Drug+delivery
-
 Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 22057
Researchers Describe a Mechanism Inducing Self-Killing of Cancer Cells
(Professor Kim (left) and lead author Lee)
Researchers have described a new mechanism which induces the self-killing of cancer cells by perturbing ion homeostasis. A research team from the Department of Biochemical Engineering has developed helical polypeptide potassium ionophores that lead to the onset of programmed cell death. The ionophores increase the active oxygen concentration to stress endoplasmic reticulum to the point of cellular death.
The electrochemical gradient between extracellular and intracellular conditions plays an important role in cell growth and metabolism. When a cell’s ion homeostasis is disturbed, critical functions accelerating the activation of apoptosis are inhibited in the cell.
Although ionophores have been intensively used as an ion homeostasis disturber, the mechanisms of cell death have been unclear and the bio-applicability has been limited. In the study featured at Advanced Science, the team presented an alpha helical peptide-based anticancer agent that is capable of transporting potassium ions with water solubility. The cationic, hydrophilic, and potassium ionic groups were combined at the end of the peptide side chain to provide both ion transport and hydrophilic properties.
These peptide-based ionophores reduce the intracellular potassium concentration and at the same time increase the intracellular calcium concentration. Increased intracellular calcium concentrations produce intracellular reactive oxygen species, causing endoplasmic reticulum stress, and ultimately leading to apoptosis.
Anticancer effects were evaluated using tumor-bearing mice to confirm the therapeutic effect, even in animal models. It was found that tumor growth was strongly inhibited by endoplasmic stress-mediated apoptosis.
Lead author Dr. Dae-Yong Lee said, “A peptide-based ionophore is more effective than conventional chemotherapeutic agents because it induces apoptosis via elevated reactive oxygen species levels. Professor Yeu-Chun Kim said he expects this new mechanism to be widely used as a new chemotherapeutic strategy. This research was funded by the National Research Foundation.
2019.08.28 View 22057 -
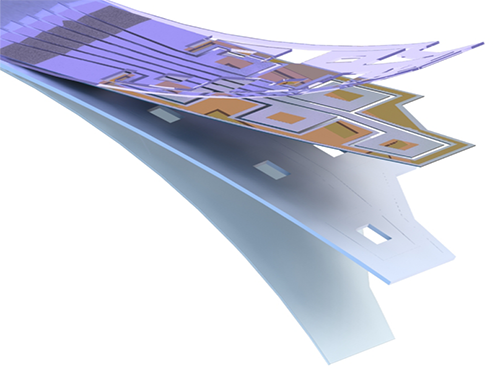 Flexible Drug Delivery Microdevice to Advance Precision Medicine
(Schematic view of flexible microdevice: The flexible drug delivery device for controlled release fabricated via inorganic laser lift off.)
A KAIST research team has developed a flexible drug delivery device with controlled release for personalized medicine, blazing the path toward theragnosis.
Theragnosis, an emerging medical technology, is gaining attention as key factor to advance precision medicine for its featuring simultaneous diagnosis and therapeutics. Theragnosis devices including smart contact lenses and microneedle patches integrate physiological data sensors and drug delivery devices. The controlled drug delivery boasts fewer side-effects, uniform therapeutic results, and minimal dosages compared to oral ingestion. Recently, some research groups conducted in-human applications of controlled-release bulky microchips for osteoporosis treatment. However they failed to demonstrate successful human-friendly flexible drug delivery systems for controlled release.
For this microdevice, the team under Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Science and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, fabricated a device on a rigid substrate and transferred a 50 µm-thick active drug delivery layer to the flexible substrate via inorganic laser lift off. The fabricated device shows mechanical flexibility while maintaining the capability of precise administration of exact dosages at desired times. The core technology is to produce a freestanding gold capping layer directly on top of the microreservoir with the drugs inside, which had been regarded as impossible in conventional microfabrication.
The developed flexible drug delivery system can be applied to smart contact lenses or the brain disease treatments by implanting them into cramped and corrugated organs. In addition, when powered wirelessly, it will represent a novel platform for personalized medicine. The team already proved through animal experimentation that treatment for brain epilepsy made progress by releasing anti-epileptic medication through the device.
Professor Lee believes the flexible microdevice will further expand the applications of smart contact lenses, therapeutic treatments for brain disease, and subcutaneous implantations for daily healthcare system. This study “Flexible Wireless Powered Drug Delivery System for Targeted Administration on Cerebral Cortex” was described in the June online issue of Nano Energy.
(Photo: The flexible drug delivery device for contolled relase attached on a glass rod.)
2018.08.13 View 9905
Flexible Drug Delivery Microdevice to Advance Precision Medicine
(Schematic view of flexible microdevice: The flexible drug delivery device for controlled release fabricated via inorganic laser lift off.)
A KAIST research team has developed a flexible drug delivery device with controlled release for personalized medicine, blazing the path toward theragnosis.
Theragnosis, an emerging medical technology, is gaining attention as key factor to advance precision medicine for its featuring simultaneous diagnosis and therapeutics. Theragnosis devices including smart contact lenses and microneedle patches integrate physiological data sensors and drug delivery devices. The controlled drug delivery boasts fewer side-effects, uniform therapeutic results, and minimal dosages compared to oral ingestion. Recently, some research groups conducted in-human applications of controlled-release bulky microchips for osteoporosis treatment. However they failed to demonstrate successful human-friendly flexible drug delivery systems for controlled release.
For this microdevice, the team under Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Science and Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, fabricated a device on a rigid substrate and transferred a 50 µm-thick active drug delivery layer to the flexible substrate via inorganic laser lift off. The fabricated device shows mechanical flexibility while maintaining the capability of precise administration of exact dosages at desired times. The core technology is to produce a freestanding gold capping layer directly on top of the microreservoir with the drugs inside, which had been regarded as impossible in conventional microfabrication.
The developed flexible drug delivery system can be applied to smart contact lenses or the brain disease treatments by implanting them into cramped and corrugated organs. In addition, when powered wirelessly, it will represent a novel platform for personalized medicine. The team already proved through animal experimentation that treatment for brain epilepsy made progress by releasing anti-epileptic medication through the device.
Professor Lee believes the flexible microdevice will further expand the applications of smart contact lenses, therapeutic treatments for brain disease, and subcutaneous implantations for daily healthcare system. This study “Flexible Wireless Powered Drug Delivery System for Targeted Administration on Cerebral Cortex” was described in the June online issue of Nano Energy.
(Photo: The flexible drug delivery device for contolled relase attached on a glass rod.)
2018.08.13 View 9905