Cancer+Treatment
-
 Identification of How Chemotherapy Drug Works Could Deliver Personalized Cancer Treatment
The chemotherapy drug decitabine is commonly used to treat patients with blood cancers, but its response rate is somewhat low. Researchers have now identified why this is the case, opening the door to more personalized cancer therapies for those with these types of cancers, and perhaps further afield.
Researchers have identified the genetic and molecular mechanisms within cells that make the chemotherapy drug decitabine—used to treat patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) —work for some patients but not others. The findings should assist clinicians in developing more patient-specific treatment strategies.
The findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science on March 30.
The chemotherapy drug decitabine, also known by its brand name Dacogen, works by modifying our DNA that in turn switches on genes that stop the cancer cells from growing and replicating. However, decitabine’s response rate is somewhat low (showing improvement in just 30-35% of patients), which leaves something of a mystery as to why it works well for some patients but not for others. To find out why this happens, researchers from the KAIST investigated the molecular mediators that are involved with regulating the effects of the drug.
Decitabine works to activate the production of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), which in turn induces an immune response. ERVs are viruses that long ago inserted dormant copies of themselves into the human genome. Decitabine in essence, ‘reactivates’ these viral elements and produces double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) that the immune system views as a foreign body.
“However, the mechanisms involved in this process, in particular how production and transport of these ERV dsRNAs were regulated within the cell were understudied,” said corresponding author Yoosik Kim, professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST.
“So to explain why decitabine works in some patients but not others, we investigated what these molecular mechanisms were,” added Kim.
To do so, the researchers used image-based RNA interference (RNAi) screening. This is a relatively new technique in which specific sequences within a genome are knocked out of action or “downregulated.” Large-scale screening, which can be performed in cultured cells or within live organisms, works to investigate the function of different genes. The KAIST researchers collaborated with the Institut Pasteur Korea to analyze the effect of downregulating genes that recognize ERV dsRNAs and could be involved in the cellular response to decitabine.
From these initial screening results, they performed an even more detailed downregulation screening analysis. Through the screening, they were able to identify two particular gene sequences involved in the production of an RNA-binding protein called Staufen1 and the production of a strand of RNA that does not in turn produce any proteins called TINCR that play a key regulatory role in response to the drug. Staufen1 binds directly to dsRNAs and stabilizes them in concert with the TINCR.
If a patient is not producing sufficient Staufen1 and TINCR, then the dsRNA viral mimics quickly degrade before the immune system can spot them. And, crucially for cancer therapy, this means that patients with lower expression (activation) of these sequences will show inferior response to decitabine. Indeed, the researchers confirmed that MDS/AML patients with low Staufen1 and TINCR expression did not benefit from decitabine therapy.
“We can now isolate patients who will not benefit from the therapy and direct them to a different type of therapy,” said first author Yongsuk Ku. “This serves as an important step toward developing a patient-specific treatment cancer strategy.”
As the researchers used patient samples taken from bone marrow, the next step will be to try to develop a testing method that can identify the problem from just blood samples, which are much easier to acquire from patients.
The team plans to investigate if the analysis can be extended to patients with solid tumors in addition to those with blood cancers.
-Profile
Professor Yoosik Kim
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
-Publication
Noncanonical immune response to the inhibition of DNA methylation by Staufen1 via stabilization of endogenous retrovirus RNAs, PNAS
2021.05.24 View 11786
Identification of How Chemotherapy Drug Works Could Deliver Personalized Cancer Treatment
The chemotherapy drug decitabine is commonly used to treat patients with blood cancers, but its response rate is somewhat low. Researchers have now identified why this is the case, opening the door to more personalized cancer therapies for those with these types of cancers, and perhaps further afield.
Researchers have identified the genetic and molecular mechanisms within cells that make the chemotherapy drug decitabine—used to treat patients with myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) —work for some patients but not others. The findings should assist clinicians in developing more patient-specific treatment strategies.
The findings were published in the Proceedings of the National Academies of Science on March 30.
The chemotherapy drug decitabine, also known by its brand name Dacogen, works by modifying our DNA that in turn switches on genes that stop the cancer cells from growing and replicating. However, decitabine’s response rate is somewhat low (showing improvement in just 30-35% of patients), which leaves something of a mystery as to why it works well for some patients but not for others. To find out why this happens, researchers from the KAIST investigated the molecular mediators that are involved with regulating the effects of the drug.
Decitabine works to activate the production of endogenous retroviruses (ERVs), which in turn induces an immune response. ERVs are viruses that long ago inserted dormant copies of themselves into the human genome. Decitabine in essence, ‘reactivates’ these viral elements and produces double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) that the immune system views as a foreign body.
“However, the mechanisms involved in this process, in particular how production and transport of these ERV dsRNAs were regulated within the cell were understudied,” said corresponding author Yoosik Kim, professor in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST.
“So to explain why decitabine works in some patients but not others, we investigated what these molecular mechanisms were,” added Kim.
To do so, the researchers used image-based RNA interference (RNAi) screening. This is a relatively new technique in which specific sequences within a genome are knocked out of action or “downregulated.” Large-scale screening, which can be performed in cultured cells or within live organisms, works to investigate the function of different genes. The KAIST researchers collaborated with the Institut Pasteur Korea to analyze the effect of downregulating genes that recognize ERV dsRNAs and could be involved in the cellular response to decitabine.
From these initial screening results, they performed an even more detailed downregulation screening analysis. Through the screening, they were able to identify two particular gene sequences involved in the production of an RNA-binding protein called Staufen1 and the production of a strand of RNA that does not in turn produce any proteins called TINCR that play a key regulatory role in response to the drug. Staufen1 binds directly to dsRNAs and stabilizes them in concert with the TINCR.
If a patient is not producing sufficient Staufen1 and TINCR, then the dsRNA viral mimics quickly degrade before the immune system can spot them. And, crucially for cancer therapy, this means that patients with lower expression (activation) of these sequences will show inferior response to decitabine. Indeed, the researchers confirmed that MDS/AML patients with low Staufen1 and TINCR expression did not benefit from decitabine therapy.
“We can now isolate patients who will not benefit from the therapy and direct them to a different type of therapy,” said first author Yongsuk Ku. “This serves as an important step toward developing a patient-specific treatment cancer strategy.”
As the researchers used patient samples taken from bone marrow, the next step will be to try to develop a testing method that can identify the problem from just blood samples, which are much easier to acquire from patients.
The team plans to investigate if the analysis can be extended to patients with solid tumors in addition to those with blood cancers.
-Profile
Professor Yoosik Kim
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
KAIST
-Publication
Noncanonical immune response to the inhibition of DNA methylation by Staufen1 via stabilization of endogenous retrovirus RNAs, PNAS
2021.05.24 View 11786 -
 What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 16794
What Fuels a “Domino Effect” in Cancer Drug Resistance?
KAIST researchers have identified mechanisms that relay prior acquired resistance to the first-line chemotherapy to the second-line targeted therapy, fueling a “domino effect” in cancer drug resistance. Their study featured in the February 7 edition of Science Advances suggests a new strategy for improving the second-line setting of cancer treatment for patients who showed resistance to anti-cancer drugs.
Resistance to cancer drugs is often managed in the clinic by chemotherapy and targeted therapy. Unlike chemotherapy that works by repressing fast-proliferating cells, targeted therapy blocks a single oncogenic pathway to halt tumor growth. In many cases, targeted therapy is engaged as a maintenance therapy or employed in the second-line after front-line chemotherapy.
A team of researchers led by Professor Yoosik Kim from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the KAIST Institute for Health Science and Technology (KIHST) has discovered an unexpected resistance signature that occurs between chemotherapy and targeted therapy. The team further identified a set of integrated mechanisms that promotes this kind of sequential therapy resistance.
“There have been multiple clinical accounts reflecting that targeted therapies tend to be least successful in patients who have exhausted all standard treatments,” said the first author of the paper Mark Borris D. Aldonza. He continued, “These accounts ignited our hypothesis that failed responses to some chemotherapies might speed up the evolution of resistance to other drugs, particularly those with specific targets.”
Aldonza and his colleagues extracted large amounts of drug-resistance information from the open-source database the Genomics of Drug Sensitivity in Cancer (GDSC), which contains thousands of drug response data entries from various human cancer cell lines. Their big data analysis revealed that cancer cell lines resistant to chemotherapies classified as anti-mitotic drugs (AMDs), toxins that inhibit overacting cell division, are also resistant to a class of targeted therapies called epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (EGFR-TKIs).
In all of the cancer types analyzed, more than 84 percent of those resistant to AMDs, representatively ‘paclitaxel’, were also resistant to at least nine EGFR-TKIs. In lung, pancreatic, and breast cancers where paclitaxel is often used as a first-line, standard-of-care regimen, greater than 92 percent showed resistance to EGFR-TKIs. Professor Kim said, “It is surprising to see that such collateral resistance can occur specifically between two chemically different classes of drugs.”
To figure out how failed responses to paclitaxel leads to resistance to EGFR-TKIs, the team validated co-resistance signatures that they found in the database by generating and analyzing a subset of slow-doubling, paclitaxel-resistant cancer models called ‘persisters’.
The results demonstrated that paclitaxel-resistant cancers remodel their stress response by first becoming more stem cell-like, evolving the ability to self-renew to adapt to more stressful conditions like drug exposures. More surprisingly, when the researchers characterized the metabolic state of the cells, EGFR-TKI persisters derived from paclitaxel-resistant cancer cells showed high dependencies to energy-producing processes such as glycolysis and glutaminolysis.
“We found that, without an energy stimulus like glucose, these cells transform to becoming more senescent, a characteristic of cells that have arrested cell division. However, this senescence is controlled by stem cell factors, which the paclitaxel-resistant cancers use to escape from this arrested state given a favorable condition to re-grow,” said Aldonza.
Professor Kim explained, “Before this research, there was no reason to expect that acquiring the cancer stem cell phenotype that dramatically leads to a cascade of changes in cellular states affecting metabolism and cell death is linked with drug-specific sequential resistance between two classes of therapies.”
He added, “The expansion of our work to other working models of drug resistance in a much more clinically-relevant setting, perhaps in clinical trials, will take on increasing importance, as sequential treatment strategies will continue to be adapted to various forms of anti-cancer therapy regimens.”
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2016R1C1B2009886), and the KAIST Future Systems Healthcare Project (KAISTHEALTHCARE42) funded by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT). Undergraduate student Aldonza participated in this research project and presented the findings as the lead author as part of the Undergraduate Research Participation (URP) Program at KAIST.
< Figure 1. Schematic overview of the study. >
< Figure 2. Big data analysis revealing co-resistance signatures between classes of anti-cancer drugs. >
Publication:
Aldonza et al. (2020) Prior acquired resistance to paclitaxel relays diverse EGFR-targeted therapy persistence mechanisms. Science Advances, Vol. 6, No. 6, eaav7416. Available online at http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aav7416
Profile: Prof. Yoosik Kim, MA, PhD
ysyoosik@kaist.ac.kr
https://qcbio.kaist.ac.kr/
Assistant Professor
Bio Network Analysis Laboratory
Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile: Mark Borris D. Aldonza
borris@kaist.ac.kr
Undergraduate Student
Department of Biological Sciences
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
2020.02.10 View 16794 -
 Complex responsible for protein breakdown in cells identified using Bio TEM
Professor Ho-Min Kim
- High resolution 3D structure analysis success using Bio Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), a giant step towards new anticancer treatment development
- Published in Nature on May 5th
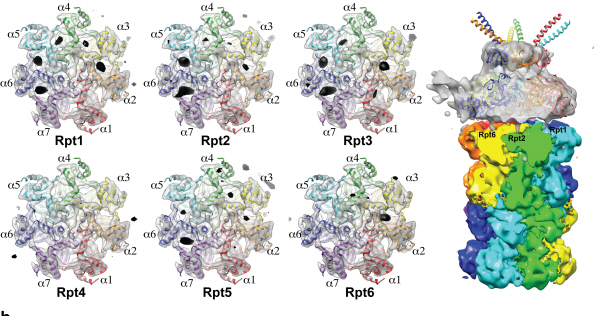
Using TEM to observe protein molecules and analysing its high resolution 3D structure is now possible. KAIST Biomedical Science and Engineering Department’s Professor Ho-Min Kim has identified the high resolution structure of proteasome complexes, which is responsible for protein breakdown in cells, using Bio TEM.
This research has been published on the world"s most prestigious journal, Nature, online on May 5th. Our body controls many cellular processes through production and degradation of proteins to maintain homeostasis. A proteasome complex acts as a garbage disposal system and degrades cellular proteins when needed for regulation, which is one of the central roles of the body.
However, a mutation in proteasome complex leads to diseases such as cancer, degenerative brain diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Currently, the anticancer drug Velcade is used to decrease proteasome function to treat Multiple Myeloma, a form of blood cancer. Research concerning proteasome complexes for more effective anticancer drugs and treatments with fewer side effects has been taking place for more than 20 years. There have been many difficulties in understanding proteasome function through 3D structure analysis since a proteasome complex, consisting of around 30 different proteins, has a great size and complexity.
The research team used Bio TEM instead of conventionally used protein crystallography technique. The protein sample was inserted into Bio TEM, hundreds of photographs were taken from various angles, and then a high–performance computer was used to analyse its structure. Bio TEM requires a smaller sample and can analyse the complexes of great size of proteins.
Professor Ho-Min Kim said, “Identifying proteasome complex assembly process and 3D structure will increase our understanding of cellular protein degradation process and hence assist in new drug development using this knowledge.” He added, “High resolution protein structure analysis using Bio TEM, used for the first time in Korea, will enable us to observe structure analysis of large protein complexes that were difficult to approach using protein crystallography.” Professor Kim continued, “If protein crystallography technology and Bio TEM could be used together to complement one another, it would bring a great synergetic effect to protein complex 3D structure analysis research in the future.”
Professor Ho-Min Kim has conducted this research since his post-doctorate at the University of California, San Francisco, under the advice of Professor Yifan Cheng; in co-operation with Harvard University and Colorado University.
Figure 1: A picture taken by Bio TEM of open state protein sample (proteasome complex)
Figure 2: Bio TEM image analysis showing protein 3D structure
2013.05.25 View 11933
Complex responsible for protein breakdown in cells identified using Bio TEM
Professor Ho-Min Kim
- High resolution 3D structure analysis success using Bio Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM), a giant step towards new anticancer treatment development
- Published in Nature on May 5th
Using TEM to observe protein molecules and analysing its high resolution 3D structure is now possible. KAIST Biomedical Science and Engineering Department’s Professor Ho-Min Kim has identified the high resolution structure of proteasome complexes, which is responsible for protein breakdown in cells, using Bio TEM.
This research has been published on the world"s most prestigious journal, Nature, online on May 5th. Our body controls many cellular processes through production and degradation of proteins to maintain homeostasis. A proteasome complex acts as a garbage disposal system and degrades cellular proteins when needed for regulation, which is one of the central roles of the body.
However, a mutation in proteasome complex leads to diseases such as cancer, degenerative brain diseases, and autoimmune diseases.
Currently, the anticancer drug Velcade is used to decrease proteasome function to treat Multiple Myeloma, a form of blood cancer. Research concerning proteasome complexes for more effective anticancer drugs and treatments with fewer side effects has been taking place for more than 20 years. There have been many difficulties in understanding proteasome function through 3D structure analysis since a proteasome complex, consisting of around 30 different proteins, has a great size and complexity.
The research team used Bio TEM instead of conventionally used protein crystallography technique. The protein sample was inserted into Bio TEM, hundreds of photographs were taken from various angles, and then a high–performance computer was used to analyse its structure. Bio TEM requires a smaller sample and can analyse the complexes of great size of proteins.
Professor Ho-Min Kim said, “Identifying proteasome complex assembly process and 3D structure will increase our understanding of cellular protein degradation process and hence assist in new drug development using this knowledge.” He added, “High resolution protein structure analysis using Bio TEM, used for the first time in Korea, will enable us to observe structure analysis of large protein complexes that were difficult to approach using protein crystallography.” Professor Kim continued, “If protein crystallography technology and Bio TEM could be used together to complement one another, it would bring a great synergetic effect to protein complex 3D structure analysis research in the future.”
Professor Ho-Min Kim has conducted this research since his post-doctorate at the University of California, San Francisco, under the advice of Professor Yifan Cheng; in co-operation with Harvard University and Colorado University.
Figure 1: A picture taken by Bio TEM of open state protein sample (proteasome complex)
Figure 2: Bio TEM image analysis showing protein 3D structure
2013.05.25 View 11933