Scientific+Reports
-
 Attachable Skin Monitors that Wick the Sweat Away
- A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals. -
A new preparation technique fabricates thin, silicone-based patches that rapidly wick water away from the skin. The technique could reduce the redness and itching caused by wearable biosensors that trap sweat beneath them. The technique was developed by bioengineer and professor Young-Ho Cho and his colleagues at KAIST and reported in the journal Scientific Reports last month.
“Wearable bioelectronics are becoming more attractive for the day-to-day monitoring of biological compounds found in sweat, like hormones or glucose, as well as body temperature, heart rate, and energy expenditure,” Professor Cho explained. “But currently available materials can cause skin irritation, so scientists are looking for ways to improve them,” he added.
Attachable biosensors often use a silicone-based compound called polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), as it has a relatively high water vapour transmission rate compared to other materials. Still, this rate is only two-thirds that of skin’s water evaporation rate, meaning sweat still gets trapped underneath it.
Current fabrication approaches mix PDMS with beads or solutes, such as sugars or salts, and then remove them to leave pores in their place. Another technique uses gas to form pores in the material. Each technique has its disadvantages, from being expensive and complex to leaving pores of different sizes.
A team of researchers led by Professor Cho from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was able to form small, uniform pores by crystallizing citric acid in PDMS and then removing the crystals using ethanol. The approach is significantly cheaper than using beads, and leads to 93.2% smaller and 425% more uniformly-sized pores compared to using sugar. Importantly, the membrane transmits water vapour 2.2 times faster than human skin.
The team tested their membrane on human skin for seven days and found that it caused only minor redness and no itching, whereas a non-porous PDMS membrane did.
Professor Cho said, “Our method could be used to fabricate porous PDMS membranes for skin-attachable devices used for daily monitoring of physiological signals.”
“We next plan to modify our membrane so it can be more readily attached to and removed from skin,” he added.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) of Korea under the Alchemist Project.
Image description:
Smaller, more uniformly-sized pores are made in the PDMS membrane by mixing PDMS, toluene, citric acid, and ethanol. Toluene dilutes PDMS so it can easily mix with the other two constituents. Toluene and ethanol are then evaporated, which causes the citric acid to crystallize within the PDMS material. The mixture is placed in a mould where it solidifies into a thin film. The crystals are then removed using ethanol, leaving pores in their place.
Image credit:
Professor Young-Ho Cho, KAIST
Image usage restrictions:
News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Yoon, S, et al. (2021) Wearable porous PDMS layer of high moisture permeability for skin trouble reduction. Scientific Reports 11, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78580-z
Profile:
Young-Ho Cho, Ph.D
Professor
mems@kaist.ac.kr
https://mems.kaist.ac.kr
NanoSentuating Systems Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
https://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.02.22 View 15166
Attachable Skin Monitors that Wick the Sweat Away
- A silicone membrane for wearable devices is more comfortable and breathable thanks to better-sized pores made with the help of citric acid crystals. -
A new preparation technique fabricates thin, silicone-based patches that rapidly wick water away from the skin. The technique could reduce the redness and itching caused by wearable biosensors that trap sweat beneath them. The technique was developed by bioengineer and professor Young-Ho Cho and his colleagues at KAIST and reported in the journal Scientific Reports last month.
“Wearable bioelectronics are becoming more attractive for the day-to-day monitoring of biological compounds found in sweat, like hormones or glucose, as well as body temperature, heart rate, and energy expenditure,” Professor Cho explained. “But currently available materials can cause skin irritation, so scientists are looking for ways to improve them,” he added.
Attachable biosensors often use a silicone-based compound called polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS), as it has a relatively high water vapour transmission rate compared to other materials. Still, this rate is only two-thirds that of skin’s water evaporation rate, meaning sweat still gets trapped underneath it.
Current fabrication approaches mix PDMS with beads or solutes, such as sugars or salts, and then remove them to leave pores in their place. Another technique uses gas to form pores in the material. Each technique has its disadvantages, from being expensive and complex to leaving pores of different sizes.
A team of researchers led by Professor Cho from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering was able to form small, uniform pores by crystallizing citric acid in PDMS and then removing the crystals using ethanol. The approach is significantly cheaper than using beads, and leads to 93.2% smaller and 425% more uniformly-sized pores compared to using sugar. Importantly, the membrane transmits water vapour 2.2 times faster than human skin.
The team tested their membrane on human skin for seven days and found that it caused only minor redness and no itching, whereas a non-porous PDMS membrane did.
Professor Cho said, “Our method could be used to fabricate porous PDMS membranes for skin-attachable devices used for daily monitoring of physiological signals.”
“We next plan to modify our membrane so it can be more readily attached to and removed from skin,” he added.
This work was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) of Korea under the Alchemist Project.
Image description:
Smaller, more uniformly-sized pores are made in the PDMS membrane by mixing PDMS, toluene, citric acid, and ethanol. Toluene dilutes PDMS so it can easily mix with the other two constituents. Toluene and ethanol are then evaporated, which causes the citric acid to crystallize within the PDMS material. The mixture is placed in a mould where it solidifies into a thin film. The crystals are then removed using ethanol, leaving pores in their place.
Image credit:
Professor Young-Ho Cho, KAIST
Image usage restrictions:
News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Yoon, S, et al. (2021) Wearable porous PDMS layer of high moisture permeability for skin trouble reduction. Scientific Reports 11, Article No. 938. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78580-z
Profile:
Young-Ho Cho, Ph.D
Professor
mems@kaist.ac.kr
https://mems.kaist.ac.kr
NanoSentuating Systems Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
https://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2021.02.22 View 15166 -
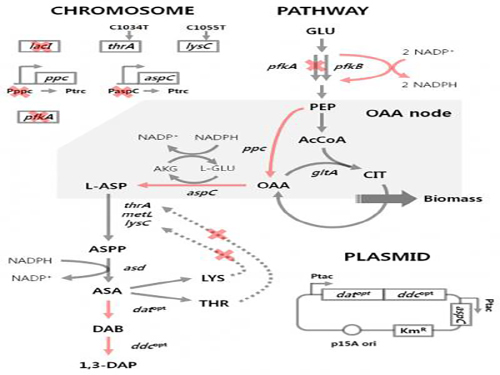 'Engineered Bacterium Produces 1,3-Diaminopropane'
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported, for the first time, the production of 1,3-diaminopropane via fermentation of an engineered bacterium.
1,3-Diaminopropane is a three carbon diamine, which has a wide range of industrial applications including epoxy resin and cross-linking agents, as well as precursors for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and organic chemicals. It can also be polymerized with dicarboxylic acids to make polyamides (nylons) for use as engineering plastics, medical materials, and adhesives.
Traditionally, 1,3-diaminopropane is derived from petroleum-based processes. In effort to address critical problems such as the depletion of petroleum and environmental issues inherent to the petroleum-based processes, the research team has developed an Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain capable of producing 1,3-diaminopropane. Using this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can now be produced from renewable biomass instead of petroleum.
E. coli as found in nature is unable to produce 1,3-diaminopropane. Metabolic engineering, a technology to transform microorganisms into highly efficient microbial cell factories capable of producing chemical compounds of interest, was utilized to engineer the E. coli strain. First, naturally existing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of 1,3-diaminopropane were introduced into a virtual cell in silico to determine the most efficient metabolic pathway for the 1,3-diaminopropane production. The metabolic pathway selected was then introduced into an E. coli strain and successfully produced 1,3-diaminopropane for the first time in the world.
The research team applied metabolic engineering additionally, and the production titer of 1,3-diaminopropane increased about 21 fold. The Fed-batch fermentation of the engineered E. coli strain produced 13 grams per liter of 1,3-diaminoproapne. With this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can be produced using renewable biomass, and it will be the starting point for replacing the current petroleum-based processes with bio-based processes.
Professor Lee said, “Our study suggested a possibility to produce 1,3-diaminopropane based on biorefinery. Further study will be done to increase the titer and productivity of 1,3-diaminopropane.”
This work was published online in Scientific Reports on August 11, 2015.
Reference: Chae, T.U. et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,3-diaminopropane, a three carbon diamine," Scientific Reports:
http://www.nature.com/articles/srep13040
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Figure 1: Metabolic engineering strategies for 1,3-diaminopropane production using C4 pathway
Figure 2: Fed-batch fermentation profiles of two final engineered E. coli strains
2015.08.12 View 12018
'Engineered Bacterium Produces 1,3-Diaminopropane'
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST reported, for the first time, the production of 1,3-diaminopropane via fermentation of an engineered bacterium.
1,3-Diaminopropane is a three carbon diamine, which has a wide range of industrial applications including epoxy resin and cross-linking agents, as well as precursors for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and organic chemicals. It can also be polymerized with dicarboxylic acids to make polyamides (nylons) for use as engineering plastics, medical materials, and adhesives.
Traditionally, 1,3-diaminopropane is derived from petroleum-based processes. In effort to address critical problems such as the depletion of petroleum and environmental issues inherent to the petroleum-based processes, the research team has developed an Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain capable of producing 1,3-diaminopropane. Using this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can now be produced from renewable biomass instead of petroleum.
E. coli as found in nature is unable to produce 1,3-diaminopropane. Metabolic engineering, a technology to transform microorganisms into highly efficient microbial cell factories capable of producing chemical compounds of interest, was utilized to engineer the E. coli strain. First, naturally existing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of 1,3-diaminopropane were introduced into a virtual cell in silico to determine the most efficient metabolic pathway for the 1,3-diaminopropane production. The metabolic pathway selected was then introduced into an E. coli strain and successfully produced 1,3-diaminopropane for the first time in the world.
The research team applied metabolic engineering additionally, and the production titer of 1,3-diaminopropane increased about 21 fold. The Fed-batch fermentation of the engineered E. coli strain produced 13 grams per liter of 1,3-diaminoproapne. With this technology, 1,3-diaminopropane can be produced using renewable biomass, and it will be the starting point for replacing the current petroleum-based processes with bio-based processes.
Professor Lee said, “Our study suggested a possibility to produce 1,3-diaminopropane based on biorefinery. Further study will be done to increase the titer and productivity of 1,3-diaminopropane.”
This work was published online in Scientific Reports on August 11, 2015.
Reference: Chae, T.U. et al. "Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of 1,3-diaminopropane, a three carbon diamine," Scientific Reports:
http://www.nature.com/articles/srep13040
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries from Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Figure 1: Metabolic engineering strategies for 1,3-diaminopropane production using C4 pathway
Figure 2: Fed-batch fermentation profiles of two final engineered E. coli strains
2015.08.12 View 12018 -
 Professor YongKeun Park Produces Undergraduate Students with International Achievements
Three undergraduate students under the supervision of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, KAIST, have published papers in globally renowned academic journals.
The most recent publication was made by YoungJu Jo, a senior in physics. Jo’s paper entitled “Angle-resolved light scattering of individual rod-shaped bacteria based on Fourier transform light scattering” was published in the May 28th edition of Scientific Reports.
Analyzing bacteria is a very important task in the field of health and food hygiene, but using the conventional biochemical methods of analysis takes days. However, observation with Jo’s newly developed method using light scattering analyzes bacteria within a matter of seconds.
SangYeon Cho from the Department of Chemistry also published papers in Cell (2012) and Nature (2013), respectively, under the guidance of Professor Park. SangYeon Cho’s outstanding research achievements were recognized by Harvard and MIT. He was accepted with a full scholarship to Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology Graduate School. He will begin his graduate studies at Harvard-MIT this September.
Last March, SeoEun Lee from the Department of Biology was the recipient of the Best Paper Award by the Optical Society of Korea. She plans to pursue a doctoral degree at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University in New York.
Professor Park said, “Undergraduate students, who are learning a variety of subjects concurrently, are at the most creative time of their lives. KAIST has offered many opportunities to undergraduate students to partake in various research programs.”
- Picture (a) and (b): Rod-shaped bacteria’s phase image and light-scattering patterns
- Picture (c): Quantitative analysis to illustrate the extraction of information from bacteria
2014.06.03 View 15072
Professor YongKeun Park Produces Undergraduate Students with International Achievements
Three undergraduate students under the supervision of Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics, KAIST, have published papers in globally renowned academic journals.
The most recent publication was made by YoungJu Jo, a senior in physics. Jo’s paper entitled “Angle-resolved light scattering of individual rod-shaped bacteria based on Fourier transform light scattering” was published in the May 28th edition of Scientific Reports.
Analyzing bacteria is a very important task in the field of health and food hygiene, but using the conventional biochemical methods of analysis takes days. However, observation with Jo’s newly developed method using light scattering analyzes bacteria within a matter of seconds.
SangYeon Cho from the Department of Chemistry also published papers in Cell (2012) and Nature (2013), respectively, under the guidance of Professor Park. SangYeon Cho’s outstanding research achievements were recognized by Harvard and MIT. He was accepted with a full scholarship to Harvard-MIT Health Sciences and Technology Graduate School. He will begin his graduate studies at Harvard-MIT this September.
Last March, SeoEun Lee from the Department of Biology was the recipient of the Best Paper Award by the Optical Society of Korea. She plans to pursue a doctoral degree at the College of Physicians and Surgeons, Columbia University in New York.
Professor Park said, “Undergraduate students, who are learning a variety of subjects concurrently, are at the most creative time of their lives. KAIST has offered many opportunities to undergraduate students to partake in various research programs.”
- Picture (a) and (b): Rod-shaped bacteria’s phase image and light-scattering patterns
- Picture (c): Quantitative analysis to illustrate the extraction of information from bacteria
2014.06.03 View 15072