battery
-
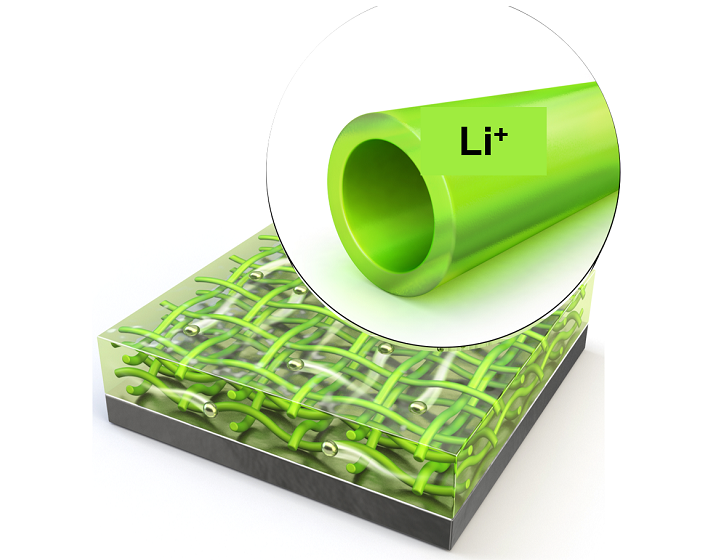 KAIST Extends Lithium Metal Battery Lifespan by 750% Using Water
Lithium metal, a next-generation anode material, has been highlighted for overcoming the performance limitations of commercial batteries. However, issues inherent to lithium metal have caused shortened battery lifespans and increased fire risks. KAIST researchers have achieved a world-class breakthrough by extending the lifespan of lithium metal anodes by approximately 750% only using water.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2nd of December that Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Jiyoung Lee from Ajou University, successfully stabilized lithium growth and significantly enhanced the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries using eco-friendly hollow nanofibers as protective layers.
Conventional protective layer technologies, which involve applying a surface coating onto lithium metal in order to create an artificial interface with the electrolyte, have relied on toxic processes and expensive materials, with limited improvements in the lifespan of lithium metal anodes.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the newly developed protective membrane by eco-friendly electrospinning process using water >
To address these limitations, Professor Kim’s team proposed a hollow nanofiber protective layer capable of controlling lithium-ion growth through both physical and chemical means. This protective layer was manufactured through an environmentally friendly electrospinning process* using guar gum** extracted from plants as the primary material and utilizing water as the sole solvent.
*Electrospinning process: A method where polymer solutions are subjected to an electric field, producing continuous fibers with diameters ranging from tens of nanometers to several micrometers.
**Guar gum: A natural polymer extracted from guar beans, composed mainly of monosaccharides. Its oxidized functional groups regulate interactions with lithium ions.
< Figure 2. Physical and chemical control of Lithium dendrite by the newly developed protective membrane >
The nanofiber protective layer effectively controlled reversible chemical reactions between the electrolyte and lithium ions. The hollow spaces within the fibers suppressed the random accumulation of lithium ions on the metal surface, stabilizing the interface between the lithium metal surface and the electrolyte.
< Figure 3. Performance of Lithium metal battery full cells with the newly developed protective membrane >
As a result, the lithium metal anodes with this protective layer demonstrated approximately a 750% increase in lifespan compared to conventional lithium metal anodes. The battery retained 93.3% of its capacity even after 300 charge-discharge cycles, achieving world-class performance.
The researchers also verified that this natural protective layer decomposes entirely within about a month in soil, proving its eco-friendly nature throughout the manufacturing and disposal process.
< Figure 4. Excellent decomposition rate of the newly developed protective membrane >
Professor Il-Doo Kim explained, “By leveraging both physical and chemical protective functions, we were able to guide reversible reactions between lithium metal and the electrolyte more effectively and suppress dendrite growth, resulting in lithium metal anodes with unprecedented lifespan characteristics.”
He added, “As the environmental burden caused by battery production and disposal becomes a pressing issue due to surging battery demand, this water-based manufacturing method with biodegradable properties will significantly contribute to the commercialization of next-generation eco-friendly batteries.”
This study was led by Dr. Jiyoung Lee (now a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Ajou University) and Dr. Hyunsub Song (currently at Samsung Electronics), both graduates of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering. The findings were published as a front cover article in Advanced Materials, Volume 36, Issue 47, on November 21.
(Paper title: “Overcoming Chemical and Mechanical Instabilities in Lithium Metal Anodes with Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Artificial SEI Layer”)
The research was supported by the KAIST-LG Energy Solution Frontier Research Lab (FRL), the Alchemist Project funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Top-Tier Research Support Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.12.12 View 6606
KAIST Extends Lithium Metal Battery Lifespan by 750% Using Water
Lithium metal, a next-generation anode material, has been highlighted for overcoming the performance limitations of commercial batteries. However, issues inherent to lithium metal have caused shortened battery lifespans and increased fire risks. KAIST researchers have achieved a world-class breakthrough by extending the lifespan of lithium metal anodes by approximately 750% only using water.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2nd of December that Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Jiyoung Lee from Ajou University, successfully stabilized lithium growth and significantly enhanced the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries using eco-friendly hollow nanofibers as protective layers.
Conventional protective layer technologies, which involve applying a surface coating onto lithium metal in order to create an artificial interface with the electrolyte, have relied on toxic processes and expensive materials, with limited improvements in the lifespan of lithium metal anodes.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the newly developed protective membrane by eco-friendly electrospinning process using water >
To address these limitations, Professor Kim’s team proposed a hollow nanofiber protective layer capable of controlling lithium-ion growth through both physical and chemical means. This protective layer was manufactured through an environmentally friendly electrospinning process* using guar gum** extracted from plants as the primary material and utilizing water as the sole solvent.
*Electrospinning process: A method where polymer solutions are subjected to an electric field, producing continuous fibers with diameters ranging from tens of nanometers to several micrometers.
**Guar gum: A natural polymer extracted from guar beans, composed mainly of monosaccharides. Its oxidized functional groups regulate interactions with lithium ions.
< Figure 2. Physical and chemical control of Lithium dendrite by the newly developed protective membrane >
The nanofiber protective layer effectively controlled reversible chemical reactions between the electrolyte and lithium ions. The hollow spaces within the fibers suppressed the random accumulation of lithium ions on the metal surface, stabilizing the interface between the lithium metal surface and the electrolyte.
< Figure 3. Performance of Lithium metal battery full cells with the newly developed protective membrane >
As a result, the lithium metal anodes with this protective layer demonstrated approximately a 750% increase in lifespan compared to conventional lithium metal anodes. The battery retained 93.3% of its capacity even after 300 charge-discharge cycles, achieving world-class performance.
The researchers also verified that this natural protective layer decomposes entirely within about a month in soil, proving its eco-friendly nature throughout the manufacturing and disposal process.
< Figure 4. Excellent decomposition rate of the newly developed protective membrane >
Professor Il-Doo Kim explained, “By leveraging both physical and chemical protective functions, we were able to guide reversible reactions between lithium metal and the electrolyte more effectively and suppress dendrite growth, resulting in lithium metal anodes with unprecedented lifespan characteristics.”
He added, “As the environmental burden caused by battery production and disposal becomes a pressing issue due to surging battery demand, this water-based manufacturing method with biodegradable properties will significantly contribute to the commercialization of next-generation eco-friendly batteries.”
This study was led by Dr. Jiyoung Lee (now a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Ajou University) and Dr. Hyunsub Song (currently at Samsung Electronics), both graduates of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering. The findings were published as a front cover article in Advanced Materials, Volume 36, Issue 47, on November 21.
(Paper title: “Overcoming Chemical and Mechanical Instabilities in Lithium Metal Anodes with Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Artificial SEI Layer”)
The research was supported by the KAIST-LG Energy Solution Frontier Research Lab (FRL), the Alchemist Project funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Top-Tier Research Support Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.12.12 View 6606 -
 KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5864
KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5864 -
 KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 5899
KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 5899 -
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6389
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6389 -
 KAIST Employs Image-recognition AI to Determine Battery Composition and Conditions
An international collaborative research team has developed an image recognition technology that can accurately determine the elemental composition and the number of charge and discharge cycles of a battery by examining only its surface morphology using AI learning.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on July 2nd that Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and Drexel University in the United States, has developed a method to predict the major elemental composition and charge-discharge state of NCM cathode materials with 99.6% accuracy using convolutional neural networks (CNN)*.
*Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): A type of multi-layer, feed-forward, artificial neural network used for analyzing visual images.
The research team noted that while scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used in semiconductor manufacturing to inspect wafer defects, it is rarely used in battery inspections. SEM is used for batteries to analyze the size of particles only at research sites, and reliability is predicted from the broken particles and the shape of the breakage in the case of deteriorated battery materials.
The research team decided that it would be groundbreaking if an automated SEM can be used in the process of battery production, just like in the semiconductor manufacturing, to inspect the surface of the cathode material to determine whether it was synthesized according to the desired composition and that the lifespan would be reliable, thereby reducing the defect rate.
< Figure 1. Example images of true cases and their grad-CAM overlays from the best trained network. >
The researchers trained a CNN-based AI applicable to autonomous vehicles to learn the surface images of battery materials, enabling it to predict the major elemental composition and charge-discharge cycle states of the cathode materials. They found that while the method could accurately predict the composition of materials with additives, it had lower accuracy for predicting charge-discharge states. The team plans to further train the AI with various battery material morphologies produced through different processes and ultimately use it for inspecting the compositional uniformity and predicting the lifespan of next-generation batteries.
Professor Joshua C. Agar, one of the collaborating researchers of the project from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics of Drexel University, said, "In the future, artificial intelligence is expected to be applied not only to battery materials but also to various dynamic processes in functional materials synthesis, clean energy generation in fusion, and understanding foundations of particles and the universe."
Professor Seungbum Hong from KAIST, who led the research, stated, "This research is significant as it is the first in the world to develop an AI-based methodology that can quickly and accurately predict the major elemental composition and the state of the battery from the structural data of micron-scale SEM images. The methodology developed in this study for identifying the composition and state of battery materials based on microscopic images is expected to play a crucial role in improving the performance and quality of battery materials in the future."
< Figure 2. Accuracies of CNN Model predictions on SEM images of NCM cathode materials with additives under various conditions. >
This research was conducted by KAIST’s Materials Science and Engineering Department graduates Dr. Jimin Oh and Dr. Jiwon Yeom, the co-first authors, in collaboration with Professor Josh Agar and Dr. Kwang Man Kim from ETRI. It was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the KAIST Global Singularity project, and international collaboration with the US research team. The results were published in the international journal npj Computational Materials on May 4. (Paper Title: “Composition and state prediction of lithium-ion cathode via convolutional neural network trained on scanning electron microscopy images”)
2024.07.02 View 6841
KAIST Employs Image-recognition AI to Determine Battery Composition and Conditions
An international collaborative research team has developed an image recognition technology that can accurately determine the elemental composition and the number of charge and discharge cycles of a battery by examining only its surface morphology using AI learning.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on July 2nd that Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and Drexel University in the United States, has developed a method to predict the major elemental composition and charge-discharge state of NCM cathode materials with 99.6% accuracy using convolutional neural networks (CNN)*.
*Convolutional Neural Network (CNN): A type of multi-layer, feed-forward, artificial neural network used for analyzing visual images.
The research team noted that while scanning electron microscopy (SEM) is used in semiconductor manufacturing to inspect wafer defects, it is rarely used in battery inspections. SEM is used for batteries to analyze the size of particles only at research sites, and reliability is predicted from the broken particles and the shape of the breakage in the case of deteriorated battery materials.
The research team decided that it would be groundbreaking if an automated SEM can be used in the process of battery production, just like in the semiconductor manufacturing, to inspect the surface of the cathode material to determine whether it was synthesized according to the desired composition and that the lifespan would be reliable, thereby reducing the defect rate.
< Figure 1. Example images of true cases and their grad-CAM overlays from the best trained network. >
The researchers trained a CNN-based AI applicable to autonomous vehicles to learn the surface images of battery materials, enabling it to predict the major elemental composition and charge-discharge cycle states of the cathode materials. They found that while the method could accurately predict the composition of materials with additives, it had lower accuracy for predicting charge-discharge states. The team plans to further train the AI with various battery material morphologies produced through different processes and ultimately use it for inspecting the compositional uniformity and predicting the lifespan of next-generation batteries.
Professor Joshua C. Agar, one of the collaborating researchers of the project from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Mechanics of Drexel University, said, "In the future, artificial intelligence is expected to be applied not only to battery materials but also to various dynamic processes in functional materials synthesis, clean energy generation in fusion, and understanding foundations of particles and the universe."
Professor Seungbum Hong from KAIST, who led the research, stated, "This research is significant as it is the first in the world to develop an AI-based methodology that can quickly and accurately predict the major elemental composition and the state of the battery from the structural data of micron-scale SEM images. The methodology developed in this study for identifying the composition and state of battery materials based on microscopic images is expected to play a crucial role in improving the performance and quality of battery materials in the future."
< Figure 2. Accuracies of CNN Model predictions on SEM images of NCM cathode materials with additives under various conditions. >
This research was conducted by KAIST’s Materials Science and Engineering Department graduates Dr. Jimin Oh and Dr. Jiwon Yeom, the co-first authors, in collaboration with Professor Josh Agar and Dr. Kwang Man Kim from ETRI. It was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the KAIST Global Singularity project, and international collaboration with the US research team. The results were published in the international journal npj Computational Materials on May 4. (Paper Title: “Composition and state prediction of lithium-ion cathode via convolutional neural network trained on scanning electron microscopy images”)
2024.07.02 View 6841 -
 KAIST Develops Sodium Battery Capable of Rapid Charging in Just a Few Seconds
Sodium (Na), which is over 500 times more abundant than lithium (Li), has recently garnered significant attention for its potential in sodium-ion battery technologies. However, existing sodium-ion batteries face fundamental limitations, including lower power output, constrained storage properties, and longer charging times, necessitating the development of next-generation energy storage materials.
On the 11th of April, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery capable of rapid charging.
The innovative hybrid energy storage system integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors. This combination allows the device to achieve both high storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates, positioning it as a viable next-generation alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
However, the development of a hybrid battery with high energy and high power density requires an improvement to the slow energy storage rate of battery-type anodes as well as the enhancement of the relatively low capacity of supercapacitor-type cathode materials.
< Figure 1. Schematic synthetic procedures of high-capacity/high-rate anode and cathode materials for a sodium-ion hybrid energy storages (SIHES) and their proposed energy storage mechanisms. Synthetic procedures for (a) ultrafine iron sulfide-embedded S-doped carbon/graphene (FS/C/G) anode and (b) zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived porous carbon (ZDPC) cathode materials. (c) Proposed energy storage mechanisms of Na+ ions in FS/C/G anode and ClO-4 ions in ZDPC cathode for an SIHES. >
To account for this, Professor Kang's team utilized two distinct metal-organic frameworks for the optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries. This approach led to the development of an anode material with improved kinetics through the inclusion of fine active materials in porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. Additionally, a high-capacity cathode material was synthesized, and the combination of the cathode and anode materials allowed for the development of a sodium-ion storage system optimizing the balance and minimizing the disparities in energy storage rates between the electrodes.
The assembled full cell, comprising the newly developed anode and cathode, forms a high-performance hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device. This device surpasses the energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries and exhibits the characteristics of supercapacitors' power density. It is expected to be suitable for rapid charging applications ranging from electric vehicles to smart electronic devices and aerospace technologies.
< Figure 2. Electrochemical characterizations of FS/C/G-20//ZDPC SIHES full cells (left). Ragone plots for FS/C/G-20//ZDPC (this work) and other previously reported sodium-ion electrochemical energy storage devices (right). >
Professor Kang noted that the hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device, capable of rapid charging and achieving an energy density of 247 Wh/kg and a power density of 34,748 W/kg, represents a breakthrough in overcoming the current limitations of energy storage systems. He anticipates broader applications across various electronic devices, including electric vehicles.
This research, co-authored by KAIST doctoral candidates Jong Hui Choi and Dong Won Kim, was published in the international journal Energy Storage Materials on March 29 with the title "Low-crystallinity conductive multivalence iron sulfide-embedded S-doped anode and high-surface-area O-doped cathode of 3D porous N-rich graphitic carbon frameworks for high-performance sodium-ion hybrid energy storages."
The study was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project.
2024.04.18 View 18577
KAIST Develops Sodium Battery Capable of Rapid Charging in Just a Few Seconds
Sodium (Na), which is over 500 times more abundant than lithium (Li), has recently garnered significant attention for its potential in sodium-ion battery technologies. However, existing sodium-ion batteries face fundamental limitations, including lower power output, constrained storage properties, and longer charging times, necessitating the development of next-generation energy storage materials.
On the 11th of April, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a high-energy, high-power hybrid sodium-ion battery capable of rapid charging.
The innovative hybrid energy storage system integrates anode materials typically used in batteries with cathodes suitable for supercapacitors. This combination allows the device to achieve both high storage capacities and rapid charge-discharge rates, positioning it as a viable next-generation alternative to lithium-ion batteries.
However, the development of a hybrid battery with high energy and high power density requires an improvement to the slow energy storage rate of battery-type anodes as well as the enhancement of the relatively low capacity of supercapacitor-type cathode materials.
< Figure 1. Schematic synthetic procedures of high-capacity/high-rate anode and cathode materials for a sodium-ion hybrid energy storages (SIHES) and their proposed energy storage mechanisms. Synthetic procedures for (a) ultrafine iron sulfide-embedded S-doped carbon/graphene (FS/C/G) anode and (b) zeolitic imidazolate framework-derived porous carbon (ZDPC) cathode materials. (c) Proposed energy storage mechanisms of Na+ ions in FS/C/G anode and ClO-4 ions in ZDPC cathode for an SIHES. >
To account for this, Professor Kang's team utilized two distinct metal-organic frameworks for the optimized synthesis of hybrid batteries. This approach led to the development of an anode material with improved kinetics through the inclusion of fine active materials in porous carbon derived from metal-organic frameworks. Additionally, a high-capacity cathode material was synthesized, and the combination of the cathode and anode materials allowed for the development of a sodium-ion storage system optimizing the balance and minimizing the disparities in energy storage rates between the electrodes.
The assembled full cell, comprising the newly developed anode and cathode, forms a high-performance hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device. This device surpasses the energy density of commercial lithium-ion batteries and exhibits the characteristics of supercapacitors' power density. It is expected to be suitable for rapid charging applications ranging from electric vehicles to smart electronic devices and aerospace technologies.
< Figure 2. Electrochemical characterizations of FS/C/G-20//ZDPC SIHES full cells (left). Ragone plots for FS/C/G-20//ZDPC (this work) and other previously reported sodium-ion electrochemical energy storage devices (right). >
Professor Kang noted that the hybrid sodium-ion energy storage device, capable of rapid charging and achieving an energy density of 247 Wh/kg and a power density of 34,748 W/kg, represents a breakthrough in overcoming the current limitations of energy storage systems. He anticipates broader applications across various electronic devices, including electric vehicles.
This research, co-authored by KAIST doctoral candidates Jong Hui Choi and Dong Won Kim, was published in the international journal Energy Storage Materials on March 29 with the title "Low-crystallinity conductive multivalence iron sulfide-embedded S-doped anode and high-surface-area O-doped cathode of 3D porous N-rich graphitic carbon frameworks for high-performance sodium-ion hybrid energy storages."
The study was conducted with support from the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Nanomaterial Technology Development Project.
2024.04.18 View 18577 -
 Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 15209
Streamlining the Process of Materials Discovery
The materials platform M3I3 reduces the time for materials discovery by reverse engineering future materials using multiscale/multimodal imaging and machine learning of the processing-structure-properties relationship
Developing new materials and novel processes has continued to change the world. The M3I3 Initiative at KAIST has led to new insights into advancing materials development by implementing breakthroughs in materials imaging that have created a paradigm shift in the discovery of materials. The Initiative features the multiscale modeling and imaging of structure and property relationships and materials hierarchies combined with the latest material-processing data.
The research team led by Professor Seungbum Hong analyzed the materials research projects reported by leading global institutes and research groups, and derived a quantitative model using machine learning with a scientific interpretation. This process embodies the research goal of the M3I3: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration.
The researchers discussed the role of multiscale materials and molecular imaging combined with machine learning and also presented a future outlook for developments and the major challenges of M3I3. By building this model, the research team envisions creating desired sets of properties for materials and obtaining the optimum processing recipes to synthesize them.
“The development of various microscopy and diffraction tools with the ability to map the structure, property, and performance of materials at multiscale levels and in real time enabled us to think that materials imaging could radically accelerate materials discovery and development,” says Professor Hong.
“We plan to build an M3I3 repository of searchable structural and property maps using FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, and Reusable) principles to standardize best practices as well as streamline the training of early career researchers.”
One of the examples that shows the power of structure-property imaging at the nanoscale is the development of future materials for emerging nonvolatile memory devices. Specifically, the research team focused on microscopy using photons, electrons, and physical probes on the multiscale structural hierarchy, as well as structure-property relationships to enhance the performance of memory devices.
“M3I3 is an algorithm for performing the reverse engineering of future materials. Reverse engineering starts by analyzing the structure and composition of cutting-edge materials or products. Once the research team determines the performance of our targeted future materials, we need to know the candidate structures and compositions for producing the future materials.”
The research team has built a data-driven experimental design based on traditional NCM (nickel, cobalt, and manganese) cathode materials. With this, the research team expanded their future direction for achieving even higher discharge capacity, which can be realized via Li-rich cathodes.
However, one of the major challenges was the limitation of available data that describes the Li-rich cathode properties. To mitigate this problem, the researchers proposed two solutions: First, they should build a machine-learning-guided data generator for data augmentation. Second, they would use a machine-learning method based on ‘transfer learning.’ Since the NCM cathode database shares a common feature with a Li-rich cathode, one could consider repurposing the NCM trained model for assisting the Li-rich prediction. With the pretrained model and transfer learning, the team expects to achieve outstanding predictions for Li-rich cathodes even with the small data set.
With advances in experimental imaging and the availability of well-resolved information and big data, along with significant advances in high-performance computing and a worldwide thrust toward a general, collaborative, integrative, and on-demand research platform, there is a clear confluence in the required capabilities of advancing the M3I3 Initiative.
Professor Hong said, “Once we succeed in using the inverse “property−structure−processing” solver to develop cathode, anode, electrolyte, and membrane materials for high energy density Li-ion batteries, we will expand our scope of materials to battery/fuel cells, aerospace, automobiles, food, medicine, and cosmetic materials.”
The review was published in ACS Nano in March. This study was conducted through collaborations with Dr. Chi Hao Liow, Professor Jong Min Yuk, Professor Hye Ryung Byon, Professor Yongsoo Yang, Professor EunAe Cho, Professor Pyuck-Pa Choi, and Professor Hyuck Mo Lee at KAIST, Professor Joshua C. Agar at Lehigh University, Dr. Sergei V. Kalinin at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Professor Peter W. Voorhees at Northwestern University, and Professor Peter Littlewood at the University of Chicago (Article title: Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics, and Integration).This work was supported by the KAIST Global Singularity Research Program for 2019 and 2020.
Publication:
“Reducing Time to Discovery: Materials and Molecular Modeling, Imaging, Informatics and Integration,” S. Hong, C. H. Liow, J. M. Yuk, H. R. Byon, Y. Yang, E. Cho, J. Yeom, G. Park, H. Kang, S. Kim, Y. Shim, M. Na, C. Jeong, G. Hwang, H. Kim, H. Kim, S. Eom, S. Cho, H. Jun, Y. Lee, A. Baucour, K. Bang, M. Kim, S. Yun, J. Ryu, Y. Han, A. Jetybayeva, P.-P. Choi, J. C. Agar, S. V. Kalinin, P. W. Voorhees, P. Littlewood, and H. M. Lee, ACS Nano 15, 3, 3971–3995 (2021) https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.1c00211
Profile:
Seungbum Hong, PhD
Associate Professor
seungbum@kaist.ac.kr
http://mii.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2021.04.05 View 15209 -
 Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 14853
Researchers Report Longest-lived Aqueous Flow Batteries
New technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries
A research team led by Professor Hee-Tak Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed water-based zinc/bromine redox flow batteries (ZBBs) with the best life expectancy among all the redox flow batteries reported by identifying and solving the deterioration issue with zinc electrodes.
Professor Kim, head of the Advanced Battery Center at KAIST's Nano-fusion Research Institute, said, "We presented a new technology to overcome the life limit of next-generation water-cell batteries. Not only is it cheaper than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but it can contribute to the expansion of renewable energy and the safe supply of energy storage systems that can run with more than 80 percent energy efficiency."
ZBBs were found to have stable life spans of more than 5,000 cycles, even at a high current density of 100 mA/cm2. It was also confirmed that it represented the highest output and life expectancy compared to Redox flow batteries (RFBs) reported worldwide, which use other redox couples such as zinc-bromine, zinc-iodine, zinc-iron, and vanadium.
Recently, more attention has been focused on energy storage system (ESS) that can improve energy utilization efficiency by storing new and late-night power in large quantities and supplying it to the grid if necessary to supplement the intermittent nature of renewable energy and meet peak power demand.
However, lithium-ion batteries (LIBs), which are currently the core technology of ESSs, have been criticized for not being suitable for ESSs, which store large amounts of electricity due to their inherent risk of ignition and fire. In fact, a total of 33 cases of ESSs using LIBs in Korea had fire accidents, and 35% of all ESS facilities were shut down. This is estimated to have resulted in more than 700 billion won in losses.
As a result, water-based RFBs have drawn great attention. In particular, ZBBs that use ultra-low-cost bromide (ZnBr2) as an active material have been developed for ESSs since the 1970s, with their advantages of high cell voltage, high energy density, and low price compared to other RFBs. Until now, however, the commercialization of ZBBs has been delayed due to the short life span caused by the zinc electrodes. In particular, the uneven "dendrite" growth behavior of zinc metals during the charging and discharging process leads to internal short circuits in the battery which shorten its life.
The research team noted that self-aggregation occurs through the surface diffusion of zinc nuclei on the carbon electrode surface with low surface energy, and determined that self-aggregation was the main cause of zinc dendrite formation through quantum mechanics-based computer simulations and transmission electron microscopy. Furthermore, it was found that the surface diffusion of the zinc nuclei was inhibited in certain carbon fault structures so that dendrites were not produced.
Single vacancy defect, where one carbon atom is removed, exchanges zinc nuclei and electrons, and is strongly coupled, thus inhibiting surface diffusion and enabling uniform nuclear production/growth. The research team applied carbon electrodes with high density fault structure to ZBBs, achieving life characteristics of more than 5,000 cycles at a high charge current density (100 mA/cm2), which is 30 times that of LIBs.
This ESS technology, which can supply eco-friendly electric energy such as renewable energy to the private sector through technology that can drive safe and cheap redox flow batteries for long life, is expected to draw attention once again.
Publication:
Ju-Hyuk Lee, Riyul Kim, Soohyun Kim, Jiyun Heo, Hyeokjin Kwon, Jung Hoon Yang, and Hee-Tak Kim. 2020. Dendrite-free Zn electrodeposition triggered by interatomic orbital hybridization of Zn and single vacancy carbon defects for aqueous Zn-based flow batteries. Energy and Environmental Science, 2020, 13, 2839-2848.
Link to download the full-text paper:http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=D0EE00723D
Profile: Prof. Hee-Tak Kimheetak.kim@kaist.ac.krhttp://eed.kaist.ac.krAssociate ProfessorDepartment of Chemical & Biomolecular EngineeringKAIST
2020.12.16 View 14853 -
 Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage technology and widely used in electric vehicles.
Lithium-oxygen batteries in principle can generate ten times higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but they suffer from very poor cyclability. One of the methods to improve cycle stability is to reduce the overpotential of electrocatalysts in cathode electrodes. When the size of an electrocatalyst material is reduced to the atomic level, the increased surface energy leads to increased activity while significantly accelerating the material’s agglomeration.
As a solution to this challenge, Professor Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering aimed to maintain the improved activity by stabilizing atomic-scale sized electrocatalysts into the sub-nanometric spaces. This is a novel strategy for simultaneously producing and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Metal-organic frameworks continuously assemble metal ions and organic linkers.
The team controlled hydrogen affinities between water molecules to separate them and transfer the isolated water molecules one by one through the sub-nanometric pores of MOFs. The transferred water molecules reacted with cobalt ions to form di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide under precisely controlled synthetic conditions, then the atomic-level cobalt hydroxide is stabilized inside the sub-nanometric pores.
The di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide that is stabilized in the sub-nanometric pores of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) reduced the overpotential by 63.9% and showed ten-fold improvements in the life cycle.
Professor Kang said, “Simultaneously generating and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within MOFs can diversify materials according to numerous combinations of metal and organic linkers. It can expand not only the development of electrocatalysts, but also various research fields such as photocatalysts, medicine, the environment, and petrochemicals.”
This study was reported in Advanced Science (Title: Autogenous Production and Stabilization of Highly Loaded Sub-Nanometric Particles within Multishell Hollow Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Utilization for High Performance in Li-O2 Batteries).
This research was mainly supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Planning (Grant No. 2013M3A6B1078884) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. 2019M3E6A1104196).
Profile:Professor Jeung Ku Kang
jeungku@kaist.ac.kr
http://nanosf.kaist.ac.kr/
Nano Materials Simulation and Fabrication Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.15 View 14243
Energy Storage Using Oxygen to Boost Battery Performance
Researchers have presented a novel electrode material for advanced energy storage device that is directly charged with oxygen from the air. Professor Jeung Ku Kang’s team synthesized and preserved the sub-nanometric particles of atomic cluster sizes at high mass loadings within metal-organic frameworks (MOF) by controlling the behavior of reactants at the molecular level. This new strategy ensures high performance for lithium-oxygen batteries, acclaimed as a next-generation energy storage technology and widely used in electric vehicles.
Lithium-oxygen batteries in principle can generate ten times higher energy densities than conventional lithium-ion batteries, but they suffer from very poor cyclability. One of the methods to improve cycle stability is to reduce the overpotential of electrocatalysts in cathode electrodes. When the size of an electrocatalyst material is reduced to the atomic level, the increased surface energy leads to increased activity while significantly accelerating the material’s agglomeration.
As a solution to this challenge, Professor Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering aimed to maintain the improved activity by stabilizing atomic-scale sized electrocatalysts into the sub-nanometric spaces. This is a novel strategy for simultaneously producing and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within metal-organic frameworks (MOFs).
Metal-organic frameworks continuously assemble metal ions and organic linkers.
The team controlled hydrogen affinities between water molecules to separate them and transfer the isolated water molecules one by one through the sub-nanometric pores of MOFs. The transferred water molecules reacted with cobalt ions to form di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide under precisely controlled synthetic conditions, then the atomic-level cobalt hydroxide is stabilized inside the sub-nanometric pores.
The di-nuclear cobalt hydroxide that is stabilized in the sub-nanometric pores of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) reduced the overpotential by 63.9% and showed ten-fold improvements in the life cycle.
Professor Kang said, “Simultaneously generating and stabilizing atomic-level electrocatalysts within MOFs can diversify materials according to numerous combinations of metal and organic linkers. It can expand not only the development of electrocatalysts, but also various research fields such as photocatalysts, medicine, the environment, and petrochemicals.”
This study was reported in Advanced Science (Title: Autogenous Production and Stabilization of Highly Loaded Sub-Nanometric Particles within Multishell Hollow Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Utilization for High Performance in Li-O2 Batteries).
This research was mainly supported by the Global Frontier R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Planning (Grant No. 2013M3A6B1078884) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning, and the National Research Foundation of Korea (Grant No. 2019M3E6A1104196).
Profile:Professor Jeung Ku Kang
jeungku@kaist.ac.kr
http://nanosf.kaist.ac.kr/
Nano Materials Simulation and Fabrication Laboratory
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
2020.06.15 View 14243 -
 Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park Won the IBA Technology Award 2018
(Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park)
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the IBA Technology Award from the International Battery Association (IBA).
IBA 2018 was held from March 11 to 16 on Jeju Island, which was the first time it was hosted in Korea. The conference was an excellent opportunity to let the world know the level of the Korean rechargeable battery industry and its technology.
Professor Park delivered his keynote speech titled Advances in Lithium Batteries in Korea at the conference and received the IBA Technology Award as the first Korean recipient.
Professor Park is a world-renowned scholar who was a groundbreaker in the rechargeable battery industry. He was recognized by the IBA Award Committee for his contributions carrying out research and development, fostering competent people, and enhancing the lithium rechargeable battery industry in Korea over the last 30 years.
Professor Park said, “It is my great honor to receive this award, which is the best international award in the field of rechargeable batteries. I would like to share this with my colleagues and students. As competition in the rechargeable industry intensifies, systemic cooperation among industries, academia, and government is needed for the continued development of the battery industry in Korea.
2018.03.19 View 8547
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park Won the IBA Technology Award 2018
(Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park)
Professor Emeritus Jung Ki Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering received the IBA Technology Award from the International Battery Association (IBA).
IBA 2018 was held from March 11 to 16 on Jeju Island, which was the first time it was hosted in Korea. The conference was an excellent opportunity to let the world know the level of the Korean rechargeable battery industry and its technology.
Professor Park delivered his keynote speech titled Advances in Lithium Batteries in Korea at the conference and received the IBA Technology Award as the first Korean recipient.
Professor Park is a world-renowned scholar who was a groundbreaker in the rechargeable battery industry. He was recognized by the IBA Award Committee for his contributions carrying out research and development, fostering competent people, and enhancing the lithium rechargeable battery industry in Korea over the last 30 years.
Professor Park said, “It is my great honor to receive this award, which is the best international award in the field of rechargeable batteries. I would like to share this with my colleagues and students. As competition in the rechargeable industry intensifies, systemic cooperation among industries, academia, and government is needed for the continued development of the battery industry in Korea.
2018.03.19 View 8547 -
 KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 12076
KAIST Ph.D. Candidate Wins the Next Generation of Engineers Award
Joo-Sung Kim, a doctoral student at the EEWS (Environment, Energy, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School won the inaugural Next Generation of Engineers Award in Leadership on December 14, 2016.
The National Academy of Engineering of Korea hosts this award to support creative and ambitious students who have the potential to become leaders in engineering and who will serve as role models for future Korean engineers. Based on the recommendations of university professors in engineering and members of the academy, seven students are selected for the award in the categories of leadership and entrepreneurship.
With his research focus on the development of high-performance, next-generation secondary cells for wearable devices such as smart watches, health bands, and smart eyewear, Joo-Sung created a startup, Lithium-ion Battery Energy Science and Technology (LiBEST), Inc. He plans to base his company at the Office of University and Industry Cooperation, KAIST, where he can receive assistance for launching the mass-production system for his technology.
His adviser, Professor Jang-Wook Choi of the EEWS Graduate School, noted, “Joo-Sung has been a great student who has a strong sense of curiosity and perseverance. The award is the by-product of his hard work.”
“I have always enjoyed my work and study as a researcher, but eventually would like to expand my career into business based on the results of my research. It would be wonderful if I could become a businessman like Elon Musk, Masayoshi Son, or Ma Yun and create a role model for aspiring engineers in Korea by combining science and technology with business demand to create social values that benefit many people,” Joo-Young said.
2016.12.26 View 12076 -
 The First Demonstration of a Self-powered Cardiac Pacemaker
As the number of pacemakers implanted each year reaches into the millions worldwide, improving the lifespan of pacemaker batteries has been of great concern for developers and manufacturers. Currently, pacemaker batteries last seven years on average, requiring frequent replacements, which may pose patients to a potential risk involved in medical procedures.
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST and Professor Boyoung Joung, M.D. of the Division of Cardiology at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University, has developed a self-powered artificial cardiac pacemaker that is operated semi-permanently by a flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator.
The artificial cardiac pacemaker is widely acknowledged as medical equipment that is integrated into the human body to regulate the heartbeats through electrical stimulation to contract the cardiac muscles of people who suffer from arrhythmia. However, repeated surgeries to replace pacemaker batteries have exposed elderly patients to health risks such as infections or severe bleeding during operations.
The team’s newly designed flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator directly stimulated a living rat’s heart using electrical energy converted from the small body movements of the rat. This technology could facilitate the use of self-powered flexible energy harvesters, not only prolonging the lifetime of cardiac pacemakers but also realizing real-time heart monitoring.
The research team fabricated high-performance flexible nanogenerators utilizing a bulk single-crystal PMN-PT thin film (iBULe Photonics). The harvested energy reached up to 8.2 V and 0.22 mA by bending and pushing motions, which were high enough values to directly stimulate the rat’s heart.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said:
“For clinical purposes, the current achievement will benefit the development of self-powered cardiac pacemakers as well as prevent heart attacks via the real-time diagnosis of heart arrhythmia. In addition, the flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator could also be utilized as an electrical source for various implantable medical devices.”
This research result was described in the April online issue of Advanced Materials (“Self-Powered Cardiac Pacemaker Enabled by Flexible Single Crystalline PMN-PT Piezoelectric Energy Harvester”: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201400562/abstract).
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZWYT2cU_Mog&feature=youtu.be
Picture Caption: A self-powered cardiac pacemaker is enabled by a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester.
2014.06.25 View 18091
The First Demonstration of a Self-powered Cardiac Pacemaker
As the number of pacemakers implanted each year reaches into the millions worldwide, improving the lifespan of pacemaker batteries has been of great concern for developers and manufacturers. Currently, pacemaker batteries last seven years on average, requiring frequent replacements, which may pose patients to a potential risk involved in medical procedures.
A research team from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), headed by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST and Professor Boyoung Joung, M.D. of the Division of Cardiology at Severance Hospital of Yonsei University, has developed a self-powered artificial cardiac pacemaker that is operated semi-permanently by a flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator.
The artificial cardiac pacemaker is widely acknowledged as medical equipment that is integrated into the human body to regulate the heartbeats through electrical stimulation to contract the cardiac muscles of people who suffer from arrhythmia. However, repeated surgeries to replace pacemaker batteries have exposed elderly patients to health risks such as infections or severe bleeding during operations.
The team’s newly designed flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator directly stimulated a living rat’s heart using electrical energy converted from the small body movements of the rat. This technology could facilitate the use of self-powered flexible energy harvesters, not only prolonging the lifetime of cardiac pacemakers but also realizing real-time heart monitoring.
The research team fabricated high-performance flexible nanogenerators utilizing a bulk single-crystal PMN-PT thin film (iBULe Photonics). The harvested energy reached up to 8.2 V and 0.22 mA by bending and pushing motions, which were high enough values to directly stimulate the rat’s heart.
Professor Keon Jae Lee said:
“For clinical purposes, the current achievement will benefit the development of self-powered cardiac pacemakers as well as prevent heart attacks via the real-time diagnosis of heart arrhythmia. In addition, the flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator could also be utilized as an electrical source for various implantable medical devices.”
This research result was described in the April online issue of Advanced Materials (“Self-Powered Cardiac Pacemaker Enabled by Flexible Single Crystalline PMN-PT Piezoelectric Energy Harvester”: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201400562/abstract).
Youtube link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZWYT2cU_Mog&feature=youtu.be
Picture Caption: A self-powered cardiac pacemaker is enabled by a flexible piezoelectric energy harvester.
2014.06.25 View 18091