who helped participants’ ideation as one of four mentors said, “The winning team perfectly met all the components of the evaluation criteria, Solution, Acceleration, and Pitch.”
At this sprint, 10 students from Denmark and 29 KAIST students were divided into 6 teams and given the challenges of three companies. The Danish window facility company Velux presented its future glass window system and the paint company Hempel their circular economic new business model. SK challenged the students to help it become a global clean energy solution company. The event was based on a hacker blueprint that found the optimal solution to the topics proposed.
2019.05.23 View 10218
'Think Out of the Box,' Team Circos Wins the P4G Innovation Sprint
<The winning team of the P4G Innovation Sprint poses with the Crown Prince of Denmark (sixth from the left in the first row) and President Shin (fifth from the left in the first row) during the awarding ceremony.>
Team Circos from KAIST and Denmark made a new sustainable business model for Hempel, a global coating supplier group in Denmark, and won the first prize at the P4G (the Partnership for Green Growth and Global Goals) Innovation Sprint held at KAIST’s Seoul campus on May 22. The six-member team was awarded one million KRW in prize money by the Crown Prince of Denmark. Two of winning team members have the privilege of traveling to visit Hempel in Denmark.
The winning team thought outside the box, inspired by box wine which reduced the sales price from traditional bottled wine. Six teams made up of members from different academic disciplines spent two nights and three days brainstorming ways to resolve the challenges of corporations such as Velux and Hempel from Denmark and SK from Korea.
The P4G Innovation Sprint is one of the events co-hosted by KAIST and Technological University of Denmark in celebration of the 60th anniversary of diplomatic relations establishment between Denmark and Korea and the 8th anniversary of the Green Growth Alliance between the two countries. The Crown Prince Couple also made a royal visit to Korea in honor of the 60th anniversary celebration and Green Growth Alliance between the two countries.
This Innovation Sprint aimed to develop young academics’ perspectives, skills, and talents for the next generation to better research the Sustainable Development Goals set by UN.
Three teams made their final five-minute pitches before the Crown Prince and President Sung-Chul
Shin and responded to questions from the four-member jury.
The Crown Prince of Denmark and President Shin both agreed that the collaborative and convergent ideas will address global problems.
The Crown Prince stressed in his congratulatory remarks the importance of partnership in this polarizing world to achieve sustainable improvements saying, “Partnerships are only possible to sustain through collaboration and hard work while staying curious, creative, and critical. " He also shared the special relationship with KAIST. His father-in-law Professor John Donaldson used to be a visiting professor of applied mathmatics at KAIST back in 2003.
President Shin added, “Collaboration across boundaries is most critical for responding to these issues. In that sense, this P4G Innovation Sprint is a shining example for demonstrating the collaborative efforts between teammates from diverse disciplines. When we work together and build convergent ideas, we will be more innovative and go further.”
<Winning team member Nicolai Thorball from DTU pitches at the final in the presence of the Crown Prince of Denmark and KAIST President Shin.>
“The canned packaging in the paint industry results in 40 times more carbon emission in the course of production. However, when using aluminum packaging which is recyclable, the waste amount will be cut dramatically,” pitched Nicolai Thorball from DTU on exchange at Seoul National University. Nicolai, whose major is environmental engineering, is one of two Danish students including Thomsen Xandra Flyvbjerg from the University of Southern Denmark. Flyvbjergy, majoring in business, is now on exchange at Sungkynkwan University.
“I am very glad to have the chance to understand the concept of the circular economy and green growth at the sprint. It was also very challenging to make ideation from so many ideas brainstormed,” said Dong-Eun Lee, a KAIST undergraduate from the Department of Biological Sciences. He said that he learned a lot from his two other teammates who are from the Program of Green Business & Policy at KAIST College of Business, Jae-Hee Park and Kyung-Hyun Kim. Juho Park majoring in mechanical engineering at KAIST was one of the team.
Circos’ solution for a sustainable model received acclaim from the jury members. DTU Senior Vice President Marianne Thellerson, one of jurors, claimed their model has very high market feasibility, saying, “Their idea could be commercialized right now into the market.” Professor Hee-Kyung Park from KAIST who helped participants’ ideation as one of four mentors said, “The winning team perfectly met all the components of the evaluation criteria, Solution, Acceleration, and Pitch.”
At this sprint, 10 students from Denmark and 29 KAIST students were divided into 6 teams and given the challenges of three companies. The Danish window facility company Velux presented its future glass window system and the paint company Hempel their circular economic new business model. SK challenged the students to help it become a global clean energy solution company. The event was based on a hacker blueprint that found the optimal solution to the topics proposed.
2019.05.23 View 10218 -
 Participation in the 2018 Bio-Digital City Workshop in Paris
(A student make a presentatiion during the Bio-Digital City Workshop in Paris last month.)
KAIST students explored ideas for developing future cities during the 2018 Bio-Digital City Workshop held in Paris last month.
This international workshop hosted by Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie was held under the theme “Biomimicry, Digital City and Big Data.” During the workshop from July 10 to July 20, students teamed up with French counterparts to develop innovative urban design ideas. Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie is the largest science museum in Europe and is operated by Universcience, a specialized institute of science and technology in France.
Professor Seongju Chang from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Professor Jihyun Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology Students led the students group.
Participants presented their ideas and findings on new urban solutions that combine biomimetic systems and digital technology. Each student group analyzed a special natural ecosystem such as sand dunes, jellyfish communities, or mangrove forests and conducted research to extract algorithms for constructing sustainable urban building complexes based on the results. The extracted algorithm was used to conceive a sustainable building complex forming a part of the urban environment by applying it to the actual Parisian city segment given as the virtual site for the workshop.
Students from diverse background in both countries participated in this convergence workshop. KAIST students included Ph.D. candidate Hyung Min Cho, undergraduates Min-Woo Jeong, Seung-Hwan Cha, and Sang-Jun Park from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, undergraduate Kyeong-Keun Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, JiWhan Jeong (Master’s course) from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Ph.D. candidate Bo-Yoon Zang from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. They teamed up with French students from diverse backgrounds, including Design/Science, Visual Design, Geography, Computer Science and Humanities and Social Science.
This workshop will serve as another opportunity to expand academic and human exchange efforts in the domain of smart and sustainable cities with Europe in the future as the first international cooperation activity of KAIST and the Paris La Villette Science Museum.
Professor Seong-Ju Chang who led the research group said, "We will continue to establish a cooperative relationship between KAIST and the European scientific community. This workshop is a good opportunity to demonstrate the competence of KAIST students and their scientific and technological excellence on the international stage.”
2018.08.01 View 12529
Participation in the 2018 Bio-Digital City Workshop in Paris
(A student make a presentatiion during the Bio-Digital City Workshop in Paris last month.)
KAIST students explored ideas for developing future cities during the 2018 Bio-Digital City Workshop held in Paris last month.
This international workshop hosted by Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie was held under the theme “Biomimicry, Digital City and Big Data.” During the workshop from July 10 to July 20, students teamed up with French counterparts to develop innovative urban design ideas. Cité des Sciences et de l'Industrie is the largest science museum in Europe and is operated by Universcience, a specialized institute of science and technology in France.
Professor Seongju Chang from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and Professor Jihyun Lee of the Graduate School of Culture Technology Students led the students group.
Participants presented their ideas and findings on new urban solutions that combine biomimetic systems and digital technology. Each student group analyzed a special natural ecosystem such as sand dunes, jellyfish communities, or mangrove forests and conducted research to extract algorithms for constructing sustainable urban building complexes based on the results. The extracted algorithm was used to conceive a sustainable building complex forming a part of the urban environment by applying it to the actual Parisian city segment given as the virtual site for the workshop.
Students from diverse background in both countries participated in this convergence workshop. KAIST students included Ph.D. candidate Hyung Min Cho, undergraduates Min-Woo Jeong, Seung-Hwan Cha, and Sang-Jun Park from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, undergraduate Kyeong-Keun Seo from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, JiWhan Jeong (Master’s course) from the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, Ph.D. candidate Bo-Yoon Zang from the Graduate School of Culture Technology. They teamed up with French students from diverse backgrounds, including Design/Science, Visual Design, Geography, Computer Science and Humanities and Social Science.
This workshop will serve as another opportunity to expand academic and human exchange efforts in the domain of smart and sustainable cities with Europe in the future as the first international cooperation activity of KAIST and the Paris La Villette Science Museum.
Professor Seong-Ju Chang who led the research group said, "We will continue to establish a cooperative relationship between KAIST and the European scientific community. This workshop is a good opportunity to demonstrate the competence of KAIST students and their scientific and technological excellence on the international stage.”
2018.08.01 View 12529 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Receives 2018 George Washington Carver Award
(Distinguished Professor Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will become the 11th recipient of the George Washington Carver Award. The award ceremony will be held during the 2018 Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO) World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology from July 16 through 19 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia.
The annual Carver award recognizes an individual who has made a significant contribution to building the bio-based economy by applying industrial biotechnology to create environmentally sustainable products. It serves as a lasting memorial to the original vision of George Washington Carver who, over a century ago, pioneered bio-based products, materials, and energy derived from renewable agricultural feedstock. Previous recipients include the founder and CEO of POET Jeff Broin, the CEO of DuPont Ellen Kullman, and Professor Gregory Stephanopoulos at MIT.
Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of systems metabolic engineering, leveraging technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environment-friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass. He also serves as the dean of the multi-and interdisciplinary research center hub, KAIST Institute.Through his work, Professor Lee has garnered countless achievements, including being one of only 13 people in the world elected as a foreign member of both the National Academy of Sciences USA and the National Academy of Engineering USA.
He has actively promoted the importance of industrial biotechnology through engagement with the public, policymakers, and decision makers around the world. He currently serves as the co-chairman of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology for the World Economic Forum and served as the Chairman of the Emerging Technologies Council and Biotechnology Council for the World Economic Forum.
Upon the award announcement, Dr. Brent Erickson, executive vice president of BIO’s Industrial & Environmental Section lauded Professor Lee’s achievement, saying “Dr. Lee has advanced the bio-based economy by developing innovative products and processes that are sustainable and environmentally friendly. In doing so, he has become a leader in advocating on the importance of industrial biotechnology. His contributions to the advancement of the industry are a continuation of the legacy left behind by George Washington Carver.”
Professor Lee thanked his research team who has worked together for the past few decades, adding, “Industrial biotechnology is becoming increasingly important to help achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. We should continue to work together to advance the field and establish a solid foundation for the sustainable future.”
The George Washington Carver Award is sponsored by the Iowa Biotechnology Association. Joe Hrdlicka, executive director of the Iowa Biotechnology Association, said, “Dr. Sang Yup Lee’s significant contributions to the advancement of industrial biotechnology make him the perfect recipient for the George Washington Carver Award. Having published more than 575 peer-reviewed papers, contributed to 82 books, and holding 636 patents, the culmination of Dr. Lee’s work has led to the establishment of sustainable systems for bio-based production of chemicals, fuels, and materials, thus reducing environmental impact and improving quality of life for all.”
2018.07.12 View 13659
Distinguished Professor Lee Receives 2018 George Washington Carver Award
(Distinguished Professor Lee)
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering will become the 11th recipient of the George Washington Carver Award. The award ceremony will be held during the 2018 Biotechnology Innovation Organization (BIO) World Congress on Industrial Biotechnology from July 16 through 19 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia.
The annual Carver award recognizes an individual who has made a significant contribution to building the bio-based economy by applying industrial biotechnology to create environmentally sustainable products. It serves as a lasting memorial to the original vision of George Washington Carver who, over a century ago, pioneered bio-based products, materials, and energy derived from renewable agricultural feedstock. Previous recipients include the founder and CEO of POET Jeff Broin, the CEO of DuPont Ellen Kullman, and Professor Gregory Stephanopoulos at MIT.
Professor Lee is a pioneering scholar of systems metabolic engineering, leveraging technology to develop microbial bioprocesses for the sustainable and environment-friendly production of chemicals, fuels, and materials from non-food renewable biomass. He also serves as the dean of the multi-and interdisciplinary research center hub, KAIST Institute.Through his work, Professor Lee has garnered countless achievements, including being one of only 13 people in the world elected as a foreign member of both the National Academy of Sciences USA and the National Academy of Engineering USA.
He has actively promoted the importance of industrial biotechnology through engagement with the public, policymakers, and decision makers around the world. He currently serves as the co-chairman of the Global Future Council on Biotechnology for the World Economic Forum and served as the Chairman of the Emerging Technologies Council and Biotechnology Council for the World Economic Forum.
Upon the award announcement, Dr. Brent Erickson, executive vice president of BIO’s Industrial & Environmental Section lauded Professor Lee’s achievement, saying “Dr. Lee has advanced the bio-based economy by developing innovative products and processes that are sustainable and environmentally friendly. In doing so, he has become a leader in advocating on the importance of industrial biotechnology. His contributions to the advancement of the industry are a continuation of the legacy left behind by George Washington Carver.”
Professor Lee thanked his research team who has worked together for the past few decades, adding, “Industrial biotechnology is becoming increasingly important to help achieve the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals. We should continue to work together to advance the field and establish a solid foundation for the sustainable future.”
The George Washington Carver Award is sponsored by the Iowa Biotechnology Association. Joe Hrdlicka, executive director of the Iowa Biotechnology Association, said, “Dr. Sang Yup Lee’s significant contributions to the advancement of industrial biotechnology make him the perfect recipient for the George Washington Carver Award. Having published more than 575 peer-reviewed papers, contributed to 82 books, and holding 636 patents, the culmination of Dr. Lee’s work has led to the establishment of sustainable systems for bio-based production of chemicals, fuels, and materials, thus reducing environmental impact and improving quality of life for all.”
2018.07.12 View 13659 -
 KAIST Team Reaching Out with Appropriate Technology
(The gold prize winning team of KATT)
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of international students at KAIST won the gold and silver prizes at ‘The 10th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90 Percent.’
More than 218 students from 50 teams nationwide participated in the competition hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT last month.
The competition was created to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance the quality of life for those with no or few accessible technologies.
A team led by Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, graduate student from the School of Electrical Engineering received the gold prize for presenting a prosthetic arm. Their artificial arm was highly recognized for its affordability and good manageability. The team said that it cost less than 10 US dollars to construct from materials available in underprivileged regions and was easy to assemble.
Sophomore Hutomo Calvin from the Department of Materials Science & Engineering also worked on the prosthetic arm project with freshmen Bella Godiva, Stephanie Tan, and Koptieuov Yearbola.
Alexandra Tran, senior from the School of Electrical Engineering led the silver prize winning team. Her team developed a portable weather monitor, ‘Breathe Easy’. She worked with Alisher Tortay, senior from the School of Computing, Ashar Alam, senior from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bereket Eshete, junior from the School of Computing, and Marthens Hakzimana, sophomore from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
This weather monitor is a low-cost but efficient air quality monitor. The team said it just cost less than seven US dollars to construct the monitor.KAIST students have now won the gold prize for two consecutive years.
2018.06.19 View 13176
KAIST Team Reaching Out with Appropriate Technology
(The gold prize winning team of KATT)
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of international students at KAIST won the gold and silver prizes at ‘The 10th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90 Percent.’
More than 218 students from 50 teams nationwide participated in the competition hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT last month.
The competition was created to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance the quality of life for those with no or few accessible technologies.
A team led by Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, graduate student from the School of Electrical Engineering received the gold prize for presenting a prosthetic arm. Their artificial arm was highly recognized for its affordability and good manageability. The team said that it cost less than 10 US dollars to construct from materials available in underprivileged regions and was easy to assemble.
Sophomore Hutomo Calvin from the Department of Materials Science & Engineering also worked on the prosthetic arm project with freshmen Bella Godiva, Stephanie Tan, and Koptieuov Yearbola.
Alexandra Tran, senior from the School of Electrical Engineering led the silver prize winning team. Her team developed a portable weather monitor, ‘Breathe Easy’. She worked with Alisher Tortay, senior from the School of Computing, Ashar Alam, senior from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bereket Eshete, junior from the School of Computing, and Marthens Hakzimana, sophomore from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
This weather monitor is a low-cost but efficient air quality monitor. The team said it just cost less than seven US dollars to construct the monitor.KAIST students have now won the gold prize for two consecutive years.
2018.06.19 View 13176 -
 ISCN and GULF Share Best Practices Report
The International Sustainable Campus Network (ISCN) and the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) co-hosted a conference at the 2016 World Economic Forum held on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos, Switzerland, to present exemplary campus sustainability case studies provided by the world’s leading universities.
A total of 20 universities, including KAIST, Harvard University, University of Oxford, Yale University, the National University of Singapore, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (Zurich), reported on their endeavors to demonstrate sustainable development in higher education in three different panels at the conference: Developing Skills and Building Capacities, Collaborating to Catalyze Change, and Innovating for Efficient Built Environments.
President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST gave a presentation on the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center as a sustainable development model for KAIST.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, the world’s leading fossil-fuel provider, joined forces in 2013 to establish a joint research center on the reduction and management of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, a major driver of climate change.
The research center, located at the KAIST campus in Daejeon, South Korea, is currently sponsoring ten research projects involving more than 20 doctoral-level researchers and over 100 students.
The goal of the center is to develop materials for more energy-efficient CO2 capture, catalysts and processes for converting CO2 into valuable products, novel storage methods, and system-level analyses of major CO2 emitting industries to suggest industry-specific CO2 reduction strategies including energy efficiency improvement.
The center’s work also includes analyzing the impact of potential government or industry-wide policies in the face of uncertainties, some of which are technological and economic as well as political. Besides its research activities, the center has also sponsored seminars and workshops throughout the year to raise awareness of the importance of CO2 management in building a sustainable future.
President Kang said that, from the beginning, the center has prompted researchers and students with different academic backgrounds and skill sets to work together to find integrative and systematic solutions to address real problems of critical importance to the world’s sustainability.
ISCN is a global non-profit association of leading colleges and universities representing over 20 countries, working together to holistically integrate sustainability into campus operations, research, and teaching. As of now, more 75 universities worldwide are the members of ISCN.
The GULF is composed of the presidents of the top 25 universities in the world. The World Economic Forum created it in 2006 to offer a non-competitive platform for high-level dialogue in academia. KAIST is the only Korean GULF member.
For the full report of the 2016 ISCN and GULF conference, go to http://www.international-sustainable-campus-network.org/downloads/general/441-2016-iscn-gulf-best-practice-report/file.
2016.01.25 View 11077
ISCN and GULF Share Best Practices Report
The International Sustainable Campus Network (ISCN) and the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) co-hosted a conference at the 2016 World Economic Forum held on January 20-23, 2016 in Davos, Switzerland, to present exemplary campus sustainability case studies provided by the world’s leading universities.
A total of 20 universities, including KAIST, Harvard University, University of Oxford, Yale University, the National University of Singapore, the Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, and the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (Zurich), reported on their endeavors to demonstrate sustainable development in higher education in three different panels at the conference: Developing Skills and Building Capacities, Collaborating to Catalyze Change, and Innovating for Efficient Built Environments.
President Sung-Mo Kang of KAIST gave a presentation on the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center as a sustainable development model for KAIST.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, the world’s leading fossil-fuel provider, joined forces in 2013 to establish a joint research center on the reduction and management of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, a major driver of climate change.
The research center, located at the KAIST campus in Daejeon, South Korea, is currently sponsoring ten research projects involving more than 20 doctoral-level researchers and over 100 students.
The goal of the center is to develop materials for more energy-efficient CO2 capture, catalysts and processes for converting CO2 into valuable products, novel storage methods, and system-level analyses of major CO2 emitting industries to suggest industry-specific CO2 reduction strategies including energy efficiency improvement.
The center’s work also includes analyzing the impact of potential government or industry-wide policies in the face of uncertainties, some of which are technological and economic as well as political. Besides its research activities, the center has also sponsored seminars and workshops throughout the year to raise awareness of the importance of CO2 management in building a sustainable future.
President Kang said that, from the beginning, the center has prompted researchers and students with different academic backgrounds and skill sets to work together to find integrative and systematic solutions to address real problems of critical importance to the world’s sustainability.
ISCN is a global non-profit association of leading colleges and universities representing over 20 countries, working together to holistically integrate sustainability into campus operations, research, and teaching. As of now, more 75 universities worldwide are the members of ISCN.
The GULF is composed of the presidents of the top 25 universities in the world. The World Economic Forum created it in 2006 to offer a non-competitive platform for high-level dialogue in academia. KAIST is the only Korean GULF member.
For the full report of the 2016 ISCN and GULF conference, go to http://www.international-sustainable-campus-network.org/downloads/general/441-2016-iscn-gulf-best-practice-report/file.
2016.01.25 View 11077 -
 Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 13624
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee Participates in the 2014 Summer Davos Forum
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, was invited to lead four sessions at the Annual Meeting 2014, the World Economic Forum, also known as the Summer Davos Forum, which was held in Tianjin, China, from September 10th to 12th.
Two of the four sessions Professor Lee participated in were held on September 10th. At the first session entitled “Biotechnology Ecosystem,” he examined with other panelists the future of bioengineering in depth and discussed major policies and industry trends that will be necessary for the development of future biotechnologies.
Professor Lee later attended the “Strategic Shifts in Healthcare” session as a moderator. Issues related to transforming the health industry such as the next-generation genomics, mobile health and telemedicine, and wearable devices and predictive analytics were addressed.
On September 12, Professor Lee joined the “IdeasLab with KAIST” and gave a presentation on nanotechnology. There was a total of ten IdeasLab sessions held at the Summer Davos Forum, and KAIST was the only Korean university ever invited to host this session. In addition to Professor Lee’s presentation, three more presentations were made by KAIST professors on such topics as “Sustainable Energy and Materials” and “Next-generation Semiconductors.”
Lastly, Professor Lee participated in the “Global Promising Technology” session with the World Economic Forum’s Global Agenda Council members. At this session, he explained the selection of the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” and “Bio Sector’s Top 10 Technologies” and led discussions about the “2015 Top 10 Technologies” with the council members.
The Davos Forum has been announcing the “World’s Top 10 Most Promising Technologies” since 2012, and Professor Lee has played a key role in the selection while working as the Chairman of Global Agenda Council. The selection results are presented at the Davos Forum every year and have attracted a lot of attention from around the world.
2014.09.15 View 13624 -
 Top Ten Ways Biotechnology Could Improve Our Everyday Life
The Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology, one of the global networks under the World Economic Forum, which is composed of the world’s leading experts in the field of biotechnology, announced on February 25, 2013 that the council has indentified “ten most important biotechnologies” that could help meet rapidly growing demand for energy, food, nutrition, and health. These new technologies, the council said, also have the potential to increase productivity and create new jobs.
“The technologies selected by the members of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology represent almost all types of biotechnology.Utilization of waste, personalized medicine,and ocean agricultureare examples of the challenges where biotechnology can offer solutions,”said Sang Yup Lee, Chair of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). He also added that “the members of the council concluded that regulatory certainty, public perception, and investment are the key enablers for the growth of biotechnology.”
These ideas will be further explored during “Biotechnology Week” at the World Economic Forum’s Blog (http://wef.ch/blog) from Monday, 25 February, 2013. The full list follows below:
Bio-based sustainable production of chemicals, energy, fuels and materials
Through the last century, human activity has depleted approximately half of the world’s reserves of fossil hydrocarbons. These reserves, which took over 600 million years to accumulate, are non-renewable and their extraction, refining and use contribute significantly to human emissions of greenhouse gases and the warming of our planet. In order to sustain human development going forward, a carbon-neutral alternative must be implemented. The key promising technology is biological synthesis; that is, bio-based production of chemicals, fuels and materials from plants that can be re-grown.
Engineering sustainable food production
The continuing increase in our numbers and affluence are posing growing challenges to the ability of humanity to produce adequate food (as well as feed, and now fuel). Although controversial, modern genetic modification of crops has supported growth in agricultural productivity. In 2011, 16.7 million farmers grew biotechnology-developed crops on almost 400 million acres in 29 countries, 19 of which were developing countries. Properly managed, such crops have the potential to lower both pesticide use and tilling which erodes soil.
Sea-water based bio-processes
Over 70% of the earth surface is covered by seawater, and it is the most abundant water source available on the planet. But we are yet to discover the full potential of it. For example with halliophic bacteria capable of growing in the seawater can be engineered to grow faster and produce useful products including chemicals, fuels and polymeric materials. Ocean agriculture is also a promising technology. It is based on the photosynthetic biomass from the oceans, like macroalgae and microalgae.
Non-resource draining zero waste bio-processing
The sustainable goal of zero waste may become a reality with biotechnology. Waste streams can be processed at bio-refineries and turned into valuable chemicals and fuels, thereby closing the loop of production with no net waste. Advances in biotechnology are now allowing lower cost, less draining inputs to be used, including methane, and waste heat. These advances are simplifying waste streams with the potential to reduce toxicity as well as support their use in other processes, moving society progressively closer to the sustainable goal of zero waste.
Using carbon dioxide as a raw material
Biotechnology is poised to contribute solutions to mitigate the growing threat of rising CO2 levels. Recent advances are rapidly increasing our understanding of how living organisms consume and use CO2. By harnessing the power of these natural biological systems, scientists are engineering a new wave of approaches to convert waste CO2 and C1 molecules into energy, fuels, chemicals, and new materials.
Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine has become increasingly important due to both increased longevity and treatment of injury. Tissue engineering based on various bio-materials has been developed to speed up the regenerative medicine. Recently, stem cells, especially the induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), have provided another great opportunity for regenerative medicine. Combination of tissue engineering and stem cell (including iPS) technologies will allow replacements of damaged or old human organs with functional ones in the near future.
Rapid and precise development and manufacturing of medicine and vaccines
A global pandemic remains one of the most real and serious threats to humanity. Biotechnology has the potential to rapidly identify biological threats, develop and manufacture potential cures. Leading edge biotechnology is now offering the potential to rapidly produce therapeutics and vaccines against virtually any target. These technologies, including messenger therapeutics, targeted immunotherapies, conjugated nanoparticles, and structure-based engineering, have already produced candidates with substantial potential to improve human health globally.
Accurate, fast, cheap, and personalized diagnostics and prognostics
Identification of better targets and combining nanotechnology and information technology it will be possible to develop rapid, accurate, personalized and inexpensive diagnostics and prognostics systems.
Bio-tech improvements to soil and water
Arable land and fresh water are two of the most important, yet limited, resources on earth. Abuse and mis-appropriation have threatened these resources, as the demand on them has increased. Advances in biotechnology have already yielded technologies that can restore the vitality and viability of these resources. A new generation of technologies: bio-remediation, bio-regeneration and bio-augmentation are being developed, offering the potential to not only further restore these resources, but also augment their potential.
Advanced healthcare through genome sequencing
It took more than 13 years and $1.5 billion to sequence the first human genome and today we can sequence a complete human genome in a single day for less than $1,000. When we analyze the roughly 3 billion base pairs in such a sequence we find that we differ from each other in several million of these base pairs. In the vast majority of cases these difference do not cause any issues but in rare cases they cause disease, or susceptibility to disease. Medical research and practice will increasingly be driven by our understanding of such genetic variations together with their phenotypic consequences.
2013.03.19 View 13379
Top Ten Ways Biotechnology Could Improve Our Everyday Life
The Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology, one of the global networks under the World Economic Forum, which is composed of the world’s leading experts in the field of biotechnology, announced on February 25, 2013 that the council has indentified “ten most important biotechnologies” that could help meet rapidly growing demand for energy, food, nutrition, and health. These new technologies, the council said, also have the potential to increase productivity and create new jobs.
“The technologies selected by the members of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology represent almost all types of biotechnology.Utilization of waste, personalized medicine,and ocean agricultureare examples of the challenges where biotechnology can offer solutions,”said Sang Yup Lee, Chair of the Global Agenda Council on Biotechnology and Distinguished Professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). He also added that “the members of the council concluded that regulatory certainty, public perception, and investment are the key enablers for the growth of biotechnology.”
These ideas will be further explored during “Biotechnology Week” at the World Economic Forum’s Blog (http://wef.ch/blog) from Monday, 25 February, 2013. The full list follows below:
Bio-based sustainable production of chemicals, energy, fuels and materials
Through the last century, human activity has depleted approximately half of the world’s reserves of fossil hydrocarbons. These reserves, which took over 600 million years to accumulate, are non-renewable and their extraction, refining and use contribute significantly to human emissions of greenhouse gases and the warming of our planet. In order to sustain human development going forward, a carbon-neutral alternative must be implemented. The key promising technology is biological synthesis; that is, bio-based production of chemicals, fuels and materials from plants that can be re-grown.
Engineering sustainable food production
The continuing increase in our numbers and affluence are posing growing challenges to the ability of humanity to produce adequate food (as well as feed, and now fuel). Although controversial, modern genetic modification of crops has supported growth in agricultural productivity. In 2011, 16.7 million farmers grew biotechnology-developed crops on almost 400 million acres in 29 countries, 19 of which were developing countries. Properly managed, such crops have the potential to lower both pesticide use and tilling which erodes soil.
Sea-water based bio-processes
Over 70% of the earth surface is covered by seawater, and it is the most abundant water source available on the planet. But we are yet to discover the full potential of it. For example with halliophic bacteria capable of growing in the seawater can be engineered to grow faster and produce useful products including chemicals, fuels and polymeric materials. Ocean agriculture is also a promising technology. It is based on the photosynthetic biomass from the oceans, like macroalgae and microalgae.
Non-resource draining zero waste bio-processing
The sustainable goal of zero waste may become a reality with biotechnology. Waste streams can be processed at bio-refineries and turned into valuable chemicals and fuels, thereby closing the loop of production with no net waste. Advances in biotechnology are now allowing lower cost, less draining inputs to be used, including methane, and waste heat. These advances are simplifying waste streams with the potential to reduce toxicity as well as support their use in other processes, moving society progressively closer to the sustainable goal of zero waste.
Using carbon dioxide as a raw material
Biotechnology is poised to contribute solutions to mitigate the growing threat of rising CO2 levels. Recent advances are rapidly increasing our understanding of how living organisms consume and use CO2. By harnessing the power of these natural biological systems, scientists are engineering a new wave of approaches to convert waste CO2 and C1 molecules into energy, fuels, chemicals, and new materials.
Regenerative medicine
Regenerative medicine has become increasingly important due to both increased longevity and treatment of injury. Tissue engineering based on various bio-materials has been developed to speed up the regenerative medicine. Recently, stem cells, especially the induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS), have provided another great opportunity for regenerative medicine. Combination of tissue engineering and stem cell (including iPS) technologies will allow replacements of damaged or old human organs with functional ones in the near future.
Rapid and precise development and manufacturing of medicine and vaccines
A global pandemic remains one of the most real and serious threats to humanity. Biotechnology has the potential to rapidly identify biological threats, develop and manufacture potential cures. Leading edge biotechnology is now offering the potential to rapidly produce therapeutics and vaccines against virtually any target. These technologies, including messenger therapeutics, targeted immunotherapies, conjugated nanoparticles, and structure-based engineering, have already produced candidates with substantial potential to improve human health globally.
Accurate, fast, cheap, and personalized diagnostics and prognostics
Identification of better targets and combining nanotechnology and information technology it will be possible to develop rapid, accurate, personalized and inexpensive diagnostics and prognostics systems.
Bio-tech improvements to soil and water
Arable land and fresh water are two of the most important, yet limited, resources on earth. Abuse and mis-appropriation have threatened these resources, as the demand on them has increased. Advances in biotechnology have already yielded technologies that can restore the vitality and viability of these resources. A new generation of technologies: bio-remediation, bio-regeneration and bio-augmentation are being developed, offering the potential to not only further restore these resources, but also augment their potential.
Advanced healthcare through genome sequencing
It took more than 13 years and $1.5 billion to sequence the first human genome and today we can sequence a complete human genome in a single day for less than $1,000. When we analyze the roughly 3 billion base pairs in such a sequence we find that we differ from each other in several million of these base pairs. In the vast majority of cases these difference do not cause any issues but in rare cases they cause disease, or susceptibility to disease. Medical research and practice will increasingly be driven by our understanding of such genetic variations together with their phenotypic consequences.
2013.03.19 View 13379 -
 Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 15417
Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 15417 -
 Prof. Woo's Team Discovers Eco-Friendly Solid-Oxide Fuel Cell System
A KAIST research team led by Prof. Seong-Ihl Woo of the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering has found a method to use glycerol, a byproduct from the production of biodiesel, as fuel for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC), university authorities said on Tuesday (Oct. 27).
The research finding shows that glycerol can be an environmentally sustainable fuel when it is used for operating SOFCs with internal reforming, instead of hydrogen and methane. The finding was published in the Oct. 14, 2009 online edition of ChemSusChem, a sister journal of Angewandte Chemie, the world"s leading chemistry journal.
Biodiesel is an attractive alternative energy source because of its low sulfur content and demand is growing worldwide as oil price soars. Bio-derived glycerol will not contribute to the greenhouse effect and has the potential to contribute to reducing global warming.
Currently, glycereol is used as a raw material in the cosmetic, pharmacy, food, and tobacco industries. However, its supply exceeds its demand as the volume of biodiesel production increases. The production of 1 ton of biodiesel produces 0.1 ton of glycerol. Many researchers have investigated various routes for the consumption of surplus glycerol.
The research is expected to contribute to sustainable growth by reducing the emissions of carbon dioxide and reusing generated carbon dioxide for the production of biomass. The new method enables manufacturers to use glycerol as a fuel for operating SOFC.
2009.10.28 View 15175
Prof. Woo's Team Discovers Eco-Friendly Solid-Oxide Fuel Cell System
A KAIST research team led by Prof. Seong-Ihl Woo of the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering has found a method to use glycerol, a byproduct from the production of biodiesel, as fuel for solid oxide fuel cells (SOFC), university authorities said on Tuesday (Oct. 27).
The research finding shows that glycerol can be an environmentally sustainable fuel when it is used for operating SOFCs with internal reforming, instead of hydrogen and methane. The finding was published in the Oct. 14, 2009 online edition of ChemSusChem, a sister journal of Angewandte Chemie, the world"s leading chemistry journal.
Biodiesel is an attractive alternative energy source because of its low sulfur content and demand is growing worldwide as oil price soars. Bio-derived glycerol will not contribute to the greenhouse effect and has the potential to contribute to reducing global warming.
Currently, glycereol is used as a raw material in the cosmetic, pharmacy, food, and tobacco industries. However, its supply exceeds its demand as the volume of biodiesel production increases. The production of 1 ton of biodiesel produces 0.1 ton of glycerol. Many researchers have investigated various routes for the consumption of surplus glycerol.
The research is expected to contribute to sustainable growth by reducing the emissions of carbon dioxide and reusing generated carbon dioxide for the production of biomass. The new method enables manufacturers to use glycerol as a fuel for operating SOFC.
2009.10.28 View 15175