PET
-
 Hyung Kyu Lim, Former KAIST Alumni Association President, Donates 100 Million Won for a Challenge to Follow “I am a KAIST”
Hyung Kyu Lim, a former President of the KAIST Alumni Association, has donated 100 million won as the prize money for the School Song and National Anthem Challenge. This donation will be used as prize money starting from the 2026 competition and is expected to play a significant role in spreading KAIST's educational culture and fostering a sense of community.
< Photo 1. KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee (left) and the former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim at the ceremony for the signing of the pledge for Dr. Lim's donation. >
The School Song and National Anthem Challenge was first conceived in 2024 at the suggestion of President Kwang-Hyung Lee to enhance consensus on KAIST's values and educational philosophy and to inspire patriotism and school spirit. Participants express their sense of belonging and pride in KAIST by singing the KAIST school song, the national anthem, or the 'I'm a KAIST,' dedicated by Professor Sumi Jo, a visiting scholar at the Graduate School of Culture Technology. Notably, this year, a new category has been added where participants sing their self-composed 'My Own School Song,' making the stage more diverse.
The grand prize-winning team receives the President's Award and a prize of 1 million won. The top excellence award and participating teams also receive prizes and awards totaling 2 million won.
< Photo 2. At the ceremony for the signing of the donation pledge, KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee (left) is relaying a bouquet of flower and the plaque of appreciation to the former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim. >
Former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim stated, Love for the national community is the foundation of a sound global citizen consciousness. For me, love for this national community, along with family love, has been a great source of energy for growth.
He added, I hope this challenge of singing the national anthem and school song becomes a good nourishment for KAIST members to grow into global citizens with roots, expressing his thoughts on the donation.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I am grateful to former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim for his generous support of this meaningful program, which fosters pride in the school and raises interest in loving the country through the national anthem.” He added, “This donation will serve as an opportunity for KAIST members to cultivate a sense of belonging to the school and a sense of responsibility to the national community.”
Since 2018, former President Lim has annually donated prize money for the 'Linkgenesis Best Teacher Award,' encouraging faculty members who embody the values of creativity, challenge, and consideration. Furthermore, he has consistently contributed to KAIST's talent development and advancement by continuing to provide funds totaling 1 billion won, including scholarship funds for the Department of Electrical Engineering and the Alumni Academic Scholarship Foundation.
< Photo 3. Grand prize-winning team of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge >
Meanwhile, the '2nd School Song and National Anthem Challenge' was successfully held on May 21st at the main auditorium of KAIST, with over 150 spectators participating. Eight teams performed in the finals, and the final winning team was selected based on audience evaluation (10%) and judges' scores (90%).
< Photo 4. Grand prize-winning team of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge, Aeguk-Rock in performance >
The grand prize was awarded to the 'Aeguk-Rock' team, who arranged the national anthem into a rock version and performed it as a band. The top excellence award went to the 'Form of the Conductor' team, who sang the school song a cappella. The excellence award was given to Eun-Jin Choi, a student from the Graduate School of Culture Technology, who performed her self-composed school song written with an AI tool, 'Radiant You – You Are KAIST.' The 'Aeguk-Rock’ team also won the audience popularity award, and five other teams received participation awards.
< Photo 5. Group photo of the winners of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge >
2025.05.23 View 1821
Hyung Kyu Lim, Former KAIST Alumni Association President, Donates 100 Million Won for a Challenge to Follow “I am a KAIST”
Hyung Kyu Lim, a former President of the KAIST Alumni Association, has donated 100 million won as the prize money for the School Song and National Anthem Challenge. This donation will be used as prize money starting from the 2026 competition and is expected to play a significant role in spreading KAIST's educational culture and fostering a sense of community.
< Photo 1. KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee (left) and the former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim at the ceremony for the signing of the pledge for Dr. Lim's donation. >
The School Song and National Anthem Challenge was first conceived in 2024 at the suggestion of President Kwang-Hyung Lee to enhance consensus on KAIST's values and educational philosophy and to inspire patriotism and school spirit. Participants express their sense of belonging and pride in KAIST by singing the KAIST school song, the national anthem, or the 'I'm a KAIST,' dedicated by Professor Sumi Jo, a visiting scholar at the Graduate School of Culture Technology. Notably, this year, a new category has been added where participants sing their self-composed 'My Own School Song,' making the stage more diverse.
The grand prize-winning team receives the President's Award and a prize of 1 million won. The top excellence award and participating teams also receive prizes and awards totaling 2 million won.
< Photo 2. At the ceremony for the signing of the donation pledge, KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee (left) is relaying a bouquet of flower and the plaque of appreciation to the former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim. >
Former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim stated, Love for the national community is the foundation of a sound global citizen consciousness. For me, love for this national community, along with family love, has been a great source of energy for growth.
He added, I hope this challenge of singing the national anthem and school song becomes a good nourishment for KAIST members to grow into global citizens with roots, expressing his thoughts on the donation.
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I am grateful to former Alumni Association President Hyung Kyu Lim for his generous support of this meaningful program, which fosters pride in the school and raises interest in loving the country through the national anthem.” He added, “This donation will serve as an opportunity for KAIST members to cultivate a sense of belonging to the school and a sense of responsibility to the national community.”
Since 2018, former President Lim has annually donated prize money for the 'Linkgenesis Best Teacher Award,' encouraging faculty members who embody the values of creativity, challenge, and consideration. Furthermore, he has consistently contributed to KAIST's talent development and advancement by continuing to provide funds totaling 1 billion won, including scholarship funds for the Department of Electrical Engineering and the Alumni Academic Scholarship Foundation.
< Photo 3. Grand prize-winning team of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge >
Meanwhile, the '2nd School Song and National Anthem Challenge' was successfully held on May 21st at the main auditorium of KAIST, with over 150 spectators participating. Eight teams performed in the finals, and the final winning team was selected based on audience evaluation (10%) and judges' scores (90%).
< Photo 4. Grand prize-winning team of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge, Aeguk-Rock in performance >
The grand prize was awarded to the 'Aeguk-Rock' team, who arranged the national anthem into a rock version and performed it as a band. The top excellence award went to the 'Form of the Conductor' team, who sang the school song a cappella. The excellence award was given to Eun-Jin Choi, a student from the Graduate School of Culture Technology, who performed her self-composed school song written with an AI tool, 'Radiant You – You Are KAIST.' The 'Aeguk-Rock’ team also won the audience popularity award, and five other teams received participation awards.
< Photo 5. Group photo of the winners of the School Song and National Anthem Challenge >
2025.05.23 View 1821 -
 KAIST Develops Novel Catalyst With 100-Fold Platinum Efficiency
Propylene, a key building block used in producing plastics, textiles, automotive components, and electronics, is essential to the petrochemical industry. A KAIST research team has developed a novel catalyst that dramatically enhances the efficiency of propylene production while significantly reducing costs.
< Photo. Professor Minkee Choi (left), and Ph.D. Candidate Susung Lee (right) of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of May that a research group led by Professor Minkee Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully developed a new catalyst using inexpensive metals—gallium (Ga) and alumina (Al₂O₃)—with only a trace amount of platinum (100 ppm, or 0.01%). Remarkably, this new catalyst outperforms conventional industrial catalysts that use high concentrations of platinum (10,000 ppm).
Propylene is commonly produced through the propane dehydrogenation (PDH) process, which removes hydrogen from propane. Platinum has long been used as a catalyst in PDH due to its high efficiency in breaking carbon-hydrogen bonds and facilitating hydrogen removal. However, platinum is costly and suffers from performance degradation over repeated use.
To address this, the KAIST team engineered a catalyst that incorporates only a minimal amount of platinum, relying on gallium and alumina as the primary components.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram showing the catalytic cooperation between gallium (Ga) and platinum (Pt) >
The core mechanism of the catalyst involves a cooperative function between the metals: gallium activates the C–H bond in propane to produce propylene, while platinum bonds the residual hydrogen atoms on the surface to form hydrogen gas (H₂), which is then released. This division of roles allows for high catalytic efficiency despite the drastic reduction in platinum content.
The researchers identified an optimal platinum-to-gallium ratio that delivered peak performance and provided a scientific rationale and quantitative metrics to predict this ideal composition.
Additionally, the team addressed a major limitation of traditional platinum catalysts: sintering—the agglomeration of platinum particles during repeated use, which causes performance loss. By adding a small amount of cerium (Ce), the researchers successfully suppressed this aggregation. As a result, the new catalyst maintained stable performance even after more than 20 reaction-regeneration cycles.
< Figure 2. Performance comparison of KAIST's newly developed catalyst (100 ppm platinum) and existing commercial platinum catalyst (10,000 ppm platinum) >
Professor Choi stated, “This research demonstrates the possibility of reducing platinum usage to 1/100th of current levels without compromising, and even enhancing, performance. It presents significant economic and environmental advantages, including lower catalyst costs, extended replacement intervals, and reduced catalyst waste.”
He added, “We are planning to evaluate this technology for large-scale process demonstration and commercialization. If adopted in industry, it could greatly improve the economic viability and efficiency of propylene production.”
The study was led by Professor Minkee Choi as corresponding author, with Ph.D. candidate Susung Lee as the first author. The findings were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), a leading journal in chemistry and chemical engineering, on February 13.※ Paper title: Ideal Bifunctional Catalysis for Propane Dehydrogenation over Pt-Promoted Gallia-Alumina and Minimized Use of Precious Elements※ DOI: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c13787
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and Hanwha Solutions Corporation.
2025.05.12 View 1569
KAIST Develops Novel Catalyst With 100-Fold Platinum Efficiency
Propylene, a key building block used in producing plastics, textiles, automotive components, and electronics, is essential to the petrochemical industry. A KAIST research team has developed a novel catalyst that dramatically enhances the efficiency of propylene production while significantly reducing costs.
< Photo. Professor Minkee Choi (left), and Ph.D. Candidate Susung Lee (right) of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of May that a research group led by Professor Minkee Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully developed a new catalyst using inexpensive metals—gallium (Ga) and alumina (Al₂O₃)—with only a trace amount of platinum (100 ppm, or 0.01%). Remarkably, this new catalyst outperforms conventional industrial catalysts that use high concentrations of platinum (10,000 ppm).
Propylene is commonly produced through the propane dehydrogenation (PDH) process, which removes hydrogen from propane. Platinum has long been used as a catalyst in PDH due to its high efficiency in breaking carbon-hydrogen bonds and facilitating hydrogen removal. However, platinum is costly and suffers from performance degradation over repeated use.
To address this, the KAIST team engineered a catalyst that incorporates only a minimal amount of platinum, relying on gallium and alumina as the primary components.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram showing the catalytic cooperation between gallium (Ga) and platinum (Pt) >
The core mechanism of the catalyst involves a cooperative function between the metals: gallium activates the C–H bond in propane to produce propylene, while platinum bonds the residual hydrogen atoms on the surface to form hydrogen gas (H₂), which is then released. This division of roles allows for high catalytic efficiency despite the drastic reduction in platinum content.
The researchers identified an optimal platinum-to-gallium ratio that delivered peak performance and provided a scientific rationale and quantitative metrics to predict this ideal composition.
Additionally, the team addressed a major limitation of traditional platinum catalysts: sintering—the agglomeration of platinum particles during repeated use, which causes performance loss. By adding a small amount of cerium (Ce), the researchers successfully suppressed this aggregation. As a result, the new catalyst maintained stable performance even after more than 20 reaction-regeneration cycles.
< Figure 2. Performance comparison of KAIST's newly developed catalyst (100 ppm platinum) and existing commercial platinum catalyst (10,000 ppm platinum) >
Professor Choi stated, “This research demonstrates the possibility of reducing platinum usage to 1/100th of current levels without compromising, and even enhancing, performance. It presents significant economic and environmental advantages, including lower catalyst costs, extended replacement intervals, and reduced catalyst waste.”
He added, “We are planning to evaluate this technology for large-scale process demonstration and commercialization. If adopted in industry, it could greatly improve the economic viability and efficiency of propylene production.”
The study was led by Professor Minkee Choi as corresponding author, with Ph.D. candidate Susung Lee as the first author. The findings were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), a leading journal in chemistry and chemical engineering, on February 13.※ Paper title: Ideal Bifunctional Catalysis for Propane Dehydrogenation over Pt-Promoted Gallia-Alumina and Minimized Use of Precious Elements※ DOI: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c13787
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and Hanwha Solutions Corporation.
2025.05.12 View 1569 -
 KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 4918
KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 4918 -
 Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
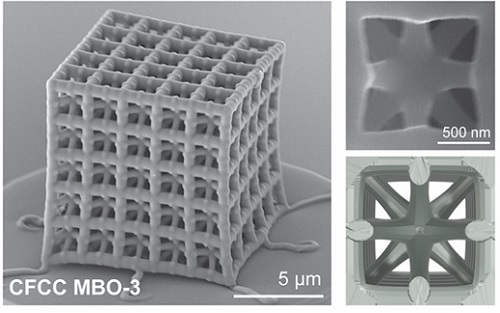
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4959
Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 4959 -
 KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
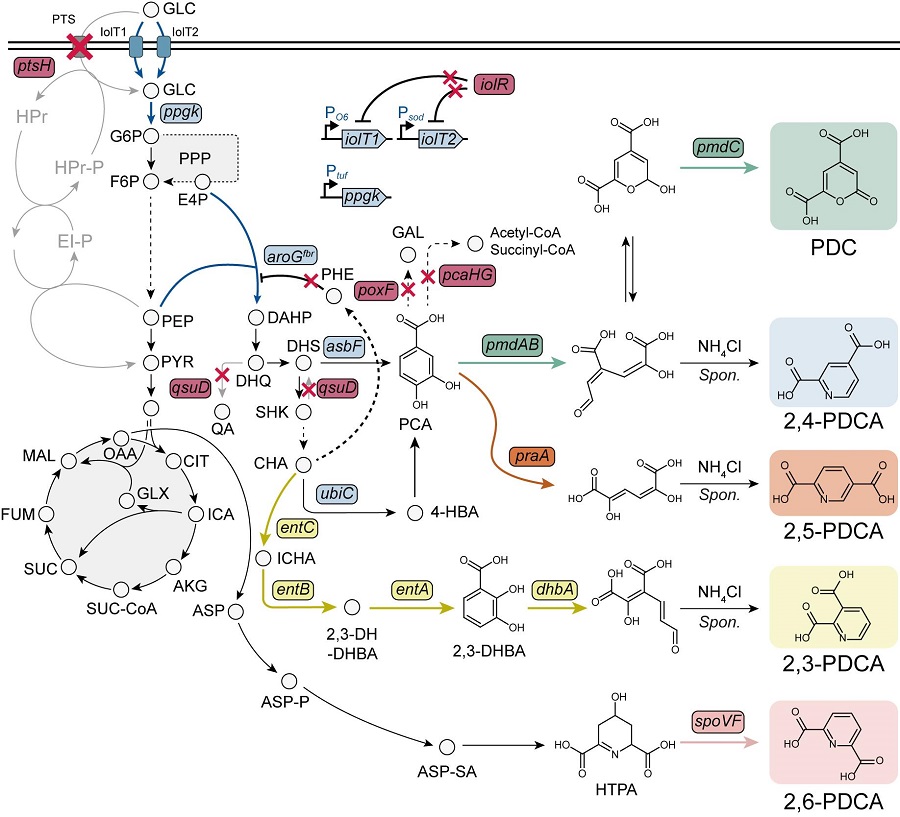
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 9057
KAIST Researchers Suggest an Extraordinary Alternative to Petroleum-based PET - Bacteria!
< (From left) Dr. Cindy Pricilia, Ph.D. Candidate Cheon Woo Moon, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee >
Currently, the world is suffering from environmental problems caused by plastic waste. The KAIST research team has succeeded in producing a microbial-based plastic that is biodegradable and can replace existing PET bottles, making it a hot topic.
Our university announced on the 7th of November that the research team of Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has succeeded in developing a microbial strain that efficiently produces pseudoaromatic polyester monomer to replace polyethylene terephthalate (PET) using systems metabolic engineering.
Pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids have better physical properties and higher biodegradability than aromatic polyester (PET) when synthesized as polymers, and are attracting attention as an eco-friendly monomer* that can be synthesized into polymers. The production of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids through chemical methods has the problems of low yield and selectivity, complex reaction conditions, and the generation of hazardous waste.
*Monomer: A material for making polymers, which is used to synthesize polymers by polymerizing monomers together
< Figure. Overview of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acid production using metabolically engineered C. glutamicum. >
To solve this problem, Professor Sang Yup Lee's research team used metabolic engineering to develop a microbial strain that efficiently produces five types of pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, including 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid and four types of pyridine dicarboxylic acids (2,3-, 2,4-, 2,5-, 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids), in Corynebacterium, a bacterium mainly used for amino acid production.
The research team used metabolic engineering techniques to build a platform microbial strain that enhances the metabolic flow of protocatechuic acid, which is used as a precursor for several pseudoaromatic dicarboxylic acids, and prevents the loss of precursors.
Based on this, the genetic manipulation target was discovered through transcriptome analysis, producing 76.17 g/L of 2-pyrone-4,6-dicarboxylic acid, and by newly discovering and constructing three types of pyridine dicarboxylic acid production metabolic pathways, successfully producing 2.79 g/L of 2,3-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, 0.49 g/L of 2,4-pyridine dicarboxylic acid, and 1.42 g/L of 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid.
In addition, the research team confirmed the production of 15.01 g/L through the construction and reinforcement of the 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid biosynthesis pathway, successfully producing a total of five similar aromatic dicarboxylic acids with high efficiency.
In conclusion, the team succeeded in producing 2,4-, 2,5-, and 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acids at the world's highest concentration. In particular, 2,4-, 2,5-pyridine dicarboxylic acid achieved production on the scale of g/L, which was previously produced in extremely small amounts (mg/L).
Based on this study, it is expected that it will be applied to various polyester production industrial processes, and it is also expected that it will be actively utilized in research on the production of similar aromatic polyesters.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, the corresponding author, said, “The significance lies in the fact that we have developed an eco-friendly technology that efficiently produces similar aromatic polyester monomers based on microorganisms,” and “This study will help the microorganism-based bio-monomer industry replace the petrochemical-based chemical industry in the future.”
The results of this study were published in the international academic journal, the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of United States of America (PNAS) on October 30th.
※ Paper title: Metabolic engineering of Corynebacterium glutamicum for the production of pyrone and pyridine dicarboxylic acids
※ Author information: Jae Sung Cho (co-first author), Zi Wei Luo (co-first author), Cheon Woo Moon (co-first author), Cindy Prabowo (co-author), Sang Yup Lee (corresponding author) - a total of 5 people
This study was conducted with the support of the Development of Next-generation Biorefinery Platform Technologies for Leading Bio-based Chemicals Industry Project and the Development of Platform Technologies of Microbial Cell Factories for the Next-generation Biorefineries Project (Project leader: Professor Sang Yup Lee) from the National Research Foundation supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology and ICT of Korea.
2024.11.08 View 9057 -
 KAIST Civil Engineering Students named Runner-up at the 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific
A team of five students from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) were awarded second place in a premier urban design student competition hosted by the Urban Land Institute and Hines, 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific.
The competition, which was held for the first time in the Asia-Pacific region, is an internationally recognized event which typically attract hundreds of applicants.
Jonah Remigio, Sojung Noh, Estefania Rodriguez, Jihyun Kang, and Ayantu Teshome, who joined forces under the name of “Team Hashtag Development”, were supported by faculty advisors Dr. Albert Han and Dr. Youngchul Kim of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering to imagine a more sustainable and enriched way of living in the Jurong district of Singapore.
Their submission, titled “Proposal: The Nest”, analyzed the big data within Singapore, using the data to determine which real estate business strategies would best enhance the quality of living and economy of the region.
Their final design, "The Nest" utilized mixed-use zoning to integrate the site’s scenic waterfront with homes, medical innovation, and sustainable technology, altogether creating a place to innovate, inhabit, and immerse.
< The Nest by Team Hashtag Development (Jonah Remigio, Ayantu Teshome Mossisa, Estefania Ayelen Rodriguez del Puerto, Sojung Noh, Jihyun Kang) ©2023 Urban Land Institute >
Ultimately, the team was recognized for their hard work and determination, imprinting South Korea’s indelible footprint in the arena of international scholastic achievement as they were named to be one of the Finalists on April 13th.
< Members of Team Hashtag Development >
Team Hashtag Development gave a virtual presentation to a jury of six ULI members on April 20th along with the "Team The REAL" from the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City of Vietnam and "Team Omusubi" from the Waseda University of Japan, the team that submitted the proposal "Jurong Urban Health Campus" which was announced to be the winner on the 31st of May, after the virtual briefing by the top three finalists.
2023.06.26 View 9288
KAIST Civil Engineering Students named Runner-up at the 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific
A team of five students from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) were awarded second place in a premier urban design student competition hosted by the Urban Land Institute and Hines, 2023 ULI Hines Student Competition - Asia Pacific.
The competition, which was held for the first time in the Asia-Pacific region, is an internationally recognized event which typically attract hundreds of applicants.
Jonah Remigio, Sojung Noh, Estefania Rodriguez, Jihyun Kang, and Ayantu Teshome, who joined forces under the name of “Team Hashtag Development”, were supported by faculty advisors Dr. Albert Han and Dr. Youngchul Kim of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering to imagine a more sustainable and enriched way of living in the Jurong district of Singapore.
Their submission, titled “Proposal: The Nest”, analyzed the big data within Singapore, using the data to determine which real estate business strategies would best enhance the quality of living and economy of the region.
Their final design, "The Nest" utilized mixed-use zoning to integrate the site’s scenic waterfront with homes, medical innovation, and sustainable technology, altogether creating a place to innovate, inhabit, and immerse.
< The Nest by Team Hashtag Development (Jonah Remigio, Ayantu Teshome Mossisa, Estefania Ayelen Rodriguez del Puerto, Sojung Noh, Jihyun Kang) ©2023 Urban Land Institute >
Ultimately, the team was recognized for their hard work and determination, imprinting South Korea’s indelible footprint in the arena of international scholastic achievement as they were named to be one of the Finalists on April 13th.
< Members of Team Hashtag Development >
Team Hashtag Development gave a virtual presentation to a jury of six ULI members on April 20th along with the "Team The REAL" from the University of Economics Ho Chi Minh City of Vietnam and "Team Omusubi" from the Waseda University of Japan, the team that submitted the proposal "Jurong Urban Health Campus" which was announced to be the winner on the 31st of May, after the virtual briefing by the top three finalists.
2023.06.26 View 9288 -
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11485
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 11485 -
 Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 7448
Chem-E-Car Team to Vie for World Title
Team KAItalyst, composed of KAIST undergraduate students, celebrated victory in the regional qualifying rounds of the 2019 International Chem-E-Car Competition held at KAIST’s Main Campus in Daejeon on July 20. The high finish in the national rankings qualified the team for a trip to the world finals to be held in Orlando, Florida, USA, in November.
The Chem-E-Car Competition involves designing and building a shoebox-sized model car that is powered and controlled by chemical reactions. University students from all over the world have been actively participating in this competition since the competition was introduced by the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE) in 1999.
KAIST first entered the competition in 2014, won the world finals in 2016, and then received the Most Consistent Award in 2017 and 2018. In recognition of KAIST’s consistently outstanding performance in the competition, AIChE asked KAIST to host this year’s regional competition for the first time in Korea.
Although a number of Korean university student teams have shown great interest in participating in this regional competition, most were not able to successfully implement their technology, and only two teams each from KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU) joined the competition.
Each team collaborated to fabricate a chemically powered model car that could carry a payload, and travel any distance between 15 and 30 meters. The weight of the payload and the travelling distance were randomly set an hour before the competition started, to require the participating teams adapt and perform calculations in a short period of time. The goal was to stop travelling exactly at the randomly chosen distance. The car closest to the finish line at the end of the race earned the highest amount of points. Precise control over chemical reactions was key to landing directly on the mark.
Team KAItalyst, consisting of six KAIST undergraduate students majoring in chemical and biomolecular engineering and mechanical engineering, beat their SNU rivals by stopping their car 1.5 meters closer to the goal at the end of the 22.5 meter-long race. Team KAItalyst loaded vanadium redox flow batteries onto their car to stabilize its output, and further increased the accuracy and velocity of chemical reactions through iodine clock reactions. 200 USD was awarded to Team KAItalyst, and 100 USD in prize money went to the SNU team.
KAItalyst team leader Jee-Hyun Hong said, “This was the first time for us to develop and drive our own chemically-powered model car, and we learned a lot from the challenges we faced,” Hong continued, “We will step up our efforts to perform better in the upcoming international competition.” The world finals will be held during the AIChE Fall Meeting in Orlando, Florida in November. Students from over 50 universities worldwide including the Georgia Institute of Technology and Carnegie Mellon University will compete against each other. The first, second, and third prizes at the finals will be 2,000, 1,000, and 500 USD respectively.
Professor Dong-Yeun Koh of the KAIST Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department who advised Team KAItalyst remarked, “I hope this year’s regional competition that KAIST held for the first time as a Korean university will be a possible starting point for more Korean universities to participate and compete in the future.”
(END)
2019.08.05 View 7448 -
 'Flying Drones for Rescue'
(Video Credit: ⓒNASA JPL)
< Team USRG and Professor Shim (second from the right) >
Having recently won the AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition in Korea, Team USRG (Unmanned System Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering is all geared up to take on their next challenges: the ‘Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Subterranean Challenge (DARPA SubT Challenge)’ and ‘Lockheed Martin’s AlphaPilot Challenge’ next month.
Team USRG won the obstacle course race in the ‘2019 AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition’ on July 12. They managed to successfully dominate the challenging category of ‘control intelligence.’ Having to complete the obstacle course race solely using AI systems without any connection to the internet made it difficult for most of the eight participating teams to pass the third section of the race, and only Team USRG passed the long pipeline course during their attempt in the main event. They also demonstrated, after the main event, that their drone can navigate all of the checkpoints including landing on the “H” mark using deep learning.
Their drone flew through polls and pipes, and escaped from windows and mazes against strong winds, amid cheers and groans from the crowd gathered at the Korea Exhibition Center (KINTEX) in Goyang, Korea. The team was awarded three million KRW in prize money, and received a research grant worth six hundred million KRW from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
“Being ranked first in the race for which we were never given a chance for a test flight means a lot to our team. Considering that we had no information on the exact size of the course in advance, this is a startling result,” said Professor Shim. “We will carry out further research with this funding, and compete once again with the improved AI and drone technology in the 2020 competition,” he added.
The AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition, which was first started in 2017, has been designed to promote AI research and development and expand its application to addressing high-risk technical challenges with significant socio-economic impact.
This year’s competition presented participants with a task where they had to develop AI software technology for drones to navigate themselves autonomously during complex disaster relief operations such as aid delivery.
Each team participated in one of the four tracks of the competition, and their drones were evaluated based on the criteria for each track. The divisions were broken up into intelligent context-awareness, intelligent character recognition, auditory intelligence, and control intelligence.
Team USRG’s technological prowess has been already well acclaimed among international peer groups. Teamed up with NASA JPL, Caltech, and MIT, they will compete in the subterranean mission during the ‘DARPA SubT Challenge’.
Team CoSTAR, as its name stands for, is working together to build ‘Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Resilient Robots.’ Professor Shim emphasized the role KAIST plays in Team CoSTAR as a leader in drone technology.
“I think when our drone technology will be added to our peers’ AI and robotics, Team CoSTAR will bring out unsurpassable synergy in completing the subterrestrial and planetary applications. I would like to follow the footprint of Hubo, the winning champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge and even extend it to subterranean exploration,” he said.
These next generation autonomous subsurface explorers are now all optimizing the physical AI robot systems developed by Team CoSTAR. They will test their systems in more realistic field environments August 15 through 22 in Pittsburgh, USA. They have already received funding from DARPA for participating.
Team CoSTAR will compete in three consecutive yearly events starting this year, and the last event, planned for 2021, will put the team to the final test with courses that incorporate diverse challenges from all three events. Two million USD will be awarded to the winner after the final event, with additional prizes of up to 200,000 USD for self-funded teams.
Team USRG also ranked third in the recent Hyundai Motor Company’s ‘Autonomous Vehicle Competition’ and another challenge is on the horizon: Lockheed Martin’s ‘AlphaPilot Challenge’. In this event, the teams will be flying their drones through a series of racing gates, trying to beat the best human pilot. The challenge is hosted by Lockheed Martin, the world’s largest military contractor and the maker of the famed F-22 and F-35 stealth fighters, with the goal of stimulating the development of autonomous drones. Team USRG was selected from out of more than 400 teams from around the world and is preparing for a series of races this fall, beginning from the end of August.
Professor Shim said, “It is not easy to perform in a series of competitions in just a few months, but my students are smart, hardworking, and highly motivated. These events indeed demand a lot, but they really challenge the researchers to come up with technologies that work in the real world. This is the way robotics really should be.”
(END)
2019.07.26 View 14249
'Flying Drones for Rescue'
(Video Credit: ⓒNASA JPL)
< Team USRG and Professor Shim (second from the right) >
Having recently won the AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition in Korea, Team USRG (Unmanned System Research Group) led by Professor Hyunchul Shim from the School of Electrical Engineering is all geared up to take on their next challenges: the ‘Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency Subterranean Challenge (DARPA SubT Challenge)’ and ‘Lockheed Martin’s AlphaPilot Challenge’ next month.
Team USRG won the obstacle course race in the ‘2019 AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition’ on July 12. They managed to successfully dominate the challenging category of ‘control intelligence.’ Having to complete the obstacle course race solely using AI systems without any connection to the internet made it difficult for most of the eight participating teams to pass the third section of the race, and only Team USRG passed the long pipeline course during their attempt in the main event. They also demonstrated, after the main event, that their drone can navigate all of the checkpoints including landing on the “H” mark using deep learning.
Their drone flew through polls and pipes, and escaped from windows and mazes against strong winds, amid cheers and groans from the crowd gathered at the Korea Exhibition Center (KINTEX) in Goyang, Korea. The team was awarded three million KRW in prize money, and received a research grant worth six hundred million KRW from the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT).
“Being ranked first in the race for which we were never given a chance for a test flight means a lot to our team. Considering that we had no information on the exact size of the course in advance, this is a startling result,” said Professor Shim. “We will carry out further research with this funding, and compete once again with the improved AI and drone technology in the 2020 competition,” he added.
The AI R&D Grand Challenge Competition, which was first started in 2017, has been designed to promote AI research and development and expand its application to addressing high-risk technical challenges with significant socio-economic impact.
This year’s competition presented participants with a task where they had to develop AI software technology for drones to navigate themselves autonomously during complex disaster relief operations such as aid delivery.
Each team participated in one of the four tracks of the competition, and their drones were evaluated based on the criteria for each track. The divisions were broken up into intelligent context-awareness, intelligent character recognition, auditory intelligence, and control intelligence.
Team USRG’s technological prowess has been already well acclaimed among international peer groups. Teamed up with NASA JPL, Caltech, and MIT, they will compete in the subterranean mission during the ‘DARPA SubT Challenge’.
Team CoSTAR, as its name stands for, is working together to build ‘Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Resilient Robots.’ Professor Shim emphasized the role KAIST plays in Team CoSTAR as a leader in drone technology.
“I think when our drone technology will be added to our peers’ AI and robotics, Team CoSTAR will bring out unsurpassable synergy in completing the subterrestrial and planetary applications. I would like to follow the footprint of Hubo, the winning champion of the 2015 DARPA Robotics Challenge and even extend it to subterranean exploration,” he said.
These next generation autonomous subsurface explorers are now all optimizing the physical AI robot systems developed by Team CoSTAR. They will test their systems in more realistic field environments August 15 through 22 in Pittsburgh, USA. They have already received funding from DARPA for participating.
Team CoSTAR will compete in three consecutive yearly events starting this year, and the last event, planned for 2021, will put the team to the final test with courses that incorporate diverse challenges from all three events. Two million USD will be awarded to the winner after the final event, with additional prizes of up to 200,000 USD for self-funded teams.
Team USRG also ranked third in the recent Hyundai Motor Company’s ‘Autonomous Vehicle Competition’ and another challenge is on the horizon: Lockheed Martin’s ‘AlphaPilot Challenge’. In this event, the teams will be flying their drones through a series of racing gates, trying to beat the best human pilot. The challenge is hosted by Lockheed Martin, the world’s largest military contractor and the maker of the famed F-22 and F-35 stealth fighters, with the goal of stimulating the development of autonomous drones. Team USRG was selected from out of more than 400 teams from around the world and is preparing for a series of races this fall, beginning from the end of August.
Professor Shim said, “It is not easy to perform in a series of competitions in just a few months, but my students are smart, hardworking, and highly motivated. These events indeed demand a lot, but they really challenge the researchers to come up with technologies that work in the real world. This is the way robotics really should be.”
(END)
2019.07.26 View 14249 -
 KAIST Team Reaching Out with Appropriate Technology
(The gold prize winning team of KATT)
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of international students at KAIST won the gold and silver prizes at ‘The 10th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90 Percent.’
More than 218 students from 50 teams nationwide participated in the competition hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT last month.
The competition was created to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance the quality of life for those with no or few accessible technologies.
A team led by Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, graduate student from the School of Electrical Engineering received the gold prize for presenting a prosthetic arm. Their artificial arm was highly recognized for its affordability and good manageability. The team said that it cost less than 10 US dollars to construct from materials available in underprivileged regions and was easy to assemble.
Sophomore Hutomo Calvin from the Department of Materials Science & Engineering also worked on the prosthetic arm project with freshmen Bella Godiva, Stephanie Tan, and Koptieuov Yearbola.
Alexandra Tran, senior from the School of Electrical Engineering led the silver prize winning team. Her team developed a portable weather monitor, ‘Breathe Easy’. She worked with Alisher Tortay, senior from the School of Computing, Ashar Alam, senior from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bereket Eshete, junior from the School of Computing, and Marthens Hakzimana, sophomore from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
This weather monitor is a low-cost but efficient air quality monitor. The team said it just cost less than seven US dollars to construct the monitor.KAIST students have now won the gold prize for two consecutive years.
2018.06.19 View 13242
KAIST Team Reaching Out with Appropriate Technology
(The gold prize winning team of KATT)
The KAIST Appropriate Technology Team (KATT) consisting of international students at KAIST won the gold and silver prizes at ‘The 10th Creative Design Competition for the Other 90 Percent.’
More than 218 students from 50 teams nationwide participated in the competition hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT last month.
The competition was created to discover appropriate technology and sustainable design items to enhance the quality of life for those with no or few accessible technologies.
A team led by Juan Luis Gonzalez Bello, graduate student from the School of Electrical Engineering received the gold prize for presenting a prosthetic arm. Their artificial arm was highly recognized for its affordability and good manageability. The team said that it cost less than 10 US dollars to construct from materials available in underprivileged regions and was easy to assemble.
Sophomore Hutomo Calvin from the Department of Materials Science & Engineering also worked on the prosthetic arm project with freshmen Bella Godiva, Stephanie Tan, and Koptieuov Yearbola.
Alexandra Tran, senior from the School of Electrical Engineering led the silver prize winning team. Her team developed a portable weather monitor, ‘Breathe Easy’. She worked with Alisher Tortay, senior from the School of Computing, Ashar Alam, senior from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, Bereket Eshete, junior from the School of Computing, and Marthens Hakzimana, sophomore from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
This weather monitor is a low-cost but efficient air quality monitor. The team said it just cost less than seven US dollars to construct the monitor.KAIST students have now won the gold prize for two consecutive years.
2018.06.19 View 13242 -
 Czech Technology Mission with KAIST
Members of the Czech research community visited KAIST to discuss medium to long-term cooperation with KAIST. This visit was hosted by the Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC).
The community is comprised of people from Czech enterprises and academic institutes that are leading core technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in the fields of AI, robotics, and biotechnology. They had a chance to meet KAIST professors and visit research labs.
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Seongsu Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor Hyun Uk Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering attended the meeting, which took place in the Mechatronics, Systems, and Control Lab under the Vice President for Planning and Budget Soo Hyun Kim and Professor Kyung Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Professor Petr Novák from the Technical University of Ostrava said, “It was a meaningful meeting to help understand research trends on industrial robots in Korea.” Professor So Young Kim from FIRIC said, “The Czech research community is strong in basic research where KAIST has outstanding source technology. I hope this visit will open up a path for medium to long-term cooperation on sharing research and technology know-how between the Czech research community and KAIST.”
2018.06.07 View 7723
Czech Technology Mission with KAIST
Members of the Czech research community visited KAIST to discuss medium to long-term cooperation with KAIST. This visit was hosted by the Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC).
The community is comprised of people from Czech enterprises and academic institutes that are leading core technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution in the fields of AI, robotics, and biotechnology. They had a chance to meet KAIST professors and visit research labs.
Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Seongsu Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, and Professor Hyun Uk Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering attended the meeting, which took place in the Mechatronics, Systems, and Control Lab under the Vice President for Planning and Budget Soo Hyun Kim and Professor Kyung Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering.
Professor Petr Novák from the Technical University of Ostrava said, “It was a meaningful meeting to help understand research trends on industrial robots in Korea.” Professor So Young Kim from FIRIC said, “The Czech research community is strong in basic research where KAIST has outstanding source technology. I hope this visit will open up a path for medium to long-term cooperation on sharing research and technology know-how between the Czech research community and KAIST.”
2018.06.07 View 7723 -
 KAIST Welcomes Global Participants to AI World Cup 2018
KAIST will host the AI (Artificial Intelligence) World Cup 2018 in August, and this time it is open to the international community. AI World Cup 2018 will be a very exciting challenge for extending the limit of academic and industrial applications based on AI technology.
KAIST, after launching its AI World Cup 2017 for domestic participants, is now hosting the AI World Cup 2018 for everyone. The AI World Cup will be comprised of three events: 1) Five on five AI Soccer 2) AI Commentator and 3) AI Reporter. Winner of each category, runner-up of AI Soccer, and 2nd runner-up of AI Soccer will receive awards with cash prizes.
For AI Soccer in which AI controlled robots team up to compete, the preliminary rounds will be held in July in a league format, and the final rounds will be played on August 20-22.
For AI Commentator and AI Reporter, eight finalists will be selected for each category based on scoring criteria, and their performance will be evaluated by the judges to select the winner from each category on August 22.
During the final rounds, a variety of events will also take place at KAIST, including tutorial sessions on AI technology, a poster session where students present their research works on AI, not necessarily limited to the scope of AI Soccer, AI Commentator, and AI Reporter, and panel discussions by prominent experts in the field of AI.
Moreover, renowned experts on AI will deliver their keynote addresses. The Cyberbotics CEO Olivier Michel will address his keynote speech on the topic ‘Simulation benchmarks and competitions: a fundamental tool to foster robotics research.’
The AI World Cup was established by the College of Engineering at KAIST to show that AI technology can be further extended to sports, soccer in particular.
Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the inventor of AI World Cup and chairman of the organizing committee said, “I hope that this event will offer a great chance to develop AI technology for use in the coming years. I wish many people can enjoy the AI World Cup 2018. I would recommend that prospective teams not worry about the technical barrier when deciding whether to participate in the games. Participants from academia and industry can test whether their code runs well in the competition simulator; this way, they will know their level of play and perhaps they can further develop their algorithms.”
“We will also broadcast the final round of AI Soccer online so that people in remote areas can also enjoy watching the games. I am looking forward to seeing all of you at the AI World Cup. Any participant with a passion to prove excellence in AI technology is welcomed with open arms,” he added.
Anyone interested in the AI World Cup 2018 can register online via aiworldcup.org . Registration starts from April 1. The deadline for registration and final code submission is June 30.
(Cubical players in the figure for domestic AI Soccer competition have been replaced with cylindrical players for more agile movements while playing)
(Opening ceremony of AI World Cup 2017)
(Trophy and prize)
(Interview of participant)
(Casters commentating on game playing)
2018.03.30 View 9241
KAIST Welcomes Global Participants to AI World Cup 2018
KAIST will host the AI (Artificial Intelligence) World Cup 2018 in August, and this time it is open to the international community. AI World Cup 2018 will be a very exciting challenge for extending the limit of academic and industrial applications based on AI technology.
KAIST, after launching its AI World Cup 2017 for domestic participants, is now hosting the AI World Cup 2018 for everyone. The AI World Cup will be comprised of three events: 1) Five on five AI Soccer 2) AI Commentator and 3) AI Reporter. Winner of each category, runner-up of AI Soccer, and 2nd runner-up of AI Soccer will receive awards with cash prizes.
For AI Soccer in which AI controlled robots team up to compete, the preliminary rounds will be held in July in a league format, and the final rounds will be played on August 20-22.
For AI Commentator and AI Reporter, eight finalists will be selected for each category based on scoring criteria, and their performance will be evaluated by the judges to select the winner from each category on August 22.
During the final rounds, a variety of events will also take place at KAIST, including tutorial sessions on AI technology, a poster session where students present their research works on AI, not necessarily limited to the scope of AI Soccer, AI Commentator, and AI Reporter, and panel discussions by prominent experts in the field of AI.
Moreover, renowned experts on AI will deliver their keynote addresses. The Cyberbotics CEO Olivier Michel will address his keynote speech on the topic ‘Simulation benchmarks and competitions: a fundamental tool to foster robotics research.’
The AI World Cup was established by the College of Engineering at KAIST to show that AI technology can be further extended to sports, soccer in particular.
Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the inventor of AI World Cup and chairman of the organizing committee said, “I hope that this event will offer a great chance to develop AI technology for use in the coming years. I wish many people can enjoy the AI World Cup 2018. I would recommend that prospective teams not worry about the technical barrier when deciding whether to participate in the games. Participants from academia and industry can test whether their code runs well in the competition simulator; this way, they will know their level of play and perhaps they can further develop their algorithms.”
“We will also broadcast the final round of AI Soccer online so that people in remote areas can also enjoy watching the games. I am looking forward to seeing all of you at the AI World Cup. Any participant with a passion to prove excellence in AI technology is welcomed with open arms,” he added.
Anyone interested in the AI World Cup 2018 can register online via aiworldcup.org . Registration starts from April 1. The deadline for registration and final code submission is June 30.
(Cubical players in the figure for domestic AI Soccer competition have been replaced with cylindrical players for more agile movements while playing)
(Opening ceremony of AI World Cup 2017)
(Trophy and prize)
(Interview of participant)
(Casters commentating on game playing)
2018.03.30 View 9241