Construction
-
 Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4191
Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4191 -
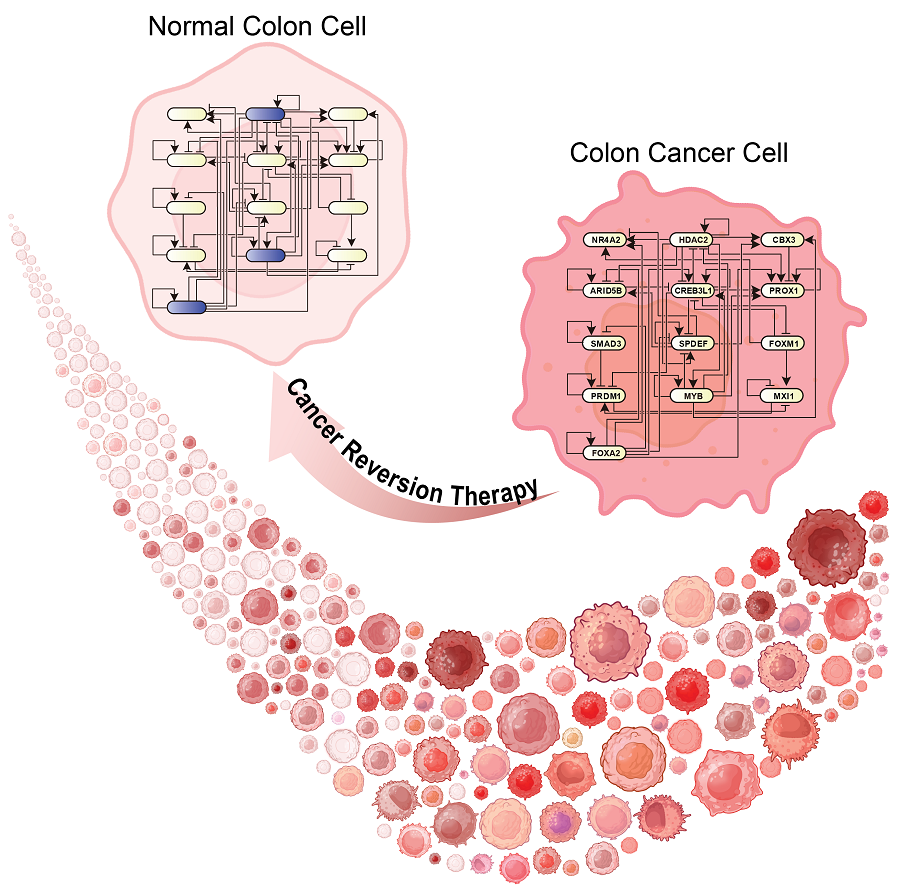 KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 104392
KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 104392 -
 Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems Opens
(Distinguished guests including President Shin (fourth from the right) and Director Lee (third from left) at the opening ceremony)
The Research Center for a Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems was recently established at KAIST with the purpose of taking the lead in developing fundamental and applicable technology for submerged floating tunnels as well as fostering creative and talented people. Haeng-Ki Lee, a professor in the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering at KAIST is heading the center.
KAIST held its opening ceremony on September 7, 2017 in the Applied Engineering Building located on the main campus.
Distinguished guests, including KAIST president Sung-Chul Shin, the President of the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology Gi-Hoon Hong, the President of the Korean Society of Civil Engineering Young-Seok Park, and the Director in the Division of Engineering at the National Research Foundation of Korea Joong-Kon Park attended the ceremony.
The National Research Foundation of Korea provides Engineering Research Center (ERC) projects which find and foster groups with outstanding research performance in a field of engineering. The projects support these groups so that they can strengthen their global competitiveness while enhancing national competence in basic research.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ was selected as one of the ERC projects in 2017. For the next seven years, the research center will work to develop a submerged floating tunnel system resistant depths greater than 100 meters.
To achieve its goal, the center has defined crucial research topics including: i) a structural analysis program and integrated design technology specific for submerged floating tunnel systems, ii) high-durability marine construction materials and submerged construction integrated systems, and iii) safety and maintenance integrated technology for smart submerged floating tunnel systems.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ will devote itself to developing a variety of fundamental and applicable technology that will be leading global maritime construction. Moreover, it will concentrate on fostering professional research manpower in related areas.
The Director of the Center Lee said, “The center will cooperate with KAIST researchers who are experts in various fields, including structures, materials, construction, and maritime research. Based on this collaboration, the center will contribute to achieving autonomous technologies by developing fundamental and applicable technology related with submerged floating tunnel systems. It will also take the role of a leading global research hub in the field of submerged floating tunnels as well as construction technologies.”
2017.09.07 View 11659
Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems Opens
(Distinguished guests including President Shin (fourth from the right) and Director Lee (third from left) at the opening ceremony)
The Research Center for a Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems was recently established at KAIST with the purpose of taking the lead in developing fundamental and applicable technology for submerged floating tunnels as well as fostering creative and talented people. Haeng-Ki Lee, a professor in the Department of Civil & Environmental Engineering at KAIST is heading the center.
KAIST held its opening ceremony on September 7, 2017 in the Applied Engineering Building located on the main campus.
Distinguished guests, including KAIST president Sung-Chul Shin, the President of the Korea Institute of Ocean Science and Technology Gi-Hoon Hong, the President of the Korean Society of Civil Engineering Young-Seok Park, and the Director in the Division of Engineering at the National Research Foundation of Korea Joong-Kon Park attended the ceremony.
The National Research Foundation of Korea provides Engineering Research Center (ERC) projects which find and foster groups with outstanding research performance in a field of engineering. The projects support these groups so that they can strengthen their global competitiveness while enhancing national competence in basic research.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ was selected as one of the ERC projects in 2017. For the next seven years, the research center will work to develop a submerged floating tunnel system resistant depths greater than 100 meters.
To achieve its goal, the center has defined crucial research topics including: i) a structural analysis program and integrated design technology specific for submerged floating tunnel systems, ii) high-durability marine construction materials and submerged construction integrated systems, and iii) safety and maintenance integrated technology for smart submerged floating tunnel systems.
The ‘Research Center for Smart Submerged Floating Tunnel Systems’ will devote itself to developing a variety of fundamental and applicable technology that will be leading global maritime construction. Moreover, it will concentrate on fostering professional research manpower in related areas.
The Director of the Center Lee said, “The center will cooperate with KAIST researchers who are experts in various fields, including structures, materials, construction, and maritime research. Based on this collaboration, the center will contribute to achieving autonomous technologies by developing fundamental and applicable technology related with submerged floating tunnel systems. It will also take the role of a leading global research hub in the field of submerged floating tunnels as well as construction technologies.”
2017.09.07 View 11659 -
 KAIST's Student Job Fair 2015
KAIST’s Undergraduate Student Council and Graduate Student Council jointly hosted the 2015 KAIST Job Fair on September 2-3, 2015 at the Sports Complex on campus.
The Job Fair took place for the sixth time this year. Forty-three companies, including some of the largest ones in Korea such as Samsung, Hyundai, LG, SK Construction, Hankook Tires, as well as those owned by KAIST graduates, have participated.
The Job Fair specialized in three fields: information technology (IT) and electronic and mechanical engineering. The event included one-to-one employment counseling between human resources managers and students, mock interviews, employment orientations, job consulting, interview makeup lessons, resume writing and photo-shooting, etc.
The international students who attended the event received information packages on employment from the participating companies.
This event was open not only to KAIST students but also to students from other universities in the local community, offering more job opportunities to a wider range of people.
Last year alone, a total of 1,200 people including KAIST students and graduates joined the KAIST’s Job Fair.
2015.09.04 View 7930
KAIST's Student Job Fair 2015
KAIST’s Undergraduate Student Council and Graduate Student Council jointly hosted the 2015 KAIST Job Fair on September 2-3, 2015 at the Sports Complex on campus.
The Job Fair took place for the sixth time this year. Forty-three companies, including some of the largest ones in Korea such as Samsung, Hyundai, LG, SK Construction, Hankook Tires, as well as those owned by KAIST graduates, have participated.
The Job Fair specialized in three fields: information technology (IT) and electronic and mechanical engineering. The event included one-to-one employment counseling between human resources managers and students, mock interviews, employment orientations, job consulting, interview makeup lessons, resume writing and photo-shooting, etc.
The international students who attended the event received information packages on employment from the participating companies.
This event was open not only to KAIST students but also to students from other universities in the local community, offering more job opportunities to a wider range of people.
Last year alone, a total of 1,200 people including KAIST students and graduates joined the KAIST’s Job Fair.
2015.09.04 View 7930 -
 10 Technolgies to Change the World in 2012: The Future Technology Global Agenda Council
The Future Technology Global Agenda Council which is under the World Economy Forum and which KAIST’s biochemical engineering department’s Prof. Sang Yeob Lee is the head of, chose the 10 new technologies that will change the world in year 2012.
The ten technologies include: IT, synthetic biology and metabolic engineering, Green Revolution 2.0, material construction nanotechnology, systematic biology and the simulation technology of biological systems, the technology to use CO2 as a natural resource, wireless power transmission technology, high density energy power system, personalized medical/nutritional/disease preventing system, and new education technology.
The technologies were chosen on the basis of the opinions various science, industry, and government specialists and is deemed to have high potential to change the world in the near future.
The Future Technology Global Agenda Council will choose ten new technologies yearly starting this year in order to solve the problems the world now faces.
The informatics systems that was ranked 1st place, sifts only the data necessary for decision making out of the overflowing amount of data. Much interest has been spurred at the Davos forum.
The synthetic biology and metabolic engineering chosen is expected to play an important role in creating new medicines and producing chemical substances and materials from reusable resources.
Biomass has also been chosen as one of the top ten most important technologies as it was seen to be necessary to lead the second Green Revolution in order to stably provide food for the increasing population and to create bio refineries.
Nanomaterials structured at the molecular level are expected to help us solve problems regarding energy, food, and resources.
Systematic biology and computer modeling is gaining importance in availing humans to construct efficient remedies, materials, and processes while causing minimum effects on the environment, resource reserves, and other people.
The technology to convert CO2, which is considered a problem all over the world, into a useful resource is also gaining the spotlight
Together with such technologies, wireless power transmission technology, high density energy power system, personalized medical/nutritional/disease preventing system, and new education technology are also considered the top ten technologies to change the world.
Prof. Lee said, “Many new discoveries are being made due to the accelerating rate of technological advancements. Many of the technologies that the council has found are sustainable and important for the construction of our future.”
2012.04.04 View 14115
10 Technolgies to Change the World in 2012: The Future Technology Global Agenda Council
The Future Technology Global Agenda Council which is under the World Economy Forum and which KAIST’s biochemical engineering department’s Prof. Sang Yeob Lee is the head of, chose the 10 new technologies that will change the world in year 2012.
The ten technologies include: IT, synthetic biology and metabolic engineering, Green Revolution 2.0, material construction nanotechnology, systematic biology and the simulation technology of biological systems, the technology to use CO2 as a natural resource, wireless power transmission technology, high density energy power system, personalized medical/nutritional/disease preventing system, and new education technology.
The technologies were chosen on the basis of the opinions various science, industry, and government specialists and is deemed to have high potential to change the world in the near future.
The Future Technology Global Agenda Council will choose ten new technologies yearly starting this year in order to solve the problems the world now faces.
The informatics systems that was ranked 1st place, sifts only the data necessary for decision making out of the overflowing amount of data. Much interest has been spurred at the Davos forum.
The synthetic biology and metabolic engineering chosen is expected to play an important role in creating new medicines and producing chemical substances and materials from reusable resources.
Biomass has also been chosen as one of the top ten most important technologies as it was seen to be necessary to lead the second Green Revolution in order to stably provide food for the increasing population and to create bio refineries.
Nanomaterials structured at the molecular level are expected to help us solve problems regarding energy, food, and resources.
Systematic biology and computer modeling is gaining importance in availing humans to construct efficient remedies, materials, and processes while causing minimum effects on the environment, resource reserves, and other people.
The technology to convert CO2, which is considered a problem all over the world, into a useful resource is also gaining the spotlight
Together with such technologies, wireless power transmission technology, high density energy power system, personalized medical/nutritional/disease preventing system, and new education technology are also considered the top ten technologies to change the world.
Prof. Lee said, “Many new discoveries are being made due to the accelerating rate of technological advancements. Many of the technologies that the council has found are sustainable and important for the construction of our future.”
2012.04.04 View 14115 -
 International Center was built to promote greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
On July 9, 2010, KAIST held an opening ceremony for the construction of International Center. The Center will serve as an internal and external liaison for the university, providing a source of assistance to faculty, administrators, and students on matters related to international activities and initiatives. It will also pursue greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
The facility accommodates various meetings, exhibitions, library, language services, and other amenities. The International Cooperation Team of KAIST will be moved into this building and provide a variety of services, such as immigration regulations, cultural adjustment, employment, to assist international students, scholars, faculty, and staff at KAIST, as well as Korean students seeking opportunities to study, work, or travel abroad. An international nursery school will also be inside the building so that foreign faculty and students with children can have convenience and quality child care while they are teaching or studying.
At the center will be held many different kinds of international event—one among them is KAIST-ONE, a festival held twice a year in spring and fall to introduce and share culture, education, and food of the global community at KAIST.
2010.07.19 View 14143
International Center was built to promote greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
On July 9, 2010, KAIST held an opening ceremony for the construction of International Center. The Center will serve as an internal and external liaison for the university, providing a source of assistance to faculty, administrators, and students on matters related to international activities and initiatives. It will also pursue greater exchanges and collaborations between the international community and KAIST.
The facility accommodates various meetings, exhibitions, library, language services, and other amenities. The International Cooperation Team of KAIST will be moved into this building and provide a variety of services, such as immigration regulations, cultural adjustment, employment, to assist international students, scholars, faculty, and staff at KAIST, as well as Korean students seeking opportunities to study, work, or travel abroad. An international nursery school will also be inside the building so that foreign faculty and students with children can have convenience and quality child care while they are teaching or studying.
At the center will be held many different kinds of international event—one among them is KAIST-ONE, a festival held twice a year in spring and fall to introduce and share culture, education, and food of the global community at KAIST.
2010.07.19 View 14143 -
 KAIST held an opening ceremony for the completion of KAIST Institute Building.
A Korean American businessman and his wife, Byiung Jun Park and Chunghi Hong, donated 10 million USD for the construction of the building.
KAIST hosted an opening ceremony on May 11, 2010 for the new addition to its campus, called the Chunghi & Byiung Jun (BJ) Park KAIST Institute Building. The KI Building will serve as a hub for creative multidisciplinary researches.
A Korean American businessman and his wife made a considerable contribution for the construction of the building, worth 10 million USD. KAIST called the building Byiung Jun (BJ) Park and Chunghi Hong in recognition of their contribution. Chairman Park was the founder of the Merchandise Testing Laboratory, a leading textile quality control multinational.
It took 19 months to finish the construction of the KI Building with a total cost of 36 billion Korean won. The building consists of one basement and five ground floors. At the basement, there are clean room and equipment storage room; on the 2nd and 3rd floors, conference and exhibition halls; and on the rest of the floors, research labs and administration offices are to be located.
KAIST’s eight integral research institutes will be placed inside the building: the BioCentury; Information Technology Convergence; Design of Complex Systems; Entertainment Engineering; the NanoCentury; Eco-Energy; Urban Space and Systems; and Optical Science and Technology. Approximately 230 professors from 25 departments of various academic fields will make the KI Building home for study and research. The KI Building will play a great role in producing world-class convergence research works by KAIST researchers and professors, thereby making a contribution to the improvement of national competitiveness.
Vice President of KI Building, Sang-Soo Kim, said, “There has been no such place for us to concentrate research manpower and equipment scattered around the campus. By having all the necessary resources at one place will allow us to conduct convergence researches more efficiently and effectively. I’d like to express my appreciation for the Ministry of Education and Science and Technology as well as Chairman Byiung Jun (BJ) Park, who gave us tremendous supports in the process of constructing the KI Building.”
“The building’s inside has a unique office structure, getting rid of walls or partitions between institutes or departments, to stimulate an environment conducive to convergence researches. We hope to present a new model for creative multidisciplinary researches through a selective and focused approach to be facilitated by institutes at the KI Building,” added by the vice president.
2010.05.20 View 14658
KAIST held an opening ceremony for the completion of KAIST Institute Building.
A Korean American businessman and his wife, Byiung Jun Park and Chunghi Hong, donated 10 million USD for the construction of the building.
KAIST hosted an opening ceremony on May 11, 2010 for the new addition to its campus, called the Chunghi & Byiung Jun (BJ) Park KAIST Institute Building. The KI Building will serve as a hub for creative multidisciplinary researches.
A Korean American businessman and his wife made a considerable contribution for the construction of the building, worth 10 million USD. KAIST called the building Byiung Jun (BJ) Park and Chunghi Hong in recognition of their contribution. Chairman Park was the founder of the Merchandise Testing Laboratory, a leading textile quality control multinational.
It took 19 months to finish the construction of the KI Building with a total cost of 36 billion Korean won. The building consists of one basement and five ground floors. At the basement, there are clean room and equipment storage room; on the 2nd and 3rd floors, conference and exhibition halls; and on the rest of the floors, research labs and administration offices are to be located.
KAIST’s eight integral research institutes will be placed inside the building: the BioCentury; Information Technology Convergence; Design of Complex Systems; Entertainment Engineering; the NanoCentury; Eco-Energy; Urban Space and Systems; and Optical Science and Technology. Approximately 230 professors from 25 departments of various academic fields will make the KI Building home for study and research. The KI Building will play a great role in producing world-class convergence research works by KAIST researchers and professors, thereby making a contribution to the improvement of national competitiveness.
Vice President of KI Building, Sang-Soo Kim, said, “There has been no such place for us to concentrate research manpower and equipment scattered around the campus. By having all the necessary resources at one place will allow us to conduct convergence researches more efficiently and effectively. I’d like to express my appreciation for the Ministry of Education and Science and Technology as well as Chairman Byiung Jun (BJ) Park, who gave us tremendous supports in the process of constructing the KI Building.”
“The building’s inside has a unique office structure, getting rid of walls or partitions between institutes or departments, to stimulate an environment conducive to convergence researches. We hope to present a new model for creative multidisciplinary researches through a selective and focused approach to be facilitated by institutes at the KI Building,” added by the vice president.
2010.05.20 View 14658 -
 KAIST Dedicates Geocentrifuge Experiment Center
KAIST dedicated the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Experiment Center for researches in monitoring natural disasters such as earthquake and embankment collapse through miniature simulation tests on Wednesday (April 9) after a two-year construction work.
The experiment center is part of the Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Program (KOCED) which has been sponsored by the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs to build an infrastructure for construction engineering researches at a national level. The ministry plans to build a total of 5 similar centers nationwide by the end of the year.
On hand at the dedication ceremony were Jae-Choon Lee, President of the Korea Institute of Construction & Transportation Technology Evaluation and Planning, KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, and scores of experts and administration officials.
The construction of the five-story building on an area of about 3,328 square meters cost 8.4 billion won (US$6.3 million).
The center is expected to serve as a major laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering. It is equipped with such state-of-the-art facilities as geocentrifuge, a useful tool for studying flow in unsaturated soil under well-controlled, repeatable conditions, a bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquake-like wave; and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by remote control.
Geocentrifuge experiment allows detecting ground and structure motions easily and rapidly by simulation tests. Thus, it is widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, soft ground movement, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by the geocentrifuge experiment.
The geocentrifuge research facility is available for use by outside researchers, so scientists from other universities, research institutes and corporations can perform research and test their scientific and engineering hypotheses.
The center is divided into two sections, experiment building and research building. The experiment building is composed of a geocentrifuge laboratory, model-making rooms, workshops, a geotechnical engineering laboratory and specimen storehouse, while the research building has a control room, a video conference room, an electronic library and research rooms.
2009.04.09 View 15375
KAIST Dedicates Geocentrifuge Experiment Center
KAIST dedicated the KOCED Geo-Centrifuge Experiment Center for researches in monitoring natural disasters such as earthquake and embankment collapse through miniature simulation tests on Wednesday (April 9) after a two-year construction work.
The experiment center is part of the Korea Construction Engineering Development Collaboratory Program (KOCED) which has been sponsored by the Ministry of Land, Transport and Maritime Affairs to build an infrastructure for construction engineering researches at a national level. The ministry plans to build a total of 5 similar centers nationwide by the end of the year.
On hand at the dedication ceremony were Jae-Choon Lee, President of the Korea Institute of Construction & Transportation Technology Evaluation and Planning, KAIST President Nam-Pyo Suh, and scores of experts and administration officials.
The construction of the five-story building on an area of about 3,328 square meters cost 8.4 billion won (US$6.3 million).
The center is expected to serve as a major laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering. It is equipped with such state-of-the-art facilities as geocentrifuge, a useful tool for studying flow in unsaturated soil under well-controlled, repeatable conditions, a bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquake-like wave; and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by remote control.
Geocentrifuge experiment allows detecting ground and structure motions easily and rapidly by simulation tests. Thus, it is widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, soft ground movement, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by the geocentrifuge experiment.
The geocentrifuge research facility is available for use by outside researchers, so scientists from other universities, research institutes and corporations can perform research and test their scientific and engineering hypotheses.
The center is divided into two sections, experiment building and research building. The experiment building is composed of a geocentrifuge laboratory, model-making rooms, workshops, a geotechnical engineering laboratory and specimen storehouse, while the research building has a control room, a video conference room, an electronic library and research rooms.
2009.04.09 View 15375 -
 KAIST to Build Branch Campus in New Administrative City
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Multifunctional Administrative City Construction Agency and the Korea Land Corporation on March 4 to build a branch campus in the city now under construction to house many government organizations to be relocated from Seoul.
The MOU calls for building a well-facilitated KAIST campus on 310,000 square meters of land within the planned city, about 30 kilometers west of Daejeon. The multifunctional city, named Sejong City, is scheduled to be dedicated in 2014.
The MAC now being built in the Yongi-Gongju area of South Chungcheong Province is geographically in the center of South Korea, and many governmental agencies and major public organizations will move in from 2015.
The KAIST campus is envisioned to be home to a newly established College of Strategy and Policy, a Strategy and Policy Research Center, and an Innovative Technology Research Center. The College of Medical Science currently based in the Daejeon campus will be relocated to the campus. With a research-oriented hospital and a medical engineering research center, KAIST hopes to become a leading institution in disease treatment and medical engineering technologies.
The new campus is also expected to house new KAIST colleges now in the planning stage which will offer interdisciplinary courses such as the College of IT and Contents and the College of Life Sciences. KAIST also seeks to resolve housing shortage problems by building an in-campus village designed to provide international living environment for professors and students on the planned campus
2008.03.18 View 17941
KAIST to Build Branch Campus in New Administrative City
KAIST signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the Multifunctional Administrative City Construction Agency and the Korea Land Corporation on March 4 to build a branch campus in the city now under construction to house many government organizations to be relocated from Seoul.
The MOU calls for building a well-facilitated KAIST campus on 310,000 square meters of land within the planned city, about 30 kilometers west of Daejeon. The multifunctional city, named Sejong City, is scheduled to be dedicated in 2014.
The MAC now being built in the Yongi-Gongju area of South Chungcheong Province is geographically in the center of South Korea, and many governmental agencies and major public organizations will move in from 2015.
The KAIST campus is envisioned to be home to a newly established College of Strategy and Policy, a Strategy and Policy Research Center, and an Innovative Technology Research Center. The College of Medical Science currently based in the Daejeon campus will be relocated to the campus. With a research-oriented hospital and a medical engineering research center, KAIST hopes to become a leading institution in disease treatment and medical engineering technologies.
The new campus is also expected to house new KAIST colleges now in the planning stage which will offer interdisciplinary courses such as the College of IT and Contents and the College of Life Sciences. KAIST also seeks to resolve housing shortage problems by building an in-campus village designed to provide international living environment for professors and students on the planned campus
2008.03.18 View 17941 -
 KAIST to build large-scale civil engineering experiment center
- Geo-Centrifuge experiment center of an area of about 1,712 square meters and an estimated construction cost of total 8.4 billion won
- Simulation laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering with state-of-the-art experiment equipment- Ground-breaking ceremony held on April 3 at 4 pm
KAIST will construct ‘distributed shared-type Geo-Centrifuge experiment center’, a large-scale civil engineering laboratory that will study natural disasters such as earthquake, embankment collapse, etc. with ground structure miniatures.
A two-story building with a basement occupying an area of about 1,712 square meters will become a landmark laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering that can be used for the education, research, and social infrastructure design by universities, institutes, and corporations via high-speed information and communication network. The estimated construction cost is 8.4 billion won.
The center will be composed of experiment building including geo-centrifuge laboratory, model-making room, workshop, geotechnical engineering laboratory, and specimen storehouse; and research building including control room, video conference room, electronic library, and research rooms. A variety of convenience facilities for researchers and video conference and remote monitoring system, with which researcher at remote distances can directly participate in experiments, will be provided in the research building, and world’s top-class experiment equipment such as geo-centrifuge with a turning radius of 5 meters, a maximum acceleration of 130 G (130 times faster than the acceleration of gravity), a preload of 2,400 kg and bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquakes-like wave during experiments, and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by a remote control will be installed.
Geo-Centrifuge experiment refers to an experiment that reproduces natural disaster-like motions by making miniatures of large-scale ground structures such as dams, slopes, etc. and using centrifugal forces generated from high-speed rotation. This experiment can easily and rapidly reproduce actual motions of ground structures at a low cost, thereby being widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, movement of soft ground, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by simulation tests by this experiment.
“The center will make possible a variety of experiments and researches that have never been available in Korea due to the lack of experiment infrastructure, therefore activate researches over the design and construction of large-scale social infrastructures. Making possible civil engineering researches demanding the use of large-scale equipment like Centrifuge, severely dependent on overseas technologies so far, will enhance the global competitiveness of Korean construction industry,” said Dong-soo Kim, President of the center.
The center will be constructed as part of the Ministry of Construction & Transportation (MOCT)’s project for the establishment of distributed shared-style construction research infrastructure, which is designed to establish construction research infrastructures in a national level. The ground breaking ceremony was held at KAIST on April 3 at 4 pm.
2007.04.12 View 18752
KAIST to build large-scale civil engineering experiment center
- Geo-Centrifuge experiment center of an area of about 1,712 square meters and an estimated construction cost of total 8.4 billion won
- Simulation laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering with state-of-the-art experiment equipment- Ground-breaking ceremony held on April 3 at 4 pm
KAIST will construct ‘distributed shared-type Geo-Centrifuge experiment center’, a large-scale civil engineering laboratory that will study natural disasters such as earthquake, embankment collapse, etc. with ground structure miniatures.
A two-story building with a basement occupying an area of about 1,712 square meters will become a landmark laboratory in the field of geotechnical engineering that can be used for the education, research, and social infrastructure design by universities, institutes, and corporations via high-speed information and communication network. The estimated construction cost is 8.4 billion won.
The center will be composed of experiment building including geo-centrifuge laboratory, model-making room, workshop, geotechnical engineering laboratory, and specimen storehouse; and research building including control room, video conference room, electronic library, and research rooms. A variety of convenience facilities for researchers and video conference and remote monitoring system, with which researcher at remote distances can directly participate in experiments, will be provided in the research building, and world’s top-class experiment equipment such as geo-centrifuge with a turning radius of 5 meters, a maximum acceleration of 130 G (130 times faster than the acceleration of gravity), a preload of 2,400 kg and bidirectional shaking-table that can reproduce earthquakes-like wave during experiments, and robots that can reproduce construction procedures by a remote control will be installed.
Geo-Centrifuge experiment refers to an experiment that reproduces natural disaster-like motions by making miniatures of large-scale ground structures such as dams, slopes, etc. and using centrifugal forces generated from high-speed rotation. This experiment can easily and rapidly reproduce actual motions of ground structures at a low cost, thereby being widely used for various geotechnical engineering researches such as evaluation of seismic safety, movement of soft ground, slope stability analysis, etc. The causes of the embankment collapse in New Orleans by Hurricane Katrina in 2005 were also revealed by simulation tests by this experiment.
“The center will make possible a variety of experiments and researches that have never been available in Korea due to the lack of experiment infrastructure, therefore activate researches over the design and construction of large-scale social infrastructures. Making possible civil engineering researches demanding the use of large-scale equipment like Centrifuge, severely dependent on overseas technologies so far, will enhance the global competitiveness of Korean construction industry,” said Dong-soo Kim, President of the center.
The center will be constructed as part of the Ministry of Construction & Transportation (MOCT)’s project for the establishment of distributed shared-style construction research infrastructure, which is designed to establish construction research infrastructures in a national level. The ground breaking ceremony was held at KAIST on April 3 at 4 pm.
2007.04.12 View 18752