CES
-
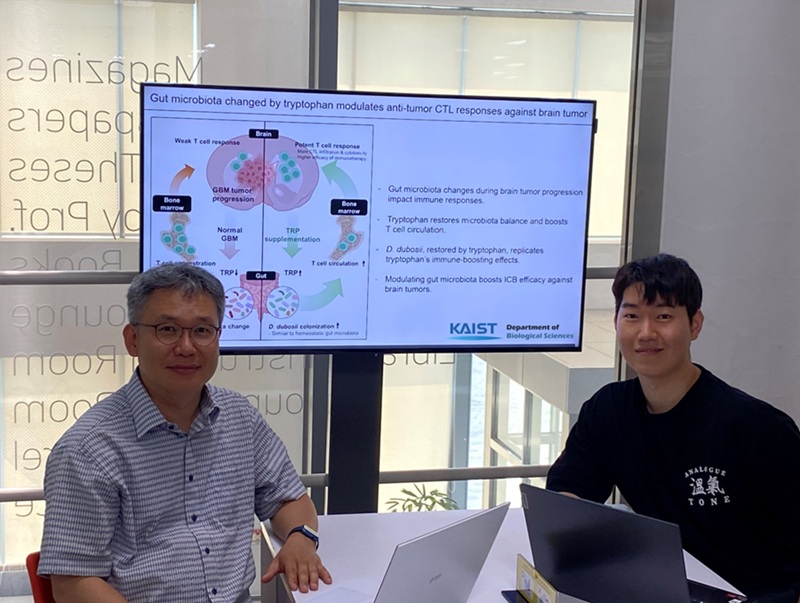 KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut Microbiota
< Photo 1.(From left) Prof. Heung Kyu Lee, Department of Biological Sciences,
and Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim>
Advanced treatments, known as immunotherapies that activate T cells—our body's immune cells—to eliminate cancer cells, have shown limited efficacy as standalone therapies for glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain tumor. This is due to their minimal response to glioblastoma and high resistance to treatment.
Now, a KAIST research team has now demonstrated a new therapeutic strategy that can enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy for brain tumors by utilizing gut microbes and their metabolites. This also opens up possibilities for developing microbiome-based immunotherapy supplements in the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July 1 that a research team led by Professor Heung Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences discovered and demonstrated a method to significantly improve the efficiency of glioblastoma immunotherapy by focusing on changes in the gut microbial ecosystem.
The research team noted that as glioblastoma progresses, the concentration of ‘tryptophan’, an important amino acid in the gut, sharply decreases, leading to changes in the gut microbial ecosystem. They discovered that by supplementing tryptophan to restore microbial diversity, specific beneficial strains activate CD8 T cells (a type of immune cell) and induce their infiltration into tumor tissues. Through a mouse model of glioblastoma, the research team confirmed that tryptophan supplementation enhanced the response of cancer-attacking T cells (especially CD8 T cells), leading to their increased migration to tumor sites such as lymph nodes and the brain.
In this process, they also revealed that ‘Duncaniella dubosii’, a beneficial commensal bacterium present in the gut, plays a crucial role. This bacterium helped T cells effectively redistribute within the body, and survival rates significantly improved when used in combination with immunotherapy (anti-PD-1).
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that even when this commensal bacterium was administered alone to germ-free mice (mice without any commensal microbes), the survival rate for glioblastoma increased. This is because the bacterium utilizes tryptophan to regulate the gut environment, and the metabolites produced in this process strengthen the ability of CD8 T cells to attack cancer cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This research is a meaningful achievement, showing that even in intractable brain tumors where immune checkpoint inhibitors had no effect, a combined strategy utilizing gut microbes can significantly enhance treatment response."
Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim of KAIST (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute for Biological Sciences) participated as the first author. The research findings were published online in Cell Reports, an international journal in the life sciences, on June 26.
This research was conducted as part of the Basic Research Program and Bio & Medical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
※Paper Title: Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by brain tumor modulates the efficacy of immunotherapy
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115825
2025.07.02 View 43
KAIST Enhances Immunotherapy for Difficult-to-Treat Brain Tumors with Gut Microbiota
< Photo 1.(From left) Prof. Heung Kyu Lee, Department of Biological Sciences,
and Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim>
Advanced treatments, known as immunotherapies that activate T cells—our body's immune cells—to eliminate cancer cells, have shown limited efficacy as standalone therapies for glioblastoma, the most lethal form of brain tumor. This is due to their minimal response to glioblastoma and high resistance to treatment.
Now, a KAIST research team has now demonstrated a new therapeutic strategy that can enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy for brain tumors by utilizing gut microbes and their metabolites. This also opens up possibilities for developing microbiome-based immunotherapy supplements in the future.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July 1 that a research team led by Professor Heung Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences discovered and demonstrated a method to significantly improve the efficiency of glioblastoma immunotherapy by focusing on changes in the gut microbial ecosystem.
The research team noted that as glioblastoma progresses, the concentration of ‘tryptophan’, an important amino acid in the gut, sharply decreases, leading to changes in the gut microbial ecosystem. They discovered that by supplementing tryptophan to restore microbial diversity, specific beneficial strains activate CD8 T cells (a type of immune cell) and induce their infiltration into tumor tissues. Through a mouse model of glioblastoma, the research team confirmed that tryptophan supplementation enhanced the response of cancer-attacking T cells (especially CD8 T cells), leading to their increased migration to tumor sites such as lymph nodes and the brain.
In this process, they also revealed that ‘Duncaniella dubosii’, a beneficial commensal bacterium present in the gut, plays a crucial role. This bacterium helped T cells effectively redistribute within the body, and survival rates significantly improved when used in combination with immunotherapy (anti-PD-1).
Furthermore, it was demonstrated that even when this commensal bacterium was administered alone to germ-free mice (mice without any commensal microbes), the survival rate for glioblastoma increased. This is because the bacterium utilizes tryptophan to regulate the gut environment, and the metabolites produced in this process strengthen the ability of CD8 T cells to attack cancer cells.
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This research is a meaningful achievement, showing that even in intractable brain tumors where immune checkpoint inhibitors had no effect, a combined strategy utilizing gut microbes can significantly enhance treatment response."
Dr. Hyeon Cheol Kim of KAIST (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the Institute for Biological Sciences) participated as the first author. The research findings were published online in Cell Reports, an international journal in the life sciences, on June 26.
This research was conducted as part of the Basic Research Program and Bio & Medical Technology Development Program supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
※Paper Title: Gut microbiota dysbiosis induced by brain tumor modulates the efficacy of immunotherapy
※DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115825
2025.07.02 View 43 -
 KAIST Develops Customized Tactile Sensor That Can Detect Light Breath, Pressure and Sound
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Inkyu Park of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME), Dr. Jungrak Choi of ETRI, Ph.D. Candidate Donho Lee and M.S. Graduate Chankyu Han of KAIST ME >
When a robot grabs an object or a medical device detects a pulse, the tactile sensor is the technology that senses pressure like a fingertip. Existing sensors had disadvantages, such as slow responses or declining accuracy after repeated use, but Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a sensor that can quickly and accurately detect even light breath, pressure, and sound. This sensor can be used across a broad range — from everyday movements to medical diagnostics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 23rd of June that Professor Inkyu Park’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, through a collaborative research project with the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI, President Seung Chan Bang ) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young Sik Kim), has developed an innovative technology that overcomes the structural limitations of existing tactile sensors.
The core of this joint research is the implementation of a customized tactile sensor that simultaneously achieves flexibility, precision, and repeatable durability by applying Thermoformed 3D Electronics (T3DE).
< Figure 1. Comparative evaluation of soft elastomer–based 3D structure versus thermoforming-based 3D structure in terms of mechanical properties. >
In particular, soft elastomer-based sensors (rubber, silicone, etc. — materials that stretch and return to their original shape) have structural problems such as slow response times, high hysteresis*, and creep**, but this new platform operates precisely in diverse environments and overcomes these limitations.
*Hysteresis: A phenomenon where the previously applied force or change is retained like a “memory,” so that the same stimulus does not always produce the same result.
**Creep: The phenomenon where a material slowly deforms when a force is continuously applied.
T3DE sensors are manufactured by precisely forming electrodes on a 2D film, then thermoforming them into a 3D structure under heat and pressure. Specifically, the top electrodes and supporting pillar structures of the sensor are designed to allow the fine-tuning of the mechanical properties for different purposes. By adjusting microstructural parameters — such as the thickness, length, and number of support pillars — the sensor’s Young’s modulus* can be tuned across a broad range of 10 Pa to 1 MPa. This matches the stiffness of biological tissues like skin, muscle, and tendons, making them highly suitable as bio-interface sensors.
*Young’s modulus: An index representing a material's stiffness; this research can control this index to match various biological tissues.
The newly developed T3DE sensor uses air as a dielectric material to reduce power consumption and demonstrates outstanding performance in sensitivity, response time, thermal stability, and repeatable accuracy.
Experimental results showed that the sensor achieved △sensitivity of 5,884 kPa⁻¹, △response time of 0.1 ms (less than one-thousandth of a second), △hysteresis of less than 0.5%, and maintained a repeatable precision of 99.9% or higher even after 5,000 repeated measurements.
< Figure 2. Graphic Overview of thermoformed 3D electronics (T3DE) >
The research team also constructed a high-resolution 40×70 array, comprising a total of 2,800 densely packed sensors, to visualize the pressure distribution on the sole of the foot in real time during exercise and confirmed the possibility of using the sensor for wrist pulse measurement to assess vascular health. Furthermore, successful results were also achieved in sound-detection experiments at a level comparable to commercial acoustic sensors. In short, the sensor can precisely and quickly measure foot pressure, pulse, and sound, allowing it to be applied in areas such as sports, health, and sound sensing.
The T3DE technology was also applied to an augmented-reality(AR)-based surgical training system. By adjusting the stiffness of each sensor element to match that of biological tissues, the system provided real-time visual and tactile feedback according to the pressure applied during surgical incisions. It also offered real-time warnings if an incision was too deep or approached a risky area, making it a promising technology for enhancing immersion and accuracy in medical training.
KAIST Professor Inkyu Park stated, “Because this sensor can be precisely tuned from the design stage and operates reliably across diverse environments, it can be used not only in everyday life, but also in a variety of fields such as healthcare, rehabilitation, and virtual reality.”
The research was co-led as first authors by Dr. Jungrak Choi of ETRI, KAIST master’s student Chankyu Han, and Ph.D. candidate Donho Lee, under the overall guidance of Professor Inkyu Park. The research results were published in the May 2025 issue of ‘Science Advances’ and introduced to the global research community through the journal’s official SNS channels (Facebook, Twitter).
※ Thesis Title: Thermoforming 2D films into 3D electronics for high-performance, customizable tactile sensing
※ DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv0057
< Figure 3. The introduction of the study on the official SNS posting by Science Advances >
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.23 View 429
KAIST Develops Customized Tactile Sensor That Can Detect Light Breath, Pressure and Sound
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Inkyu Park of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME), Dr. Jungrak Choi of ETRI, Ph.D. Candidate Donho Lee and M.S. Graduate Chankyu Han of KAIST ME >
When a robot grabs an object or a medical device detects a pulse, the tactile sensor is the technology that senses pressure like a fingertip. Existing sensors had disadvantages, such as slow responses or declining accuracy after repeated use, but Korean researchers have succeeded in developing a sensor that can quickly and accurately detect even light breath, pressure, and sound. This sensor can be used across a broad range — from everyday movements to medical diagnostics.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 23rd of June that Professor Inkyu Park’s team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, through a collaborative research project with the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI, President Seung Chan Bang ) under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Young Sik Kim), has developed an innovative technology that overcomes the structural limitations of existing tactile sensors.
The core of this joint research is the implementation of a customized tactile sensor that simultaneously achieves flexibility, precision, and repeatable durability by applying Thermoformed 3D Electronics (T3DE).
< Figure 1. Comparative evaluation of soft elastomer–based 3D structure versus thermoforming-based 3D structure in terms of mechanical properties. >
In particular, soft elastomer-based sensors (rubber, silicone, etc. — materials that stretch and return to their original shape) have structural problems such as slow response times, high hysteresis*, and creep**, but this new platform operates precisely in diverse environments and overcomes these limitations.
*Hysteresis: A phenomenon where the previously applied force or change is retained like a “memory,” so that the same stimulus does not always produce the same result.
**Creep: The phenomenon where a material slowly deforms when a force is continuously applied.
T3DE sensors are manufactured by precisely forming electrodes on a 2D film, then thermoforming them into a 3D structure under heat and pressure. Specifically, the top electrodes and supporting pillar structures of the sensor are designed to allow the fine-tuning of the mechanical properties for different purposes. By adjusting microstructural parameters — such as the thickness, length, and number of support pillars — the sensor’s Young’s modulus* can be tuned across a broad range of 10 Pa to 1 MPa. This matches the stiffness of biological tissues like skin, muscle, and tendons, making them highly suitable as bio-interface sensors.
*Young’s modulus: An index representing a material's stiffness; this research can control this index to match various biological tissues.
The newly developed T3DE sensor uses air as a dielectric material to reduce power consumption and demonstrates outstanding performance in sensitivity, response time, thermal stability, and repeatable accuracy.
Experimental results showed that the sensor achieved △sensitivity of 5,884 kPa⁻¹, △response time of 0.1 ms (less than one-thousandth of a second), △hysteresis of less than 0.5%, and maintained a repeatable precision of 99.9% or higher even after 5,000 repeated measurements.
< Figure 2. Graphic Overview of thermoformed 3D electronics (T3DE) >
The research team also constructed a high-resolution 40×70 array, comprising a total of 2,800 densely packed sensors, to visualize the pressure distribution on the sole of the foot in real time during exercise and confirmed the possibility of using the sensor for wrist pulse measurement to assess vascular health. Furthermore, successful results were also achieved in sound-detection experiments at a level comparable to commercial acoustic sensors. In short, the sensor can precisely and quickly measure foot pressure, pulse, and sound, allowing it to be applied in areas such as sports, health, and sound sensing.
The T3DE technology was also applied to an augmented-reality(AR)-based surgical training system. By adjusting the stiffness of each sensor element to match that of biological tissues, the system provided real-time visual and tactile feedback according to the pressure applied during surgical incisions. It also offered real-time warnings if an incision was too deep or approached a risky area, making it a promising technology for enhancing immersion and accuracy in medical training.
KAIST Professor Inkyu Park stated, “Because this sensor can be precisely tuned from the design stage and operates reliably across diverse environments, it can be used not only in everyday life, but also in a variety of fields such as healthcare, rehabilitation, and virtual reality.”
The research was co-led as first authors by Dr. Jungrak Choi of ETRI, KAIST master’s student Chankyu Han, and Ph.D. candidate Donho Lee, under the overall guidance of Professor Inkyu Park. The research results were published in the May 2025 issue of ‘Science Advances’ and introduced to the global research community through the journal’s official SNS channels (Facebook, Twitter).
※ Thesis Title: Thermoforming 2D films into 3D electronics for high-performance, customizable tactile sensing
※ DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv0057
< Figure 3. The introduction of the study on the official SNS posting by Science Advances >
This research was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology.
2025.06.23 View 429 -
 High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST Researchers
- Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering develops an ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer using 'double-layer disordered metasurfaces' that generate unique random patterns depending on light's color.
- Unlike conventional dispersion-based spectrometers that were difficult to apply to portable devices, this new concept spectrometer technology achieves 1nm-level high resolution in a device smaller than 1cm, comparable in size to a fingernail.
- It can be utilized as a built-in spectrometer in smartphones and wearable devices in the future, and can be expanded to advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging and ultrafast imaging.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Mooseok Jang, Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate), Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) >
Color, as the way light's wavelength is perceived by the human eye, goes beyond a simple aesthetic element, containing important scientific information like a substance's composition or state. Spectrometers are optical devices that analyze material properties by decomposing light into its constituent wavelengths, and they are widely used in various scientific and industrial fields, including material analysis, chemical component detection, and life science research. Existing high-resolution spectrometers were large and complex, making them difficult for widespread daily use. However, thanks to the ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer developed by KAIST researchers, it is now expected that light's color information can be utilized even within smartphones or wearable devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 13th that Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has successfully developed a reconstruction-based spectrometer technology using double-layer disordered metasurfaces*.
*Double-layer disordered metasurface: An innovative optical device that complexly scatters light through two layers of disordered nanostructures, creating unique and predictable speckle patterns for each wavelength.
Existing high-resolution spectrometers have a large form factor, on the order of tens of centimeters, and require complex calibration processes to maintain accuracy. This fundamentally stems from the operating principle of traditional dispersive elements, such as gratings and prisms, which separate light wavelengths along the propagation direction, much like a rainbow separates colors. Consequently, despite the potential for light's color information to be widely useful in daily life, spectroscopic technology has been limited to laboratory or industrial manufacturing environments.
< Figure 1. Through a simple structure consisting of a double layer of disordered metasurfaces and an image sensor, it was shown that speckles of predictable spectral channels with high spectral resolution can be generated in a compact form factor. The high similarity between the measured and calculated speckles was used to solve the inverse problem and verify the ability to reconstruct the spectrum. >
The research team devised a method that departs from the conventional spectroscopic paradigm of using diffraction gratings or prisms, which establish a one-to-one correspondence between light's color information and its propagation direction, by utilizing designed disordered structures as optical components. In this process, they employed metasurfaces, which can freely control the light propagation process using structures tens to hundreds of nanometers in size, to accurately implement 'complex random patterns (speckle*)'.
*Speckle: An irregular pattern of light intensity created by the interference of multiple wavefronts of light.
Specifically, they developed a method that involves implementing a double-layer disordered metasurface to generate wavelength-specific speckle patterns and then reconstructing precise color information (wavelength) of the light from the random patterns measured by a camera.
As a result, they successfully developed a new concept spectrometer technology that can accurately measure light across a broad range of visible to infrared (440-1,300nm) with a high resolution of 1 nanometer (nm) in a device smaller than a fingernail (less than 1cm) using only a single image capture.
< Figure 2. A disordered metasurface is a metasurface with irregularly arranged structures ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers in size. In a double-layer structure, a propagation space is placed between the two metasurfaces to control the output speckle with high degrees of freedom, thereby achieving a spectral resolution of 1 nm even in a form factor smaller than 1 cm. >
Dong-gu Lee, a lead author of this study, stated, "This technology is implemented in a way that is directly integrated with commercial image sensors, and we expect that it will enable easy acquisition and utilization of light's wavelength information in daily life when built into mobile devices in the future."
Professor Mooseok Jang said, "This technology overcomes the limitations of existing RGB three-color based machine vision fields, which only distinguish and recognize three color components (red, green, blue), and has diverse applications. We anticipate various applied research for this technology, which expands the horizon of laboratory-level technology to daily-level machine vision technology for applications such as food component analysis, crop health diagnosis, skin health measurement, environmental pollution detection, and bio/medical diagnostics." He added, "Furthermore, it can be extended to various advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging, which records wavelength and spatial information simultaneously with high resolution, 3D optical trapping technology, which precisely controls light of multiple wavelengths into desired forms, and ultrafast imaging technology, which captures phenomena occurring in very short periods."
This research was collaboratively led by Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering as co-first authors, with Professor Mooseok Jang as the corresponding author. The findings were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 28, 2025.* Paper Title: Reconstructive spectrometer using double-layer disordered metasurfaces* DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv2376
This research was supported by the Samsung Research Funding and Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics grant, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT), and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT).
2025.06.13 View 1215
High-Resolution Spectrometer that Fits into Smartphones Developed by KAIST Researchers
- Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering develops an ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer using 'double-layer disordered metasurfaces' that generate unique random patterns depending on light's color.
- Unlike conventional dispersion-based spectrometers that were difficult to apply to portable devices, this new concept spectrometer technology achieves 1nm-level high resolution in a device smaller than 1cm, comparable in size to a fingernail.
- It can be utilized as a built-in spectrometer in smartphones and wearable devices in the future, and can be expanded to advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging and ultrafast imaging.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Mooseok Jang, Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate), Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) >
Color, as the way light's wavelength is perceived by the human eye, goes beyond a simple aesthetic element, containing important scientific information like a substance's composition or state. Spectrometers are optical devices that analyze material properties by decomposing light into its constituent wavelengths, and they are widely used in various scientific and industrial fields, including material analysis, chemical component detection, and life science research. Existing high-resolution spectrometers were large and complex, making them difficult for widespread daily use. However, thanks to the ultra-compact, high-resolution spectrometer developed by KAIST researchers, it is now expected that light's color information can be utilized even within smartphones or wearable devices.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 13th that Professor Mooseok Jang's research team at the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has successfully developed a reconstruction-based spectrometer technology using double-layer disordered metasurfaces*.
*Double-layer disordered metasurface: An innovative optical device that complexly scatters light through two layers of disordered nanostructures, creating unique and predictable speckle patterns for each wavelength.
Existing high-resolution spectrometers have a large form factor, on the order of tens of centimeters, and require complex calibration processes to maintain accuracy. This fundamentally stems from the operating principle of traditional dispersive elements, such as gratings and prisms, which separate light wavelengths along the propagation direction, much like a rainbow separates colors. Consequently, despite the potential for light's color information to be widely useful in daily life, spectroscopic technology has been limited to laboratory or industrial manufacturing environments.
< Figure 1. Through a simple structure consisting of a double layer of disordered metasurfaces and an image sensor, it was shown that speckles of predictable spectral channels with high spectral resolution can be generated in a compact form factor. The high similarity between the measured and calculated speckles was used to solve the inverse problem and verify the ability to reconstruct the spectrum. >
The research team devised a method that departs from the conventional spectroscopic paradigm of using diffraction gratings or prisms, which establish a one-to-one correspondence between light's color information and its propagation direction, by utilizing designed disordered structures as optical components. In this process, they employed metasurfaces, which can freely control the light propagation process using structures tens to hundreds of nanometers in size, to accurately implement 'complex random patterns (speckle*)'.
*Speckle: An irregular pattern of light intensity created by the interference of multiple wavefronts of light.
Specifically, they developed a method that involves implementing a double-layer disordered metasurface to generate wavelength-specific speckle patterns and then reconstructing precise color information (wavelength) of the light from the random patterns measured by a camera.
As a result, they successfully developed a new concept spectrometer technology that can accurately measure light across a broad range of visible to infrared (440-1,300nm) with a high resolution of 1 nanometer (nm) in a device smaller than a fingernail (less than 1cm) using only a single image capture.
< Figure 2. A disordered metasurface is a metasurface with irregularly arranged structures ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers in size. In a double-layer structure, a propagation space is placed between the two metasurfaces to control the output speckle with high degrees of freedom, thereby achieving a spectral resolution of 1 nm even in a form factor smaller than 1 cm. >
Dong-gu Lee, a lead author of this study, stated, "This technology is implemented in a way that is directly integrated with commercial image sensors, and we expect that it will enable easy acquisition and utilization of light's wavelength information in daily life when built into mobile devices in the future."
Professor Mooseok Jang said, "This technology overcomes the limitations of existing RGB three-color based machine vision fields, which only distinguish and recognize three color components (red, green, blue), and has diverse applications. We anticipate various applied research for this technology, which expands the horizon of laboratory-level technology to daily-level machine vision technology for applications such as food component analysis, crop health diagnosis, skin health measurement, environmental pollution detection, and bio/medical diagnostics." He added, "Furthermore, it can be extended to various advanced optical technologies such as hyperspectral imaging, which records wavelength and spatial information simultaneously with high resolution, 3D optical trapping technology, which precisely controls light of multiple wavelengths into desired forms, and ultrafast imaging technology, which captures phenomena occurring in very short periods."
This research was collaboratively led by Dong-gu Lee (Ph.D. candidate) and Gookho Song (Ph.D. candidate) from the KAIST Department of Bio and Brain Engineering as co-first authors, with Professor Mooseok Jang as the corresponding author. The findings were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 28, 2025.* Paper Title: Reconstructive spectrometer using double-layer disordered metasurfaces* DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adv2376
This research was supported by the Samsung Research Funding and Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics grant, the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT), and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT).
2025.06.13 View 1215 -
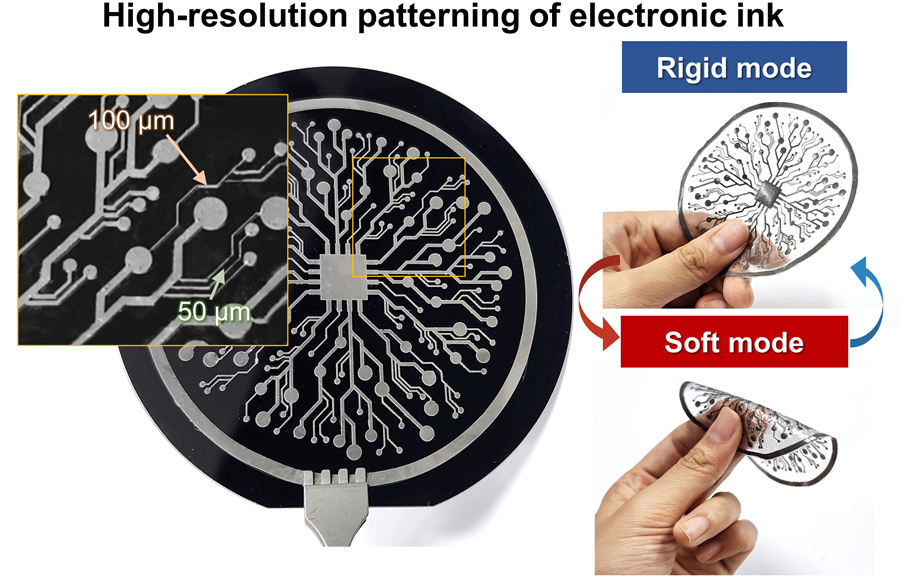 KAIST Research Team Develops Electronic Ink for Room-Temperature Printing of High-Resolution, Variable-Stiffness Electronics
A team of researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University has developed a groundbreaking electronic ink that enables room-temperature printing of variable-stiffness circuits capable of switching between rigid and soft modes. This advancement marks a significant leap toward next-generation wearable, implantable, and robotic devices.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and PhD candidate Simok Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering, (in separate bubbles, from left) Professor Gun-Hee Lee of Pusan National University, Professor Seongjun Park of Seoul National University, Professor Steve Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering>
Variable-stiffness electronics are at the forefront of adaptive technology, offering the ability for a single device to transition between rigid and soft modes depending on its use case. Gallium, a metal known for its high rigidity contrast between solid and liquid states, is a promising candidate for such applications. However, its use has been hindered by challenges including high surface tension, low viscosity, and undesirable phase transitions during manufacturing.
On June 4th, a research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Professor Seongjun Park from the Digital Healthcare Major at Seoul National University, and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST introduced a novel liquid metal electronic ink. This ink allows for micro-scale circuit printing – thinner than a human hair – at room temperature, with the ability to reversibly switch between rigid and soft modes depending on temperature.
The new ink combines printable viscosity with excellent electrical conductivity, enabling the creation of complex, high-resolution multilayer circuits comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). These circuits can dynamically change stiffness in response to temperature, presenting new opportunities for multifunctional electronics, medical technologies, and robotics.
Conventional electronics typically have fixed form factors – either rigid for durability or soft for wearability. Rigid devices like smartphones and laptops offer robust performance but are uncomfortable when worn, while soft electronics are more comfortable but lack precise handling. As demand grows for devices that can adapt their stiffness to context, variable-stiffness electronics are becoming increasingly important.
< Figure 1. Fabrication process of stable, high-viscosity electronic ink by dispersing micro-sized gallium particles in a polymer matrix (left). High-resolution large-area circuit printing process through pH-controlled chemical sintering (right). >
To address this challenge, the researchers focused on gallium, which melts just below body temperature. Solid gallium is quite stiff, while its liquid form is fluid and soft. Despite its potential, gallium’s use in electronic printing has been limited by its high surface tension and instability when melted.
To overcome these issues, the team developed a pH-controlled liquid metal ink printing process. By dispersing micro-sized gallium particles into a hydrophilic polyurethane matrix using a neutral solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide, or DMSO), they created a stable, high-viscosity ink suitable for precision printing. During post-print heating, the DMSO decomposes to form an acidic environment, which removes the oxide layer on the gallium particles. This triggers the particles to coalesce into electrically conductive networks with tunable mechanical properties.
The resulting printed circuits exhibit fine feature sizes (~50 μm), high conductivity (2.27 × 10⁶ S/m), and a stiffness modulation ratio of up to 1,465 – allowing the material to shift from plastic-like rigidity to rubber-like softness. Furthermore, the ink is compatible with conventional printing techniques such as screen printing and dip coating, supporting large-area and 3D device fabrication.
< Figure 2. Key features of the electronic ink. (i) High-resolution printing and multilayer integration capability. (ii) Batch fabrication capability through large-area screen printing. (iii) Complex three-dimensional structure printing capability through dip coating. (iv) Excellent electrical conductivity and stiffness control capability.>
The team demonstrated this technology by developing a multi-functional device that operates as a rigid portable electronic under normal conditions but transforms into a soft wearable healthcare device when attached to the body. They also created a neural probe that remains stiff during surgical insertion for accurate positioning but softens once inside brain tissue to reduce inflammation – highlighting its potential for biomedical implants.
< Figure 3. Variable stiffness wearable electronics with high-resolution circuits and multilayer structure comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). Functions as a rigid portable electronic device at room temperature, then transforms into a wearable healthcare device by softening at body temperature upon skin contact.>
“The core achievement of this research lies in overcoming the longstanding challenges of liquid metal printing through our innovative technology,” said Professor Jeong. “By controlling the ink’s acidity, we were able to electrically and mechanically connect printed gallium particles, enabling the room-temperature fabrication of high-resolution, large-area circuits with tunable stiffness. This opens up new possibilities for future personal electronics, medical devices, and robotics.”
< Figure 4. Body-temperature softening neural probe implemented by coating electronic ink on an optical waveguide structure. (Left) Remains rigid during surgery for precise manipulation and brain insertion, then softens after implantation to minimize mechanical stress on the brain and greatly enhance biocompatibility. (Right) >
This research was published in Science Advances under the title, “Phase-Change Metal Ink with pH-Controlled Chemical Sintering for Versatile and Scalable Fabrication of Variable Stiffness Electronics.” The work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Boston-Korea Project, and the BK21 FOUR Program.
2025.06.04 View 2009
KAIST Research Team Develops Electronic Ink for Room-Temperature Printing of High-Resolution, Variable-Stiffness Electronics
A team of researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University has developed a groundbreaking electronic ink that enables room-temperature printing of variable-stiffness circuits capable of switching between rigid and soft modes. This advancement marks a significant leap toward next-generation wearable, implantable, and robotic devices.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and PhD candidate Simok Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering, (in separate bubbles, from left) Professor Gun-Hee Lee of Pusan National University, Professor Seongjun Park of Seoul National University, Professor Steve Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering>
Variable-stiffness electronics are at the forefront of adaptive technology, offering the ability for a single device to transition between rigid and soft modes depending on its use case. Gallium, a metal known for its high rigidity contrast between solid and liquid states, is a promising candidate for such applications. However, its use has been hindered by challenges including high surface tension, low viscosity, and undesirable phase transitions during manufacturing.
On June 4th, a research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Professor Seongjun Park from the Digital Healthcare Major at Seoul National University, and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST introduced a novel liquid metal electronic ink. This ink allows for micro-scale circuit printing – thinner than a human hair – at room temperature, with the ability to reversibly switch between rigid and soft modes depending on temperature.
The new ink combines printable viscosity with excellent electrical conductivity, enabling the creation of complex, high-resolution multilayer circuits comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). These circuits can dynamically change stiffness in response to temperature, presenting new opportunities for multifunctional electronics, medical technologies, and robotics.
Conventional electronics typically have fixed form factors – either rigid for durability or soft for wearability. Rigid devices like smartphones and laptops offer robust performance but are uncomfortable when worn, while soft electronics are more comfortable but lack precise handling. As demand grows for devices that can adapt their stiffness to context, variable-stiffness electronics are becoming increasingly important.
< Figure 1. Fabrication process of stable, high-viscosity electronic ink by dispersing micro-sized gallium particles in a polymer matrix (left). High-resolution large-area circuit printing process through pH-controlled chemical sintering (right). >
To address this challenge, the researchers focused on gallium, which melts just below body temperature. Solid gallium is quite stiff, while its liquid form is fluid and soft. Despite its potential, gallium’s use in electronic printing has been limited by its high surface tension and instability when melted.
To overcome these issues, the team developed a pH-controlled liquid metal ink printing process. By dispersing micro-sized gallium particles into a hydrophilic polyurethane matrix using a neutral solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide, or DMSO), they created a stable, high-viscosity ink suitable for precision printing. During post-print heating, the DMSO decomposes to form an acidic environment, which removes the oxide layer on the gallium particles. This triggers the particles to coalesce into electrically conductive networks with tunable mechanical properties.
The resulting printed circuits exhibit fine feature sizes (~50 μm), high conductivity (2.27 × 10⁶ S/m), and a stiffness modulation ratio of up to 1,465 – allowing the material to shift from plastic-like rigidity to rubber-like softness. Furthermore, the ink is compatible with conventional printing techniques such as screen printing and dip coating, supporting large-area and 3D device fabrication.
< Figure 2. Key features of the electronic ink. (i) High-resolution printing and multilayer integration capability. (ii) Batch fabrication capability through large-area screen printing. (iii) Complex three-dimensional structure printing capability through dip coating. (iv) Excellent electrical conductivity and stiffness control capability.>
The team demonstrated this technology by developing a multi-functional device that operates as a rigid portable electronic under normal conditions but transforms into a soft wearable healthcare device when attached to the body. They also created a neural probe that remains stiff during surgical insertion for accurate positioning but softens once inside brain tissue to reduce inflammation – highlighting its potential for biomedical implants.
< Figure 3. Variable stiffness wearable electronics with high-resolution circuits and multilayer structure comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). Functions as a rigid portable electronic device at room temperature, then transforms into a wearable healthcare device by softening at body temperature upon skin contact.>
“The core achievement of this research lies in overcoming the longstanding challenges of liquid metal printing through our innovative technology,” said Professor Jeong. “By controlling the ink’s acidity, we were able to electrically and mechanically connect printed gallium particles, enabling the room-temperature fabrication of high-resolution, large-area circuits with tunable stiffness. This opens up new possibilities for future personal electronics, medical devices, and robotics.”
< Figure 4. Body-temperature softening neural probe implemented by coating electronic ink on an optical waveguide structure. (Left) Remains rigid during surgery for precise manipulation and brain insertion, then softens after implantation to minimize mechanical stress on the brain and greatly enhance biocompatibility. (Right) >
This research was published in Science Advances under the title, “Phase-Change Metal Ink with pH-Controlled Chemical Sintering for Versatile and Scalable Fabrication of Variable Stiffness Electronics.” The work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Boston-Korea Project, and the BK21 FOUR Program.
2025.06.04 View 2009 -
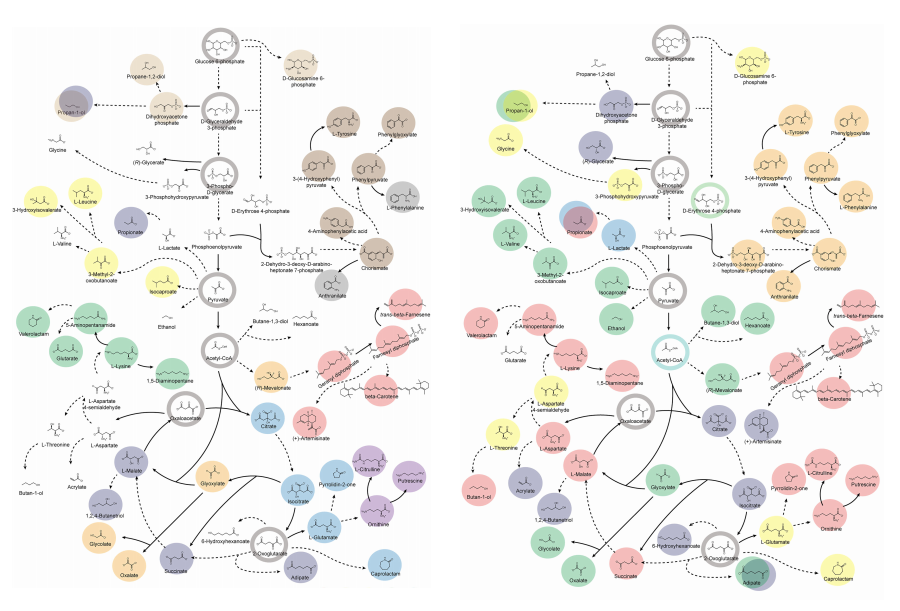 KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 3680
KAIST provides a comprehensive resource on microbial cell factories for sustainable chemical production
In silico analysis of five industrial microorganisms identifies optimal strains and metabolic engineering strategies for producing 235 valuable chemicals
Climate change and the depletion of fossil fuels have raised the global need for sustainable chemical production. In response to these environmental challenges, microbial cell factories are gaining attention as eco-friendly platforms for producing chemicals using renewable resources, while metabolic engineering technologies to enhance these cell factories are becoming crucial tools for maximizing production efficiency. However, difficulties in selecting suitable microbial strains and optimizing complex metabolic pathways continue to pose significant obstacles to practical industrial applications.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on 27th of March that Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering comprehensively evaluated the production capabilities of various industrial microbial cell factories using in silico simulations and, based on these findings, identified the most suitable microbial strains for producing specific chemicals as well as optimal metabolic engineering strategies.
Previously, researchers attempted to determine the best strains and efficient metabolic engineering strategies among numerous microbial candidates through extensive biological experiments and meticulous verification processes. However, this approach required substantial time and costs. Recently, the introduction of genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs), which reconstruct the metabolic networks within an organism based on its entire genome information, has enabled systematic analysis of metabolic fluxes via computer simulations. This development offers a new way to overcome limitations of conventional experimental approaches, revolutionizing both strain selection and metabolic pathway design.
Accordingly, Professor Lee’s team at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, KAIST, evaluated the production capabilities of five representative industrial microorganisms—Escherichia coli, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis, Corynebacterium glutamicum, and Pseudomonas putida—for 235 bio-based chemicals. Using GEMs, the researchers calculated both the maximum theoretical yields and the maximum achievable yields under industrial conditions for each chemical, thereby establishing criteria to identify the most suitable strains for each target compound.
< Figure 1. Outline of the strategy for improving microbial cell factories using a genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) >
The team specifically proposed strategies such as introducing heterologous enzyme reactions derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors used by microbes to expand metabolic pathways. These strategies were shown to increase yields beyond the innate metabolic capacities of the microorganisms, resulting in higher production of industrially important chemicals such as mevalonic acid, propanol, fatty acids, and isoprenoids.
Moreover, by applying a computational approach to analyze metabolic fluxes in silico, the researchers suggested strategies for improving microbial strains to maximize the production of various chemicals. They quantitatively identified the relationships between specific enzyme reactions and target chemical production, as well as the relationships between enzymes and metabolites, determining which enzyme reactions should be up- or down-regulated. Through this, the team presented strategies not only to achieve high theoretical yields but also to maximize actual production capacities.
< Figure 2. Comparison of production routes and maximum yields of useful chemicals using representative industrial microorganisms >
Dr. Gi Bae Kim, the first author of this paper from the KAIST BioProcess Engineering Research Center, explained, “By introducing metabolic pathways derived from other organisms and exchanging cofactors, it is possible to design new microbial cell factories that surpass existing limitations. The strategies presented in this study will play a pivotal role in making microbial-based production processes more economical and efficient.” In addition, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee noted, “This research serves as a key resource in the field of systems metabolic engineering, reducing difficulties in strain selection and pathway design, and enabling more efficient development of microbial cell factories. We expect it to greatly contribute to the future development of technologies for producing various eco-friendly chemicals, such as biofuels, bioplastics, and functional food materials.”
This research was conducted with the support from the Development of platform technologies of microbial cell factories for the next-generation biorefineries project and Development of advanced synthetic biology source technologies for leading the biomanufacturing industry project (Project Leader: Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, KAIST) from National Research Foundation supported by the Korean Ministry of Science and ICT.
2025.03.27 View 3680 -
 KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3783
KAIST Captures Hot Holes: A Breakthrough in Light-to-Electricity Energy Conversion
When light interacts with metallic nanostructures, it instantaneously generates plasmonic hot carriers, which serve as key intermediates for converting optical energy into high-value energy sources such as electricity and chemical energy. Among these, hot holes play a crucial role in enhancing photoelectrochemical reactions. However, they thermally dissipate within picoseconds (trillionths of a second), making practical applications challenging. Now, a Korean research team has successfully developed a method for sustaining hot holes longer and amplifying their flow, accelerating the commercialization of next-generation, high-efficiency, light-to-energy conversion technologies.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, in collaboration with Professor Moonsang Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Inha University, has successfully amplified the flow of hot holes and mapped local current distribution in real time, thereby elucidating the mechanism of photocurrent enhancement.
The team designed a nanodiode structure by placing a metallic nanomesh on a specialized semiconductor substrate (p-type gallium nitride) to facilitate hot hole extraction at the surface. As a result, in gallium nitride substrates aligned with the hot hole extraction direction, the flow of hot holes was amplified by approximately two times compared to substrates aligned in other directions.
To fabricate the Au nanomesh, a polystyrene nano-bead monolayer assembly was first placed on a gallium nitride (p-GaN) substrate, and then the polystyrene nano-beads were etched to form a nanomesh template (Figure 1A). Then, a 20 nm thick gold nano-film was deposited, and the etched polystyrene nano-beads were removed to realize the gold nano-mesh structure on the GaN substrate (Figure 1B). The fabricated Au nanomesh exhibited strong light absorption in the visible range due to the plasmonic resonance effect (Figure 1C). >
Furthermore, using a photoconductive atomic force microscopy (pc-AFM)-based photocurrent mapping system, the researchers analyzed the flow of hot holes in real time at the nanometer scale (one hundred-thousandth the thickness of a human hair). They observed that hot hole activation was strongest at "hot spots," where light was locally concentrated on the gold nanomesh. However, by modifying the growth direction of the gallium nitride substrate, hot hole activation extended beyond the hot spots to other areas as well.
Through this research, the team discovered an efficient method for converting light into electrical and chemical energy. This breakthrough is expected to significantly advance next-generation solar cells, photocatalysts, and hydrogen production technologies.
Professor Jeong Young Park stated, "For the first time, we have successfully controlled the flow of hot holes using a nanodiode technique. This innovation holds great potential for various optoelectronic devices and photocatalytic applications. For example, it could lead to groundbreaking advancements in solar energy conversion technologies, such as solar cells and hydrogen production. Additionally, the real-time analysis technology we developed can be applied to the development of ultra-miniaturized optoelectronic devices, including optical sensors and nanoscale semiconductor components."
The study was led by Hyunhwa Lee (PhD., KAIST Department of Chemistry) and Yujin Park (Postdoc Researcher, University of Texas at Austin Department of Chemical Engineering) as co-first authors and Professors Moonsang Lee (Inha University, Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Jeong Young Park (KAIST, Department of Chemistry) serving as corresponding authors. The research findings were published online in Science Advances on March 7.
(Paper Title: “Reconfiguring hot-hole flux via polarity modulation of p-GaN in plasmonic Schottky architectures”, DOI: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.adu0086)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.03.17 View 3783 -
 KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 3262
KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 3262 -
 KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 6778
KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 6778 -
 KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 4315
KAIST Proves Possibility of Preventing Hair Loss with Polyphenol Coating Technology
- KAIST's Professor Haeshin Lee's research team of the Department of Chemistry developed tannic scid-based hair coating technology
- Hair protein (hair and hair follicle) targeting delivery technology using polyphenol confirms a hair loss reduction effect of up to 90% to manifest within 7 Days
- This technology, first applied to 'Grabity' shampoo, proves effect of reducing hair loss chemically and physically
< Photo. (From left) KAIST Chemistry Department Ph.D. candidate Eunu Kim, Professor Haeshin Lee >
Hair loss is a problem that hundreds of millions of people around the world are experiencing, and has a significant psychological and social impact. KAIST researchers focused on the possibility that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, could contribute to preventing hair loss, and through research, discovered that tannic acid is not a simple coating agent, but rather acts as an 'adhesion mediator' that alleviates hair loss.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that the Chemistry Department Professor Haeshin Lee's research team developed a new hair loss prevention technology that slowly releases hair loss-alleviating functional ingredients using tannic acid-based coating technology.
Hair loss includes androgenetic alopecia (AGA) and telogen effluvium (TE), and genetic, hormonal, and environmental factors work together, and there is currently a lack of effective treatments with few side effects.
Representative hair loss treatments, minoxidil and finasteride, show some effects, but require long-term use, and not only do their effects vary depending on the body type, but some users also experience side effects.
Professor Haeshin Lee's research team proved that tannic acid can strongly bind to keratin, the main protein in hair, and can be continuously attached to the hair surface, and confirmed that this can be used to release specific functional ingredients in a controlled manner.
In particular, the research team developed a combination that included functional ingredients for hair loss relief, such as salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL), and named it 'SCANDAL.' The research results showed that the Scandal complex combined with tannic acid is gradually released when it comes into contact with water and is delivered to the hair follicles along the hair surface.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the hair loss relief mechanism by the tannic acid/SCANDAL complex. Tannic acid is a polyphenol compound containing a galol group that has a 360-degree adhesive function, and it binds to the hair surface on one side and binds to the hair loss relief functional ingredient SCANDAL on the other side to store it on the hair surface. Afterwards, when it comes into contact with moisture, SCANDAL is gradually released and delivered to the scalp and hair follicles to show the hair loss relief effect. >
The research team of Goodmona Clinic (Director: Geon Min Lee) applied the shampoo containing tannic acid/Scandal complex to 12 hair loss patients for 7 days, and observed a significant hair loss reduction effect in all clinicians. The results of the experiment showed a reduction in average hair loss of 56.2%, and there were cases where hair loss was reduced by up to 90.2%.
This suggests that tannic acid can be effective in alleviating hair loss by stably maintaining the Scandal component on the hair surface and gradually releasing it and delivering it to the hair follicles.
< Figure 2. When a tannic acid coating is applied to untreated bleached hair, a coating is formed as if the cuticles are tightly attached to each other. This was confirmed through X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) analysis, and a decrease in signal intensity was observed in the surface analysis of nitrogen of amino acids contained in keratin protein after tannic acid coating. This proves that tannic acid successfully binds to the hair surface and covers the existing amino acids. To verify this more clearly, the oxidation-reduction reaction was induced through gold ion treatment, and as a result, the entire hair turned black, and it was confirmed that tannic acid reacted with gold ions on the hair surface to form a tannic acid-gold complex. >
Professor Haeshin Lee said, “We have successfully proven that tannic acid, a type of natural polyphenol, has a strong antioxidant effect and has the property of strongly binding to proteins, so it can act as a bio-adhesive.”
Professor Lee continued, “Although there have been cases of using it as a skin and protein coating material in previous studies, this study is the first case of combining with hair and delivering hair loss relief ingredients, and it was applied to ‘Grabity’ shampoo commercialized through Polyphenol Factory, a startup company. We are working to commercialize more diverse research results, such as shampoos that dramatically increase the strength of thin hair that breaks and products that straighten curly hair.”
< Figure 3. Tannic acid and the hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) formed a stable complex through hydrogen bonding, and it was confirmed that tannic acid bound to the hair could effectively store SCANDAL. In addition, the results of transmission electron microscopy analysis of salicylic acid (SCA), niacinamide (N), and dexpanthenol (DAL) showed that all of them formed tannic acid-SCANDAL nanocomplexes. >
The results of this study, in which a Ph.D. candidate KAIST Department of Chemistry, Eunu Kim, was the first author and Professor Haeshin Lee was the corresponding author, were published in the online edition of the international academic journal ‘Advanced Materials Interfaces’ on January 6. (Paper title: Leveraging Multifaceted Polyphenol Interactions: An Approach for Hair Loss Mitigation) DOI: 10.1002/admi.202400851
< Figure 4. The hair loss relief functional ingredient (SCANDAL) stored on the hair surface with tannic acid was slowly released upon contact with moisture and delivered to the hair follicle along the hair surface. Salicylic acid (SCA) and niacinamide (N) were each released by more than 25% within 10 minutes. When shampoo containing tannic acid/SCANDAL complex was applied to the hair of 12 participants, hair loss was reduced by about 56.2% on average, and the reduction rate ranged from a minimum of 26.6% to a maximum of 90.2%. These results suggest that tannic acid stably binds SCANDAL to the hair surface, which allows for its gradual release into the hair follicle, resulting in a hair loss alleviation effect. >
This study was conducted with the support of Polyphenol Factory, a KAIST faculty startup company.
2025.02.06 View 4315 -
 KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 5993
KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 5993 -
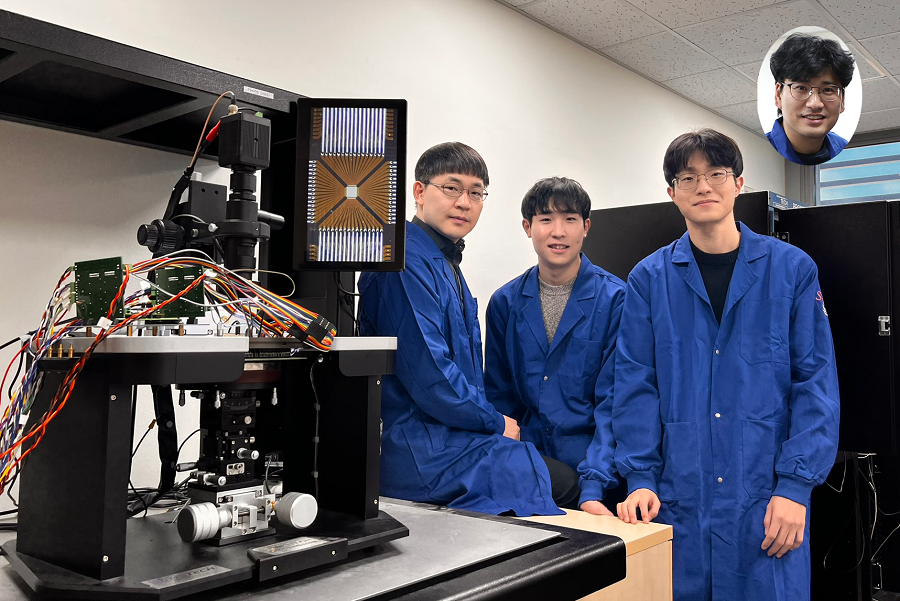 KAIST Develops Neuromorphic Semiconductor Chip that Learns and Corrects Itself
< Photo. The research team of the School of Electrical Engineering posed by the newly deveoped processor. (From center to the right) Professor Young-Gyu Yoon, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program Students Seungjae Han and Hakcheon Jeong and Professor Shinhyun Choi >
- Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon’s Joint Research Team from the School of Electrical Engineering developed a computing chip that can learn, correct errors, and process AI tasks
- Equipping a computing chip with high-reliability memristor devices with self-error correction functions for real-time learning and image processing
Existing computer systems have separate data processing and storage devices, making them inefficient for processing complex data like AI. A KAIST research team has developed a memristor-based integrated system similar to the way our brain processes information. It is now ready for application in various devices including smart security cameras, allowing them to recognize suspicious activity immediately without having to rely on remote cloud servers, and medical devices with which it can help analyze health data in real time.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of January that the joint research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon of the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based ultra-small computing chip that can learn and correct errors on its own.
< Figure 1. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of a computing chip equipped with a highly reliable selector-less 32×32 memristor crossbar array (left). Hardware system developed for real-time artificial intelligence implementation (right). >
What is special about this computing chip is that it can learn and correct errors that occur due to non-ideal characteristics that were difficult to solve in existing neuromorphic devices. For example, when processing a video stream, the chip learns to automatically separate a moving object from the background, and it becomes better at this task over time.
This self-learning ability has been proven by achieving accuracy comparable to ideal computer simulations in real-time image processing. The research team's main achievement is that it has completed a system that is both reliable and practical, beyond the development of brain-like components.
The research team has developed the world's first memristor-based integrated system that can adapt to immediate environmental changes, and has presented an innovative solution that overcomes the limitations of existing technology.
< Figure 2. Background and foreground separation results of an image containing non-ideal characteristics of memristor devices (left). Real-time image separation results through on-device learning using the memristor computing chip developed by our research team (right). >
At the heart of this innovation is a next-generation semiconductor device called a memristor*. The variable resistance characteristics of this device can replace the role of synapses in neural networks, and by utilizing it, data storage and computation can be performed simultaneously, just like our brain cells.
*Memristor: A compound word of memory and resistor, next-generation electrical device whose resistance value is determined by the amount and direction of charge that has flowed between the two terminals in the past.
The research team designed a highly reliable memristor that can precisely control resistance changes and developed an efficient system that excludes complex compensation processes through self-learning. This study is significant in that it experimentally verified the commercialization possibility of a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based integrated system that supports real-time learning and inference.
This technology will revolutionize the way artificial intelligence is used in everyday devices, allowing AI tasks to be processed locally without relying on remote cloud servers, making them faster, more privacy-protected, and more energy-efficient.
“This system is like a smart workspace where everything is within arm’s reach instead of having to go back and forth between desks and file cabinets,” explained KAIST researchers Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, who led the development of this technology. “This is similar to the way our brain processes information, where everything is processed efficiently at once at one spot.”
The research was conducted with Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, the students of Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program at KAIST School of Electrical Engineering being the co-first authors, the results of which was published online in the international academic journal, Nature Electronics, on January 8, 2025.
*Paper title: Self-supervised video processing with self-calibration on an analogue computing platform based on a selector-less memristor array ( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01318-6 )
This research was supported by the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, Excellent New Researcher Project and PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Research and Development Support Project of the Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2025.01.17 View 7455
KAIST Develops Neuromorphic Semiconductor Chip that Learns and Corrects Itself
< Photo. The research team of the School of Electrical Engineering posed by the newly deveoped processor. (From center to the right) Professor Young-Gyu Yoon, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program Students Seungjae Han and Hakcheon Jeong and Professor Shinhyun Choi >
- Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon’s Joint Research Team from the School of Electrical Engineering developed a computing chip that can learn, correct errors, and process AI tasks
- Equipping a computing chip with high-reliability memristor devices with self-error correction functions for real-time learning and image processing
Existing computer systems have separate data processing and storage devices, making them inefficient for processing complex data like AI. A KAIST research team has developed a memristor-based integrated system similar to the way our brain processes information. It is now ready for application in various devices including smart security cameras, allowing them to recognize suspicious activity immediately without having to rely on remote cloud servers, and medical devices with which it can help analyze health data in real time.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of January that the joint research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon of the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based ultra-small computing chip that can learn and correct errors on its own.
< Figure 1. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of a computing chip equipped with a highly reliable selector-less 32×32 memristor crossbar array (left). Hardware system developed for real-time artificial intelligence implementation (right). >
What is special about this computing chip is that it can learn and correct errors that occur due to non-ideal characteristics that were difficult to solve in existing neuromorphic devices. For example, when processing a video stream, the chip learns to automatically separate a moving object from the background, and it becomes better at this task over time.
This self-learning ability has been proven by achieving accuracy comparable to ideal computer simulations in real-time image processing. The research team's main achievement is that it has completed a system that is both reliable and practical, beyond the development of brain-like components.
The research team has developed the world's first memristor-based integrated system that can adapt to immediate environmental changes, and has presented an innovative solution that overcomes the limitations of existing technology.
< Figure 2. Background and foreground separation results of an image containing non-ideal characteristics of memristor devices (left). Real-time image separation results through on-device learning using the memristor computing chip developed by our research team (right). >
At the heart of this innovation is a next-generation semiconductor device called a memristor*. The variable resistance characteristics of this device can replace the role of synapses in neural networks, and by utilizing it, data storage and computation can be performed simultaneously, just like our brain cells.
*Memristor: A compound word of memory and resistor, next-generation electrical device whose resistance value is determined by the amount and direction of charge that has flowed between the two terminals in the past.
The research team designed a highly reliable memristor that can precisely control resistance changes and developed an efficient system that excludes complex compensation processes through self-learning. This study is significant in that it experimentally verified the commercialization possibility of a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based integrated system that supports real-time learning and inference.
This technology will revolutionize the way artificial intelligence is used in everyday devices, allowing AI tasks to be processed locally without relying on remote cloud servers, making them faster, more privacy-protected, and more energy-efficient.
“This system is like a smart workspace where everything is within arm’s reach instead of having to go back and forth between desks and file cabinets,” explained KAIST researchers Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, who led the development of this technology. “This is similar to the way our brain processes information, where everything is processed efficiently at once at one spot.”
The research was conducted with Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, the students of Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program at KAIST School of Electrical Engineering being the co-first authors, the results of which was published online in the international academic journal, Nature Electronics, on January 8, 2025.
*Paper title: Self-supervised video processing with self-calibration on an analogue computing platform based on a selector-less memristor array ( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01318-6 )
This research was supported by the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, Excellent New Researcher Project and PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Research and Development Support Project of the Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2025.01.17 View 7455 -
 KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7377
KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 7377