SPE
-
 Simultaneous Analysis of 21 Chemical Reactions... AI to Transform New Drug Development
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hyunwoo Kim and students Donghun Kim and Gyeongseon Choi in the Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program of the Department of Chemistry >
Thalidomide, a drug once used to alleviate morning sickness in pregnant women, exhibits distinct properties due to its optical isomers* in the body: one isomer has a sedative effect, while the other causes severe side effects like birth defects. As this example illustrates, precise organic synthesis techniques, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, are crucial in new drug development. Overcoming the traditional methods that struggled with simultaneously analyzing multiple reactants, our research team has developed the world's first technology to precisely analyze 21 types of reactants simultaneously. This breakthrough is expected to make a significant contribution to new drug development utilizing AI and robots.
*Optical Isomers: A pair of molecules with the same chemical formula that are mirror images of each other and cannot be superimposed due to their asymmetric structure. This is analogous to a left and right hand, which are similar in form but cannot be perfectly overlaid.
KAIST's Professor Hyunwoo Kim's research team in the Department of Chemistry announced on the 16th that they have developed an innovative optical isomer analysis technology suitable for the era of AI-driven autonomous synthesis*. This research is the world's first technology to precisely analyze asymmetric catalytic reactions involving multiple reactants simultaneously using high-resolution fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (19F NMR). It is expected to make groundbreaking contributions to various fields, including new drug development and catalyst optimization.
*AI-driven Autonomous Synthesis: An advanced technology that automates and optimizes chemical substance synthesis processes using artificial intelligence (AI). It is gaining attention as a core element for realizing automated and intelligent research environments in future laboratories. AI predicts and adjusts experimental conditions, interprets results, and designs subsequent experiments independently, minimizing human intervention in repetitive experiments and significantly increasing research efficiency and innovativeness.
Currently, while autonomous synthesis systems can automate everything from reaction design to execution, reaction analysis still relies on individual processing using traditional equipment. This leads to slower speeds and bottlenecks, making it unsuitable for high-speed repetitive experiments.
Furthermore, multi-substrate simultaneous screening techniques proposed in the 1990s garnered attention as a strategy to maximize reaction analysis efficiency. However, limitations of existing chromatography-based analysis methods restricted the number of applicable substrates. In asymmetric synthesis reactions, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, simultaneously analyzing more than 10 types of substrates was nearly impossible.
< Figure 1. Conventional organic reaction evaluation methods follow a process of deriving optimal reaction conditions using a single substrate, then expanding the substrate scope one by one under those conditions, leaving potential reaction areas unexplored. To overcome this, high-throughput screening is introduced to broadly explore catalyst reactivity for various substrates. When combined with multi-substrate screening, this approach allows for a much broader and more systematic understanding of reaction scope and trends. >
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a 19F NMR-based multi-substrate simultaneous screening technology. This method involves performing asymmetric catalytic reactions with multiple reactants in a single reaction vessel, introducing a fluorine functional group into the products, and then applying their self-developed chiral cobalt reagent to clearly quantify all optical isomers using 19F NMR.
Utilizing the excellent resolution and sensitivity of 19F NMR, the research team successfully performed asymmetric synthesis reactions of 21 substrates simultaneously in a single reaction vessel and quantitatively measured the product yield and optical isomer ratio without any separate purification steps.
Professor Hyunwoo Kim stated, "While anyone can perform asymmetric synthesis reactions with multiple substrates in one reactor, accurately analyzing all the products has been a challenging problem to solve until now. We expect that achieving world-class multi-substrate screening analysis technology will greatly contribute to enhancing the analytical capabilities of AI-driven autonomous synthesis platforms."
< Figure 2. A method for analyzing multi-substrate asymmetric catalytic reactions, where different substrates react simultaneously in a single reactor, using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance has been implemented. By utilizing the characteristics of fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance, which has a clean background signal and a wide chemical shift range, the reactivity of each substrate can be quantitatively analyzed. It is also shown that the optical activity of all reactants can be simultaneously measured using a cobalt metal complex. >
He further added, "This research provides a technology that can rapidly verify the efficiency and selectivity of asymmetric catalytic reactions essential for new drug development, and it is expected to be utilized as a core analytical tool for AI-driven autonomous research."
< Figure 3. It can be seen that in a multi-substrate reductive amination reaction using a total of 21 substrates, the yield and optical activity of the reactants according to the catalyst system were simultaneously measured using a fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance-based analysis platform. The yield of each reactant is indicated by color saturation, and the optical activity by numbers. >
Donghun Kim (first author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) and Gyeongseon Choi (second author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) from the KAIST Department of Chemistry participated in this research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on May 27, 2025.※ Paper Title: One-pot Multisubstrate Screening for Asymmetric Catalysis Enabled by 19F NMR-based Simultaneous Chiral Analysis※ DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03446
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Researcher Program, the Asymmetric Catalytic Reaction Design Center, and the KAIST KC30 Project.
< Figure 4. Conceptual diagram of performing multi-substrate screening reactions and utilizing fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. >
2025.06.16 View 1093
Simultaneous Analysis of 21 Chemical Reactions... AI to Transform New Drug Development
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hyunwoo Kim and students Donghun Kim and Gyeongseon Choi in the Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program of the Department of Chemistry >
Thalidomide, a drug once used to alleviate morning sickness in pregnant women, exhibits distinct properties due to its optical isomers* in the body: one isomer has a sedative effect, while the other causes severe side effects like birth defects. As this example illustrates, precise organic synthesis techniques, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, are crucial in new drug development. Overcoming the traditional methods that struggled with simultaneously analyzing multiple reactants, our research team has developed the world's first technology to precisely analyze 21 types of reactants simultaneously. This breakthrough is expected to make a significant contribution to new drug development utilizing AI and robots.
*Optical Isomers: A pair of molecules with the same chemical formula that are mirror images of each other and cannot be superimposed due to their asymmetric structure. This is analogous to a left and right hand, which are similar in form but cannot be perfectly overlaid.
KAIST's Professor Hyunwoo Kim's research team in the Department of Chemistry announced on the 16th that they have developed an innovative optical isomer analysis technology suitable for the era of AI-driven autonomous synthesis*. This research is the world's first technology to precisely analyze asymmetric catalytic reactions involving multiple reactants simultaneously using high-resolution fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (19F NMR). It is expected to make groundbreaking contributions to various fields, including new drug development and catalyst optimization.
*AI-driven Autonomous Synthesis: An advanced technology that automates and optimizes chemical substance synthesis processes using artificial intelligence (AI). It is gaining attention as a core element for realizing automated and intelligent research environments in future laboratories. AI predicts and adjusts experimental conditions, interprets results, and designs subsequent experiments independently, minimizing human intervention in repetitive experiments and significantly increasing research efficiency and innovativeness.
Currently, while autonomous synthesis systems can automate everything from reaction design to execution, reaction analysis still relies on individual processing using traditional equipment. This leads to slower speeds and bottlenecks, making it unsuitable for high-speed repetitive experiments.
Furthermore, multi-substrate simultaneous screening techniques proposed in the 1990s garnered attention as a strategy to maximize reaction analysis efficiency. However, limitations of existing chromatography-based analysis methods restricted the number of applicable substrates. In asymmetric synthesis reactions, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, simultaneously analyzing more than 10 types of substrates was nearly impossible.
< Figure 1. Conventional organic reaction evaluation methods follow a process of deriving optimal reaction conditions using a single substrate, then expanding the substrate scope one by one under those conditions, leaving potential reaction areas unexplored. To overcome this, high-throughput screening is introduced to broadly explore catalyst reactivity for various substrates. When combined with multi-substrate screening, this approach allows for a much broader and more systematic understanding of reaction scope and trends. >
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a 19F NMR-based multi-substrate simultaneous screening technology. This method involves performing asymmetric catalytic reactions with multiple reactants in a single reaction vessel, introducing a fluorine functional group into the products, and then applying their self-developed chiral cobalt reagent to clearly quantify all optical isomers using 19F NMR.
Utilizing the excellent resolution and sensitivity of 19F NMR, the research team successfully performed asymmetric synthesis reactions of 21 substrates simultaneously in a single reaction vessel and quantitatively measured the product yield and optical isomer ratio without any separate purification steps.
Professor Hyunwoo Kim stated, "While anyone can perform asymmetric synthesis reactions with multiple substrates in one reactor, accurately analyzing all the products has been a challenging problem to solve until now. We expect that achieving world-class multi-substrate screening analysis technology will greatly contribute to enhancing the analytical capabilities of AI-driven autonomous synthesis platforms."
< Figure 2. A method for analyzing multi-substrate asymmetric catalytic reactions, where different substrates react simultaneously in a single reactor, using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance has been implemented. By utilizing the characteristics of fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance, which has a clean background signal and a wide chemical shift range, the reactivity of each substrate can be quantitatively analyzed. It is also shown that the optical activity of all reactants can be simultaneously measured using a cobalt metal complex. >
He further added, "This research provides a technology that can rapidly verify the efficiency and selectivity of asymmetric catalytic reactions essential for new drug development, and it is expected to be utilized as a core analytical tool for AI-driven autonomous research."
< Figure 3. It can be seen that in a multi-substrate reductive amination reaction using a total of 21 substrates, the yield and optical activity of the reactants according to the catalyst system were simultaneously measured using a fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance-based analysis platform. The yield of each reactant is indicated by color saturation, and the optical activity by numbers. >
Donghun Kim (first author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) and Gyeongseon Choi (second author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) from the KAIST Department of Chemistry participated in this research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on May 27, 2025.※ Paper Title: One-pot Multisubstrate Screening for Asymmetric Catalysis Enabled by 19F NMR-based Simultaneous Chiral Analysis※ DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03446
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Researcher Program, the Asymmetric Catalytic Reaction Design Center, and the KAIST KC30 Project.
< Figure 4. Conceptual diagram of performing multi-substrate screening reactions and utilizing fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. >
2025.06.16 View 1093 -
 High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST Researchers
- Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering develops an ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer using 'double-layer disordered metasurfaces' that generate unique random patterns depending on light's color.
- Unlike conventional dispersion-based spectrometers that were difficult to apply to portable devices, this new concept spectrometer technology achieves 1nm-level high resolution in a device smaller than 1cm, comparable in size to a fingernail.
- It can be utilized as a built-in spectrometer in smartphones and wearable devices in the future, and can be expanded to advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging and ultrafast imaging.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Mooseok Jang, Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate), Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) >
Color, as the way light's wavelength is perceived by the human eye, goes beyond a simple aesthetic element, containing important scientific information like a substance's composition or state. Spectrometers are optical devices that analyze material properties by decomposing light into its constituent wavelengths, and they are widely used in various scientific and industrial fields, including material analysis, chemical component detection, and life science research. Existing high-resolution spectrometers were large and complex, making them difficult for widespread daily use. However, thanks to the ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer developed by KAIST researchers, it is now expected that light's color information can be utilized even within smartphones or wearable devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 13th that Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has successfully developed a reconstruction-based spectrometer technology using double-layer disordered metasurfaces*.
*Double-layer disordered metasurface: An innovative optical device that complexly scatters light through two layers of disordered nanostructures, creating unique and predictable speckle patterns for each wavelength.
Existing high-resolution spectrometers have a large form factor, on the order of tens of centimeters, and require complex calibration processes to maintain accuracy. This fundamentally stems from the operating principle of traditional dispersive elements, such as gratings and prisms, which separate light wavelengths along the propagation direction, much like a rainbow separates colors. Consequently, despite the potential for light's color information to be widely useful in daily life, spectroscopic technology has been limited to laboratory or industrial manufacturing environments.
< Figure 1. Through a simple structure consisting of a double layer of disordered metasurfaces and an image sensor, it was shown that speckles of predictable spectral channels with high spectral resolution can be generated in a compact form factor. The high similarity between the measured and calculated speckles was used to solve the inverse problem and verify the ability to reconstruct the spectrum. >
The research team devised a method that departs from the conventional spectroscopic paradigm of using diffraction gratings or prisms, which establish a one-to-one correspondence between light's color information and its propagation direction, by utilizing designed disordered structures as optical components. In this process, they employed metasurfaces, which can freely control the light propagation process using structures tens to hundreds of nanometers in size, to accurately implement 'complex random patterns (speckle*)'.
*Speckle: An irregular pattern of light intensity created by the interference of multiple wavefronts of light.
Specifically, they developed a method that involves implementing a double-layer disordered metasurface to generate wavelength-specific speckle patterns and then reconstructing precise color information (wavelength) of the light from the random patterns measured by a camera.
As a result, they successfully developed a new concept spectrometer technology that can accurately measure light across a broad range of visible to infrared (440-1,300nm) with a high resolution of 1 nanometer (nm) in a device smaller than a fingernail (less than 1cm) using only a single image capture.
< Figure 2. A disordered metasurface is a metasurface with irregularly arranged structures ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers in size. In a double-layer structure, a propagation space is placed between the two metasurfaces to control the output speckle with high degrees of freedom, thereby achieving a spectral resolution of 1 nm even in a form factor smaller than 1 cm. >
Dong-gu Lee, a lead author of this study, stated, "This technology is implemented in a way that is directly integrated with commercial image sensors, and we expect that it will enable easy acquisition and utilization of light's wavelength information in daily life when built into mobile devices in the future."
Professor Mooseok Jang said, "This technology overcomes the limitations of existing RGB three-color based machine vision fields, which only distinguish and recognize three color components (red, green, blue), and has diverse applications. We anticipate various applied research for this technology, which expands the horizon of laboratory-level technology to daily-level machine vision technology for applications such as food component analysis, crop health diagnosis, skin health measurement, environmental pollution detection, and bio/medical diagnostics." He added, "Furthermore, it can be extended to various advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging, which records wavelength and spatial information simultaneously with high resolution, 3D optical trapping technology, which precisely controls light of multiple wavelengths into desired forms, and ultrafast imaging technology, which captures phenomena occurring in very short periods."
This research was collaboratively led by Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering as co-first authors, with Professor Mooseok Jang as the corresponding author. The findings were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 28, 2025.* Paper Title: Reconstructive spectrometer using double-layer disordered metasurfaces* DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv2376
This research was supported by the Samsung Research Funding and Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics grant, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT), and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT).
2025.06.13 View 1145
High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST Researchers
- Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering develops an ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer using 'double-layer disordered metasurfaces' that generate unique random patterns depending on light's color.
- Unlike conventional dispersion-based spectrometers that were difficult to apply to portable devices, this new concept spectrometer technology achieves 1nm-level high resolution in a device smaller than 1cm, comparable in size to a fingernail.
- It can be utilized as a built-in spectrometer in smartphones and wearable devices in the future, and can be expanded to advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging and ultrafast imaging.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Mooseok Jang, Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate), Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) >
Color, as the way light's wavelength is perceived by the human eye, goes beyond a simple aesthetic element, containing important scientific information like a substance's composition or state. Spectrometers are optical devices that analyze material properties by decomposing light into its constituent wavelengths, and they are widely used in various scientific and industrial fields, including material analysis, chemical component detection, and life science research. Existing high-resolution spectrometers were large and complex, making them difficult for widespread daily use. However, thanks to the ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer developed by KAIST researchers, it is now expected that light's color information can be utilized even within smartphones or wearable devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 13th that Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has successfully developed a reconstruction-based spectrometer technology using double-layer disordered metasurfaces*.
*Double-layer disordered metasurface: An innovative optical device that complexly scatters light through two layers of disordered nanostructures, creating unique and predictable speckle patterns for each wavelength.
Existing high-resolution spectrometers have a large form factor, on the order of tens of centimeters, and require complex calibration processes to maintain accuracy. This fundamentally stems from the operating principle of traditional dispersive elements, such as gratings and prisms, which separate light wavelengths along the propagation direction, much like a rainbow separates colors. Consequently, despite the potential for light's color information to be widely useful in daily life, spectroscopic technology has been limited to laboratory or industrial manufacturing environments.
< Figure 1. Through a simple structure consisting of a double layer of disordered metasurfaces and an image sensor, it was shown that speckles of predictable spectral channels with high spectral resolution can be generated in a compact form factor. The high similarity between the measured and calculated speckles was used to solve the inverse problem and verify the ability to reconstruct the spectrum. >
The research team devised a method that departs from the conventional spectroscopic paradigm of using diffraction gratings or prisms, which establish a one-to-one correspondence between light's color information and its propagation direction, by utilizing designed disordered structures as optical components. In this process, they employed metasurfaces, which can freely control the light propagation process using structures tens to hundreds of nanometers in size, to accurately implement 'complex random patterns (speckle*)'.
*Speckle: An irregular pattern of light intensity created by the interference of multiple wavefronts of light.
Specifically, they developed a method that involves implementing a double-layer disordered metasurface to generate wavelength-specific speckle patterns and then reconstructing precise color information (wavelength) of the light from the random patterns measured by a camera.
As a result, they successfully developed a new concept spectrometer technology that can accurately measure light across a broad range of visible to infrared (440-1,300nm) with a high resolution of 1 nanometer (nm) in a device smaller than a fingernail (less than 1cm) using only a single image capture.
< Figure 2. A disordered metasurface is a metasurface with irregularly arranged structures ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers in size. In a double-layer structure, a propagation space is placed between the two metasurfaces to control the output speckle with high degrees of freedom, thereby achieving a spectral resolution of 1 nm even in a form factor smaller than 1 cm. >
Dong-gu Lee, a lead author of this study, stated, "This technology is implemented in a way that is directly integrated with commercial image sensors, and we expect that it will enable easy acquisition and utilization of light's wavelength information in daily life when built into mobile devices in the future."
Professor Mooseok Jang said, "This technology overcomes the limitations of existing RGB three-color based machine vision fields, which only distinguish and recognize three color components (red, green, blue), and has diverse applications. We anticipate various applied research for this technology, which expands the horizon of laboratory-level technology to daily-level machine vision technology for applications such as food component analysis, crop health diagnosis, skin health measurement, environmental pollution detection, and bio/medical diagnostics." He added, "Furthermore, it can be extended to various advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging, which records wavelength and spatial information simultaneously with high resolution, 3D optical trapping technology, which precisely controls light of multiple wavelengths into desired forms, and ultrafast imaging technology, which captures phenomena occurring in very short periods."
This research was collaboratively led by Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering as co-first authors, with Professor Mooseok Jang as the corresponding author. The findings were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 28, 2025.* Paper Title: Reconstructive spectrometer using double-layer disordered metasurfaces* DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv2376
This research was supported by the Samsung Research Funding and Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics grant, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT), and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT).
2025.06.13 View 1145 -
 Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
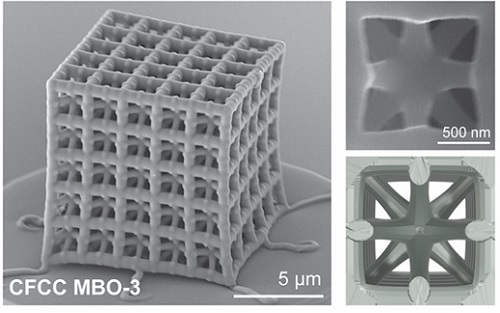
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4816
Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4816 -
 KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7286
KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7286 -
 KAIST Develops CamBio - a New Biotemplating Method
- Professor Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung’s joint research team of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a highly tunable bio-templating method “CamBio” that makes use of intracellular protein structures
- Substrate performance improvement of up to 230% demonstrated via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
- Expected to have price competitiveness over bio-templating method as it expands the range of biological samples
- Expected to expand the range of application of nanostructure synthesis technology by utilizing various biological structures
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Yeon Sik Jung, Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song, Professor Jae-Byum Chang, and (from top right) Dr. Chang Woo Song and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
Biological structures have complex characteristics that are difficult to replicate artificially, but biotemplating methods* that directly utilize these biological structures have been used in various fields of application. The KAIST research team succeeded in utilizing previously unusable biological structures and expanding the areas in which biotemplate methods can be applied.
*Biotemplating: A method of using biotemplates as a mold to create functional structural materials, utilizing the functions of these biological structures, from viruses to the tissues and organs that make up our bodies
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a joint research team of Professors Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a biotemplating method that utilizes specific intracellular proteins in biological samples and has high tunability.
Existing biotemplate methods mainly utilize only the external surface of biological samples or have limitations in utilizing the structure-function correlation of various biological structures due to limited dimensions and sample sizes, making it difficult to create functional nanostructures.
To solve this problem, the research team studied a way to utilize various biological structures within the cells while retaining high tunability.
< Figure 1. CamBio utilizing microtubules, a intracellular protein structure. The silver nanoparticle chains synthesized along the microtubules that span the entire cell interior can be observed through an electron microscope, and it is shown that this can be used as a successful SERS substrate. >
As a result of the research, the team developed the “Conversion to advanced materials via labeled Biostructure”, shortened as “CamBio”, which enables the selective synthesis of nanostructures with various characteristics and sizes from specific protein structures composed of diverse proteins within biological specimens.
The CamBio method secures high tunability of functional nanostructures that can be manufactured from biological samples by merging various manufacturing and biological technologies.
Through the technology of repeatedly attaching antibodies, arranging cells in a certain shape, and thinly slicing tissue, the functional nanostructures made with CamBio showed improved performance on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)* substrate used for material detection.
*Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): A technology that can detect very small amounts of substances using light, based on the principle that specific substances react to light and amplifies signals on surfaces of metals such as gold or silver.
The research team found that the nanoparticle chains made using the intracellular protein structures through the process of repeated labeling with antibodies allowed easier control, and improved SERS performance by up to 230%.
In addition, the research team expanded from utilizing the structures inside cells to obtaining samples of muscle tissues inside meat using a cryostat and successfully producing a substrate with periodic bands made of metal particles by performing the CamBio process. This method of producing a substrate not only allows large-scale production using biological samples, but also shows that it is a cost-effective method.
< Figure 2. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the cell level. Examples of controlling characteristics by integrating iterative labeling and cell pattering techniques with CamBio are shown. >
The CamBio developed by the research team is expected to be used as a way to solve problems faced by various research fields as it is to expand the range of bio-samples that can be produced for various usage.
The first author, Dae-Hyeon Song, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering said, “Through CamBio, we have comprehensively accumulated biotemplating methods that can utilize more diverse protein structures,” and “If combined with the state-of-the-art biological technologies such as gene editing and 3D bioprinting and new material synthesis technologies, biostructures can be utilized in various fields of application.”
< Figure 3. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the tissue level. In order to utilize proteins inside muscle tissue, the frozen tissue sectioning technology is combined, and through this, a substrate with a periodic nanoparticle band pattern is successfully produced, and it is shown that large-area acquisition of samples and price competitiveness can be achieved. >
This study, in which the Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song along with Dr. Chang Woo Song, and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the same department participated as the first authors, was published online in the international academic journal, Advanced Science, on November 13th, 2024.
(Paper title: Highly Tunable, Nanomaterial-Functionalized Structural Templating of Intracellular Protein Structures Within Biological Species) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202406492
This study was conducted with a combination of support from various programs including the National Convergence Research of Scientific Challenges (National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) 2024), Engineering Reseach Center (ERC) (Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, NRF 2023), ERC (Global Bio-integrated Materials Center, NRF 2024), and the National Advanced Program for Biological Research Resources (Bioimaging Data Curation Center, NRF 2024) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.01.10 View 4846
KAIST Develops CamBio - a New Biotemplating Method
- Professor Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung’s joint research team of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a highly tunable bio-templating method “CamBio” that makes use of intracellular protein structures
- Substrate performance improvement of up to 230% demonstrated via surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)
- Expected to have price competitiveness over bio-templating method as it expands the range of biological samples
- Expected to expand the range of application of nanostructure synthesis technology by utilizing various biological structures
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Yeon Sik Jung, Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song, Professor Jae-Byum Chang, and (from top right) Dr. Chang Woo Song and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering >
Biological structures have complex characteristics that are difficult to replicate artificially, but biotemplating methods* that directly utilize these biological structures have been used in various fields of application. The KAIST research team succeeded in utilizing previously unusable biological structures and expanding the areas in which biotemplate methods can be applied.
*Biotemplating: A method of using biotemplates as a mold to create functional structural materials, utilizing the functions of these biological structures, from viruses to the tissues and organs that make up our bodies
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th that a joint research team of Professors Jae-Byum Chang and Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a biotemplating method that utilizes specific intracellular proteins in biological samples and has high tunability.
Existing biotemplate methods mainly utilize only the external surface of biological samples or have limitations in utilizing the structure-function correlation of various biological structures due to limited dimensions and sample sizes, making it difficult to create functional nanostructures.
To solve this problem, the research team studied a way to utilize various biological structures within the cells while retaining high tunability.
< Figure 1. CamBio utilizing microtubules, a intracellular protein structure. The silver nanoparticle chains synthesized along the microtubules that span the entire cell interior can be observed through an electron microscope, and it is shown that this can be used as a successful SERS substrate. >
As a result of the research, the team developed the “Conversion to advanced materials via labeled Biostructure”, shortened as “CamBio”, which enables the selective synthesis of nanostructures with various characteristics and sizes from specific protein structures composed of diverse proteins within biological specimens.
The CamBio method secures high tunability of functional nanostructures that can be manufactured from biological samples by merging various manufacturing and biological technologies.
Through the technology of repeatedly attaching antibodies, arranging cells in a certain shape, and thinly slicing tissue, the functional nanostructures made with CamBio showed improved performance on the surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS)* substrate used for material detection.
*Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS): A technology that can detect very small amounts of substances using light, based on the principle that specific substances react to light and amplifies signals on surfaces of metals such as gold or silver.
The research team found that the nanoparticle chains made using the intracellular protein structures through the process of repeated labeling with antibodies allowed easier control, and improved SERS performance by up to 230%.
In addition, the research team expanded from utilizing the structures inside cells to obtaining samples of muscle tissues inside meat using a cryostat and successfully producing a substrate with periodic bands made of metal particles by performing the CamBio process. This method of producing a substrate not only allows large-scale production using biological samples, but also shows that it is a cost-effective method.
< Figure 2. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the cell level. Examples of controlling characteristics by integrating iterative labeling and cell pattering techniques with CamBio are shown. >
The CamBio developed by the research team is expected to be used as a way to solve problems faced by various research fields as it is to expand the range of bio-samples that can be produced for various usage.
The first author, Dae-Hyeon Song, a Ph.D. candidate of KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering said, “Through CamBio, we have comprehensively accumulated biotemplating methods that can utilize more diverse protein structures,” and “If combined with the state-of-the-art biological technologies such as gene editing and 3D bioprinting and new material synthesis technologies, biostructures can be utilized in various fields of application.”
< Figure 3. A method for securing tunability using CamBio at the tissue level. In order to utilize proteins inside muscle tissue, the frozen tissue sectioning technology is combined, and through this, a substrate with a periodic nanoparticle band pattern is successfully produced, and it is shown that large-area acquisition of samples and price competitiveness can be achieved. >
This study, in which the Ph.D. candidate Dae-Hyeon Song along with Dr. Chang Woo Song, and Dr. Seunghee H. Cho of the same department participated as the first authors, was published online in the international academic journal, Advanced Science, on November 13th, 2024.
(Paper title: Highly Tunable, Nanomaterial-Functionalized Structural Templating of Intracellular Protein Structures Within Biological Species) https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202406492
This study was conducted with a combination of support from various programs including the National Convergence Research of Scientific Challenges (National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) 2024), Engineering Reseach Center (ERC) (Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center, NRF 2023), ERC (Global Bio-integrated Materials Center, NRF 2024), and the National Advanced Program for Biological Research Resources (Bioimaging Data Curation Center, NRF 2024) funded by Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.01.10 View 4846 -
 KAIST Scientifically Identifies a Method to Prevent Dental Erosion from Carbonated Drinks
A Korean research team, which had previously visualized and scientifically proven the harmful effects of carbonated drinks like cola on dental health using nanotechnology, has now identified a mechanism for an effective method to prevent tooth damage caused by these beverages.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of December that a team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Seoul National University's School of Dentistry (Departments of Pediatric Dentistry and Oral Microbiology) and Professor Hye Ryung Byon’s research team from the Department of Chemistry, has revealed through nanotechnology that silver diamine fluoride (SDF)* forms a fluoride-containing protective layer on the tooth surface, effectively inhibiting cola-induced erosion.
*SDF (Silver Diamine Fluoride): A dental agent primarily used for the treatment and prevention of tooth decay. SDF strengthens carious lesions, suppresses bacterial growth, and halts the progression of cavities.
The team analyzed the surface morphology and mechanical properties of tooth enamel on a nanoscale using atomic force microscopy (AFM). They also examined the chemical properties of the nano-film formed by SDF treatment using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)* and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)*.
*XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy): A powerful surface analysis technique used to investigate the chemical composition and electronic structure of materials.
*FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): An analytical method that identifies the molecular structure and composition of materials by analyzing how they absorb or transmit infrared light.
The findings showed significant differences in surface roughness and elastic modulus between teeth exposed to cola with and without SDF treatment. Teeth treated with SDF exhibited minimal changes in surface roughness due to erosion (from 64 nm to 70 nm) and maintained a high elastic modulus (from 215 GPa to 205 GPa).
This was attributed to the formation of a fluoroapatite* layer by SDF, which acted as a protective shield.
*Fluoroapatite: A phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Ca₅(PO₄)₃F (calcium fluoro-phosphate). It can occur naturally or be synthesized biologically/artificially and plays a crucial role in strengthening teeth and bones.
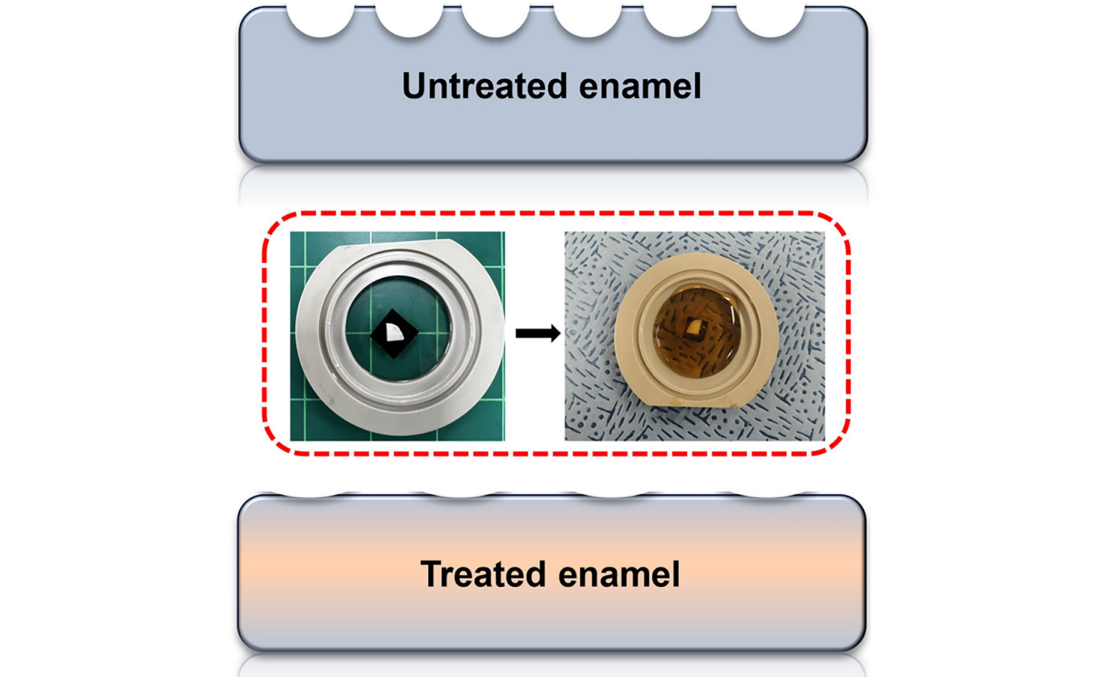
< Figure 1. Schematic of the workflow. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of untreated and treated silver diamine fluoride (SDF) treated enamel exposed to cola were analyzed over time using atomic force microscopy (AFM). >
Professor Young J. Kim from Seoul National University's Department of Pediatric Dentistry noted, "This technology could be applied to prevent dental erosion and strengthen teeth for both children and adults. It is a cost-effective and accessible dental treatment."
< Figure 2. Changes in surface roughness and elastic modulus according to time of exposure to cola for SDF untreated and treated teeth. After 1 hour, the surface roughness of the SDF untreated teeth rapidly became rougher from 83 nm to 287 nm and the elastic modulus weakened from 125 GPa to 13 GPa, whereas the surface roughness of the SDF treated teeth changed only slightly from 64 nm to 70 nm and the elastic modulus barely changed from 215 GPa to 205 GPa, maintaining a similar state to the initial state. >
Professor Seungbum Hong emphasized, "Dental health significantly impacts quality of life. This research offers an effective non-invasive method to prevent early dental erosion, moving beyond traditional surgical treatments. By simply applying SDF, dental erosion can be prevented and enamel strengthened, potentially reducing pain and costs associated with treatment."
This study, led by the first author Aditi Saha, a PhD student in KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was published in the international journal Biomaterials Research on November 7 under the title "Nanoscale Study on Noninvasive Prevention of Dental Erosion of Enamel by Silver Diamine Fluoride". The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.12.11 View 4999
KAIST Scientifically Identifies a Method to Prevent Dental Erosion from Carbonated Drinks
A Korean research team, which had previously visualized and scientifically proven the harmful effects of carbonated drinks like cola on dental health using nanotechnology, has now identified a mechanism for an effective method to prevent tooth damage caused by these beverages.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of December that a team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Seoul National University's School of Dentistry (Departments of Pediatric Dentistry and Oral Microbiology) and Professor Hye Ryung Byon’s research team from the Department of Chemistry, has revealed through nanotechnology that silver diamine fluoride (SDF)* forms a fluoride-containing protective layer on the tooth surface, effectively inhibiting cola-induced erosion.
*SDF (Silver Diamine Fluoride): A dental agent primarily used for the treatment and prevention of tooth decay. SDF strengthens carious lesions, suppresses bacterial growth, and halts the progression of cavities.
The team analyzed the surface morphology and mechanical properties of tooth enamel on a nanoscale using atomic force microscopy (AFM). They also examined the chemical properties of the nano-film formed by SDF treatment using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)* and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)*.
*XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy): A powerful surface analysis technique used to investigate the chemical composition and electronic structure of materials.
*FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): An analytical method that identifies the molecular structure and composition of materials by analyzing how they absorb or transmit infrared light.
The findings showed significant differences in surface roughness and elastic modulus between teeth exposed to cola with and without SDF treatment. Teeth treated with SDF exhibited minimal changes in surface roughness due to erosion (from 64 nm to 70 nm) and maintained a high elastic modulus (from 215 GPa to 205 GPa).
This was attributed to the formation of a fluoroapatite* layer by SDF, which acted as a protective shield.
*Fluoroapatite: A phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Ca₅(PO₄)₃F (calcium fluoro-phosphate). It can occur naturally or be synthesized biologically/artificially and plays a crucial role in strengthening teeth and bones.
< Figure 1. Schematic of the workflow. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of untreated and treated silver diamine fluoride (SDF) treated enamel exposed to cola were analyzed over time using atomic force microscopy (AFM). >
Professor Young J. Kim from Seoul National University's Department of Pediatric Dentistry noted, "This technology could be applied to prevent dental erosion and strengthen teeth for both children and adults. It is a cost-effective and accessible dental treatment."
< Figure 2. Changes in surface roughness and elastic modulus according to time of exposure to cola for SDF untreated and treated teeth. After 1 hour, the surface roughness of the SDF untreated teeth rapidly became rougher from 83 nm to 287 nm and the elastic modulus weakened from 125 GPa to 13 GPa, whereas the surface roughness of the SDF treated teeth changed only slightly from 64 nm to 70 nm and the elastic modulus barely changed from 215 GPa to 205 GPa, maintaining a similar state to the initial state. >
Professor Seungbum Hong emphasized, "Dental health significantly impacts quality of life. This research offers an effective non-invasive method to prevent early dental erosion, moving beyond traditional surgical treatments. By simply applying SDF, dental erosion can be prevented and enamel strengthened, potentially reducing pain and costs associated with treatment."
This study, led by the first author Aditi Saha, a PhD student in KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was published in the international journal Biomaterials Research on November 7 under the title "Nanoscale Study on Noninvasive Prevention of Dental Erosion of Enamel by Silver Diamine Fluoride". The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.12.11 View 4999 -
 KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5758
KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5758 -
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6280
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 6280 -
 KAIST begins full-scale cooperation with Taiwan’s Formosa Group
< (From left) Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-Soo Kim, and Professor Minee Choi of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences of KAIST along with Chairman of Formosa Group Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee, and Dean Daesoo Kim of KAIST College of Life Science and Bioengineering >
KAIST is pursuing cooperation in the fields of advanced biotechnology and eco-friendly energy with Formosa Plastics Group, one of Taiwan's three largest companies.
To this end, Chairman Sandy Wang, a member of Formosa Group's standing committee and leader of the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sector, will visit KAIST on the 13th of this month. This is the first time that the owner of Formosa Group has made an official visit to KAIST.
Cooperation between the two institutions began last March when our university signed a memorandum of understanding on comprehensive exchange and cooperation with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University(長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital(長庚記念醫院), three of many institutions established and supported by Formosa Group.
Based on this, Chairman Sandy Wang, who visits our university to promote more exchanges and cooperation, talked about ‘the education of children and corporate social return and practice of his father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang,’ through a special lecture for the school leadership as a part of the Monthly Lecture on KAIST’s Leadership Innovation Day.
She then visited KAIST's research and engineering facilities related to Taiwan's future industries, such as advanced biotechnology and eco-friendly energy, and discussed global industry-academic cooperation plans. In the future, the two organizations plan to appoint adjunct professors and promote practical global cooperation, including joint student guidance and research cooperation. We plan to pursue effective mid- to long-term cooperation, such as conducting battery application research with the KAIST Next-Generation ESS Research Center and opening a graduate program specialized in stem cell and gene editing technology in connection with Chang Gung University and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. The newly established cooperative relationship will also promote Formosa Group's investment and cooperation with KAIST's outstanding venture companies related to bio and eco-friendly energy to lay the foundation for innovative industrial cooperation between Taiwan and Korea.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The Formosa Group has a global network, so we regard it to be a key partner that will position KAIST’s bio and engineering technology in the global stages.” He also said, “With Chairman Sandy Wang’s visit, Taiwan is emerging as a global economic powerhouse,” and added, “We expect to continue our close cooperative relationship with the company.”
Formosa Group is a company founded by the late Chairman Yung-Ching Wang, the father of Chairman Sandy Wang. As the world's No. 1 plastic PVC producer, it is leading the core industries of Taiwan's economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people by setting an example of returning his wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he built ‘belonged to the people.’ Chang Gung University, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, and Ming Chi University of Technology, which are pursuing cooperation with our university, were also established as part of the social contribution promoted by Chairman Yung-Ching Wang and are receiving financial support from Formosa Group.
2024.05.09 View 6673
KAIST begins full-scale cooperation with Taiwan’s Formosa Group
< (From left) Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-Soo Kim, and Professor Minee Choi of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences of KAIST along with Chairman of Formosa Group Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee, and Dean Daesoo Kim of KAIST College of Life Science and Bioengineering >
KAIST is pursuing cooperation in the fields of advanced biotechnology and eco-friendly energy with Formosa Plastics Group, one of Taiwan's three largest companies.
To this end, Chairman Sandy Wang, a member of Formosa Group's standing committee and leader of the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sector, will visit KAIST on the 13th of this month. This is the first time that the owner of Formosa Group has made an official visit to KAIST.
Cooperation between the two institutions began last March when our university signed a memorandum of understanding on comprehensive exchange and cooperation with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University(長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital(長庚記念醫院), three of many institutions established and supported by Formosa Group.
Based on this, Chairman Sandy Wang, who visits our university to promote more exchanges and cooperation, talked about ‘the education of children and corporate social return and practice of his father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang,’ through a special lecture for the school leadership as a part of the Monthly Lecture on KAIST’s Leadership Innovation Day.
She then visited KAIST's research and engineering facilities related to Taiwan's future industries, such as advanced biotechnology and eco-friendly energy, and discussed global industry-academic cooperation plans. In the future, the two organizations plan to appoint adjunct professors and promote practical global cooperation, including joint student guidance and research cooperation. We plan to pursue effective mid- to long-term cooperation, such as conducting battery application research with the KAIST Next-Generation ESS Research Center and opening a graduate program specialized in stem cell and gene editing technology in connection with Chang Gung University and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. The newly established cooperative relationship will also promote Formosa Group's investment and cooperation with KAIST's outstanding venture companies related to bio and eco-friendly energy to lay the foundation for innovative industrial cooperation between Taiwan and Korea.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “The Formosa Group has a global network, so we regard it to be a key partner that will position KAIST’s bio and engineering technology in the global stages.” He also said, “With Chairman Sandy Wang’s visit, Taiwan is emerging as a global economic powerhouse,” and added, “We expect to continue our close cooperative relationship with the company.”
Formosa Group is a company founded by the late Chairman Yung-Ching Wang, the father of Chairman Sandy Wang. As the world's No. 1 plastic PVC producer, it is leading the core industries of Taiwan's economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people by setting an example of returning his wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he built ‘belonged to the people.’ Chang Gung University, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, and Ming Chi University of Technology, which are pursuing cooperation with our university, were also established as part of the social contribution promoted by Chairman Yung-Ching Wang and are receiving financial support from Formosa Group.
2024.05.09 View 6673 -
 'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 9324
'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 9324 -
 KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 11318
KAIST’s unmanned racing car to race in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 as the only contender representing Asia
- Professor David Hyunchul Shim of the School of Electrical Engineering, is at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway in Las Vegas, Nevada with his students of the Unmanned Systems Research Group (USRG), participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES as the only Asian team in the race.
Photo 1. Nine teams that competed at the first Indy Autonomous Challenge on October 23, 2021. (KAIST team is the right most team in the front row)
- The EE USRG team won the slot to race in the IAC @ CES 2023 rightly as the semifinals entree of the IAC @ CES 2022’ held in January of last year
- Through the partnership with Hyundai Motor Company, USRG received support to participate in the competition, and is to share the latest developments and trends of the technology with the company researchers
- With upgrades from last year, USRG is to race with a high-speed Indy racing car capable of driving up to 300 km/h and the technology developed in the process is to be used in further advancement of the high-speed autonomous vehicle technology of the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that it will participate in the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC) @ CES 2023”, an official event of the world's largest electronics and information technology exhibition held every year in Las Vegas, Nevada, of the United States from January 5th to 8th.
Photo 2. KAIST Racing Team participating in the Indy Autonomous Challenge @ CES 2023 (Team Leader: Sungwon Na, Team Members: Seongwoo Moon, Hyunwoo Nam, Chanhoe Ryu, Jaeyoung Kang)
“IAC @ CES 2023”, which is to be held at the Las Vegas Motor Speedway (LVMS) on January 7, seeks to advance technology developed as the result of last year's competition to share the results of such advanced high-speed autonomous vehicle technology with the public.
This competition is the 4th competition following the “Indy Autonomous Challenge (IAC)” held for the first time in Indianapolis, USA on October 23, 2021. At the IAC @ CES 2022 following the first IAC competition, the Unmmaned Systems Research Group (USRG) team led by Professor David Hyunchul Shim advanced to the semifinals out of a total of nine teams and won a spot to participate in CES 2023. As a result, the USRG comes into the challenge as the only Asian team to compete with other teams comprised of students and researchers of American and European backgrounds where the culture of motorsports is more deep-rooted.
For CES 2022, Professor David Hyunchul Shim’s research team was able to successfully develop a software that controlled the racing car to comply with the race flags and regulations while going up to 240 km/h all on its on.
Photo 3. KAIST Team’s vehicle on Las Vegas Motor Speedway during the IAC @ CES 2022
In the IAC @ CES 2023, the official racing vehicle AV-23, is a converted version of IL-15, the official racing car for Indy 500, fully automated while maintaining the optimal design for high-speed racing, and was upgraded from the last year’s competition taking up the highest speed up to 300 km/h.
This year’s competition, will develop on last year’s head-to-head autonomous racing and take the form of the single elimination tournament to have the cars overtake the others without any restrictions on the driving course, which would have the team that constantly drives at the fastest speed will win the competition.
Photo 4. KAIST Team’s vehicle overtaking the Italian team, PoliMOVE’s vehicle during one of the race in the IAC @ CES 2022
Professor Shim's team further developed on the CES 2022 certified software to fine tune the external recognition mechanisms and is now focused on precise positioning and driving control technology that factors into maintaining stability even when driving at high speed.
Professor Shim's research team won the Autonomous Driving Competition hosted by Hyundai Motor Company in 2021. Starting with this CES 2023 competition, they signed a partnership contract with Hyundai to receive financial support to participate in the CES competition and share the latest developments and trends of autonomous driving technology with Hyundai Motor's research team.
During CES 2023, the research team will also participate in other events such as the exhibition by the KAIST racing team at the IAC’s official booth located in the West Hall.
Professor David Hyunchul Shim said, “With these competitions being held overseas, there were many difficulties having to keep coming back, but the students took part in it diligently, for which I am deeply grateful. Thanks to their efforts, we were able to continue in this competition, which will be a way to verify the autonomous driving technology that we developed ourselves over the past 13 years, and I highly appreciate that.”
“While high-speed autonomous driving technology is a technology that is not yet sought out in Korea, but it can be applied most effectively for long-distance travel in the Korea,” he went on to add. “It has huge advantages in that it does not require constructions for massive infrastructure that costs enormous amount of money such as high-speed rail or urban aviation and with our design, it is minimally affected by weather conditions.” he emphasized.
On a different note, the IAC @ CES 2023 is co-hosted by the Consumer Technology Association (CTA) and Energy Systems Network (ESN), the organizers of CES. Last year’s IAC winner, Technische Universität München of Germany, and MIT-PITT-RW, a team of Massachusetts Institute of Technology (Massachusetts), University of Pittsburgh (Pennsylvania), Rochester Institute of Technology (New York), University of Waterloo (Canada), with and the University of Waterloo, along with TII EuroRacing - University of Modena and Reggio Emilia (Italy), Technology Innovation Institute (United Arab Emirates), and five other teams are in the race for the win against KAIST.
Photo 5. KAIST Team’s vehicle on the track during the IAC @ CES 2022
The Indy Autonomous Challenge is scheduled to hold its fifth competition at the Monza track in Italy in June 2023 and the sixth competition at CES 2024.
2023.01.05 View 11318 -
 'Fingerprint' Machine Learning Technique Identifies Different Bacteria in Seconds
A synergistic combination of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and deep learning serves as an effective platform for separation-free detection of bacteria in arbitrary media
Bacterial identification can take hours and often longer, precious time when diagnosing infections and selecting appropriate treatments. There may be a quicker, more accurate process according to researchers at KAIST. By teaching a deep learning algorithm to identify the “fingerprint” spectra of the molecular components of various bacteria, the researchers could classify various bacteria in different media with accuracies of up to 98%.
Their results were made available online on Jan. 18 in Biosensors and Bioelectronics, ahead of publication in the journal’s April issue.
Bacteria-induced illnesses, those caused by direct bacterial infection or by exposure to bacterial toxins, can induce painful symptoms and even lead to death, so the rapid detection of bacteria is crucial to prevent the intake of contaminated foods and to diagnose infections from clinical samples, such as urine. “By using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analysis boosted with a newly proposed deep learning model, we demonstrated a markedly simple, fast, and effective route to classify the signals of two common bacteria and their resident media without any separation procedures,” said Professor Sungho Jo from the School of Computing.
Raman spectroscopy sends light through a sample to see how it scatters. The results reveal structural information about the sample — the spectral fingerprint — allowing researchers to identify its molecules. The surface-enhanced version places sample cells on noble metal nanostructures that help amplify the sample’s signals.
However, it is challenging to obtain consistent and clear spectra of bacteria due to numerous overlapping peak sources, such as proteins in cell walls. “Moreover, strong signals of surrounding media are also enhanced to overwhelm target signals, requiring time-consuming and tedious bacterial separation steps,” said Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
To parse through the noisy signals, the researchers implemented an artificial intelligence method called deep learning that can hierarchically extract certain features of the spectral information to classify data. They specifically designed their model, named the dual-branch wide-kernel network (DualWKNet), to efficiently learn the correlation between spectral features. Such an ability is critical for analyzing one-dimensional spectral data, according to Professor Jo.
“Despite having interfering signals or noise from the media, which make the general shapes of different bacterial spectra and their residing media signals look similar, high classification accuracies of bacterial types and their media were achieved,” Professor Jo said, explaining that DualWKNet allowed the team to identify key peaks in each class that were almost indiscernible in individual spectra, enhancing the classification accuracies. “Ultimately, with the use of DualWKNet replacing the bacteria and media separation steps, our method dramatically reduces analysis time.”
The researchers plan to use their platform to study more bacteria and media types, using the information to build a training data library of various bacterial types in additional media to reduce the collection and detection times for new samples.
“We developed a meaningful universal platform for rapid bacterial detection with the collaboration between SERS and deep learning,” Professor Jo said. “We hope to extend the use of our deep learning-based SERS analysis platform to detect numerous types of bacteria in additional media that are important for food or clinical analysis, such as blood.”
The National R&D Program, through a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, supported this research.
-PublicationEojin Rho, Minjoon Kim, Seunghee H. Cho, Bongjae Choi, Hyungjoon Park, Hanhwi Jang, Yeon Sik Jung, Sungho Jo, “Separation-free bacterial identification in arbitrary media via deepneural network-based SERS analysis,” Biosensors and Bioelectronics online January 18, 2022 (doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113991)
-ProfileProfessor Yeon Sik JungDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sungho JoSchool of ComputingKAIST
2022.03.04 View 23016
'Fingerprint' Machine Learning Technique Identifies Different Bacteria in Seconds
A synergistic combination of surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy and deep learning serves as an effective platform for separation-free detection of bacteria in arbitrary media
Bacterial identification can take hours and often longer, precious time when diagnosing infections and selecting appropriate treatments. There may be a quicker, more accurate process according to researchers at KAIST. By teaching a deep learning algorithm to identify the “fingerprint” spectra of the molecular components of various bacteria, the researchers could classify various bacteria in different media with accuracies of up to 98%.
Their results were made available online on Jan. 18 in Biosensors and Bioelectronics, ahead of publication in the journal’s April issue.
Bacteria-induced illnesses, those caused by direct bacterial infection or by exposure to bacterial toxins, can induce painful symptoms and even lead to death, so the rapid detection of bacteria is crucial to prevent the intake of contaminated foods and to diagnose infections from clinical samples, such as urine. “By using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) analysis boosted with a newly proposed deep learning model, we demonstrated a markedly simple, fast, and effective route to classify the signals of two common bacteria and their resident media without any separation procedures,” said Professor Sungho Jo from the School of Computing.
Raman spectroscopy sends light through a sample to see how it scatters. The results reveal structural information about the sample — the spectral fingerprint — allowing researchers to identify its molecules. The surface-enhanced version places sample cells on noble metal nanostructures that help amplify the sample’s signals.
However, it is challenging to obtain consistent and clear spectra of bacteria due to numerous overlapping peak sources, such as proteins in cell walls. “Moreover, strong signals of surrounding media are also enhanced to overwhelm target signals, requiring time-consuming and tedious bacterial separation steps,” said Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering.
To parse through the noisy signals, the researchers implemented an artificial intelligence method called deep learning that can hierarchically extract certain features of the spectral information to classify data. They specifically designed their model, named the dual-branch wide-kernel network (DualWKNet), to efficiently learn the correlation between spectral features. Such an ability is critical for analyzing one-dimensional spectral data, according to Professor Jo.
“Despite having interfering signals or noise from the media, which make the general shapes of different bacterial spectra and their residing media signals look similar, high classification accuracies of bacterial types and their media were achieved,” Professor Jo said, explaining that DualWKNet allowed the team to identify key peaks in each class that were almost indiscernible in individual spectra, enhancing the classification accuracies. “Ultimately, with the use of DualWKNet replacing the bacteria and media separation steps, our method dramatically reduces analysis time.”
The researchers plan to use their platform to study more bacteria and media types, using the information to build a training data library of various bacterial types in additional media to reduce the collection and detection times for new samples.
“We developed a meaningful universal platform for rapid bacterial detection with the collaboration between SERS and deep learning,” Professor Jo said. “We hope to extend the use of our deep learning-based SERS analysis platform to detect numerous types of bacteria in additional media that are important for food or clinical analysis, such as blood.”
The National R&D Program, through a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, supported this research.
-PublicationEojin Rho, Minjoon Kim, Seunghee H. Cho, Bongjae Choi, Hyungjoon Park, Hanhwi Jang, Yeon Sik Jung, Sungho Jo, “Separation-free bacterial identification in arbitrary media via deepneural network-based SERS analysis,” Biosensors and Bioelectronics online January 18, 2022 (doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.113991)
-ProfileProfessor Yeon Sik JungDepartment of Materials Science and EngineeringKAIST
Professor Sungho JoSchool of ComputingKAIST
2022.03.04 View 23016